engine SUZUKI JIMNY 2005 3.G Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: JIMNY, Model: SUZUKI JIMNY 2005 3.GPages: 687, PDF Size: 13.38 MB
Page 241 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3E-22 REAR SUSPENSION
Tightening Torque Specifications
Required Service Materials
Fastening portionTightening torque
Nm kg-m lb-ft
Shock absorber upper and lower bolt 85 8.5 61.5
Bump stopper 50 5.0 36.5
Lateral rod bolt and nut
90 9.0 65.0
Trailing arm nut (Front and Rear)
Brake back plate nut 23 2.3 17.0
Brake pipe flare nut 16 1.6 11.5
Rear differential carrier bolt 23 2.3 17.0
Rear propeller shaft bolt (Differential case side) 50 5.0 36.5
Rear propeller shaft bolt (Shaft No.3 transfer case side) 33 3.3 24.0
Wheel nut 95 9.5 69.0
Wheel speed sensor bolt and harness clamp bolt 10 1.0 7.5
MaterialRecommended SUZUKI product
(Part Number)Use
Lithium greaseSUZUKI SUPER GREASE A
(99000-25010)Oil seal lip
SealantSUZUKI BOND NO. 1215
(99000-31110)Joint seam of differential carrier and
axle housing
Water tight sealantSEALING COMPOUND 366E
(99000-31090)To apply to mating surfaces of brake
back plate and rear axle.
Gear oilFor gear oil information, refer to “Mainte-
nance Service” in Section 7E of this manual.Differential gear
(Rear axle housing)
Page 242 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine REAR SUSPENSION 3E-23
Special Tools
09913-75520 09913-85210 09924-74510 1) 09927-18411
Universal puller
Bearing installer Oil seal installer Bearing installer handle 2) 09921-57810
Bearing remover
09941-66010 09942-15510 09943-35511 or
09943-3551209944-96010
Bearing outer race
remover
Bump stopper wrench Sliding hammer Brake drum remover 09921-26010
Bearing outer race
remover collar
09951-16030 09951-26010
Bush remover Bush remover plate
Page 243 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3E-24 REAR SUSPENSION
Page 244 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine WHEELS AND TIRES 3F-1
6F1
6F2
6G
3F
8A
8B
8C
8B
8C
8D
8E
9
10
10A
10B
SECTION 3F
WHEELS AND TIRES
CONTENTS
General Description ........................................ 3F-2
Tires .............................................................. 3F-2
Wheels .......................................................... 3F-2
Replacement Tires ........................................ 3F-2
Replacement Wheels ................................ 3F-3
How To Measure Wheel Runout ............... 3F-3
Metric Lug Nuts and Wheel Studs ............. 3F-3
Diagnosis ......................................................... 3F-4
Diagnosis Table ............................................ 3F-4
Balancing Wheels ......................................... 3F-4
General Balance Procedure .......................... 3F-4
Off-vehicle balancing ................................. 3F-4
On-vehicle balancing ................................. 3F-4
Maintenance and Minor Adjustments ........... 3F-6Wheel and Tire.............................................. 3F-6
Studs ......................................................... 3F-6
Matched tires and wheels
(For vehicle equipped with steel
wheels) ...................................................... 3F-6
Inflation of Tires ............................................ 3F-6
Tire placard ............................................... 3F-7
Tire rotation ............................................... 3F-7
On-Vehicle Service ......................................... 3F-8
Wheel ............................................................ 3F-8
Tire ................................................................ 3F-9
Mounting and demounting......................... 3F-9
Repair........................................................ 3F-9
NOTE:
All wheel fasteners are important attaching parts in that they could affect the performance of vital
parts and systems, and/or could result in major repair expense. They must be replaced with one of the
same part number or with an equivalent part if replacement becomes necessary. Do not use a replace-
ment part of lesser quality or substitute design. Torque values must be used as specified during reas-
sembly to assure proper retention of all parts.
There is to be no welding as it may result in extensive damage and weakening of the metal.
