engine SKODA SUPERB 2014 2.G / (B6/3T) Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SKODA, Model Year: 2014, Model line: SUPERB, Model: SKODA SUPERB 2014 2.G / (B6/3T)Pages: 246, PDF Size: 17.16 MB
Page 145 of 246

The following modes can be selected with the selector lever » Fig. 138.P
– Parking mode
The driven wheels are locked mechanically in this mode.
The parking mode must only be selected when the vehicle is stationary.
R
- Reverse gear
Reverse gear can only be engaged when the vehicle is stationary and the en-
gine is at idling speed.
Before moving into mode R from mode P or N, depress the brake pedal while
simultaneously pressing the lock button in the direction of the ar-
row » Fig. 139 .
N
- Neutral
The power transmission to the drive wheels is interrupted in this mode.
D
- Mode for forwards travel (normal programme)
In mode D, the forward gears are automatically changed according to the en-
gine load, accelerator pedal actuation and driving speed.
S
- Mode for forwards travel (sports programme)
In mode S, the forward gears are shifted automatically up and down at higher
engine speeds than in mode D.
Before changing to mode S from mode D, press the lock button in the direction
of the arrow » Fig. 139.
Releasing selector lever from mode P or N (selector lever lock)
The selector lever is locked in modes P and N to prevent the forwards travel
mode from being selected accidentally and setting the vehicle in motion. The
warning light illuminates in the instrument cluster
» page 39.
The selector lever is released by depressing the brake pedal while simultane-
ously pressing the lock button in the direction of the arrow » Fig. 139.
The selector lever is not locked when quickly moving via position N (e.g. from R
to D). This, for example, helps to rock out a vehicle that is stuck, e.g. in a bank
of snow. The selector lever lock will engage if the lever is in position N for
more than approx. 2 seconds without the brake pedal being depressed.
The selector lever is locked only when the vehicle is stationary and at speeds up to 5 km/h.
NoteIf you want to move the selector lever from mode P to mode D or vice versa,
move the selector lever quickly. This prevents modes R or N from being acci-
dentally selected.
Manual shifting of gears (Tiptronic)
Fig. 140
Selector lever / multi-function steering wheel
Read and observe
and on page 142 first.
Tiptronic mode makes it possible to manually shift gears with the selector lev-
er or multifunction steering wheel. This mode can be selected both while stop-
ping and while driving.
The currently selected gear is indicated in the display » Fig. 138 on page 142 .
The gearshift indicator must be observed when changing gear » page 40.
Switching to manual shifting
›
Push the gear selector from position D towards the right, or left in a right-
hand drive vehicle.
Shifting up gears
›
Press the selector lever forwards
+
» Fig. 140 .
›
Pull the right-hand paddle +
» Fig. 140 briefly towards the steering wheel.
Shifting down gears
›
Press the selector lever backwards
-
» Fig. 140 .
›
Pull the left-hand paddle -
» Fig. 140 briefly towards the steering wheel.
Temporarily switch to manual gear changing in mode D or S
›
Pull one of the -/+ paddles
» Fig. 140 briefly towards the steering wheel .
143Starting-off and Driving
Page 146 of 246

If one of the rocker switches -/+ is not pulled for more than 1 minute, manual
gear changing is deactivated. The temporary switch to manual gear changing
can also be deactivated by pulling the right-hand rocker switch +
towards the
steering wheel for more than 1 second.
When accelerating, the gearbox automatically shifts up into the higher gear
just before the maximum permissible engine speed is reached.
If a lower gear is selected, the gearbox does not shift down until there is no risk of the engine overrevving.
Note
It may be beneficial, for example, when travelling downhill, to use manual
shifting of gears. Shifting to a lower gear reduces the load on the brakes and
hence the wear of the brakes » page 140.
Starting-off and driving
Read and observe
and on page 142 first.
Starting off
›
Start the engine.
›
Firmly depress and hold the brake pedal.
›
Press the lock button in the direction of to arrow » Fig. 139 on page 142 and
hold.
