diagram SSANGYONG KORANDO 1997 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 1997, Model line: KORANDO, Model: SSANGYONG KORANDO 1997Pages: 2053, PDF Size: 88.33 MB
Page 434 of 2053

1F2 -- 12 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
KAB1F120
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (2.3L DOHC -- 6 OF 7) (MSE 3.53S)
Page 435 of 2053

M161 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F2 -- 13
D AEW OO M Y_2000
KAB1F130
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (2.3L DOHC -- 7 OF 7) (MSE 3.53S)
Page 473 of 2053

M161 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F2 -- 55
D AEW OO M Y_2000
The pressure difference between the fuel pressure and
the intake manifold is about 3.8 bars during the full load.
YAA1F500
1. Fuel Pressure Regulator
2. Intake Manifold
3. Fuel Return (to fuel tank)
4. Fuel Supply (from fuel pump)
5. Fuel Pressure (approx. 3.8 bars)
6. Intake Manifold Negative Pressure (0 bar)
The spring chamber (9) is connected to the intake man-
ifold with the vacuum hose at the intake pipe connection
(7). The negative pressure generated in the intake man-
ifold activates the diaphragm, and thus the fuel pressure
gets reduced to the rate of the operating extent of the
diaphragm by the intake manifold’s negative pressure.
YAA1F510
Consequently, the fuel pressure in the fuel distributor
changes by the intake manifold’s negative pressure, and
the injector ’s fuel pressure gets reduced independentlyto the throttle valve’s position. Thus, the fuel injection
volume can only be determined according to the injec-
tor’s injecting duration.
The pressure difference between the fuel pressure and
the intake manifold is approx. 3.2 bars during idling.
YAA1F520
1. Fuel Pressure Regulator
2. Intake Manifold
3. Fuel Return (to fuel tank)
4. Fuel Supply (from fuel pump)
7. Fuel Pressure (approx. 3.2 bars)
8. Intake Manifold Negative Pressure (0.6 bars)
YAA1F530
A. Fuel pressure
B. Intake Manifold Negative Pressure
LL. Idling
TL. Partial load
VL. Full load
Page 795 of 2053

1F3 -- 38 OM600 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
Digital Tester, RIV Method
(Connection Diagram for Testers Without Adapter)
1 Fuel Injection Pump
2 Rl Sensor
3 Digital Tester4 TDC Pulse Sender Unit
5 Battery
Page 796 of 2053
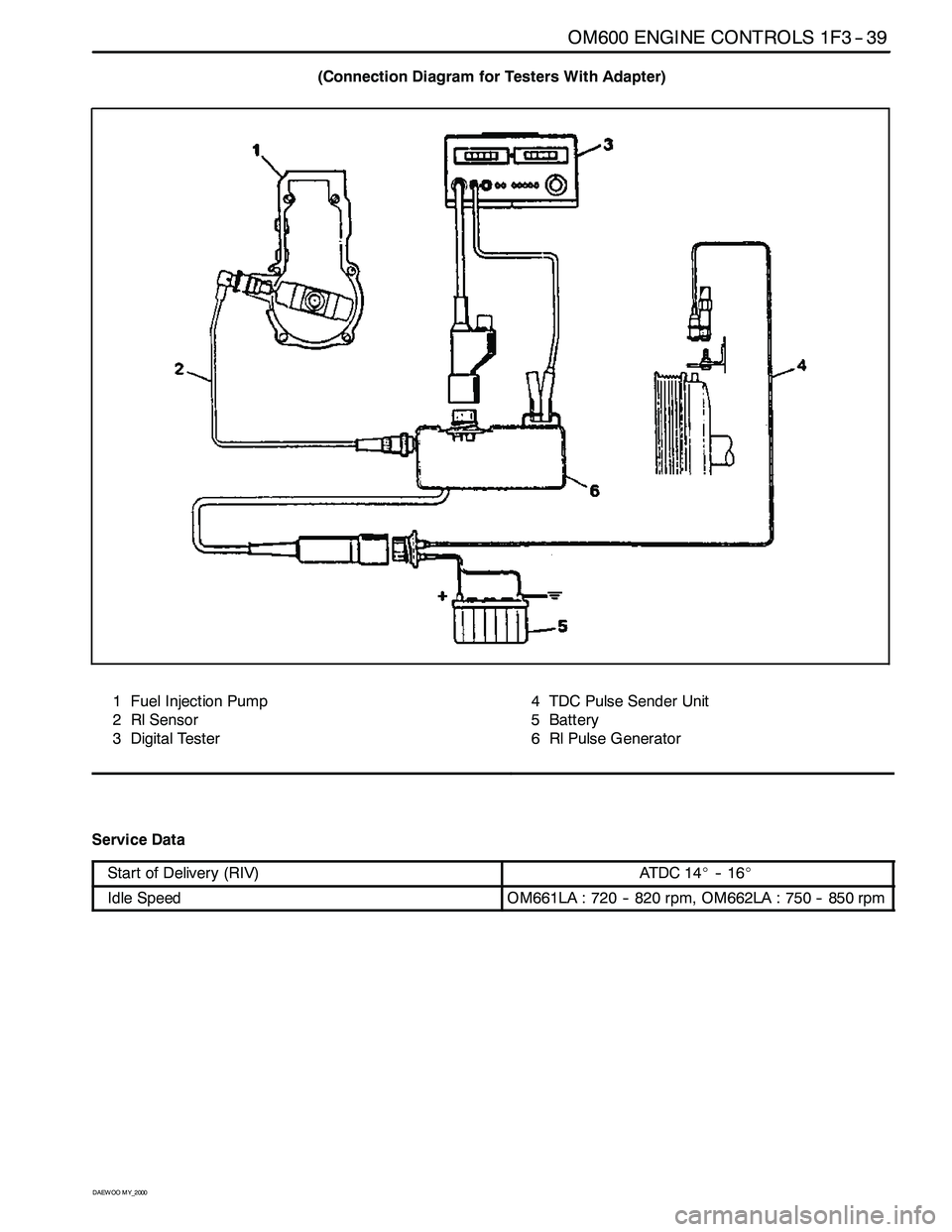
OM600 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F3 -- 39
D AEW OO M Y_2000
