oil dipstick PONTIAC FIERO 1988 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: PONTIAC, Model Year: 1988, Model line: FIERO, Model: PONTIAC FIERO 1988Pages: 1825, PDF Size: 99.44 MB
Page 67 of 1825
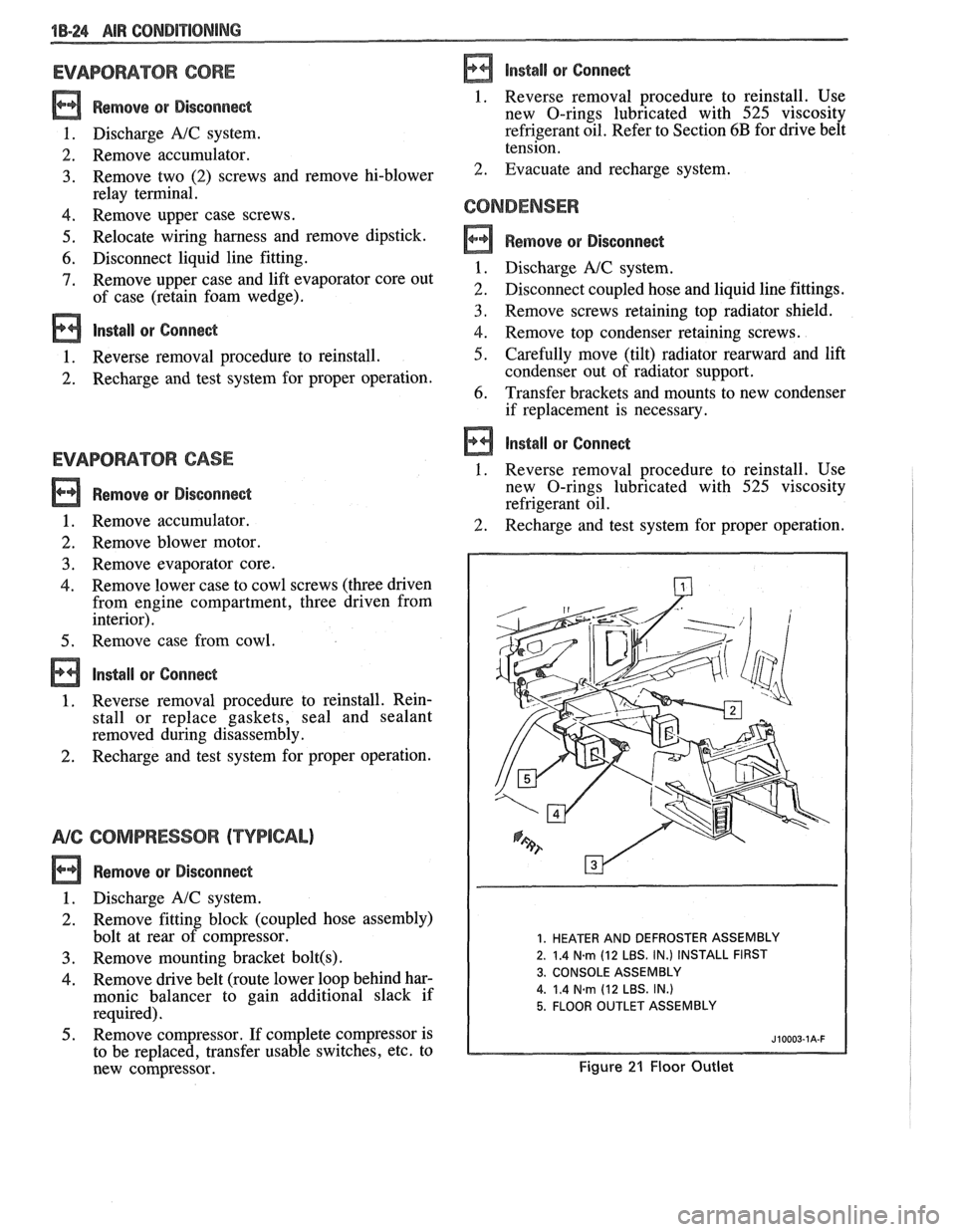
1B-24 AIR CONDPTIBNING
EVAPORATOR CORE
Remove QP Disconnect
1. Discharge A/C system.
2. Remove accumulator.
3. Remove two (2) screws and remove hi-blower
relay terminal.
