check engine light SSANGYONG KORANDO 1997 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 1997, Model line: KORANDO, Model: SSANGYONG KORANDO 1997Pages: 2053, PDF Size: 88.33 MB
Page 13 of 2053

GENERAL INFORMATION 0B -- 13
D AEW OO M Y_2000
OWNER INSPECTIONS AND SERVICES
WHILE OPERATING THE VEHICLE
Horn Operation
Blow the horn occasionally to make sure it works. Check
all the button locations.
Brake System Operation
Be alert for abnormal sounds, increased brake pedal
travel or repeated puling to one side when braking. Also,
if the brake warning light goes on, or flashes, something
may be wrong with part of the brake system.
Exhaust System Operation
Be alert to any changes inthe sound of the system or
the smell of the fumes. These are signs that the system
may be leaking or overheating. Have the system in-
spected and repaired immediately.
Tires, Wheels and Alignment Operation
Be alert to any vibration of the steering wheel or the
seats at normal highway speeds. This may mean a
wheel needs to be balanced. Also, a pull right or left on a
straight, level road may show the need for a tire pres-
sure adjustment or a wheel alignment.
Steering System Operation
Be alert to changes in the steering action. An inspection
is needed when the steering wheel is hard to turn or has
too much free play, or is unusual sounds are noticed
when turning or parking.
Headlight Aim
Take note of the light pattern occasionally. Adjust the
headlights if the beams seem improperly aimed.
AT EACH FUEL FILL
A fluid loss in any (except windshield washer) system
may indicate a problem. Have the system inspected and
repaired immediately.
Engine Oil Level
Check the oil level and add oil if necessary. The best
time to check the engine oil level is when the oil is warm.
1. After stopping the engine, wait a few minutes for the
oil to drain back to the oil pan.
2. Pull out the oil level indicator (dip stick).
3. Wipe it clean, and push the oil level indicator back
down all the way.
4. Pull out the oil level indicator and look at the oil level
on it.
5. Add oil, if needed, to keep the oil level above the low-
er mark. Avoid overfilling theengine, since this may
cause engine damage.
6. Push the indicator all the way back down into the en-
gine after taking the reading.If you check the oil level when the oil is cold, do not run
the engine first. The cold oil will not drain back to the pan
fast enough to give a true oil level reading.
Engine Coolant Level and Condition
Check the coolant level in the coolant reservoir tank and
add coolant if necessary. Inspect the coolant. Replace
dirty or rusty coolant.
Windshield Washer Fluid Level
Check the washer fluid level in the reservoir. Add fluid if
necessary.
AT LEAST TWICE A MONTH
Tire And Wheel Inspection and Pressure
Check
Check the tire for abnormal wear or damage. Also check
for damaged wheels. Check the tire pressure when the
tires are cold ( check the spare also, unless it is a stow-
away). Maintain the recommended pressures. Refer to
“Tire and Wheel” is in section 0B.
AT LEAST MONTHLY
Light Operation
Check the operation of the license plate light, the head-
lights (including the high beams), the parking lights, the
fog lights, the taillight, the brake lights, the turn signals,
the backup lights and the hazard warning flasher.
Fluid Leak Check
Periodically inspect the surface beneath the vehicle for
water, oil, fuel or other fluids, after the vehicle has been
parked for a while. Water dripping from the air condition-
ing system after use is normal. If you notice fuel leaks or
fumes, find the cause and correct it at once.
AT LEAST TWICE A YEAR
Power Steering System Reservoir Level
Check the power steering fluid level. Keep the power
steering fluid at the proper level. Refer to Section 6A,
Power Steering System.
Brake Master Cylinder Reservoir Level
Check the fluid and keep it at the proper level. A low fluid
level can indicate worn disc brake pads which may need
to be serviced. Check the breather hole in the reservoir
cover to be free from dirt and check for an open pas-
sage.
Weather- Strip Lubrication
Apply a thin film silicone grease using a clean cloth.
Page 26 of 2053

1A1 -- 6 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
D AEW OO M Y_2000
DIAGNOSIS
OIL LEAK DIAGNOSIS
Most fluid oil leaks are easily located and repaired by
visually finding the leak and replacing or repairing the
necessary parts. On some occasions a fluid leak may be
difficult to locate or repair. The following procedures may
help you in locating and repairing most leaks.
