fuel consumption Seat Alhambra 2012 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SEAT, Model Year: 2012, Model line: Alhambra, Model: Seat Alhambra 2012Pages: 388, PDF Size: 6.72 MB
Page 233 of 388
231
Driving and the environment
Other factors which increase fuel consumption (examples):
● Fault in engine management.
● Driving on hills.
● Trailer towing.
Saving fuel while driving
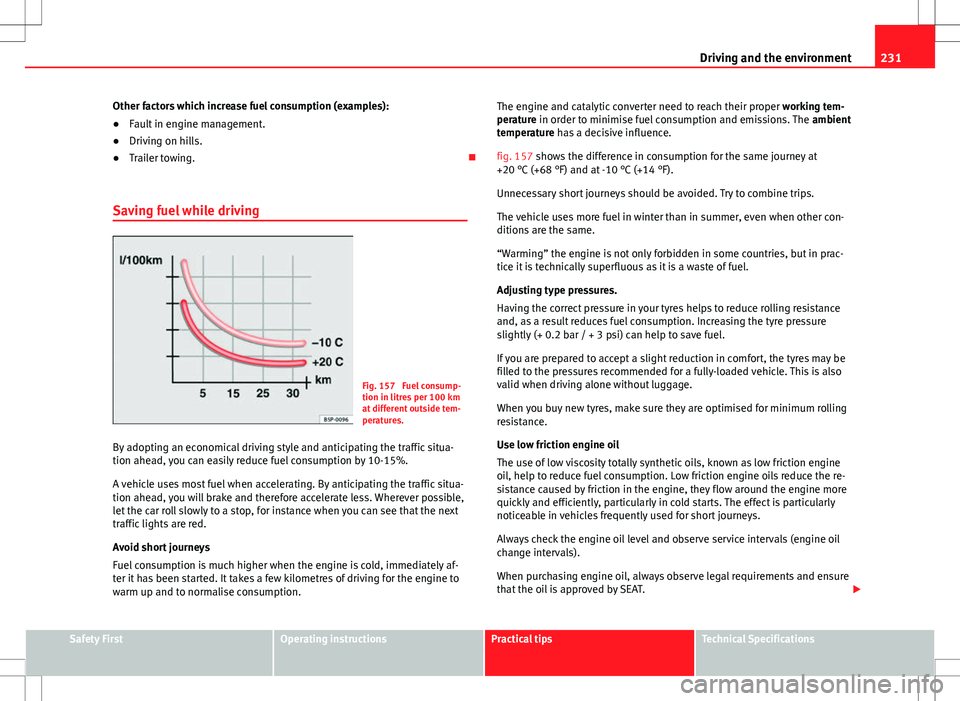
Fig. 157 Fuel consump-
tion in litres per 100 km
at different outside tem-
peratures.
By adopting an economical driving style and anticipating the traffic situa-
tion ahead, you can easily reduce fuel consumption by 10-15%.
A vehicle uses most fuel when accelerating. By anticipating the traffic situa-
tion ahead, you will brake and therefore accelerate less. Wherever possible,
let the car roll slowly to a stop, for instance when you can see that the next
traffic lights are red.
Avoid short journeys
Fuel consumption is much higher when the engine is cold, immediately af-
ter it has been started. It takes a few kilometres of driving for the engine to
warm up and to normalise consumption. The engine and catalytic converter need to reach their proper
working tem-
perature in order to minimise fuel consumption and emissions. The ambient
temperature has a decisive influence.
fig. 157 shows the difference in consumption for the same journey at
+20 °C (+68 °F) and at -10 °C (+14 °F).
Unnecessary short journeys should be avoided. Try to combine trips.
The vehicle uses more fuel in winter than in summer, even when other con-
ditions are the same.
“Warming” the engine is not only forbidden in some countries, but in prac-
tice it is technically superfluous as it is a waste of fuel.
Adjusting type pressures.
Having the correct pressure in your tyres helps to reduce rolling resistance
and, as a result reduces fuel consumption. Increasing the tyre pressure
slightly (+ 0.2 bar / + 3 psi) can help to save fuel.
If you are prepared to accept a slight reduction in comfort, the tyres may be
filled to the pressures recommended for a fully-loaded vehicle. This is also
valid when driving alone without luggage.
When you buy new tyres, make sure they are optimised for minimum rolling
resistance.