Page 245 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3F-2 WHEELS AND TIRES
General Description
Tires
This vehicle is equipped with following tire.
Tire size
: 205/70 R15 or 175/80 R15
The tires are of tubeless type. The tires are designed to operate satisfactorily with loads up to the full rated load
capacity when inflated to the recommended inflation pressure.
Correct tire pressures and driving habits have an important influence on tire life Heavy cornering, excessively
rapid acceleration, and unnecessary sharp braking increase tire wear.
Wheels
Standard equipment wheels are following steel wheels.
15 x 5 1/2 JJ
Replacement Tires
When replacement is necessary, the original equipment type tire should be used. Refer to the Tire Placard.
Replacement tires should be of the same size, load range and construction as those originally on the vehicle.
Use of any other size or type tire may affect ride, handling, speedometer / odometer calibration, vehicle ground
clearance and tire or snow chain clearance to the body and chassis.
It is recommended that new tires be installed in pairs on the same axle. If necessary to replace only one tire, it
should be paired with the tire having the most tread, to equalize braking traction.
The metric term for tire inflation pressure is the kilopascal (kPa).
Tire pressures will usually be printed in both kPa and psi on the
Tire Placard. Metric tire gauges are available from tool suppliers.
The following chart, converts commonly used inflation pressures
from kPa to psi. WARNING:
Do not mix different types of tires on the same vehicle such as radial, bias and bias-belted tires except
in emergencies, because vehicle handling may be seriously affected and may result in loss of control.
kPa
kgf/cm2psi
160
180
200
220
240
260
280
300
320
3401.6
1.8
2.0
2.2
2.4
2.6
2.8
3.0
3.2
3.423
26
