oil change PONTIAC FIERO 1988 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: PONTIAC, Model Year: 1988, Model line: FIERO, Model: PONTIAC FIERO 1988Pages: 1825, PDF Size: 99.44 MB
Page 10 of 1825
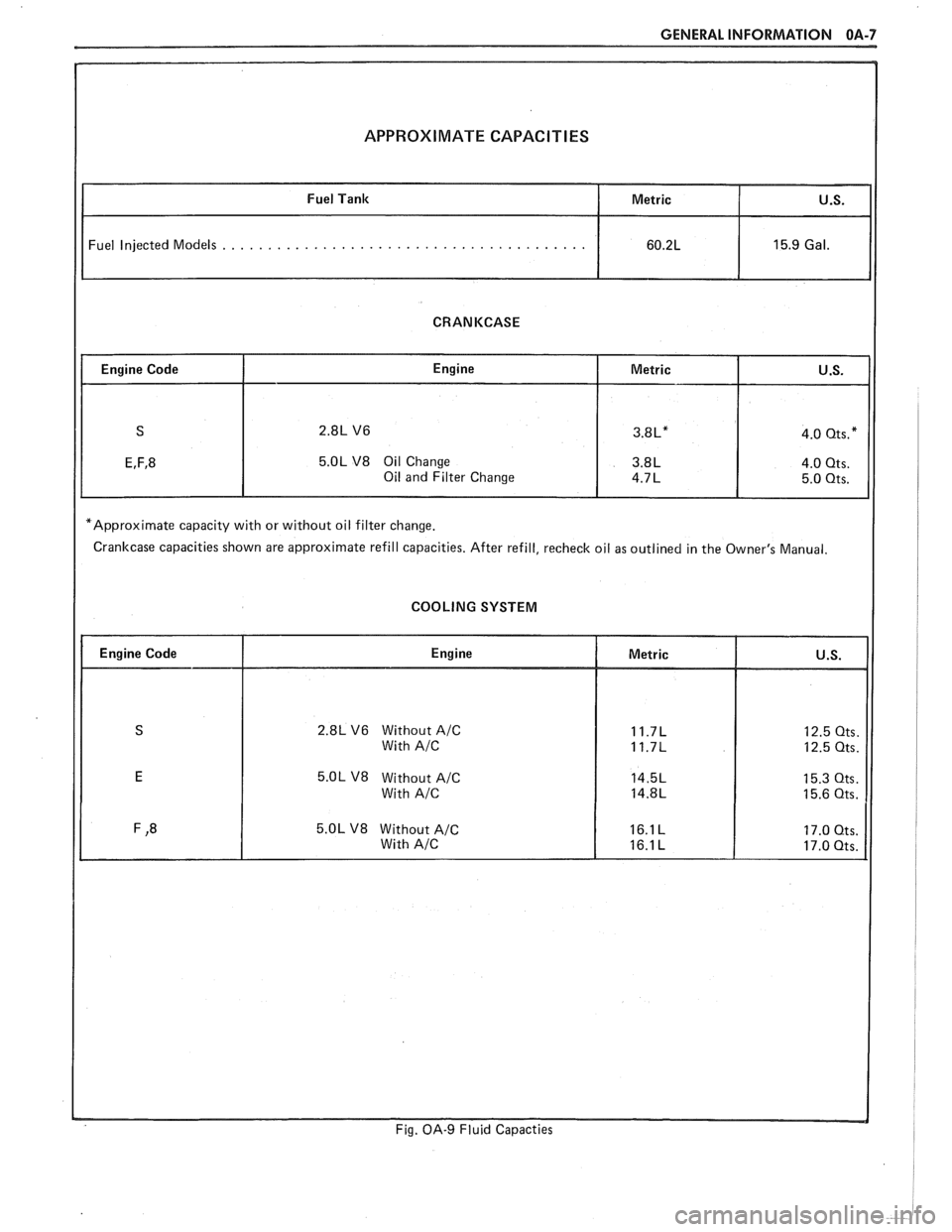
GENERAL INFORMATION OA-7
APPROXIMATE CAPACITIES
Fuel Injected Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CRANKCASE
5.OL V8 Oil Change
*Approximate capacity with or without oil filter change.
Crankcase capacities shown are approximate refill capacities. After refill, recheck oil as outlined in the Owner's Manual.
COOLING SYSTEM
2.8L V6 Without A/C
5.OL V8 Without A/C
Fig. OA-9 Fluid Capacties
Page 18 of 1825

MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION OB-1
SECTION OB
NTENANCE AND LUBR
CONTENTS
Maintenance Schedule, Gasoline .............................................. OB-l
Maintenance Schedules I and 11 .............................................. OB-2
Owner Inspections
......................................................... OB-3
Recommended Fluids and Lubricants ......................................... OB-6
PASSENGER CAR MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
VEHICLES
WITH GASOLINE ENGINE
NORMAL CAR USE ITEM 4
The maintenance services contained in Schedules I Carburetor or Throttle Body Mounting Bolt
and 11 are based on the assumption that your car will be Torque* used as designed:
Check torque of mounting bolts and/or nuts. @ To carry passengers and cargo within the limits
shown on the Tire Placard located on the edge of the ITEM 5 driver's door.