Use low friction engine oil
The use of low viscosity totally synthetic oils, known as low friction engine
oil, help to reduce fuel consumption. Low friction engine oils reduce the re-
sistance caused by friction in the engine, they flow around the engine more
quickly and efficiently, particularly in cold starts. The effect is particularly
noticeable in vehicles frequently used for short journeys.
Always check the engine oil level and observe service intervals (engine oil
change intervals).
When purchasing engine oil, always observe legal requirements and ensure
that the oil is approved by SEAT.
Safety FirstOperating instructionsPractical tipsTechnical Specifications
Page 234 of 388
232Driving and the environment
Avoid carrying unnecessary loads
The lighter the vehicle, the more economical and ecological the driving
style. For example, an additional weight of 100 kg will increase fuel con-
sumption up to 0.3 l/100 km.
Remove any unnecessary objects or loads from the vehicle.
Remove optional equipment and unnecessary accessories
The more aerodynamic the vehicle, the lower the fuel consumption. Option-
al equipment and accessories (such as roof racks or bike carriers) reduce
the aerodynamic benefits of the vehicle.
Therefore, we recommend you remove all optional and unnecessary equip-
ment and racks, especially if you intend to drive at high speeds.
Engine management and exhaust gas
purification system Introduction
Additional information and warnings:
● Changing gear ⇒ page 176
● Refuelling ⇒ page 268
● Fuel ⇒ page 271
● Engine oil ⇒ page 283
● Vehicle battery ⇒ page 292
● Information stored in the control units ⇒ page 261
● Tow-starting and towing away ⇒ page 344
WARNING
The components of the exhaust system reach very high temperatures.
This could cause a fire.
● Always park your vehicle so that no part of the exhaust system can
come in contact with flammable materials (such as dried grass).
● Do not apply additional underseal or anti-corrosion coatings to the
exhaust pipes, catalytic converter, heat shields or the diesel particulate
filter.
Warning lamps
lights upPossible causeSolution
Fault in engine management
(Electronic Power Control).Take the vehicle to a Technical
Service as soon as possible and
have the engine checked.
Pre-heating a diesel engine
before starting the engine.⇒ page 172
Fault in catalytic converter.
You should reduce speed ac-
cordingly. Drive carefully until
you reach the next qualified
workshop. Have the engine
checked there.
Diesel particulate filter
blocked
Drive for 15 minutes in 4th gear
(manual gearbox), or in D (auto-
matic gearbox) at a minimum
speed of 70 km/h (45 mph).
Observe speed limits ⇒
.
If the warning lamp remains lit
up, take the vehicle to a Techni-
cal Service ⇒ page 233.
Page 235 of 388
233
Driving and the environment
flashesPossible causeSolution
Fault in the engine manage-
ment (diesel engines).Take the vehicle to a Technical
Service as soon as possible and
have the engine checked.
Combustion fault which could
damage the catalytic convert-
er.You should reduce speed ac-
cordingly. Drive carefully until
you reach the next qualified
workshop. Have the engine
checked there.
Several warning and control lamps should light up for a few seconds when
the ignition is switched. This signals that the lamp is working properly. They
will switch off after a few seconds.
WARNING
Observe traffic regulations when cleaning the diesel particulate filter
while driving.
● Only carry on driving if visibility, weather, road and traffic conditions
so permit.
● Never endanger your safety or that of other road users.
CAUTION
Always pay attention to any lit lamps and to the corresponding descriptions
and instructions to avoid damage to the vehicle.
Note
While the indicators , or remain lit, there may be engine problems,
fuel consumption may be greater and the engine may lose power. Catalytic converter
The catalytic converter permits the subsequent treatment of the exhaust
gases thus reducing contaminating gas emissions. To ensure a longer work-
ing life for the exhaust system and catalytic converter in a petrol engine:
●
Always use unleaded petrol.
● Never run the tank completely dry.
● Do not top up with too much engine oil ⇒ page 283.
● Do not tow-start the vehicle; use the starter cables ⇒ page 341.
If you should notice misfiring, uneven running or loss of power when the car
is moving, reduce speed immediately. Have the car inspected by a Technical
Service. If this happens, unburnt fuel can enter the exhaust system and es-
cape into the atmosphere. The catalytic converter can also be damaged by
overheating.
For the sake of the environment
Even when the emission control system is working perfectly, there may be a
smell of sulphur from the exhaust gas under some conditions. This depends
on the sulphur content of the fuel being used.
