transfer case Ram 3500 2019 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: RAM, Model Year: 2019, Model line: 3500, Model: Ram 3500 2019Pages: 696, PDF Size: 13.89 MB
Page 315 of 696

STARTING AND OPERATING 313
NOTE:
The four-wheel drive system will not allow shifts between
2WD/4WD HIGH if the front and/or rear wheels are spin-
ning (no traction). In this situation, the selected position indi -
cator light will flash and the original position indicator light
will remain ON. At this time, reduce speed and stop spin -
ning the wheels to complete the shift.
2WD Or 4WD HIGH To 4WD LOW
NOTE:
When shifting into or out of 4WD LOW some gear noise may
be heard. This noise is normal and is not detrimental to the
vehicle or occupants.
Shifting can be performed with the vehicle rolling 2 to 3 mph
(3 to 5 km/h) or completely stopped. You can use either of
the following procedures:
Preferred Procedure
1. With the engine running, slow the vehicle to 2 to 3 mph (3 to 5 km/h).
2. Shift the transmission into NEUTRAL.
3. While still rolling, push the desired position on the transfer case control switch. 4. After the desired position indicator light is ON (not
flashing), shift the transmission back into gear.
Alternate Procedure
1. Bring the vehicle to a complete stop.
2. With the ignition switch in the ON position and the engine running, shift the transmission into NEUTRAL.
3. Push the desired position on the transfer case control switch.
4. After the desired position indicator light is ON (not flashing), shift the transmission back into gear.
NOTE:
• If Steps 1 or 2 of either the Preferred or Alternate Proce -
dure are not satisfied prior to attempting the shift, then the
desired position indicator light will flash continuously
while the original position indicator light is ON, until all
requirements have been met.
• The ignition switch must be in the ON position for a shift to take place and for the position indicator lights to be
operable. If the ignition switch is not in the ON position,
the shift will not take place and no position indicator lights
will be on or flashing.
5
Page 316 of 696

314 STARTING AND OPERATING
Manually Shifted Transfer Case — If Equipped
The transfer case provides four mode positions:
• Two-Wheel Drive High Range (2H)
• Four-Wheel Drive Lock High Range (4H)
• Neutral (N)
• Four-Wheel Drive Low Range (4L)
For additional information on the appropriate use of each
transfer case mode position, see the information below:
2H
Two-Wheel Drive High Range — This range is for normal
street and highway driving on dry, hard surfaced roads.
4H
Four-Wheel Drive Lock High Range — This range locks the
front and rear driveshafts together forcing the front and rear
wheels to rotate at the same speed. Additional traction for
loose, slippery road surfaces only.
NEUTRAL (N)
Neutral — This range disengages both the front and rear
driveshafts from the powertrain. To be used for flat towingbehind another vehicle. Refer to “Recreational Towing” in
“Starting And Operating” for further information.
4L
Four-Wheel Drive Low Range — This range locks the front
and rear driveshafts together forcing the front and rear
wheels to rotate at the same speed. Additional traction and
maximum pulling power for loose, slippery road surfaces
only. Do not exceed 25 mph (40 km/h).
This transfer case is intended to be driven in the 2H position
for normal street and highway conditions such as dry, hard
surfaced roads.
When additional traction is required, the 4H and 4L posi -
tions can be used to lock the front and rear driveshafts
together and force the front and rear wheels to rotate at the
same speed. This is accomplished by simply moving the gear
selector to the desired positions once the appropriate speed
and gear requirements are met, refer to “Shifting Procedure
– Manually Shifted Transfer Case” in this section for further
information.
The 4H and 4L positions are intended for loose, slippery road
surfaces only. Driving in the 4H and 4L positions on dry,
hard surfaced roads may cause increased tire wear and
damage to the driveline components.
Page 317 of 696