29
32
35
38
41
44
47
50
Page 246 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine WHEELS AND TIRES 3F-3
Replacement Wheels
Wheels must be replaced if they are bent, dented, have excessive
lateral or radial runout, leak air through welds, have elongated
bolt holes, if lug nuts won’t stay tight, or if they are heavily rusted.
Wheels with greater runout than shown in “How to Measure
Wheel Runout” may cause objectional vibrations.
Wheels for replacement must be equivalent to the originally
equipped wheels in load capacity, diameter, rim width, off-set and
mounting configuration. A wheel of improper size or type may
affect wheel and bearing life, brake cooling, speedometer / odom-
eter calibration, ground clearance to the body and chassis.
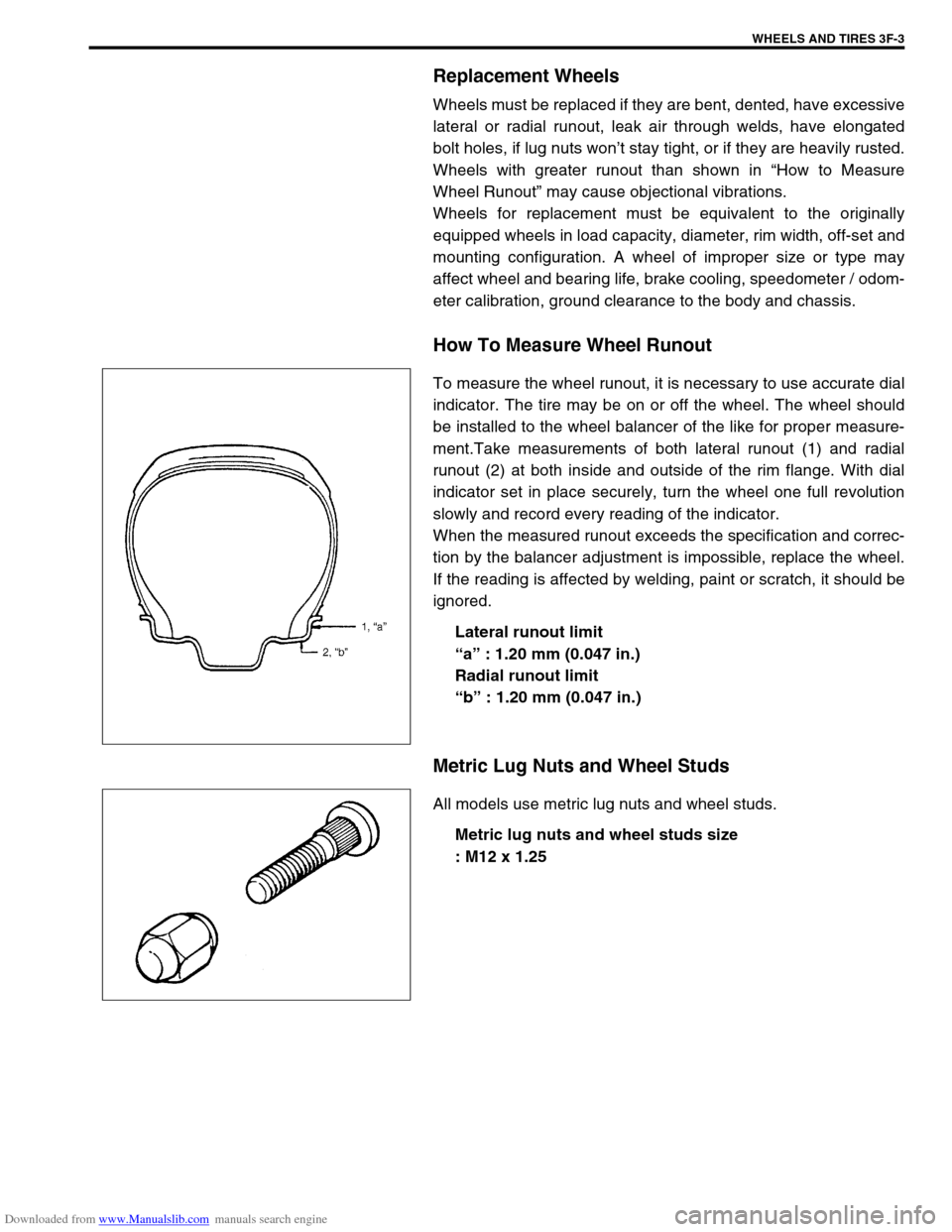
How To Measure Wheel Runout
To measure the wheel runout, it is necessary to use accurate dial
indicator. The tire may be on or off the wheel. The wheel should
be installed to the wheel balancer of the like for proper measure-
ment.Take measurements of both lateral runout (1) and radial
runout (2) at both inside and outside of the rim flange. With dial
indicator set in place securely, turn the wheel one full revolution
slowly and record every reading of the indicator.
When the measured runout exceeds the specification and correc-
tion by the balancer adjustment is impossible, replace the wheel.
If the reading is affected by welding, paint or scratch, it should be
ignored.
Lateral runout limit
“a” : 1.20 mm (0.047 in.)
Radial runout limit
“b” : 1.20 mm (0.047 in.)
Metric Lug Nuts and Wheel Studs
All models use metric lug nuts and wheel studs.
Metric lug nuts and wheel studs size
: M12 x 1.25
Page 247 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3F-4 WHEELS AND TIRES
Diagnosis
Diagnosis Table
Refer to “Diagnosis Table” in Section 3.
