steering PONTIAC GRAND AM 2003 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: PONTIAC, Model Year: 2003, Model line: GRAND AM, Model: PONTIAC GRAND AM 2003Pages: 354, PDF Size: 16.3 MB
Page 123 of 354

Interior Lamps
Instrument Panel Brightness
This feature controls the brightness of the instrument
panel lights.
The thumbwheel for this feature
is located on the
instrument panel
to the left of the steering wheel.
Entry/Exit Lighting
When you lift the driver’s door handle or open any door,
the lamps inside your vehicle will go on. These lamps
will fade out after about
10 seconds after all of the doors
have been closed or when the ignition is turned to
ON. These lamps will also go on when you press the
trunk release, unlock symbol button or the horn symbol on the keyless entry system transmitter (if equipped).
The lamps inside your vehicle will stay on for about
10 seconds after your key is removed from the ignition
to provide an illuminated exit.
Dome Lamp
If your vehicle has this feature, the switch on this lamp
has three positions. The
ON position will turn on the
light. The
DOOR position will turn on the light whenever
a door is opened or when the instrument panel
brightness thumbwheel is moved up. The OFF position
will shut
off the lamp completely, even when a door
is opened.
Move the thumbwheel right
to brighten the lights and left
to dim them.
3-1 6
Page 176 of 354

Audio Steering Wheel Controls
If your vehicle has this feature, you can control certain
radio functions using the buttons on your steering
wheel.
A SEEK v: Press the up or the down arrow to tune
to the next or to the previous radio station. If a
cassette tape or compact disc is playing, the player will
down arrow.
zwi\mn~~ \A!ith thp [Ip a.rrn\A/ a.nd reverse with the
PRESET: Press this button to play a station you have
programmed on the radio preset pushbuttons. Every
press of this button will take you to the next preset
station that you have prgrammed.
If a cassette tape is
playing, press this button to play the other side of
the tape.
BAND: Press this button to choose AM, FMI, FM2, or
XM1 or XM2, or DAB1 or DAB2. If a cassette tape
or compact disc is playing, it will stop and the radio
will play.
A VOLUME : Press the up or the down arrow to
increase or to decrease volume.
PLAY: Press this button to play a cassette tape or
compact disc when listening to the radio.
MUTE: Press this button
to silence the system. Press it
again, or any other radio button, to turn on the sound.
3-69
Page 180 of 354

Section 4 Driving Your Vehicle
Your Driving. the Road. and Your Vehicle .......... 4-2
Defensive Driving
........................................... 4.2
Drunken Driving
............................................. 4.2
Control of
a Vehicle ........................................ 4-6
Braking
......................................................... 4-6
Enhanced Traction System (ETS)
..................... 4-9
Steering
...................................................... 4-1 1
Passing ....................................................... 4-14
Loss of Control ............................................. 4-15
Driving at Night
............................................ 4-17
Driving in Rain and on Wet Roads
.................. 4-19
Off-Road
Recovery
....................................... 4-13 City Driving
.................................................. 4-21
Freeway Driving
........................................... 4.22
Before Leaving on a Long Trip
....................... 4-23
Highway Hypnosis
........................................ 4.24
Hill and Mountain Roads
................................ 4-25
Winter Driving
.............................................. 4.26
If You Are Stuck: In Sand, Mud, Ice or Snow ........ 4-31
Towing
.......................................................... 4.32
Towing Your Vehicle
..................................... 4.32
Recreational Vehicle Towing
........................... 4.32
Loading Your Vehicle
.................................... 4-35
Towing a Trailer
........................................... 4.37
4-
1
Page 185 of 354
Control of a Vehicle
You have three systems that make your vehicle go
where you want it
to go. They are the brakes, the
steering and the accelerator.
All three systems have to
do their work at the places where the tires meet
the road. Sometimes,
as when you’re driving
on snow or ice, it’s
easy to ask more of those control systems than the
tires and road can provide. That means you can lose
control
of your vehicle. Also see Enhanced Traction
System
(ETS) on page 4-9.
Braking
Braking action involves perception time and
reaction time.
First, you have to decide to push on the brake pedal.
That’s
perception time. Then you have to bring up your
foot and do it. That’s
reaction time.
Average reaction time is about 3/4 of a second. But
that’s only an average. It might be less with one driver
and as long as two or three seconds or more with
another. Age, physical condition, alertness, coordination
and eyesight all play a part.
So do alcohol, drugs and
frustration. But even in
3/4 of a second, a vehicle moving
at
60 mph (1 00 km/h) travels 66 feet (20 m). That
could be a lot of distance in an emergency,
so keeping
enough space between your vehicle and others is
important.
4-6
Page 188 of 354

