air cond SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.G Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2005 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 287 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-2
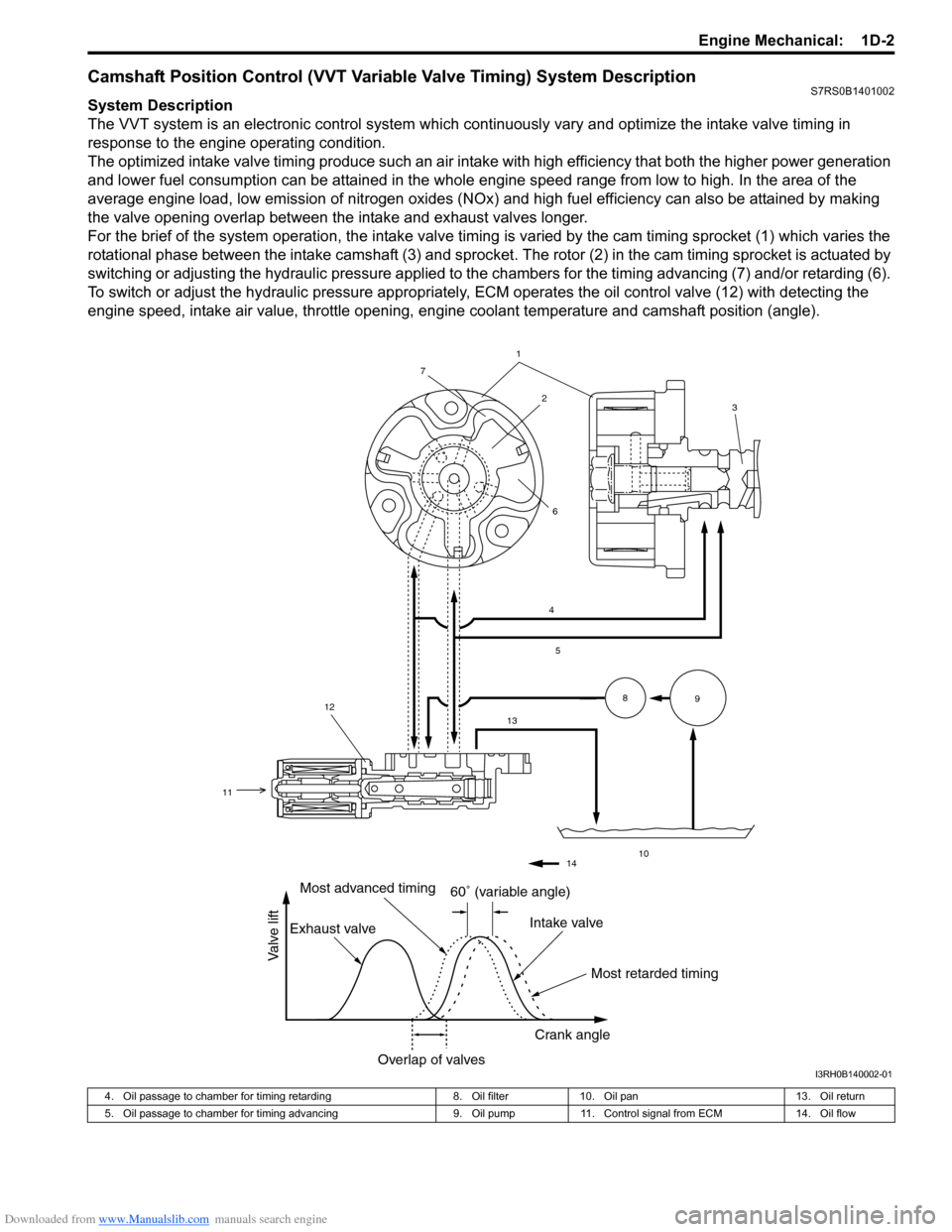
Camshaft Position Control (VVT Variable Valve Timing) System DescriptionS7RS0B1401002
System Description
The VVT system is an electronic control system which continuously vary and optimize the intake valve timing in
response to the engine operating condition.
