ECU SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.G RG413 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2000, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.GPages: 698, PDF Size: 16.01 MB
Page 643 of 698

6E1-22 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
6) Start engine and warm it up to normal operating tempera-
ture.
7) Measure fuel pressure at idling.
If measured pressure does not satisfy specification, refer to
“Diagnostic Flow Table B-3” in “Engine Diagnosis” section
and check each possibly defective part. Replace if found
defective.
8) After checking fuel pressure, remove fuel pressure gauge.
9) Remove special tools from fuel delivery pipe.
10) Connect fuel feed hose to fuel delivery pipe and clamp it
securely.
11) With engine “OFF” and ignition switch “ON”, check for fuel
leaks.
FUEL PUMP WITH PRESSURE REGULATOR
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION
1) Remove filler cap and turn ON ignition switch. Then fuel
pump operating sound should be heard from fuel filler for
about 2 seconds and stop. Be sure to reinstall fuel filler cap
after checking.
If above check result is not satisfactory, advance to “Diag-
nostic Flow Table B-2”. CAUTION:
As fuel feed line is still under high fuel pressure, make
sure to release fuel pressure according to following pro-
cedures.
Place fuel container under joint.
Cover joint with rag and loosen joint nut slowly to
release fuel pressure gradually.
CAUTION:
When fuel filler cap is removed in any procedure, work
must be done in a well-ventilated area, keep away from
any open flames and without smoking.
NOTE:
The fuel pressure regulator is the one body with the fuel
pump assembly so individual inspection of it is impossi-
ble.
1. Fuel filler
2. Ignition switch
Page 644 of 698

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM 6E1-23
2) Turn OFF ignition switch and leave over 10 minutes as it is.
3) Fuel pressure should be felt at fuel feed hose (1) for about 2
seconds after ignition switch ON.
If fuel pressure is not felt, advance to “Diagnostic Flow Table
B-3”.
REMOVAL
Remove fuel tank from body according to procedure described in
Section 6C and remove fuel pump from fuel tank.
INSPECTION
Check fuel pump filter for evidence of dirt and contamination. If
present, clean and check for presence of dirt in fuel tank.
INSTALLATION
1) Install fuel pump to its bracket.
2) Install fuel pump to fuel tank and then install fuel tank to
body according to procedure described in Section 6C.
FUEL INJECTOR
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION
1) Using sound scope (1) or such, check operating sound of
injector (2) when engine is running or cranking.
Cycle of operating sound should vary according to engine
speed.
If no sound or an unusual sound is heard, check injector cir-
cuit (wire or connector) or injector (2).
2) Disconnect connector (1) from injector, connect ohmmeter
between terminals of injector and check resistance.
If resistance is out of specification, replace.
Resistance of fuel injector
: 11.3 – 13.8
Ω at 20°C (68°F)
3) Connect connector (1) to injector securely.
Page 648 of 698

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM 6E1-27
ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
REMOVAL
1) Disconnect battery negative cable at battery.
2) Disable air bag system, referring to “Disabling The Air Bag
System” in Section 10B if equipped.
3) Disconnect ECM (1) and TCM (2) (if equipped) connectors.
4) Remove bolt and nuts, remove ECM and TCM (if equipped).
INSTALLATION
Reverse removal procedure noting the following:
Connect connectors to ECM and TCM (if equipped) securely.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR (MAP
SENSOR)
INSPECTION
Check MAP sensor referring to “MAP Sensor Individual Check” in
DTC P0105 (No.11) Flow Table. If malfunction is found, replace.CAUTION:
As ECM consists of precision parts, be careful not to
expose it to excessive shock.
2
1
Page 649 of 698

6E1-28 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TP SENSOR)
INSPECTION
1) Disconnect negative cable at battery and connector from IAT
sensor.
2) Remove air cleaner assembly with air cleaner outlet hose
and disconnect TP sensor connector.
3) Using ohmmeter, check resistance between terminals under
each condition given in table below.
If check result is not satisfactory, replace TP sensor.
TP sensor resistance
4) Connect TP sensor connector securely.
5) Connect negative cable to battery.
REMOVAL
1) Disconnect battery negative cable at battery.
2) Remove throttle body from intake manifold referring to
“Throttle Body Removal” in this section.
3) Remove TP sensor from throttle body.
INSTALLATION
1) Install TP sensor (1) to throttle body.
Fit TP sensor to throttle body in such way that its holes (3)
are a little away from TP sensor screw holes (2) as shown in
left figure and turn TP sensor clockwise so that those holes
align (4).
Tightening torque
TP sensor screw (a) : 2.5 N·m (0.25 kg-m, 1.8 lb-ft)
2) Connect connector to TP sensor securely.
3) Connect battery negative cable to battery.TERMINALS RESISTANCE
Between 1 and
3 terminals4.0 – 6.0 k
Ω
Between 2 and
3 terminals20
Ω – 6.0 k
Ω, varying according to throt-
tle valve opening.
NOTE:
There should be more than 2 k
Ω resistance difference
between when throttle valve is at idle position and when
it is fully open.
1. Reference voltage terminal
2. Output voltage terminal
3. Ground terminal
Page 650 of 698

