steering SKODA SUPERB 2007 1.G / (B5/3U) Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SKODA, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SUPERB, Model: SKODA SUPERB 2007 1.G / (B5/3U)Pages: 259, PDF Size: 14.71 MB
Page 132 of 259

Seat belts131
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
The physical principle of a frontal collision
The physical principle of a frontal a ccident can be explained quite simply:
Motion energy, so-called kinetic energy, is produced as soon as the vehicle is
moving, both for the vehicle and its occupants. The magnitude of this kinetic energy
depends essentially on the speed at which the vehicle is travelling and on the
weight of the vehicle and the occupants. The greater the speed and weight increase, the greater the amount of energy which has to be absorbed in the event of an acci-
dent.
The speed of the vehicle is, nevertheless,
the most important factor. Doubling the
speed of the vehicle from 25 km/h up to 50 km/h increases the kinetic energy four
times.
The common opinion that it is possible to support your body in a minor accident
with your hands, is incorrect. Even in a collision at only a low speed, the forces
acting on the body are such that it is no longer possible to support your body.
Even if you only drive at a speed within the range from 30 km/h to 50 km/h, the
forces which are produced on your body in the event of an accident can easily
exceed 10.000 N (Newton). This equals a weight of one tonne (1 000 kg).
In the event of a frontal collision, occupants of the car not wearing a seat belt, are
thrown forward and strike in an uncontrolle d way parts of the interior of the car,
such as steering wheel, dash panel, windscreen, ⇒fig. 138 . The occupants of a
vehicle who have not fastened their seat belts may even be thrown out of the
vehicle. This can resu lt in fatal injuries.
It is also important that rear seat occupants fasten their seat belts as they will other-
wise be thrown through the vehicle in an uncontrolled manner in the event of an
accident A rear seat passenger who has not fastened the seat belt is a danger not
only to himself but also fo r those seated at the front ⇒fig. 139 .
Important safety information regarding the use of
seat belts
The correct use of the seat belts considerably reduces the risk of
injury!
WARNING
•The belt webbing must not be jammed in-between at any point or
twisted, or chafe against any sharp edges.
•It is important that the belt webbing is properly routed if the seat belts
are to offer their maximum protection ⇒page 132, “How are seat belts
correctly fa stened?”.
Fig. 138 The driver is
thrown forward if not
wearing a belt
Fig. 139 The rear seat
occupant is thrown
forward if not wearing a
belt
NKO B5 20.book Page 131 Friday, March 2, 2007 1:46 PM
Page 139 of 259

Airbag system
138
Front airbag
Description of the front airbags
The airbag system is not a su bstitute for the seat belt!
The front airbag for the driver is housed in the steering wheel ⇒fig. 144 . The front
airbag for the front passenger is housed in the dash panel above the storage
compartment ⇒fig. 145 . The installation positions are each marked with the
“AIRBAG” logo. The front airbag system, in combination with three-point safety belts, offers addi-
tional protection for the head and chest ar
ea of the driver and front passenger in
the event of a frontal colli sion of major severity ⇒ in “Important safety informa-
tion regarding the front airbag system” on page 139.
The airbag is not a substitute for the seat belt, but is part of the complete passive
vehicle safety concept. Please note that an airbag can only offer you optimal
protection in combination with a seat belt which is fastened .
Apart from their normal protective function, a further task of the seat belts is to
also hold the driver and front passenger in a correct seated position in the event of
a frontal collision so as to enable the fr ont airbags to offer the maximum protection.
You should therefore always fasten the seat belts, not only because this is required
by law, but also for safety reasons and for your own protection ⇒page 130, “Why
seat belts?”.
Note
The dash panel must be replaced afte r the front passenger airbag has been
deployed.Fig. 144 Driver airbag in
the steering wheel
Fig. 145 Front passenger
airbag in the dash panel
NKO B5 20.book Page 138 Friday, March 2, 2007 1:46 PM
Page 140 of 259

Airbag system139
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
Function of the front airbags
Risk of injury to the head and chest area is reduced by fully inflated
airbags.
