steering SSANGYONG TURISMO 2013 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2013, Model line: TURISMO, Model: SSANGYONG TURISMO 2013Pages: 796, PDF Size: 78.99 MB
Page 652 of 796
09-6
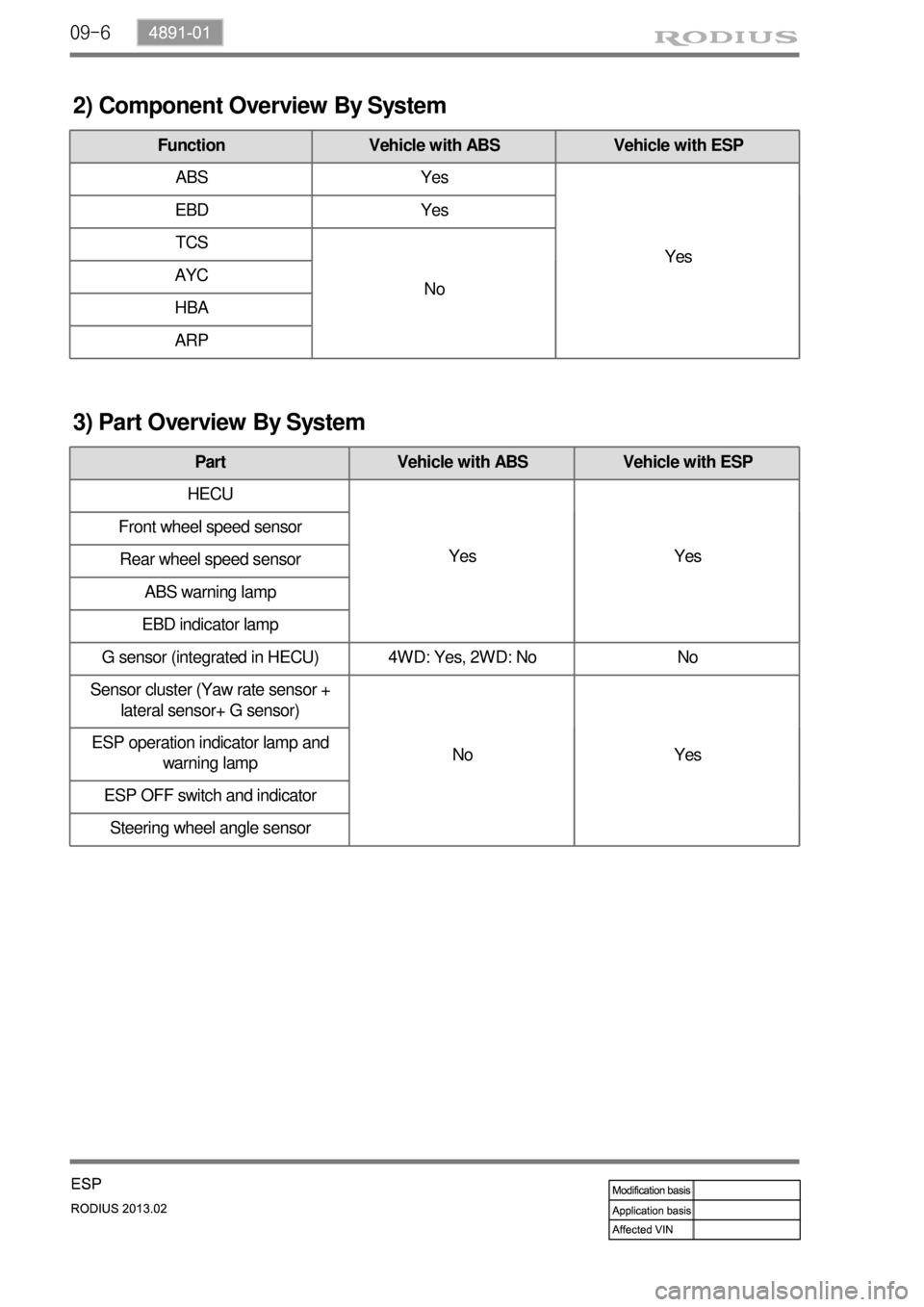
2) Component Overview By System
Function Vehicle with ABS Vehicle with ESP
ABS Yes
Yes EBD Yes
TCS
No AYC
HBA
ARP
3) Part Overview By System
Part Vehicle with ABS Vehicle with ESP
HECU
Yes Yes Front wheel speed sensor
Rear wheel speed sensor
ABS warning lamp
EBD indicator lamp
G sensor (integrated in HECU) 4WD: Yes, 2WD: No No
Sensor cluster (Yaw rate sensor +
lateral sensor+ G sensor)
No Yes ESP operation indicator lamp and
warning lamp
ESP OFF switch and indicator
Steering wheel angle sensor
Page 654 of 796

09-8
Steering wheel angle sensor
Appearance change due to changed multifunction switch
4. CHANGES IN ESP
Steering wheel angle sensor changed ▶
Wheel speed sensor changed ▶
Wheel speed sensor
Front Rear Front Rear
Connector's appearance and length changed
Sensor cluster changed ▶
Sensor cluster
Appearance and its connector (6-pin → 4-pin) changed
Page 657 of 796
09-114891-01
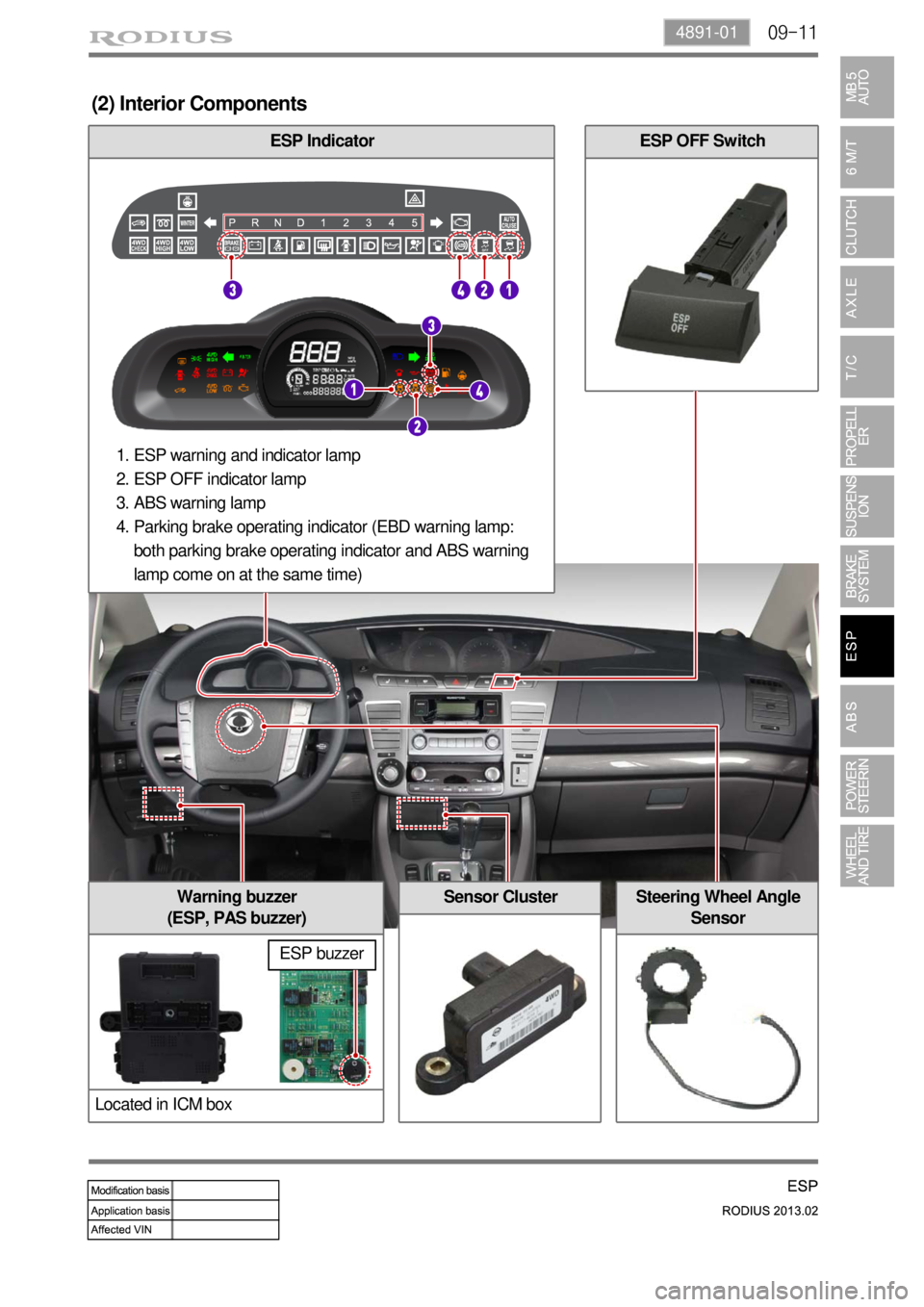
(2) Interior Components
ESP Indicator
