EGR SSANGYONG TURISMO 2013 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2013, Model line: TURISMO, Model: SSANGYONG TURISMO 2013Pages: 796, PDF Size: 78.99 MB
Page 333 of 796
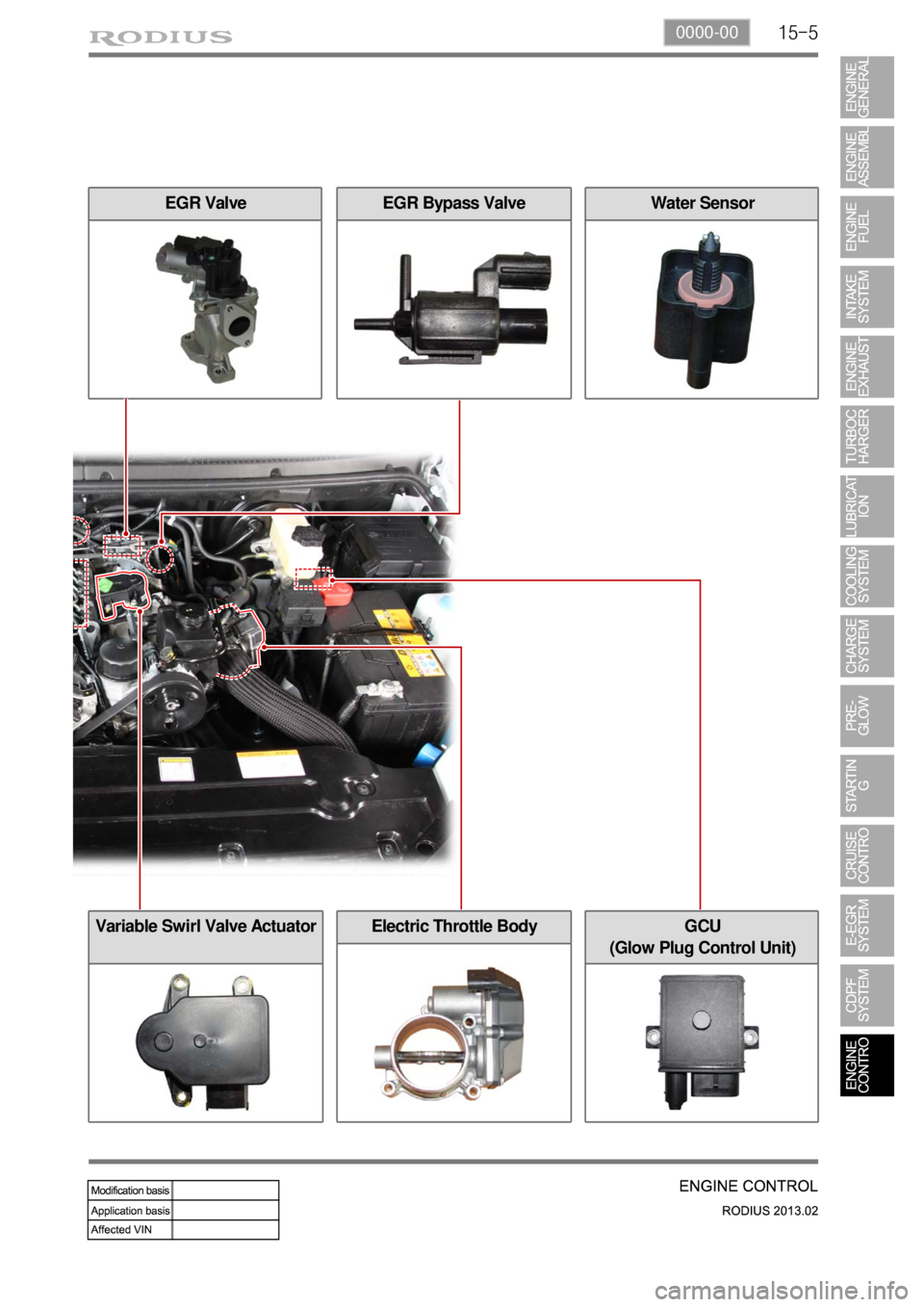
15-50000-00
GCU
(Glow Plug Control Unit)
EGR Bypass ValveEGR Valve
Electric Throttle Body
Water Sensor
Variable Swirl Valve Actuator
Page 337 of 796
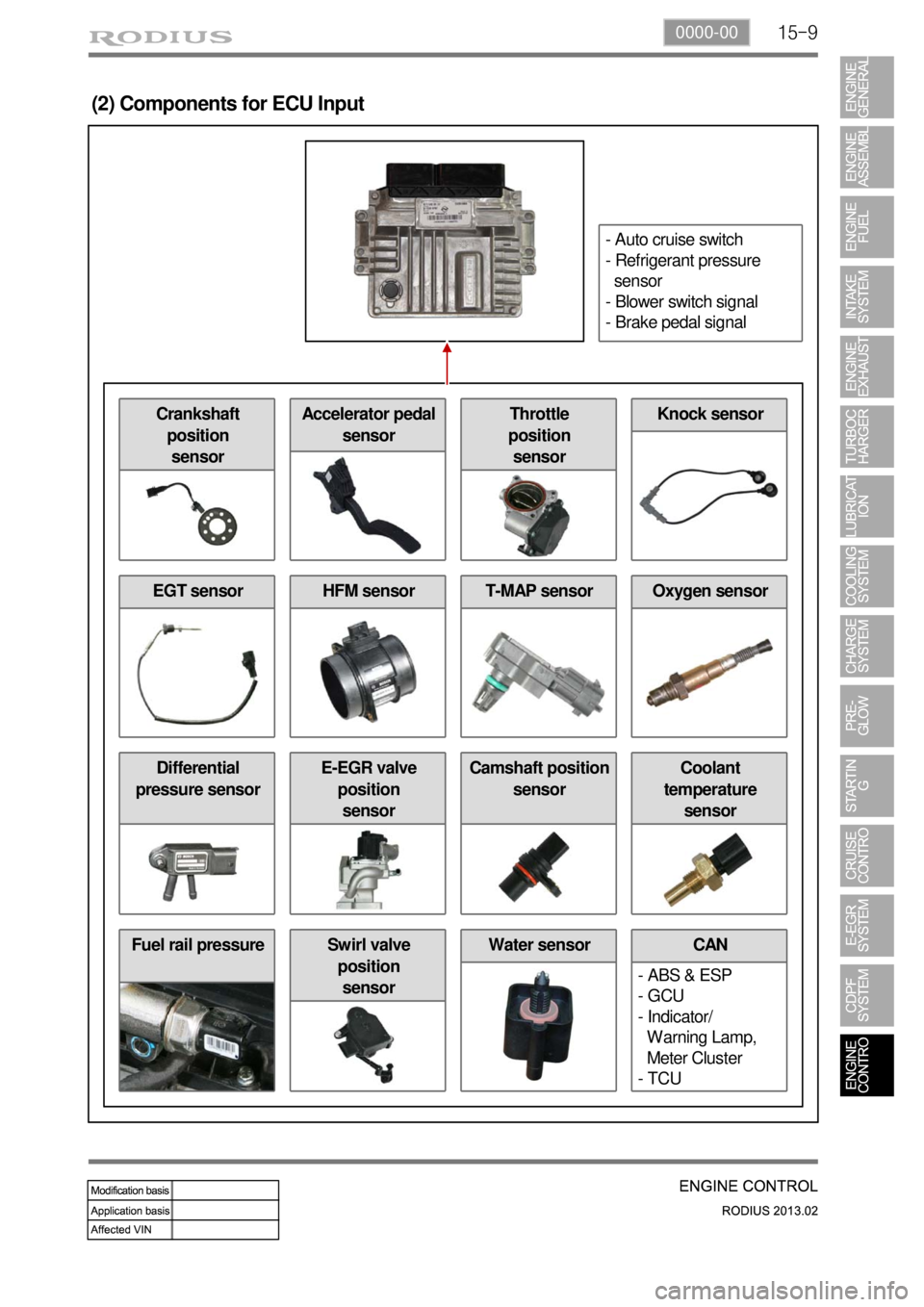
15-90000-00
Fuel rail pressure Water sensor
(2) Components for ECU Input
CAN
- ABS & ESP
- GCU
- Indicator/
Warning Lamp,
Meter Cluster
- TCUSwirl valve
position
sensor
Differential
pressure sensorE-EGR valve
position
sensorCamshaft position
sensorCoolant
temperature
sensor
EGT sensorHFM sensorOxygen sensorT-MAP sensor
Crankshaft
position
sensorAccelerator pedal
sensorThrottle
position
sensorKnock sensor
- Auto cruise switch
- Refrigerant pressure
sensor
- Blower switch signal
- Brake pedal signal
Page 338 of 796
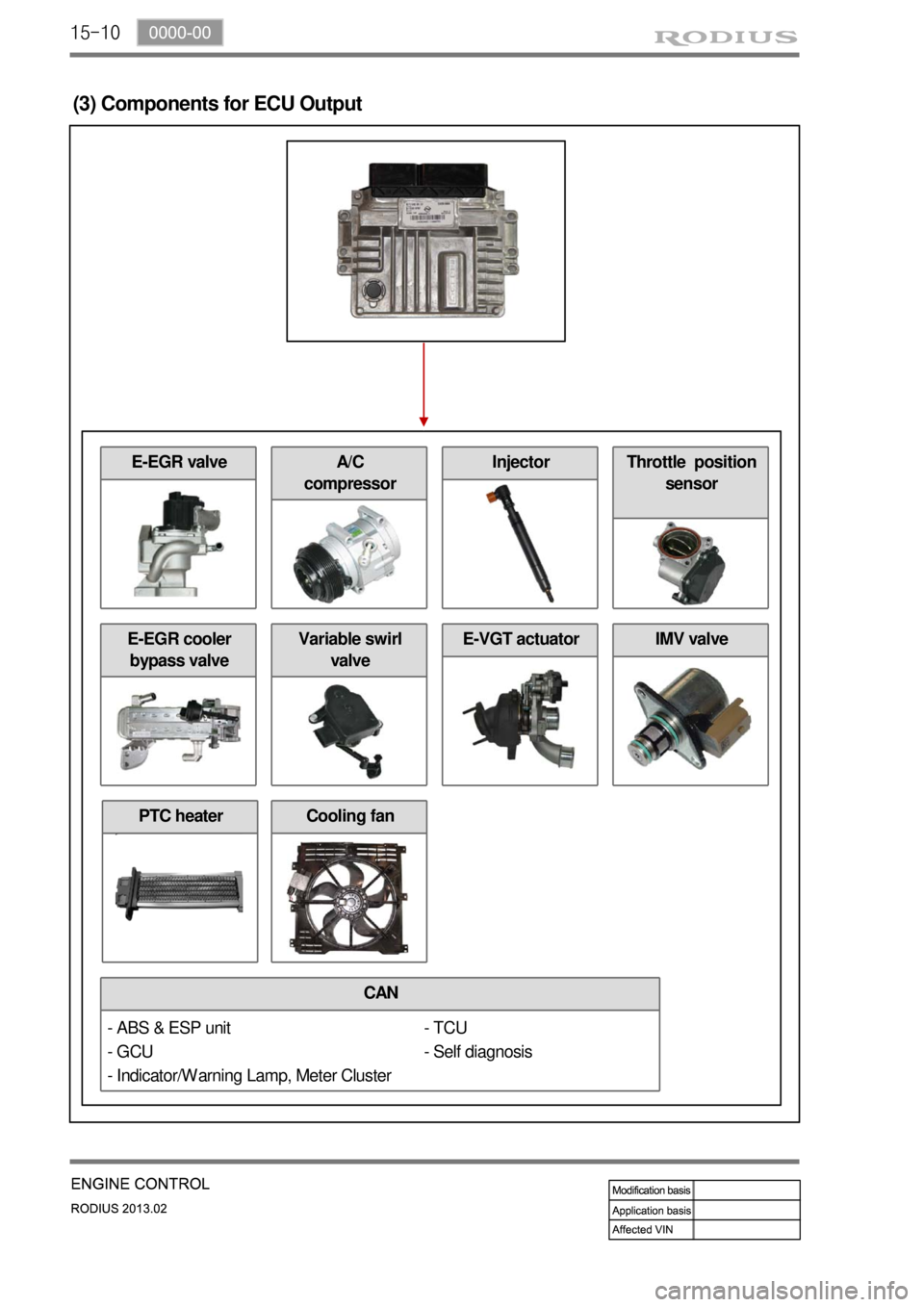
15-10
(3) Components for ECU Output
CAN
