ESP SUBARU FORESTER 2004 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUBARU, Model Year: 2004, Model line: FORESTER, Model: SUBARU FORESTER 2004Pages: 2870, PDF Size: 38.67 MB
Page 1428 of 2870
FU(H4DOTC)-73
FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM)
Fuel System Trouble in General
34.Fuel System Trouble in General
A: INSPECTION
NOTE:
When the vehicle is left unattended for an ex-
tended period of time, water may accumulate in the
fuel tank.
To prevent water condensation.
(1) Top off the fuel tank or drain the fuel com-
pletely.
(2) Drain the water condensation from the fuel
filter.
Refilling the fuel tank.
Refill the fuel tank while there is still some fuel left in
the tank.
Protecting the fuel system against freezing and
water condensation.
Cold areas
In snow-covered areas, mountainous areas, skiing
areas, etc. where ambient temperatures drop be-
low 0°C (32°F) throughout the winter season, use
an anti-freeze solution in the fuel tank. Refueling
will also complement the effect of anti-freeze solu-
tion each time the fuel level drops to about one-half. After the winter season, drain the water which
may have accumulated in the fuel filter and fuel
tank in the manner same as that described under
Affected areas below.
Affected areas
When the water condensation is notched in the fuel
filter, drain the water from both the fuel filter and
fuel tank or use a water removing agent (or anti-
freeze solution) in the fuel tank.
Observe the instructions, notes, etc., indicated
on the label affixed to the anti-freeze solution (wa-
ter removing agent) container before use.
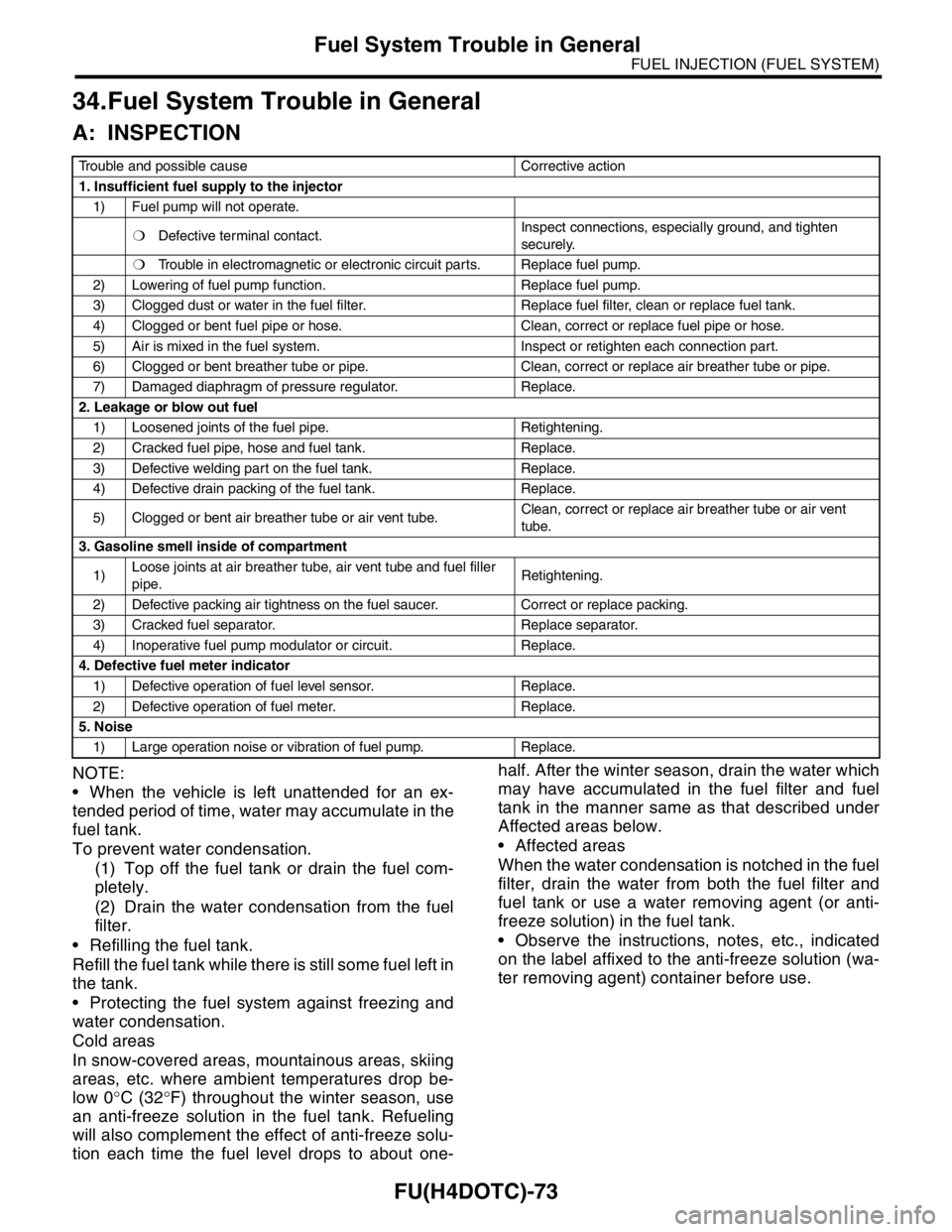
Trouble and possible cause Corrective action
1. Insufficient fuel supply to the injector
1) Fuel pump will not operate.