4. Remove upper case screws.
5. Relocate wiring harness and remove dipstick.
6. Disconnect liquid line fitting.
7. Remove upper case and lift evaporator core out
of case (retain foam wedge).
Install or Connect
1. Reverse removal procedure to reinstall.
2. Recharge and test system for proper operation.
EVAPBRAWORCASE
Remove or Disconnect
1. Remove accumulator.
2. Remove blower motor.
3. Remove evaporator core.
Remove lower case to cowl screws (three driven from engine compartment, three driven from
interior).
Remove case from cowl.
Install or Connect
Reverse removal procedure to reinstall. Rein-
stall or replace gaskets, seal and sealant
removed during disassembly.
Recharge and test system for proper operation.
NG COMPRESSOR (TYPICAL)
Remove or Disconnect
1. Discharge A/C system.
2. Remove fitting block (coupled hose assembly)
bolt at rear of compressor.
3. Remove mounting bracket bolt(s) .
4. Remove drive belt (route lower loop behind har-
monic balancer to gain additional slack if
required).
5. Remove compressor. If complete compressor is
to be replaced, transfer usable switches, etc. to
new compressor.
Install or Connect
1. Reverse removal
procedure to reinstall. Use
new O-rings lubricated with
525 viscosity
refrigerant oil. Refer to Section
6B for drive belt
tension.
2. Evacuate and recharge system.
CONDENSER
a Remove or Disconnect
1. Discharge A/C system.
2. Disconnect coupled hose and liquid line fittings.
3, Remove screws retaining top radiator shield.
4. Remove top condenser retaining screws.
5. Carefully move (tilt) radiator rearward and lift
condenser out of radiator support.
6. Transfer brackets and mounts to new condenser
if replacement is necessary.
Install or Connect
1. Reverse removal procedure to reinstall. Use
new O-rings lubricated with
525 viscosity
refrigerant oil.
2. Recharge and test system for proper operation.
1. HEATER AND DEFROSTER ASSEMBLY
2. 1.4
N.m (12 LBS. IN.) INSTALL FIRST
3. CONSOLE ASSEMBLY
4.
1.4 Narn (12 LBS. IN.)
5. FLOOR OUTLET ASSEMBLY
Figure 21 Floor Outlet
Page 348 of 1825

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION 6-3
B, Section 6E2 - Fuel Injection (TBI)
B, Section 6E3 - Fuel Injection (Ported)
ENGINE MECHANICAL DIAGNOSIS
The following diagnostic information covers common problems and possible causes. When
the proper diagnosis is made, the problem should be corrected by adjustment, repair or part
replacement as required. Refer to the appropriate section of the manual for these procedures.
EXCESSIVE OIL LOSS
B, External oil leaks. Tighten bolts and/or replace o Continuous high speed driving, and/or severe
gaskets and seals as necessary. usage
such as trailer hauling, will normally cause
decreased oil mileage.
e Improper reading of dipstick. Check oil with car PCV system malfunctioning. on a level surface and allow adequate drain-down Valve guides and/or valve stem seals worn, or time.
seals omitted. Ream guides and install oversize
service valves and/or new valve stem seals.
Improper Use S.A'E' Piston rings broken, worn, or not seateded. Allow viscosity for prevailing temperatures. See
adequate time for rings to seat. Replace broken
Owner's Manual for proper specifications.
or worn rings, as necessary.
Piston improperly installed or misfitted.
LOW OIL PRESSURE
Slow idle speed. Set idle speed to correct
specification, if not ECM controlled.
Incorrect, or malfunctioning, oil pressure switch.
Incorrect, or malfunctioning, oil pressure gage.
Replace with proper gage.
.*
Improper oil viscosity, or diluted oil. install oil of
proper viscosity for expected temperature, or
install new oil if diluted with moisture or
unburned fuel mixtures.
o Oil pump worn or dirty.
e Plugged oil filter.
e Oil pickup screen loose or plugged.
