technical specifications Seat Ibiza SC 2012 Owner's manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SEAT, Model Year: 2012, Model line: Ibiza SC, Model: Seat Ibiza SC 2012Pages: 280, PDF Size: 3.67 MB
Page 241 of 280
239
If and when
– Once the bulb holder has been removed, press downwards in
the direction of the arrow 1
and at the same time, turn in the
direction of the arrow 2 ⇒ Fig. 164.
Changing bulbs. LED lamps
Carry out the same operations as in lights fitted with bulbs.
If necessary, remove the socket, as if it were a bulb.
If the brake light and/or side light with LEDs have to be replaced, the tail
light must be replaced.
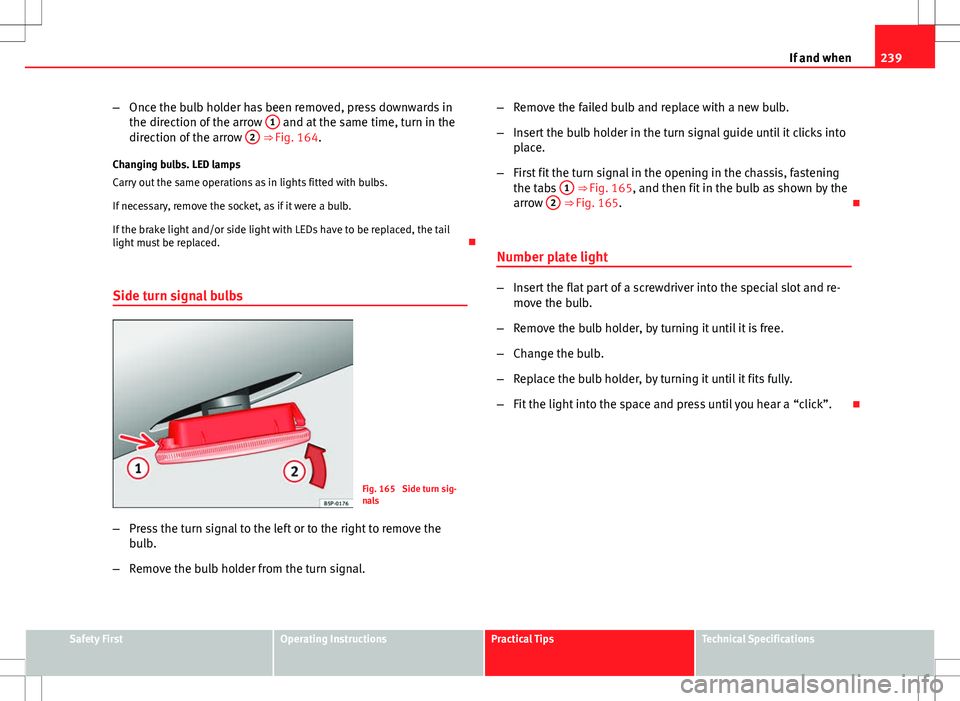
Side turn signal bulbs
Fig. 165 Side turn sig-
nals
– Press the turn signal to the left or to the right to remove the
bulb.
– Remove the bulb holder from the turn signal. –
Remove the failed bulb and replace with a new bulb.
– Insert the bulb holder in the turn signal guide until it clicks into
place.
– First fit the turn signal in the opening in the chassis, fastening
the tabs 1
⇒ Fig. 165, and then fit in the bulb as shown by the
arrow 2 ⇒ Fig. 165.
Number plate light
– Insert the flat part of a screwdriver into the special slot and re-
move the bulb.
– Remove the bulb holder, by turning it until it is free.
– Change the bulb.
– Replace the bulb holder, by turning it until it fits fully.
– Fit the light into the space and press until you hear a “click”.
