Temp SKODA CITIGO 2013 1.G Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SKODA, Model Year: 2013, Model line: CITIGO, Model: SKODA CITIGO 2013 1.GPages: 176, PDF Size: 10.54 MB
Page 70 of 176
It is still fully possible to steer the vehicle if the power steering fails or if the en-gine is not running (e.g. when towing). However, greater physical effort is re-
quired to turn the steering wheel.
If there is a fault in the power steering, the warning light or
lights up in the
instrument cluster » page 18.
Starting and stopping the engine
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Electronic immobilizer
68
Ignition lock
68
Starting the engine
68
Switching off the engine
68
The engine can only be started using a correctly coded original key.
The engine running noises may louder at first be louder for a short time afterstarting the cold engine. This is quite normal and is not an operating problem.
WARNING■ When driving, the ignition key must always be in the position 2 » Fig. 68 on
page 68 (ignition switched on) without the engine running. This position is
indicated by the warning lights coming on. If this is not the case, this could re-
sult in unexpected locking of the steering wheel – risk of accident!■
Only pull the ignition key from the ignition lock when the vehicle has come
to a complete stop (by applying the handbrake). Otherwise, the steering could
be blocked – risk of accident!
■
When leaving the vehicle, the ignition must always be removed. This is par-
ticularly important if children are left in the vehicle. Children could otherwise
start the engine for example – risk of accident or injury!
■
Never leave the vehicle unattended with the engine running.
■
Never switch off the engine before the vehicle is stationary – risk of acci-
dent!
WARNING■ Never leave the engine running in unventilated or closed rooms. The ex-
haust gases from the engine contain substances such as odourless and col-
ourless carbon monoxide (a poisonous gas) – risk to life!■
Carbon monoxide can cause unconsciousness and death.
CAUTION
■ The starter must only be operated when the engine is not running and the vehi-
cle is at a standstill. The starter or engine can be damaged if the starter is activa-
ted when the engine is running 3
» Fig. 68 on page 68.
■
If the engine does not start up after a second attempt, the fuse for the fuel
pump may have a fault. Check the fuse and replace if necessary » page 154,
Fuses on the underside of the dash panel , or seek assistance from a specialist ga-
rage.
■
Let go of the ignition key as soon as the engine starts otherwise the starter
could be damaged.
■
Do not tow start the engine – there is a risk of damaging the engine and the
catalytic converter. The battery from another vehicle can be used as a jump-start
aid » page 150 , Jump-starting .
CAUTION
■
Avoid high engine revolutions, full throttle and high engine loads before the en-
gine has reached its operating temperature – risk of damaging the engine!■
Do not switch the engine off immediately at the end of your journey after the
engine has been operated over a prolonged period at high loads but leave it to
run at an idling speed for about 1 minute. This prevents any possible accumulation
of heat when the engine is switched off.
For the sake of the environment
Do not warm up the engine while the vehicle is stationary. If possible, start your
journey as soon as the engine has started. Through this the engine reaches its
operating temperature more rapidly and the pollutant emissions are lower.
Note
After switching off the ignition, the radiator fan can intermittently continue to op-
erate for approx. 10 minutes.
67Starting-off and Driving
Page 71 of 176

Electronic immobilizerFirst read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 67.
An electronic chip is integrated in the head of the key. The immobiliser is deacti-vated with the aid of this chip when the key is inserted in the ignition lock. The
electronic immobiliser is automatically activated when the ignition key is with-
drawn from the lock.
The engine will not start if a non-authorized ignition key is used.
Ignition lock
Fig. 68
Positions of the vehicle key in
the ignition lock
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 67.
Ignition switched off, engine off, the steering can be locked
Ignition switched on
Starting engine
To lock the steering , with the ignition key withdrawn, turn the steering wheel
until the steering locking pin engages audibly.
If the steering is locked and the key cannot or can only be turned with difficulty
into position
2
» Fig. 68 , move the steering wheel back and forth and the steer-
ing lock unlocks.