Finding the Leak
1. Identify the fluid. Determine whether it is engine oil,
automatic transmission fluid, power steering fluid,
etc.
2. Identify where the fluid is leaking from.
2.1 After running the vehicle at normal operating
temperature, park the vehicle over a large sheet
of paper.
2.2 Wait a few minutes.
2.3 You should be able to find the approximate loca-
tion of the leak by the drippings on the paper.
3. Visually check around the suspected component.
Check around all the gasket mating surfaces for
leaks. A mirror is useful for finding leaks in areas that
are hard to reach.
4. If the leak still cannot be found, it may be necessary
to clean the suspected area with a degreaser, steam
or spray solvent.
4.1 Clean the area well.
4.2 Dry the area.
4.3 Operate the vehicle for several miles at normal
operating temperature and varying speeds.
4.4 After operating the vehicle, visually check the
suspected component.
4.5 If you still cannot locate the leak, try using the
powder or black light and dye method.
Powder Method
1. Clean the suspected area.
2. Apply an aerosol-- type powder (such as foot powder)
to the suspected area.
3. Operate the vehicle under normal operating condi-
toins.
4. Visually inspect the suspected component. You
should be able to trace the leak path over the white
powder surface to the source.
Black Light and Dye Method
A dye and light kit is available for finding leaks, Refer to
the manufacturer ’s directions when using the kit.
1. Pour the specified amount of dye into the engine oil fill
tube.
2. Operate the vehicle normal operating conditions as
directed in the kit.
3. Direct the light toward the suspected area. The dyed
fluid willappear as a yellow path leading to the
source.
Repairing the Leak
Once the origin of the leak has been pinpointed and
traced back to its source, the cause of the leak must be
determined n order for it to be repaired properly. If a gas-
ket is replaced, but the sealing flange is bent, the new
gasket will not repair the leak. Thebent flange must be
repaired also. Before attempting to repair a leak, check
for the following conditions and correct them as they
may cause a leak.
Gaskets
DThe fluid level/pressure is too high.
DThe crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
