differential SSANGYONG NEW ACTYON SPORTS 2012 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2012, Model line: NEW ACTYON SPORTS, Model: SSANGYONG NEW ACTYON SPORTS 2012Pages: 828, PDF Size: 91.28 MB
Page 348 of 828

15-450000-00
(15) CDPF control
A. Overview
As the solution for environmental regulations and PM Particle Material) of diesel engine, the low
emission vehicle is getting popular. This vehicle is equipped with an extra filter to collect the soot
and burn it again so that the amount of PM in the exhaust gas passed through the DOC (Diesel
Oxidation Catalyst) is reduced. The CDPF (Catalyst & Diesel Particulate Filter) is an integrated filter
including DOC (Diesel Oxidation Catalyst) and DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter).
For details, refer to Chapter "CDPF".
B. Components
Oxygen
sensorFront
EGT sensorCDPF
(DOC + DPF)Rear
EGT sensor
Differential pressure
sensorD20DTR ECUElectric throttle body
Page 350 of 828

15-470000-00
Diff. pres. sensor: Measure
pressure between front sid
e
and rear side of CDPF
ECU (DCM 3.7)
Injector: Control post
injection
D. Operation process
When the differential pressure sensor detects the pressure difference between the front and the
rear side of CDPF, the sensor sends signal indicating the soot is accumulated and the post
injection is performed to raise the temperature of exhaust gas. The amount of fuel injected is
determined according to the temperature of exhaust gas detected by the rear temperature sensor.
If the temperature is below 600°C, the amount of fuel injected is increased to raise the
<009b008c00940097008c00990088009b009c0099008c005500470070008d0047009b008f008c0047009b008c00940097008c00990088009b009c0099008c00470090009a00470096009d008c00990047005d0057005700b6006a00530047009b008f008c00
47008800940096009c0095009b00470096008d0047008d009c>el injected is decreased or not
controlled. When the engine is running in low load range, the amount of post injection and the
amount of intake air are controlled. It is to raise the temperature by increasing the amount of fuel
while decreasing the amount of intake air.
Front EGT sensor: Measure
DOC temp.
Rear EGT sensor: Measure
DPF temp.
Electronic throttle body
Control intake air mass
T-MAP sensor
Intake air
mass
Exceed PM
limitBooster
pressure/
temperaturePost injection
Control intake
air mass
Page 625 of 828