Note
We recommend locking the steering wheel
whenever leaving the vehicle. This
acts as a deterrent against the attempted theft of your car.
123Starting the engine
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 67.
›
Move the gearshift lever into neutral or move the selector lever into position N
and firmly apply the handbrake.
›
Switch on the ignition
2
» Fig. 68 on page 68.
›
Depress and hold the clutch pedal (vehicles with a manual gearbox) or brake
pedal (vehicles with an automatic gearbox) until the engine starts.
›
Turn the key into position
3
to the stop and release immediately after the en-
gine has been started – do not apply the accelerator.
After letting go, the vehicle key will return to position
2
.
›
Release the handbrake.
If the engine does not start within 10 seconds, turn the key to position
1
. Repeat
the start-up process after approx. half a minute.
Switching off the engine
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 67.
Switch off the engine by turning the ignition key into position
1
» Fig. 68 on
page 68.
Brakes
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Information on braking
69
Handbrake
70
68Driving
Page 77 of 176
With vehicles with a manual gearbox, do not drive at unnecessarily low engine
speeds. Shift down a gear when the engine is no longer running smoothly. Ob-
serve the recommended gear » page 12, Recommended gear .
CAUTION
■
The engine is not protected from excessive engine revs caused by shifting
down at the wrong time. This can result in a sudden increase in revs beyond the
permissible maximum rpm, thereby causing engine damage.■
Never rev up a cold engine when the vehicle is stationary or when driving in in-
dividual gears.
For the sake of the environment
Do not drive at unnecessarily high engine speeds. Shifting up sooner helps save
fuel, reduces engine noise and protects the environment.
New tyres
First read and observe the introductory information given on page 73.
New tyres must firstly be “run in” since they do not offer optimal grip at first.
Therefore, drive especially carefully for the first 500 km or so.
New brake pads
First read and observe the introductory information given on page 73.
New brake pads do not initially provide optimal braking performance. They firstneed to be “run in”. Therefore, drive especially carefully for the first 200 km or so.
Economical driving and environmental sustainability
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Looking ahead
75
Economical gear changing
75
Avoiding full throttle
75
Reducing idling
75
Avoiding short distances
76
Checking tyre inflation pressure
76
Avoiding unnecessary ballast
76
Regular maintenance
76
Saving electrical energy
77
Environmental compatibility
77
The technical requirements for low fuel usage and economic efficiency of the ve-
hicle have already been built into the vehicle at the works. ŠKODA places a partic-
ular emphasis on minimising negative effects on the environment.
It is necessary to take note of the guidelines given in this chapter in order tomake best use of these characteristics and to maintain their effectiveness.
Fuel consumption, environmental pollution and the wear to the engine, brakes
and tyres depend essentially on the following three factors:
› your personal driving style
› operating conditions
› technical requirements
The fuel economy by can be improved by 10 -15 % by always looking ahead and
driving in an economical way.
Fuel consumption is also be influenced by external factors which are beyond the
driver's control. Consumption increases during the winter or under difficult condi-
tions, on poor roads, etc.
Fuel consumption can vary considerably from the manufacturer's data, as a result
of outside temperatures, weather and driving style.
Such an engine speed should be adhered to when accelerating, in order to avoid a
high fuel consumption and resonance of the vehicle.
74Driving
Page 78 of 176
CAUTIONAll the speed and engine revolution figures apply only when the engine is at its
normal operating temperature.
Looking ahead
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 74.
A vehicle's highest fuel consumption occurs when accelerating, therefore unnec-
essary accelerating and braking should be avoided. If looking ahead when driving, less braking and consequently less accelerating are required.
If possible, let your vehicle coast to a stop, or use the engine brake, if you can see that the next set of traffic lights is on red, for example.