❍Defective terminal contact.Inspect connections, especially ground, and tighten
securely.
❍Trouble in electromagnetic or electronic circuit parts. Replace fuel pump.
2) Lowering of fuel pump function. Replace fuel pump.
3) Clogged dust or water in the fuel filter. Replace fuel filter, clean or replace fuel tank.
4) Clogged or bent fuel pipe or hose. Clean, correct or replace fuel pipe or hose.
5) Air is mixed in the fuel system. Inspect or retighten each connection part.
6) Clogged or bent breather tube or pipe. Clean, correct or replace air breather tube or pipe.
7) Damaged diaphragm of pressure regulator. Replace.
2. Leakage or blow out fuel
1) Loosened joints of the fuel pipe. Retightening.
2) Cracked fuel pipe, hose and fuel tank. Replace.
3) Defective welding part on the fuel tank. Replace.
4) Defective drain packing of the fuel tank. Replace.
5) Clogged or bent air breather tube or air vent tube.Clean, correct or replace air breather tube or air vent
tube.
3. Gasoline smell inside of compartment
1)Loose joints at air breather tube, air vent tube and fuel filler
pipe.Retightening.
2) Defective packing air tightness on the fuel saucer. Correct or replace packing.
3) Cracked fuel separator. Replace separator.
4) Inoperative fuel pump modulator or circuit. Replace.
4. Defective fuel meter indicator
1) Defective operation of fuel level sensor. Replace.
2) Defective operation of fuel meter. Replace.
5. Noise
1) Large operation noise or vibration of fuel pump. Replace.
Page 1494 of 2870
ME(H4DOTC)-38
MECHANICAL
Valve Clearance
(5) Move the washer tank upward.
(6) Disconnect the ignition coil connector.
(7) Remove the ignition coil.
(8) Place a suitable container under the vehicle.
(9) Disconnect the PCV hose from rocker cover
(LH).
(10)Remove the bolts, and then remove the
rocker cover (LH).
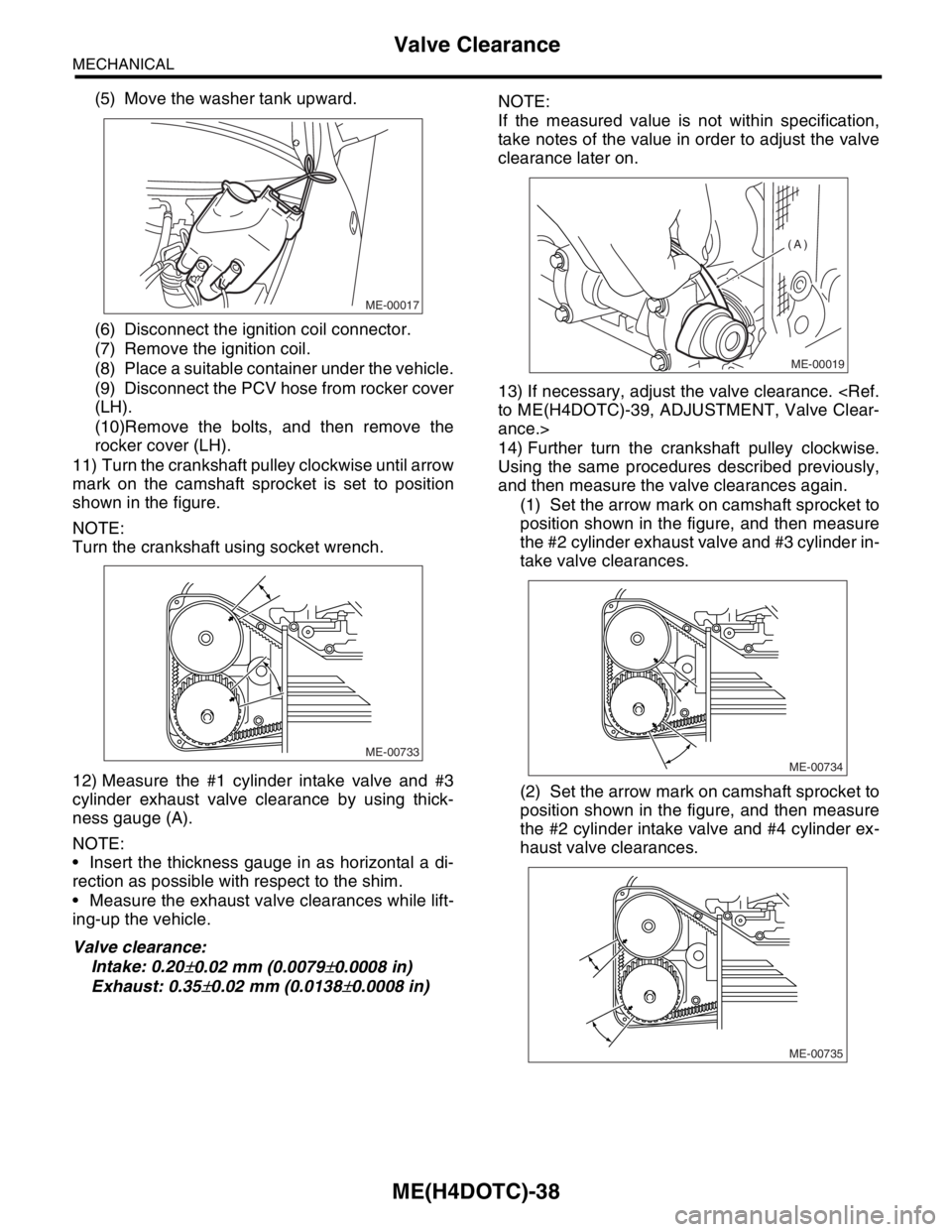
11) Turn the crankshaft pulley clockwise until arrow
mark on the camshaft sprocket is set to position
shown in the figure.