Balancing Wheels
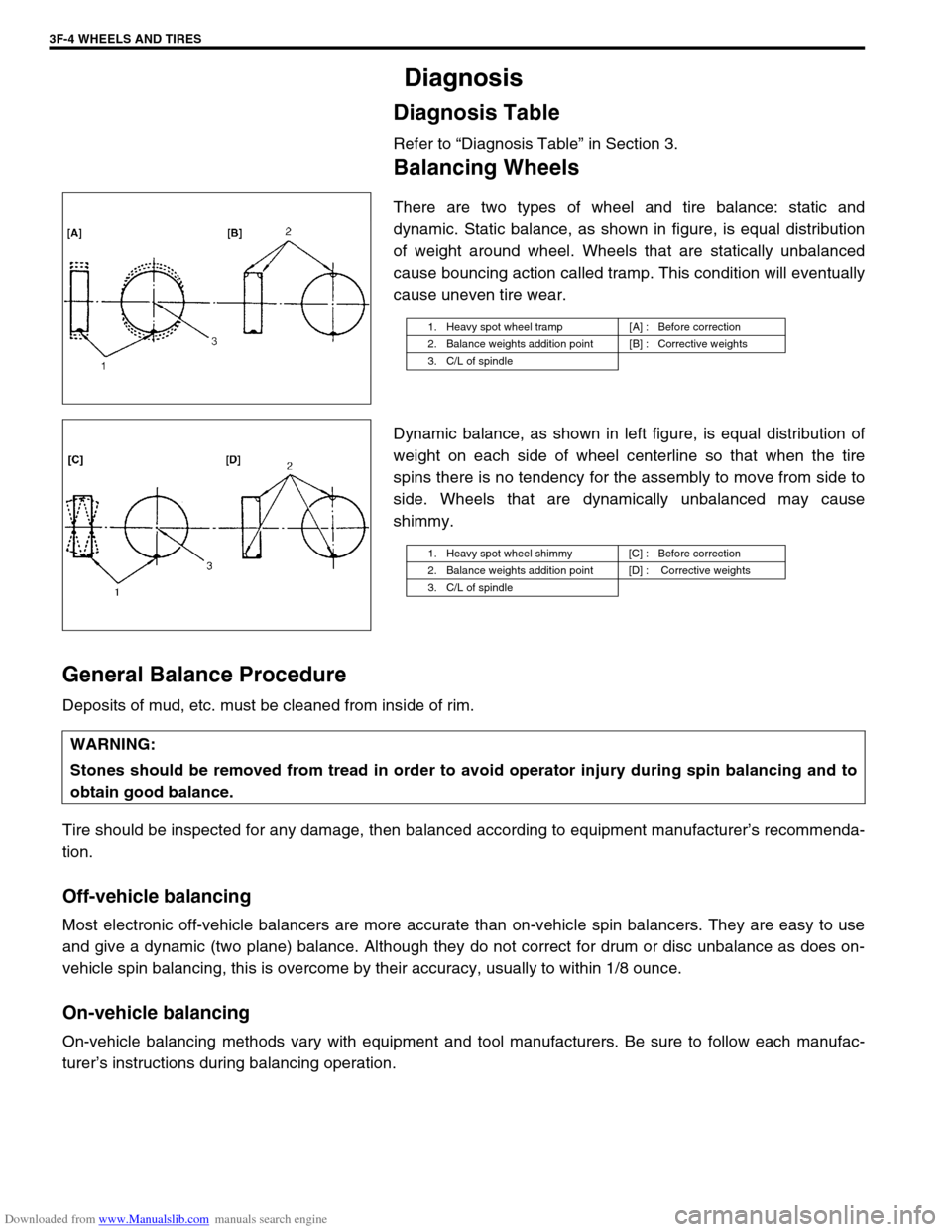
There are two types of wheel and tire balance: static and
dynamic. Static balance, as shown in figure, is equal distribution
of weight around wheel. Wheels that are statically unbalanced
cause bouncing action called tramp. This condition will eventually
cause uneven tire wear.
Dynamic balance, as shown in left figure, is equal distribution of
weight on each side of wheel centerline so that when the tire
spins there is no tendency for the assembly to move from side to
side. Wheels that are dynamically unbalanced may cause
shimmy.
General Balance Procedure
Deposits of mud, etc. must be cleaned from inside of rim.
Tire should be inspected for any damage, then balanced according to equipment manufacturer’s recommenda-
tion.
Off-vehicle balancing
Most electronic off-vehicle balancers are more accurate than on-vehicle spin balancers. They are easy to use
and give a dynamic (two plane) balance. Although they do not correct for drum or disc unbalance as does on-
vehicle spin balancing, this is overcome by their accuracy, usually to within 1/8 ounce.