B, Hole in oil pickup tube.
e Excessive bearing clearance. Replace if necessary.
o Cracked, porous or plugged oil galleys. Repair or
replace block.
o Galley plugs missing or misinstalled. Install
plugs, or repair as necessary.
VALVE TRAIN NOISE
e Low oil pressure. Repair as necessary. (See o Broken valve spring.
preceding diagnosis for low oil pressure.)
o Sticking valves.
o Loose rocker arm attachments. Inspect and B, Lifters worn, dirty, or defective. Clean, inspect,
test and replace as necessary.
repair as necessary.
o Camshaft worn, or poor machining. Replace
o Worn rocker arm and/or pushrod. camshaft.
B, Worn valve guides.
ENGINE KNOCK DIAGNOSIS
KNOCKS COLD AND CONTINUES FOR TWO TO THREE MINUTES
INCREASES
WITH TORQUE
o Vacuum operated EFE engines may have valve o Excessive piston to bore clearance. Replace
knock. Replace EFE valve. piston.
e Flywheel contacting splash shield. Reposition
splash shield.
e Loose or broken balancer or drive pulleys.
Tighten, or replace as necessary. Cold engine piston knock usually
disappears when the cylinder is grounded
out. Cold engine piston knock which
disappears in 1.5 minutes should be
considered acceptable.
Page 363 of 1825
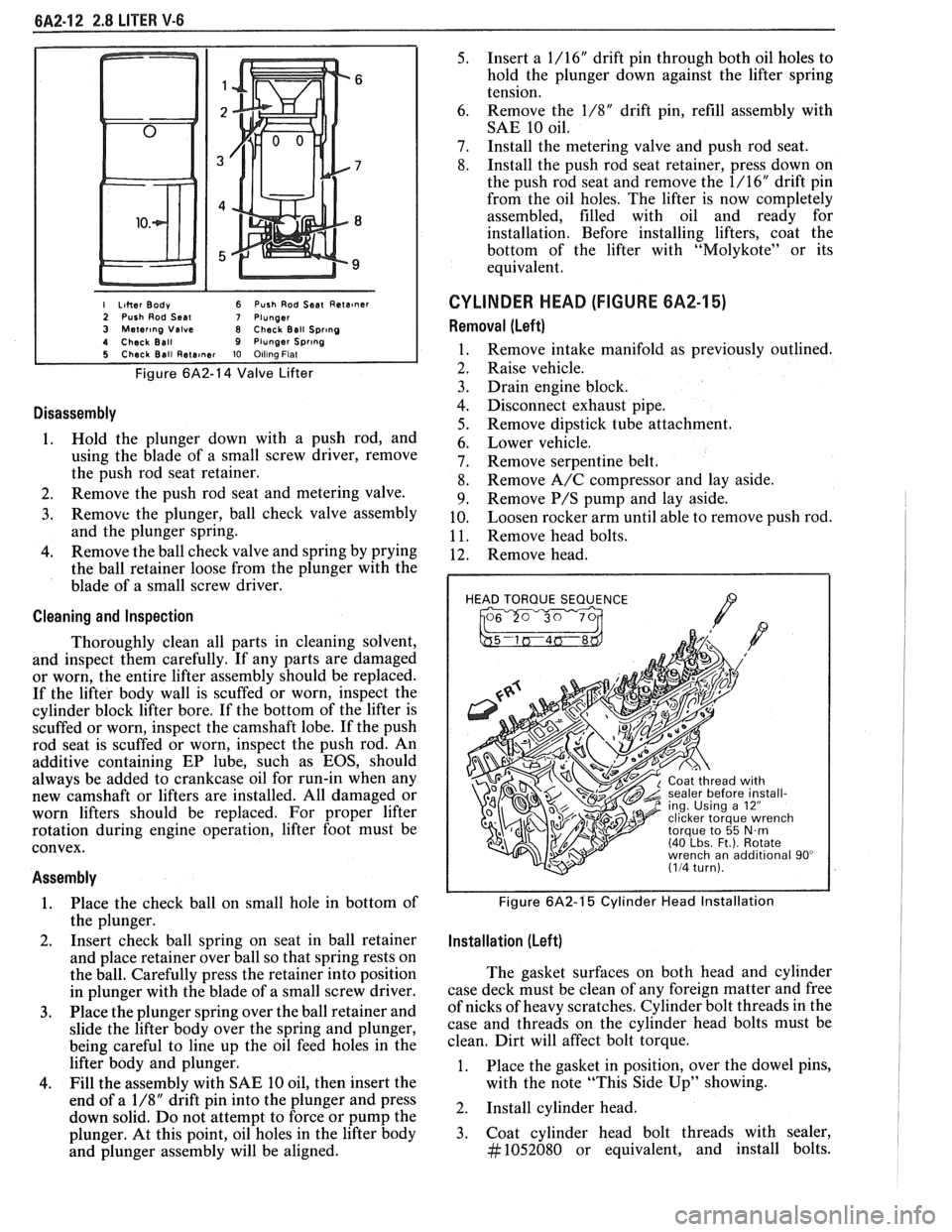
I Liher Body 6 Push Rod Seat Reta~ner 2 Push Rod Seal 7 Plunger 3 Mater~ng Valve 8 Check Ball Spr~ng 4 Check Ball 9 Plunger Spr~ng 5 Check Ball Rete~ner 10 Olllna Flat
Figure 6A2-14 Valve Lifter
Disassembly
1. Hold the plunger down with a push rod, and
using the blade of a small screw driver, remove
the push rod seat retainer.
2. Remove the push rod seat and metering valve.
3. Remove the plunger, ball check valve assembly
and the plunger spring.
4. Remove the ball check valve and spring by prying
the ball retainer loose from the plunger with the
blade of a small screw driver.
Cleaning and Inspection
Thoroughly clean all parts in cleaning solvent,
and inspect them carefully. If any parts are damaged
or worn, the entire lifter assembly should be replaced.
If the lifter body wall is scuffed or worn, inspect the