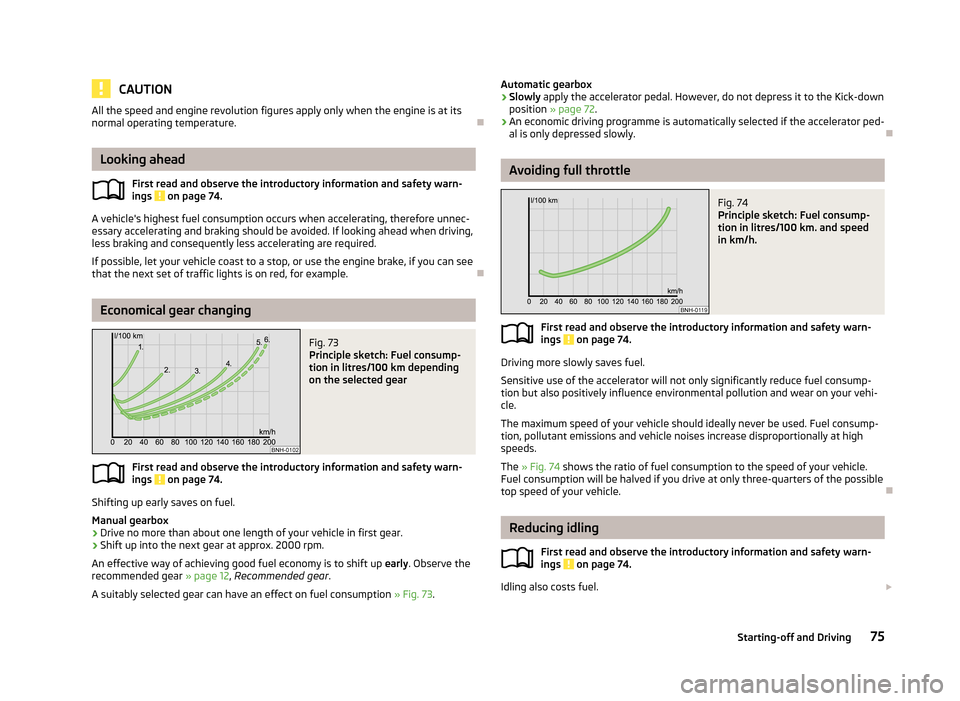
Economical gear changing
Fig. 73
Principle sketch: Fuel consump-
tion in litres/100 km depending
on the selected gear
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 74.
Shifting up early saves on fuel.
Manual gearbox › Drive no more than about one length of your vehicle in first gear.
› Shift up into the next gear at approx. 2000 rpm.
An effective way of achieving good fuel economy is to shift up early. Observe the
recommended gear » page 12, Recommended gear .
A suitably selected gear can have an effect on fuel consumption » Fig. 73.
Automatic gearbox
› Slowly
apply the accelerator pedal. However, do not depress it to the Kick-down
position » page 72 .
› An economic driving programme is automatically selected if the accelerator ped-
al is only depressed slowly.
Avoiding full throttle
Fig. 74
Principle sketch: Fuel consump-
tion in litres/100 km. and speed
in km/h.
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 74.
Driving more slowly saves fuel.
Sensitive use of the accelerator will not only significantly reduce fuel consump- tion but also positively influence environmental pollution and wear on your vehi- cle.
The maximum speed of your vehicle should ideally never be used. Fuel consump-
tion, pollutant emissions and vehicle noises increase disproportionally at high
speeds.
The » Fig. 74 shows the ratio of fuel consumption to the speed of your vehicle.
Fuel consumption will be halved if you drive at only three-quarters of the possible top speed of your vehicle.
Reducing idling
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 74.
Idling also costs fuel.
75Starting-off and Driving
Page 79 of 176
In vehicles not equipped with the START-STOP system, turn off the engine when
in a traffic jam, at a level crossing or traffic lights with longer wait times.
Even after just 30 – 40 seconds you will have saved more fuel than that is needed
when you start the engine up again.
If an engine is only idling it takes much longer for it to reach its normal operating
temperature. Wear-and-tear and pollutant emissions, though, are particularly
high in the warming-up phase. Therefore, start driving as soon as the engine has
started, High engine speeds should however be avoided.