@ On reasonable road surfaces within legal driving Engine Idle Speed Adjustment*
limits. (Engines
without Idle Speed Control or Idle Air
Control) - Adjust to specifications shown on the under- @ On unleaded gasoline.
hood label. If no specifications are shown on the label, no
adjustment is necessary. Calibrated test equipment must
EXPLANATION OF SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE be used. SERVICES
The services listed in Maintenance Scheduies I and ITEM 6
11 are further explained below. When the following main- ~i~~ and wheel aotation tenance services are performed, make sure all parts are
replaced and all necessary repairs are done before driving To equalize wear and obtain maximum tire life,
your car. Be sure to use the proper fluid and lubricants as rotate in accordance with patterns shown in Owner's
shown in Figure OB-2. Manual.
ITEM 1
Engine Oil and Oil Filter Change*
ALWAYS USE SFICC OR SF/CD ENERGY CON-
SERVING OILS OF PROPER VISCOSITY
- Also.
always change oil and filter as soon as possible after
driving in a dust storm. See your Owner's Manual for
further details.
ITEM 2
Chassis Lubrication
Lubricate all grease fittings in suspension and steer-
ing linkage. Lubricate
transmissionltransaxle shift
linkage, parking brake cable guides, underbody contact
points and linkage. Also lubricate clutch cross shaft lever
every
30,000 miles (50 000 km) on rear-wheel-drive cars
only.
ITEM 3
Carburetor Choke and Hoses*
If your car is equipped with a carburetor, verify that
choke and vacuum break work properly and are within
specifications. Correct any binding caused by damage or
gum on the choke shaft. Inspect hoses for proper hookup,
cracks, chafing or decay. Correct as necessary.
Vacuum or A.I.R. Pump Drive Belt Inspection*
When a separate belt is used to drive the vacuum or
A.I.R.
pump, inspect it for cracks, fraying, wear and
proper tension. Adjust or replace as needed.
ITEM 8
Cooling System Service*
Drain, flush and refill system with new coolant. See
your Owner's Manual
for further details.
ITEM 9
Wheel Bearing Repack (Rear-Wheel-Drive Cars
Only Except Corvette)
Clean and repack front wheel bearings at each brake
relining or 15,000 miles
(25 000 km), whichever comes
first, when car is used in such service as police, taxi or
door-to-door delivery. If you do not use your car in such
service, clean and repack bearings at each brake relining
or 30,000 miles
(50 000 km), whichever comes first.
Corvette models do not require wheel bearing repack.
Page 21 of 1825

OB-4 MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION
Tire and wheel operation - Be alert to a vibra-
tion of the steering wheel or seat at normal highway
speeds. This may mean a wheel balance is needed. Also, a
pull right or left on a straight, level road may show the
need for
a tire pressure adjustment or wheel alignment.
Steering system operation - Be alert to
changes in steering action. An inspection is needed when
the steering wheel is harder to turn or has too much free
play or if unusual sounds are noted when turning or
parking.
Headlight aim operation - Take note of light
pattern occasionally. If beam aim doesn't look right,
headlights should be adjusted.
AT EACH FUEL FILL
Engine oil level check - Check engine oil level
and add if necessary. See your Owner's
Manual for further
details.
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have it inspected and repaired at once.
Engine coolant level and condition - Check
engine coolant level in coolant reservoir tank and add if
necessary. Replace if dirty or rusty. See your Owner's
Manual for further details.
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have it inspected and repaired at once.
Windshield washer fluid level check -- Check
washer fluid level in container and add if necessary.
Hood latch operation - When opening hood on
cars equipped with hoods that open from the front, note
the operation of secondary latch. It should keep hood from
opening all the way when primary latch is released. Make
sure that hood closes firmly.
AT LEAST MONTI-ILY
Tire and wheel inspection and pressure
check--
Check tires for abnormal wear or damage. Also,
check for damaged wheels. Keep pressures as shown on
Tire Placard on the driver's door (include spare unless it is
a stowaway). Pressure should b\: checked when tires are
"cold". See "Tires" in Owner's Manual for further
infomation.
Light operation check - Check operation of
license plate light, side-marker lights, headlights includ-
ing high beams, parking lights, taillights, brake lights.
turn signals, backup lights, instrument panel and interior
lights and hazard warning flashers.
Fluid leak check - After the car has been parked
for a while, inspect the surface beneath the car for water,
oil, fuel or other fluids. Water dripping from the air
conditioning system after use is normal. If you notice fuel
leaks or fumes, the cause should be found and corrected at
once.
AT LEAST TWICE A YEAR (FOR EXAMPLE,
EVERY SPRING AND FALL)
Power steering pump fluid level check --
Check power steering pump fluid level in accordance with
Owner's Manual instructions and keep at proper level.
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have it inspected and repaired at once.
Brake master cylinder reservoir fluid level
check ---- Check fluid and keep at proper level. Note: It is
normal for the brake fluid level to go down slightly as the
brake pads wear
- so be sure to keep reservoir filled.
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have
it inspected and repaired at once.
Clutch system service --- manual transmis-
sionltransaxle --- For cars equipped with hydraulic
clutch system, check the reservoir fluid level and add fluid
as required. All others, check clutch pedal free travel and
adjust as necessary. See your Owner's Manual for further
details.
~
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have it inspected and repaired at once.
Weatherstrip Lubrication - Clean surface and
then apply a thin film of silicone grease with a clean cloth.
EACH TIME OIL IS CHANGED
Automatic and manual transmissionltrans-
axle fluid level check - Check transmission/transaxle
fluid level and add as required. (Corvette only) if equipped
with manual transmission
- check fluid in the overdrive
unit and add as required.
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have
it inspected and repaired at once.
Brake systems inspection - For convenience,
the following should be done when wheels are removed
for rotation: Inspect lines and hoses for proper hookup,
binding, leaks, cracks, chafing, etc. Inspect disc brake
pads for wear and rotors for surface condition. Also in-
spect drum brake linings for wear and cracks. Inspect
other brake parts, including drums, wheel cylinders, park-
ing brake, etc. at the same time. Check parking brake
adjustment.