cylinder block lifter bore. If the bottom of the lifter is
scuffed or worn, inspect the camshaft lobe. If the push
rod seat is scuffed or worn, inspect the push rod. An
additive containing EP lube, such as EOS, should
always be added to crankcase oil for run-in when any
new camshaft or lifters are installed. All damaged or
worn lifters should be replaced. For proper lifter
rotation during engine operation, lifter foot must be
convex.
Assembly
1. Place
the check ball on small hole in bottom of
the plunger.
2. Insert
check ball spring on seat in ball retainer
and place retainer over ball so that spring rests on
the ball. Carefully press the retainer into position
in plunger with the blade of a small screw driver.
3. Place the plunger spring over the ball retainer and
slide the lifter body over the spring and plunger,
being careful to line up the oil feed holes in the
lifter body and plunger.
4. Fill the assembly with SAE 10 oil, then insert the
end of a
1/8" drift pin into the plunger and press
down solid. Do not attempt to force or pump the
plunger. At this point, oil holes in the lifter body
and plunger assembly will be aligned.
5. Insert a 1/16" drift pin through both oil holes to
hold the plunger down against the lifter spring
tension.
6. Remove
the
1/8" drift pin, refill assembly with
SAE 10 oil.
7. Install the metering valve and push rod seat.
8. Install the push rod seat retainer, press down on
the push rod seat and remove the 1/16" drift pin
from the oil holes. The lifter is now completely
assembled, filled with oil and ready for
installation. Before installing lifters, coat the
bottom of the lifter with "Molykote" or its
equivalent.
CYLINDER HEAD (FIGURE 6A2-15)
Removal (Left)
Remove intake manifold as previously outlined.
Raise vehicle.
Drain engine block.
Disconnect exhaust pipe.
Remove dipstick tube attachment.
Lower vehicle.
Remove serpentine belt.
Remove A/C compressor and lay aside.
Remove
P/S pump and lay aside.
Loosen rocker arm until able to remove push rod.
Remove head bolts.
Remove head.