The airbag system is designed in such a way that the driver and front passenger
airbag are deployed in the event of a frontal collision of major severity.
In certain accident situations both the front airbags as well as the head* and side
airbags may be deployed together.
If the airbags are deployed, the airbags are filled with a propellant gas and inflated
in front of the driver and front passenger ⇒fig. 146 . The airbags inflate in fractions
of a second and at a high speed in order to be able to offer that additional protec-
tion in the event of an accident. The forward movement of the driver and of the
front passenger is cushioned when they make contact with the fully inflated airbag
and the risk of injury to head and chest is thus reduced.
The specially developed airbag allows the gas to flow out of the inflated airbag in a
controlled manner (depending on the load of the particular car occupant) in order
to cushion head and chest areas. The airbag then deflates subsequently to such an
extent, after an accident, to again provide a clear view forward.
A grey white, non harmful gas is released when airbag is inflated. This is perfectly
normal and is not an indication of a fire in the vehicle. The airbag develops enormous forces when triggered, which can lead to injuries if
the sitting position or seated position is not correct
⇒ in “Important safety
information regarding the front airbag system”.
Important safety information r egarding the front airbag system
Correct use of the airbag system considerably reduces the risk of
injury!
WARNING
•Never transport children on the front seat of a vehicle without using a
proper restraint system. If airbags are deployed in the event of an accident,
the child might suffer severe or even fatal injuries!
•For the driver and front passenger it is important to maintain a distance
of at least 25 cm from the steering wheel or dash panel ⇒fig. 147 . Not main-
taining this minimum distance will mean that the airbag system will not be
able to properly protect you - hazard! The front seats and the head restraints
must always also be correctly adjusted to match the body size of the occu-
pant.
•It is essential to always switch off ⇒page 144, “Deactivating an airbag”
the front passenger airbag when attaching a child safety seat on the front
passenger seat where the child is seated with its back facing in direction of
travel (in some countries al so when the child is facing the direction of travel).
Fig. 146 Inflated airbagsFig. 147 Safe distance to
steering wheel
NKO B5 20.book Page 139 Friday, March 2, 2007 1:46 PM
Page 141 of 259

Airbag system
140
If this is not done, there is a risk of the child suffering severe or even fatal
injuries if the front passenger airbag is deployed. In certain countries
national legal provisions also requir e that the side or head passenger
airbags be deactivated. When transporting a child on the front passenger
seat, please comply with the appropri ate national regulations regarding the
use of child safety seats.
•There must not by any further persons, animals or objects positioned
between the front seated occupants and the deployment area of the airbag.
•The steering wheel and the surface of the airbag module in the dash
panel on the passenger side must not be stuck onto, covered or modified in
any other way. These parts should only be cleaned with a dry cloth or a cloth
moistened with water. No objects such as cup holders, mobile phone
mounts, etc. may be attached to the covers of the airbag modules or be
located within the immediate area.
•No modifications of any kind may be made to parts of the airbag system.
Any work on the airbag system including installing and removing system
components because of other repair work (e.g. removing the steering
wheel) must only be carried out by a specialist garage.
•Never carry out changes on the front bumper or on the body.
•Never place any objects on the surfac e of the front passenger airbag in
the dash panel.
Side airbag
Description of side airbags
The side airbag together with the head airbag offers enhanced occu-
pant protection in the ev ent of a side collision.
The side airbags are housed in the upholstery of the backrests of the front seats and
are marked ⇒fig. 148 with the lettering “AIRBAG” on the middle part.
The side airbag system in combination with the three-point seat belts, offers addi-
tional protection for the upper area of the body (chest, stomach and pelvis) of the
occupants of the car in the event of a side collision of major severity ⇒ in
“Important safety information on the side airbag” on page 141.