›
Move the selector lever into the desired position » page 142 and then release
the lock button.
›
Release the brake pedal and accelerate.
Stop
›
Fully depress and hold the brake pedal and bring the vehicle to a stop.
›
Keep holding the brake pedal until driving is resumed.
The selector lever position N does not have to be selected when stopping for a
short time, such as at a cross roads.
Parking
›
Fully depress and hold the brake pedal and bring the vehicle to a stop.
›
Firmly apply the handbrake.
›
Press the lock button in the direction of to arrow » Fig. 139 on page 142 and
hold.
› Move the selector lever into the position
P and then release the locking but-
ton.
Launch control 1)
The Launch control function allows the vehicle to reach maximum acceleration
when starting off in mode S or Tiptronic.›
Activate the ASR » page 151, Brake assist systems .
›
START STOP deactivate » page 161.
›
Fully depress and hold the brake pedal with your left foot.
›
Fully depress the accelerator pedal with your right foot.
›
Release the brake pedal.
The vehicle starts off with maximum acceleration.
Reactivate the ASR and START-STOP as soon as the desired speed is reached.
Kickdown
The kickdown function allows you to achieve the maximum acceleration of
your vehicle while driving.
When the accelerator pedal is fully depressed, the kickdown function is activa-
ted in any forward driving mode.
The gearbox shifts down one or more gears depending on the vehicle speed
and engine speed, and the vehicle accelerates.
The gearbox does not shift up into the highest gear until the engine has
reached its maximum revolutions for this gear range.
WARNINGRapid acceleration, particularly on slippery roads, can lead to loss of control
of the vehicle – risk of accident!
Malfunction
Read and observe
and on page 142 first.
Emergency programme
The transmission switches to the emergency programme, if there is a fault in
system of the automatic gearbox.
1)
This function is only valid for some engines.
144Driving
Page 147 of 246

Indications of an activated emergency programme include the following:
› Only certain gears are selected.
› The reverse gear
R cannot be used.
› Shifting gears in Tiptronic mode is not possible.
Gearbox overheating The gearbox may, for example, become too hot due to frequent repeated
starting or stop-and-go traffic. Overheating is indicated by the warning
light » page 31 ,
Clutches of the automatic DSG gearbox are too hot .
Defective selector lever lock
If the selector lever lock is defective or its power supply is interrupted (e.g. dis-
charged vehicle battery, faulty fuse), the selector lever can no longer be moved
out of position P in the normal manner, and the vehicle can no longer be driv-
en. The selector lever must be unlocked specially » page 213.
Note
If the gearbox has switched to the emergency programme, visit a specialist ga-
rage.
Running in
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
New engine
145
New tyres
145
New brake pads
145
New engine
The engine has to be run in during the first 1 500 kilometres.
Up to 1 000 kilometres
›
Do not drive faster than 3/4 of the maximum speed of the gear in use, i.e. 3/4
of the maximum permissible engine speed.
›
No full throttle.
›
Avoid high engine speeds.
›
Do not tow a trailer.
From 1 000 up to 1 500 kilometres
Gradually increase the power output of the engine up to the full speed of the
gear engaged, i.e. up to the maximum permissible engine speed.
The red scale of the rev counter indicates the range in which the system be-
gins to limit the engine speed.
During the first operating hours the engine has higher internal friction than
later until all of the moving parts have harmonized. The driving style which you
adopt during the first approx.1 500 kilometres plays a decisive part in the suc-
cess of running in your car.
Never drive at unnecessarily high engine speeds even after the running-in pe-
riod.
On vehicles fitted with a manual gearbox, at the very latest shift up into the
next gear when the red area is reached. Observe the recommended
gear » page 40 , Gear recommendation . Very high engine speeds when acceler-
ating (accelerator) are automatically restricted »
.
In vehicles with manual transmission, do not drive at unnecessarily low engine
speeds. Shift down a gear when the engine is no longer running smoothly. Ob-
serve the recommended gear » page 40, Gear recommendation .