HEAD TORQUE SEQUENCE
/7 , 2 ing. Using a 12"
Figure 6A2-1'5 Cylinder Head Installation
Installation (Left)
The gasket surfaces on both head and cylinder
case deck must be clean of any foreign matter and free
of nicks of heavy scratches. Cylinder bolt threads in the
case and threads on the cylinder head bolts must be
clean. Dirt will affect bolt torque.
1. Place the gasket in position, over the dowel pins,
with the note "This Side Up" showing.
2. Install cylinder head.
3. Coat cylinder head bolt threads with sealer,
#1052080 or equivalent, and install bolts.
Page 364 of 1825

2.8 LITER V.6 6A2.13
Torque bolts as shown in Figure 6A2-15.
4. Install
push rods and loosely retain with rocker
arms. Make sure lower ends of
pushrods are in
lifter seats.
5. Install intake manifold.
6. Raise vehicle.
7. Install dipstick tube bracket.
8. Connect exhaust pipe
to exhaust manifold flange.
9. Lower vehicle.
10. Adjust
valve lash as previously outlined.
11. Continue
following intake manifold installation
for build up.
Removal (Right)
Remove intake manifold as previously outlined.
Raise vehicle.
Disconnect exhaust pipe.
Drain engine block.
Lower vehicle.
Loosen rocker arms until able to remove push
rod.
Remove serpentine belt.
Remove tensioner.
Remove A.I.R. bracket.
Remove generator bracket.
Remove head bolts.
Remove head.
Installation (Right)
The gasket surfaces on both the head and cylinder
case
deck must be clean of any foreign matter and free
of nicks of heavy scratches. Cylinder bolt threads in the
case and threads on the cylinder head bolts must be
clean. Dirt will affect bolt torque.
1. Place the gasket in position, over the dowel pins,
with the note "This Side Up" showing.
2. Install cylinder head.
3. Coat cylinder head bolt threads with sealer,
#lo52080 or equivalent, and install bolts.
Torque bolts as shown in (Figure
6A2-15).
Install push rods and loosely retain with rocker
arms. Make sure lower ends of push rods are in
lifter seats.
Install intake manifold.
Raise vehicle.
Install exhaust pipe to exhaust manifold flange.
Lower vehicle.
Adjust valve lash as previously outlined.
Install AIR bracket.
Install tensioner.
Install generator bracket.
Continue following intake manifold installation
for build up.
Disassembly
1. With cylinder head removed, remove rocker arm
nuts, balls and rocker arms (if not previously
done).
2. Using tool J-8062, compress the valve springs and
remove valve keys. Release the compressor tool and
remove spring caps, oil shedders, springs and
damper assemblies, then remove oil seals.
3. Remove valves from cylinder head and place
them in a rack so they can be installed in their
original positions.
Cleaning and Inspection
Clean all carbon from combustion chambers and
valve ports using 'tool
5-8089.
Thoroughly clean valve guides using 5-8 10 1.
Clean all carbon and sludge from push rods,
rocker arms and push rod guides.
Clean valve stems and heads on a buffing wheel.
Clean carbon deposits from head gasket mating
surface.
Inspect cylinder head for cracks in the exhaust
ports, combustion chambers, or external cracks
to the water jacket.
Inspect the valves for burned heads, cracked faces
or damaged stems.
NOTICE: Excessive valve stem to bore clearance
will cause high oil consumption and may cause
valve breakage. Insufficient clearance will result in
noise and sticky functioning of the valve and
disturb engine smoothness.
8. Measure valve stem clearance as follows:
a. Clamp
a dial indicator on one side of the
cylinder head. Locate the indicator so that
movement of the valve stem from side to
side (crosswise to the head) will cause direct
movement of the indicator stem. The
indicator stem must contact the side of the
valve stem just above the guide.
b. Drop
the valve head
1.5mm off the valve
seat.
c. Move
the stem of the valve from side to side,
using light pressure, to obtain a clearance
reading. If clearance exceeds specifications,
it will be necessary to ream valve guides for
oversize valves. Service valves are available
in std., 089,
.394 and .775mm O.S. sizes.
9. Check
valve spring tension with tool J-8056,
spring tester. Springs should be compressed to the
specified height and checked against the
specifications chart. Springs should be replaced if
not within 44
N (10 Ibs.) of the specified load
(without dampers).