The optimized intake valve timing produce such an air intake with high efficiency that both the higher power generation
and lower fuel consumption can be attained in the whole engine speed range from low to high. In the area of the
average engine load, low emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and high fuel efficiency can also be attained by making
the valve opening overlap between the intake and exhaust valves longer.
For the brief of the system operation, the intake valve timing is varied by the cam timing sprocket (1) which varies the
rotational phase between the intake camshaft (3) and sprocket . The rotor (2) in the cam timing sprocket is actuated by
switching or adjusting the hydraulic pressure applied to the chambers for the timing advancing (7) and/or retarding (6).
To switch or adjust the hydraulic pressure appropriately, ECM operates the oil control valve (12) with detecting the
engine speed, intake air value, throttle opening, engine coolant temperature and camshaft position (angle).
1
4
5
13
10
89
2
7
6
12
11
3
14
60� (variable angle)
Most retarded timing
Most advanced timing
Exhaust valve Intake valve
Crank angle
Overlap of valves
Valve lift
I3RH0B140002-01
4. Oil passage to chamber for timing retarding 8. Oil filter10. Oil pan 13. Oil return
5. Oil passage to chamber for timing advancing 9. Oil pump11. Control signal from ECM 14. Oil flow
Page 289 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-4
Targeted Timing Varying Operation
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Compression CheckS7RS0B1404001
Check compression pressure on all 4 cylinders as
follows:
1) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
2) Stop engine after warming up.
NOTE
After warming up engine, place transaxle
gear shift lever in “Neutral”, and set parking
brake and block drive wheels.
3) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
4) Remove engine cover.
5) Remove air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
6) Remove cylinder head upper cover.
7) Disconnect ignition coil couplers (1).
8) Remove ignition coil assemblies (2) with high- tension cord (3).
9) Remove all spark plugs.
10) Disconnect fuel injector wires (4) at the coupler. Driving condition Valve timing Target of control Effect
Engine running at idle
speed Most retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to in
take manifold. Stabilization of the engine
rotation at idle speed.
Average engine load
range To the advanced
sideTo lengthen the valve opening overlap
in order to enhance the internal
exhaust gas recirculation and reduce
the pumping loss. Improvement of the fuel
efficiency.
Lowering of the exhaust
emission.
Light engine load
range To the retarded sideTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to in
take manifold. Keeping of the engine stability.
Low or average
engine speed range
with heavy engine
load To the advanced
side
To advance the closing timing of the
intake valve in order to improve the
volumetric efficiency. Improvement of generating the
engine torque at low and
average engine speed.
High engine speed
range with heavy
engine load To the retarded sideTo retard the closing timing of the
intake valve in order to improve the
volumetric efficiency. Improvement of generating the
engine power.
Low engine coolant
temperature Most retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to intake manifold and
reduce the fuel increasing.
To slow the fast idle speed of the
engine as a result of stabilizing the
engine idling. Stabilization of the fast idling of
the engine.
Improvement of the fuel
efficiency.
At engine starting and
stopping Most retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to in
take manifold. Improvement of start ability.I2RH0B140003-01
Page 290 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-5 Engine Mechanical:
11) Connect negative cable at battery.
12) Install special tools (Compression gauge) into spark plug hole.
Special tool
(A): 09915–64512
(B): 09915–64530
(C): 09915–67010
13) Disengage clutch (1) (to lighten starting load on engine) for M/T vehicle, and depress accelerator
pedal (2) all the way to make throttle fully open.
14) Crank engine with fully charged battery, and read the highest pressure on compression gauge.
NOTE
• For measuring compression pressure, crank engine at least 250 r/min. by using
fully charged battery.
• If measured compression pressure is lower than limit value, check installation
condition of special tool. If it is properly
installed, possibility is compression
pressure leakage from where piston ring
and valve contact.
Compression pressure
Standard: 1400 kPa (14.0 kg/cm2, 199.0 psi)
Limit: 1100 kPa (11.0 kg/cm2, 156.0 psi)
Max. difference between any two cylinders: 100
kPa (1.0 kg/cm
2, 14.2 psi) 15) Carry out Steps 12) through 14) on each cylinder to
obtain 4 readings.
16) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
17) After checking, install spark plugs and ignition coil assemblies (2) with high-tension cord (3).
18) Connect ignition coil couplers (1).
19) Connect fuel injector wires (4) at the coupler.
20) Install cylinder head upper cover.
21) Install air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
22) Install engine cover.
23) Connect negative cable at battery.
Engine Vacuum CheckS7RS0B1404002
The engine vacuum that develops in the intake line is a
good indicator of the condition of the engine. The
vacuum checking procedure is as follows:
1) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
NOTE
After warming up engine, be sure to place
transaxle gear shift lever in “Neutral”, and set
parking brake and block drive wheels.
2) Stop engine and turn off the all electric switches.
3) Remove engine cover.
4) Remove air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
5) Remove PCV hose (1) from PCV valve (2).
(A)
(C)
(B)
I3RH0B140009-01
I2RH0B140005-01
I2RH0B140003-01
2
1
I6RS0B141001-01
Page 298 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-13 Engine Mechanical:
Throttle Body On-Vehicle InspectionS7RS0B1406006
Check electric throttle body assembly referring to
“Throttle Valve Operation Check” and “Electric Throttle
Body Assembly Operation Check” under “Electric
Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle Inspection in
Section 1C”.
Electric Throttle Body Assembly Removal and
Installation
S7RS0B1406007
CAUTION!
Never disassemble electric throttle body.
Disassembly will spoil its original
performance. If faulty condition is found,
replace it with new one.
NOTE
After replacing electric throttle body
