gas type SSANGYONG MUSSO 1998 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 1998, Model line: MUSSO, Model: SSANGYONG MUSSO 1998Pages: 1463, PDF Size: 19.88 MB
Page 14 of 1463
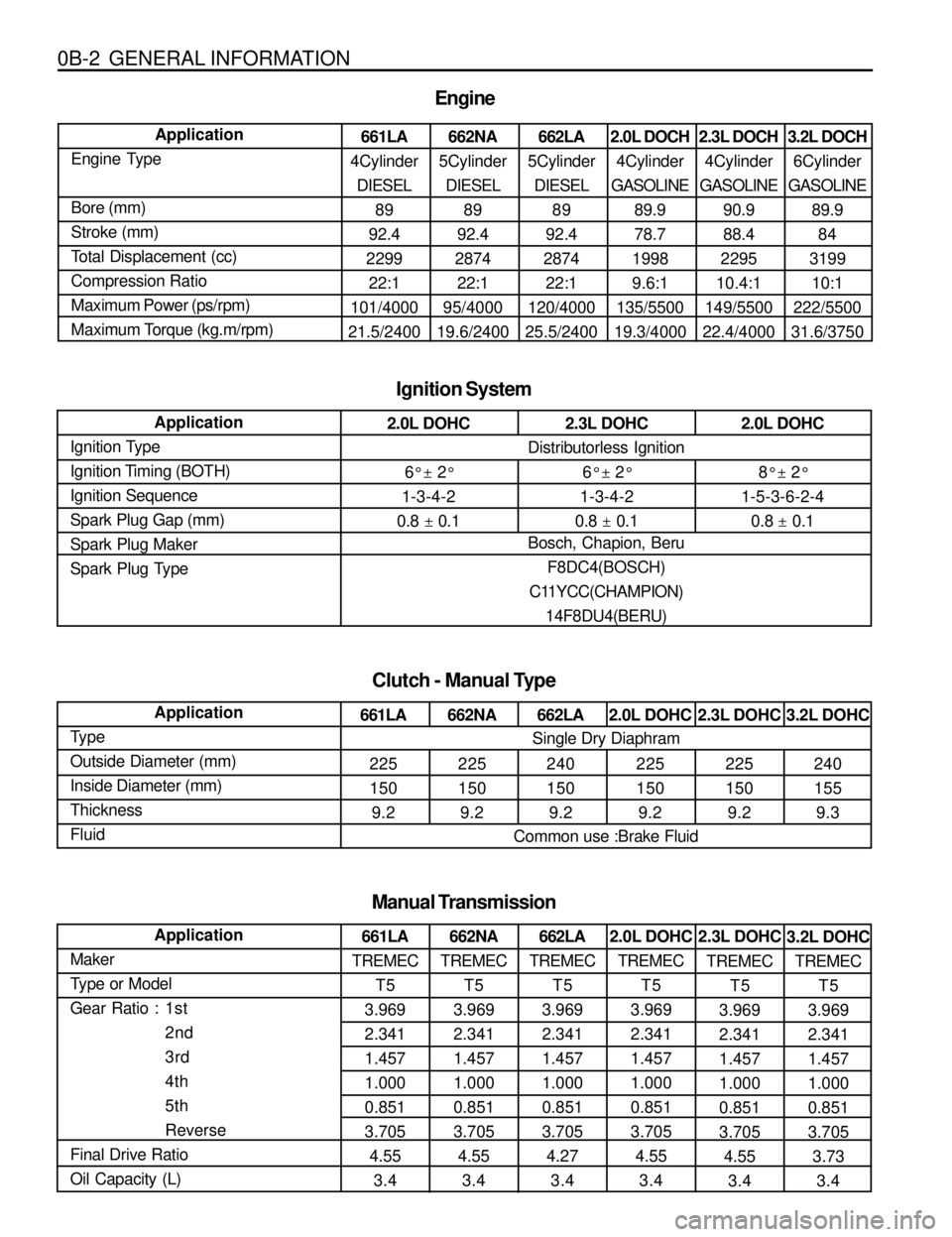
0B-2 GENERAL INFORMATION
661LA
4Cylinder
DIESEL
89
92.4
2299
22:1
101/4000
21.5/2400 Application
Engine Type
Bore (mm)
Stroke (mm)
Total Displacement (cc)
Compression Ratio
Maximum Power (ps/rpm)
Maximum Torque (kg.m/rpm)
Engine
662NA
5Cylinder
DIESEL
89
92.4
2874
22:1
95/4000
19.6/2400662LA
5Cylinder
DIESEL
89
92.4
2874
22:1
120/4000
25.5/24002.0L DOCH
4Cylinder
GASOLINE
89.9
78.7
1998
9.6:1
135/5500
19.3/40002.3L DOCH
4Cylinder
GASOLINE
90.9
88.4
2295
10.4:1
149/5500
22.4/40003.2L DOCH
6Cylinder
GASOLINE
89.9
84
3199
10:1
222/5500
31.6/3750
661LA
TREMEC
T5
3.969
2.341
1.457
1.000
0.851
3.705
4.55
3.4 Application
Ignition Type
Ignition Timing (BOTH)
Ignition Sequence
Spark Plug Gap (mm)
Spark Plug Maker
Spark Plug Type
Ignition System
Clutch - Manual Type
2.0L DOHC
6° ± 2°
1-3-4-2
0.8 ± 0.12.3L DOHC
6° ± 2°
1-3-4-2
0.8 ± 0.12.0L DOHC
8° ± 2°
1-5-3-6-2-4
0.8 ± 0.1 Distributorless Ignition
Bosch, Chapion, Beru
F8DC4(BOSCH)
C11YCC(CHAMPION)
14F8DU4(BERU)
661LA
225
150
9.2
662NA
225
150
9.2662LA
240
150
9.22.0L DOHC
225
150
9.22.3L DOHC
225
150
9.23.2L DOHC
240
155
9.3 Application
Type
Outside Diameter (mm)
Inside Diameter (mm)
Thickness
Fluid
Single Dry Diaphram
Common use :Brake Fluid
Application
Maker
Type or Model
Gear Ratio : 1st
2nd
3rd
4th
5th
Reverse
Final Drive Ratio
Oil Capacity (L)
Manual Transmission
662NA
TREMEC
T5
3.969
2.341
1.457
1.000
0.851
3.705
4.55
3.4662LA
TREMEC
T5
3.969
2.341
1.457
1.000
0.851
3.705
4.27
3.42.0L DOHC
TREMEC
T5
3.969
2.341
1.457
1.000
0.851
3.705
4.55
3.42.3L DOHC
TREMEC
T5
3.969
2.341
1.457
1.000
0.851
3.705
4.55
3.43.2L DOHC
TREMEC
T5
3.969
2.341
1.457
1.000
0.851
3.705
3.73
3.4
Page 19 of 1463
GENERAL INFORMATION 0B-7
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR
MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION
Fuel Filter Replacement