Remember: Anti-lock doesn’t change the time you need
to get your foot up to the brake pedal or always
decrease stopping distance. If you get
too close to the
vehicle in front of you, you won’t have time to apply
your brakes
if that vehicle suddenly slows or stops.
Always leave enough room up ahead
to stop, even
though you have anti-lock brakes.
Using Anti-Lock
Don’t pump the brakes. Just hold the brake pedal down
firmly and let anti-lock work for you. You may feel a
slight brake pedal pulsation or notice some noise, but
this is normal.
Braking in Emergencies
At some time, nearly every driver gets into a situation
that requires hard braking.
If you have anti-lock, you can steer and brake at the
same time. However,
if you don’t have anti-lock,
your first reaction
- to hit the brake pedal hard and hold
it down
- may be the wrong thing to do. Your wheels
can stop rolling. Once they do, the vehicle can’t respond
to your steering. Momentum will carry it in whatever
direction it was headed when the wheels stopped rolling.
That could be
off the road, into the very thing you
LAtara tnrinn tn 9 rni VGI G 11 yll ILJ 1W ,\,Id, Gr intG traffic. If
you don’t have anti-lock, use a “squeeze” braking
technique. This will give you maximum braking while
maintaining steering control. You can do this by pushing
on the brake pedal with steadily increasing pressure.
In an emergency, you will probably want
to squeeze the
brakes hard without locking the wheels. If you hear or
feel the wheels sliding, ease
off the brake pedal.
This will help you retain steering control. If you
do have
anti-lock,
it’s different. See “Anti-Lock Brakes.’’
In many emergencies, steering can help you more than
even the very best braking.
Enhanced Traction System (ETS)
Your vehicle may have an Enhanced Traction System
(ETS) that limits wheel spin. This is especially useful in
slippery road conditions. The system operates only
if
it senses that one or both of the front wheels are
spinning or beginning
to lose traction. When this
happens, the system reduces engine power and may
aiso upshiii ihe iransaxie io iirrlii wheei spirl.
4-9
Page 190 of 354

To limit wheel spin, especially in slippery road
conditions, you should always leave the Enhanced
Traction System on. But you can turn the system
off if
you prefer.
To turn the system on or off, press the ETS button on
the instrument panel.
When you turn the system
off, the Enhanced Traction
System warning light will come on and stay on.
If
the Enhanced Traction System is limiting wheel spin
when you press the button
to turn the system off,
the warning light will come on
- but the system won’t
turn
off right away. It will wait until there’s no longer
a current need
to limit wheel spin.
You can turn the system back on at any time by
pressing the button again. The Enhanced Traction
System warning light should go off.
Steering
Power Steerin
If you lose power steering assist because the engine
stops or the system is not functioning, you can steer but
it will take much more effort.
Steering Tips
Driving on Curves
It’s important to take curves at a reasonable speed.
A lot of the “driver lost control” accidents mentioned on
the news happen on curves. Here’s why:
Experienced driver or beginner, each of us is subject
to
the same laws of physics when driving on curves.
The traction of the tires against the road surface makes
it possible
for the vehicle to change its path when
you turn the front wheels.
If there’s no traction, inertia
will keep the vehicle going in the same direction. If
you’ve ever tried to steer a vehicle on wet ice, you’ll
understand this.
The traction you can get in a curve depends on the
condition of your tires and the road surface, the angle at
which the curve
is banked, and your speed. While
you’re in a curve, speed
is the one factor you can
control.
4-1 1
Page 191 of 354