Diesel particulate filter
The diesel particulate filter removes soot particulates from the exhaust gas.
The filter retains these particulates and burns them. To assist the combus-
tion process, SEAT recommends you avoid frequent short trips.
● Always use diesel with a low sulphur content ⇒ page 271.
● Never use petrol or fuel oil.
● Never use biodiesel. However, a blend prepared by the diesel manufac-
turer containing biodiesel within the limits established by the EN 590
standard may be used ⇒ page 271.
Safety FirstOperating instructionsPractical tipsTechnical Specifications
Page 237 of 388

235
Trailer towing
Trailer towing Introduction
Always be aware of the legal requirements for each country to drive with a
trailer and to use a trailer bracket.
Your car is intended mainly for transporting passengers however, it can also
be used to tow a trailer provided that it is fitted with the necessary equip-
ment. The additional load has an effect on the useful life, fuel consumption
and the vehicle performance and, in some cases, reduce the service inter-
vals.
Driving with a trailer requires more force from the vehicle and, thus, more
concentration from the driver.
For wintertime temperatures, fit winter tyres to the vehicle and the trailer.
Drawbar load
The maximum permitted Drawbar load exerted by the trailer drawbar on the
ball joint of the tow hitch must not exceed 100 kg (approximately 220 lbs).
Vehicles with the Start-Stop function
With a SEAT factory fitted or retrofitted trailer bracket, the Start-Stop func-
tion is automatically deactivated when a trailer is connected. For trailer
brackets not installed by SEAT, the Start-Stop function must be deactivated
manually using a button located on the dashboard before driving with a
trailer and it must remain off for the entire journey ⇒
.
Additional information and warnings:
● Anti-theft alarm system ⇒ page 74
● Light ⇒ page 95
● Ecological driving ⇒ page 229
● Starter assist systems (Start-Stop function) ⇒ page 196●
Wheels and tyres ⇒ page 297
● Accessories, parts replacement, repairs and modifications ⇒ page 261
WARNING
Never transport people in a trailer: this will endanger in their life and is
against the law.
WARNING
The incorrect use of the tow hitch can cause accidents and injury.
● Only use a tow hitch in good condition and correctly installed.
● Never change or repair a tow hitch.
● To reduce the risk of injury in case of a reversing collision, injury to
pedestrians and cyclists when parking, always keep the ball joint in
when a trailer is not being used.
● Never fit a trailer tow hitch “that distributes the load” or “balances
the load”. Your vehicle has not been designed for this type of tow hitch.
The tow hitch may fail and the trailer will separate from the vehicle.
WARNING
Driving with a trailer and transporting heavy or large objects can affect
vehicle handling and even cause an accident.
● Always secure loads correctly with suitable and undamaged attach-
ment rope or straps.
● Adjust your speed and driving style to visibility, road, traffic and
weather conditions.
Safety FirstOperating instructionsPractical tipsTechnical Specifications
Page 274 of 388
272Checking and refilling levels
WARNING
Refuelling or handling fuel carelessly can cause an explosion or fire re-
sulting in serious burns and injuries.
● Fuel is a highly explosive, easily flammable substance.
● Observe current safety instructions and local regulations concerning
the handling of fuel.
Types of fuel
The type of fuel to use when refilling will depend on the vehicle's engine.
You will find a factory-fitted sticker containing information on the type of
fuel for your vehicle on the inside of the fuel tank flap.
SEAT recommends the use of sulphur-free or low sulphur fuel to reduce con-
sumption and prevent engine damage.
Possible types of fuelAlternative namesFurther information
91a)
RONNormal petrol, normal unlea-
ded petrol
⇒ page 27295 a)
RONPremium unleaded petrol (95
RON)
98 a)
RONPremium unleaded petrol (98
RON)
Diesel ⇒ page 273a) RON = Regulation Octane Number Petrol
Petrol types
Vehicles with petrol engines must refuel using unleaded petrol according to
European norm EN 228 ⇒
.
Petrol types are categorised according to their octane number (e.g. 91, 95,
98 or 99 RON (RON = “Research Octane Number”). You may use petrol with
a high octane number than the one recommended for your engine. Howev-
er, this has no advantage in terms of fuel consumption and engine power.
SEAT recommends refuelling with a low sulphur content or sulphur-free pet-
rol to reduce petrol consumption for petrol engines.