INSPECT BRAKES MORE OFTEN IF DRIVING
HABITS OR CONDITIONS RESULT IN FREQUENT
BRAKING.
Steering, suspension and front drive axle
boot and seal inspection
- Inspect front and rear
suspension and steering system for damaged, loose or
missing parts, signs of wear or lack of lubrication. Inspect
power steering lines and hoses for proper hookup, bind-
ing, leaks, cracks, chafing, etc. (On cars equipped with
manual steering gear, check for seal leakage.) On
front-
wheel-drive cars, clean then inspect drive axle boot seals
for damage, tears or leakage. Replace seals if necessary.
Exhaust system inspection - Inspect complete
system. Inspect body near the exhaust system. Look for
broken, damaged, missing or out-of-position parts as well
as open seams, holes, loose connections or other condi-
tions which could cause a heat buildup in the tloor pan or
could let exhaust fumes seep into the trunk or passenger
compartment.
Page 22 of 1825

MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION OB-5
Throttle linkage inspection -- Inspect for inter-
ference, binding, damaged or missing parts.
Engine drive belts inspection - Inspect all
belts for cracks, fraying and wear. Adjust or replace as
needed.
Rear axle service (if equipped) - Check gear
lubricant level and add if needed. For cars equipped with a
limited slip rear axle, fluid does not require changing
(except Caprice and Corvette
- change fluid and required
additive at first
7,500 miles (12 500 km). See your
Owner's Manual or "Recommended Fluids
& Lubricants
Chart" in this section.
IF YOU USE YOUR GAR TO PULL A TRAILER,
CHANGE GEAR LUBRICANT EVERY 7,500 MILES
(12 500 KM).
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have it inspected and repaired at once.
Power antenna - Clean and then lubricate power
antenna mast. The proper lubricant as shown in Figure
OB-2 should be used.
AT LEAST ONCE A YEAR
Lap and shoulder belts condition and opera-
tion
- Inspect belt system, including webbing, buckles,
latch plates, retractors, guide loops and anchors.
Moveable head restraint operation - On cars
with moveable restraints, make sure restraints stay in the
desired position. (See adjustment instructions in your
Owner's Manual.)
Seatback latch and recliner operation on
cars equipped
with recliner seat --- Be sure seat-
backs latch on those cars with folding seats using mechan-
ical latches. Make sure the recliner is holding by pushing
and pulling on the top of the
seatback while it is reclined.
See your Owner's Manual for seat operating information.
Spare tire and jack storage- Be alert to rattles
in rear of car. Make sure the space tire, all jacking equip-
ment, any tire inflator and any covers or doors are securely
stowed at all times. Oil jack ratchet or screw mechanism
after each use.
Key lock service - Lubricate key lock cylinder at
least annually.
Body lubrication service - Lubricate all body
door hinges including the tailgate or hatchback lid (if
equipped). Also lubricate the body hood, fuel door and
rear compartment hinges and latches including interior
glove box and counsel doors, and any folding seat
hardware.
"Fansmissionltransaxle neutral or clutch
starl switch operation
CAUnON: Before pedorming the follow-
ing safety switch check, be sure to have
enough room around the car. Then, firmly
apply both the parking brake (see your
Owner's Manual for procedure) and the
regular brakes. Do not use the accelerator pedal.
If the engine
starls, be ready to turn
off the ignition promptly. Take these pre-
cautions because the car could move
without warning and possibly cause per-
sonal injury or properly damage. On auto-
matic transmissionltransaxle cars, try to
starl the engine in each gear. The starler
should crank only in "Park" or "Neutral."
On manual transmissionltransaxle cars,
place the
shiR lever in "Neutral," push the
clutch halfway and try to starl. The starler
should crank only when the clutch is fully
depressed.
Steering column lock operation
- While
parked, try to turn key to "Lock" in each gear range. The
key should turn to "Lock" only when gear is in "Park" on
automatic or "Reverse" on manual
transmissionltransax-
le. On cars with key release lever, try to turn key toULock"
without depressing the lever. The key should turn to
"Lock" only with the key lever depressed. On all vehicles,
the key should come out only in "Lock."
Parking brake and transmissionltransaxle
"Park" mechanism operation
CAUT1ON:Before checking the holding
ability of the parking brake and automatic
transmissionltransaxle "Park" mecha-
nism, park on a fairly steep hill with
enough room for movement in the down-
hill direction. To reduce the risk of person-
al injury or property damage, be prepared
to apply the regular brakes promptly if the
car begins to move.
To check the parking brake, with the engine running and
transmission/transaxle in "Neutral." slowly remove foot
pressure from the regular brake pedal (until the car is held
by only the parking brake).
To check the automatic transmissionltransaxle "Park"
mechanism holding ability, release all brakes after shift-
ing the transmissionltransaxle to "Park."
ljnderbody flushing - At least every spring,
tlush from the underbody with plain water any corrosive
materials used for ice and snow removal and dust control.
Take care to thoroughly clean any areas where mud and
other debris can collect.
Sediment packed in closed areas
of the vehicle should be loosened before being flushed.
Engine cooling system service - Inspect
coolant and freeze protection. If dirty or rusty, drain, flush
and refill with new coolant. Keep coolant
at the proper
mixture as specified in your Owner's Manual. This pro-
vides proper freeze protection. corrosion inhibitor level
and engine operating temperature. Inspect hoses and re-
place if cracked. swollen or deteriorated. Tighten hose
clamps. Clean outside of radiator and air conditioning
condensor. Wash radiator filler cap and neck.