Replace the engine fuel filter every.
lGasoline Engine : 60,000km (36,000 miles)
lDiesel Engine : 45,000km (24,000 miles)
Spark Plug Replacement
Replace spark plugs with same type.
lType : BOSCH : F8DC4
BERU : 14F-8DU4
Champion : C11YCC
lGap : 0.8 ± 0.1 mm
Spark Plug Wire Replacement
Clean wires and inspect them for burns, cracks or other
damage. Check the wire boot fit at the Distributor and at
the spark plugs. Replace the wires as needed.
Brake System Service
Check the disc brake pads or the drum brake linings.
Check the pad and the lining thickness carefully.
Tire and Wheel Inspection and Rotation
Check the tires for abnormal wear or damage. To
equalize wear and obtain maximum tire life, rotate the
tires. If irregular or premature wear exists, check the
wheel alignment and check for damaged wheels. While
the tires and wheels are removed, inspect the brakes.
NORMAL VEHICLE USE
The maintenance instructions contained in the
maintenance schedule are based on the assumption
that the vehicle will be used for the following reasons:
lTo carry passengers and cargo within the limitation
of the tire inflation prassure. Refer to “Tire and Wheel”
in section 2E.
lTo be driven on reasonable road surfaces and within
legal operating limits.
EXPLANATION OF SCHEDULED
MAINTENANCE SERVICES
The services listed in the maintenance schedule are
further explained below. When the following maintenance
services are performed, make sure all the parts are
replaced and all the necessary repairs are done before
driving the vehicle. Always use the proper fluid and
lubricants.
Engine Oil and Oil Filter Change
Always use above the API SH grade or recommended
engine oil.
Engine Oil Viscosity
Engine oil viscosity (thickness) has an effect on fuel
economy and cold weather operation. Lower viscosity
engine oils can provide better fuel economy and cold
weather performance; however, higher temperature
weather conditions require higher viscosity engine oils
for satisfactory lubrication. Using oils of any viscosity
other than those viscosities recommended could result
in engine damage.