Safety FirstOperating InstructionsPractical TipsTechnical Specifications
Page 243 of 280
241
If and when
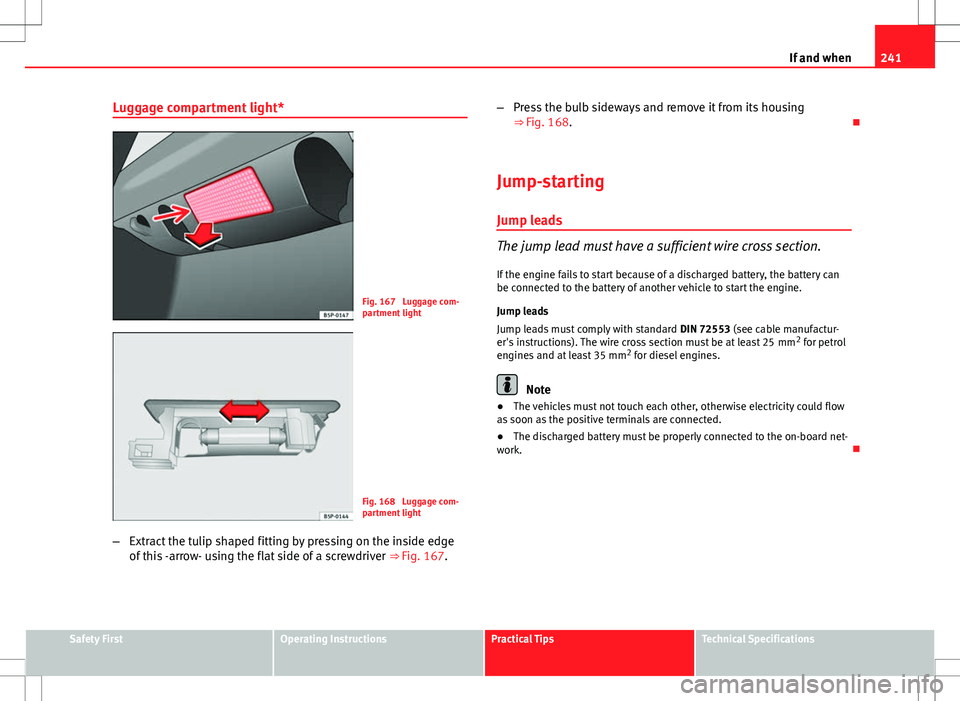
Luggage compartment light*
Fig. 167 Luggage com-
partment light
Fig. 168 Luggage com-
partment light
– Extract the tulip shaped fitting by pressing on the inside edge
of this -arrow- using the flat side of a screwdriver ⇒ Fig. 167.–
Press the bulb sideways and remove it from its housing
⇒ Fig. 168.
Jump-starting
Jump leads
The jump lead must have a sufficient wire cross section. If the engine fails to start because of a discharged battery, the battery can
be connected to the battery of another vehicle to start the engine.
Jump leads
Jump leads must comply with standard DIN 72553 (see cable manufactur-
er's instructions). The wire cross section must be at least 25 mm 2
for petrol
engines and at least 35 mm 2
for diesel engines.
Note
● The vehicles must not touch each other, otherwise electricity could flow
as soon as the positive terminals are connected.
● The discharged battery must be properly connected to the on-board net-
work.
Safety FirstOperating InstructionsPractical TipsTechnical Specifications
Page 245 of 280

243
If and when
Starting
5. Start the engine of the vehicle with the boosting battery and let it run at idling speed.
6. Start the engine of the vehicle with the flat battery and wait two or three minutes until the engine is “running”.
Removing the jump leads
7. Before you remove the jump leads, switch off the dipped beam headlights (if they are switched on).
8. Turn on the heater blower and heated rear window in the vehi- cle with the flat battery. This helps minimise voltage peaks
which are generated when the leads are disconnected.
9. When the engine is running, disconnect the leads in reverse or- der to the details given above.
Connect the battery clamps so they have good metal-to-metal contact with
the battery terminals.
If the engine fails to start, switch off the starter after about 10 seconds and
try again after about half a minute.
WARNING
● Please note the safety warnings referring to working in the engine
compartment ⇒ page 193, Working in the engine compartment.
● The battery providing assistance must have the same voltage as the
flat battery (12V) and approximately the same capacity (see imprint on
battery). Failure to comply could result in an explosion.
WARNING (Continued)
● Never use jump leads when one of the batteries is frozen. Danger of
explosion! Even after the battery has thawed, battery acid could leak and
cause chemical burns. If a battery freezes, it should be replaced.
● Keep sparks, flames and lighted cigarettes away from batteries, dan-
ger of explosion. Failure to comply could result in an explosion.
● Observe the instructions provided by the manufacturer of the jump
leads.
● Do not connect the negative cable from the other vehicle directly to
the negative terminal of the flat battery. The gas emitted from the battery
could be ignited by sparks. Danger of explosion.
● Do not attach the negative cable from the other vehicle to parts of the
fuel system or to the brake line.
● The non-insulated parts of the battery clamps must not be allowed to
touch. The jump lead attached to the positive battery terminal must not
touch metal parts of the vehicle, this can cause a short circuit.
● Position the leads in such a way that they cannot come into contact
with any moving parts in the engine compartment.
