charging RENAULT SCENIC 2010 J95 / 3.G Petrol Injection S3000 Injection Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: RENAULT, Model Year: 2010, Model line: SCENIC, Model: RENAULT SCENIC 2010 J95 / 3.GPages: 230, PDF Size: 0.92 MB
Page 7 of 230

PETROL INJECTION
Fault finding - System operation
17B
17B - 7
PETROL INJECTION
Fault finding - System operation
17B
17B - 7V9 MR-372-J84-17B050$094.mif
S3000 Injection
Program No.: AD
Vdiag No.: 4C / 54PETROL INJECTION
Fault finding - System operation
1. SYSTEM OPERATION
Composition
The injection system consists of the:
– accelerator potentiometer,
– clutch pedal switch,
– TDC sensor,
– atmospheric pressure sensor,
– air temperature sensor,
– coolant temperature sensor,
– upstream oxygen sensor,
– downstream oxygen sensor,
– cruise control switch,
– steering column switch,
– cruise control on/off switch,
– fuel vapour absorber,
– injection computer,
– motorised throttle valve,
– 4 injectors,
– 4 pencil coils,
– pinking sensor,
– camshaft dephaser solenoid valve (non-LPG K4M only),
– camshaft position sensor (non-LPG K4M only),
– turbocharging pressure sensor (F4R turbo only)
– electric coolant pump (F4R turbo only),
– wastegate solenoid valve (only on F4R Turbo),
– turbocharging solenoid valve (only on F4R-Turbo)
Computer
128 track SAGEM type S3000 FLASH EEPROM computer controlling injection and ignition.
Multipoint injection in sequential mode.
Connections to the other computers:
– air conditioning,
– UCH,
– protection and switching unit (UPC)
– Automatic Gearbox Electronic Control Unit (AUTO).
– airbag,
– ABS/ESP,
– instrument panel.
MR-372-J84-17B050$094.mif
Page 8 of 230

PETROL INJECTION
Fault finding - System operation
17B
17B - 8
PETROL INJECTION
Fault finding - System operation
17B
17B - 8V9 MR-372-J84-17B050$094.mif
S3000 Injection
Program No.: AD
Vdiag No.: 4C / 54
2. Role of components, operating strategy
Engine immobiliser
The Verlog 4 type immobiliser function is managed by the UCH computer and the engine management computer.
Before any starting request, the engine management computer is protected.
When a starting request is made, the injection computer and the UCH exchange authentication data via the multiplex
network; this determines whether the engine start is authorised.
After more than 5 consecutive failed authentication attempts, the engine management computer goes into protection
(antiscanning) mode and no longer tries to authenticate the UCH computer. It only exits this mode when the
following sequence of operations occurs:
– the ignition is left on for at least 20 seconds,
– the message is switched off,
– the injection computer self-supply cuts out when it should (the time varies according to engine temperature).
After this, only one authentication attempt is allowed. If this fails again, repeat the sequence of operations described
above.
If the engine management computer still fails to unlock, contact the Techline.
Impact detected
If an impact has been stored by the injection computer, switch off the ignition for 10 seconds, then switch it back on
so that the engine can be started. Clear the faults.
Torque management
The torque structure is the system for managing engine torque. It is necessary for some functions such as the
electronic stability program (ESP) and the automatic gearbox.
Each inter-system (ESP and automatic gearbox) sends a request for torque via the multiplex network to the injection
computer. It arbitrates between the inter-system torque requests and the driver's request (pedal or cruise control/
speed limiter). The result of the arbitration gives the torque setpoint. The torque structure uses the torque setpoint to
calculate the throttle position setpoint, the advance and, if there is turbocharging, the turbocharger valve setpoint
(wastegate) for engines fitted with a turbocharger. WARNING
Disconnect the injection computer when carrying out any welding work on the vehicle.
Page 12 of 230