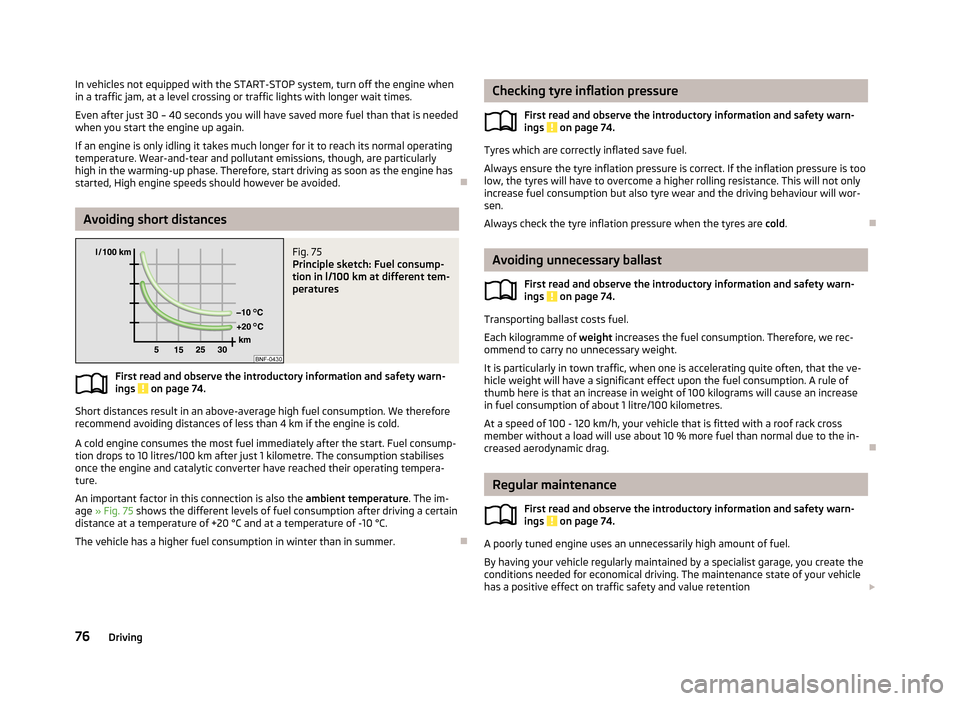
Avoiding short distances
Fig. 75
Principle sketch: Fuel consump-
tion in l/100 km at different tem-
peratures
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 74.
Short distances result in an above-average high fuel consumption. We therefore
recommend avoiding distances of less than 4 km if the engine is cold.
A cold engine consumes the most fuel immediately after the start. Fuel consump-tion drops to 10 litres/100 km after just 1 kilometre. The consumption stabilises
once the engine and catalytic converter have reached their operating tempera- ture.
An important factor in this connection is also the ambient temperature. The im-
age » Fig. 75 shows the different levels of fuel consumption after driving a certain
distance at a temperature of +20 °C and at a temperature of -10 °C.
The vehicle has a higher fuel consumption in winter than in summer.
Checking tyre inflation pressure
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 74.
Tyres which are correctly inflated save fuel.
Always ensure the tyre inflation pressure is correct. If the inflation pressure is too
low, the tyres will have to overcome a higher rolling resistance. This will not only increase fuel consumption but also tyre wear and the driving behaviour will wor-
sen.
Always check the tyre inflation pressure when the tyres are cold.
Avoiding unnecessary ballast
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 74.
Transporting ballast costs fuel.
Each kilogramme of weight increases the fuel consumption. Therefore, we rec-
ommend to carry no unnecessary weight.
It is particularly in town traffic, when one is accelerating quite often, that the ve-
hicle weight will have a significant effect upon the fuel consumption. A rule of
thumb here is that an increase in weight of 100 kilograms will cause an increase in fuel consumption of about 1 litre/100 kilometres.
At a speed of 100 - 120 km/h, your vehicle that is fitted with a roof rack crossmember without a load will use about 10 % more fuel than normal due to the in-
creased aerodynamic drag.