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM 6E1-29
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR (IAT SENSOR)
REMOVAL
1) Disconnect battery negative cable at battery.
2) Disconnect coupler (1) from IAT sensor.
3) Remove IAT sensor from air cleaner case (2).
INSPECTION
Immerse temperature sensing part of IAT sensor in water (or ice)
and measure resistance between sensor terminals while heating
water gradually.
If measured resistance does not show such characteristic as
shown in left figure, replace IAT sensor.
INSTALLATION
Reverse removal procedure noting the following.
Clean mating surfaces of IAT sensor and air cleaner case.
Connect IAT sensor connector (1) securely.
1
2
1
Page 651 of 698
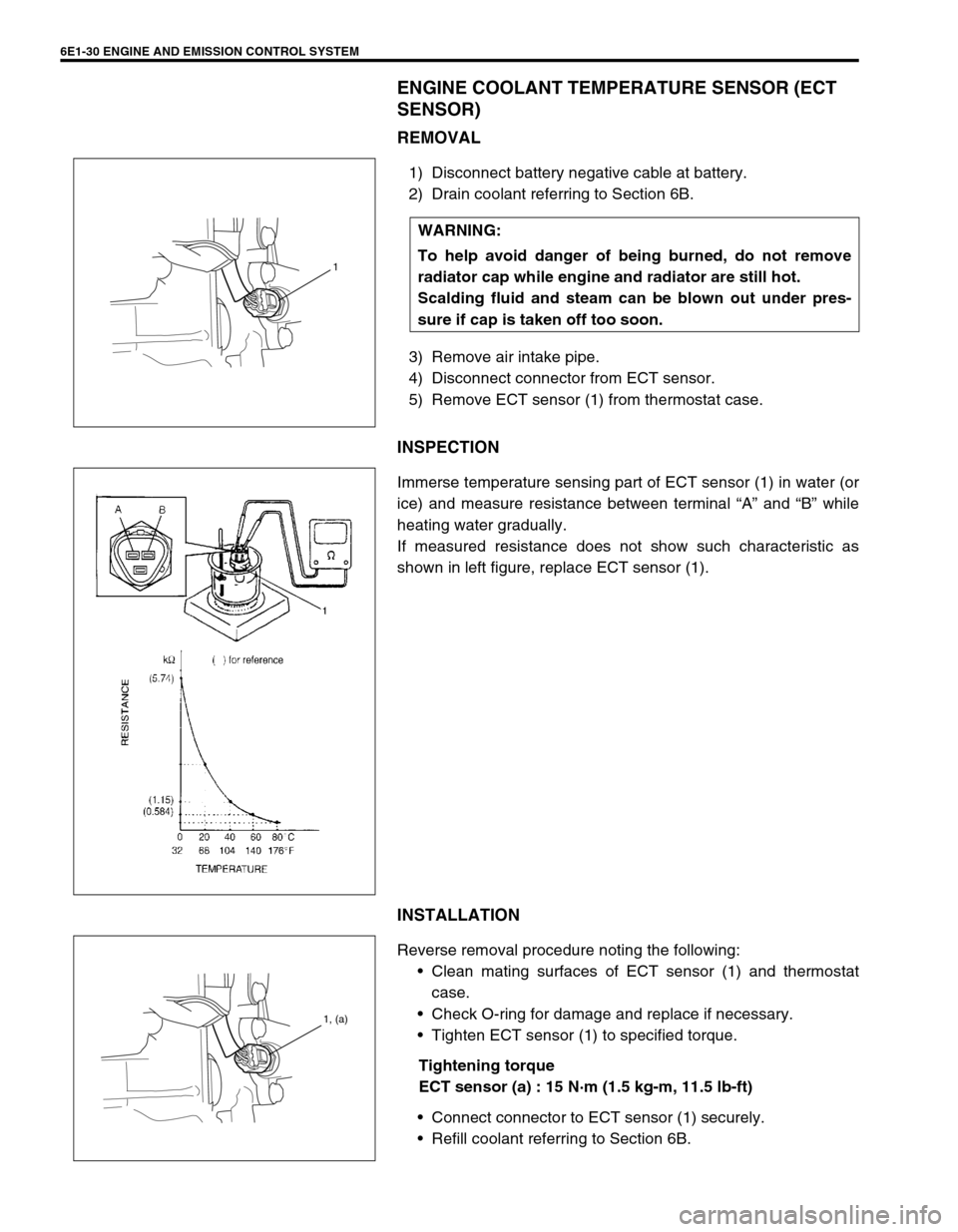
6E1-30 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR (ECT
SENSOR)
REMOVAL
1) Disconnect battery negative cable at battery.
2) Drain coolant referring to Section 6B.
3) Remove air intake pipe.
4) Disconnect connector from ECT sensor.
5) Remove ECT sensor (1) from thermostat case.
INSPECTION
Immerse temperature sensing part of ECT sensor (1) in water (or
ice) and measure resistance between terminal “A” and “B” while
heating water gradually.
If measured resistance does not show such characteristic as
shown in left figure, replace ECT sensor (1).
INSTALLATION
Reverse removal procedure noting the following:
Clean mating surfaces of ECT sensor (1) and thermostat
case.
Check O-ring for damage and replace if necessary.
Tighten ECT sensor (1) to specified torque.
Tightening torque
ECT sensor (a) : 15 N·m (1.5 kg-m, 11.5 lb-ft)
Connect connector to ECT sensor (1) securely.
Refill coolant referring to Section 6B. WARNING:
To help avoid danger of being burned, do not remove
radiator cap while engine and radiator are still hot.
Scalding fluid and steam can be blown out under pres-
sure if cap is taken off too soon.
1
1, (a)
Page 652 of 698