Suppose you’re steering through a sharp curve.
Then you suddenly accelerate. Both control
systems
- steering and braking - have to do their work
where the tires meet the road. Unless you have
four-wheel anti-lock brakes, adding the hard braking can
demand
too much of those places. You can lose
control.
The same thing can happen
if you’re steering through a
sharp curve and you suddenly accelerate. Those two
control systems
- steering and acceleration - can
overwhelm those places where the tires meet the road
and make you lose control. See
Enhanced Traction
System
(ETS) on page 4-9.
What should you do if this ever happens? Ease up on
the brake or accelerator pedal, steer the vehicle the way
you want it
to go, and slow down.
Speed limit signs near curves warn that you should
adjust your speed. Of course, the posted speeds
are based on good weather and road conditions. Under
less favorable conditions you’ll want
to go slower.
If you need
to reduce your speed as you approach a
curve, do it before you enter the curve, while your front
wheels are straight ahead.
Try to adjust your speed so you can “drive” through the
curve. Maintain a reasonable, steady speed. Wait
to
accelerate until you are out of the curve, and then
accelerate gently into the straightaway.
4-1 2
Steering in Emergencies
There are times when steering can be more effective
than braking. For example, you come over a hill and find
a truck stopped in your lane, or
a car suddenly pulls
out from nowhere, or a child darts out from between
parked cars and stops right in front of you. You
can avoid these problems by braking
- if you can stop
in time. But sometimes you can’t; there isn’t room.
That’s the time for evasive action
- steering around the
problem.
Your vehicle can perform very well in emergencies like
these. First apply your brakes
- but, unless you
have anti-lock, not enough
to lock your wheels.
See
Braking on page 4-6. It is better to remove as much
speed as you can from a possible collision. Then
steer around the problem,
to the left or right depending
on the space available.
Page 192 of 354
An emergency like this requires close attention and a
quick decision. If you are holding the steering wheel at
the recommended
9 and 3 o’clock positions, you
can turn it a
full 180 degrees very quickly without
removing either hand. But you have
to act fast, steer
quickly, and just as quickly straighten the wheel
The fact that such emergency situations are always
possible is a good reason
to practice defensive driving
at all times and wear safety belts properly.
UI ILG yuu I lavt avwlutu LI IG VUJG~L. ---- ..-.. L-..- -.,-;&-A +hn -Limn+
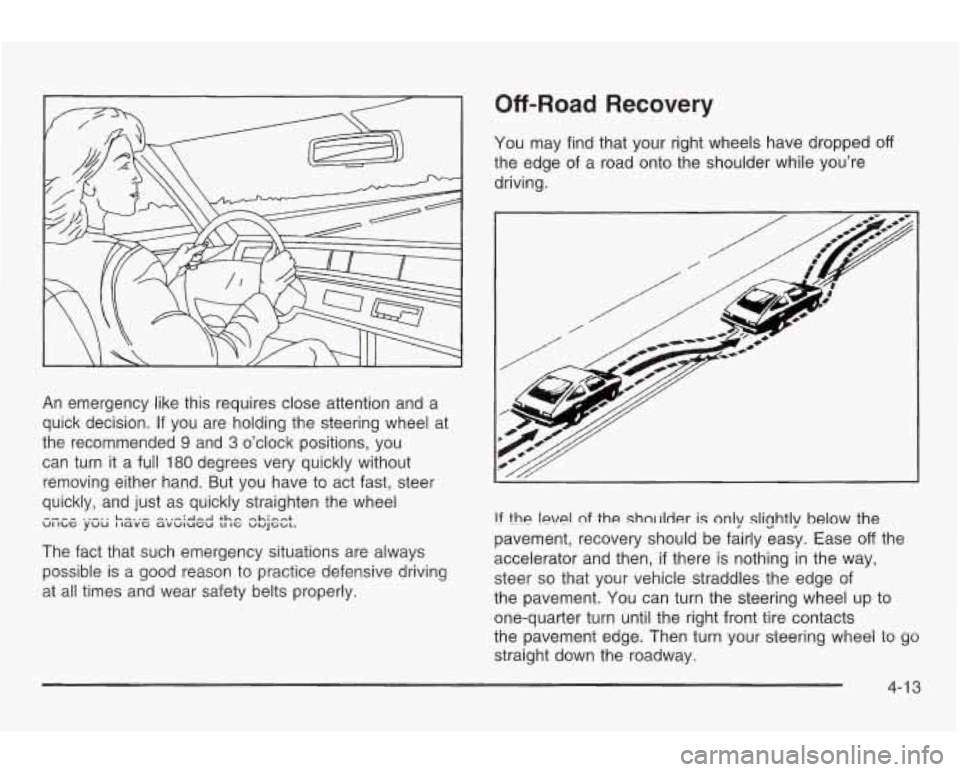
Off-Road Recovery
You may find that your right wheels have dropped off
the edge of a road onto the shoulder while you’re
driving.
!f the !eve! nf the sholrlder is only slightly below the
pavement, recovery should be fairly easy. Ease
off the
accelerator and then,
if there is nothing in the way,
steer
so that your vehicle straddles the edge of
the pavement. You can turn the steering wheel up to
one-quarter turn until the right front tire contacts
tne pavement edge. Then turn your steering wheel
io yo
straight down the roadway.
4-1 3
Page 194 of 354