DThe fasteners are tightened improperly or the threads
are dirty or damaged.
DThe flanges or the sealing surface is warped.
DThere are scratches, burrs or other damage to the
sealing surface.
DThe gasket is damaged or worn.
DThere is cracking or porosity of the component.
DAn improper seal was used (where applicable).
Seals
DThe fluid level/pressure is too high.
DThe crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
DThe seal bore is damaged (scratched, burred or
nicked).
DThe seal is damaged or worn.
DImproper installation is evident.
DThere are cracks in the components.
DThe shaft surface is scratched, nicked or damaged.
DA loose or worn bearing is causing excess seal wear.
Page 96 of 2053
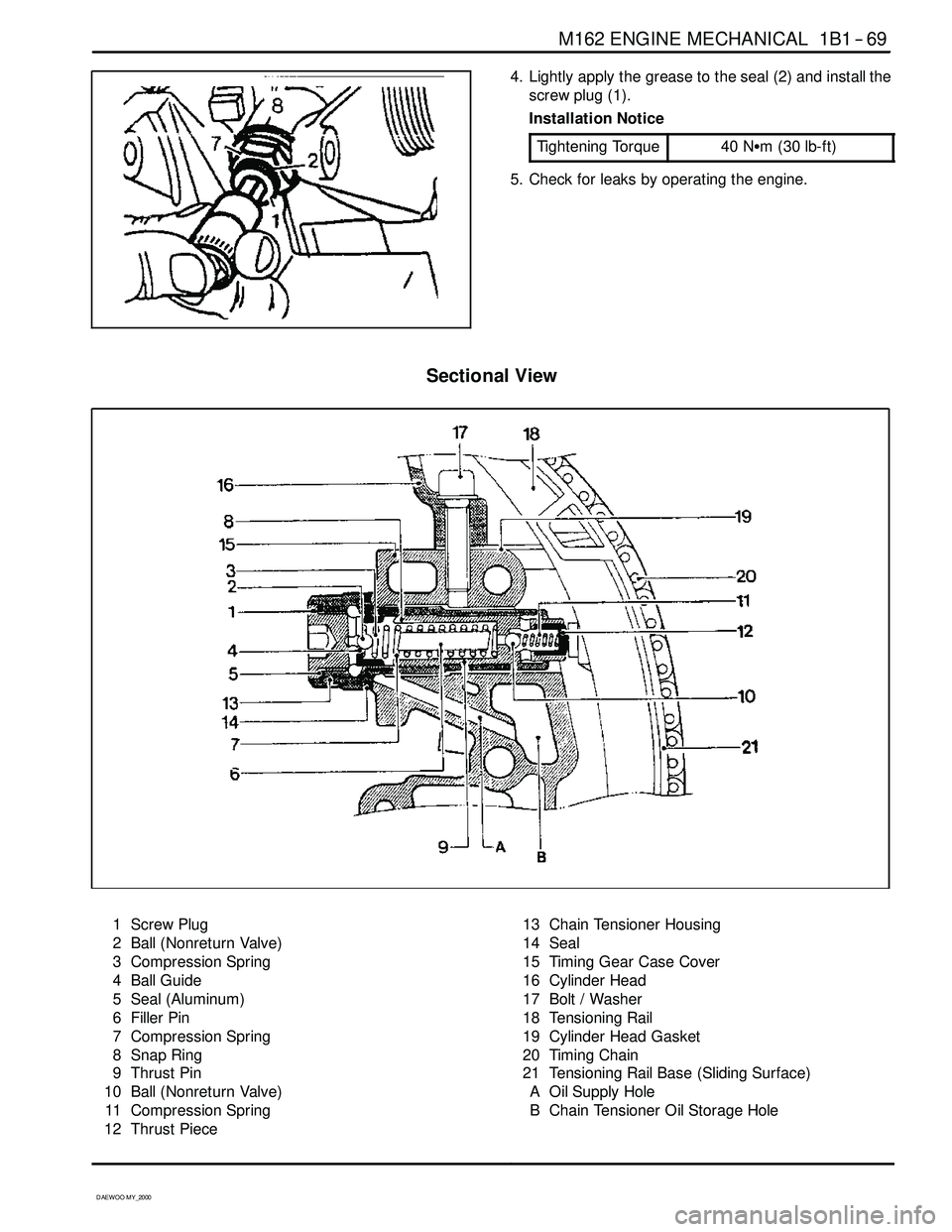
M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1 -- 69
D AEW OO M Y_2000
4. Lightly apply the grease to the seal (2) and install the
screw plug (1).
Installation Notice
Tightening Torque
40 NSm (30 lb-ft)
5. Check for leaks by operating the engine.
Sectional View
1 Screw Plug
2 Ball (Nonreturn Valve)
3 Compression Spring
4 Ball Guide
5 Seal (Aluminum)
6 Filler Pin
7 Compression Spring
8 Snap Ring
9 Thrust Pin
10 Ball (Nonreturn Valve)
11 Compression Spring
12 Thrust Piece13 Chain Tensioner Housing
14 Seal
15 Timing Gear Case Cover
16 Cylinder Head
17 Bolt / Washer
18 Tensioning Rail
19 Cylinder Head Gasket
20 Timing Chain
21 Tensioning Rail Base (Sliding Surface)
A Oil Supply Hole
B Chain Tensioner Oil Storage Hole
Page 291 of 2053

GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A2 -- 7
D AEW OO M Y_2000
DIAGNOSIS
OIL LEAK DIAGNOSIS
Most fluid oil leaks are easily located and repaired by
visually finding the leak and replacing or repairing the
necessary parts. On some occasions a fluid leak may be
difficult to locate or repair. The following procedures may
help you in locating and repairing most leaks.
Finding the Leak
1. Identify the fluid. Determine whether it is engine oil,
automatic transmission fluid, power steering fluid,
etc.
2. Identify where the fluid is leaking from.
2.1 After running the vehicle at normal operating
temperature, park the vehicle over a large sheet
of paper.
2.2 Wait a few minutes.
2.3 You should be able to find the approximate loca-
tion of the leak by the drippings on the paper.