Apart from their normal protective function, a further task of the seat belts is to
also hold the driver and front passenger in a correct seated position in the event of
a side collision so as to enable the side airbags to offer the maximum protection.
You should therefore always fasten the seat belts, not only because this is required
by law, but also for safety reasons and for your own protection ⇒page 130, “Why
seat belts?”.
Each time the side airbag is deployed, the head airbag* on the relevant side is auto-
matically deployed at the same time in order to provide the occupant with
enhanced protection ⇒page 142.
WARNING (continued)
Fig. 148 Installation
position of side airbag in
driver seat
NKO B5 20.book Page 140 Friday, March 2, 2007 1:46 PM
Page 145 of 259

Airbag system
144
Deactivating an airbag
Deactivating airbags
If any airbags have been deactivated, switch them on again as soon
as possible so that they are able to again provide their proper protec-
tion.
There is the technical means installed within your vehicle to switch off the front,
side or head airbag (take out of commission).
This is why you should have the deactiva tion of the airbags carried out by a
specialist garage.
On vehicles equipped with the switch for deactivation of the airbags, you can deac-
tivate the front and side passenger airbag by means of this switch ⇒page 144.
Deactivation of airbags is envisaged only for particular instances, such as if:
•you must in exceptional cases use a child seat on the front passenger seat
where the child has its back to the directio n of travel of the vehicle (in some coun-
tries this must be in the direction of trav el due to other legal regulations applying)
⇒ page 146, “Important safety information regarding the use of child safety seats”
•you are not able to maintain the distance of at least 25 cm between middle of
steering wheel and chest, despite the driver seat being correctly adjusted,
•special attachments are required in the area of the steering wheel because of a
physical disability,
•you have installed other seats (e.g. orthopaedic seats without side airbags).
Monitoring the airbag system
The functionality of the airbag system is also monitored electronically, when one
airbag has been switched off
If the airbag was switched off using diagnostic equipment:
•The warning light for the airbag system lights up for 3 seconds after switching
on the ignition and then flashes for 12 seconds afterwards in 2 second intervals.
Front passenger airbags sw itched off using the switch for front passenger
airbags* in stowage compartmen t on the front passenger side:
•The airbag warning light comes on in th e instrument cluster for about 3 seconds
each time the ignition is switched on.
•Switching off airbags is indicated in the middle of the dash panel by the lighting
up of the indicator light ⇒ fig. 153 .
Note
Your Škoda Service Partner will be able to advise you whether national legislation in
your country allows airbags in your vehicle to be deactivated, and which ones.
Switch for the front seat passenger airbags*
Fig. 152 Storage
compartment: Switch for
the front seat passenger
airbags
Fig. 153 Indicator light
for a switched off front
seat passenger airbag
NKO B5 20.book Page 144 Friday, March 2, 2007 1:46 PM
Page 156 of 259

Intelligent Technology155
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
Driving Tips
Intelligent Technology
Electronic stability programme (ESP)*
General
General
The ESP aids you maintain control of your vehicle in situations in borderline driving
situations such as when negotiating a curve too fast. The risk of skidding is reduced
and your car thus offers greater driving stability depending on the conditions of the
road surface. This occurs at all speeds.
The following systems are integrated into the electronic stability programme:
•Electronic Differential Lock (EDL),
•Traction control system (TCS),
•Antilock brake system ABS,
•Brake Assist. Operating principle
The ESP switches on automatically when the engine is started and then conducts a
self-test. The ESP control unit processes data from the individual systems. It also
processes additional measurement data which are supplied by highly sensitive
sensors: the rotational velocity of the vehi
cle about its vertical axis, the lateral accel-
eration of the vehicle, the brakin g pressure and the steering angle.
The direction which the driver wishes to ta ke is determined based on the steering
angle and the speed of the vehicle and is constantly compared with the actual
behaviour of the vehicle. If differences exis t, such as the car beginning to skid, the
ESP will automatically brake the appropriate wheel.