CAUTION
■
The engine is not protected from excessive engine revs caused by shifting
down at the wrong time. This can result in a sudden increase in revs beyond
the permissible maximum rpm, thereby causing engine damage.■
Never rev up a cold engine when the vehicle is stationary or when driving in
individual gears.
For the sake of the environment
Do not drive at unnecessarily high engine speeds. Shifting up sooner helps
save fuel, reduces engine noise and protects the environment.
New tyres
New tyres must firstly be “run in”, as they do not offer optimal grip at first.
Therefore, drive especially carefully for the first 500 km or so.
New brake pads
New brake pads do not initially provide optimal braking performance. They first
need to be “run in”. Therefore, drive especially carefully for the first 200 km or
so.
145Starting-off and Driving
Page 148 of 246
Economical driving and environmental sustainability
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Looking ahead
146
Economical gear changing
146
Avoiding full throttle
147
Reducing idling
147
Avoiding short distances
147
Checking tyre inflation pressure
147
Avoiding unnecessary ballast
147
Regular maintenance
148
Saving electrical energy
148
Environmental compatibility
148
The technical requirements for low fuel usage and economic efficiency of the
vehicle have already been built into the vehicle at the works. ŠKODA places a
particular emphasis on minimising negative effects on the environment.
It is necessary to take note of the guidelines given in this chapter in order to make best use of these characteristics and to maintain their effectiveness.
Fuel consumption, environmental pollution and the wear to the engine, brakes
and tyres depend essentially on the following three factors:
› your personal driving style
› operating conditions
› technical requirements
The fuel economy by can be improved by 10 -15 % by always looking ahead and
driving in an economical way.
Fuel consumption is also be influenced by external factors which are beyond
the driver's control. Consumption increases during the winter or under difficult
conditions, on poor roads, etc.
Fuel consumption can vary considerably from the manufacturer's data, as a re-
sult of outside temperatures, the weather and driving style.
The optimal engine speed should be obtained when accelerating, in order to
avoid a high fuel consumption and resonance of the vehicle.
CAUTIONAll the speed and engine revolution figures apply only when the engine is at
its normal operating temperature.
Looking ahead
Read and observe
on page 146 first.
A vehicle's highest fuel consumption occurs when accelerating, therefore un-necessary accelerating and braking should be avoided. If looking ahead when
driving, less braking and consequently less accelerating are required.
If possible, let your vehicle coast to a stop, or use the engine brake, if you can see that the next set of traffic lights is on red, for example.
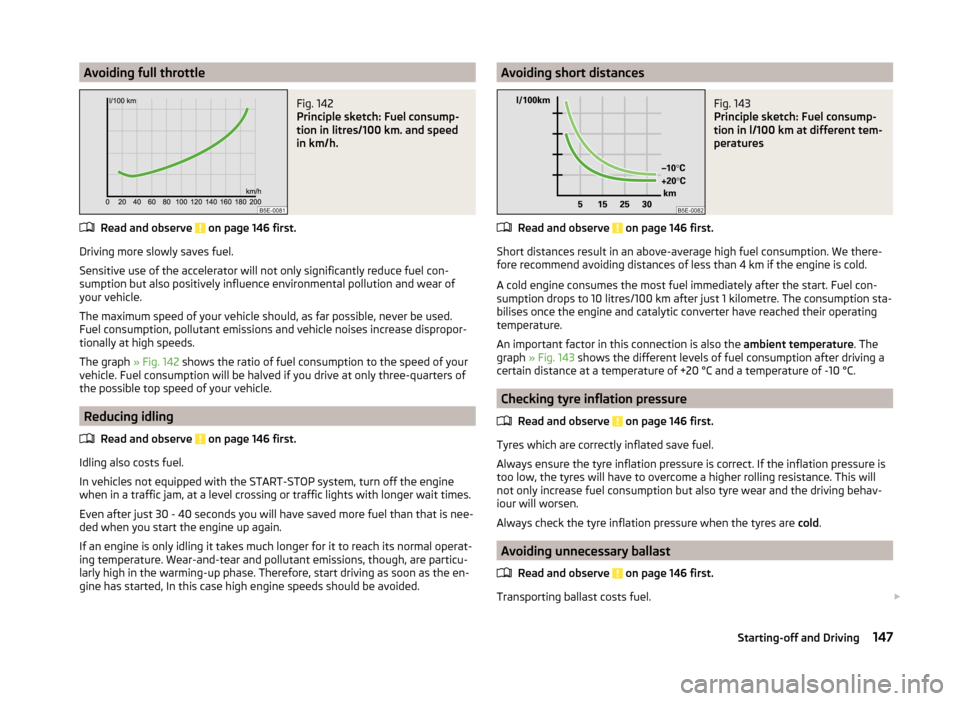
Economical gear changing
Fig. 141
Principle sketch: Fuel consump-
tion in litres/100 km depending
on the selected gear
Read and observe on page 146 first.