3. Visually check around the suspected component.
Check around all the gasket mating surfaces for
leaks. A mirror is useful for finding leaks in areas that
are hard to reach.
4. If the leak still cannot be found, it may be necessary
to clean the suspected area with a degreaser, steam
or spray solvent.
4.1 Clean the area well.
4.2 Dry the area.
4.3 Operate the vehicle for several miles at normal
operating temperature and varying speeds.
4.4 After operating the vehicle, visually check the
suspected component.
4.5 If you still cannot locate the leak, try using the
powder or black light and dye method.
Powder Method
1. Clean the suspected area.
2. Apply an aerosol-- type powder (such as foot powder)
to the suspected area.
3. Operate the vehicle under normal operating condi-
toins.
4. Visually inspect the suspected component. You
should be able to trace the leak path over the white
powder surface to the source.
Black Light and Dye Method
A dye and light kit is available for finding leaks, Refer to
the manufacturer ’s directions when using the kit.
1. Pour the specified amount of dye into the engine oil fill
tube.
2. Operate the vehicle normal operating conditions as
directed in the kit.
3. Direct the light toward the suspected area. The dyed
fluid willappear as a yellow path leading to the
source.
Repairing the Leak
Once the origin of the leak has been pinpointed and
traced back to its source, the cause of the leak must be
determined n order for it to be repaired properly. If a gas-
ket is replaced, but the sealing flange is bent, the new
gasket will not repair the leak. Thebent flange must be
repaired also. Before attempting to repair a leak, check
for the following conditions and correct them as they
may cause a leak.
Gaskets
DThe fluid level/pressure is too high.
DThe crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
DThe fasteners are tightened improperly or the threads
are dirty or damaged.
DThe flanges or the sealing surface is warped.
DThere are scratches, burrs or other damage to the
sealing surface.
DThe gasket is damaged or worn.
DThere is cracking or porosity of the component.
DAn improper seal was used (where applicable).
Seals
DThe fluid level/pressure is too high.
DThe crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
DThe seal bore is damaged (scratched, burred or
nicked).
DThe seal is damaged or worn.
DImproper installation is evident.
DThere are cracks in the components.
DThe shaft surface is scratched, nicked or damaged.
DA loose or worn bearing is causing excess seal wear.
Page 363 of 2053

1B2 -- 70 M161 ENGINE MECHANICAL
D AEW OO M Y_2000
4. Lightly apply the grease to the seal (2) and install the
screw plug (1).
Installation Notice
Tightening Torque
40 NSm (30 lb-ft)
5. Check for leaks by operating the engine.
Page 545 of 2053

1A3 -- 10 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
D AEW OO M Y_2000
DIAGNOSIS
OIL LEAK DIAGNOSIS
Most fluid oil leaks are easily located and repaired by
visually finding the leak and replacing or repairing the
necessary parts. On some occasions a fluid leak may be
difficult to locate or repair. The following procedures may
help you in locating and repairing most leaks.
Finding the Leak
1. Identify the fluid. Determine whether it is engine oil,
automatic transmission fluid, power steering fluid,
etc.
2. Identify where the fluid is leaking from.
2.1 After running the vehicle at normal operating
temperature, park the vehicle over a large sheet
of paper.
2.2 Wait a few minutes.
2.3 You should be able to find the approximate loca-
tion of the leak by the drippings on the paper.
3. Visually check around the suspected component.
Check around all the gasket mating surfaces for
leaks. A mirror is useful for finding leaks in areas that
are hard to reach.
4. If the leak still cannot be found, it may be necessary
to clean the suspected area with a degreaser, steam
or spray solvent.
4.1 Clean the area well.
4.2 Dry the area.
4.3 Operate the vehicle for several miles at normal
operating temperature and varying speeds.
4.4 After operating the vehicle, visually check the
suspected component.
4.5 If you still cannot locate the leak, try using the
powder or black light and dye method.
Powder Method
1. Clean the suspected area.
2. Apply an aerosol-- type powder (such as foot powder)
to the suspected area.
3. Operate the vehicle under normal operating condi-
tions.
4. Visually inspect the suspected component. You
should be able to trace the leak path over the white
powder surface to the source.
