change wheel SSANGYONG NEW ACTYON SPORTS 2013 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2013, Model line: NEW ACTYON SPORTS, Model: SSANGYONG NEW ACTYON SPORTS 2013Pages: 751, PDF Size: 72.63 MB
Page 530 of 751

07-53240-01
Operation ▶
Description Mode Conditions
Driving
mode2H 2 Wheel drive
(rear wheel)Rear-wheel drive mode. This is used under
normal or high-speed driving conditions on
public roads or highways.
4H 4 Wheel drive
(high speed)This is used under sandy, muddy or snow-
covered road conditions
4L 4 Wheel drive
(low speed)This is used for maximum traction.
When cornering with low speed in 4WD
condition, there could be tire dragging, some
mechanical shocks and resistances in
vehicle’s drive train. These are normal
conditions due to internal resistance in the drive
train when the 4WD system is properly working
Mode change2H←4H2 Wheel drive
↔4 Wheel driveShifting is possible while driving at the speed of
70 km/h or less
2H,
4H↔4L2 Wheel drive,
4 Wheel drive (high
speed)
↔4 Wheel drive
(low speed)For Automatic Transmission:
For Manual Transmission:
Stop the vehicle on level ground and
move the gear selector lever into the
“N” position. Turn the switch to the
desired position. ·
Stop the vehicle on level ground and
move the gear selector lever into the
“N” position. Then turn the switch to
the desired position while depressing the
clutch pedal. ·
To make the mode change easily, stop the
vehicle on level ground and turn the mode
switch to the desired position and move the
shift lever to "N"-"R"-"N" while depressing
the brake pedal.
Page 598 of 751

10-18
4) ABS Control Pattern
The ABS control is performed by comparing the reference speed with each wheel speed. Firstly, it is
determined whether the vehicle is in the deceleration or acceleration state using the wheel speed
change ratio. Then, a signal is transmitted to the valve.
Finally, the brake pressure is adjusted via the signal.
△V: Vehicle speed
Vref: Vehicle speed reference
Vw: Wheel speed
Page 607 of 751

11-54890-10
2. MAJOR CHANGES
Steering wheel angle sensor
<00540047007a009b008c008c009900900095008e0047009e008f008c008c0093004700880095008e0093008c0047009a008c0095009a0096009902c5009a0047008800970097008c0088009900880095008a008c004700880095008b0047009e0090009900
900095008e004700990096009c009b008c0047008a008f0088>nged
Page 612 of 751

11-10
3. FUNCTION
1) Term Definition
ABS: Anti-Lock Brake System ▶
When the brake pedal is abruptly depressed, the HECU calculates the slip ratio of each wheel based on
information received from the wheel speed sensors and controls the hydraulic module data quickly and
precisely in order to maintain the friction between the road surface and tire optimal (static friction).
Therefore, by keeping the friction between the road surface and tire optimal, it is possible to obtain
following effects: Enhanced steering stability, improved direction stability, reduced stopping distance and
etc.
EBD: Electronic brake-Force Distribution ▶
This is to detect the tire speed from the wheel speed sensor in order to supply the braking pressure to
the rear tires individually. In other words, the HECU measures the tire deceleration speed continuously
and controls the rear inlet valve on the hydraulic modulator to obtain optimal braking force as much as
possible. Thereby, stopping distance, braking effect and straight stability are improved.
ESP: Electronic Stability Program ▶
This is used to make the vehicle stabilized to recognize the emergency driving conditions, and to control
the brake for each wheels and the engine power when the brake system or acceleration will not work
any more in dangerous circumstances.
TCS: Traction Control System ▶
When the wheel is slipping due to an excessive engine torque while starting off or driving, this controls
the driving force (braking force + engine torque) in order to prevent the wheel from slipping through the
engine or brake control.
AYC: Active Yaw Control ▶
This has been developed to help a driver avoid danger of losing control of the vehicle stability due to
understeer or oversteer during cornering, which is a part of the ESP function.
HBA: Hydraulic Brake Assistant ▶
Developed based on the fact that elderly drivers depress the brake pedal too soft even when hard
braking is necessary, this an assist system to operate the HECU drive motor immediately and apply high
braking force to the wheels when the brake pedal is depressed softly and the vehicle should be braked
in emergency.
ARP: Active Rollover Protection ▶
This is a supplementary device for safety in ESP system and can help minimize the rollover accidents by
detecting a potential rollover situation through the brake and engine control when making sudden lane
change or turning sharply by adding only the software, without any separate device or switch.
Page 614 of 751