Sensor Cluster
ESP OFF Switch
Steering Wheel Angle
SensorWarning buzzer
(ESP, PAS buzzer)
Located in ICM box
ESP warning and indicator lamp
ESP OFF indicator lamp
ABS warning lamp
Parking brake operating indicator (EBD warning lamp:
both parking brake operating indicator and ABS warning
lamp come on at the same time) 1.
2.
3.
4.
ESP buzzer
Page 659 of 796

09-134891-01
2) Operation of ESP System
(1) Under steering
What is understeering? ▶
ESP controls during understeer ▶ Understeer is a term for a condition in which the steering wheel is steered to a certain angle during
driving and the front tires slip toward the reverse direction of the desired direction. Generally, vehicles
are designed to have understeer. It is because that the vehicle can return back to inside of cornering
line when the steering wheel is steered toward the inside even when the front wheels are slipped
outward.
As the centrifugal force increases, the tires can easily lose the traction and the vehicle tends to slip
outward when the curve angle gets bigger and the speed increases.
The ESP system recognizes the directional angle with the steering wheel angle sensor and senses the
slipping route that occurs reversely against the vehicle cornering direction during understeer with the
yaw rate sensor and lateral sensor. Then, the ESP system applies the braking force to the rear inner
wheel to compensate the yaw moment value. In this way, the vehicle does not lose its driving direction
and the driver can steer the vehicle as intended.
Page 660 of 796

09-14
(2) Over steering
What is oversteering? ▶
ESP controls during oversteer ▶ Oversteer is a term of a condition in which the steering wheel is steered to a certain angle during
driving and the rear tires slip outward losing traction.
Compared to understeering vehicles, it is hard to control the vehicle during cornering and the vehicle
can spin due to rear wheel moment when the rear tires lose traction and the vehicle speed increases.
The ESP system recognizes the directional angle with the steering wheel angle sensor and senses the
slipping route that occurs towards the vehicle cornering direction during oversteer with the yaw rate
sensor and lateral sensor. Then the ESP system applies the braking force to the front outer wheel to
compensate the yaw moment value. In this way, the vehicle does not lose its driving direction and the
driver can steer the vehicle as intended.