The car is stabilised again by the forces which take effect when the wheel is braked.
Intervention into the brake system takes place primarily on the outer front wheel of
a vehicle which tends to oversteer (tendency for the rear of the vehicle to break
away) while occurs this is on the inner re ar wheel of a vehicle which tends to under-
steer (tendency to shift out of the curve). This braking control cycle is accompanied
by noises.
The ESP operates in combination with the ABS ⇒page 159, “Antilock brake system
(ABS)”. If there is a fault in the ABS system, the ESP also does not operate.
The ESP warning light ⇒page 28 lights up in the instrument cluster when there is a
fault on the ESP.
Switching off
You can switch the ESP off and on again as you wish, by pressing the button
⇒ fig. 163 . The ESP warning light ⇒page 28 lights up in the instrument cluster
when the ESP is switched off.
The ESP should normally always be switched on. It may be good practice to switch
the system off only in particular exceptional situations if you desire wheel slip.
Examples:
•when driving with snow chains,
B1Z-0042HB1Z-0042HFig. 163 ESP switch
NKO B5 20.book Page 155 Friday, March 2, 2007 1:46 PM
Page 160 of 259

Intelligent Technology159
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
WARNING
•Never switch off the engine before the vehicle is stationary.
•The brake booster only operates when the engine is running. Greater
physical effort for braking is required when engine is switched off. Because
if you do not stop as normal, this can cause an accident and severe injuries.
Antilock brake system (ABS)
ABS prevents the wheels locking when braking.
General
The ABS contributes significan tly to enhancing the active safety of your vehicle.
Compared to a car not fitted with the ABS brake system, you are able to retain
optimal steering ability even during a fu ll brake application on a slippery road
surface because the wheels do not lock up.
You must not expect, however, that the br aking distance will be shorter under all
circumstances as a result of the ABS. Th e braking distance for example on gravel
and fresh snow, when you should anyway be driving slowly and cautiously, will be
longer.
Operating principle
As soon as the vehicle speed has increa sed to about 6 km/h an automatic test
procedure is conducted during which you wi ll be able to hear a pumping noise for
about 1 second.
The brake pressure will be reduced on a wheel which is rotating at a speed which is
too low for the speed of the vehicle and tend ing to lock. This control cycle is notice-
able from a pulsating movement of the brake pedal which is accompanied by
noises. This is consciously intended to pr ovide the driver with the information that
the wheels are tending to lock (ABS control range). You must always keep the brake
pedal depressed to enable the ABS to optima lly control the brake application in this
braking range. Never interrupt the application of the brakes!
WARNING
•The ABS can also not overcome the physic al limits of your vehicle. Please
do not forget this, particularly when driv ing on icy or wet road surfaces. If the
ABS is operating within the control ra nge, adapt your speed immediately to
the conditions of the road surface and the traffic situation. The increased
safety offered by the ABS must not tempt you to take greater risks than
otherwise - risk of an accident!
•The normal braking system is still fully functional if there is an ABS fault.
Visit a specialist garage as quickly as po ssible and adjust your style of driving
to take account of the ABS fault in the meantime since you will not know how
great the damage is.
Note
•A warning light comes on if a fault occurs in the ABS system ⇒page 29.
•Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or other assign-
ment of tyres and wheels) can in fluence the function of the ABS ⇒page 205,
“Accessories, changes and replacement of parts”.
Brake Assist*
During a severe brake application (e.g. if a hazard exists), the Brake Assist increases
the braking force and thus makes it possible to rapidly produce the pressure
required in the brake system.
The majority of drivers do apply the brakes in good time in dangerous situations,
but do not depress the brake pedal with suff icient pressure. Consequently, it is not
possible for the car to achieve its maxi mum deceleration and the car covers a
greater distance than necessary.