NOTE:
Turn the crankshaft using socket wrench.
12) Measure the #1 cylinder intake valve and #3
cylinder exhaust valve clearance by using thick-
ness gauge (A).
NOTE:
Insert the thickness gauge in as horizontal a di-
rection as possible with respect to the shim.
Measure the exhaust valve clearances while lift-
ing-up the vehicle.
Valve clearance:
Intake: 0.20
±0.02 mm (0.0079±0.0008 in)
Exhaust: 0.35
±0.02 mm (0.0138±0.0008 in)NOTE:
If the measured value is not within specification,
take notes of the value in order to adjust the valve
clearance later on.
13) If necessary, adjust the valve clearance.
ance.>
14) Further turn the crankshaft pulley clockwise.
Using the same procedures described previously,
and then measure the valve clearances again.
(1) Set the arrow mark on camshaft sprocket to
position shown in the figure, and then measure
the #2 cylinder exhaust valve and #3 cylinder in-
take valve clearances.
(2) Set the arrow mark on camshaft sprocket to
position shown in the figure, and then measure
the #2 cylinder intake valve and #4 cylinder ex-
haust valve clearances.
ME-00017
ME-00733
ME-00019
(A)
ME-00734
ME-00735
Page 1537 of 2870
ME(H4DOTC)-79
MECHANICAL
Cylinder Head Assembly
3. VALVE GUIDE
1) Check the clearance between valve guide and
stem. The clearance can be checked by measuring
the outside diameter of valve stem and the inside
diameter of valve guide with outside and inside mi-
crometers respectively.
Clearance between the valve guide and valve
stem:
Standard
Intake
0.030 — 0.057 mm (0.0012 — 0.0022 in)
Exhaust
0.040 — 0.067 mm (0.0016 — 0.0026 in)
Limit
0.15 mm (0.0059 in)
2) If the clearance between valve guide and stem
exceeds the limit, replace the valve guide or valve
itself whichever shows greater amount of wear.
See the following procedure for valve guide re-
placement.
Valve guide inner diameter:
6.000 — 6.012 mm (0.2362 — 0.2367 in)
Valve stem outer diameters:
Intake
5.955 — 5.970 mm (0.2344 — 0.2350 in)
Exhaust
5.945 — 5.960 mm (0.2341 — 0.2346 in)
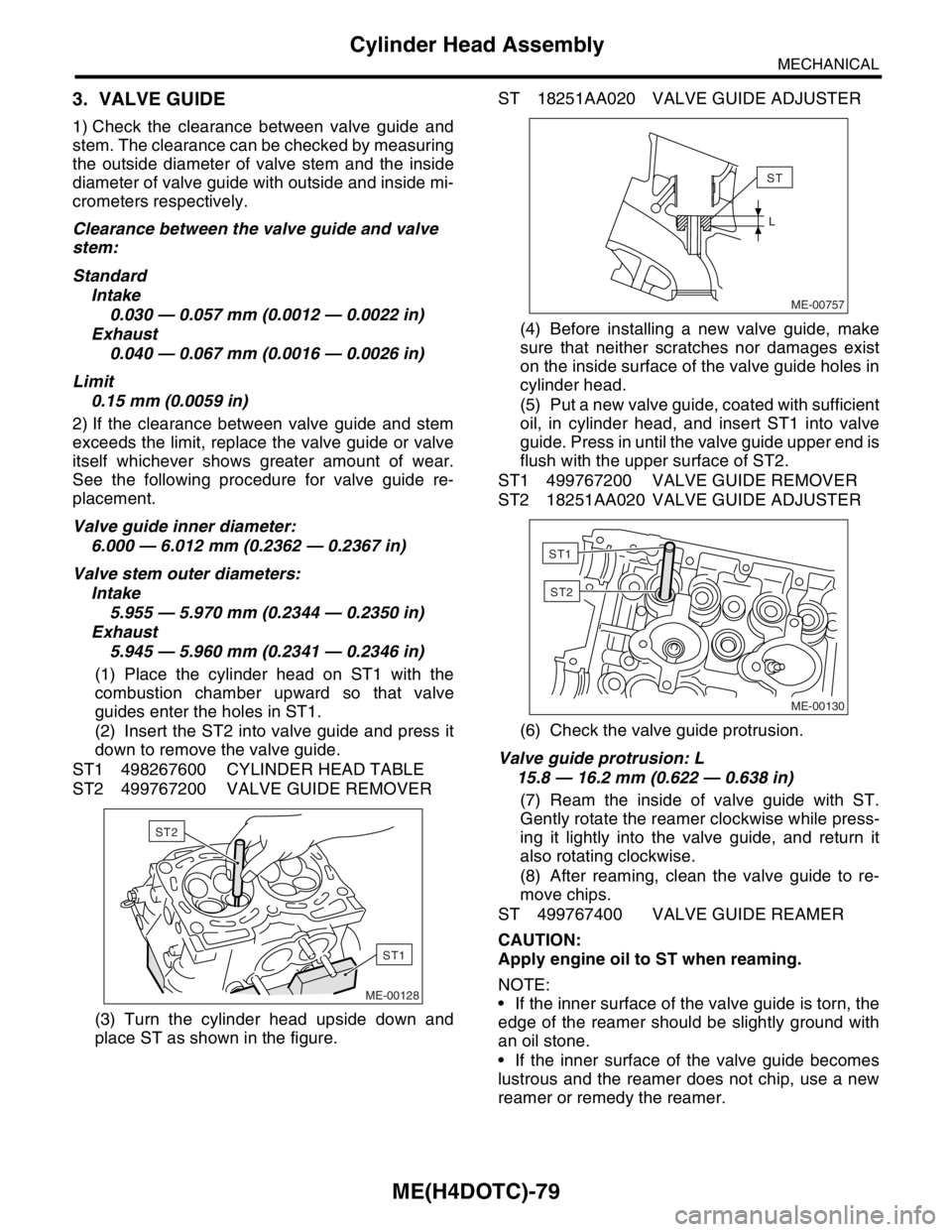
(1) Place the cylinder head on ST1 with the
combustion chamber upward so that valve
guides enter the holes in ST1.
(2) Insert the ST2 into valve guide and press it
down to remove the valve guide.
ST1 498267600 CYLINDER HEAD TABLE
ST2 499767200 VALVE GUIDE REMOVER
(3) Turn the cylinder head upside down and
place ST as shown in the figure.ST 18251AA020 VALVE GUIDE ADJUSTER