Regular maintenance
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 74.
A poorly tuned engine uses an unnecessarily high amount of fuel.
By having your vehicle regularly maintained by a specialist garage, you create the conditions needed for economical driving. The maintenance state of your vehicle has a positive effect on traffic safety and value retention
76Driving
Page 83 of 176
Assist systems
Brake assist systems
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
80
Antilock Braking System (ABS)
81
Traction Control System (TCS)
81
Electronic Differential Lock (EDL)
81WARNING■ A lack of fuel can cause irregular engine running or cause the engine to shut
down. The brake assist systems would then fail to function – risk of accident!■
Adjust the speed and driving style to the current visibility, weather, road and
traffic conditions. The increased safety provided by the brake assist systems
must not tempt you to take safety risks – risk of accident!
■
In the event of an ABS fault, visit a specialist garage immediately. Adjust
your style of driving according to the damage to the ABS, as you will not know
the exact extent of the damage or the extent to which this is limiting the
braking efficiency.
CAUTION
■ All four wheels must be fitted with the same tyres approved by the manufactur-
er to ensure the brake assist systems operate correctly.■
Changes to the vehicle (e.g. to the engine, brakes, chassis) can influence the
functionality of the brake assist systems » page 110, Modifications, adjustments
and technical alterations .
■
If a fault occurs in the ABS system, the ESC, ASR and EDL will also fail to work.
An ABS fault is indicated with the warning light » page 19 .
Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 80.
The ESC system helps improve control of the vehicle in situations where it is be-
ing operated at its dynamic limits, such as a sudden change to the direction of
travel. Depending on the conditions of the road surface, the risk of skidding is re-
duced, thereby improving the vehicle's driving stability .
The ESC system is automatically activated each time the ignition is switched on.The direction which the driver wishes to take is determined based on the steering angle and the speed of the vehicle and is constantly compared with the actualbehaviour of the vehicle. In the event of deviations, such as the car beginning to
skid, the ESC system will automatically brake the appropriate wheel.
During an intervention of the system, the warning light
flashes in the instru-
ment cluster.
The following systems are integrated into the electronic stabilisation control
(ESC) :
› Antilock brake system (ABS),
› Traction control (TCS);
› Electronic Differential Lock (EDL)
› Hydraulic Brake Assist (HBA)
› Hill Hold Control (HHC).
In the event of an ESC fault, the ESC warning light
illuminates in the instru-
ment cluster » page 18.
Hydraulic Brake Assist (HBA)
HBA increases the braking effect and helps to shorten the braking distance.
The HBA is activated by very quick operation of the brake pedal. In order to ach-
ieve the shortest possible braking distance, the brake pedal must be applied firm-
ly until the vehicle has come to a standstill.
The HBA function is automatically switched off when the brake pedal is released. The ABS is activated faster and more effectively with the intervention of the HBA.
Hill Hold Control (HHC)
When driving on slopes, HHC allows you to move your foot from the brake pedal to the accelerator pedal without having to use the handbrake.
The system holds the brake pressure produced by the activation of the brakepedal for approx. 2 seconds after the brake pedal is released.
80Driving
Page 86 of 176
WARNINGConcentrate fully at all times on your driving! As the driver you are fully re-
sponsible for the operation of your vehicle. Only use the system so that you
are in full control of your vehicle in every traffic situation - risk of accident!
Note
■ The visual parking system is shown in the screen of the multifunction device
Move & Fun within a few seconds of shifting into reverse gear.■
More information about the mobile multifunction device Move & Fun can be
found in the digital operating manual in the device » page 64, Multifunction de-
viceMove & Fun .
Cruise Control System
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Storing a speed
84
Changing a stored speed
84
Off temporarily
84
Switch off completely
84
The Cruise Control System (CCS) maintains a set speed, more than 25 km/h, with-
out you having to actuate the accelerator pedal.
This is only possible within the range which is permitted by the power output and
braking power of the engine.
The warning light
illuminates in the instrument cluster when the cruise control
system is switched on.