The Brake Assist is activated by the very quick operation of the brake pedal. In such
cases, a much greater braking pressure ex ists than during a normal brake applica-
tion. This makes it possible, even with a relatively low resistance of the brake pedal,
to produce an adequate pressure in the brake system in the shortest possible time,
which is required for maximum deceleration of the car. You must apply the brake
NKO B5 20.book Page 159 Friday, March 2, 2007 1:46 PM
Page 161 of 259
Intelligent Technology
160
pedal firmly and hold it in this position in order to achieve the shortest possible
braking distance.
The Brake Assist is able to help you achieve a shorter braking distance in emergency
situations by rapidly producing the pressure required in the brake system. It fully
exploits the attributes of the ABS. After you release the brake pedal, the function of
the Brake Assist is automatically switched off and the brakes operate in the normal
way.
WARNING
•The Brake Assist is also not able to overcome the physical limits of your
car in terms of the braking distance required.
•Adapt your speed to the conditions of the road surface and to the traffic
situation.
•The increased safety offered by the Brake Assist must not tempt you to
take a greater safety risk than otherwise.
Power steering
Power steering assists the driver in steering the vehicle and reduces the physical
force needed for steering.
The steering characteristics can be changed by a specialist garage.
It is still possible to fully steer the vehicle if the power steering fails or if the engine
is not running (vehicle being towed in). The only difference is that greater physical
effort is required.
If the steering is turned to full lock when the car is stationary, you will place great
stresses on the power steering system. Turning the steering to full lock in such a
situation will be accompanied by noises. In addition, the idling speed of the engine
will drop briefly.
Caution
Do not leave the steering at full lock for more than 15 seconds when the engine is
running - risk of damagi ng the power steering!
Note
•Have the steering inspected as soon as po ssible by a specialist garage if there is
a leak or fault in the system.
•The power steering requires a special hydraulic oil. The oil reservoir is located
at the front left of the engine compartment ⇒page 186. The correct hydraulic oil
level is important for proper oper ation of the power steering system.
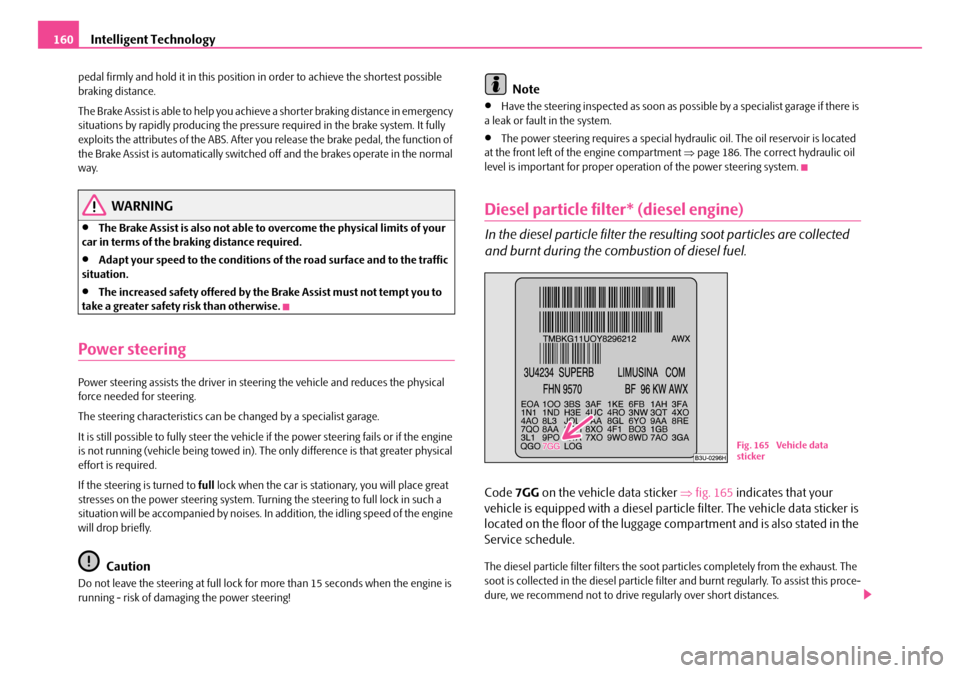
Diesel particle filter* (diesel engine)
In the diesel particle filter the resulting soot particles are collected
and burnt during the combustion of diesel fuel.