(Connection Diagram for Testers With Adapter)
1 Fuel Injection Pump
2 Rl Sensor
3 Digital Tester4 TDC Pulse Sender Unit
5 Battery
6 Rl Pulse Generator
Service Data
Start of Delivery (RIV)AT DC 1 4_-- 1 6_
Idle SpeedOM661LA : 720 -- 820 rpm, OM662LA : 750 -- 850 rpm
Page 797 of 2053
1F3 -- 40 OM600 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
Tools Required
617 589 09 21 00 Rl Sensor
617589102100 TimingTester
667589002100 TDCPulseGenerator
Commercial Tools
ItemTools
Digigal TesterWith Pulse GeneratorBosch, MOT 001.03gg
Hartmann & Braun, EOMT3
Without Pulse GeneratorBosch, ETD 019.00
Sun, DIT 9000
ALV, Diesel -- Tester 875
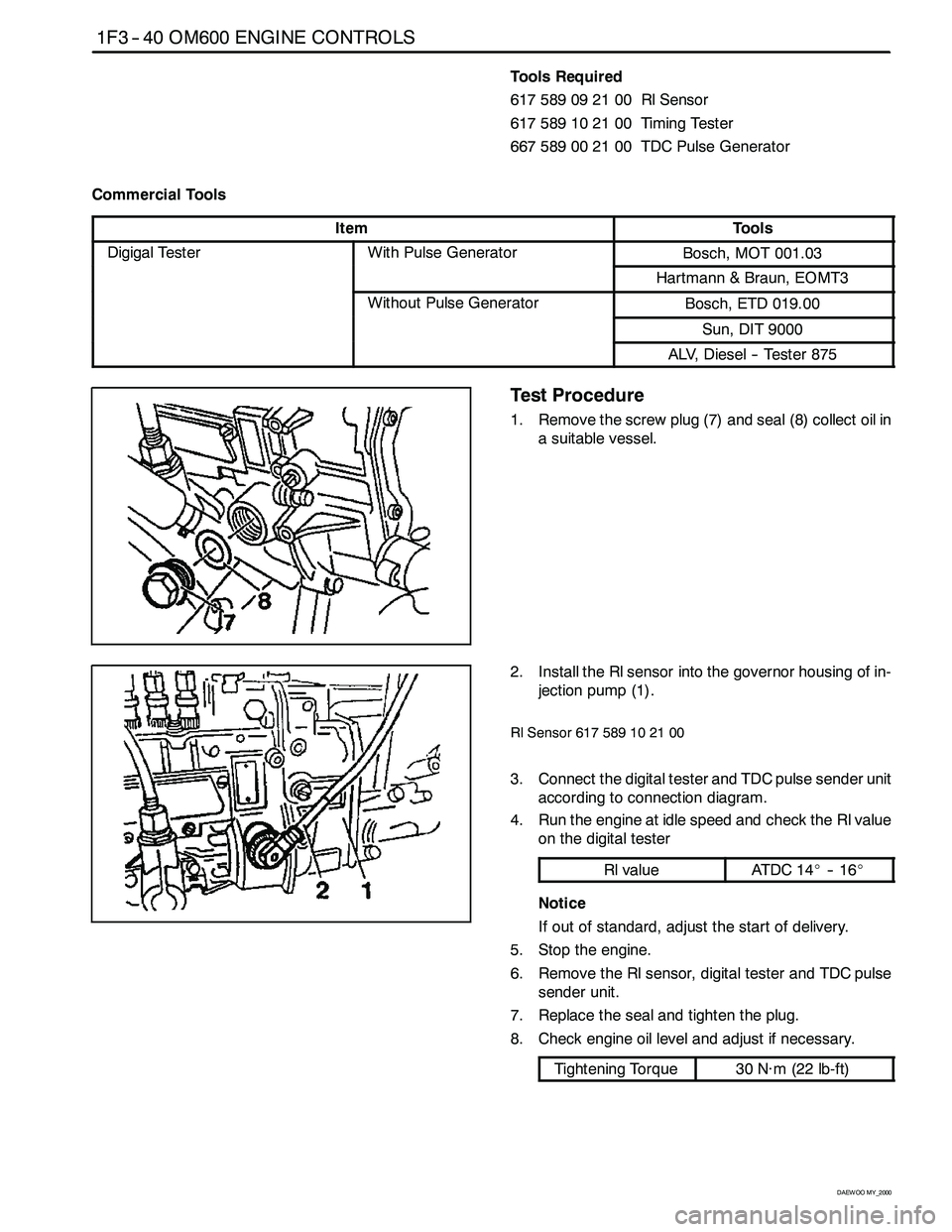
Test Procedure
1. Remove the screw plug (7) and seal (8) collect oil in
a suitable vessel.
2. Install the Rl sensor into the governor housing of in-
jection pump (1).
Rl Sensor 617 589 10 21 00
3. Connect the digital tester and TDC pulse sender unit
according to connection diagram.
4. Run the engine at idle speed and check the Rl value
on the digital tester
Rl valueAT DC 1 4_-- 1 6_
Notice
If out of standard, adjust the start of delivery.
5. Stop the engine.
6. Remove the Rl sensor, digital tester and TDC pulse
sender unit.