E-EGR cooler
bypass valve
- TCU
- Self diagnosis
Cooling fan
E-EGR valve
Variable swirl
valveE-VGT actuatorIMV valve
A/C
compressorInjectorThrottle position
sensor
- ABS & ESP unit
- GCU
- Indicator/Warning Lamp, Meter Cluster
PTC heater
Page 339 of 796

15-110000-00
2) ECU Control
(1) Function
a. ECU Function
ECU receives and analyzes signals from various sensors and then modifies those signals into
permissible voltage levels and analyzes to control respective actuators.
ECU microprocessor calculates injection period and injection timing proper for engine piston speed
and crankshaft angle based on input data and stored specific map to control the engine power and
emission gas.
Output signal of the ECU microprocessor drives pressure control valve to control the rail pressure and
activates injector solenoid valve to control the fuel injection period and injection timing; so controls
various actuators in response to engine changes. Auxiliary function of ECU has adopted to reduce
emission gas, improve fuel economy and enhance safety, comforts and conveniences. For example,
there are EGR, booster pressure control, autocruise (export only) and immobilizer and adopted CAN
communication to exchange data among electrical systems (automatic T/M and brake system) in the
vehicle fluently. And Scanner can be used to diagnose vehicle status and defectives.
Operating temperature range of ECU is normally -40 to +85°C and protected from factors like
oil, water and electromagnetism and there should be no mechanical shocks.
To control the fuel volume precisely under repeated injections, high current should be applied instantly
so there is injector drive circuit in the ECU to generate necessary current during injector drive stages.
Current control circuit divides current applying time (injection time) into full-in-current-phase and hold-
current-phase and then the injectors should work very correctly under every working condition.
b. Control Function
Controls by operating stages
To make optimum combustion under every operating stage, ECU should calculate proper injection
volume in each stage by considering various factors.
Starting injection volume control
During initial starting, injecting fuel volume will be calculated by function of temperature and engine
cranking speed. Starting injection continues from when the ignition switch is turned to ignition
position to till the engine reaches to allowable minimum speed.
Driving mode control
If the vehicle runs normally, fuel injection volume will be calculated by accelerator pedal travel and
engine rpm and the drive map will be used to match the drivers inputs with optimum engine power. -
-
-
Page 343 of 796

15-150000-00
(3) Fuel Pressure Control
Fuel pressure is controlled by IMV opening according to the calculated value by ECU.
Pressure in the fuel rail is determined according to engine speed and load on the engine. ▶
When engine speed and load are high
The degree of turbulence is very great and the fuel can be injected at very high pressure in order to
optimize combustion.