Black Light and Dye Method
A dye and light kit is available for finding leaks, Refer to
the manufacturer ’s directions when using the kit.
1. Pour the specified amount of dye into the engine oil fill
tube.
2. Operate the vehicle normal operating conditions as
directed in the kit.
3. Direct the light toward the suspected area. The dyed
fluid willappear as a yellow path leading to the
source.
Repairing the Leak
Once the origin of the leak has been pinpointed and
traced back to its source, the cause of the leak must be
determined n order for it to be repaired properly. If a gas-
ket is replaced, but the sealing flange is bent, the new
gasket will not repair the leak. Thebent flange must be
repaired also. Before attempting to repair a leak, check
for the following conditions and correct them as they
may cause a leak.
Gaskets
DThe fluid level/pressure is too high.
DThe crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
DThe fasteners are tightened improperly or the threads
are dirty or damaged.
DThe flanges or the sealing surface is warped.
DThere are scratches, burrs or other damage to the
sealing surface.
DThe gasket is damaged or worn.
DThere is cracking or porosity of the component.
DAn improper seal was used (where applicable).
Seals
DThe fluid level/pressure is too high.
DThe crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
DThe seal bore is damaged (scratched, burred or
nicked).
DThe seal is damaged or worn.
DImproper installation is evident.
DThere are cracks in the components.
DThe shaft surface is scratched, nicked or damaged.
DA loose or worn bearing is causing excess seal wear.
Page 651 of 2053

1B3 -- 102 OM600 ENGINE MECHANICAL
D AEW OO M Y_2000
Checking
Notice
The noise which continues short time during short
travel (frequent starting of the engine) or engine
starting after a long time storage is normal operating
conditions. So, it does not need to be repaired. De-
termine the malfunctions in valve clearance com-
pensation device with noise through following tests.
If defective, replace as respectively.
1. Run the engine at more than 3000rpm for approx. 4
minutes.
2. Stop the engine. After 5minutes, check the engine
oil level and adjust if necessary.
3. Remove the cylinder head cover.
4. Check the valve tappets at TDC position of each cyl-
inders.
5. Using a drift, lightly press the valve tappet and mea-
sure clearance between the cam and valve tappet.
Notice
If the clearance exceeds 0.4mm, replace the valve
tappet.
6. If a valve tappet moves down too far in comparison
to the others, replace the valve tappet.
7. Rotate the engine and check the remaining valve
tappets.
Notice
DUnnecessary rotation of the engine will damage
the valve tappets.
DDo not rotate the engine by using the camshaft
sprocket bolt or to the opposite direction of the
engine rotation.
Page 794 of 2053

OM600 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F3 -- 37
D AEW OO M Y_2000
Tools Required
617 589 08 21 00 Position Sensor
Test Procedure
1. Remove the screw plug (5) and seal (4) and collect
oil in a suitable vessel.
2. Install the position sensor (1) into the governor
housing of the injection pump to be the guide pin of
the position sensor facing up.
3. Connect the battery terminal of position sensor (1)
to positive terminal (+) of battery.
Position Sensor 617 589 08 21 00
4. Rotate the crankshaft by hand (in direction of engine
rotation) until the lamp ’B’ lights up. Rotate the
crankshaft carefully further until both lamps ’A and
B’ come on. In this position, check the Rl value on
the crankshaft vibration damper.
SpecificationAT DC 1 4_-- 1 6_
Notice
If only lamp ’A’ lights up, repeat the test and if out of
specification, adjust start of delivery.
Page 923 of 2053

HYDRAULIC BRAKES 4A-3
SSANGYONG MY2002
DIAGNOSTIC INFORMATION AND PROCEDURES
BRAKE SYSTEM TESTING
Brakes should be tested on a dry, clean, reasonably
smooth and level roadway. A true test of brake perfor-
mance cannot be made if the roadway is wet, greasy,
or covered with loose dirt which can cause tires not to
grip the road unequally. Testing also will be inaccurate
on a crowned roadway because the wheels tend to
bounce.