Page 661 of 796
09-154891-01
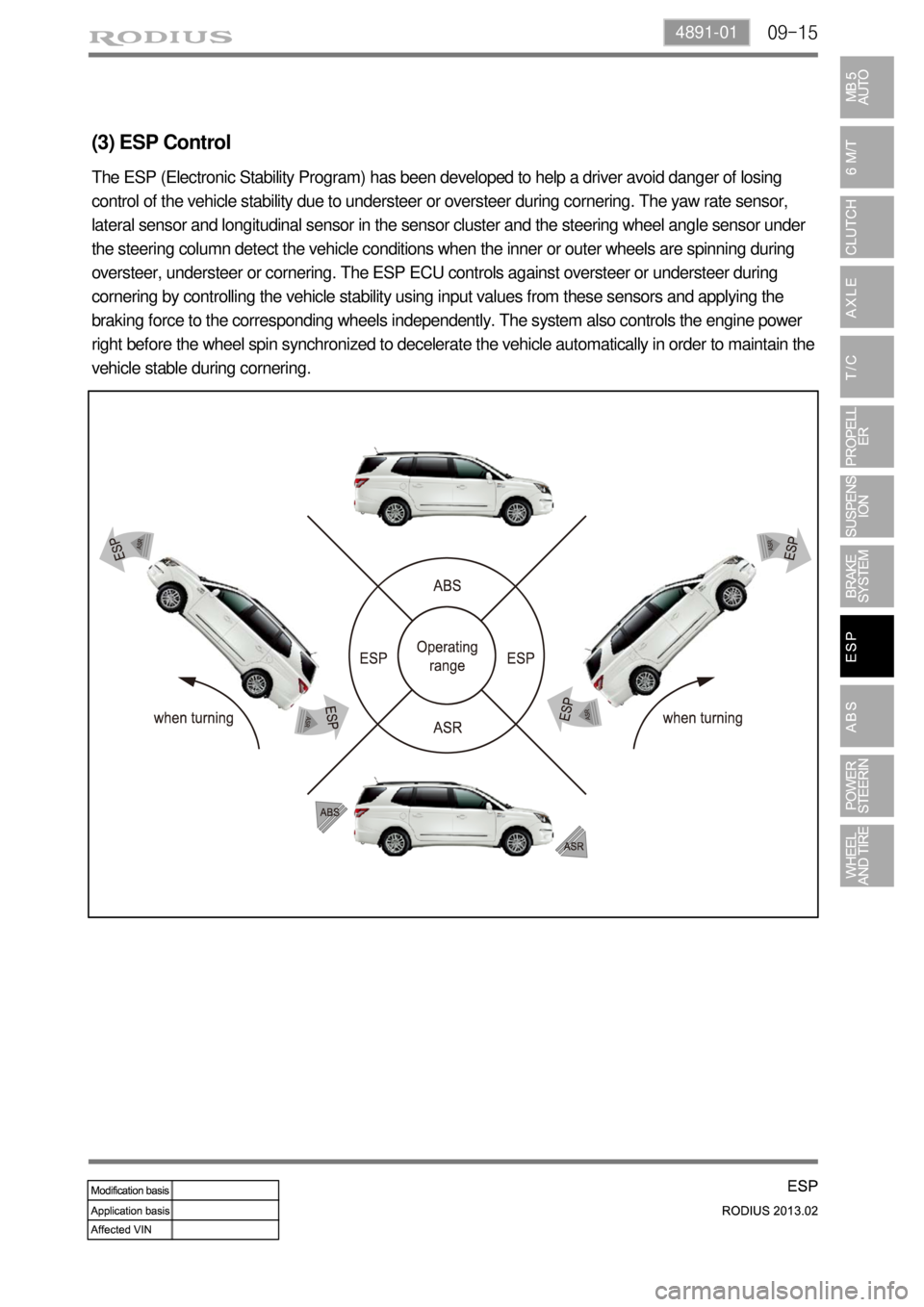
(3) ESP Control
The ESP (Electronic Stability Program) has been developed to help a driver avoid danger of losing
control of the vehicle stability due to understeer or oversteer during cornering. The yaw rate sensor,
lateral sensor and longitudinal sensor in the sensor cluster and the steering wheel angle sensor under
the steering column detect the vehicle conditions when the inner or outer wheels are spinning during
oversteer, understeer or cornering. The ESP ECU controls against oversteer or understeer during
cornering by controlling the vehicle stability using input values from these sensors and applying the
braking force to the corresponding wheels independently. The system also controls the engine power
right before the wheel spin synchronized to decelerate the vehicle automatically in order to maintain the
vehicle stable during cornering.