assembly, perform calibration of throttle
valve referring to “Electric Throttle Body
System Calibration in Section 1C”.
Removal
1) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
2) Drain coolant referring to “Cooling System Draining in Section 1F”.
3) Remove air cleaner assembly referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
4) Detach EVAP canister and purge valve chamber, and remove air cleaner outlet hose.
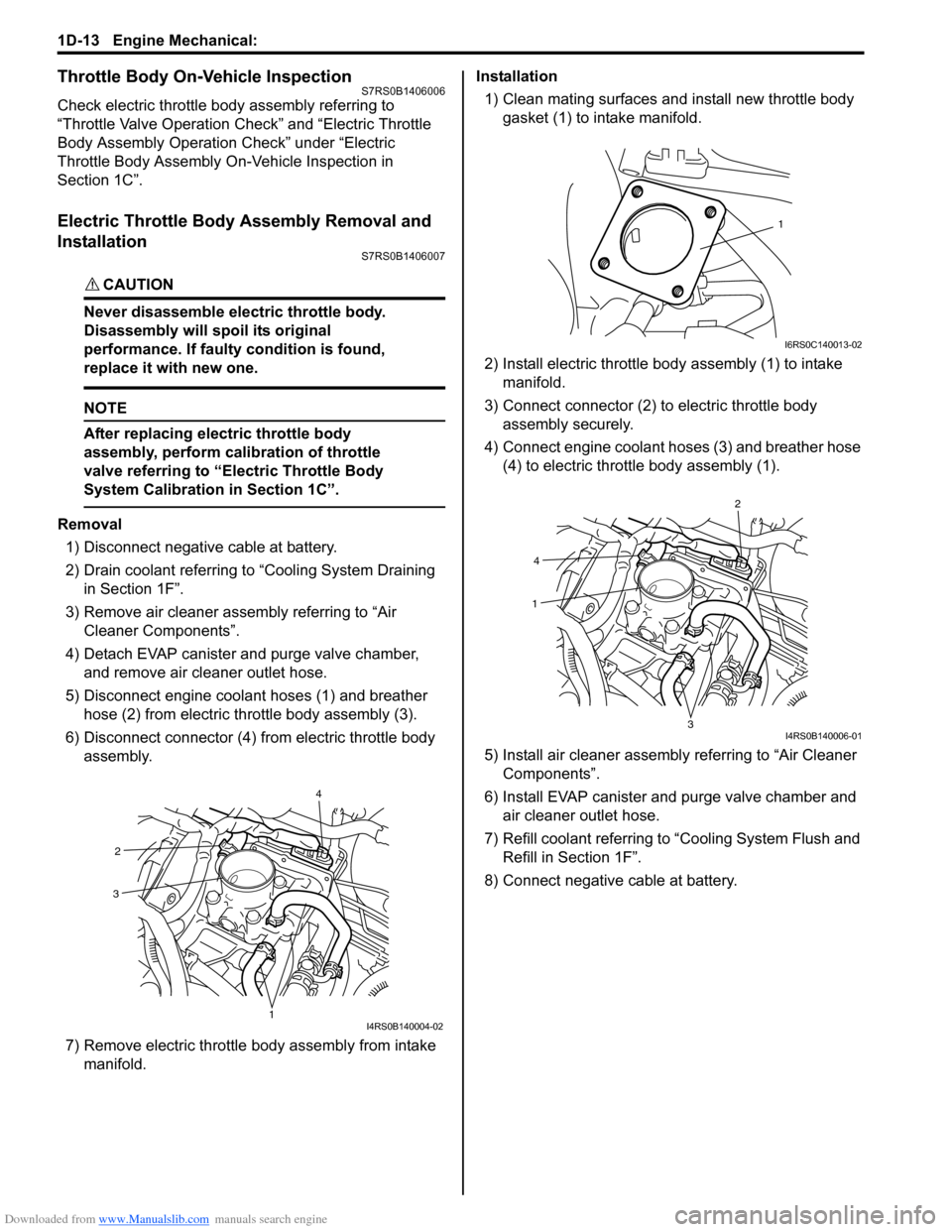
5) Disconnect engine coolant hoses (1) and breather hose (2) from electric throttle body assembly (3).
6) Disconnect connector (4) from electric throttle body assembly.
7) Remove electric throttle body assembly from intake
manifold. Installation
1) Clean mating surfaces and install new throttle body gasket (1) to intake manifold.
2) Install electric throttle bo dy assembly (1) to intake
manifold.
3) Connect connector (2) to electric throttle body assembly securely.
4) Connect engine coolant hoses (3) and breather hose (4) to electric thrott le body assembly (1).
5) Install air cleaner assembly referring to “Air Cleaner
Components”.
6) Install EVAP canister and purge valve chamber and air cleaner outlet hose.
7) Refill coolant referring to “Cooling System Flush and
Refill in Section 1F”.
8) Connect negative cable at battery.
2
4
3
1I4RS0B140004-02
1
I6RS0C140013-02
4
2
1
3I4RS0B140006-01
Page 326 of 1496
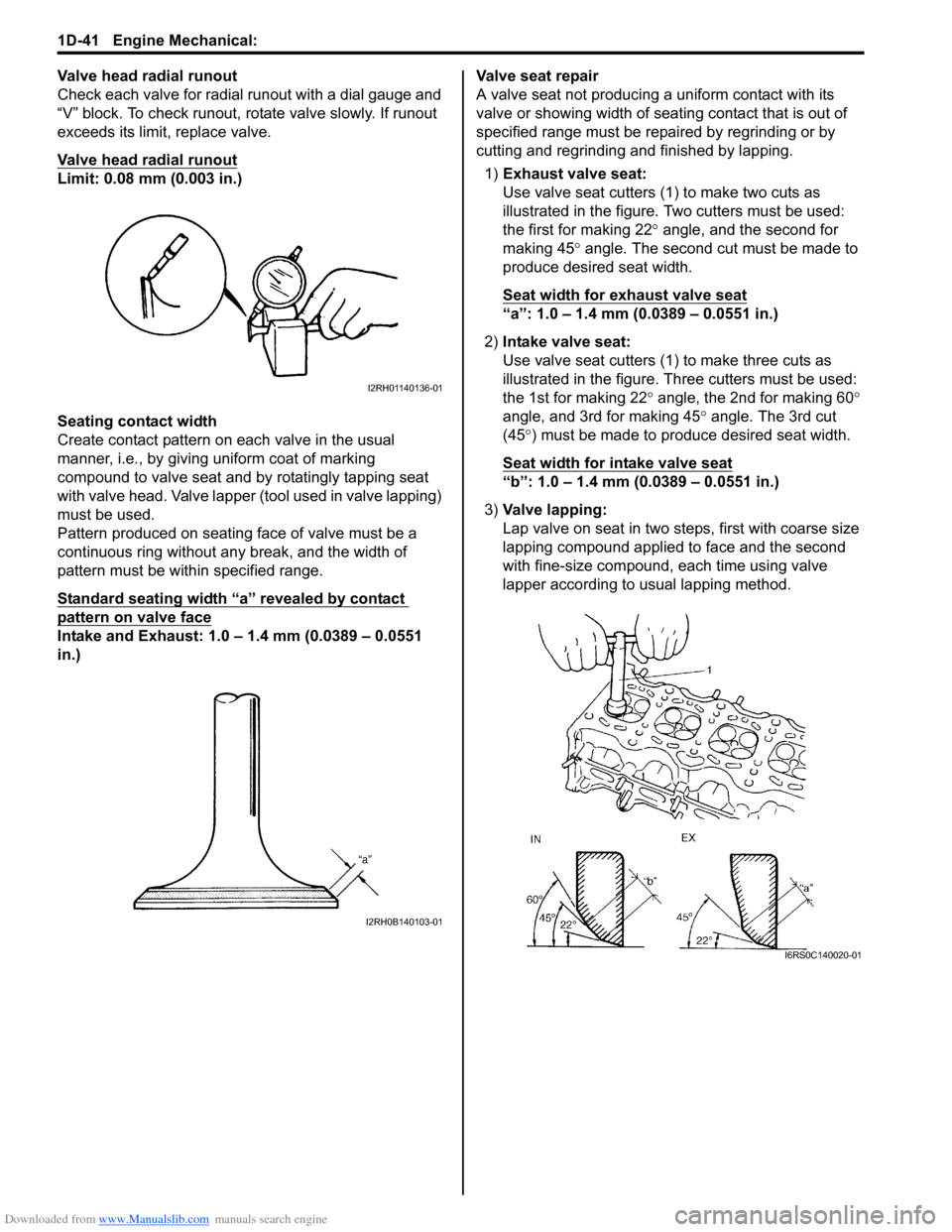
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-41 Engine Mechanical:
Valve head radial runout
Check each valve for radial runout with a dial gauge and
“V” block. To check runout, rotate valve slowly. If runout
exceeds its limit, replace valve.
Valve head radial runout
Limit: 0.08 mm (0.003 in.)