11-12
4. PRECAUTIONS
The warning lamp flashes and warning beep sounds when the ESP is operating
When the ESP operates during vehicle movement, the ESP warning lamp on the instrument panel
flashes and beep comes on every 0.1 second. The ESP system is only a supplementary device for
comfortable driving. When the vehicle exceeds its physical limits, it cannot be controlled.
Do not rely on the system. Keep on the safe driving.
Feeling when ESP is working
When the ESP system activates, the feeling can be different depending on vehicle driving
conditions.
For example, you will feel differently when the ESP system is activated during the ABS is operating
with the brakes applied and when the brakes are not applied on a curve.
If the ESP system operates when the brake is applied, the brake pressure will be increased on the
corresponding wheel which already has braking pressure for the ESP controls.
ARP Operation
During the ARP operation, vehicle safety (rollover prevention) takes the first priority and thus,
stronger engine control is in effect. Consequently, the vehicle speed decreases rapidly, so the driver
must take caution for the vehicle may drift away from the lane.
Noise and vibration that driver feels when ESP system is operating
The ESP system may transfer noise and vibration to the driver due to the pressure changes caused
by the motor and valve operations in a very short period of time. And, keep in mind that the output
and vehicle speed could be decreased without rpm increase due to the ASR function that controls
the engine power.
Page 621 of 751

11-194890-10
4) HBA (Hydraulic Brake Assist System)
(1) Purpose
HBA (Hydraulic Brake Assist) system helps in an emergency braking situation when the driver applies
the brake fast, but not with sufficient pressure, which leads to dangerously long braking distance. ECU
recognizes the attempt at full braking and transmits the signal calling for full brake pressure from the
hydraulic booster. An inexperienced, elderly or physically weak driver may suffer from the accident by not
fully pressing the brake pedal when hard braking is required under emergency. The HBA System
increases the braking force under urgent situations to enhance the inputted braking force from the driver.
Based on the fact that some drivers depress the brake pedal too soft even under when hard braking is
necessary, the HECU system is a safety supplementary system that builds high braking force during
initial braking according to pressure value of the brake pressure sensor and the pressure changes of the
pressure sensor intervals. When the system is designed to apply high braking force when brake pedal is
depressed softly by an elderly or physically weak driver, the vehicle will make abrupt stopping under
normal braking situation due to high braking pressure at each wheels.
(2) Operation
The brake pressure value and the changed value of the pressure sensor are the conditions in which the
HBA System operates. There are 2 pressure sensors under the master cylinder. When the ESP ECU
system determines that emergency braking is present, the pump operates, the brake fluid in the master
cylinder is sent to the pump and the braking pressure is delivered to the wheels via the inlet valves . If the
drive depress the brake pedal slowly, the pressure change is not high. In this case, only the conventional
brake system with booster is activated.
(3) Operating conditions
Sensor pressure: over 40 bar
Pressure changes: over 850 bar/sec
Vehicle speed: over 30 km/h -
-
-
Page 622 of 751
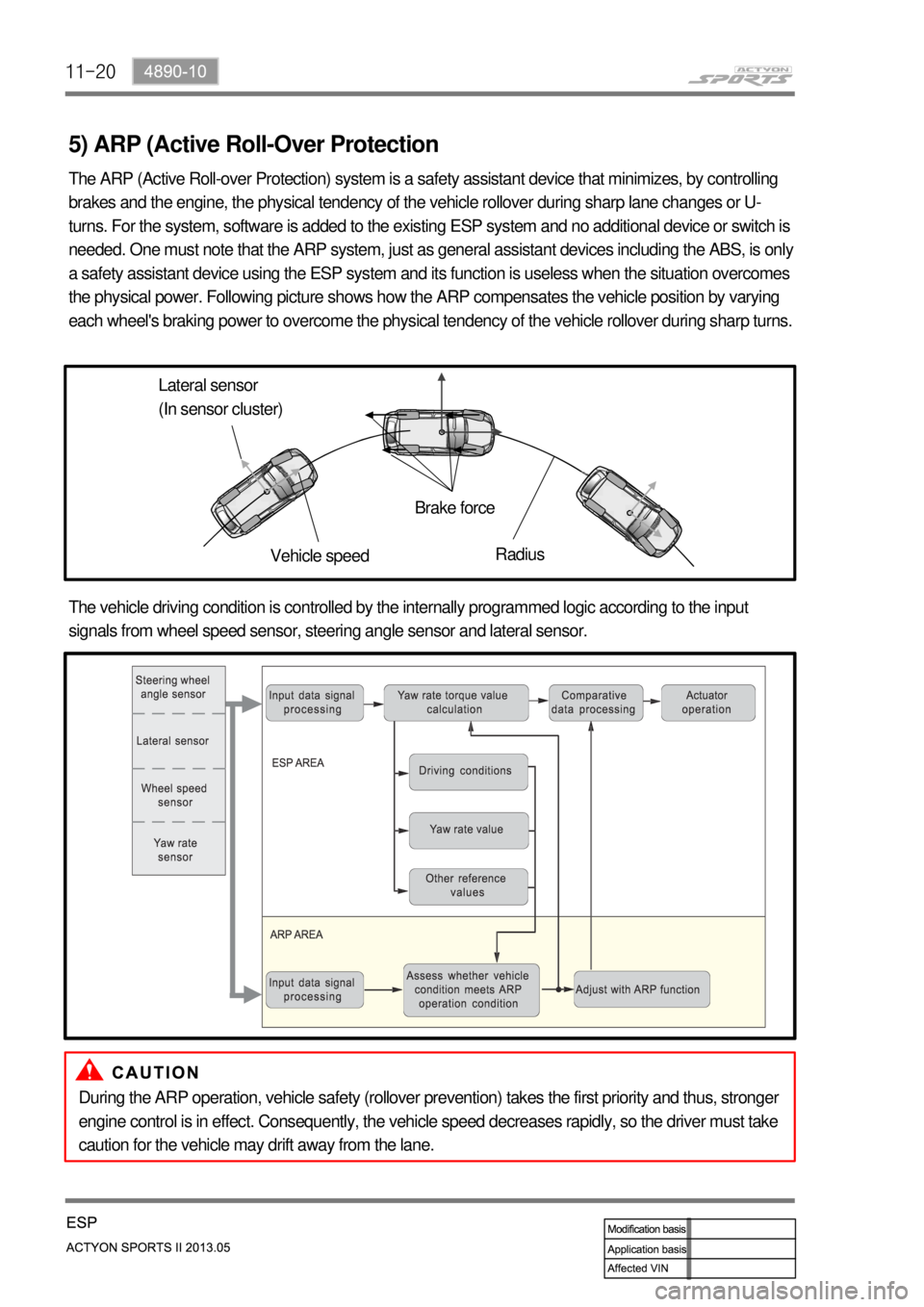
11-20
5) ARP (Active Roll-Over Protection
The ARP (Active Roll-over Protection) system is a safety assistant device that minimizes, by controlling
brakes and the engine, the physical tendency of the vehicle rollover during sharp lane changes or U-
turns. For the system, software is added to the existing ESP system and no additional device or switch is
needed. One must note that the ARP system, just as general assistant devices including the ABS, is only
a safety assistant device using the ESP system and its function is useless when the situation overcomes
the physical power. Following picture shows how the ARP compensates the vehicle position by varying
each wheel's braking power to overcome the physical tendency of the vehicle rollover during sharp turns.
Lateral sensor
(In sensor cluster)
Vehicle speedBrake force
Radius
The vehicle driving condition is controlled by the internally programmed logic according to the input
signals from wheel speed sensor, steering angle sensor and lateral sensor.
During the ARP operation, vehicle safety (rollover prevention) takes the first priority and thus, stronger
engine control is in effect. Consequently, the vehicle speed decreases rapidly, so the driver must take
caution for the vehicle may drift away from the lane.
Page 624 of 751

