Vacuum SSANGYONG MUSSO 1998 Workshop User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 1998, Model line: MUSSO, Model: SSANGYONG MUSSO 1998Pages: 1463, PDF Size: 19.88 MB
Page 355 of 1463

OM600 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B3-53
5. Tighten the cylinder head bolts to specified torque and
torque angle.
OM 662LA
OM 661LA
6. Install the socket bolts in the chain box.
Tightening Torque 25 Nm
Stage 1
Stage 2
Torque angle
Wait for
Torque angle15 Nm
35 Nm
90°
10 minutes
90°
7. Connect the vacuum pipe to the thermo valve.
Page 356 of 1463

1B3-54 OM600 ENGINE MECHANICAL
8. Connect the vacuum lines to the vacuum pump.
9. Install the fuel filter and connect the pipe.
Tightening Torque 25 Nm
Notice
Be careful not to be confused the connections and hoses.
10. Connect the fuel pipe to the injection pump.
11. Install the sliding rail(24) and insert the sliding rail pins(25,
26).
Notice
Apply sealing compound on the each collar of the sliding
rail pins.
Sliding Hammer 116 589 20 33 00
Threaded Pin 116 589 02 34 00
Page 366 of 1463

1B3-64 OM600 ENGINE MECHANICAL
8. Remove the guide pulley bracket (24).
Tools Required
116 589 03 07 00 Socket Wrench
Removal Procedure
1. Remove the fan clutch and cooling fan belt pulley.
2. Drain the engine oil completely.
3. Remove the oil dipstick tube bracket bolts.
4. Remove the crankshaft pulley.
5. Loosen the bolt (1) and then remove the cylinder head cover
(2) and gasket.
6. Remove the vacuum pump.
7. Detach the closing cover (20). Remove the bolts(21) and
then remove the guide pulley (22).
Page 371 of 1463

OM600 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B3-69
10. Install the fuel filter.
11. Install the vacuum pump.
12. Install the power steering pump.
13. Install the power steering pump pulley.
Tightening Torque 25 Nm
Tightening Torque 10 Nm
Tightening Torque 23 Nm
Tightening Torque 32 Nm
14. Install the guide pulley bracket.
Tightening Torque 9 Nm
Page 571 of 1463

SECTION 1F1
M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a
tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals. Disconnecting this cable
will help prevent personal injury and damage to the vehicle. The ignition must also be in LOCK unless otherwise
noted.
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-2
Fastener Tightening Specifications . . . . . . . . 1F1-2
Special Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-3
Special Tools Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-3
Schematic and Routing Diagrams . . . . . . . 1F1-4
E32 ECU (HFM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-4
E32 ECU (MSE) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-5
Diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-6
Self Diagnosis Socket Pin Numbers and
Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-6
Self Diagnosis Failure Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-7
Test Box Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-10
Fuel Injection System Test (MSE3.62) . . . . . 1F1-11
Ignition System Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-21
Idling Control and Electronic Pedal
System Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-26
Air Conditioner Control System Test . . . . . . 1F1-28
Fuel Pressure and Internal Leakage Test . . 1F1-29
Fuel Pump Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-31Injector Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-33
Maintenance and Repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-35
On-Vehicle Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-35
ECU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-35
Fuel Pressure Regulator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-46
Fuel Distributor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-50
Injector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-54
Fuel Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-57
Fuel Pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-58
Purge Switchover Valve . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-62
Vacuum System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-64
Crankshaft Position Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-65
Camshaft Position Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-67
Hot Film Air Mass (HFM) Sensor . . . . . . . . . 1F1-69
Oxygen Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-72
Knock Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-74
Coolant Temperature Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-75
Accelerator Pedal Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F1-78
Page 588 of 1463