STARTING AND OPERATING 315
The “Transfer Case Position Indicator Light” in the instru-
ment cluster will alert the driver that the vehicle is in
four-wheel drive and that the front and rear driveshafts are
locked together. This light will illuminate when the transfer
case is shifted into either the 4H or 4L position. There is no
light for the 2H or NEUTRAL positions on some models.
When operating your vehicle in 4L, the engine speed is
approximately three times that of the 2H or 4H positions at a
given road speed. Take care not to overspeed the engine and
do not exceed 25 mph (40 km/h).
Proper operation of four-wheel drive vehicles depends on
tires of equal size, type and circumference on each wheel.
Any difference will adversely affect shifting and can cause
damage to the drivetrain.
NOTE:
Do not attempt to make a shift while only the front or rear
wheels are spinning, as this can cause damage to driveline
components.
Because four-wheel drive provides improved traction, there
is a tendency to exceed safe turning and stopping speeds. Do
not go faster than road conditions permit.NOTE:
Delayed shifts out of four-wheel drive may be experienced
due to uneven tire wear, low or uneven tire pressures, exces
-
sive vehicle loading, or cold temperatures.
Two-Wheel Drive High Range (2H)
Rear-Wheel Drive High Range — This range is for normal
street and highway driving on dry hard surfaced roads.
Four-Wheel Drive High Range (4H)
Four-Wheel Drive High Range — This range locks the front
and rear driveshafts together forcing the front and rear
wheels to rotate at the same speed. Additional traction for
loose, slippery road surfaces only.
WARNING!
You or others could be injured or killed if you leave the
vehicle unattended with the transfer case in the
NEUTRAL position without first fully engaging the
parking brake. The transfer case NEUTRAL position
disengages both the front and rear drive shafts from the
powertrain and will allow the vehicle to roll, even if the
transmission is in PARK. The parking brake should
always be applied when the driver is not in the vehicle.
5
Page 318 of 696

316 STARTING AND OPERATING
Neutral (N)
Neutral — This range disengages the front and rear drivesh-
afts from the powertrain. To be used for flat towing behind
another vehicle. Refer to “Recreational Towing” in “Starting
And Operating” for further information.
Four-Wheel Drive Low Range (4L)
Four-Wheel Drive Low Range — This range locks the front
and rear driveshafts together forcing the front and rear
wheels to rotate at the same speed. Additional traction and
maximum pulling power for loose, slippery road surfaces
only. Do not exceed 25 mph (40 km/h).
Shifting Procedure — Manually Shifted Transfer Case
2H To 4H
Shifting between 2H and 4H can be made with the vehicle
stopped or in motion. If the vehicle is in motion, shifts can be
made up to 55 mph (88 km/h). With the vehicle in motion,
the transfer case will engage/disengage faster if you
momentarily release the accelerator pedal after completing the shift. Apply a constant force when shifting the transfer
case lever.
2H Or 4H To 4L
NOTE:
When shifting into or out of 4L some gear noise may be
heard. This noise is normal and is not detrimental to the
vehicle or occupants.
With the vehicle rolling at 2 to 3 mph (3 to 5 km/h), shift the
transmission into NEUTRAL. While the vehicle is coasting at
2 to 3 mph (3 to 5 km/h), shift the transfer case lever firmly
to the desired position. Do not pause in transfer case
NEUTRAL.
NOTE:
• Pausing in transfer case NEUTRAL in vehicles equipped
with an automatic transmission may require shutting the
engine OFF to avoid gear clash while completing the shift.
If difficulty occurs, shift the transmission into NEUTRAL,
hold your foot on the brake, and turn the engine OFF.
Complete the range shift to the desired mode.
• Shifting into or out of 4L is possible with the vehicle completely stopped, however difficulty may occur due to
the mating clutch teeth not being properly aligned. Several
attempts may be required for clutch teeth alignment and
CAUTION!
Do not use 4L (Low) range when operating the vehicle on
dry pavement. Driveline hardware damage can result.
Page 319 of 696
STARTING AND OPERATING 317
shift completion to occur. The preferred method is with the
vehicle rolling 2 to 3 mph (3 to 5 km/h). Avoid attempting
to engage or disengage 4L with the vehicle moving faster
than 2 to 3 mph (3 to 5 km/h).
• Do not attempt to shift into or out of 4L while the transmis -
sion is in gear.
Transfer Case Position Indicator Light
The “Transfer Case Position Indicator Light” in the instru-
ment cluster is used to alert the driver that the front axle is
fully engaged and all four wheels are driving.
AIR SUSPENSION SYSTEM (2500/3500 MODELS) — IF
EQUIPPED
Description
This air suspension system is a rear leveling ride height
system. The main purpose of this system is to maintain the
truck’s rear ride height level. There are two selectable heights
that can be chosen based on your operating conditions.
The system requires that the ignition be in ON/RUN posi -
tion or the engine running with zero vehicle speed for all
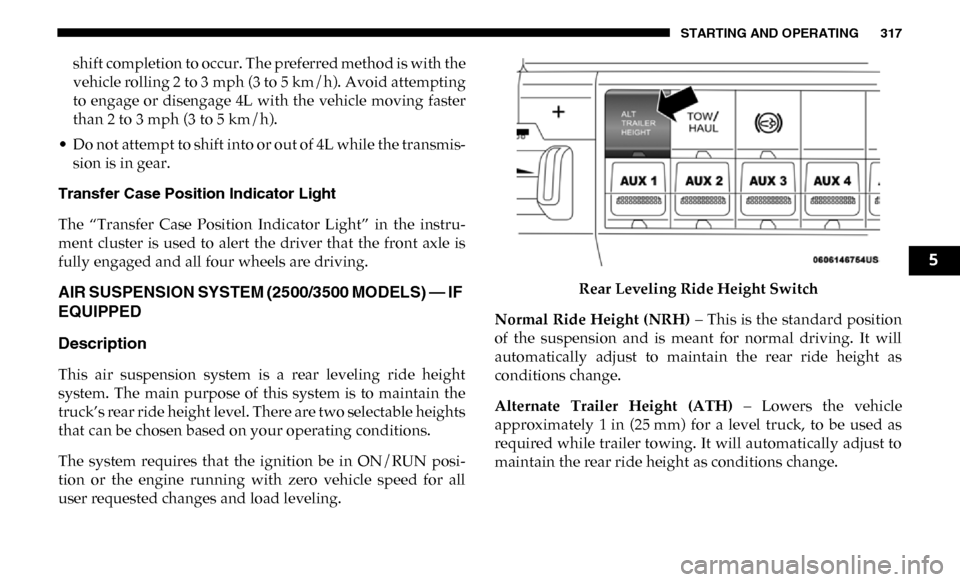
user requested changes and load leveling. Rear Leveling Ride Height Switch
Normal Ride Height (NRH) – This is the standard position
of the suspension and is meant for normal driving. It will
automatically adjust to maintain the rear ride height as
conditions change.
Alternate Trailer Height (ATH) – Lowers the vehicle
approximately 1 in (25 mm) for a level truck, to be used as
required while trailer towing. It will automatically adjust to
maintain the rear ride height as conditions change.
5
Page 326 of 696