PETROL INJECTION
Fault finding - System operation
17B
17B - 12
PETROL INJECTION
Fault finding - System operation
17B
17B - 12V9 MR-372-J84-17B050$094.mif
S3000 Injection
Program No.: AD
Vdiag No.: 4C / 54
A vehicle is fitted with an upstream sensor if the configuration reading LC003 Upstream oxygen sensor is WITH.
For the upstream sensor to be operational very rapidly, it is heated. Sensor heating ET052 Upstream O
2 sensor
heating is only ACTIVE when the engine is running. It is disabled above 84 mph (140 km/h) or with the engine
under load.
The downstream sensor is also used for richness regulation via the double loop program. The way it works is to
characterise the condition of the upstream sensor and to compensate for any upstream sensor dynamic richness
drift.
The vehicle is fitted with a downstream sensor if the configuration reading LC004 Downstream oxygen sensor is
WITH.
For the double loop ET056 Double richness loop to be ACTIVE, the vehicle must be driven with the engine warm
for approximately 1 minute 30 seconds in the absence of no load conditions.
The downstream sensor is also heated. The command is not immediate when the engine is started.
ET053 Downstream O
2 sensor heating is ACTIVE after a time that depends on the latest coolant temperature with
the engine running and in the absence of no load conditions. The heating of the downstream sensor is deactivated
under 84 mph (140 km/h) or when the engine is under load.
There are several types of control depending on the sensor type:
●BOSCH LSH25/NTK 6L (6Ω)/DELPHI AFS128 (3 wires): Continuous control,
●BOSCH LSF 4.7 (known as PLANAR): Each time the engine is started, control is first executed by means
of an OCR (opening cycle ratio) type signal of 20 Hz in frequency for approximately 20 seconds then it
becomes continuous,
●BOSCH NTK 6L (3.3Ω): each time the engine is started, the control is continuous first for 15 seconds then
executed by an OCR (Opening Cycle Ratio) type signal with a 20 Hz frequency.
Management of turbocharging pressure (F4R Turbo only)
The turbocharging pressure is adjusted via the position of the pressure regulation valve (wastegate).
Principle
This pressure regulation valve, connected via a rod to the wastegate diaphragm, is operated by the injection
computer via a solenoid valve. This solenoid valve is normally open and is fitted to the inlet pipe between the air filter
and turbocharger inlet.
At rest (open position), this solenoid valve connects the turbocharger outlet (turbocharging pressure) and the
pressure regulation valve control diaphragm.
The turbocharging pressure affects the diaphragm directly, the pressure regulation valve (wastegate) opens and the
maximum possible pressure is approximately 1,350 mbar - 1,400 mbar, irrespective of the engine speed (minimum
turbocharging for the engine).
When the solenoid valve is controlled, the turbocharging pressure signal (taken at the turbocharger outlet) is
diverted to the compressor inlet. As a result, the diaphragm is not subject to turbocharging pressure, the pressure
regulation valve (wastegate) closes back to a position imposed by the regulation system.
Page 13 of 230

PETROL INJECTION
Fault finding - System operation
17B
17B - 13
PETROL INJECTION
Fault finding - System operation
17B
17B - 13V9 MR-372-J84-17B050$094.mif
S3000 Injection
Program No.: AD
Vdiag No.: 4C / 54
In addition to turbocharging pressure management, the computer controls the engine for full load constant torque
operation.
This means that, irrespective of the engine conditions (air temperature, atmospheric pressure etc.), the maximum
torque will always be 275 Nm and the power 125 kW. So, for an air temperature of 20°C, the turbocharging pressure
at full load will be less than at 50°C. Despite controlled torque management, the turbocharging pressure can never
exceed 1800 mbar.
Ignition management
The advance is calculated for each cylinder. This may have a negative value, and is limited to between - 23.625°
and + 72° and includes any corrections due to pinking.
The slow loop anti-pinking correction is the maximum advance value that is deducted from the advance of one of the
cylinders. If none of the cylinders is pinking, this correction is zero.
Injectors
The injectors are controlled according to several modes. In particular, the engine is started in semi-full group mode
(injectors 1 and 4, then injectors 2 and 3 simultaneously), then it enters sequential mode, to ensure a correct start
whether or not it is correctly phased.
In fact in rare cases it is possible for the engine to run incorrectly phased if the Memo phasing program failed during
the last engine stop. So, since the system did not enter sequential injection mode and the cylinder 1 detection
program did not run, the injections are offset by 2 cylinders: therefore injecting in the order 4-2-1-3 rather than the
expected 1-3-4-2.
The injection time is constantly calculated and may be zero, in the event of cut-off during deceleration or overspeed
for example.
Page 14 of 230