Page 665 of 796
09-194891-01
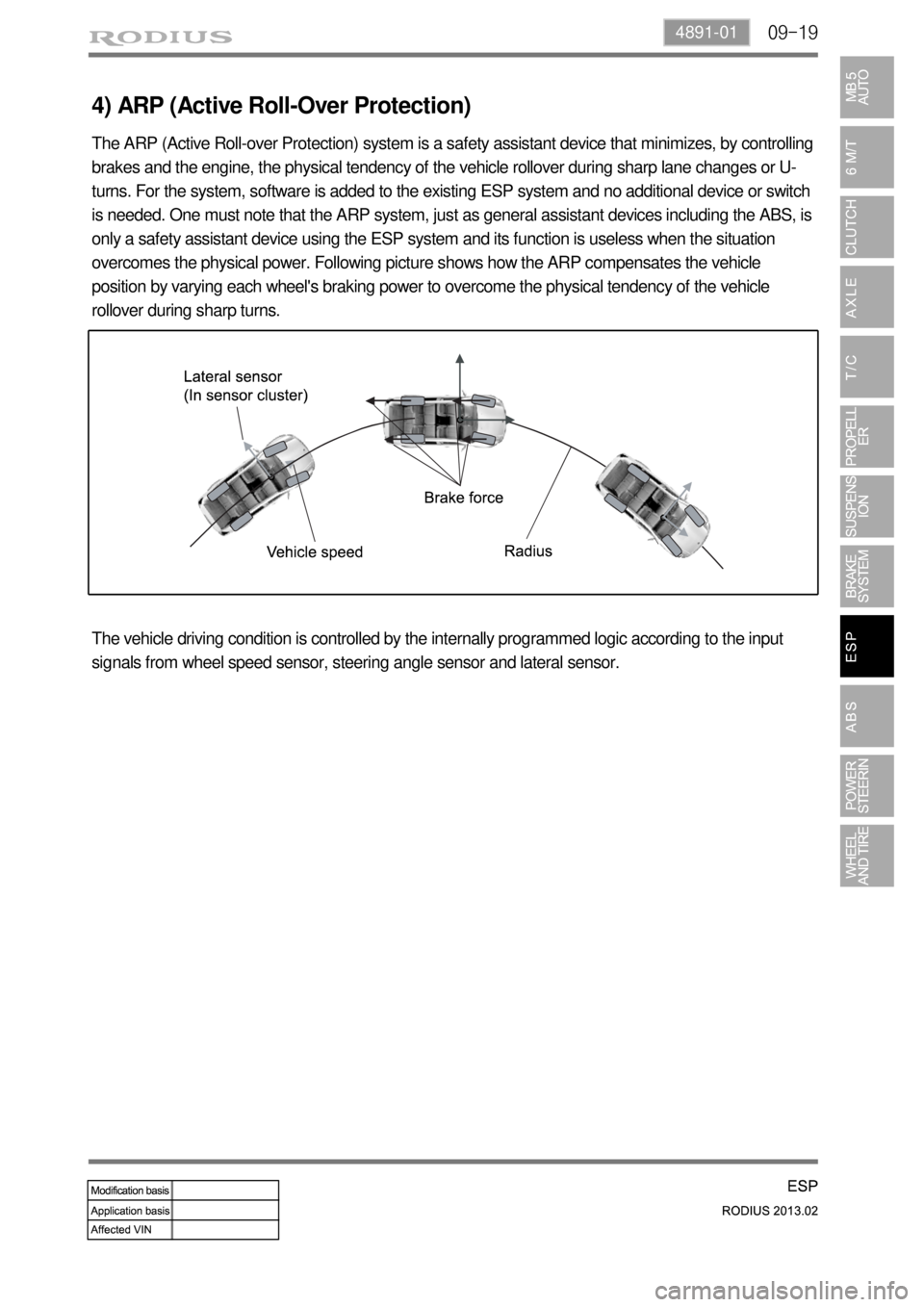
4) ARP (Active Roll-Over Protection)
The ARP (Active Roll-over Protection) system is a safety assistant device that minimizes, by controlling
brakes and the engine, the physical tendency of the vehicle rollover during sharp lane changes or U-
turns. For the system, software is added to the existing ESP system and no additional device or switch
is needed. One must note that the ARP system, just as general assistant devices including the ABS, is
only a safety assistant device using the ESP system and its function is useless when the situation
overcomes the physical power. Following picture shows how the ARP compensates the vehicle
position by varying each wheel's braking power to overcome the physical tendency of the vehicle
rollover during sharp turns.