Code 7GG on the vehicle data sticker ⇒fig. 165 indicates that your
vehicle is equipped with a diesel particle filter. The vehicle data sticker is
located on the floor of the luggage com partment and is also stated in the
Service schedule.
The diesel particle filter filters the soot particles completely from the exhaust. The
soot is collected in the diesel particle filter and burnt regularly. To assist this proce-
dure, we recommend not to drive regularly over short distances.
Fig. 165 Vehicle data
sticker
NKO B5 20.book Page 160 Friday, March 2, 2007 1:46 PM
Page 178 of 259
Taking care of your vehicle and cleaning the vehicle177
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
Wheels
Steel wheels
You should also thoroughly wash the wheels and wheel trims when giving your
vehicle its regular wash. This prevents any brake dust, dirt and road salt from
sticking to the wheel hubs. You can remove stubborn brake abrasion adhering to
t h e w h e e l s w i t h a n i n d u s tr i a l c l e a n e r. To u c h u p a n y d a m a g e to t h e p a i n tw o r k o n th e
wheels before rust is able to form.
Light alloy wheels
Regular care of light alloy wheels is necessary in order to retain their decorative
appearance over long periods. It is partic ularly important to remove any road salt
and brake abrasion from light alloy wheels every two weeks, otherwise the surface
will suffer. Wash thoroughly and then treat the wheels with a protective product for
light alloy wheels which does not contain any acidic components. You should
provide the wheel hubs with a hard wax la yer every three months. You must not use
any products which cause abrasion when treating the wheel hubs. Any damage to
the paint layer on the wheel hubs must be touched up immediately.
We recommend using a preservative from Škoda genuine accessories offered by
your Škoda dealer.
WARNING
One should remember when cleaning th e wheels that moisture, ice and road
salt may adversely affect braking ef ficiency - risk of an accident!
Note
Severe layers of dirt on the wheels can also result in wheel imbalance. This may
show itself in the form of wheel vibration which is transmitted to the steering wheel
which, in certain circumstances, can caus e premature wear of the steering. It is
therefore important to clean dirty wheels.
Underbody protection
The underside of your vehicl e is protected for life against chemical and mechanical
influences.
One cannot, however, completely rule out damage to the protective layer when
driving so we recommend that you inspect the protective layer on the underside of
your vehicle and on the chassis at certain in tervals - this is best done at the begin-
ning and end of the winter - and to touch up any damaged areas.
Škoda Service Partners have suitable spray products available as well as the neces-
sary equipment and are familiar with the instructions for use. It is therefore best to
have such touch-up work or additional corrosion protection measures carried out
by a Škoda Service Partner.
WARNING
Never use additional underbody protection or corrosion-protection agents
for the exhaust pipes, catalytic converte rs, diesel particle filter or heat
shields. When the engine reaches its operating temperature, these
substances might ignite - risk of fire!
Protection of hollow spaces
All the cavities of your vehicle which are at risk from corrosion are protected for life
by a layer of protective wax applied in the factory.
This wax protection does not require to be inspected or re-treated. Please remove
any small amount of wax which flows out of the cavities at high temperatures with
a plastic scraper and clean the spot using petroleum cleaner.
WARNING
Safety and environmental protection regulations should observed when
using petroleum cleaner to re move wax - a risk of fire!
NKO B5 20.book Page 177 Friday, March 2, 2007 1:46 PM
Page 187 of 259
Inspecting and Replenishing
186
•Please also comply with the warnin g instructions stated below when
carrying out any essential work on the fuel system or on the electrical
system:
−Always separate the car batter y from the electrical system.