(4) Before installing a new valve guide, make
sure that neither scratches nor damages exist
on the inside surface of the valve guide holes in
cylinder head.
(5) Put a new valve guide, coated with sufficient
oil, in cylinder head, and insert ST1 into valve
guide. Press in until the valve guide upper end is
flush with the upper surface of ST2.
ST1 499767200 VALVE GUIDE REMOVER
ST2 18251AA020 VALVE GUIDE ADJUSTER
(6) Check the valve guide protrusion.
Valve guide protrusion: L
15.8 — 16.2 mm (0.622 — 0.638 in)
(7) Ream the inside of valve guide with ST.
Gently rotate the reamer clockwise while press-
ing it lightly into the valve guide, and return it
also rotating clockwise.
(8) After reaming, clean the valve guide to re-
move chips.
ST 499767400 VALVE GUIDE REAMER
CAUTION:
Apply engine oil to ST when reaming.
NOTE:
If the inner surface of the valve guide is torn, the
edge of the reamer should be slightly ground with
an oil stone.
If the inner surface of the valve guide becomes
lustrous and the reamer does not chip, use a new
reamer or remedy the reamer.
ME-00128
ST1
ST2ME-00757
ST
L
ME-00130
ST1
ST2
Page 1549 of 2870

ME(H4DOTC)-89
MECHANICAL
Cylinder Block
13) Position the expander gap at (C) in the figure.
14) Position the lower rail gap at (D) in the figure.
15) Align lower rail spin stopper (F) with piston side
surface hole (E).16) Position the upper rail gap at (G) in the figure.
NOTE:
Ensure ring gaps do not face the same direction.
Ensure ring gaps are not within the piston skirt
area.
17) Install the circlip.
Install the circlips in piston holes located opposite
of service holes in cylinder block, when positioning
all pistons in the corresponding cylinders.
ME-00718
(A)(B)
180
ME-00719
(C)
ME-00720
(D)
25
ME-00152
ME-00721
(G)
0 20
Page 1559 of 2870

ME(H4DOTC)-99
MECHANICAL
Cylinder Block
19) Install the circlip.
Install the circlips in piston holes located opposite
of service holes in cylinder block, when positioning
all pistons in the corresponding cylinders.NOTE:
Use new circlips.
20) Installing the piston:
(1) Turn the cylinder block so that #1 and #2 cyl-
inders face upward.
(2) Using the ST1, turn the crankshaft so that
#1 and #2 connecting rods are set at bottom
dead center.
ST1 499987500 CRANKSHAFT SOCKET(3) Apply a coat of engine oil to the pistons and
cylinders and insert pistons in their cylinders us-
ing ST2.