The vehicle driving condition is controlled by the internally programmed logic according to the input
signals from wheel speed sensor, steering angle sensor and lateral sensor.
Page 676 of 796

10-34891-01
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
When braking suddenly or braking on slippery roads, the vehicle keeps moving forward but the wheels
are locking and not rotating. If these happen, the vehicle may lose stability or rotate resulting in an
accident. ABS helps to maintain directional stability and control of the vehicle. ABS is designed to
secure more safety and increase the control of steering wheel during emergency braking situation.
But, ABS does not guarantee perfect safety beyond its physical limit. ABS in this vehicle contains EBD
function. In normal driving conditions, the brake system operates without ABS function.
1) Basic Theory of ABS Function
To give you a better understanding of the tasks and functions of ABS, we will first look at the physics
principles.
▶Stopping distance
The stopping distance depends on the vehicle weight and initial speed when braking starts. This also
applies for vehicle with ABS, where ABS always tries to set an optimum brake force on each wheel. As
great forces are exerted between the tires and the carriageway when braking, even with ABS the
wheels may scream and rubber is left on the road. With an ABS skid mark one may be able to clearly
recognize the tire profile. The skid mark of an ABS vehicle does not however leave any hint of the
speed of the vehicle in the case of an accident, as it can only be clearly drawn at the start of braking.
▶Brake force on a wheel