WARNING■ For safety reasons, the cruise control system must not be used in dense
traffic or on unfavourable road surfaces (such as icy roads, slippery roads,
loose gravel) – risk of accident!■
The saved speed may only be resumed if it is not too high for the current
traffic conditions.
■
Always deactivate the cruise control system after use to prevent the system
being switched on unintentionally.
CAUTION
■ The cruise control system is not able to maintain a constant speed when driving
in areas with steeper gradients. The weight of the vehicle increases the speed at which it travels. Therefore, shift to a lower gear in good time or slow the vehicle
down by applying the foot brake.■
It is not possible to switch on the cruise control system on vehicles fitted with a
manual gearbox if the first gear or reverse gear is engaged.
■
It is not possible on vehicles fitted with an automatic gearbox to switch on the
cruise control system if the selector lever is in the position N or R.
■
The Cruise Control System may automatically switch off when some assist sys-
tems (e.g. ESC, City Safe Drive) intervene, when the speed exceeds maximum per-
missible engine speed, or if a similar event takes place.
83Assist systems
Page 87 of 176
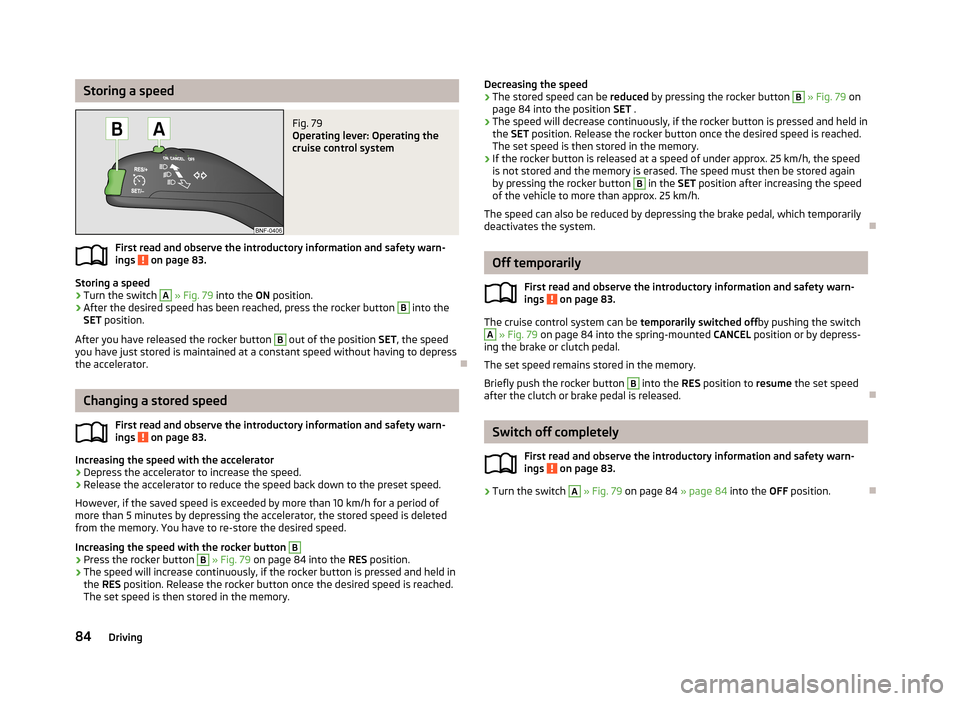
Storing a speedFig. 79
Operating lever: Operating the
cruise control system
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 83.
Storing a speed
›
Turn the switch
A
» Fig. 79 into the ON position.
›
After the desired speed has been reached, press the rocker button
B
into the
SET position.
After you have released the rocker button
B
out of the position SET, the speed
you have just stored is maintained at a constant speed without having to depress
the accelerator.
Changing a stored speed
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 83.
Increasing the speed with the accelerator
›
Depress the accelerator to increase the speed.
›
Release the accelerator to reduce the speed back down to the preset speed.