When engine speed and load are low
The degree of turbulence is low. If injection pressure is too high, the nozzle's penetration will be
excessive and part of the fuel will be sprayed directly onto the sides of the cylinder, causing
incomplete combustion. So there occurs smoke and damages engine durability. -
-
Fuel pressure is corrected according to air temperature, coolant temperature and atmospheric
pressure and to take account of the added ignition time caused by cold running or by high altitude
driving. A special pressure demand is necessary in order to obtain the additional flow required during
starts. This demand is determined according to injected fuel and coolant temperature.
Open loop determines the current which needs to be sent to the actuator in order to obtain
the flow demanded by the ECU. ▶
Closed loop will correct the current value depending on the difference between the pressure
demand and the pressure measured. ▶
If the pressure is lower than the demand, current is reduced so that the fuel sent to the high
pressure pump is increased.
If the pressure is higher than the demand, current is increased so that the fuel sent to the high
pressure pump is reduced. -
-Fuel Pressure ▶
Page 344 of 796

15-16
Pilot injection timing control ▶
The pilot injection timing is determined as a function of the engine speed and of the total flow.
The elements are:
A first correction is made according to the air and coolant temperatures. This correction allows the
pilot injection timing to be adapted to the operating temperature of the engine.
A second correction is made according to the atmospheric pressure. This correction is used to
adapt the pilot injection timing as a function of the atmospheric pressure and therefore the altitude. -
-
(4) Injection Timing Control
Injection timing is determined by the conditions below. ▶
Coolant temperature
Hot engine - Retarded to reduce Nox
Cold engine - Advanced to optimize the combustion 1.
Atmospheric pressure
Advanced according to the altitude 2.
Warming up
Advanced during warming up in cold engine 3.
Rail pressure
Retarded to prevent knocking when the rail pressure is high 4.
EEGR ratio
Advanced to decrease the cylinder temperature when EGR ratio increases 5.
Main injection timing control ▶
The pulse necessary for the main injection is determined as a function of the engine speed and of the
injected flow.
The elements are:
A first correction is made according to the air and coolant temperatures.
This correction makes it possible to adapt the timing to the operating temperature of the engine.
When the engine is warm, the timing can be retarded to reduce the combustion temperature and
polluting emissions (NOx). When the engine is cold, the timing advance must be sufficient to allow
the combustion to begin correctly.
A second correction is made according to the atmospheric pressure.
This correction is used to adapt the timing advance as a function of the atmospheric pressure and
therefore the altitude.
A third correction is made according to the coolant temperature and the time which has passed
since starting.
This correction allows the injection timing advance to be increased while the engine is warming up
(initial 30 seconds). The purpose of this correction is to reduce the misfiring and instabilities which
are liable to occur after a cold start. -
-
-
Page 345 of 796

15-170000-00
A fourth correction is made according to the pressure error.
This correction is used to reduce the injection timing advance when the pressure in the rail is higher
than the pressure demand.
A fifth correction is made according to the rate of EGR.
This correction is used to correct the injection timing advance as a function of the rate of exhaust
gas recirculation. -
-
When the EGR rate increases, the injection timing advance must in fact be increased in order to
compensate for the fall in termperature in the cylinder.
A. Main Flow Control
The main flow represents the amount of fuel injected into the cylinder during the main injection. The
pilot flow represents the amount of fuel injected during the pilot injection.
The total fuel injected during 1 cycle (main flow + pilot flow) is determined in the following manner.
When the driver depress the pedal, it is his demand which is taken into account by the system in
order to determine the fuel injected.
When the driver release the pedal, the idle speed controller takes over to determine the minimum
fuel which must be injected into the cylinder to prevent the enigne from stalling. -
-
The driver demand is the translation of the pedal position into the fuel demand. It is calculated as a
function of the pedal position and of the engine speed. The driver demand is filtered in order to limit the
hesitations caused by rapid changes of the pedal position. A mapping determines the maximum fuel
which can be injected as a function of the driver demand and the rail pressure. Since the flow is
proportional to the injection time and to the square root of the injection pressure, it is necessary to limit
the flow according to the pressure in order to avoid extending the injection for too long into the engine
cycle. The system compares the driver demand with this limit and chooses the smaller of the 2 values.