PETROL INJECTION
Fault finding - System operation
17B
17B - 14
PETROL INJECTION
Fault finding - System operation
17B
17B - 14V9 MR-372-J84-17B050$094.mif
S3000 Injection
Program No.: AD
Vdiag No.: 4C / 54
3. OBD management
Managed OBD programming is as follows:
– catalytic converter operational fault finding,
– upstream oxygen sensor operational fault finding,
– misfiring fault finding with two levels of detection: pollutant misfiring and catalytic converter breakage
misfiring,
– fuel supply system fault finding.
The misfiring and fuel supply system fault finding is performed continuously.
The operational fault finding for the upstream sensor and the catalytic converter can be only be carried out once per
journey, and can never occur at the same time.
OBD fault manager:
The OBD faults manager does not replace or modify conventional electrical fault management. Perform to comply
with OBD standard.
The requirements are:
●storing OBD faults,
●illuminate the OBD warning light for all faults where the OBD emission thresholds are exceeded,
●flash the OBD warning light for misfire faults damaging the catalytic converter.
Operating principle.
If a fault is detected and confirmed during 3 consecutive journeys then:
●an OBD stored fault is raised,
●the OBD fault warning light receives a request to be lit continuously. This request is only recognised if the
fault in question is authorised to activate the OBD warning light.
To deactivate the warning light, no OBD faults should be detected for 3 consecutive journeys.
The electrical fault finding checks taken into consideration by the OBD faults manager are as follows:
– pressure,
– turbocharging pressure,
– coolant temperature,
– air temperature
– upstream sensor,
– downstream sensor,
– upstream sensor heating,
– downstream sensor heating,
–injector1,
–injector2,
–injector3,
–injector4,– ignition coil 1,
– ignition coil 2,
– ignition coil 3,
– ignition coil 4,
– petrol pump,
– wastegate,
– canister bleed,
– air line system,
– turbocharging system
– pinking sensor,
– camshaft dephaser.
Page 17 of 230

PETROL INJECTION
Fault finding - System operation
17B
17B - 17
PETROL INJECTION
Fault finding - System operation
17B
17B - 17V9 MR-372-J84-17B050$094.mif
S3000 Injection
Program No.: AD
Vdiag No.: 4C / 54
6. Defect modes
Motorised throttle valve
In defect mode, the motorised throttle valve can have 6 different statuses.
Any entry into type 1 to 5 defect mode always leads to the application of type 6. Type 1The throttle opening is less than the Safe mode position. The throttle is no longer activated and is
automatically in Safe mode. The ESP, distance control and cruise control/speed limiter systems are
disabled. The automatic transmission is in "Safe mode".
Type 2The throttle opening is no longer actuated. The engine speed is limited by injection cut-off.
Type 3Defect mode is associated with restructuring of the pedal setpoints (constant pedal setpoint for each
gear).
Type 4The associated defect mode restricts the throttle opening. The maximum throttle valve opening
threshold results in a speed of below 54 mph (90 km/h).
Type 5The computer no longer processes torque changes requested by the ESP, distance control, cruise
control/speed limiter and automatic gearbox systems. This defect mode results from a computer
malfunction, or a fault with the manifold or turbocharging pressure sensor. The system then only uses
the accelerator pedal signal. The ESP, distance control and cruise control/speed limiter systems are
disabled. The automatic transmission is in "Safe mode".
Type 6The turbocharging valve no longer works.
Page 18 of 230

PETROL INJECTION
Fault finding - System operation
17B
17B - 18
PETROL INJECTION
Fault finding - System operation
17B
17B - 18V9 MR-372-J84-17B050$094.mif
S3000 Injection
Program No.: AD
Vdiag No.: 4C / 54
Table of defect modes:
Type 1 Type 2 Type 3 Type 4 Type 5 Type 6
DF004 Turbocharging pressure
sensor circuit---2.DEF1.DEF
2.DEF1.DEF
2.DEF
DF011 Sensor feed voltage no. 11.DEF 1.DEF - 1.DEF - -
DF012 Sensor feed voltage no. 2---1.DEF1.DEF-
DF038 Computer1.DEF 1.DEF - - 1.DEF -
DF046 Battery voltage1.DEF 1.DEF - - - -
DF054 Turbocharging solenoid valve
control circuit-----CO/CC.0./
CC.1
DF078 Motorised throttle control
circuit1.DEF 1.DEF - - - -
DF079 Motorised throttle valve
automatic control6.DEF/CO 6.DEF/CO -2.DEF
3.DEF
4.DEF--
DF089 Inlet manifold pressure sensor
circuit----1.DEF
2.DEF-
DF095 Throttle potentiometer circuit
gang 1CO.0/
CC.1CO.0/
CC.1-CO.0/
CC.1--
DF096 Throttle potentiometer circuit
gang 2CO.0/
CC.1CO.0/
CC.1-CO.0/
CC.1--
DF196 Pedal potentiometer circuit
gang 1--1.DEFCO/CC.0./
CC.1
1.DEF--
DF198 Pedal potentiometer circuit
gang 2--CO/CC.0./
CC.1CO/CC.0./
CC.1--
DF650 Accelerator pedal position
signal--1.DEF1.DEF--
Page 22 of 230