Cooling System Service
Drain, flush and refill the system with new coolant. Refer
to “Recommended Fluids And Lubricants” in this section.
Air Cleaner Element Replacement
Clean the air cleaner element every.
lGasoline Engine : 15,000km (10,000 miles)
lDiesel Engine : 10,000km (6,000 miles)
Replace the air cleaner element every .
lGasoline Engine : 60,000km (36,000 miles)
lDiesel Engine : 30,000km (18,000 miles)
Replace the air cleaner more often under dusty
conditions.
Tire Rotation (Left - Hand Drive Type)
Page 28 of 1463

0B-16 GENERAL INFORMATION
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER SYSTEM
K P T P 0 A 1 9 S W P 122357
12~17.Production Serial Number
: 000001- 999999
11.Plant Code
P : PyongTaek Plant
10.Model Year
M : 1991
N : 1992
P : 1993
R : 1994
S : 1995
T : 1996
V : 1997
W : 1998
X : 1999
Y : 2000
9. Check Digit
Constant “S”
8. Engine Type
3 : 2299cc, In-line 4Cylinder, Diesel (OM601)
4 : 2874cc, In-line 5Cylinder, Diesel (OM602)
8 : 1998cc, In-line 4Cylinder, Gasoline (E20)
6 : 2295cc, In-line 4Cylinder, Gasoline (E23)
9 : 3199cc, In-line 6Cylinder, Gasoline (E32)
A : 2299cc, In-line 4Cylinder, Diesel (OM601)
B : 2874cc, In-line 5Cylinder, Diesel (OM602)
C : 2299cc, In-line 4Cylinder, Diesel (SY662LA)
D : 2874cc, In-line 5Cylinder, Diesel (SY662LA)
7. Restraint System
0 : NO Seat Belt,
1 : 3-Point Seat Belts, 2 : 2-Point Seat Belts
6. Trim Level
A : Standard, B : Deluxe, C : Super Deluxe
5. Body Type
0 : 5-Door
1 : 4-Door
2 : 3-Door
4. Line Models
P : Musso, LHD, R : Musso, RHD
3. Vehicle Type
T (Passengr Cars)
2. Name of Mamufacturer : P
1. Nation : K
Page 29 of 1463

GENERAL INFORMATION 0B-17
Manufacturer’s Plate
Manufacturer’s Plate Location
1.Type Approval No. 2.Vehicle Identification Number.
Diesel Engine Gasoline Engine
Page 30 of 1463

0B-18 GENERAL INFORMATION
Engine Number Location
Diesel Engine
The engine number is stamped on the cylinder block in
front of injection pump.
IL6 3200
The engine number is stamped on the lower rear side
of the alternator.
Gasolind Engine Number
1 6 2 9 9 0 1 0 012345
Serial Number
0 : Manual T/M
1 : Hydr - Auto Coupling
2 : Automatic T/M
99 : 3.2L
97 : 2.3L
94 : 2.0L
0 : Common
1 : Left - Hand Drive
2 : Right - Hand Drive
ENGINE TYPE
0 : MUSSO
Diesel Engine Number
662 920 1 0 012345
Serial Number
0 : Manual T/M
1 : Hydr - Auto Coupling
2 : Automatic T/M
910 : Non-Intercooler Engine
920 : Intercooler Engine
0 : Common
1 : Left - Hand Drive
2 : Right - Hand Drive
661 : 2299cc
662 : 2874cc
Page 33 of 1463

1A1-2 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
Application
Idle Speed (rpm)
Fuel Injection Pressure (kg/cm²)
Oil Capacity (liter)
Lubrication Type
Oil Filter Type
Fuel
ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS (Cont'd)
E32 Engine
700 ± 50
3 - 4
8.2
Forced by Gear Pump
Full Flow with Paper Filter
Unleaded Gasoline
MSE 3.62S/3.53S (Motorsteuer Elektronik : German)
MSE : Engine Control Electronic
3.62S : 6 Cylinder Version
3.53S : 4 Cylinder Version
Page 38 of 1463

GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A1-7
OIL LEAK DIAGNOSIS
Most fluid oil leaks are easily located and repaired by
visually finding the leak and replacing or repairing the
necessary parts. On some occasions a fluid leak may
be difficult to locate or repair. The following procedures
may help you in locating and repairing most leaks.
Finding the Leak
1. Identify the fluid. Determine whether it is engine oil,
automatic transmission fluid, power steering fluid, etc.
2. Identify where the fluid is leaking from.
2.1 After running the vehicle at normal operating
temperature, park the vehicle over a large sheet
of paper.