ST2 498747300 PISTON GUIDE
(A) Front side
ME-00154
#4 #3
#2 #1
(A)
(1) Piston (4) GasketTightening torque: N⋅m (kgf-m, ft-lb)
(2) Piston pin (5) Service hole plugT: 70 (7.1, 51.4)
(3) Circlip
ME-00155
(1) (1)
(2)
(2) (3)
(3) (4)
(4) (5)
(5)
T
ME-00157
ST2
ST1
Page 1565 of 2870
ME(H4DOTC)-105
MECHANICAL
Cylinder Block
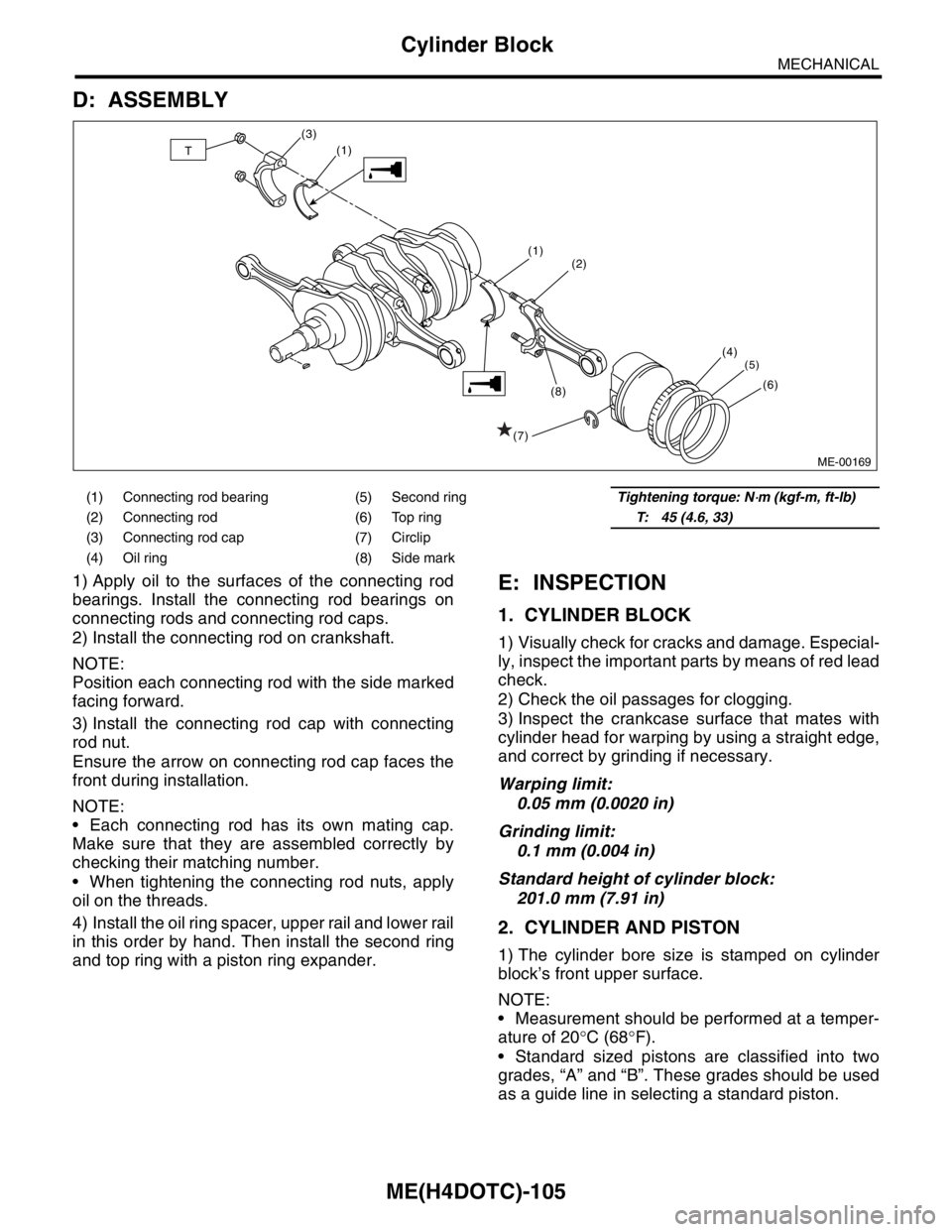
D: ASSEMBLY
1) Apply oil to the surfaces of the connecting rod
bearings. Install the connecting rod bearings on
connecting rods and connecting rod caps.
2) Install the connecting rod on crankshaft.
NOTE:
Position each connecting rod with the side marked
facing forward.
3) Install the connecting rod cap with connecting
rod nut.
Ensure the arrow on connecting rod cap faces the
front during installation.
NOTE:
Each connecting rod has its own mating cap.
Make sure that they are assembled correctly by
checking their matching number.
When tightening the connecting rod nuts, apply
oil on the threads.
4) Install the oil ring spacer, upper rail and lower rail
in this order by hand. Then install the second ring
and top ring with a piston ring expander.E: INSPECTION
1. CYLINDER BLOCK
1) Visually check for cracks and damage. Especial-
ly, inspect the important parts by means of red lead
check.
2) Check the oil passages for clogging.
3) Inspect the crankcase surface that mates with
cylinder head for warping by using a straight edge,
and correct by grinding if necessary.