05-4
1. OVERVIEW
The propeller shaft transfers the power through the transmission and transfer case to the front/rear
axle differential carrier (final reduction gear).
It is manufactured by a thin rounded steel pipe to have the strong resisting force against the torsion
and bending.
Both ends of propeller shaft are connected to the spider and the center of propeller shaft is
connected to the spline to accommodate the changes of the height and length.
The rubber bushing that covers the intermediate bearing keeps the balance of rear propeller shaft
and absorbs its vibration.
Function of propeller shaft ▶
Transmits driving torque.
Compensates the angle change (universal joint / CV joint).
Compensates the axial length change (splines for the slip joint). -
-
-
Front propeller shaft
Rear propeller shaft
Page 652 of 828
09-4
2. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
1) Terms and Definition
CBS: Conventional Brake System
ABS: Anti-Lock Brake System
EBD: Electronic brake-Force Distribution
ESP: Electronic Stability Program
ABD: Automatic Braking Differential
ASR: Acceleration Slip Regulation
AYC: Active Yaw Control (Understeer and Oversteer Control)
HBA: Hydraulic Brake Assistant
ARP: Active Rollover Protection
HSA: Hill Start Assistant
Brake pad: Brake pad is a component of disk brakes used in automotive and other
applications. Brake pad is steel backing plates with friction material bound to the surface that
faces the brake disc.
Brake disc: The brake disc is a device for slowing or stopping the rotation of a wheel while it is
in motion.
Brake caliper: To stop the wheel, friction material in the form of brake pads (mounted on a
device called a brake caliper) is forced hydraulically against both sides of the disc. Friction
causes the disc and attached wheel to slow or stop.
Brake master cylinder: The brake master cylinder is a control device that converts non-
hydraulic pressure (commonly from a driver's foot) into hydraulic pressure, in order to move
other device(s) which are located at the other end of the hydraulic system, such as one or
more slave cylinders. As piston(s) move along the bore of the master cylinder, this movement
is transferred through the hydraulic fluid, to result in a movement of the slave cylinder(s). The
hydraulic pressure created by moving a piston (inside the bore of the master cylinder) toward
the slave cylinder(s) compresses the fluid evenly, but by varying the comparative surface-area
of the master cylinder and/or each slave cylinder, one will vary the amount of force and
displacement applied to each slave cylinder (relative to the amount of force and displacement
that was applied to the master cylinder). -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
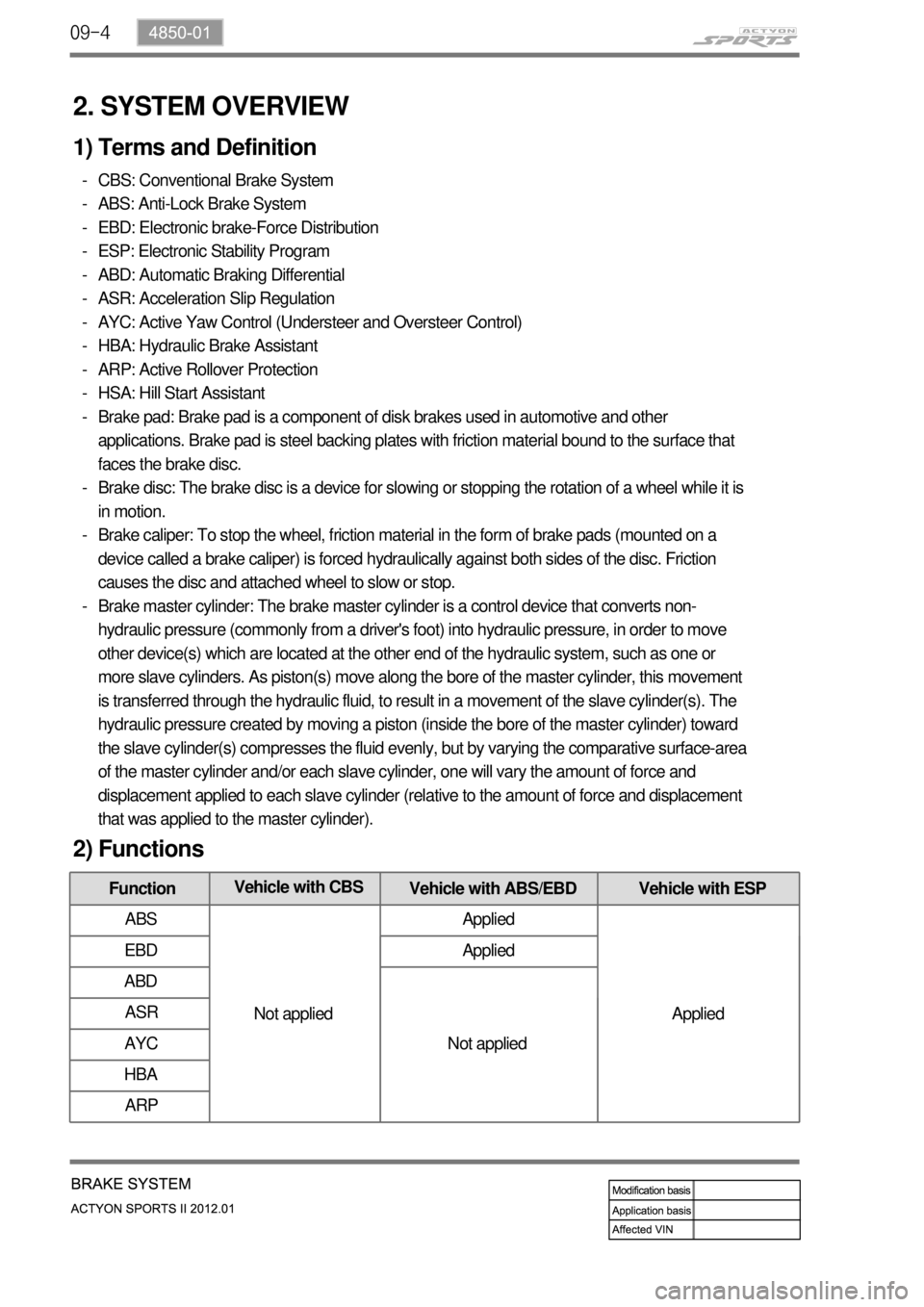
FunctionVehicle with CBS
Vehicle with ABS/EBD Vehicle with ESP
ABS
Not appliedApplied
Applied EBD Applied
ABD
Not applied ASR
AYC
HBA
ARP
2) Functions