Test the brakes at different vehicle speeds with both
light-and heavy-pedal pressure; however, avoid locking
the brakes and sliding the tires. Locked brakes and
slid-ing tires do not indicate brake efficiency since
heavily braked but turning wheels will stop the vehicle
in less distance than locked brakes. More tire-to-road
friction is present with a heavily braked, turning tire
than with a sliding tire.
Because of the high deceleration capability, a firmer
pedal may be felt at higher deceleration levels.
There are three major external conditions that affect
brake performance:
•Tires having unequal contact and grip of the road
will cause unequal braking. Tires must be equally
inflated, and the tread pattern of the right and the
left tires must be approximately equal.
Unequal loading of the vehicle can affect the brake
performance since the most heavily loaded wheels
require more braking power, and thus more braking
effort, than the others.
Misalignment of the wheels, particularly conditions
of excessive camber and caster, will cause the
brakes to pull to one side.
To check for brake fluid leaks, hold constant foot pres-
sure on the pedal with the engine running at idle and
the shift lever in NEUTRAL. If the pedal gradually falls
away with the constant pressure, the hydraulic system
may be leaking. Perform a visual check to confirm any
suspected leaks.
Check the master cylinder fluid level. While a slight
drop in the reservoir level results from normal lining
wear, an abnormally low level indicates a leak in the
system. The hydraulic system may be leaking either
internally or externally. Refer to the procedure below
to check the master cylinder. The system may appear
to pass this test while still having a slight leak. If the
fluid level is normal, check the vacuum booster pushrod
length. If an incorrect pushrod length is found, adjust
or replace the rod.Check the master cylinder using the following proce
dure:
Check for a cracked master cylinder casting or a
brake fluid leak around the master cylinder. Leaks
are indicated only if there is at least one drop of
fluid. A damp condition is not abnormal.
Check for a binding pedal linkage and for an
incorrect pushrod length. If both of these parts are
in satisfactory condition, disassemble the master
cylinder and check for an elongated or swollen
primary cylinder or piston seals. If swollen seals
are found, substandard or contaminated brake fluid
should be suspected. If contaminated brake fluid
is found, all the components should be
disassembled and cleaned, and all the rubber
components should be replaced. All of the pipes
must also be flushed.
Improper brake fluid, or mineral oil or water in the fluid,
may cause the brake fluid to boil or cause deterioration
of the rubber components. If the primary piston cups in
the master cylinder are swollen, the rubber parts have
deteriorated.
If deterioration of the rubber is evident, disassemble
all the hydraulic parts and wash the parts with alcohol.
Dry these parts with compressed air before reassembly
to keep the alcohol out of the system. Replace all the
rubber parts in the system, including the hoses. When
working on the brake mechanisms, check for fluid on
the linings. If excessive fluid is found, replace the
linings.
If the master cylinder piston seals are in satisfactory
condition, check for leaks or excessive heat conditions.
If these conditions are not found, drain the fluid, flush
the master cylinder with brake fluid, refill the master
cylinder, and bleed the system.
BRAKE HOSE INSPECTION
The hydraulic brake hoses should be inspected at least
twice a year. The brake hose assembly should be
checked for road hazard damage, cracks, chafing of
the outer cover, and for leaks or blisters. Inspect the
hoses for proper routing and mounting. A brake hose
that rubs on a suspension component will wear and
eventually fail. A light and a mirror may be needed for
an adequate inspection. If any of the above conditions
are observed on the brake hose, adjust or replace the
hose as necessary.
Page 1089 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4G-2 PARKING BRAKE
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
BRAKE CALIPER
This braking system uses a BRAKE warning light lo-
cated in the instrument panel cluster.
The following conditions will activate the BRAKE lamp:
•The parking brake is applied when the ignition is
ON. The lamp will turn off when the parking brake
is released.
The fluid level is below the minimum mark in the
master cylinder reservoir. The lamp will turn off when
the fluid level is above the minimum.
As a test of the lamp circuit, the BRAKE lamp will
glow dimly when the ignition is ON, even if the
parking brake is off and fluid level is above the
minimum. The lamp will turn off when the engine is
started. When the brake is firmly applied, the parking
brake should hold the vehicle with ample pedal
travel remaining.
Check for frayed cables, rust, etc. or any condition
that may inhibit present (or future) free movement of
the parking brake lever assembly.