1F1-18 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
Failure
codeItem
Þ 18.1
Checking method Test
stepRequirementSpecified
valuePossible cause
73 28 - 12 W
· ·· ·
· Camshaft
actuator:
Solenoid
resistance
Þ 21.0· ·· ·
· Purge
control
valve:
- Vacuum
control· Engine:in idling/
normal operating
temperature· Vacuum line
· Purge control valve
· Cable
· Camshaft actuator
Diagnosis
socket
Þ 19.0
73 69Engine is
unstable or
stopped· ·· ·
· Camshaft
actuator:
Mechanical
Actuation· Mechanical failure of
camshaft actuator
Þ 20.0
· Engine:in idling
34 11The purge
control valve
should be
operated after
approx.
1minute.
(refer to figure
5)· ·· ·
· Purge
control
valve:
- Operating
226,
227,
· ECU
· Cable
· Purge control valve
· Ignition:ON0.3 - 0.5 A - Current
consumption
10 34
Creating
above 50mbar
of vacuum
after approx.
1 minute
Þ 22.0
· Ignition:OFF
38 37· Data bus
· Þ 22.1
· Þ 22.2 55 - 65 W
· ·· ·
· CAN data
bus
· Ignition:OFF
· Engine:in idling
- connect the bridge
to the test box for
approx. 10 seconds
40,
41,
54,
Connect the vacuum
gauge between the
control valve and
canister
22,23,
24,26,
27,29,
30,31,
59,60,
Page 600 of 1463

1F1-30 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
Failure
codeItemChecking method Te s t
stepRequirementSpecified
valuePossible cause
3.2 - 3.6 bar· ·· ·
· Fuel
pressure:in
idling speed
- When the
vacuum is
applied· Engine:in idling
- Close the valve
screw on pressure
testerÞ 1.0 Connect the fuel
pressure test plug to
the pressure tester
(refer to the flgure on
previous page).· Þ Fuel pump test
· Fuel pressure
regulator
3.7 - 4.2 bar
· ·· ·
· Fuel
pressure:in
idling speed
- When the
vacuum is
not applied· Engine:in idling
- Close the valve
screw on pressure
tester Þ 2.0 Connect the fuel
pressure test plug to
the pressure tester
(refer to the flgure on
previous page).· Fuel pressure
regulator
> 3.0 bar
· ·· ·
· Fuel system
internal
leakage:· Engine:stop Þ 3.0 Connect the fuel
pressure test plug to
the pressure tester
(refer to the flgure on
previous page).· The pressure drops
rapidly:non-return
valve in fuel pump
> 2.5 bar· After 30 minutes from
engine stop· The pressure drops
slowly:
- Injector test
- Fuel pressure
regulator
- O-ring
Page 616 of 1463
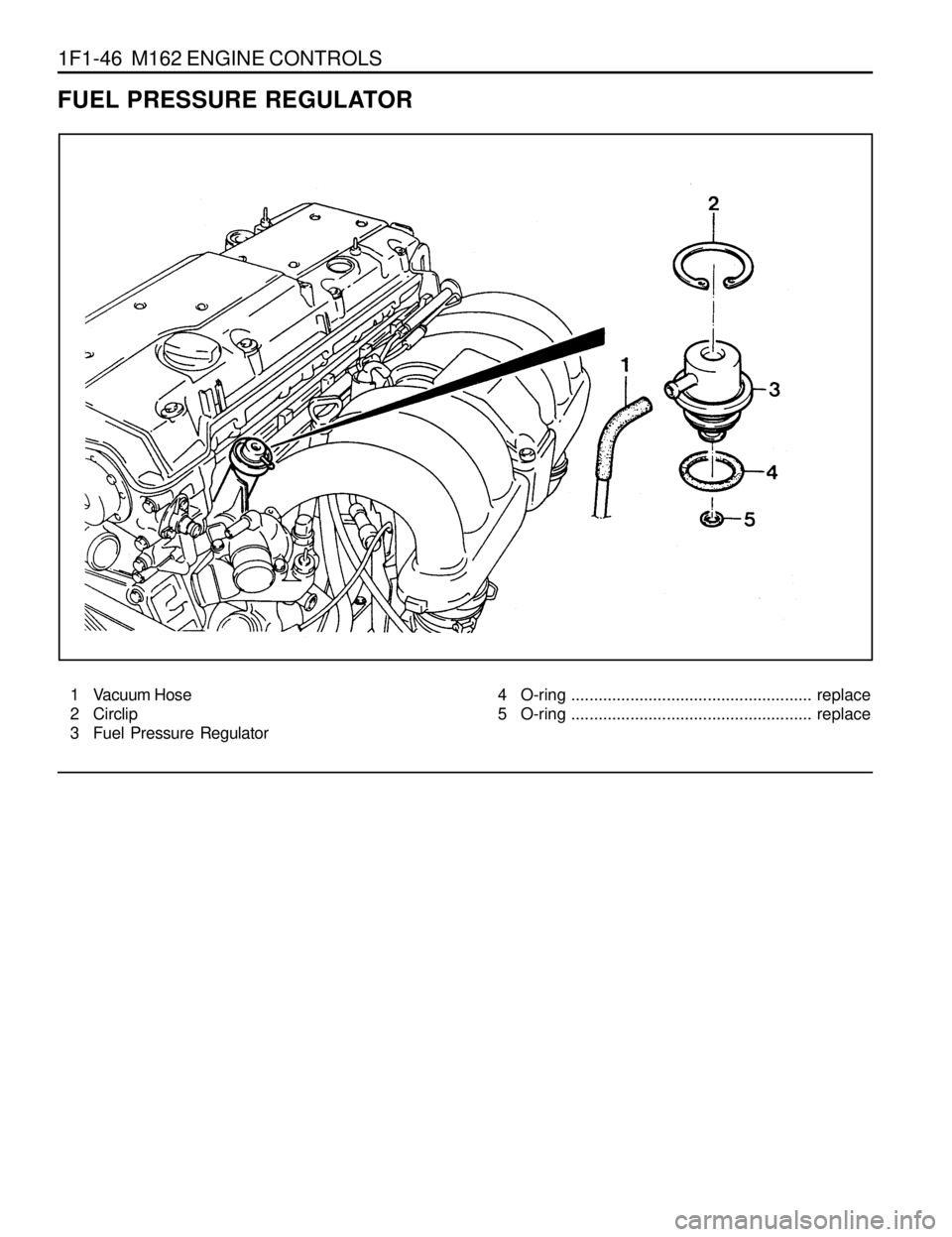
1F1-46 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
1 Vacuum Hose
2 Circlip
3 Fuel Pressure Regulator
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
4 O-ring ..................................................... replace
5 O-ring ..................................................... replace
Page 617 of 1463