To help
ensure proper operation. a pressure test of both the cooling
system and cap is also recommended. (See maintenance
schedule charts in Figure
OB-l for the recommended
coolant change interval.)
Page 57 of 1825

18-14 AIR CONDITIONING
HANDLING OF REFRIGERANT LINES AND
FI-INGS
Tighten all tubing connections as shown in
torque chart (Figure 13). INSUFFICIENT OR
EXCESSIVE TORQUE WHEN TIGHTENING CAN
RESULT IN LOOSE JOINTS OR DEFORMED
JOINT PARTS. Either condition can result in refrig-
erant leakage.
All metal tubing lines should be free of dents or
kinks to prevent loss of system capacity due to line
restriction.
@ The flexible hose lines should never be bent to a
radius of less than four (4) times the diameter of
the hose.
@ The flexible hose lines should never be allowed
to come within a distance of
63.5mm (2-112") of
the exhaust manifold.
@ Flexible hose lines should be inspected regularly
for leaks or brittleness and replaced with new
lines if deterioration or leaking is found.
@ When disconnecting any fitting in the refrigera-
tion system, the system must first be discharged
of all Refrigerant- 12. Proceed very cautiously
regardless of gauge readings. Open very slowly,
keeping face and hands away so that no injury
can occur if there happens to be liquid
Refriger-
ant-12 in the line. If pressure is noticed when
fitting is loosened, allow it to bleed off as
described under DISCHARGING, ADDING
OIL, EVACUATING AND CHARGING PRO-
CEDURES FOR
A/C SYSTEMS.
@ In the event any refrigerant line is opened to the
atmosphere, it should be immediately capped or
taped to prevent entrance of moisture and dirt,
which can cause internal compressor wear or
plugged lines, in the condenser and evaporator
core and expansion (orifice) tubes or compressor
inlet screens.
@ The use of the proper wrenches when making
connections on O-ring fittings is important. The
opposing fitting should always be backed up
with a wrench to prevent distortion of connecting
lines or components. When connecting the flexi-
ble hose connections, it is important that the
swaged fitting and the flare nut, as well as the
coupling to which it is attached, be held at the
same time using three
(3) different wrenches to
prevent turning the fitting and damaging the
ground seat.
@ O-rings and seats must be in perfect condition. A
burr or piece of dirt may cause a refrigerant leak.
When replacing the O-ring, first dip it in clean
525 viscosity refrigeration oil.
MAINTAINING CHEMICAL STABILITY IN
THE
REFRIGERATION SYSTEM
The efficient operation and life of the air condi-
tioning system is dependent upon the chemical stabil-
ity of the refrigeration system. When foreign materials, such as
dirt, air, or moisture, contaminate
the refrigeration system, they will change the stability
of the Refrigerant-12 and 525 viscosity compressor
oil. They will also affect pressure-temperature rela-
tionship, reduce efficient operation and possibly cause
interior corrosion and abnormal wear of moving parts.
The following general practices should be
observed to insure chemical stability in the system:
1. Before disconnecting a refrigerant connection,
wipe away any dirt or oil at and near the connec-
tion to reduce the possibility of dirt entering the
system. Both sides of the connection should be
capped, plugged or taped as soon as possible to
prevent the entry of dirt, foreign material and
moisture.
2. Keep tools clean and dry. This includes the
manifold gauge set and replacement parts.
3. When adding 525 viscosity refrigerant oil (see
ADDING OIL in the DISCHARGING,
ADDING OIL, EVACUATING AND
CHARGING PROCEDURES FOR
AIC SYS-
TEMS, the transfer device and container should
be clean and dry to assure that refrigeration oil
remains as moisture-free as possible.
4. When it is necessary to "open" an
AIC system,
have everything needed ready and handy so that
as little time as possible will be required to per-
form the operation. Do not leave the
AIC system
open any longer than is necessary.
5. Any time the
A/C system has been "opened," it
should be properly evacuated before recharging
with Refrigerant- 12 according to the DIS-
CHARGING, ADDING OIL, EVACUATING
& CHARGING PROCEDURES FOR AIC
SYSTEMS.
All service parts are dehydrated and sealed
prior to shipping. They should remain sealed until just
prior to making connections. All parts should be at
room temperature before uncapping. (This prevents
condensation of moisture from the air entering the
system.) If, for any reason, caps are removed but the
connections are not made, parts should be resealed as
soon as possible.
DISCHARGING, ADDING OIL,
EVACUATING AND CHARGING
PROCEDURES FOR NC SYSTEMS
The refrigerant system may be discharged,
evacuated and charged using air conditioning service
charging station J-23500-01 or equivalent, or the
manifold and gauge set
5-23575-01 and 420ml (14
oz.) disposable cans of Refrigerant-12 (Figure 16).
Charging lines from the charging station or
manifold and gauge set require the use of gauge
adapters to connect to the system service fitting.
A
straight gauge adapter 5-5420 and a 90" angle gauge
adapter
5-9459 are available (see A/C Special Tools).
Always wear goggles and wrap a clean cloth
around fittings and connections when doing work that
Page 91 of 1825

4 Dl-I 2 R-4 AIR CONDITIONING COMPRESSOR OVERHAUL
MAJOR REPAIR PROCEDURES
Service repair procedures to the
Compressor Shaft Seal,
Pressure Relief Valve
or disassembly
of the Internal Compressor
Cylinder and Shaft Assembly are considered
"MAJOR" SINCE THE REFRIGERATION
SYSTEM MUST BE DISCHARGED,
EVACUATED AND RECHARGED to complete
service and/or because major internal
operating and sealing components of the
compressor are being disassembled and
serviced.