Warping limit:
0.05 mm (0.0020 in)
Grinding limit:
0.1 mm (0.004 in)
Standard height of cylinder block:
201.0 mm (7.91 in)
2. CYLINDER AND PISTON
1) The cylinder bore size is stamped on cylinder
block’s front upper surface.
NOTE:
Measurement should be performed at a temper-
ature of 20°C (68°F).
Standard sized pistons are classified into two
grades, “A” and “B”. These grades should be used
as a guide line in selecting a standard piston.
(1) Connecting rod bearing (5) Second ringTightening torque: N⋅m (kgf-m, ft-lb)
(2) Connecting rod (6) Top ringT: 45 (4.6, 33)
(3) Connecting rod cap (7) Circlip
(4) Oil ring (8) Side mark
ME-00169
(2)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(1)
(1)
(7)(8) (3)T
Page 1675 of 2870

EN(H4DOTC)-45
ENGINE (DIAGNOSTIC)
Drive Cycle
13.Drive Cycle
A: OPERATION
There are three driving patterns on diagnosis.Following trouble can be diagnosed with driving specified pat-
terns.After repair the following trouble, be sure to check that the trouble is cleared correctly by the driving
specified patterns.
1. PREPARATION FOR DRIVE CYCLE
1) Check battery voltage is more than 12 V and fuel remains half [20 — 402 (5.3 — 10.6 US gal, 4.4 — 8.8
Imp gal)].
2) After performing the diagnostics and clearing the memory, check for any remaining unresolved trouble da-
ta.
3) Separate the test mode connector.
NOTE:
Be sure to perform the diagnosis after idling from starting the cooled engine except when the engine cool-
ant temperature is specified.
Perform the diagnosis twice when the DTC is marked * and after the completion of first diagnosis, stop the
engine and perform the second diagnosis in the same condition.
2. DRIVE THE VEHICLE 20 MINUTES AT THE SPEED OF 80 KM/H (50 MPH), AND THEN IDLE
THE ENGINE 1 MINUTE.
3. 10 MINUTES IDLING
NOTE:
Drive the vehicle more than 10 km/h (6 MPH) before diagnosis.
DTC Item On condition
*P0125 Insufficient Coolant Temperature For Closed Loop Fuel ControlEngine coolant temperature at
start is less than 20°C (68°F)
*P0133O
2 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
—
*P0420 Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) —
P0459 Evaporative Emission Control System Purge Control Valve Circuit High —
P0461 Fuel Level Sensor Circuit Range/Performance —
P0546 Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor Circuit High - Bank 1 —
P1312 Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor MalfunctionEngine coolant temperature at
start is less than 30°C (86°F)