On-vehicle balancing
On-vehicle balancing methods vary with equipment and tool manufacturers. Be sure to follow each manufac-
turer’s instructions during balancing operation.
1. Heavy spot wheel tramp [A] : Before correction
2. Balance weights addition point [B] : Corrective weights
3. C/L of spindle
1. Heavy spot wheel shimmy [C] : Before correction
2. Balance weights addition point [D] : Corrective weights
3. C/L of spindle
WARNING:
Stones should be removed from tread in order to avoid operator injury during spin balancing and to
obtain good balance.
Page 248 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine WHEELS AND TIRES 3F-5
WARNING:
Wheel spin should be limited to 35 mph (55 km/h) as indicated on speedometer.
This limit is necessary because speedometer only indicates one-half of actual wheel speed when one
drive wheel is spinning and the other drive wheel is stopped.
Unless care is taken in limiting drive wheel spin, spinning wheel can reach excessive speeds. This
can result in possible tire disintegration or differential failure, which could cause serious personal
injury or extensive vehicle damage.
CAUTION:
For vehicle equipped with ABS, using on-vehicle balancing method with ignition switch ON may set
malfunction diagnostic trouble code (DTC) of ABS even when system is in good condition.
Never turn ignition switch ON while spinning wheel.
Page 249 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3F-6 WHEELS AND TIRES
Maintenance and Minor Adjustments
Wheel and Tire
Wheel repairs that use welding, heating, or peening are not approved. All damaged wheels should be replaced.
Studs
If a broken stud is found, see Section 3E (rear) or Section 3D (front) for Note and Replacement procedure.
Matched tires and wheels
(For vehicle equipped with steel wheels)
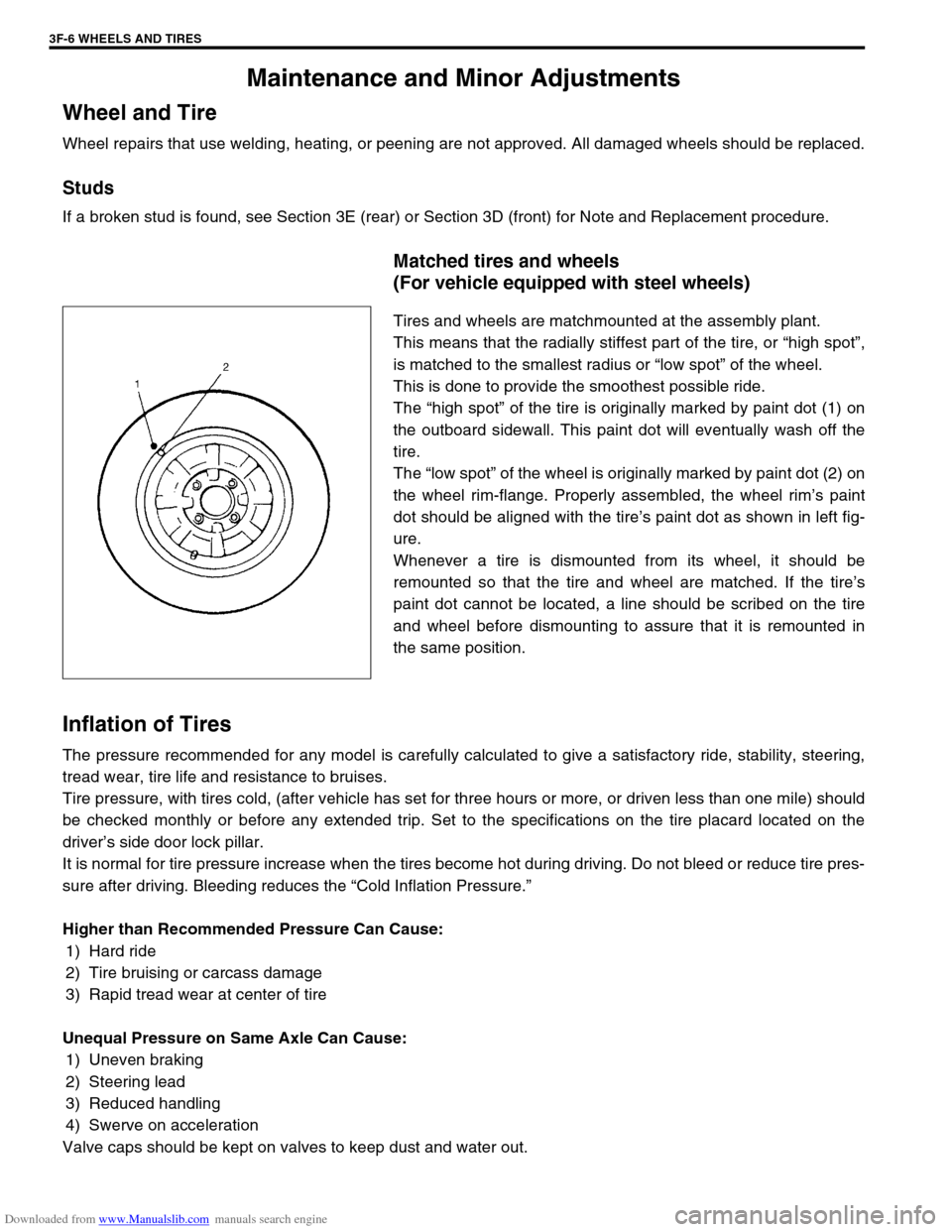
Tires and wheels are matchmounted at the assembly plant.
This means that the radially stiffest part of the tire, or “high spot”,
is matched to the smallest radius or “low spot” of the wheel.
This is done to provide the smoothest possible ride.