The driver demand is then corrected according to the coolant temperature. This correction is added to
the driver demand.
(5) Fuel Control
B. Driver Demand
Page 351 of 796

15-230000-00
This is done periodically under certain operating conditions. When the resetting is finished, the new
minimum pulse value replaces the value obtained during the previous resetting. The first MDP value is
provided by the C3I. Each resetting then allows the closed loop of the MDP to be updated according to
the deviation of the injector.
B. Detection of leaks in the cylinders
The accelerometer is also used to detect any injector which may have stuck open. The detection
principle is based on monitoring the ratio. If there is a leak in the cylinder, the accumulated fuel self-
ignites as soon as the temperature and pressure conditions are favorable (high engine speed, high
load and small leak).
This combustion is set off at about 20 degrees before TDC and before main injection.
The ratio therefore increases considerably in the detection window. It is this increase which allows the
leaks to be detected. The threshold beyond which a fault is signaled is a percentage of the maximum
possible value of the ratio.
Because of the severity of the recovery process (engine shut-down), the etection must be extremely
robust.
An increase in the ratio can be the consequence of various causes:
Pilot injection too much
Main combustion offset
Fuel leak in the cylinder -
-
-
If the ratio becomes too high, the strategy initially restricts the pilot injection flow and retards the main
injection. If the ratio remains high despite these interventions, this shows that a real leak is present, a
fault is signaled and the engine is shut down.
C. Detection of an accelerometer fault
This strategy permits the detection of a fault in the sensor or in the wiring loom connecting the sensor
to the ECU.
It is based on detection of the combustion. When the engine is idling, the detection window is set too
low for the combustion caused by the main injection. If the ratio increases, this shows that the knock
sensor is working properly, but otherwise a fault is signaled to indicate a sensor failure. The recovery
modes associated with this fault consist of inhibition of the pilot injection and discharge through the