10. Inspect
rocker arm studs for wear or damage.
ROCKER ARM STUDS
Cylinder heads use threaded rocker arm studs.
Rocker arm studs that have damaged threads should
be replaced with new studs. If, for some reason, the
threads in the head
are damaged or stripped, the head
can be retapped, and a helical type insert added. If such
an insert is not available, the head should be replaced.
VALVE GUIDES
Valves with oversize stems are available in .089,
,394 and ,775mm over sizes. To ream the valve guide
Page 380 of 1825

V-8 ENGINE BA3-1
SECVON 6A3
TER V8 V N CODE E
TER V8 V N CODE F
TER V8 V N CODE 8
CONTENTS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION .......................... 6A3- 1
ENGINE LUBRICATION .......................... 6A3-2
ON-VEHCILE SERVICE ............................... 6A3-5
...................................... Powertrain Mounts 6A3-5
Intake Manifold ........................................... 6A3-6
Dipstick Tube .............................................. 6A3-7
Exhaust Manifold ........................................... 6A3-7
........................................ Rocker Arm Cover 6A3-8
Rocker Arm and Push Rods ...................... 6A3-8
Valve Stem Oil Seal and/or
Valve Spring
................................................ 6A3-9
Valve Lifters .................................................. 6A3- 10
............................. Cylinder Head Assembly 6A3- 1 1
...................................... Rocker Arm Studs 6A3- 14
...................................... Valve Guide Bores 6A3- 14
Valve Seats .................................................. 6A3- 14
Valves ........................................................... 6A3- 15
Torsional Damper ........................................ 6A3- 15
.
............................. Crankcase Front Cover .... 6A3- 1 5
Oil Seal (Front Cover) ................................... 6A3- 16
Camshaft ...................................................... 6A3- 16
Camshaft Bearings ............................. .. ....... 6A3- 17
Oil Pan ......................................................... 6A3- 18
..................................................... Oil Pump 6A3- 18
............................. Connecting Rod Bearings 6A3- 19
.............................................. Main Bearings 6A3-20
........................................... Rear Main Seal 6A3-22
........... Connecting Rod & Piston Assemblies 6A3-23
............................................ Cylinder Block 6A3-26
............................... Oil Filter Bypass Valve 6A3-27
.......................................... Engine Assembly 6A3-27
................................................... Crankshaft 6A3-28
..................... Sprocket or Gear Replacement 6A3-28
......................................... SPECIFICATIONS 6A3-28
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
CYLINDER BLOCK CAMSHAFT AND DRIVE
The cylinder block is made of cast iron and has The
cast iron camshaft is supported by 5 bearings
8 cylinders arranged in a "V" shape with 4 cylinders and
is chain driven. A steel crankshaft sprocket drives
in each bank.
5 main bearings support the crankshaft the
timing chain which in turn drives the camshaft
which is retained by bearing caps that are machined through a cast iron 'procket.
with the block for proper alignment and clearances.
Cam lobes are ground, hardened and tapered
Cylinders are completely encircled by coolant Jackets, with the high side toward the rear. This, cou~led with
CYLINDER HEAD a sphericalYface on the lifter, causes the "alve lifters to
rotate.
Camshaft bearings are lubricated through oil
The cast iron cylinder heads feature individual
holes which intersect the main oil gallery. The main oil intake and exhaust Ports for each cylinder. Valve gallery is rifle drilled down the center of the block, guides are integral, and rocker arms are retained on above the individual pressed studs.
CRANKSHAFT AND BEARINGS
The crankshaft is cast nodular iron and is
supported by five main bearings
#5 is the end thrust
bearing.
Main bearings are lubricated from oil holes which
intersect the camshaft bearings. The camshaft bearings
are fed oil by the main oil gallery which is rifle drilled
down the center of the block, above the camshaft. Two
additional oil galleries are on either side of the main oil
gallery to provide an oil supply for the hydraulic lifters.
PISTONS AND CONNECTING RODS
The pistons are made of cast aluminum alloy
using two compression rings and one oil control ring.