However, if the saved speed is exceeded by more than 10 km/h for a period of
more than 5 minutes by depressing the accelerator, the stored speed is deleted from the memory. You have to re-store the desired speed.
Increasing the speed with the rocker button
B›
Press the rocker button
B
» Fig. 79 on page 84 into the RES position.
›
The speed will increase continuously, if the rocker button is pressed and held in
the RES position. Release the rocker button once the desired speed is reached.
The set speed is then stored in the memory.
Decreasing the speed›The stored speed can be reduced by pressing the rocker button B » Fig. 79 on
page 84 into the position SET .›
The speed will decrease continuously, if the rocker button is pressed and held in
the SET position. Release the rocker button once the desired speed is reached.
The set speed is then stored in the memory.
›
If the rocker button is released at a speed of under approx. 25 km/h, the speed is not stored and the memory is erased. The speed must then be stored again
by pressing the rocker button
B
in the SET position after increasing the speed
of the vehicle to more than approx. 25 km/h.
The speed can also be reduced by depressing the brake pedal, which temporarily deactivates the system.
Off temporarily
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 83.
The cruise control system can be temporarily switched offby pushing the switch
A
» Fig. 79 on page 84 into the spring-mounted CANCEL position or by depress-
ing the brake or clutch pedal.
The set speed remains stored in the memory.
Briefly push the rocker button
B
into the RES position to resume the set speed
after the clutch or brake pedal is released.
Switch off completely
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 83.
›
Turn the switch
A
» Fig. 79 on page 84 » page 84 into the OFF position.
84Driving
Page 88 of 176
START-STOP
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Starting/shutting down the engine
85
Operating conditions of the system
85
Manually activating/deactivating the system
86
The START-STOP system helps you to save fuel while at the same time reducing
harmful exhaust emissions and CO 2 emissions.
The function is automatically activated each time the ignition is switched on. In the start-stop mode, the engine automatically switches to the vehicle's idle phase, e.g. when stopped at traffic lights. The engine restarts automatically
where necessary.
The system can work only if the following basic conditions are met.
The driver's door is closed.
The driver has fastened the seat belt.
The bonnet is closed.The driving speed was higher than 4 km/h after the last stop.
WARNING■ The brake servo unit and power steering only operate if the engine is run-
ning.■
Never let the vehicle roll with the engine switched off.
CAUTION
Always deactivate the START-STOP system before driving through wa-
ter » page 78 .Note■
If the driver's seat belt is removed for more than 30 seconds or the driver's door
is opened during stop mode, the engine must be started manually with the key.■
After manually starting the engine on vehicles with manual transmission, auto-
matic engine shut down is not possible until the vehicle has travelled the re- quired minimum distance for START-STOPmode.
■
Changes to the outdoor temperature can have an effect on the internal temper-
ature of the vehicle battery even after several hours. If the vehicle remains out-
doors for a long time in minus temperatures or in direct sunlight, it can take sev-
eral hours until the internal temperature of the vehicle battery reaches a suitable temperature for proper operation of the START STOP system.
Starting/shutting down the engine
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 85.
›
Stop the vehicle (where necessary, apply the handbrake).
›
Put the gear stick into Neutral.
›
Release the clutch pedal.
Automatic engine shut down (STOP phase) takes place. The warning symbol
appears in the instrument cluster display.
›
Depress the clutch pedal.
The automatic start procedure takes place again (START phase). The warning
symbol
goes out.
Operating conditions of the system
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 85.
The START-STOP system is very complex. Some of the procedures are hard tocheck without servicing.
No engine shut down is carried out
Before each STOP phase, the system checks whether certain conditions have
been met. No engine shut down takes place in the following situations.
85Assist systems
Page 89 of 176
›The engine has not reached the minimum temperature for the START STOP
mode.
› The temperature inside the vehicle has not reached the desired temperature
set in the air-conditioning system/heating.
› The external temperature is very low/high.
› The windscreen defroster / ventilation is switched on at the maximum air tem-
perature (air conditioning) setting.