Petrol additives
The quality of the fuel influences running behaviour, performance and serv-
ice life of the engine. For this reason, you should use good quality petrol
containing a mixture of additives. These additives will help to prevent corro-
sion, keep the fuel system clean and prevent deposits from building up in
the engine.
If good quality petrol with additives is not available or engine problems
arise, the necessary additives must be added when refuelling.
Not all petrol additives have been shown to be effective. The use of unsuita-
ble petrol additives could damage the engine. These additives are available
from Technical Services, who will inform you of their application.
CAUTION
● Only use fuel with an octane rating that is in line with the norm EN 228,
otherwise significant damage could be caused to the engine and fuel sys-
tem. Furthermore, it could lead to a loss of performance with the conse-
quent engine fault.
● The use of unsuitable petrol additives could damage the engine.
Page 276 of 388
274Checking and refilling levels
CAUTION
● The vehicle is not prepared for the use of biodiesel. Never, under any
circumstances refuel with biodiesel. It could damage the fuel system and
subsequently lead to engine faults!
● The addition of biodiesel to diesel by the diesel producer according to
Standard EN 590 or other equivalent (DIN 51628 in Germany, for example)
is authorised and causes no type of damage to the engine or the fuel
system.
● The diesel engine has been designed for to use diesel fuel exclusively.
Therefore, never use petrol, fuel oil or other unsuitable fuels. The composi-
tion of these fuels may significantly damage the fuel system and the en-
gine.
● The use of diesel fuels with a high sulphur percentage could considera-
bly reduce the service life of the diesel particulate filter. Your Technical Serv-
ice will be able to tell you which countries have diesel with a high sulphur
content.
Information on fuel consumption
The consumption and emission values indicated do not refer to one specific
vehicle. They are only to be used to compare the values of the different ve-
hicle versions. The fuel consumption and CO 2 emissions of a vehicle not on-
ly depend on the effective use of fuel. They also depend on your driving
style and other non-technical factors.
Calculation of fuel consumption
Fuel consumption and emission values are determined according to the cur-
rent version of the 715/2007/EC or 80/1268/EEC regulation and are valid
for the vehicle kerb weight. The specifications do not refer to an individual
vehicle. Two measuring cycles are carried out on a rolling road test bed. The
test criteria are as follows:
Urban cycleMeasurement of the urban cycle starts with an engine cold
start. City driving is then simulated at between 0 and 50 km/
h.
Road cycleIn the road cycle simulation, the car undergoes frequent ac-
celeration and braking in all gears, as in normal everyday
driving. The road speed ranges from 0 to 120 km/h.
CombinedThe average combined consumption is calculated with a
weighting of around 37 % for the urban cycle and 63 % for
the road cycle.
CO 2 emis-
sions of the
combinationThe exhaust gases are collected during both driving cycles
to calculate carbon dioxide emissions (urban and road). The
gas composition is then analysed to evaluate the CO 2 con-
tent and other emissions.
Note
● The kerb weight may vary according to the vehicle equipment. This
could raise consumption and the CO 2 emissions slightly.
● In practice, consumption values could be different to the values calcula-
ted based on the 715/2007/EC or 80/1268/EEC regulations.
Page 304 of 388
302Wheels and tyres
Never deflate a hot tyre in order to obtain the required pressure. This could
result in very low tyre pressures which may lead to sudden blow-outs.
Checking tyre pressures
Tyre pressures should only be checked when the vehicle has not been driv-
en for more than a few kilometres (miles) at low speeds in the past three
hours.
● The tyre pressures should be checked regularly, and only when the tyres
are cold. Always check all the tyres. Tyre pressures should be checked more
often in colder regions, and only when the vehicle has not been driven re-
cently. Always use a correctly-operating tyre gauge.
● Adjust tyre pressures to the loads carried in the vehicle.
● After checking the pressure, always replace the valve caps, and where
applicable, observe the instructions given for adjusting the tyre control sys-
tem ⇒ page 225.
WARNING
If tyre pressures are too high or too low, the tyre may deflate or burst
suddenly while driving. This could result in serious accident.
● If the tyre pressure is too low, the tyres could overheat, resulting in
tread detachment or even burst tyres.
● When driving at high speeds and/or fully loaded, the tyre could sud-
denly overheat, burst or be subject to tread detachment, with the resul-
tant loss of control of the vehicle.