324 STARTING AND OPERATING
and left halves of the bar must be aligned. This alignment
may require that the vehicle be driven onto level ground or
rocked from side to side.
To return to the On-Road mode; push the SWAY BAR button
again.
SAFE OFF-ROAD DRIVING — POWER WAGON ONLY
Off-Road Driving Tips And Vehicle Characteristics
Your vehicle has excellent on and off-road capabilities. These
off-road capabilities will allow you to explore those wilder-
ness trails where few travel, providing a source of exciting
and satisfying recreation. Before you venture out, you
should contact your local governmental agency to determine
the designated off-road vehicle (ORV) trails or recreation areas. You should always tread lightly and only use estab
-
lished roads, trails or ORV recreational areas.
The National Forest Service, Bureau of Land Management,
or local Department of Natural Resources are a wealth of
information and usually have maps with marked trails.
Skid Plates And Underbody Protection
Steel skid plates protect the major driveline components of
the truck including the fuel tank, transfer case and steering
damper. In addition, this vehicle is equipped with boxed
cross members and fore/aft rails. This additional protection
allows the vehicle to be utilized in severe off-road situations
that would be considered impassable by a normal truck.
Ramp Travel Index (RTI)
The ramp travel index is the distance, in inches, that you can
drive your vehicle with one wheel on a 20-degree ramp
without lifting any other wheel off the ground. This distance
up the ramp divided by the wheelbase of the vehicle and
multiplied by 1,000 is the RTI. This vehicle has an RTI of 510,
which means you can articulate one front wheel 26 inches (66
cm) in the air while the other three wheels remain in contact
with the ground.
WARNING!
If the stabilizer/sway bar will not return to On-Road
mode, vehicle stability is reduced. Do not attempt to
drive the vehicle over 18 mph (29 km/h). Driving faster
than 18 mph (29 km/h) may cause loss of control of the
vehicle, which could result in serious injury or death.
Contact your local service center for assistance.
Page 328 of 696