DTC Item On condition
P0111 Intake Air Temperature Circuit Range/Performance —
P0464 Fuel Level Sensor Circuit Intermittent —
P0508 Idle Control System Circuit Low —
*P0483 Cooling Fan Rationality Check —
*P0506 Idle Control System RPM Lower Than Expected —
*P0507 Idle Control System RPM Higher Than Expected —
Page 1676 of 2870
EN(H4DOTC)-46
ENGINE (DIAGNOSTIC)
Drive Cycle
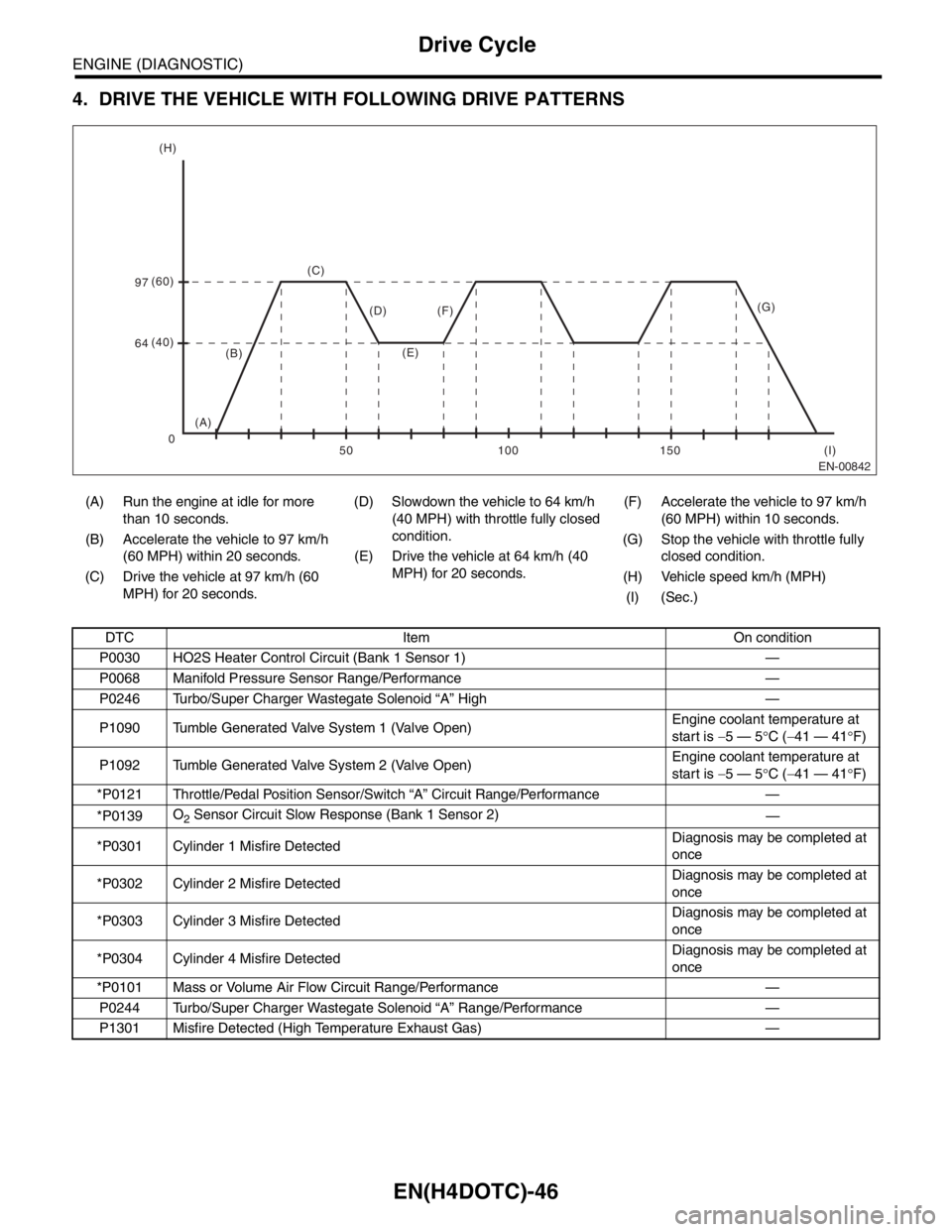
4. DRIVE THE VEHICLE WITH FOLLOWING DRIVE PATTERNS
(A) Run the engine at idle for more
than 10 seconds.(D) Slowdown the vehicle to 64 km/h
(40 MPH) with throttle fully closed
condition.(F) Accelerate the vehicle to 97 km/h
(60 MPH) within 10 seconds.
(B) Accelerate the vehicle to 97 km/h
(60 MPH) within 20 seconds.(G) Stop the vehicle with throttle fully
closed condition. (E) Drive the vehicle at 64 km/h (40
MPH) for 20 seconds.
(C) Drive the vehicle at 97 km/h (60
MPH) for 20 seconds.(H) Vehicle speed km/h (MPH)
(I) (Sec.)
DTC Item On condition
P0030 HO2S Heater Control Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor 1) —
P0068 Manifold Pressure Sensor Range/Performance —
P0246 Turbo/Super Charger Wastegate Solenoid “A” High —
P1090 Tumble Generated Valve System 1 (Valve Open)Engine coolant temperature at
start is −5 — 5°C (−41 — 41°F)
P1092 Tumble Generated Valve System 2 (Valve Open)Engine coolant temperature at
start is −5 — 5°C (−41 — 41°F)
*P0121 Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch “A” Circuit Range/Performance —
*P0139O
2 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
—
*P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire DetectedDiagnosis may be completed at
once
*P0302 Cylinder 2 Misfire DetectedDiagnosis may be completed at
once
*P0303 Cylinder 3 Misfire DetectedDiagnosis may be completed at
once
*P0304 Cylinder 4 Misfire DetectedDiagnosis may be completed at
once
*P0101 Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit Range/Performance —
P0244 Turbo/Super Charger Wastegate Solenoid “A” Range/Performance —
P1301 Misfire Detected (High Temperature Exhaust Gas) —
EN-00842
(C) (H)
(I) (60)
97
64(40)
(B)
(A)(F) (D)
(E)
150 100 50 0(G)
Page 1705 of 2870
EN(H4DOTC)-75
ENGINE (DIAGNOSTIC)
List of Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
P0121 Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/
Switch “A” Circuit Range/Perfor-
mance
cedure with Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC).>
P0122 Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/