Shifting up early saves on fuel.
Manual gearbox › Drive no more than about one length of your vehicle in first gear.
› Shift up into the next gear at approx. 2000 rpm.
An effective way of achieving good fuel economy is to shift up early. Observe
the recommended gear » page 40, Gear recommendation .
A suitably selected gear can have an effect on fuel consumption » Fig. 141.
Automatic gearbox
› Slowly
apply the accelerator pedal. However, do not depress ias far as the
kickdown position » page 144.
› An economic driving programme is automatically selected if the accelerator
pedal is only depressed slowly.
146Driving
Page 149 of 246
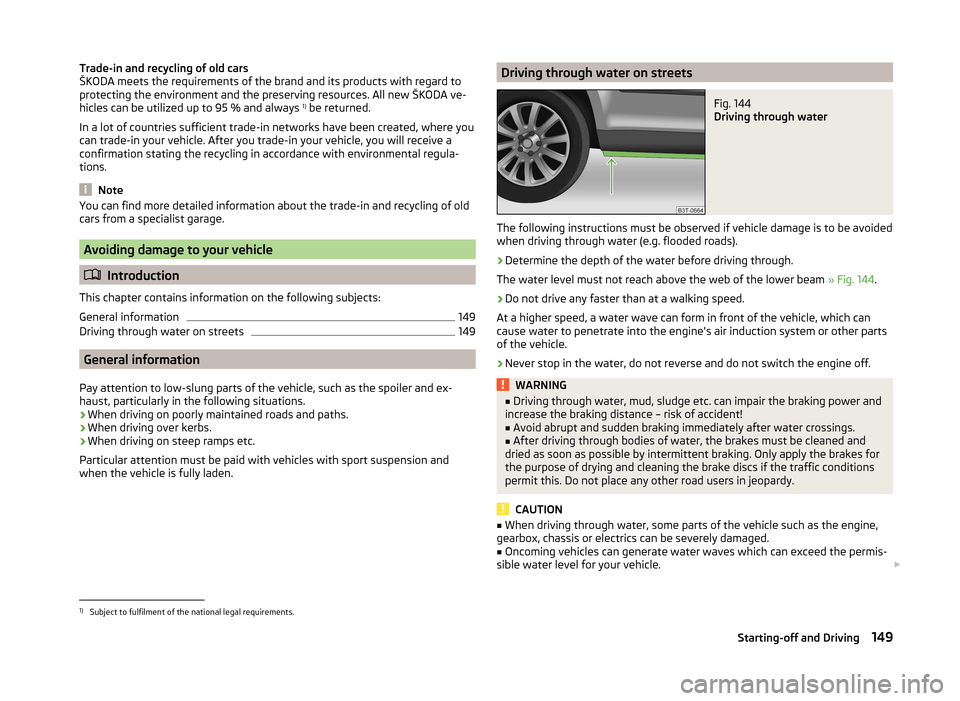
Avoiding full throttleFig. 142
Principle sketch: Fuel consump-
tion in litres/100 km. and speed
in km/h.
Read and observe on page 146 first.
Driving more slowly saves fuel.
Sensitive use of the accelerator will not only significantly reduce fuel con-
sumption but also positively influence environmental pollution and wear of
your vehicle.