The “high spot” of the tire is originally marked by paint dot (1) on
the outboard sidewall. This paint dot will eventually wash off the
tire.
The “low spot” of the wheel is originally marked by paint dot (2) on
the wheel rim-flange. Properly assembled, the wheel rim’s paint
dot should be aligned with the tire’s paint dot as shown in left fig-
ure.
Whenever a tire is dismounted from its wheel, it should be
remounted so that the tire and wheel are matched. If the tire’s
paint dot cannot be located, a line should be scribed on the tire
and wheel before dismounting to assure that it is remounted in
the same position.
Inflation of Tires
The pressure recommended for any model is carefully calculated to give a satisfactory ride, stability, steering,
tread wear, tire life and resistance to bruises.
Tire pressure, with tires cold, (after vehicle has set for three hours or more, or driven less than one mile) should
be checked monthly or before any extended trip. Set to the specifications on the tire placard located on the
driver’s side door lock pillar.
It is normal for tire pressure increase when the tires become hot during driving. Do not bleed or reduce tire pres-
sure after driving. Bleeding reduces the “Cold Inflation Pressure.”
Higher than Recommended Pressure Can Cause:
1) Hard ride
2) Tire bruising or carcass damage
3) Rapid tread wear at center of tire
Unequal Pressure on Same Axle Can Cause:
1) Uneven braking
2) Steering lead
3) Reduced handling
4) Swerve on acceleration
Valve caps should be kept on valves to keep dust and water out.
Page 250 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine WHEELS AND TIRES 3F-7
Lower than Recommended Pressure Can Cause:
1) Tire squeal on turns
2) Hard steering
3) Rapid and uneven wear on the edges of the tread
4) Tire rim bruises and rupture
5) Tire cord breakage
6) High tire temperatures
7) Reduced handling
8) High fuel consumption
Tire placard
The tire placard is located on the driver’s side door lock pillar and should be referred to for tire information. The
placard lists the maximum load, tire size and cold tire pressure where applicable.