The maximum possible brake force on a wheel depends on the wheel load and the adhesion
coefficient between tire and carriageway. With a low adhesion coefficient the brake force, which can be
obtained is very low. You are bound to know the result already from driving on winter roads. With a
high adhesion coefficient on a dry road, the brake force, which can be obtained, is considerably higher.
The brake force, which can be obtained, can be calculated from below formula:
Page 685 of 796
11-34610-00
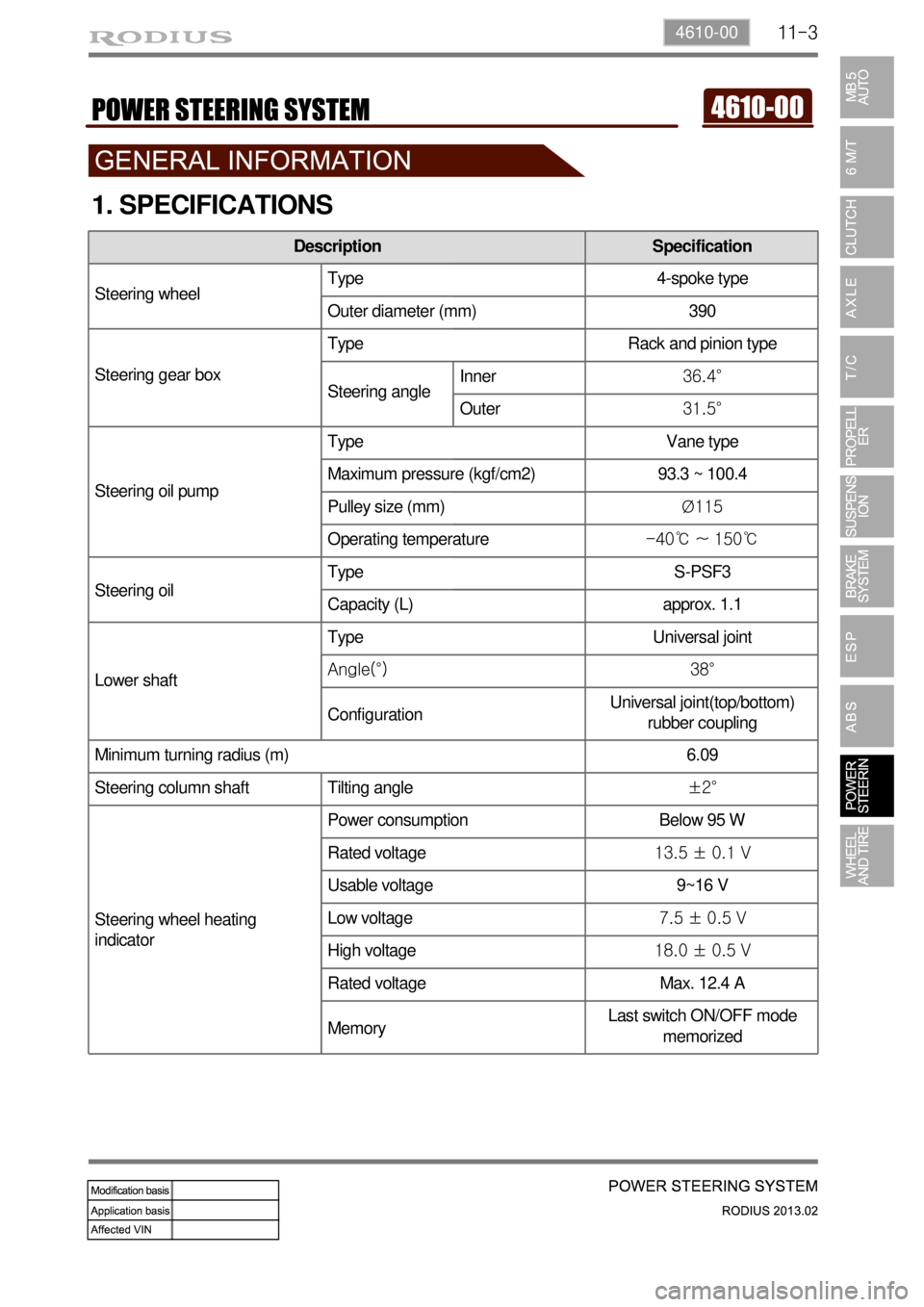
1. SPECIFICATIONS
Description Specification
Steering wheelType 4-spoke type
Outer diameter (mm) 390
Steering gear boxType Rack and pinion type
Steering angleInner36.4°
Outer31.5°
Steering oil pumpType Vane type
Maximum pressure (kgf/cm2) 93.3 ~ 100.4
Pulley size (mm)Ø115
Operating temperature-40℃ ~ 150℃
Steering oilType S-PSF3
Capacity (L) approx. 1.1
Lower shaftType Universal joint
Angle(°) 38°
ConfigurationUniversal joint(top/bottom)
rubber coupling
Minimum turning radius (m) 6.09
Steering column shaft Tilting angle±2°
Steering wheel heating
indicatorPower consumption Below 95 W
Rated voltage13.5 ± 0.1 V
Usable voltage 9~16 V
Low voltage7.5 ± 0.5 V
High voltage18.0 ± 0.5 V
Rated voltage Max. 12.4 A
MemoryLast switch ON/OFF mode
memorized
Page 686 of 796

11-4
Steering column shaft assembly
Steering column shat assembly mounting bracket changed due to change of multifunction switch
Steering wheel body and heating system
Heating controller added due to newly adopted steering wheel heating system
2. CHANGES IN STEERING SYSTEM
Steering wheel heating switch
Heated wire used in steering wheel switch
(option)
Heating controller
Mounting bracket