The maximum speed of your vehicle should, as far possible, never be used.
Fuel consumption, pollutant emissions and vehicle noises increase dispropor-
tionally at high speeds.
The graph » Fig. 142 shows the ratio of fuel consumption to the speed of your
vehicle. Fuel consumption will be halved if you drive at only three-quarters of
the possible top speed of your vehicle.
Reducing idling
Read and observe
on page 146 first.
Idling also costs fuel.
In vehicles not equipped with the START-STOP system, turn off the engine when in a traffic jam, at a level crossing or traffic lights with longer wait times.
Even after just 30 - 40 seconds you will have saved more fuel than that is nee-
ded when you start the engine up again.
If an engine is only idling it takes much longer for it to reach its normal operat-
ing temperature. Wear-and-tear and pollutant emissions, though, are particu-
larly high in the warming-up phase. Therefore, start driving as soon as the en-
gine has started, In this case high engine speeds should be avoided.
Avoiding short distancesFig. 143
Principle sketch: Fuel consump-
tion in l/100 km at different tem-
peratures
Read and observe on page 146 first.
Short distances result in an above-average high fuel consumption. We there- fore recommend avoiding distances of less than 4 km if the engine is cold.
A cold engine consumes the most fuel immediately after the start. Fuel con-
sumption drops to 10 litres/100 km after just 1 kilometre. The consumption sta-
bilises once the engine and catalytic converter have reached their operating
temperature.
An important factor in this connection is also the ambient temperature. The
graph » Fig. 143 shows the different levels of fuel consumption after driving a
certain distance at a temperature of +20 °C and a temperature of -10 °C.
Checking tyre inflation pressure
Read and observe
on page 146 first.
Tyres which are correctly inflated save fuel.
Always ensure the tyre inflation pressure is correct. If the inflation pressure is
too low, the tyres will have to overcome a higher rolling resistance. This will
not only increase fuel consumption but also tyre wear and the driving behav-
iour will worsen.
Always check the tyre inflation pressure when the tyres are cold.
Avoiding unnecessary ballast
Read and observe
on page 146 first.
Transporting ballast costs fuel.
147Starting-off and Driving
Page 150 of 246

Each kilogramme of weight increases the fuel consumption. Therefore, we rec-
ommend to carry no unnecessary weight.
It is particularly in town traffic, when one is accelerating quite often, that the
vehicle weight will have a significant effect upon the fuel consumption. A rule
of thumb here is that an increase in weight of 100 kilograms will cause an in-
crease in fuel consumption of about 1 litre/100 kilometres.
At a speed of 100 - 120 km/h, a vehicle fitted with a roof rack cross member without a load will use about 10 % more fuel than normal due to the increased
aerodynamic drag.
Regular maintenance
Read and observe
on page 146 first.
A poorly tuned engine uses an unnecessarily high amount of fuel.
By having your vehicle regularly maintained by a specialist garage, you create
the conditions needed for economical driving. The maintenance state of your
vehicle has a positive effect on traffic safety and value retention
A poorly tuned engine can result in a fuel consumption which is 10 % higher than normal.
Check the oil level at regular intervals, e.g. when filling up. Oil consumption is
dependent to a considerable extent on the load and speed of the engine. Oil
consumption could be as high as 0.5 litres/1 000 km depending on your style
of driving.
It is quite normal that a new engine has a higher oil consumption at first, and
reaches its lowest level only after a certain running in time. The oil consump-
tion of a new vehicle can therefore only be correctly assessed after driving
about 5 000 km.
For the sake of the environment
■ Additional improvements to the fuel economy can be made by using synthet-
ic high-lubricity oils.■
Regularly check the ground under the vehicle. Have your vehicle inspected by
a specialist garage if you find any stains caused by oil or other fluids on the
ground.
Note
We recommend that your vehicle be serviced on a regular basis by a ŠKODA
service partner.Saving electrical energy
Read and observe
on page 146 first.