7. Replace the seal and tighten the plug.
8. Check engine oil level and adjust if necessary.
Tightening Torque30 N∙m (22 lb-ft)
Page 985 of 2053

SECTION 4F
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM AND
TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
General Description and System Opertion..........4F-3
Basic Knowledge Required...................................4F-3
ABS System Components...................................4F-3
Traction Control System (TCS) Description...........4F-3
EBD System........................................................4F-5
EBD Failure Matrix...............................................4F-6
Tires and ABS/TCS..............................................4F-7
Hydraulic Circuit...................................................4F-8
ABS 5.3...............................................................4F-8
ABS/TCS 5.3.....................................................4F-11
Component Locator...........................................4F-14
ABS, ABS/TCS 5.3............................................4F-14
Diagnosis............................................................4F-15
Diagnostic Circuit Check....................................4F-15
ABS Indicator Lamp Inoperative.........................4F-18
Traction Control System (TCS) Indicator Lamp
Inoperative.....................................................4F-22
EBD Indicator Lamp Inoperative.........................4F-26
Power Supply to Control Module,
No DTCs Stored..............................................4F-30
ABS Indicator Lamp Illuminated Continuously,
No DTCs Stored..............................................4F-34
Self-Diagnostics................................................4F-36
Displaying DTCs................................................4F-36
Clearing DTCs...................................................4F-36
Intermittents and Poor Connections....................4F-36
DTC 03 - Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Fault ...4F-38
DTC 07 - Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Continuity Fault...............................................4F-40
DTC 04 - Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Fault...............................................................4F-42DTC 08 - Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Continuity Fault...............................................4F-44
DTC 05 - Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Fault....4F-46
DTC 09 - Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor
Continuity Fault...............................................4F-48
DTC 06 - Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Fault .4F-50
DTC 10 - Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor
Continuity Fault...............................................4F-52
DTC 11 - Wheel Speed Sensor Frequency Error ..4F-54
DTC 42 - Acceleration Sensor Fault....................4F-58
DTC 43 - Acceleration Sensor Continuity Fault.....4F-60
DTC 13/14 - Left Front Inlet and Outlet Valve
Solenoid Fault.................................................4F-62
DTC 15/16 - Right Front Inlet and Outlet Valve
Solenoid Fault.................................................4F-64
DTC 17/18 - Left Rear Inlet and Outlet Valve
Solenoid Fault.................................................4F-66
DTC 19/20 - Right Rear Inlet and Outlet Valve
Solenoid Fault.................................................4F-68
DTC 21/22 - Left Rear Prime Line and Traction
Control System (TCS) Pilot Valve Fault............4F-70
DTC 23/24 - Right Rear Prime Line and Traction
Control System (TCS) Pilot Valve Fault............4F-72
DTC 12 - Valve Relay Circuit Fault......................4F-74
DTC 24 - Pump Motor or Pump Motor
Relay Fault.....................................................4E-76
DTC 27 - Stoplamp Switch Fault.........................4E-80
DTC 28 - Low Voltage Fault................................4E-84
DTC 02 - ABS Control Module Internal Fault........4E-88
Scheatic and Routing Diagrams........................4E-90
ABS Circuit (Without TCS): Gasoline...................4E-90
ABS/TCS Circuit: Gasoline.................................4E-91
ABS/ABD (Automatic Brake
Differential Lock): Diesel.................................4E-93
Page 987 of 2053

ABS AND TCS 4F-3
SSANGYONG MY2002
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND SYSTEM OPERATION
BASIC KNOWLEDGE REQUIRED
Before using this section, it is important that you have
a basic knowledge of the following items. Without this
knowledge, it will be difficult to use the diagnostic
procedures contained in this section.
•Basic Electrical Circuits - You should understand
the basic theory of electricity and know the meaning
of voltage, current (amps), and resistance (ohms).
You should understand what happens in a circuit
with an open or shorted wire. You should be able to
read and understand a wiring diagram.
Use of Circuit Testing Tools - You should know
how to use a test light and how to bypass
components to test circuits using fused jumper
wires. You should be familiar with a digital
multimeter. You should be able to measure voltage,
resistance, and current, and be familiar with the
controls and how to use them correctly.
ABS SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The ABS 5.3 Antilock Braking System (ABS) consists
of a conventional hydraulic brake system plus antilock
components. The conventional brake system includes
a vacuum booster, master cylinder, front disc brakes,
rear disc brakes, interconnecting hydraulic brake pipes
and hoses, brake fluid level switch and the BRAKE
indicator.
The ABS components include a hydraulic unit, an elec-
tronic brake control module (EBCM), two system fuses,
four wheel speed sensors (one at each wheel), intercon-
necting wiring, the ABS indicator, the EBD indicator
and the TCS indicator. See “ABS Component Locator”
in this section for the general layout of this system.
The hydraulic unit with the attached EBCM is located
between the surge tank and the bulkhead on the left
side of the vehicle.
The basic hydraulic unit configuration consists of hy-
draulic check valves, two solenoid valves for each
wheel, a hydraulic pump, and two accumulators. The
hydraulic unit controls hydraulic pressure to the front
calipers and rear calipers by modulating hydraulic
pressure to prevent wheel lockup.