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM 6E1-31
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (HO2S-1 AND HO2S-2)
OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER INSPECTION
1) Disconnect sensor connector.
2) Using ohmmeter, measure resistance between terminals
“V
B” and “GND” of sensor connector.
If found faulty, replace oxygen sensor.
Resistance of oxygen sensor heater
HO2S-1 : 5.0 – 6.4
Ω at 20°C (68°F)
HO2S-2 : 11.7 – 14.3
Ω at 20°C (68°F)
3) Connect sensor connector securely.
REMOVAL
1) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
2) For HO2S-1, disconnect connector of heated oxygen sensor
and release its wire harness from clamps, then remove front
bumper and heat insulator panel.
3) For HO2S-2, disconnect connector of heated oxygen sensor
and release its wire harness from clamp and hoist vehicle.
4) Remove heated oxygen sensor (1) from exhaust manifold or
exhaust pipe.
INSTALLATION
Reverse removal procedure noting the following.
Tighten heated oxygen sensor (1) to specified torque.
Tightening torque
Heated oxygen sensor (a) : 45 N·m (4.5 kg-m, 32.5 lb-ft)
Connect connector of heated oxygen sensor (1) and clamp
wire harness securely.
After installing heated oxygen sensor (1), start engine and
check that no exhaust gas leakage exists. NOTE:
Temperature of sensor affects resistance value largely.
Make sure that sensor heater is at correct temperature.
1. Viewed from terminal side
WARNING:
To avoid danger of being burned, do not touch exhaust
system when system is hot. Oxygen sensor removal
should be performed when system is cool.
[A] : HO2S-1
[B] : HO2S-2
Page 653 of 698

6E1-32 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
INSPECTION
Check camshaft position sensor referring to DTC P0340 (No.15)
Diag. Flow Table in Section 6. If malfunction is found, replace.
REMOVAL
1) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
2) Disconnect connector from camshaft position sensor.
3) Remove camshaft position sensor from cylinder head.
INSTALLATION
1) Check that O-ring is free from damage.
2) Check that camshaft position sensor and signal rotor teeth
are free from any metal particles and damage.
3) Install camshaft position sensor to cylinder head.
Tightening torque
Camshaft position sensor bolt
(a) : 10 N·m (1.0 kg-m, 7.5 lb-ft)
4) Connect connector to it securely.
5) Connect negative cable to battery.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
INSPECTION
Check crankshaft position sensor referring to step 1 and 2 of DTC
P0335 (No.23) Flow Table. If malfunction is found, replace.
REMOVAL
1) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
2) Remove generator drive belt, loosen pivot bolt and move
generator outward.
3) Disconnect connector from crankshaft position sensor.
4) Remove crankshaft position sensor (1) from cylinder block.
INSTALLATION
1) Check to make sure that crankshaft position sensor and pul-
ley teeth are free from any metal particles and damage.
2) Install crankshaft position sensor to cylinder block.
3) Connect connector to it securely.
4) Adjust generator belt tension, refer to Section 6B.
5) Connect negative cable to battery.
Page 665 of 698