PETROL INJECTION
Fault finding - Allocation of computer tracks17B
17B - 22
17B
17B - 22V9 MR-372-J84-17B050$141.mif
S3000 Injection
Program No.: AD
Vdiag No.: 4C / 54
Connector (B), 48 tracks:
Track Description
A1 Injector 1 - control
A2 Injector 2 - control
A3 Injector 3 - control
A4 Injector 4 - control
B1 Not used
B2 Pinking sensor screening earth
B3 Pinking sensor + signal
B4 Pinking sensor - signal
C1 Not used
C2 Not used
C3 Engine speed (LPG) TDC - signal
C4 Not used
D1 Not used
D2 Not used
D3 Motorised throttle valve potentiometer gang 2 signal
D4 + Power latch relay feed output
E1 Turbocharging pressure sensor earth (F4RT 774 and 776 only)
E2 Air temperature sensor signal
E3 Air temperature sensor earth
E4 Position and engine speed sensor - signal (tooth signal)
F1 Turbocharging pressure sensor + signal (F4RT 774 and 776 only)
F2 Coolant temperature sensor + signal
F3 Engine speed and position sensor + signal (tooth signal)
F4 Coolant temperature sensor earth
G1 + 5 V turbocharging pressure sensor (F4RT 774 and 776 only)
G2 Motorised throttle potentiometer + 5 V feed
G3 Motorised throttle valve potentiometer gang 1 signal
G4 Motorised throttle valve potentiometers common earth
H1 Not used
H2 Manifold pressure sensor + 5 V feed
H3 Manifold pressure sensor + signal
H4 Manifold pressure sensor earth
Page 24 of 230