injectors.
Page 352 of 796
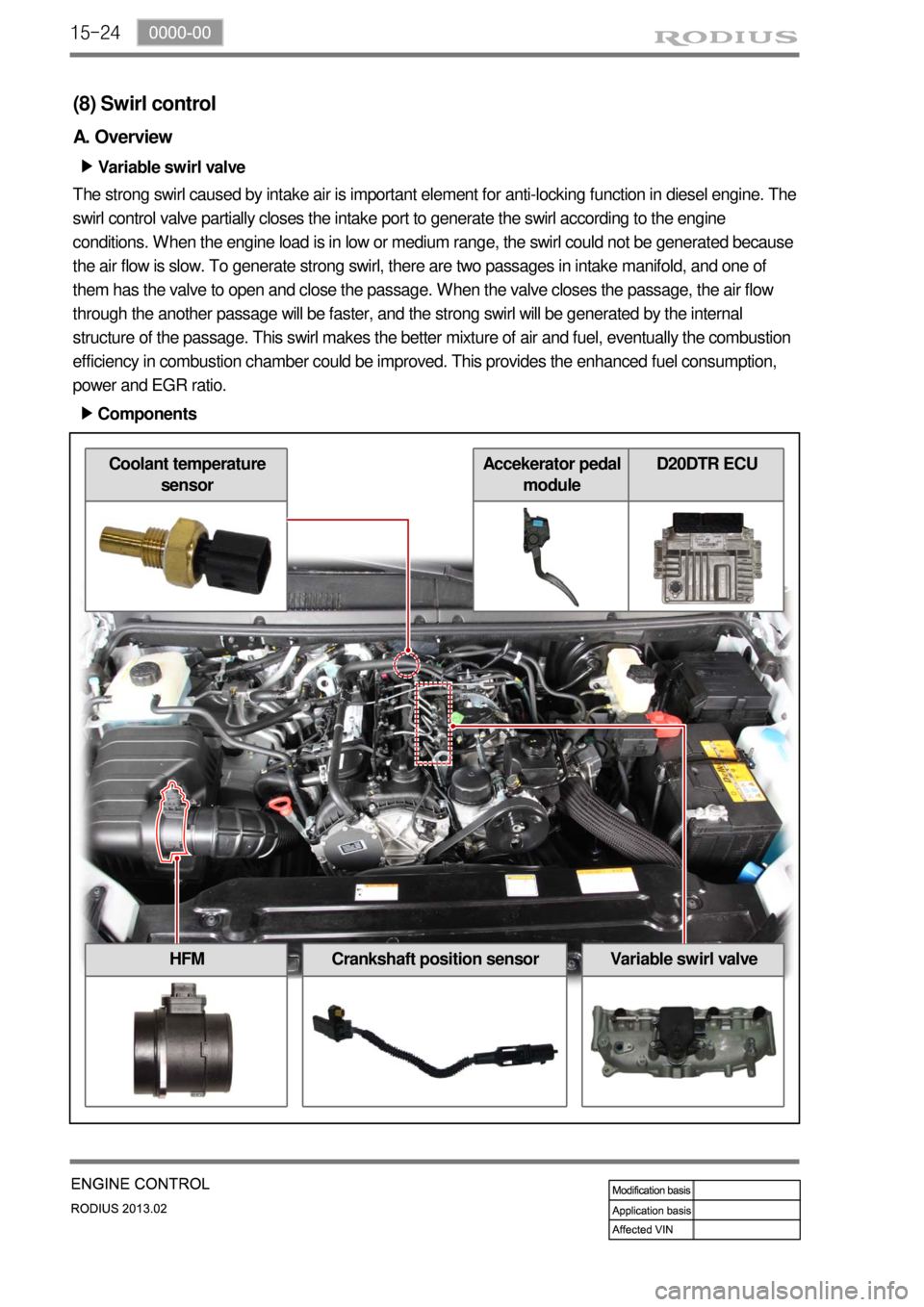
15-24
(8) Swirl control
A. Overview
Variable swirl valve ▶
The strong swirl caused by intake air is important element for anti-locking function in diesel engine. The
swirl control valve partially closes the intake port to generate the swirl according to the engine
conditions. When the engine load is in low or medium range, the swirl could not be generated because
the air flow is slow. To generate strong swirl, there are two passages in intake manifold, and one of
them has the valve to open and close the passage. When the valve closes the passage, the air flow
through the another passage will be faster, and the strong swirl will be generated by the internal
structure of the passage. This swirl makes the better mixture of air and fuel, eventually the combustion
efficiency in combustion chamber could be improved. This provides the enhanced fuel consumption,
power and EGR ratio.
Components ▶
HFMCrankshaft position sensorVariable swirl valve
Coolant temperature
sensorAccekerator pedal
moduleD20DTR ECU
Page 354 of 796

15-26
C. Types of swirl
Swirl: One cylinder has two intake air ports, one is set horizontally and
the other one is set vertically. Swirl is the horizontal air flows in
cylinder due to the horizontal intake air ports.
Tumble: Tumble is the vertical air flows in cylinder due to the vertical
intake air port
Squish is the air flow at end of compression process according to the
design of piston head. In this DI engine, the squish is generated to
bowl type.
D. Swirl control
In DI type diesel engine, the liquefied fuel is injected into the cylinder directly. If the fuel is evenly
distributed in short period, the combustion efficiency could be improved. To get this, there should be
good air flow in cylinder. In general, there are two intake ports, swirl port and tangential port, in each
cylinder. The swirl port generates the horizontal flow and the tangential port generates the longitudinal
flow. In low/mid load range, the tabgential port is closed to increase the horizontal flow. Fast flow
decreases the PM during combustion and increases the EGR ratio by better combustion efficiency.