Piston pins are offset 1/16"
(1.6mm) toward the thrust
side (right hand side) to provide a gradual change in
thrust pressure against the cylinder wall as the piston
travels its path. Pins are Chromium steel and have
a
floating fit in the pistons They are retained in the
connecting rods by a press fit. Connecting rods are
made of forged steel. Full pressure lubrication
is
directed to the connecting rods by drilled oil passages
from the adjacent main bearing journal.
Page 417 of 1825
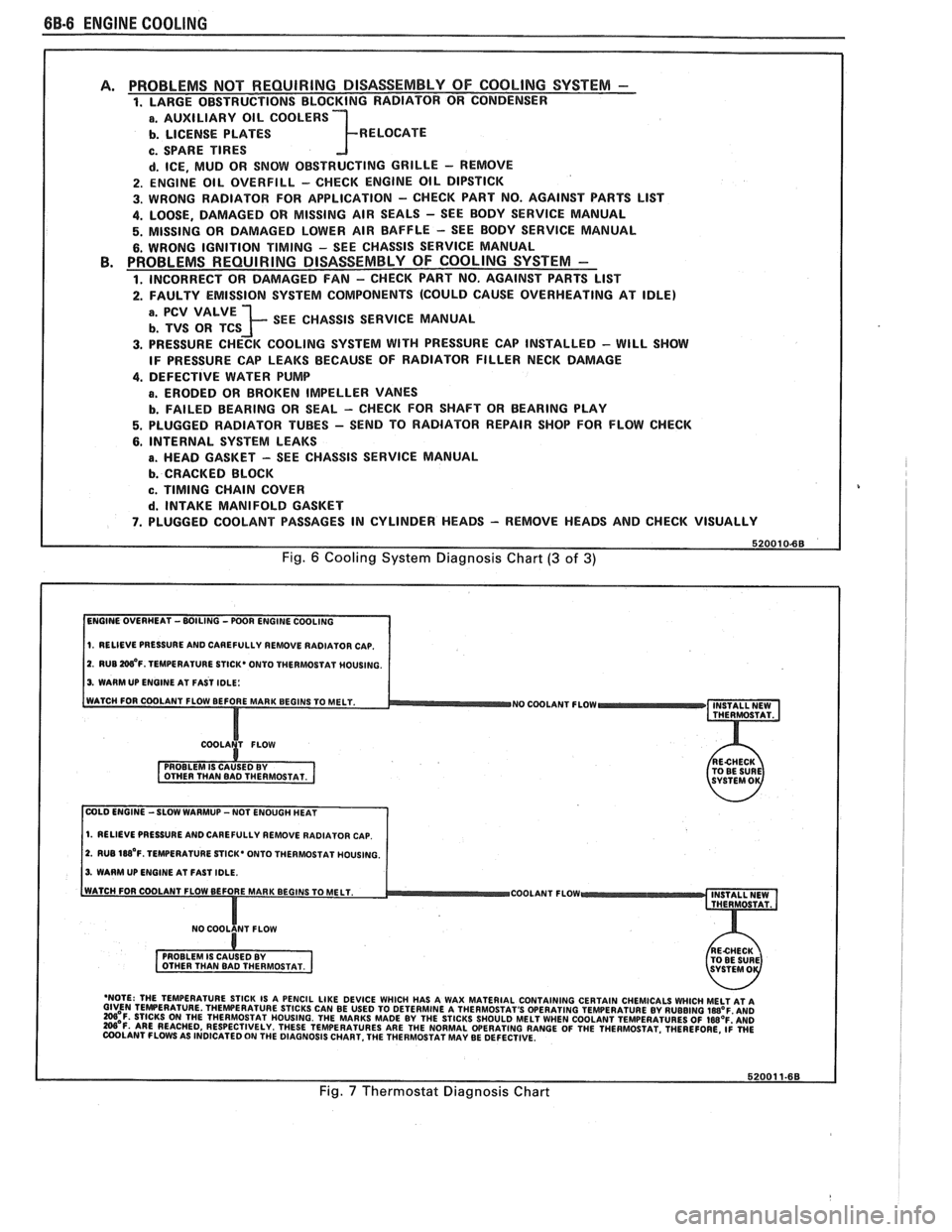
6B-8 ENGINE COOLING
PROBLEMS NOT REQUIRING DISASSEMBLY OF COOLING SYSTEM - 1. LARGE OBSTRUCTIONS BLOCKING RADIATOR OR CONDENSER
a. AUXILIARY OIL COOLERS
b. LICENSE PLATES R ELOCATE
c. SPARE TIRES
d. ICE, MUD OR SNOW OBSTRUCTING GRILLE - REMOVE
2. ENGINE OIL OVERFILL - CHECK ENGINE OIL DIPSTICK
3. WRONG RADIATOR FOR
APPLICATION - CHECK PART NO. AGAINST PARTS LlST
4. LOOSE, DAMAGED OR MISSING AIR SEALS - SEE BODY SERVICE MANUAL
5. MISSING OR DAMAGED LOWER AIR BAFFLE - SEE BODY SERVICE MANUAL
6. WRONG IGNITION TIMING - SEE CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL PROBLEMS REQUIRING DISASSEMBLY OF COOLING SYSTEM -
1. INCORRECT OR DAMAGED FAN - CHECK PART NO. AGAINST PARTS LlST
2. FAULTY EMISSION SYSTEM COMPONENTS (COULD CAUSE OVERHEATING AT IDLE)
; SEE CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
3. PRESSURE CHECK COOLING SYSTEM WITH PRESSURE CAP INSTALLED - WILL SHOW
IF PRESSURE CAP LEAKS BECAUSE OF RADIATOR FILLER NECK DAMAGE