When the engine is running, the alternator generates and supplies electricalpower. If more electrical components of the electrical system are switched on,
more fuel is needed to operate the alternator. We therefore recommend
switching off electrical components if these are no longer required.
Environmental compatibility
Read and observe
on page 146 first.
Environmental protection has played a major role in the design, material selec-
tion and production of your new ŠKODA. Particular emphasis has been placed
on the following points.
Design measures › Joints designed to be easily detached.
› Simplified disassembly due to the modular structure system.
› Improved purity of different classes of materials.
› Identification of all plastic parts in accordance with VDA Recommendation
260.
› Reduced fuel consumption and exhaust emission CO
2.
› Minimum fuel leakage during accidents.
› Reduced noise.
Choice of materials
› Extensive use of recyclable material.
› Air conditioning filled with CFC-free refrigerant.
› No cadmium.
› No asbestos.
› Reduction in the “vaporisation” of plastics.
Manufacture
› Solvent-free cavity protection.
› Solvent-free protection of the vehicle for transportation from the production
plant to the customer.
› The use of solvent-free adhesives.
› No CFCs used in the production process.
› Without use of mercury.
› Use of water-soluble paints.
148Driving
Page 151 of 246
Trade-in and recycling of old cars
ŠKODA meets the requirements of the brand and its products with regard to
protecting the environment and the preserving resources. All new ŠKODA ve-
hicles can be utilized up to 95 % and always 1)
be returned.
In a lot of countries sufficient trade-in networks have been created, where you
can trade-in your vehicle. After you trade-in your vehicle, you will receive a
confirmation stating the recycling in accordance with environmental regula-
tions.
Note
You can find more detailed information about the trade-in and recycling of old
cars from a specialist garage.
Avoiding damage to your vehicle
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
General information
149
Driving through water on streets
149
General information
Pay attention to low-slung parts of the vehicle, such as the spoiler and ex-
haust, particularly in the following situations.
› When driving on poorly maintained roads and paths.
› When driving over kerbs.
› When driving on steep ramps etc.
Particular attention must be paid with vehicles with sport suspension and
when the vehicle is fully laden.
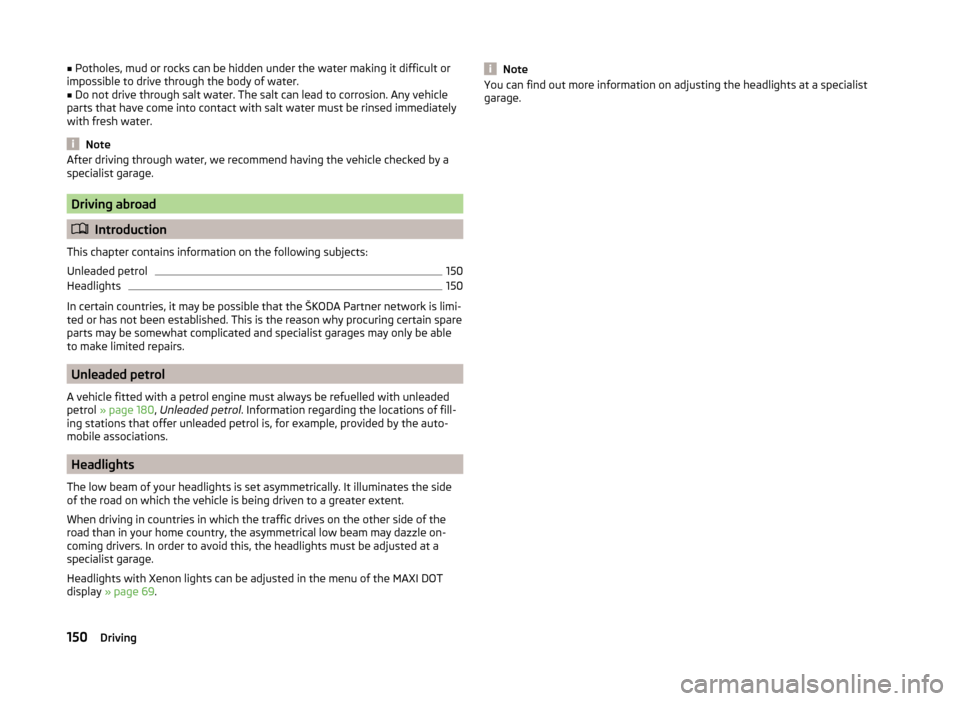
Driving through water on streetsFig. 144
Driving through water
The following instructions must be observed if vehicle damage is to be avoided
when driving through water (e.g. flooded roads).