● Tyre pressures which are too high or too low reduce the service life of
the tyre, affecting the vehicle's performance.
● Tyre pressures should be checked regularly, at least once a month
and before long journeys.
● Adjust the pressures of all the tyres to the vehicle load.
● Never deflate excess pressure from hot tyres.
CAUTION
● Take care not to tilt the manometer when placing it on the valve. Other-
wise, the valve may be damaged.
● To avoid damage to the valves, always replace valve caps correctly.
Check that the caps are identical to the standard caps and have been cor-
rectly tightened.
For the sake of the environment
Under-inflated tyres will increase the fuel consumption.
Note
When checking tyre pressures, please observe the instructions for the tyre
control system ⇒ page 225.
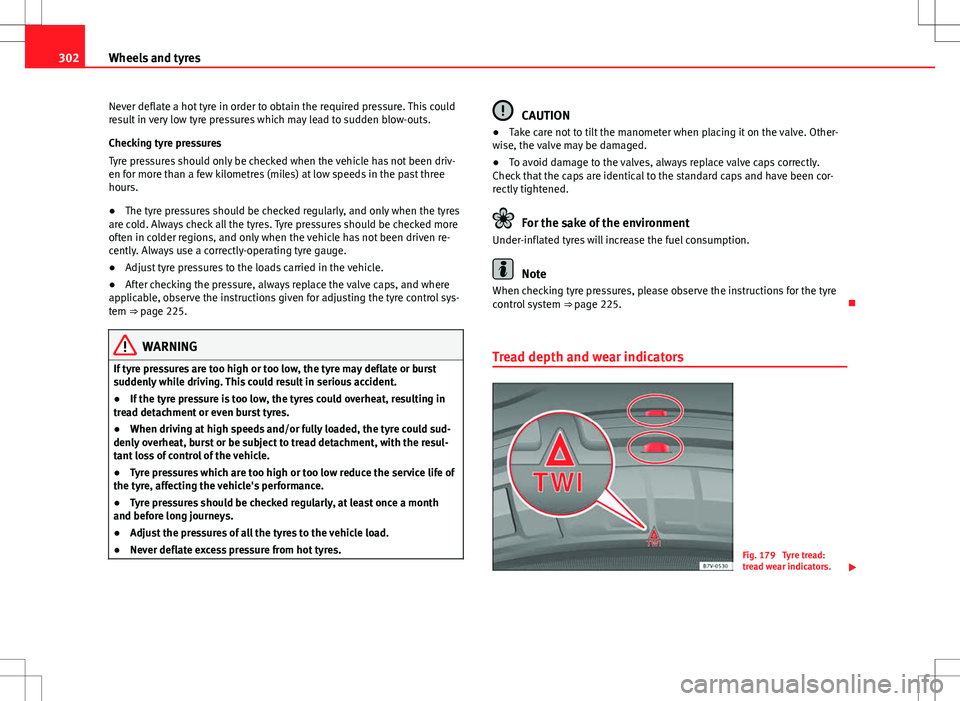
Tread depth and wear indicators
Fig. 179 Tyre tread:
tread wear indicators.
Page 307 of 388

305
Wheels and tyres
Please observe all instructions and warnings when using snow chains
⇒ page 305.
WARNING
Although winter tyres help to make driving safer in the winter, you
should not take unnecessary risks.
● Adjust your speed and driving style to visibility, road, traffic and
weather conditions.
● Never exceed the maximum permitted speed or loads specified for the
type of winter tyre fitted on your vehicle.
For the sake of the environment
When winter is over, change back to summer tyres. In temperatures above
+7 °C (+45 °F), performance will be improved if summer tyres are used. Fuel
consumption, wear and noises while driving will all be reduced.
Note
● If the vehicle is fitted with a tyre control system, this should be “reprog-
rammed” whenever a tyre is changed ⇒ page 227.
● Please ask at a Technical Service for information about the permitted
sizes for winter tyres.
Snow chains
When using snow chains, applicable local legislation and maximum permit-
ted speed limits must be observed.
In winter weather, snow chains not only help to improve grip but also im-
prove the braking capacity. Snow chains must only be mounted
on the front wheels, even on all-wheel
drive vehicles, and only with the tyre and rim combinations listed below:
Tyre sizeWheel rim205/60 R166 1/2 J x 16 ET 33
SEAT recommends you ask a Technical Service for further information on
wheel, tyre and chain sizes.