› The parking aid is activated.
› The charge state of the vehicle battery is too low.
› The stationary vehicle is on a steep slope or a steep downhill section.
› The idling speed is too high.
› The steering angle is too large (manoeuvring).
The warning symbol
appears in the instrument cluster display.
The automatic start procedure takes place again
During the STOP phase, the engine fires up without any active driver intervention, e.g. in the following situations.
› The vehicle begins to roll, e.g. on a slope.
› The difference between the temperature setting of the air-conditioning sys-
tem/heating and the temperature of the interior is too large.
› The windscreen defroster / ventilation is switched on at the maximum air tem-
perature (air conditioning) setting.
› The brake pedal was pressed several times (the pressure in the braking system
is too low).
› The charge state of the vehicle battery is too low.
› The current consumption is too high.
Manually activating/deactivating the system
Fig. 80
Button for the START-STOP sys-
tem
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 85.
Activation/deactivation
›
Press the symbol button » Fig. 80 .
When start-stop mode is deactivated, the warning light in the button lights up.
Note
If the system is deactivated during the STOP phase, the automatic start proce-
dure takes place.
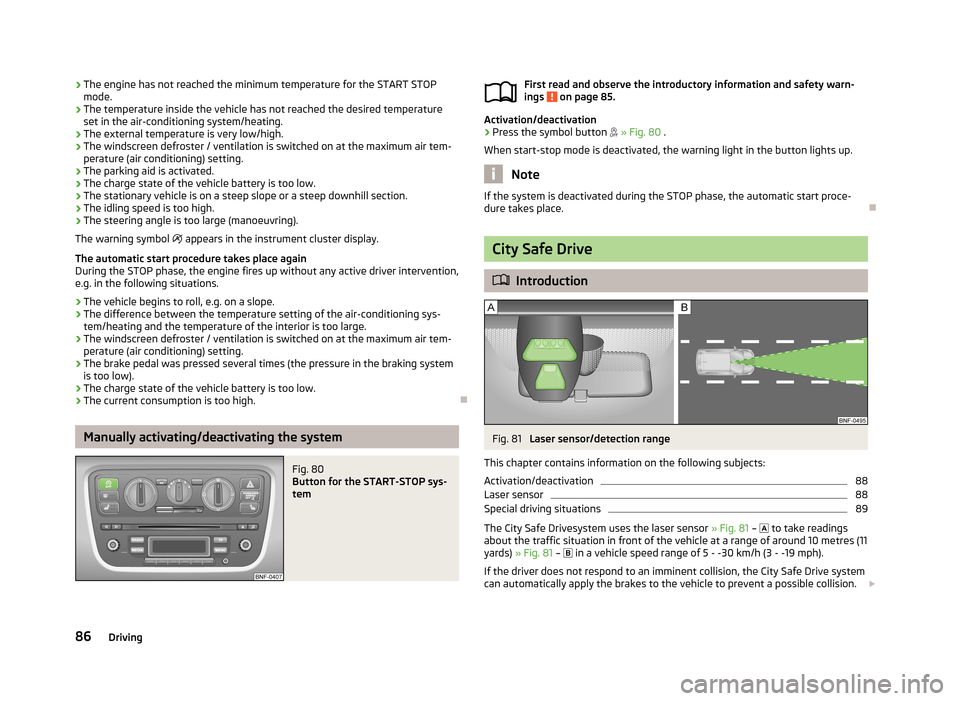
City Safe Drive
Introduction
Fig. 81
Laser sensor/detection range
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Activation/deactivation
88
Laser sensor
88
Special driving situations
89
The City Safe Drivesystem uses the laser sensor » Fig. 81 –
to take readings
about the traffic situation in front of the vehicle at a range of around 10 metres (11
yards) » Fig. 81 –
in a vehicle speed range of 5 - -30 km/h (3 - -19 mph).
If the driver does not respond to an imminent collision, the City Safe Drive system
can automatically apply the brakes to the vehicle to prevent a possible collision.
86Driving