2.2 Wait a few minutes.
2.3 You should be able to find the approximate
location of the leak by the drippings on the
paper.
3. Visually check around the suspected component.
Check around all the gasket mating surfaces for
leaks. A mirror is useful for finding leaks in areas that
are hard to reach.
4. If the leak still cannot be found, it may be necessary
to clean the suspected area with a degreaser, steam
or spray solvent.
4.1 Clean the area well.
4.2 Dry the area.
4.3 Operate the vehicle for several miles at normal
operating temperature and varying speeds.
4.4 After operating the vehicle, visually check the
suspected component.
4.5 If you still cannot locate the leak, try using the
powder or black light and dye method.
Powder Method
1. Clean the suspected area.
2. Apply an aerosol-type powder (such as foot powder)
to the suspected area.
3. Operate the vehicle under normal operating
conditoins.
4. Visually inspect the suspected component. You
should be able to trace the leak path over the white
powder surface to the source.
Black Light and Dye Method
A dye and light kit is available for finding leaks, Refer to
the manufacturer's directions when using the kit.
1. Pour the specified amount of dye into the engine oil
fill tube.2. Operate the vehicle normal operating conditions as
directed in the kit.
3. Direct the light toward the suspected area. The dyed
fluid will appear as a yellow path leading to the
source.
Repairing the Leak
Once the origin of the leak has been pinpointed and
traced back to its source, the cause of the leak must be
determined n order for it to be repaired properly. If a
gasket is replaced, but the sealing flange is bent, the
new gasket will not repair the leak. The bent flange must
be repaired also. Before attempting to repair a leak,
check for the following conditions and correct them as
they may cause a leak.
Gaskets
lThe fluid level/pressure is too high.
lThe crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
lThe fasteners are tightened improperly or the threads
are dirty or damaged.
lThe flanges or the sealing surface is warped.
lThere are scratches, burrs or other damage to the
sealing surface.
lThe gasket is damaged or worn.
lThere is cracking or porosity of the component.
lAn improper seal was used (where applicable).
Seals
lThe fluid level/pressure is too high.
lThe crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
lThe seal bore is damaged (scratched, burred or
nicked).
lThe seal is damaged or worn.
lImproper installation is evident.
lThere are cracks in the components.
lThe shaft surface is scratched, nicked or damaged.
lA loose or worn bearing is causing excess seal wear.
DIAGNOSIS
Page 46 of 1463

1A2-2 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
E20 Engine
¬
¬
¬
¬
¬
¬ Application
Idle Speed (rpm)
Fuel Injection Pressure (kg/cm²)
Oil Capacity (liter)
Lubrication Type
Oil Filter Type
Fuel
ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS (Cont'd)
E23 Engine
750 ± 50
3.2 - 4.2
7.5
Forced by Gear Pump
Full Flow with Paper Filter
Unleaded Gasoline
MSE 3.62S/3.53S (Motorsteuer Elektronik : German)
MSE : Engine Control Electronic
3.62S : 6 cylinder version
3.53S : 4 cylinder version
Page 52 of 1463

1A2-8 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
OIL LEAK DIAGNOSIS
Most fluid oil leaks are easily located and repaired by
visually finding the leak and replacing or repairing the
necessary parts. On some occasions a fluid leak may
be difficult to locate or repair. The following procedures
may help you in locating and repairing most leaks.
Finding the Leak
1. Identify the fluid. Determine whether it is engine oil,
automatic transmission fluid, power steering fluid, etc.
2. Identify where the fluid is leaking from.
2.1 After running the vehicle at normal operating
temperature, park the vehicle over a large sheet
of paper.
2.2 Wait a few minutes.
2.3 You should be able to find the approximate
location of the leak by the drippings on the
paper.
3. Visually check around the suspected component.
Check around all the gasket mating surfaces for
leaks. A mirror is useful for finding leaks in areas that
are hard to reach.
4. If the leak still cannot be found, it may be necessary
to clean the suspected area with a degreaser, steam
or spray solvent.
4.1 Clean the area well.
4.2 Dry the area.
4.3 Operate the vehicle for several miles at normal
operating temperature and varying speeds.
4.4 After operating the vehicle, visually check the
suspected component.
4.5 If you still cannot locate the leak, try using the
powder or black light and dye method.
Powder Method
1. Clean the suspected area.
2. Apply an aerosol-type powder (such as foot powder)
to the suspected area.
3. Operate the vehicle under normal operating
conditoins.