IGNITION SYSTEM (ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM 6F1-3
SYSTEM WIRING DIAGRAM
DIAGNOSIS
1. Ignition switch 7. No.1 spark plug
2. Main relay 8. No.2 spark plug
3. Ignition coil assembly for No.1 and No.4 spark plugs 9. No.3 spark plug
4. Ignition coil assembly for No.2 and No.3 spark plugs 10. No.4 spark plug
5. CMP sensor 11. Sensed information (MAP sensor, ECT sensor, IAT sensor, TP sensor, Knock sensor (if
equipped), VSS, Park/Neutral position signal, Electric load signal, Engine start signal, Test switch
terminal (Vehicle without immobilizer indicator lamp))
6. CKP sensor
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Engine cranks, but will
not start or hard to
start (No spark)Blown fuse for ignition coil Replace.
Loose connection or disconnection of lead wire
or high-tension cord(s)Connect securely.
Faulty high-tension cord(s) Replace.
Faulty spark plug(s) Adjust, clean or replace.
Faulty ignition coil Replace ignition coil assembly.
Faulty CKP sensor or CKP sensor plate Clean, tighten or replace.
Faulty ECM Replace.
Poor fuel economy or
engine performanceIncorrect ignition timing Check related sensors and CKP
sensor plate.
Faulty spark plug(s) or high-tension cord(s) Adjust, clean or replace.
Faulty ignition coil assembly Replace.
Faulty CKP sensor or CKP sensor plate Clean, tighten or replace.
Faulty ECM Replace.
Page 666 of 698

6F1-4 IGNITION SYSTEM (ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM)
IGNITION SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC FLOW TABLE
Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” in Section 6 per-
formed?Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE” in Sec-
tion 6.
2Ignition Spark Test
1) Check all spark plugs for condition and type refer-
ring to “Spark Plugs” section.
2) If OK, perform ignition spark test, referring to “Igni-
tion Spark Test” in this section.
Is spark emitted from all spark plugs?Go to Step 11. Go to Step 3.
3Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Check Is DTC stored
in ECM?Go to applicable DTC
Diag. Flow Table in
Section 6.Go to Step 4.
4Electrical Connection Check
1) Check ignition coil assemblies and high-tension
cords for electrical connection.
Are they connected securely?Go to Step 5. Connect securely.
5High-tension Cords Check
1) Check high-tension cord for resistance referring to
“High-Tension Cords” in this section.
Is check result satisfactory?Go to Step 6. Replace high-tension
cord(s).
6Ignition Coil Assembly Power Supply and Ground Cir-
cuit Check
1) Check ignition coil assembly power supply and
ground circuits for open and short.
Are circuits in good condition?Go to Step 7. Repair or replace.
7Ignition Coil Assembly Check
1) Check ignition coil for resistance referring to “Igni-
tion Coil Assembly” in this section.
Is check result satisfactory?Go to Step 8. Replace ignition coil
assembly.
8Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor Check
1) Check crankshaft position sensor referring to Step
3 and 4 of “DTC P0335 (No.23) Diag. Flow Table”
in Section 6.
Is check result satisfactory?Go to Step 9. Tighten CKP sensor
bolt, replace CKP sen-
sor or CKP sensor
plate.
9Ignition Trigger Signal Circuit Check
1) Check ignition trigger signal wire for open, short
and poor connection.
Is circuit in good condition?Go to Step 10. Repair or replace.
10A Known-good Ignition Coil Assembly Substitution
1) Substitute a known-good ignition coil assembly
and then repeat Step 2.
Is check result of Step 2 satisfactory?Go to Step 11. Substitute a known-
good ECM and then
repeat Step 2.
11Ignition Timing Check
1) Check initial ignition timing and ignition timing
advance referring to “Ignition Timing” in this sec-
tion.
Is check result satisfactory?System is in good con-
dition.Check CKP sensor,
CKP sensor plate and
input signals related to
this system.