Check your mirrors, glance over your shoulder, and
start your left lane change signal before moving out
of the right lane to pass. When you are far
enough ahead of the passed vehicle to see its front
in your inside mirror, activate your right lane
change signal and move back into the right lane.
(Remember that your right outside mirror is convex.
The vehicle you just passed may seem
to be
farther away from you than it really is.)
Try not to pass more than one vehicle at a time on
two-lane roads. Reconsider before passing the
next vehicle.
Don’t overtake a slowly moving vehicle too rapidly.
Even though the brake lamps are not flashing, it
may be slowing down or starting to turn.
0 If you’re being passed, make it easy for the
following driver to get ahead of you. Perhaps you
can ease a little
to the right.
Loss of Control
Let’s review what driving experts say about what
happens when the three control systems (brakes,
steering and acceleration) don’t have enough friction
where the tires meet the road to do what the driver has
asked.
In any emergency, don’t give up. Keep trying to steer
and constantly seek an escape route or area of
less danger.
Skidding
In a skid, a driver can lose control of the vehicle.
Defensive drivers avoid most skids by taking reasonable
care suited to existing conditions, and by not
“overdriving” those conditions. But skids are always
possible.
The three types of skids correspond to your vehicle’s
three control systems. In the braking skid, your wheels
aren’t rolling. In the steering or cornering skid,
too
much speed or steering in a curve causes tires to slip
and lose cornering force.
And In the acceleratlon
skid, too much throttle causes the driving wheels
to spin.
4-1 5
Page 195 of 354

A cornering skid is best handled by easing your foot off
the accelerator pedal.
If you have the Enhanced Traction System, remember:
It helps to avoid only the acceleration skid.
If you do
not have the Enhanced Traction System, or
if the system
is
off, then an acceleration skid is also best handled
by easing your foot
off the accelerator pedal.
If your vehicle starts
to slide, ease your foot off the
accelerator pedal and quickly steer the way you want
the vehicle to go. If you start steering quickly enough,
your vehicle may straighten out. Always be ready
for a second skid
if it occurs.
Of course, traction
is reduced when water, snow, ice,
gravel or other material is on the road. For safety, you’ll
want to slow down and adjust your driving to these
conditions. It is important to slow down on slippery
surfaces because stopping distance will be longer and
vehicle control more limited. While driving on a surface
with reduced traction, try
your best to avoid sudden steering, acceleration
or braking (including engine braking by shifting to a
lower gear). Any sudden changes could cause the tires
to slide. You may not realize the surface is slippery
until your vehicle is skidding. Learn to recognize warning
clues
- such as enough water, ice or packed snow
on the road to make a “mirrored surface”
- and slow
down when you have any doubt.
If you have the anti-lock braking system, remember: It
helps avoid only the braking skid. If you do not have
anti-lock, then in a braking skid (where the wheels are
no longer rolling), release enough pressure
on the
brakes to get the wheels rolling again. This restores
steering control. Push the brake pedal down steadily
when you have to stop suddenly. As long as the wheels
are rolling, you will have steering control.
4-1 6