− Do not smoke.
− Never carry out any work close to naked flames.
− Always keep a working fire extinguisher at hand.
Caution
When replenishing fluids in the engine, always ensure that the fluids are on no
account mixed up. This may result in major operating problems and also vehicle
damage!
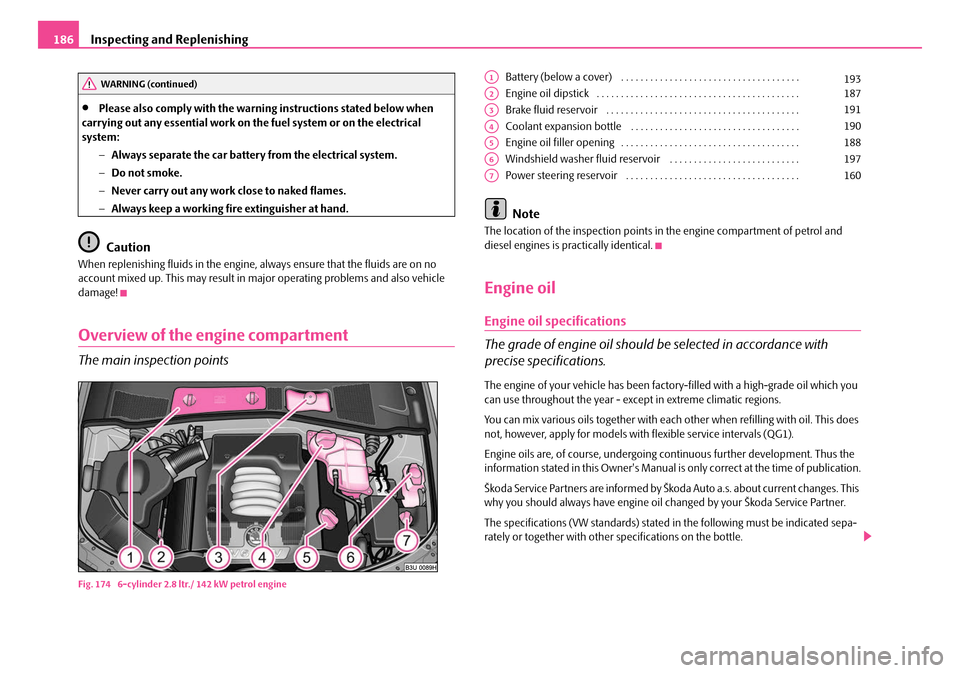
Overview of the engine compartment
The main inspection points
Fig. 174 6-cylinder 2.8 ltr./ 142 kW petrol engine
Battery (below a cover) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine oil dipstick . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Brake fluid reservoir . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Coolant expansion bottle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine oil filler opening . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Windshield washer fluid reservoir . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power steering reservoir . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Note
The location of the inspection points in the engine compartment of petrol and
diesel engines is practically identical.
Engine oil
Engine oil specifications
The grade of engine oil should be selected in accordance with
precise specifications.
The engine of your vehicle has been factor y-filled with a high-grade oil which you
can use throughout the year - except in extreme climatic regions.
You can mix various oils together with each other when refilling with oil. This does
not, however, apply for models with flexible service intervals (QG1).
Engine oils are, of course, undergoing co ntinuous further development. Thus the
information stated in this Owner's Manual is only correct at the time of publication.
Škoda Service Partners are informed by Škoda Auto a.s. about current changes. This
why you should always have engine oil changed by your Škoda Service Partner.
The specifications (VW standards) stated in the following must be indicated sepa-
rately or together with other specifications on the bottle.
WARNING (continued)A1193A2187
A3191
A4190
A5188
A6197
A7160
NKO B5 20.book Page 186 Friday, March 2, 2007 1:46 PM