● Do not lean on the batteries. This could result in chemical burns.
Note
The vehicles must not touch each other, otherwise electricity could flow as
soon as the positive terminals are connected.
Safety FirstOperating InstructionsPractical TipsTechnical Specifications
Page 247 of 280

245
If and when
Do not pull too hard with the towing vehicle and take care to avoid jerking
the tow rope. When towing on an unpaved road, there is always a risk of
overloading and damaging the anchorage points.
The ignition of the vehicle being towed must be switched on to prevent the
steering wheel from locking and also to allow the use of the turn signals,
horn, windscreen wipers and washers.
As the brake servo does not work if the engine is not running, you must ap-
ply considerably more pressure to the brake pedal than you normally would.
As the power assisted steering does not work if the engine is not running,
you will need more strength to steer than you normally would.
Towing vehicles with an automatic gearbox
● Put the selector lever into position “N”.
● Do not drive faster than 50 km/h (30 mph).
● Do not tow further than 50 km (30 miles).
● If a breakdown vehicle is used, the vehicle must be towed with the front
wheels raised.
Note
● Observe legal requirements when towing or tow-starting.
● Switch on the hazard warning lights of both vehicles. However, observe
any regulations to the contrary.
● For technical reasons, vehicles with an automatic gearbox must not be
tow-started.
● If damage to your vehicle means that there is no lubricant in the gear-
box, you must raise the driven wheels while the vehicle is being towed.
● If the vehicle has to be towed more than 50 km (30 miles), the front
wheels should be raised during towing, and towing should be carried out by
a qualified person. ●
The steering wheel is locked when the vehicle has no electrical power.
The vehicle must then be towed with the front wheels raised. Towing should
be carried out by a qualified person.
● The towline anchorage should always be kept in the vehicle.
Towline anchoragesFig. 171 Fitting the tow-
line anchorage to front of
the vehicle
Fitting the towline anchorage
– Take the towline anchorage from the on-board tool set.
– Remove the front cover by pressing down on its left-hand side.
For FR finishes, press down and pull outwards. For the rest of
the Sport finishes, remove the cover by inserting a screwdriver
into the lower slot and levering gently.
– Bolt the anchorage to its limit to the left, in the direction of the
arrow ⇒ Fig. 171.
Safety FirstOperating InstructionsPractical TipsTechnical Specifications
Page 249 of 280

247
Description of specifications
Technical Specifications
Description of specifications Important information
Important
The information in your vehicle's official documents always
take precedence over the information in the current instruc-
tion manual. All technical specifications provided in this documentation are valid for the
standard model in Spain. The vehicle data card included in the Mainte-
nance Programme or the vehicle registration documentation shows which
engine is installed in the vehicle.
The figures may be different depending whether additional equipment is fit-
ted, for different models, for special vehicles and for other countries.
Abbreviations used in the Technical Specifications section
Abbrevia- tionMeaning
kWKilowatt, engine power measurement.
PSPferdestärke (horsepower), formerly used to denote engine
power.
rpmRevolutions per minute - engine speed.NmNewton metres, unit of engine torque.l/100 kmFuel consumption in litres per 100 km.g/kmCarbon dioxide emissions in grams per km travelled.CO2Carbon dioxide
Abbrevia-
tionMeaning
CNCetane number, indication of the diesel combustion power.
RONResearch octane number, indication of the knock resistance
of petrol.
Safety FirstOperating InstructionsPractical TipsTechnical Specifications
Page 251 of 280

249
Description of specifications
Information on fuel consumption
Fuel consumption
The consumption and emission details shown on the vehicle
data sticker differ from one vehicle to another. The vehicle fuel consumption and CO 2 emissions can be consulted on the
vehicle data sticker in the spare wheel well, inside the luggage compart-
ment and on the rear cover of the Maintenance Programme.
The fuel consumption and CO 2 emission values refer to the weight category
assigned to your vehicle according to the engine and gearbox combination,
as well as the specific equipment fitted, and is only used to compare be-
tween the different models.
The fuel consumption and CO 2 emissions do not depend only on the per-
formance of the vehicle, they can also differ from the established values de-
pending on other factors such as driving style, road conditions, traffic con-
ditions, environmental conditions, load and number of passengers.
Calculation of fuel consumption
The consumption values have been calculated based on measurements per-
formed or supervised by certified CE laboratories according to the latest ver-
sion of directives 715/2007/EC and 80/1268/CEE (for more information
consult the European Union Publications Office at EUR-Lex: © European Un-
ion, http://eur-lex.europa.eu/en/index.htm) and are valid for the kerb
weight indicated for the vehicle.