Switch “A” Circuit Low Input
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC).>
P0123 Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/
Switch “A” Circuit High Input
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC).>
P0125 Insufficient Coolant Temperature
For Closed Loop Fuel Control
with Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC).>
P0129 Barometric Pressure Too Low
P0131 O
2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage
(Bank 1 Sensor 1)
Code (DTC).>
P0132 O
2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage
(Bank 1 Sensor 1)
Trouble Code (DTC).>
P0133 O
2 Sensor Circuit Slow Response
(Bank 1 Sensor 1)
Trouble Code (DTC).>
P0134 O
2 Sensor Circuit No Activity
Detected (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
tic Trouble Code (DTC).>
P0137 O
2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage
(Bank 1 Sensor 2)
Code (DTC).>
P0138 O
2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage
(Bank 1 Sensor 2)
Trouble Code (DTC).>
P0139 O
2 Sensor Circuit Slow Response
(Bank 1 Sensor 2)
Trouble Code (DTC).>
P0171 System Too Lean (Bank 1)
P0172 System Too Rich (Bank 1)
P0230 Fuel Pump Primary Circuit
P0244 Turbo/Super Charger Wastegate
Solenoid “A” Range/Performance
dure with Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC).>
P0245 Turbo/Super Charger Wastegate
Solenoid “A” Low
Trouble Code (DTC).>
P0246 Turbo/Super Charger Wastegate
Solenoid “A” High
Trouble Code (DTC).>
P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected
P0302 Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected
P0303 Cylinder 3 Misfire Detected
Page 1770 of 2870
EN(H4DOTC)-137
ENGINE (DIAGNOSTIC)
Diagnostic Procedure with Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
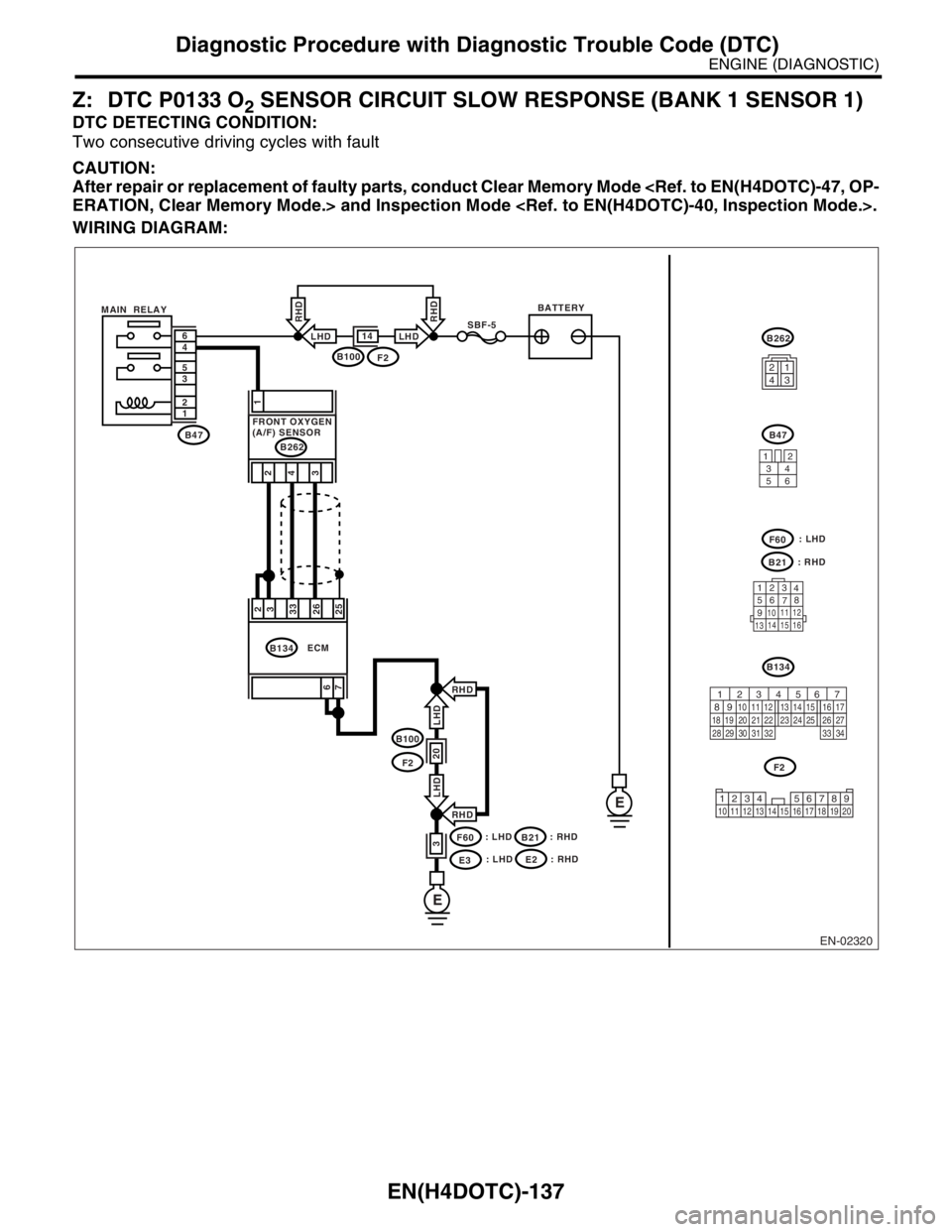
Z: DTC P0133 O2 SENSOR CIRCUIT SLOW RESPONSE (BANK 1 SENSOR 1)
DTC DETECTING CONDITION:
Two consecutive driving cycles with fault
CAUTION:
After repair or replacement of faulty parts, conduct Clear Memory Mode
WIRING DIAGRAM:
EN-02320
BATTERYMAIN RELAYSBF-5
B47 1 2 3 5 4 6
E
E
B100F2
14LHD
RHD
LHD
RHD
B100
F2
F60
E3
20
3
RHD
RHD6
72
3
33
26
25
ECMB134
: LHD: LHD
B21: RHD: RHD
1
4 2
3
B262
FRONT OXYGEN
(A/F) SENSOR
3412
56
123
4
56
78
9
1011 12
1314 15 16
B21
F60
B47
B262
B134
F2
LHD LHD
1234
56 7
82 1
94 310
24 22 23 25 11 12 13 14 15
26 27
2816 17
18 19 20 21
33 34 29
32 30 31
1234 5678910 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
: LHDE2: RHD