326 STARTING AND OPERATING
When To Use Low Range
When driving off-road, shift into 4LO (Low Range) for addi-
tional traction or to improve handling and control on slip -
pery or difficult terrain. Due to the lower gearing, low range
will allow the engine to operate in a higher power range.
This will allow you to idle over obstacles and down hills,
with improved control and less effort. Also, use 4LO (Low
Range) in rain, ice, snow, mud, sand, to get heavy loads
rolling, improve traction, or whenever 4HI (High Range)
traction will not do the job.
Driving In Snow, Mud And Sand
There is a drastic reduction in traction when driving in snow,
mud or sand. The vehicle will be less responsive to steering,
acceleration and braking inputs. Therefore you should accel -
erate slowly, leave greater stopping distances and avoid
abrupt vehicle maneuvers. You want to keep a slow constant
steady pace. The key is to maintain the vehicle's momentum. •
Snow – In heavy snow or for additional control and trac -
tion at slower speeds, shift the transmission to a low gear
and shift the transfer case to 4LO (Low Range) if necessary.
Do not shift to a lower gear than necessary to maintain
headway. Over-revving the engine can spin the wheels
and traction will be lost. If you start to slow to a stop, try
turning your steering wheel no more than a ¼ turn quickly
back and forth, while still applying throttle. This will allow
the tires to get a fresh "bite" and help maintain your
momentum.
• Mud – Deep mud creates a great deal of suction around
the tires and is very difficult to get through. You should
use 4LO (Low Range) with a gear low enough to maintain
your momentum without shifting. If you start to slow to a
stop, try turning your steering wheel no more than a ¼
turn quickly back and forth for additional traction. Mud
holes pose an increased threat of vehicle damage and
getting stuck. They are normally full of debris from
previous vehicles getting stuck. As a good practice before
CAUTION!
Never park your vehicle over dry grass or other
combustible materials. The heat from your vehicle
exhaust system could cause a fire.
CAUTION!
On icy or slippery roads, do not downshift at high
engine RPMs or vehicle speeds because engine braking
may cause skidding and loss of control.
Page 331 of 696

STARTING AND OPERATING 329
Getting High Centered
If you get hung up or high centered on an object, get out of
the vehicle and try to determine what the vehicle is hung up
on, where it is contacting the underbody and what is the best
direction to recover the vehicle. Depending on what you are
in contact with, jack the vehicle up and place a few rocks
under the tires so the weight is off of the high point when
you let the vehicle down. You can also try rocking the vehicle
or winching the vehicle off the object.
Hill Climbing
Hill climbing requires good judgment and a good under-
standing of your abilities and your vehicle's limitations. Hills
can cause serious problems. Some are just too steep to climb
and should not be attempted. You should always feel confi -
dent with the vehicle and your abilities. You should always
climb hills straight up and down. Never attempt to climb a
hill on an angle. •
Before Climbing A Steep Hill – As you approach a hill
consider its grade or steepness. Determine if it is too steep.
Look to see what the traction is on the hill side trail. Is the
trail straight up and down? What is on top and the other
side? Are there ruts, rocks, branches or other obstacles on
the path? Can you safely recover the vehicle if something
goes wrong? If everything looks good and you feel confi -
dent, then change transmission into a lower gear, shift the
transfer case into 4LO (Low) and proceed with caution.
You should use first gear and 4LO (Low Range) for very
steep hills.
• Driving Up Hill – Once you have determined your ability
to proceed and have shifted into the appropriate gear, line
your vehicle up for the straightest possible run. Accelerate
with an easy constant throttle and apply more power as
you start up the hill. Do not race forward into a steep
grade, the abrupt change of grade could cause you to lose
control. If the front end begins to bounce, ease off the
throttle slightly to bring all four tires back on the ground.
As you approach the crest of the hill ease off the throttle
and slowly proceed over the top. If the wheels start to slip
as you approach the crest of a hill, ease off the accelerator
and maintain headway by turning the steering wheel no
more than a ¼ turn quickly back and forth. This will
provide a fresh "bite" into the surface and will usually
CAUTION!
Winching or rocking the vehicle off hard objects
increases the risk of underbody damage.
5
Page 333 of 696