›
Determine the depth of the water before driving through.
The water level must not reach above the web of the lower beam » Fig. 144.
›
Do not drive any faster than at a walking speed.
At a higher speed, a water wave can form in front of the vehicle, which can
cause water to penetrate into the engine's air induction system or other parts
of the vehicle.
›
Never stop in the water, do not reverse and do not switch the engine off.
WARNING■ Driving through water, mud, sludge etc. can impair the braking power and
increase the braking distance – risk of accident!■
Avoid abrupt and sudden braking immediately after water crossings.
■
After driving through bodies of water, the brakes must be cleaned and
dried as soon as possible by intermittent braking. Only apply the brakes for
the purpose of drying and cleaning the brake discs if the traffic conditions
permit this. Do not place any other road users in jeopardy.
CAUTION
■ When driving through water, some parts of the vehicle such as the engine,
gearbox, chassis or electrics can be severely damaged.■
Oncoming vehicles can generate water waves which can exceed the permis-
sible water level for your vehicle.
1)
Subject to fulfilment of the national legal requirements.
149Starting-off and Driving
Page 152 of 246
■Potholes, mud or rocks can be hidden under the water making it difficult or
impossible to drive through the body of water.■
Do not drive through salt water. The salt can lead to corrosion. Any vehicle
parts that have come into contact with salt water must be rinsed immediately
with fresh water.
Note
After driving through water, we recommend having the vehicle checked by a
specialist garage.
Driving abroad
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Unleaded petrol
150
Headlights
150
In certain countries, it may be possible that the ŠKODA Partner network is limi-
ted or has not been established. This is the reason why procuring certain spare
parts may be somewhat complicated and specialist garages may only be able
to make limited repairs.
Unleaded petrol
A vehicle fitted with a petrol engine must always be refuelled with unleaded
petrol » page 180 , Unleaded petrol . Information regarding the locations of fill-
ing stations that offer unleaded petrol is, for example, provided by the auto-
mobile associations.
Headlights
The low beam of your headlights is set asymmetrically. It illuminates the side
of the road on which the vehicle is being driven to a greater extent.
When driving in countries in which the traffic drives on the other side of the
road than in your home country, the asymmetrical low beam may dazzle on-
coming drivers. In order to avoid this, the headlights must be adjusted at a
specialist garage.
Headlights with Xenon lights can be adjusted in the menu of the MAXI DOT
display » page 69 .
NoteYou can find out more information on adjusting the headlights at a specialist
garage.150Driving
Page 153 of 246

Assist systems
Brake assist systems
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
151
Antilock brake system (ABS)
152
Traction Control System (TCS)
152
Electronic Differential Lock (EDL)
152
Driver Steering Recommendation (DSR)
152
Hydraulic Brake Assist (HBA)
152
Hill Hold Control (HHC)
153WARNING■ A lack of fuel can cause irregular engine running or cause the engine to
shut down. The brake assist systems would then fail to function – risk of
accident!■
Adjust the speed and driving style to the current visibility, weather, road
and traffic conditions. The increased safety provided by the brake assist
systems must not tempt you to take safety risks – risk of accident!
■
In the event of an ABS fault, visit a specialist garage immediately. Adjust
your style of driving according to the damage to the ABS, as you will not
know the exact extent of the damage or the extent to which this is limiting the braking efficiency.
CAUTION
■ All four wheels must be fitted with the same tyres approved by the manufac-
turer to ensure the brake assist systems operate correctly.■
Changes to the vehicle (e.g. to the engine, brakes, chassis) can influence the
functionality of the brake assist systems » page 169, Services, modifications,
and technical alterations .