11-22
Circuit description ▶
When compared to the vehicle equipped with ABS/EBD only, the internal hydraulic circuit has a
normally-open separation valve and a shuttle valve in primary circuit and in secondary circuit.
When the vehicle brakes are not applied during engine running or when applying the non-ABS operating
brakes, the normally-open separation valve and the inlet valve are open, whereas the normally-closed
shuttle valve and the outlet valve are closed.
When the ESP system is operating, the normally-open separation valve will be closed by the solenoid
valve operation and the hydraulic circuit will be established by the shuttle valve. Then, the inlet and outlet
valves will be closed or open depending on the braking pressure RISE, HOLD or DUMP conditions.
Flashing warning lamp and warning sound during ESP operation ▶
When the ESP operates while the vehicle is moving, the ESP warning lamp on the instrument panel
flickers and the buzzer sounds at every 0.1 second. The ESP lamp operation is to inform a driver that the
vehicle is extremely unstable.
The ESP system is just a supplementary system for the vehicle and it cannot control the vehicle over the
physical limit. Do not solely rely on the system but be advised to drive the vehicle safely.
Drive feeling during ESP operation ▶
When the ESP system activates, the driving feeling can be different depending on vehicle driving
conditions. For example, it will feel different when the ESP system is activated while the ABS is operated
by depressing the brake pedal and when the ESP system is in control without the brake pedal
depressed on the same curve.
If the ESP system operates with the brake applied, the brake pressure will be increased on the
corresponding wheel which already has braking pressure for the ESP controls. In other words, the ESP
system would make the driver feel more abruptly braked compared to the situation that the braking
pressure is applied to wheel which had no braking force.
Noise and vibration that driver senses during ESP operation ▶
The ESP system may transfer noise and vibration to a driver due to the pressure changes caused by the
motor and valve operations in a very short period of time.
Extreme cornering will trigger the ESP operation and this will make the driver sense noise and vibration
due to sudden brake application.
Also, the ESP system controls the engine power. Therefore, the driver may notice the engine power
decreases even when the accelerator pedal is depressed.
Page 629 of 751

11-274890-10
5) Hydraulic Circuit of HBA
The above figure shows one front and one rear wheel and the same hydraulic circuit forms as in the
ESP operation. When HECU recognizes that it is an emergency and it is required for hard braking,
depending on the pressure value of the brake pressure sensor and pressure changes caused by the
pressure sensor timing, it operates the pump immediately to apply the brake pressure at the wheels.
Then, the pressure in the pump increases until just before the corresponding wheel gets locked. The
motor still keeps rotating and the outlet valve and the separation valve will stay closed. When the wheel
starts to lock, the HBA function cancels and switches to ABS operation.
Page 637 of 751

12-8
Change of Steering Wheel & Steering Column Shaft ▶
Appearance of steering wheel boss part changed
Steering wheel assembly boss part