4. Visually inspect the suspected component. You
should be able to trace the leak path over the white
powder surface to the source.
Black Light and Dye Method
A dye and light kit is available for finding leaks, Refer to
the manufacturer's directions when using the kit.
1. Pour the specified amount of dye into the engine oil
fill tube.
2. Operate the vehicle normal operating conditions as
directed in the kit.
3. Direct the light toward the suspected area. The dyed
fluid will appear as a yellow path leading to the
source.
Repairing the Leak
Once the origin of the leak has been pinpointed and
traced back to its source, the cause of the leak must be
determined n order for it to be repaired properly. If a
gasket is replaced, but the sealing flange is bent, the
new gasket will not repair the leak. The bent flange must
be repaired also. Before attempting to repair a leak,
check for the following conditions and correct them as
they may cause a leak.
Gaskets
lThe fluid level/pressure is too high.
lThe crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
lThe fasteners are tightened improperly or the threads
are dirty or damaged.
lThe flanges or the sealing surface is warped.
lThere are scratches, burrs or other damage to the
sealing surface.
lThe gasket is damaged or worn.
lThere is cracking or porosity of the component.
lAn improper seal was used (where applicable).
Seals
lThe fluid level/pressure is too high.
lThe crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
lThe seal bore is damaged (scratched, burred or
nicked).
lThe seal is damaged or worn.
lImproper installation is evident.
lThere are cracks in the components.
lThe shaft surface is scratched, nicked or damaged.
lA loose or worn bearing is causing excess seal wear.
DIAGNOSIS
Page 68 of 1463

1A3-10 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
OIL LEAK DIAGNOSIS
Most fluid oil leaks are easily located and repaired by
visually finding the leak and replacing or repairing the
necessary parts. On some occasions a fluid leak may
be difficult to locate or repair. The following
procedures may help you in locating and repairing
most leaks.
Finding the Leak
1. Identify the fluid. Determine whether it is engine
oil, automatic transmission fluid, power steering
fluid, etc.
2. Identify where the fluid is leaking from.
2.1 After running the vehicle at normal operating
temperature, park the vehicle over a large
sheet of paper.
2.2 Wait a few minutes.
2.3 You should be able to find the approximate
location of the leak by the drippings on the
paper.
3. Visually check around the suspected component.
Check around all the gasket mating surfaces for
leaks. A mirror is useful for finding leaks in areas
that are hard to reach.
4. If the leak still cannot be found, it may be
necessary to clean the suspected area with a
degreaser, steam or spray solvent.
4.1 Clean the area well.
4.2 Dry the area.
4.3 Operate the vehicle for several miles at
normal operating temperature and varying
speeds.
4.4 After operating the vehicle, visually check the
suspected component.
4.5 If you still cannot locate the leak, try using the
powder or black light and dye method.
Powder Method
1. Clean the suspected area.
2. Apply an aerosol-type powder (such as foot
powder) to the suspected area.
3. Operate the vehicle under normal operating
conditions.
4. Visually inspect the suspected component. You
should be able to trace the leak path over the white
powder surface to the source.
Black Light and Dye Method
A dye and light kit is available for finding leaks, Refer
to the manufacturer's directions when using the kit.1. Pour the specified amount of dye into the engine
oil fill tube.
2. Operate the vehicle normal operating conditions
as directed in the kit.
3. Direct the light toward the suspected area. The
dyed fluid will appear as a yellow path leading to
the source.
Repairing the Leak
Once the origin of the leak has been pinpointed and
traced back to its source, the cause of the leak must
be determined n order for it to be repaired properly. If
a gasket is replaced, but the sealing flange is bent,
the new gasket will not repair the leak. The bent flange
must be repaired also. Before attempting to repair a
leak, check for the following conditions and correct
them as they may cause a leak.
Gaskets
lThe fluid level/pressure is too high.
lThe crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
lThe fasteners are tightened improperly or the
threads are dirty or damaged.
lThe flanges or the sealing surface is warped.
lThere are scratches, burrs or other damage to the
sealing surface.
lThe gasket is damaged or worn.
lThere is cracking or porosity of the component.
lAn improper seal was used (where applicable).
Seals
lThe fluid level/pressure is too high.
lThe crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
lThe seal bore is damaged (scratched, burred or
nicked).
lThe seal is damaged or worn.
lImproper installation is evident.
lThere are cracks in the components.
lThe shaft surface is scratched, nicked or damaged.
lA loose or worn bearing is causing excess seal
wear.
DIAGNOSIS