Note
In practice, and considering all the factors mentioned here, consumption
values can differ from those calculated in the current European regulations. Weights
Kerb weight refers to the basic model with a fuel tank filled to 90% capacity
and without optional extras. The figure quoted includes 75 kg to allow for
the weight of the driver.
For special versions and optional equipment fittings or for the addition of
accessories, the weight of the vehicle will increase
⇒
.
WARNING
● Please note that the centre of gravity may shift when transporting
heavy objects; this may affect vehicle handling and lead to an accident.
Always adjust your speed and driving style to suit road conditions and re-
quirements.
● Never exceed the gross axle weight rating or the gross vehicle weight
rating. If the allowed axle load or the allowed total weight is exceeded,
the driving characteristics of the vehicle may change, leading to acci-
dents, injuries and damage to the vehicle.
Towing a trailer Trailer weights
Trailer weight
The trailer weights and drawbar loads approved are selected in intensive tri-
als according to precisely defined criteria. The approved trailer weights are
valid for vehicles in the EU for maximum speeds of 80 km/h (50 mph) (in
certain circumstances up to 100 km/h (60 mph)). The figures may be differ-
ent in other countries. All data in the official vehicle documentation takes
precedence over these data at all times ⇒
.
Safety FirstOperating InstructionsPractical TipsTechnical Specifications
Page 252 of 280
250Description of specifications
Drawbar loads
The maximum permitted drawbar load on the ball joint of the towing bracket
must not exceed 75 kg.
In the interest of road safety, we recommend that you always tow approach-
ing the maximum drawbar load. The response of the trailer on the road will
be poor if the drawbar load is too small.
If the maximum permissible drawbar load cannot be met (e.g. with small,
empty and light-weight single axle trailers or tandem axle trailers with a
wheelbase of less than 1 metre), a minimum of 4% of the actual trailer
weight is legally required for the drawbar load.
WARNING
● For safety reasons, do not exceed the 80 km/h (50 mph) limit. This is
also valid in countries where higher speeds are permitted.
● Never exceed the maximum trailer weights or the drawbar load. If the
permissible axle load or the permissible total weight is exceeded, the
driving characteristics of the vehicle may change, leading to accidents,
injuries and damage to the vehicle.
Wheels
Tyre pressure, snow chains, wheel bolts
Tyre pressures
The sticker with the tyre pressure values can be found on the inside of the
fuel tank flap. The tyre pressure values given there are for cold tyres. The
slightly raised pressures of warm tyres must not be reduced. ⇒
Snow chains
Snow chains may be fitted only to the front wheels, and only for the follow-
ing tyres:
175/70R14
185/60R15Chains with links not exceeding 15 mm (including the chain
closure)
215/45R16Chains with links not exceeding 9 mm (including the chain
closure)
215/40R17Chains with links not exceeding 7 mm (including the chain
closure)
Wheel bolts
After the wheels have been changed, the tightening torque of the wheel
bolts should be checked as soon as possible with a torque wrench ⇒
.
The tightening torque for steel and alloy wheels is 120 Nm.
WARNING
● Check the tyre pressure at least once per month. Checking the tyre
pressure is very important. If the tyre pressure is too high or too low,
there is an increased danger of accidents, particularly at high speeds.
● If the tightening torque of the wheel bolts is too low, they could loos-
en while the vehicle is in motion. Risk of accident! If the tightening tor-
que is too high, the wheel bolts and threads can be damaged.
Note
We recommend that you ask your Technical Service for information about
appropriate wheel, tyre and snow chain size.
Page 253 of 280
251
Technical specifications
Technical specifications
Checking fluid levels
From time to time, the levels of the different fluids in the ve-
hicle must be checked. Never fill with incorrect fluids, other-
wise serious damage to the engine may be caused.