PETROL INJECTION
Fault finding - Allocation of computer tracks17B
17B - 24
17B
17B - 24V9 MR-372-J84-17B050$141.mif
S3000 Injection
Program No.: AD
Vdiag No.: 4C / 54
Connector (C), 48 tracks:
Track Description
A1 Not used
A2 Downstream oxygen sensor + signal
A3 Not used
A4 Not used
B1 Upstream oxygen sensor + signal
B2 Downstream oxygen sensor - signal
B3 Not used
B4 Not used
C1 Upstream oxygen sensor - signal
C2 Not used
C3 Not used
C4 Not used
D1 Ignition coils and petrol pump relay control
D2 Not used
D3 Not used
D4 Not used
E1 Canister bleed solenoid valve control
E2 Camshaft position sensor earth (non-LPG K4M only)
E3 Not used
E4 Not used
F1 Inlet camshaft input frequency sensor (non-LPG K4M only)
F2 Not used
F3 Not used
F4 Not used
G1 Not used
G2 Not used
G3 Not used
G4 Turbocharging solenoid valve control (F4RT 774, 776 only)
H1 Not used
H2 Not used
H3 Not used
H4 Not used
Page 30 of 230
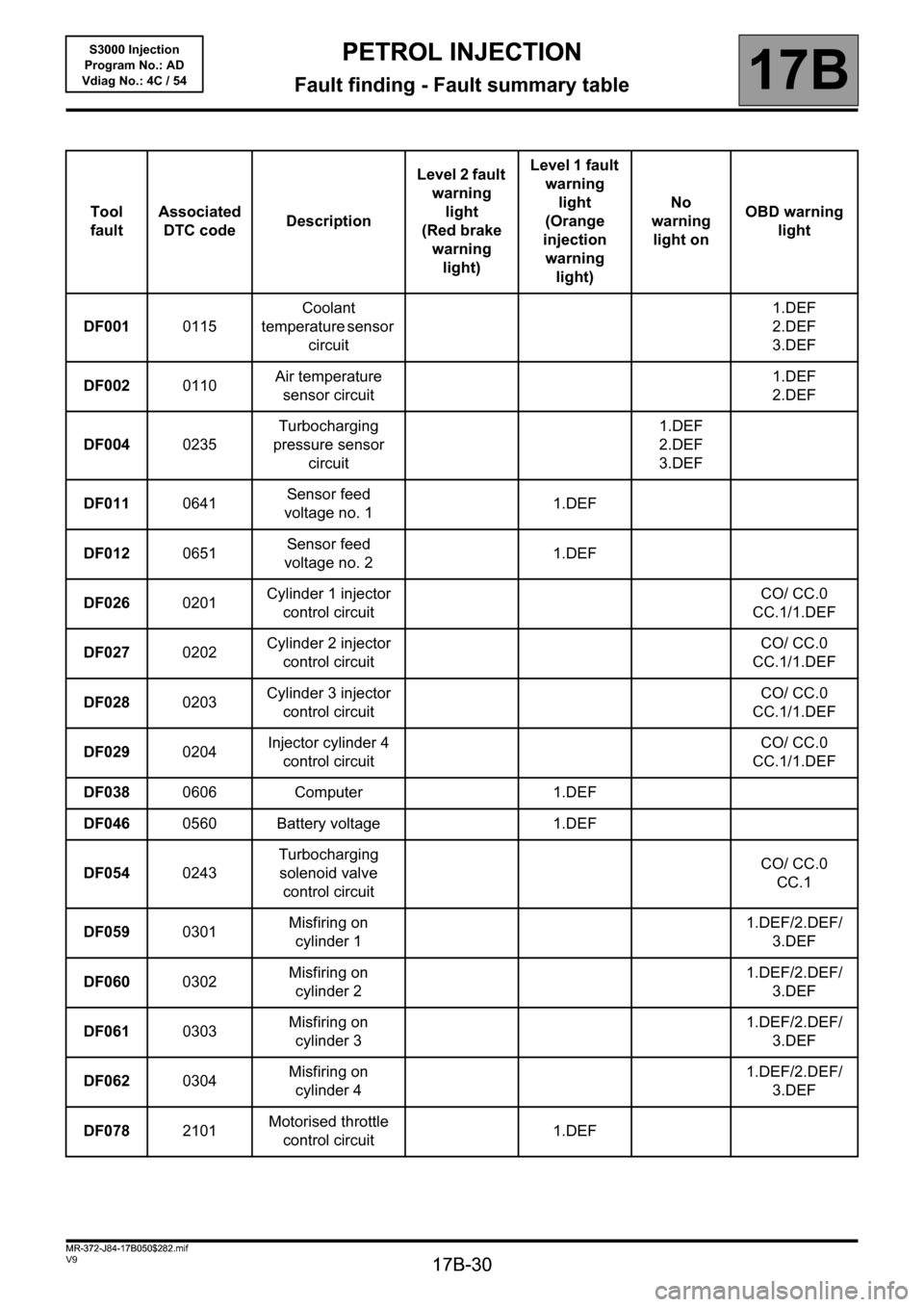
PETROL INJECTION
17B
17B-30
PETROL INJECTION
17B
17B-30V9 MR-372-J84-17B050$282.mif
S3000 Injection
Program No.: AD
Vdiag No.: 4C / 54PETROL INJECTION
Fault finding - Fault summary table
Tool
faultAssociated
DTC codeDescriptionLevel 2 fault
warning
light
(Red brake
warning
light)Level 1 fault
warning
light
(Orange
injection
warning
light)No
warning
light onOBD warning
light
DF0010115Coolant
temperature sensor
circuit1.DEF
2.DEF
3.DEF
DF0020110Air temperature
sensor circuit1.DEF
2.DEF
DF0040235Turbocharging
pressure sensor
circuit1.DEF
2.DEF
3.DEF
DF0110641Sensor feed
voltage no. 11.DEF
DF0120651Sensor feed
voltage no. 21.DEF
DF0260201Cylinder 1 injector
control circuitCO/ CC.0
CC.1/1.DEF
DF0270202Cylinder 2 injector
control circuitCO/ CC.0
CC.1/1.DEF
DF0280203Cylinder 3 injector
control circuitCO/ CC.0
CC.1/1.DEF
DF0290204Injector cylinder 4
control circuitCO/ CC.0
CC.1/1.DEF
DF0380606 Computer 1.DEF
DF0460560 Battery voltage 1.DEF
DF0540243Turbocharging
solenoid valve
control circuitCO/ CC.0
CC.1
DF0590301Misfiring on
cylinder 11.DEF/2.DEF/
3.DEF
DF0600302Misfiring on
cylinder 21.DEF/2.DEF/
3.DEF
DF061
0303Misfiring on
cylinder 31.DEF/2.DEF/
3.DEF
DF0620304Misfiring on
cylinder 41.DEF/2.DEF/
3.DEF
DF0782101Motorised throttle
control circuit1.DEF
MR-372-J84-17B050$282.mif