4. DEFECTIVE WATER PUMP
a. ERODED OR BROKEN IMPELLER VANES
b. FAILED BEARING OR SEAL - CHECK FOR SHAFT OR BEARING PLAY
5. PLUGGED RADIATOR TUBES - SEND TO RADIATOR REPAIR SHOP FOR FLOW CHECK
6. INTERNAL SYSTEM LEAKS
B. HEAD GASKET - SEE CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
b. CRACKED BLOCK
c. TIMING CHAIN COVER
d. INTAKE MANIFOLD GASKET
7. PLUGGED COOLANT PASSAGES IN CYLINDER HEADS - REMOVE HEADS AND CHECK VISUALLY
Fig. 6 Cooling System Diagnosis Chart (3 of 3)
1. RELIEVE PRESSURE AND CAREFULLY REMOVE RADIATOR CAP.
2. RUB W'F. TEMPERATURE STICK* ONTO THERMOSTAT MOUSING.
3. WARM UP ENGINE AT FAST IDLE:
WATCH FOR COOLANT FLOW BEFORE MAR
NO COOLANT FLOW INSTALL NEW
THERMOSTAT.
COLD ENGINE -SLOW WARMUP -NOT ENOUGH HEAT
1. RELIEVE PRESSURE AND CAREFULLY REMOVE RADIATOR CAP.
2. RUB 188'~. TEMPERATURE STICK' ONTO THERMOSTAT HOUSING.
3. WARM UP ENGINE AT FAST IDLE.
COOLANT FLOW
- 'NOTE: THE TEMPERATURE STICK IS A PENCIL LIKE DEVICE WHICH HAS A WAX MATERIAL CONTAINING CERTAIN CHEMICALS WHICH MELT AT A GIVEN TEMPERATURE THEWERATURE STICKS CAN BE USED TO DETERMINE A THERMOSTAT'S OPERATING TEMPERATURE BY RUBBING laB°F AN0 =OF. STICKS ON THE THERMOSTAT HOUSING. THE MARKS MADE BY THE STICKS SHOULD MELT WHEN COOLANT TEMPERATURES OF IWOF'AND W'F. ARE REACHED, RESPECTIVELY. THESE TEMPERATURES ARE THE NORMAL WERATING RANGE OF THE THERMOSTAT. THEREFORE, ~i WE COOLANT FLOWS AS INDICATED ON THE DIAGNOSIS CHART. THE THERMOSTAT MAY BE DEFECTIVE.
Fig. 7 Thermostat Diagnosis Chart