When replacing the shaft seal assembly or
pressure relief valve, even if the compressor remains on
the vehicle during the operation, it will be necessary to
discharge the system of refrigerant (see Section
1B).
Other than clutch repair procedures, the same holds
true for any disassembly of the compressor.
If the compressor shell, front head or cylinder
and shaft assembly are to be serviced or replaced, the
oil in the compressor must be drained, measured and
replaced (see Section
1B) to determine addition of
proper oil quantity to new assembly.
A clean workbench, preferably covered with a
sheet of clean paper, orderliness in the work area and
a place for all parts being removed and replaced is of
great importance, as is the use of the proper, clean
service tools.
NOTICE: Any attempt to use make-shift or
inadequate equipment may result in damage
and/or improper compressor operation.
All parts required for servicing the internal
compressor are protected by a preservation process and
packaged in a manner which will eliminate the
necessity of cleaning, washing or flushing of the parts.
The parts can be used in the internal assembly just as
they are removed from the service package.
Seals and
protective packaging should be left in tact un
ti1 just
prior to installation.
SI-IAFT SEAL
Fig. 35 thru 40
Shaft Seal Design
The shaft seal is a one piece design.
Seal Leak Detection
A shaft seal should not be changed because of an
oil-line on the hood insulator. The Seal is designed to
seep some oil for lubrication purposes. Only change a
Shaft Seal when a leak is detected by evidence of oil
sprayed in large amounts and then only after actual
refrigerant leakage is found by using an approved leak
Detector such as J-29547 or equivalent.
Should an R-4 compressor shaft seal ever have to
be replaced, the accumulator in this R-4 system must
also be removed from the vehicle. The oil in the
accumulator then must be drained, measured and
replaced according to the directions in Section
1B to
determine oil loss.
On-Car
Remove
or Disconnect
1. Discharge A/C system
2. Loosen and reposition compressor in mounting
brackets
3. Clutch Plate and Hub assembly
4. Shaft seal seat retainer ring, using Snap Ring
Pliers J-5403-A
5. Thoroughly clean inside of compressor neck area
and O-ring groove surrounding the shaft, the
exposed portion of the seal seat and the shaft
itself. Any dirt or foreign material getting into
compressor may cause damage.
6. Remove Lip Seal:
e Fully engage the knurled tangs of Seal
Remover-Installer J-23 128-A into the
recessed portion of the Seal by turning the
handle clockwise. Remove the Seal from the
compressor with a rotary-pulling motion.
Discard the Seal. The handle must be
hand-tightened securely. Do not use a
wrench or pliers.
7. Discard the seal seat O-ring from the compressor
neck using 0-Ring Remover J-9553-01.
8. Recheck the shaft and inside of the compressor
neck and O-ring groove for dirt or foreign
material and be sure these areas are perfectly
clean before installing new parts.
Inspection
Seals should not be reused. Always use a new
specification service seal kit on rebuild. Care should be
taken to prevent damage to the lip of the one piece seal.
Make sure that the Seal Seat and Seal Lip are free of
lint and dirt that could damage the seal surface or
prevent sealing.
On-Car
Install
or Connect
1. Dip
the new seal O-ring in clean 525 viscosity
refrigerant oil and assemble onto 0-Ring
Installer J-33011.
2. Insert
the 0-Ring Installer
5-3301 1 completely
down into the compressor neck until the Installer
"bottoms." Lower the moveable slide of the
0-Ring Installer to release the 0-Ring into the
seal seat O-ring lower groove. (The compressor
neck top groove is for the shaft seal retainer ring.)
Rotate the Installer to seat the O-ring and remove
the Installer.
3. Prepare Lip Seal:
Assemble seal to Seal Installer J-23128-A,
by turning handle clockwise, and then push
Seal Protector J-34614, into seal lip. The
stamped steel case side of the lip seal must
be engaged with knurled tangs of installer so
that flared-out side of lip seal is facing and
installed towards the compressor.