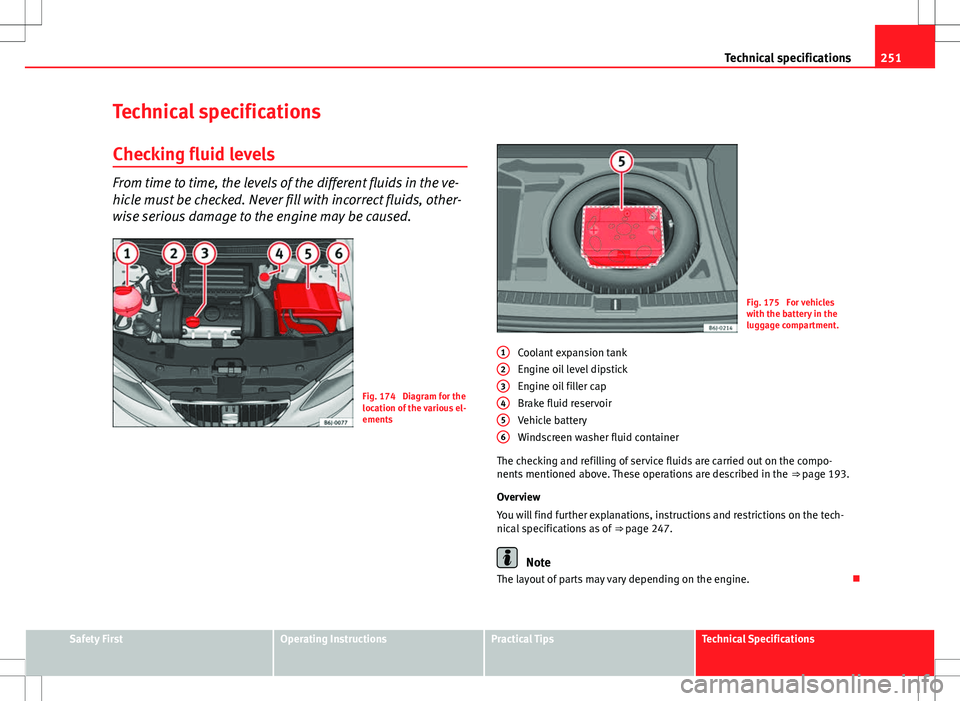
Fig. 174 Diagram for the
location of the various el-
ements
Fig. 175 For vehicles
with the battery in the
luggage compartment.
Coolant expansion tank
Engine oil level dipstick
Engine oil filler cap
Brake fluid reservoir
Vehicle battery
Windscreen washer fluid container
The checking and refilling of service fluids are carried out on the compo-
nents mentioned above. These operations are described in the ⇒ page 193.
Overview
You will find further explanations, instructions and restrictions on the tech-
nical specifications as of ⇒ page 247.
Note
The layout of parts may vary depending on the engine.
1
23456
Safety FirstOperating InstructionsPractical TipsTechnical Specifications
Page 254 of 280
252Technical specifications
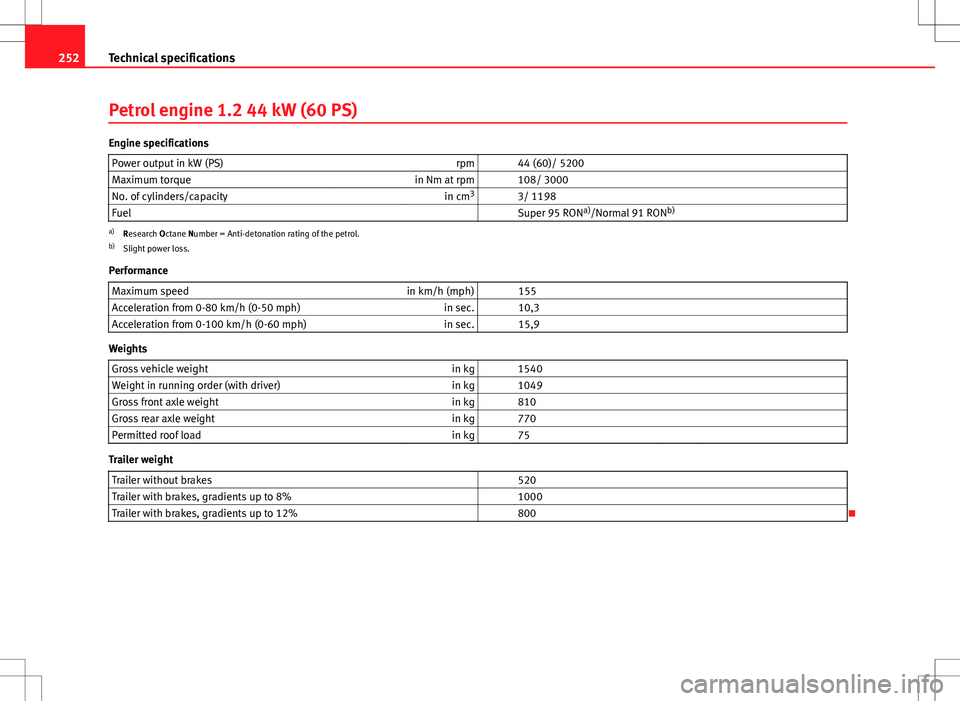
Petrol engine 1.2 44 kW (60 PS)
Engine specifications
Power output in kW (PS) rpm 44 (60)/ 5200
Maximum torque in Nm at rpm 108/ 3000
No. of cylinders/capacity in cm3
3/ 1198
Fuel Super 95 RON a)
/Normal 91 RON b)
a)
Research Octane Number = Anti-detonation rating of the petrol.
b) Slight power loss.