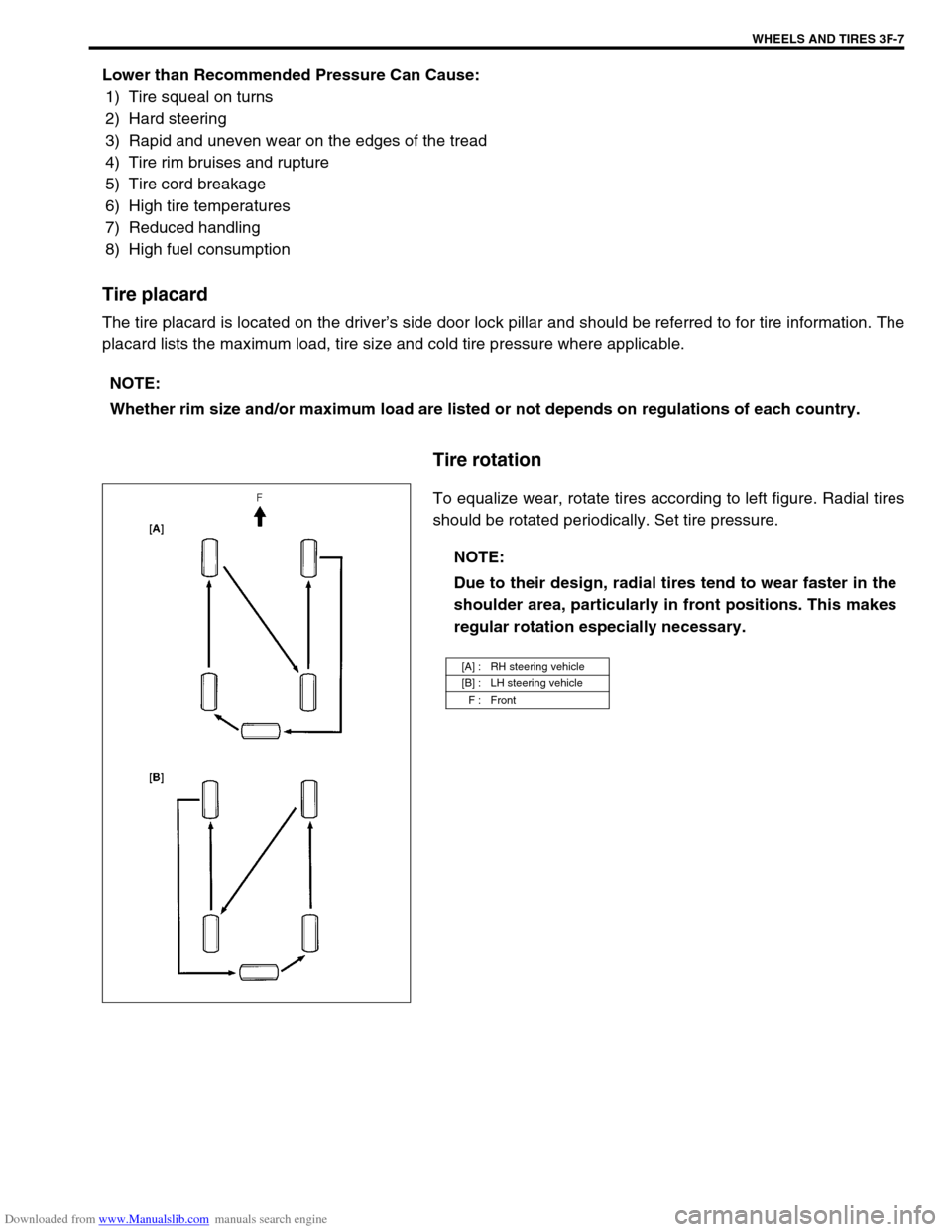
Tire rotation
To equalize wear, rotate tires according to left figure. Radial tires
should be rotated periodically. Set tire pressure. NOTE:
Whether rim size and/or maximum load are listed or not depends on regulations of each country.
NOTE:
Due to their design, radial tires tend to wear faster in the
shoulder area, particularly in front positions. This makes
regular rotation especially necessary.
[A] : RH steering vehicle
[B] : LH steering vehicle
F : Front