4. Install Lip Seal:
Page 149 of 1825
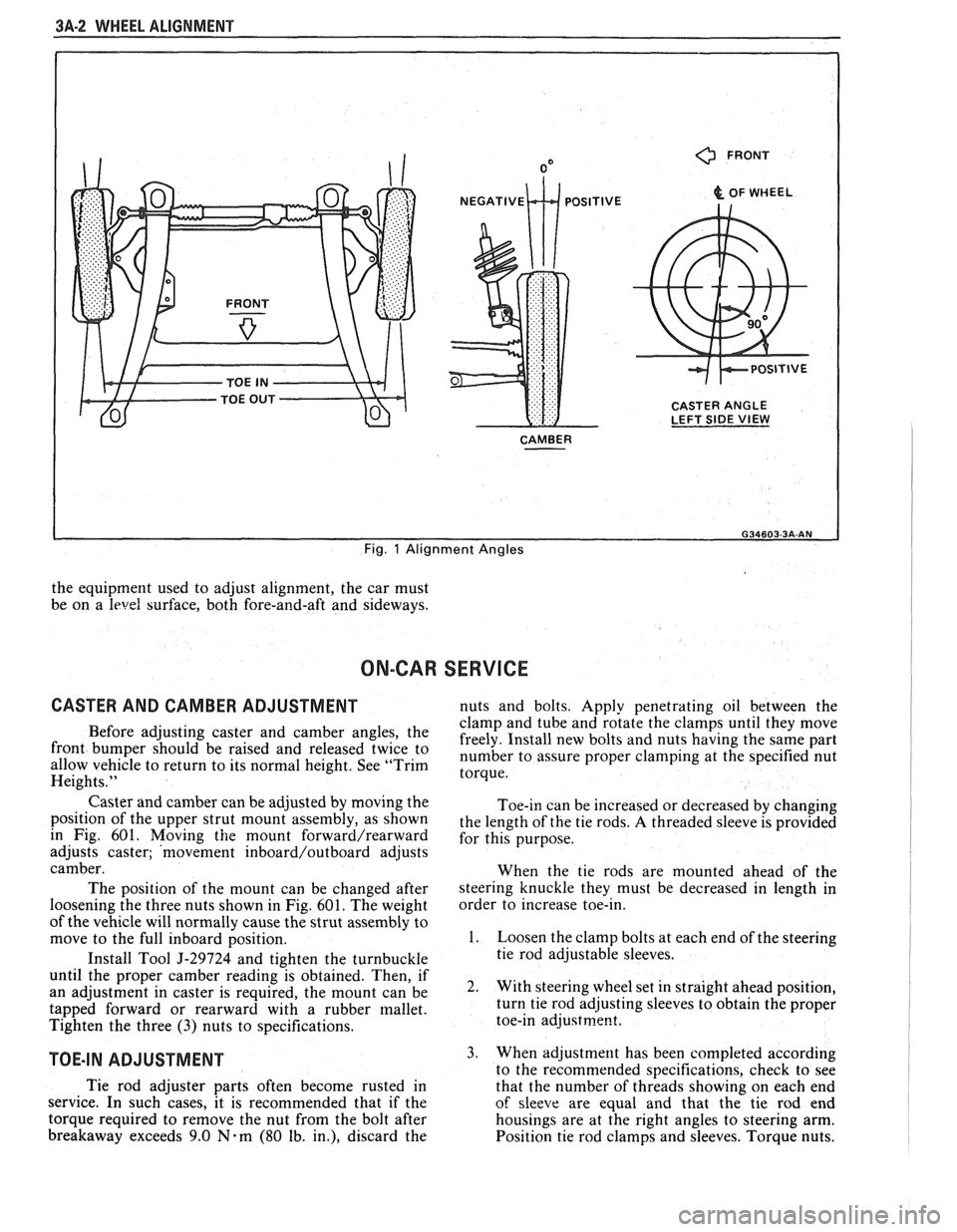
3A-2 WHEEL ALIGNMENT
0 FRONT
& OF WHEEL
CASTER ANGLE
LEFT SIDE
VIEW
CAMBER
I
Fig. 1 Alignment Angles
the equipment used to adjust alignment, the car must
be on a
level surface, both fore-and-aft and sideways.
ON-CAR SERVICE
CASTER AND CAMBER ADJUSTMENT nuts and bolts. Apply penetrating oil between the
clamp and tube and rotate the clamps until they move
Before adjusting caster and camber the freely. Install new bolts and nuts having the same part front be 'aised and twice to number to assure proper at the specified nut allow vehicle to return to its normal height. See "Trim torque. Heights."
Caster and camber can be adjusted by moving the
position of the upper strut mount assembly, as shown
in Fig. 601. Moving
the mount forward/rearward
adjusts caster; 'movement inboard/outboard adjusts
camber.
The position of the mount can be changed after
loosening the three nuts shown in Fig.
601. The weight
of the vehicle will normally cause the strut assembly to
move to the full inboard position.
Install Tool
5-29724 and tighten the turnbuckle
until the proper camber reading is obtained. Then, if
an adjustment in caster is required, the mount can be
tapped forward or rearward with a rubber mallet.
Tighten the three
(3) nuts to specifications.
TOE-IN ADJUSTMENT
Toe-in can be increased or decreased by changing
the length of the tie rods.
A threaded sleeve is provided
for this purpose.
When the tie rods are mounted ahead of the
steering knuckle they must be decreased in length in
order to increase toe-in.
1. Loosen the clamp bolts at each end of the steering
tie rod adjustable sleeves.
2. With steering wheel set in straight ahead position,
turn tie rod adjusting sleeves to obtain the proper
toe-in
adjustrne~t.
3. When adjustment has been completed according
to the recommended snecifications. check to see
Tie rod adjuster parts often become rusted in
that the number of thrkads showing on each end
service. In such cases, it is recommended that if the
of sleeve are equal and that the tie rod end
torque required to remove the nut from the bolt after housings are at the right angles to steering arm.
breakaway exceeds 9.0
Nam (80 lb. in.), discard the
Position tie rod clamps and sleeves. Torque nuts.
Page 212 of 1825

FRONT SUSPENSION 3C-1
SEC"T0RI 3C
FRONT SUSPENS
NOTICE: All front suspension fasteners are an important attaching part in that it could affect the
performance of vital parts and systems, and/or could result in major repair expense. They must be replaced with
one of the same part number or with an equivalent part if replacement becomes necessary. Do not use a
replacement part of lesser quality or substitute design. Torque values must be used as specified during reassembly
to assure proper retention of this part.
NOTICE: Never attempt to heat, quench or straighten any front suspension part. Replace it with a new part
or
damage to the part may result.