STARTING AND OPERATING 331
the brakes are required to control vehicle speed, apply
them lightly and avoid locking or skidding the tires.
Driving Through Water
Extreme care should be taken crossing any type of water.
Water crossings should be avoided if possible and only be
attempted when necessary, in a safe responsible manner.
You should only drive through areas which are designated
and approved. You should tread lightly and avoid damage
to the environment. You should know your vehicle's abilities
and be able to recover it if something goes wrong. You
should never stop or shut a vehicle off when crossing deep
water unless you ingested water into the engine air intake. If
the engine stalls do not attempt to restart it. Determine if it
has ingested water first. The key to any crossing is low andslow. You want to use first gear in 4L (Low Range) and
proceed very slowly with a constant slow speed (3-5 mph
[5–8 km/h] maximum) and light throttle. Keep the vehicle
moving; do not try to accelerate through the crossing. After
crossing any water higher than the bottom of the axle differ
-
entials, you should inspect all of the vehicle fluids for signs
of water ingestion.
• Before You Cross Any Type Of Water – As you approach
any type of water you need to determine if you can cross it
safely and responsibly. If necessary, get out and walk
through the water or probe it with a stick. You need to be
sure of its depth, approach angle, current and bottom
condition. Be careful of murky or muddy waters, check for
hidden obstacles. Make sure you will not be intruding on
any wildlife and you can recover the vehicle if necessary.
The key to a safe crossing is the water depth, current and
bottom conditions. On soft bottoms the vehicle will sink in,
WARNING!
If the engine stalls or you lose headway or cannot make
it to the top of a steep hill or grade, never attempt to turn
around. To do so may result in tipping and rolling the
vehicle, which may result in severe injury. Always back
carefully straight down a hill in REVERSE. Never back
down a hill in NEUTRAL using only the vehicle brakes.
Never drive diagonally across a hill, always drive
straight up or down.
CAUTION!
Water ingestion into the axles, transmission, transfer
case, engine or vehicle interior can occur if you drive too
fast or through too deep of water. Water can cause
permanent damage to engine, driveline or other vehicle
components and your brakes will be less effective once
wet and/or muddy.
5
Page 421 of 696

STARTING AND OPERATING 419
(Continued)
Perform the maintenance listed in the “Scheduled
Servicing”. Refer to “Scheduled Servicing” in “Servicing
And Maintenance” for the proper maintenance intervals.
When towing a trailer, never exceed the GAWR or GCWR
ratings.• Then, during the first 500 miles (805 km) that a trailer is
towed, do not drive over 50 mph (80 km/h) and do not
make starts at full throttle. This helps the engine and
other parts of the vehicle wear in at the heavier loads.
WARNING!
• Make certain that the load is secured in the trailer and will not shift during travel. When trailering cargo that
is not fully secured, dynamic load shifts can occur that
may be difficult for the driver to control. You could lose
control of your vehicle and have a collision.
• When hauling cargo or towing a trailer, do not overload your vehicle or trailer. Overloading can cause a loss of
control, poor performance or damage to brakes, axle,
engine, transmission, steering, suspension, chassis
structure or tires. CAUTION!
(Continued)
• Safety chains must always be used between your
vehicle and trailer. Always connect the chains to the
hook retainers of the vehicle hitch. Cross the chains
under the trailer tongue and allow enough slack for
turning corners.
• Vehicles with trailers should not be parked on a grade. When parking, apply the parking brake on the tow
vehicle. Put the tow vehicle transmission in PARK. For
four-wheel drive vehicles, make sure the transfer case
is not in NEUTRAL. Always, block or "chock" the
trailer wheels.
• GCWR must not be exceeded.
• Total weight must be distributed between the tow vehicle and the trailer such that the following four
ratings are not exceeded:
1. GVWR
2. GTW
3. GAWR
4. Tongue weight rating for the trailer hitch utilized.
WARNING! (Continued)
5