■
If a fault occurs in the ABS system, the ESC, ASR and EDL will also not work.
An ABS fault is indicated by the warning light
» page 36 .
Electronic Stability Control (ESC)Fig. 145
ESC system: TCS button
Read and observe and on page 151 first.
The ESC system helps improve control of the vehicle in situations where it is
being operated at its dynamic limits, such as a sudden change to the direction
of travel. Depending on the conditions of the road surface, the risk of skidding
is reduced, thereby improving the vehicle's driving stability .
The ESC system is automatically activated each time the ignition is switched
on.
The direction which the driver wishes to take is determined based on the
steering angle and the speed of the vehicle and is constantly compared with
the actual behaviour of the vehicle. In the event of deviations, such as the car
beginning to skid, the ESC system will automatically brake the appropriate
wheel.
During an intervention of the system, the indicator light flashes in the in-
strument cluster.
The following systems are integrated into the Electronic Stability Control
(ESC) .
› Antilock Brake System (ABS)
» page 152.
› Traction control (ASR)
» page 152.
› Electronic Differential Lock (EDL)
» page 152.
› Driver Steering Recommendation (DSR)
» page 152.
› Hydraulic Brake Assist (HBA)
» page 152.
› Hill Hold Control (HHC)
» page 153.
› Trailer stabilisation (TSA)
» page 168.
The ESC system cannot be deactivated. The
» Fig. 145 button can only be
used to deactivate the TCS.
151Assist systems
Page 154 of 246

The warning light lights up in the instrument cluster when the ASR is deacti-
vated.
Antilock brake system (ABS)
Read and observe
and on page 151 first.
ABS prevents the wheels locking when braking. Thus helping the driver to
maintain control of the vehicle.
The intervention of the ABS is noticeable from the pulsating movements of
the brake pedal which is accompanied by noises.
When the ABS system is active, do not brake periodically or reduce the pres- sure on the brake pedal.
Traction Control System (TCS)
Fig. 146
TCS button
Read and observe and on page 151 first.
If the wheels are slipping, the TCS adapts the engine speed to the conditions
of the road surface. The TCS makes it much easier to start off, accelerate and
climb steep hills even if the conditions of the road surface are unfavourable.
The TCS function is activated automatically each time the ignition is switched
on.
If your vehicle is fitted with the ESC system, the ASR is integrated into the ESC
system » page 151 .
During an intervention of the system, the TCS indicator light flashes in the
instrument cluster.
The TCS should normally always be enabled. The system should be deactivated
only in the following situations, for example.
› When driving with snow chains.
› When driving in deep snow or on a very loose surface.
› When “rocking a car free” when it has become stuck.
The ASR can be deactivated via the
» Fig. 146 symbol button.
The warning light
lights up in the instrument cluster when the ASR is deacti-
vated.
Ensure the TCS is activated again afterwards.
Electronic Differential Lock (EDL)
Read and observe
and on page 151 first.
If one of the wheels starts to spin, the EDL system brakes the spinning wheel
and transfers the driving force to the other wheels. This ensures the stability
of the vehicle and a quick journey.
The EDL switches off automatically in order to avoid excessive heat generation
in the disc brake of the wheel being braked. The vehicle can continue to be
driven and has the same characteristics as a vehicle not fitted with EDL. The
EDL switches on again automatically as soon as the brake has cooled down.
Driver Steering Recommendation (DSR)
Read and observe
and on page 151 first.
In critical situations, the DSR provides the driver with a steering recommenda-
tion in order to stabilise the vehicle. The DSR is activated, for example, on the
right and left vehicle side when braking sharply on different road surfaces.
Hydraulic Brake Assist (HBA)
Read and observe
and on page 151 first.
The HBA increases the braking effect and helps to reduce the braking dis-
tance.
The HBA is activated by very quick operation of the brake pedal. In order to
achieve the shortest possible braking distance, the brake pedal must be ap-
plied firmly until the vehicle has come to a standstill.
152Driving