CONTENTS
General lnformation ....................................................................................................... 3C-I
On-Car Service ................................................................................................................... 3C- I
Specifications ..................................................................................................................... 3C- 10
GENERAL INFORMATION
The front suspension is designed to allow each
wheel to compensate for changes in the road surface ON-CAR SERVICE
level without appreciably affecting the opposite wheel. WHEEL BEARINGS
Each wheel is independently connected to the frame by
The proper functioning of the front suspension
a steering
kunckle, strut assembly, ball joint, and lower cannot be maintained unless the front wheel tapered arm. The steering in a roller bearings are correctly adjusted. The bearings
prescribed three dimensional arc. The front wheels are
must be a slip fit on the spindle and the inside diameter held in proper relationship to each other by two tie rods of the bearings should be lubricated to insure proper which are connected to steering arms on the knuckles ~h~ spindle nut must be a free-running fit and to the relay rod assembly.
on the threads.
Coil chassis springs are mounted between the
spring housings on the front crossmember and the
lower control arms. Ride control is provided by double,
direct acting strut assemblies. The upper portion of
each strut assembly extends through the fender well
and attaches to the upper mount assembly with a nut.
Side roll of the front suspension is controlled by
a spring steel stabilizer shaft. It is mounted in rubber
bushings which are held to the frame side rails by
brackets. The ends of the stabilizer are connected to the
lower control arms by link bolts and are isolated by
rubber grommets.
The inner ends of the lower control arms have
pressed in bushings. Bolts (passing through the
bushings) attach the arm to the suspension
crossmember. The lower ball joint assembly is a press
fit in the arm and attaches to the steering knuckle with
a torque prevailing nut.
Rubber grease seals are provided at ball socket
assemblies to keep dirt and moisture from entering the
joint and damaging bearing surfaces.
Adjustment
Figure 602
NOTICE: See NOTICE on Page 3C-1
of this
section.
1. Remove dust cap from hub.
2. Remove cotter pin from spindle and spindle nut.
3. Tighten the spindle nut to 16 Nsm (12 lb. ft.)
while turning the wheel assembly forward by
hand to fully seat the bearings. This will remove
any grease or burrs which could cause excessive
wheel bearing play later.
4. Back off the nut to the "just loose" position.
5. Hand tighten the spindle nut. Loosen spindle nut
until either hole in the spindle lines up with a slot
in the nut. Not
nlore than 1/2 flat.
6. Install
new cotter pin. Bend the ends of the cotter
pin against nut, cut off extra length to ensure ends
will not interfere with the dust cap.
7. Measure the looseness in the hub assembly. There
will be
from .03 to . l3mm (.001 to .005 inches)
end play when properly adjusted.
8. Install dust cap on hub.
FRONT SUSPENSION
Refer to Fig. 610 for illustration of attachment
provisions for the bolted-on front suspension
suspension
crossmember.
Page 277 of 1825

4B-4 REAR AXLE
d. Incorrect driveline angle.
Noise changes on a different type of road.
a. Road noise.
b. Tire noise.
Noise tone lowers as car speed is lowered.
a. Tire noise.
Similar noise is produced with car standing and
driving.
a. Engine noise.
b. Transmission noise.
Vibration. a. Rough rear wheel bearing.
b. Unbalanced
or damaged propeller shaft.
c. Tire unbalance.
d. Worn
universal joint in propeller shaft.
e. Incorrect driveline angle.
f. Mis-indexed propeller shaft at pinion
flange.
g. Pinion
flange
runout too great.
A knock or click approximately every two
revolutions of the rear wheel.
a. A rear wheel bearing.
Noise most pronounced on turns.
a. Rear
axle side gear and pinion noise.
A continuous low pitch whirring or scraping
noise starting at relatively low speed.
a. Pinion bearing noise.
Drive noise, coast noise or float noise.
a. Ring and
pinion gear noise.
Clunk on acceleration or deceleration.
a. Worn rear
axle pinion shaft in case or side
gear hub counterbore in case worn oversize.
b. Insufficient
lubrication on propeller shaft
slip yoke.
c. Worn U-joints on
propeller shaft. Front or
rear.
Groan in "Forward" or "Reverse".
a. Wrong
or contaminated lube in rear axle.
b. Worn bushings.
Chatter on turns.
a. Wrong
or contaminated lube in rear axle.
b. Clutch
cone worn and/or
spring(s) worn.
Clunk or knock on rough road operation.
a. Excessive end play of axle shafts to
differential cross shaft.
b. Worn bushings.
PRE-REPAIR INVESTIGATION AND TROUBLE
DIAGNOSIS
A careful1 diagnosis of the rear axle prior to
disassembly will often reveal valuable information as to
the extent and type of repairs or adjustments necessary.
Since frequent causes of axle noises are improper
backlash, pinion bearing pre-load, or side bearing
pre-load, or a combination, a few simple adjustments
may be all that are necessary to correct a problem.
Therefore, before removing the rear axle from the
housing, the following checks should be made with the
results recorded and analyzed:
1) Backlash; 2) Total Assembly
Preload; 3) Tooth Contact Pattern Test;
4)
Fluid Level; and 5) Fluid Contamination.
Use care at all times to keep dirt and other foreign
matter, such as grinder dust, soot or sand, away from
differential to prevent possibility of subsequent failure.
The pinion and ring gear must be completely
assembled, installed and all pre-load and backlash
adjustments completed prior to the start of this method
of pinion depth setting. The following procedure can
be used in place of the gage method of pinion depth
setting.
Gear Tooth Nomenclature
The side of the ring gear tooth which curves
outward, or is convex, is referred to as the "drive" side.
The concave side is the "coast" side. The end of the
tooth nearest center of ring gear is referred to as the
"toe" end. The end of the tooth farthest away from the
center is the "heel" end. Toe end of tooth is smaller
than heel end.
It is very important that tooth contact be tested
before the rear axle carrier assembly is disassembled.