Units equipped with TCS add two more valves for each
drive wheel for the purpose of applying the brake to a
wheel that is slipping. This is done with pressure from
the hydraulic pump in the unit. There is also a TCS
indicator lamp on the instrument panel to alert the driver
to the fact that the TCS system is active. The
components identified in the drawing are those added
to the basic ABS 5.3 system to provide traction control.
Nothing in the hydraulic unit or the EBCM is serviceable.
In the event of any failure, the entire ABS unit withattached EBCM must be replaced. For more
information, refer to “Base Braking Mode” and
“Antilock Braking Mode” in this section.
TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM
(TCS) DESCRIPTION
General Information
The traction control system (TCS) is a traction system
by means of brake intervention only, available in a low
speed range (< 60kph).
It workes on µ - split roads with sidewise different friction
coefficients.
The spinning driven wheel is braked and the drive
torque can be transferred to the wheel on the high-µ
side. During TCS active, the TCS information lamp is
blinking.
The temperature of the brakes is calculated by a mathe-
matical model and TCS is switched passive if the calcu-
lated temperature is greater than a threshold value (500
°C).
TCS is permitted again, when the calculated tempera-
ture is less than 350 °C.
Control Algorithm
The input signals for the control algorithm are the
filtered wheel speed signals from the ABS speed
processing.
With the speed difference of the driven wheels, the
control deviation is calculated.
If the control deviation exceeds a certain threshold
value, the wheel with the greater slip is braked actively.
The threshold value depends on the vehicle speed:
It is reduced with increasing vehicle speed down to a
constant value.
KAA4F010
Page 1073 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-90 ABS AND TCS
ABS CIRCUIT (WITHOUT TCS): GASOLINE
KAA4F250
SCHEMATIC AND ROUTING DIAGRAMS
Page 1095 of 2053

SECTION 5A
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a
tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals. Disconnecting this cable
will help prevent personal injury and damage to the vehicle. The ignition must also be in LOCK unless
otherwise noted.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Description and Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-2
BTRA M74 4WD Automatic Transmission . . . . . . 5A-2
Operators Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-2
Control Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-3
Electronic Control System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-3
Hydraulic Control System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-9
Hydraulic Control Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-10
Power Train System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-14
Power Flows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-18
Park and Neutral . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-20
Reverse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-22
Manual 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-24
Drive 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-26
Drive 2 and Manual 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-28
Drive 3 and Manual 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-30
Drive 3 Lock Up and Manual 3 Lock Up . . . . . . 5A-32
Drive 4 (Overdrive) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-34
Drive 4 Lock Up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-36
Diagnostic Information and Procedures . . . . . 5A-38
Diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-38
Basic Knowledge Required . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-38
Functional Check Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-38
Transmission Fluid Level Service Procedure . . . 5A-38
Fluid Leak Diagnosis and Repair . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-39
Electrical / Garage Shift Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-40
Road Test Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-40
Electronic Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-40
Symptom Diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-41
Drive Faults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-41
Faulty Shift Pattern . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-42Shift Quality Faults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-44
After Teardown Faults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-46
Trouble Code Diagnosis - Gasoline Vehicle . . 5A-48
TCM Diagnostic System Overview . . . . . . . . . . 5A-48
Clearing Trouble Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-48
Diagnostic Trouble Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-48
Trouble Code Diagnosis - Diesel Vehicle . . . . . 5A-50
TCM Diagnostic System Overview . . . . . . . . . . 5A-50
Clearing Trouble Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-50
Diagnostic Trouble Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-50
Repair Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-157
On-Vehicle Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-157
Transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-157
Unit Repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-160
Rebuild Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-160
Disassembly Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-161
Assembly Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-171
Front and Rear Band Adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-199
Gear Shift Control Lever . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-202
Kickdown Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-202
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-203
General Specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-203
Fastener Tightening Specifications . . . . . . . . . . 5A-205
Schematic and Routing Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . 5A-206
TCM Wiring Diagrams (Gasoline Engine) . . . . . 5A-206
TCM Wiring Diagrams (Diesel Engine) . . . . . . . 5A-208
Connector End View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-210
Special Tools and Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-211
Special Tools Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-211