Wherever possible use fine-link chains measuring less than 15 mm (37/64
inch) including the lock.
Remove wheel hub covers and trim rings before fitting snow chains ⇒
.
The wheel bolts should be covered with caps for safety reasons. These are
available from Technical Services.
WARNING
The use of unsuitable or incorrectly fitted chains could lead to serious ac-
cidents and damage.
● Always the appropriate snow chains.
● Observe the fitting instructions provided by the snow chain manufac-
turer.
● Never exceed the maximum permitted speeds when driving with snow
chains.
CAUTION
● Remove the snow chains to drive on roads without snow. Otherwise they
will impair handling, damage the tyres and wear out very quickly.
● Wheel rims may be damaged or scratched if the chains come into direct
contact with them. SEAT recommends the use of covered snow chains.
Note
Snow chains are available in different sizes according to the vehicle type.
Safety FirstOperating instructionsPractical tipsTechnical Specifications
Page 350 of 388

348Description of specifications
Technical Specifications
Description of specifications
Important information
Important
The information in the vehicle documentation always has
precedence. All technical specifications provided in this manual are valid for the stand-
ard model in Spain. The vehicle data card included in the Inspection and
Maintenance Plan in the vehicle documents shows which engine is installed
in the vehicle.
The figures may be different depending on if additional equipment is fitted,
for different models, for special vehicles and for other countries.
Additional information and warnings:
● Transporting ⇒ page 13
● Ecological driving ⇒ page 229
● Fuel ⇒ page 271
● Engine oil ⇒ page 283
● Engine coolant ⇒ page 287
● Wheels and tyres ⇒ page 297
● Notes for the user ⇒ page 259 Abbreviations used in the Technical Specifications section
Abbrevia-
tionMeaning
kWKilowatt, engine power measurement.
PSPferdestärke (horsepower), formerly used to denote engine
power.
rpmRevolutions per minute - engine speed.NmNewton metres, unit of engine torque.l/100 kmFuel consumption in litres per 100 km.g/kmCarbon dioxide emissions in grams per km travelled.CO2Carbon dioxideCNCetane number, indication of the diesel combustion power.
RONResearch octane number, indication of the knock resistance
of petrol.
WARNING
Failure to observe requirements for weight, loads, dimensions and maxi-
mum speed may lead to severe accident.
Page 352 of 388
350Description of specifications
Information on fuel consumption
Fuel consumption
The consumption and emission details shown on the vehicle
data sticker differ from one vehicle to another.
The fuel consumption, CO 2 emissions and actual kerb weight of the vehicle
are noted on the vehicle data sticker.
The fuel consumption and emissions figures given are based on the vehicle
weight category, which is determined according to the engine/gearbox
combination and the equipment fitted.
The consumption and emission figures are calculated in accordance with
the EC test requirements 1999/100/EC. These test requirements specify a
realistic test method based on normal everyday driving.
The following test conditions are applied:
Urban cycleThe urban cycle starts with an engine cold start. City driving
is then simulated.
Extra urban
cycleIn the extra urban cycle simulation the vehicle frequently ac-
celerates and brakes in all gears, as in normal everyday driv-
ing. The road speed ranges from 0 to 120 km/h.
Total con-
sumptionThe average total consumption is calculated with a weight-
ing of around 37% for the urban cycle and 63% for the extra
urban cycle.
CO 2 emis-
sionsThe exhaust gases are collected during both driving cycles
to calculate carbon dioxide emissions. The gas composition
is then analysed to evaluate the CO 2 content and other
emissions.
Note
● Actual consumption may vary from quoted test values, depending on
personal driving style, road and traffic conditions, the weather and the vehi-
cle condition.
Weights
Kerb weight refers to the basic model with a fuel tank filled to 90% capacity
and without optional extras. The figure quoted includes 75 kg to allow for
the weight of the driver.
For special versions and optional equipment fittings or for the addition of
accessories, the weight of the vehicle will increase ⇒
.
WARNING
● Please note that the centre of gravity may shift when transporting
heavy objects; this may affect the vehicle's handling and lead to an acci-
dent. Always adjust your speed and driving style to suit road conditions
and requirements.
● Never exceed the gross axle weight rating or the gross vehicle weight
rating. If the allowed axle load or the allowed total weight is exceeded,
the driving characteristics of the vehicle may change, leading to acci-
dents, injuries and damage to the vehicle.