Variations in the carrier or pinion rear bearing may
cause the pinion to be too far away from, or close to,
the ring gear. Thus, the tooth contact must be tested
and corrected, if necessary, or the gears may be noisy.
Tooth Contact Pattern Test
1. Wipe oil out of carrier and carefully clean each
tooth of ring gear.
2. Use gear marking compound part number
1052351 or equivalent and apply this mixture
sparingly to all ring gear teeth, using a medium
stiff brush. When properly used, the area of
pinion tooth contact will be visible when hand
load is applied.
3. Tighten bearing cap bolts to 75
N.m (55 lb. ft.).
4. Expand
brake shoes using parking brake cables
until a torque of 54 to
70 N-m (40-50 lb. ft.) is
required to turn the pinion.
A test made without loading the gears will not
give a satisfactory pattern. Turn pinion flange
with wrench so that ring gear rotates one full
revolution, then reverse rotation so that ring gear
rotates one revolution in opposite direction.
5. Observe
pattern on ring gear teeth and compare
with Fig. 3.
Effects of Increasing Load on Teeth Contact
Pattern
When "load" on ring and pinion gear is
increased, such as when car is accelerated forward
from standstill or from normal drive, the tooth contact
will tend to spread out and, under very heavy load, will
extend from near toe to near heel on the drive side. The
entire contact also tends to shift toward heel under
increasingly heavier loads and will become somewhat
broader with respect to tops and bottoms of teeth. The
patterns obtained by this tooth contact pattern test
approximate a light load and, for this reason, they will
extend only about halfway.
Page 347 of 1825

6-2 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION
6E3 - Fuel Injection (Ported) This section has information
on all exhaust
system parts, such as tailpipes, mufflers, and the
SECTION 6F - EXHAUST SYSTEM catalytic converter.
GENERAL INFORMAflION
CLEANLINESS AND CARE
An automobile engine is a combination of many
machined, honed, polished and lapped surfaces with
tolerances that are measured in the ten-thousandths of
an inch. When any internal engine parts are serviced,
care and cleanliness are important. A liberal coating of
engine oil should be applied to friction areas during
assembly, to protect and lubricate the surfaces on
initial operation. Throughout this section, it should be
understood that proper cleaning and protection of
machined surfaces and friction areas is part of the
repair procedure. This is considered standard shop
practice, even if not specifically stated. PREVENTING
DAMAGE AND IN
CONTRIBUTING TO RELIABLE ENGINE
PERFORMANCE.
When raising or supporting the engine for any
reason, do not use a jack under the oil pan. Due to the
small clearance between the oil pan and the oil pump
screen, jacking against the oil pan may cause it to be
bent against the pump screen resulting in a damaged
oil pick-up unit.
When working on the engine, remember that the
12-volt electrical system is capable of causing short
circuits. When performing any work where electrical terminals could possibly be grounded, the ground cable
of the battery should be disconnected at the battery.
Any time the carburetor or air cleaner is
train components are removed removed, the intake opening should be covered. This for service, they should be in order' will protect against entrance of foreign be installed in the same locations, and with the same material, which could follow the intake passage into mating surfaces, as when removed
the cylinder and cause extensive damage when the -
Battery cables should be disconnected before any engin; is started.
major work is performed on the engine. Failure to IN THE MECHANICAL PROCEDURES
disconnect cables may result in damage to wire harness DESCRIBED IN THIS SECTION, GENERALLY
or other electrical parts. NO
REFERENCES WILL BE MADE TO THE
REMOVAL OF OPTIONAL EQUIPMENT SUCH
ENGINE SERVICE AS POWER STEERING PUMP, AIR
CONDITIONING COMPRESSOR, ETC.
THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION ON SHOULD IT BECOME NECESSARY TO
ENGINE SERVICE SHOULD BE NOTED REMOVE ANY SUCH ITEM TO
PERFORM
CAREFULLY, AS IT IS IMPORTANT IN OTHER SERVICE, REFER TO THE
APPROPRIATE SECTION OF THIS SERVICE
MANUAL FOR SPECIFIC INFORMATION.
ENGINE PERFORMANCE DIAGNOSIS
INTRODUCTION interchangeably for so long, it was necessary to decide
on the most common usage and then define them. If the
Engine Performance procedures are definition is not understood, and the exact Symptom is
guides that will lead to the most probable causes of not used, the Diagnostic procedure will not work. engine performance complaints. They cover the
components of the fuel, ignition, and mechanical It
is important to keep two facts in mind:
systems that could cause a particular
complaint, and 1. The procedures are written to diagnose problems
then outline repairs in a logical sequence. on cars
that have
"run well at one time" and
that time and wear have created the condition.
It is important to determine if the
"Service ~~~i~~ soon- light is "ON,~' or has come for 2. All possible causes cannot be covered,
a short interval while driving. If the
"Service Engine particularly with regard to emission controls. If
Soon" light has come "ON," the Computer doing the work prescribed does not correct the
Command Control System or DECS should be complaint, then either the wrong Symptom was
checked for stored
"Trouble Codes" (See Diagnostic used, or a more detailed analysis will have to be
Circuit Check, Section 6E, for the engine you are made.
working on) which may indicate the cause for the All of the Symptoms can be caused by worn out
performance
complaint.Each Symptom is defined, and or defective parts such as Spark Plugs, Ignition
it is important that the correct one be selected, based Wiring, etc. If time and/or mileage indicate that
on the complaints reported or found. The definition of parts should be replaced, it is recommended that
each symptom is included with the symptom. it
be done.
The words used may not be what you are used to Refer to:
in all cases, but because these terms have been used
@ Section 6E - Driveability and Emissions