Performance Maximum speed in km/h (mph) 155
Acceleration from 0-80 km/h (0-50 mph) in sec. 10,3
Acceleration from 0-100 km/h (0-60 mph) in sec. 15,9
Weights
Gross vehicle weight in kg 1540
Weight in running order (with driver) in kg 1049
Gross front axle weight in kg 810
Gross rear axle weight in kg 770
Permitted roof load in kg 75
Trailer weight
Trailer without brakes 520
Trailer with brakes, gradients up to 8% 1000
Trailer with brakes, gradients up to 12% 800
Page 255 of 280
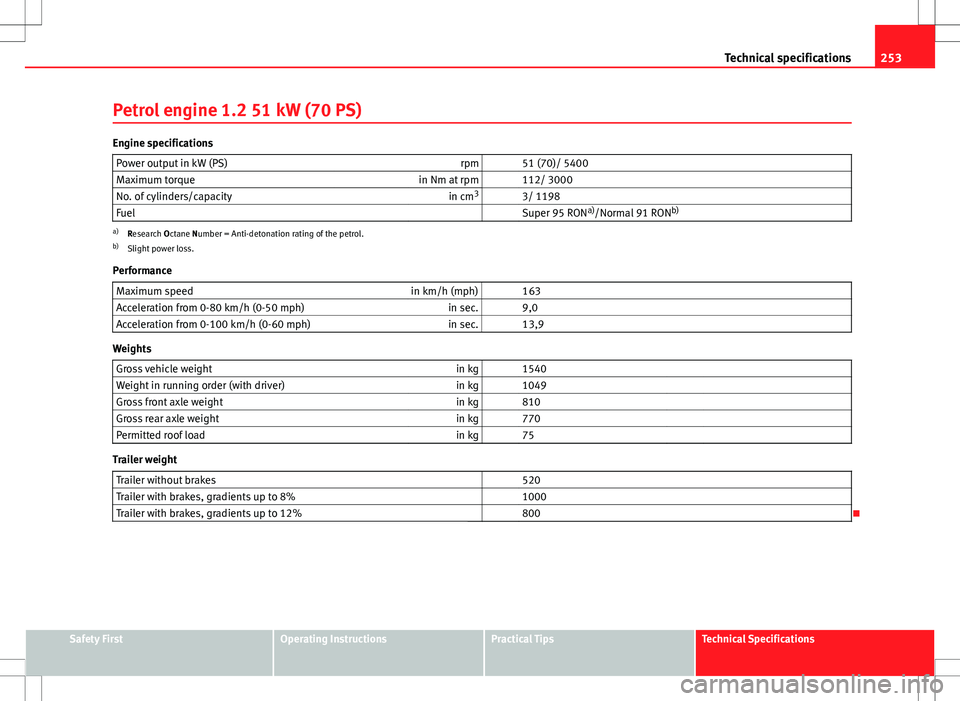
253
Technical specifications
Petrol engine 1.2 51 kW (70 PS)
Engine specifications Power output in kW (PS) rpm 51 (70)/ 5400
Maximum torque in Nm at rpm 112/ 3000
No. of cylinders/capacity in cm3
3/ 1198
Fuel Super 95 RON a)
/Normal 91 RON b)
a)
Research Octane Number = Anti-detonation rating of the petrol.
b) Slight power loss.
Performance Maximum speed in km/h (mph) 163
Acceleration from 0-80 km/h (0-50 mph) in sec. 9,0
Acceleration from 0-100 km/h (0-60 mph) in sec. 13,9
Weights
Gross vehicle weight in kg 1540
Weight in running order (with driver) in kg 1049
Gross front axle weight in kg 810
Gross rear axle weight in kg 770
Permitted roof load in kg 75
Trailer weight
Trailer without brakes 520
Trailer with brakes, gradients up to 8% 1000
Trailer with brakes, gradients up to 12% 800
Safety FirstOperating InstructionsPractical TipsTechnical Specifications