M162 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F1-47
3. Disconnect the vacuum hose.
4. Disconnect the circlip and remove the fuel pressure
regulator.
5. Apply the oil to O-ring lightly and then replace it.
6. Installation should follow the removal procedure in the
reverse order.
7. Check for fuel pressure and internal leaks by operating the
engine. 2. Discharge the pressure in fuel supply system by pressing
the service valve.
Removal & Installation Procedure
1. Remove the fuel pressure test connector.
Page 618 of 1463

1F1-48 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
A . Valves Closed
B. Valves Opened
The pressure difference between the fuel pressure and the
intake manifold is about 3.8 bars during the full load.
The spring chamber(9) is connected to the intake manifold
with the vacuum hose at the intake pipe connection(7). The
negative pressure generated in the intake manifold activates
the diaphragm, and thus the fuel pressure gets reduced to the
rate of the operating extent of the diaphragm by the intake
manifold's negative pressure.
Consequently, the fuel pressure in the fuel distributor changes
by the intake manifold's negative pressure, and the injector's
fuel pressure gets reduced independently to the throttle valve's
position. Thus, the fuel injection volume can only be determined
according to the injector's injecting duration.
2. Fuel return line
3. Valve
5. Diaphragm
6. Compression Spring
8. Fuel Chamber
9. Spring Chamber
1. Fuel Pressure Regulator
2. Intake Manifold
3. Fuel Return(to fuel tank)
4. Fuel Supply(form fuel pump)
5. Fuel Pressure(approx. 3.8 bars)
6. Intake Manifold Negative Pressure(0 bar)
Function of the Fuel Pressure Regulator
The fuel pressure regulator maintains the fuel pressure in the
fuel line with the pressure of 3.2 bars to 3.8 bars according to
the intake manifold pressure. This operating pressure cannot
be changed, and the fuel injection volume will be only
determined by the injection time. Over supplied fuel returns to
the fuel tank through the return line.
There is no negative pressure applied to the spring chamber(9)
during the full load, and it is separated from the fuel chamber(8)
by the diaphragm(5).
When the fuel pressure goes up, the diaphragm forces the
compression spring(6) in the direction of compression . At this
moment, the valve(3) sticks to the diaphragm by the fuel
pressure, and the fuel return line(2) opens. The fuel over
supplied returns to the fuel tank through the return line.