Seating contact width
Create contact pattern on each valve in the usual
manner, i.e., by giving uniform coat of marking
compound to valve seat and by rotatingly tapping seat
with valve head. Valve lapper (tool used in valve lapping)
must be used.
Pattern produced on seating face of valve must be a
continuous ring without any break, and the width of
pattern must be within specified range.
Standard seating width “a” revealed by contact
pattern on valve face
Intake and Exhaust: 1.0 – 1.4 mm (0.0389 – 0.0551
in.)Valve seat repair
A valve seat not producing
a uniform contact with its
valve or showing width of seating contact that is out of
specified range must be repaired by regrinding or by
cutting and regrinding and finished by lapping.
1) Exhaust valve seat:
Use valve seat cutters (1 ) to make two cuts as
illustrated in the figure. Two cutters must be used:
the first for making 22 ° angle, and the second for
making 45 ° angle. The second cut must be made to
produce desired seat width.
Seat width for exhaust valve seat
“a”: 1.0 – 1.4 mm (0.0389 – 0.0551 in.)
2) Intake valve seat:
Use valve seat cutters (1) to make three cuts as
illustrated in the figure. Th ree cutters must be used:
the 1st for making 22 ° angle, the 2nd for making 60 °
angle, and 3rd for making 45 ° angle. The 3rd cut
(45 °) must be made to produce desired seat width.
Seat width for intake valve seat
“b”: 1.0 – 1.4 mm (0.0389 – 0.0551 in.)
3) Valve lapping:
Lap valve on seat in two steps, first with coarse size
lapping compound applied to face and the second
with fine-size compound, each time using valve
lapper according to usual lapping method.
I2RH01140136-01
I2RH0B140103-01
I6RS0C140020-01
Page 367 of 1496
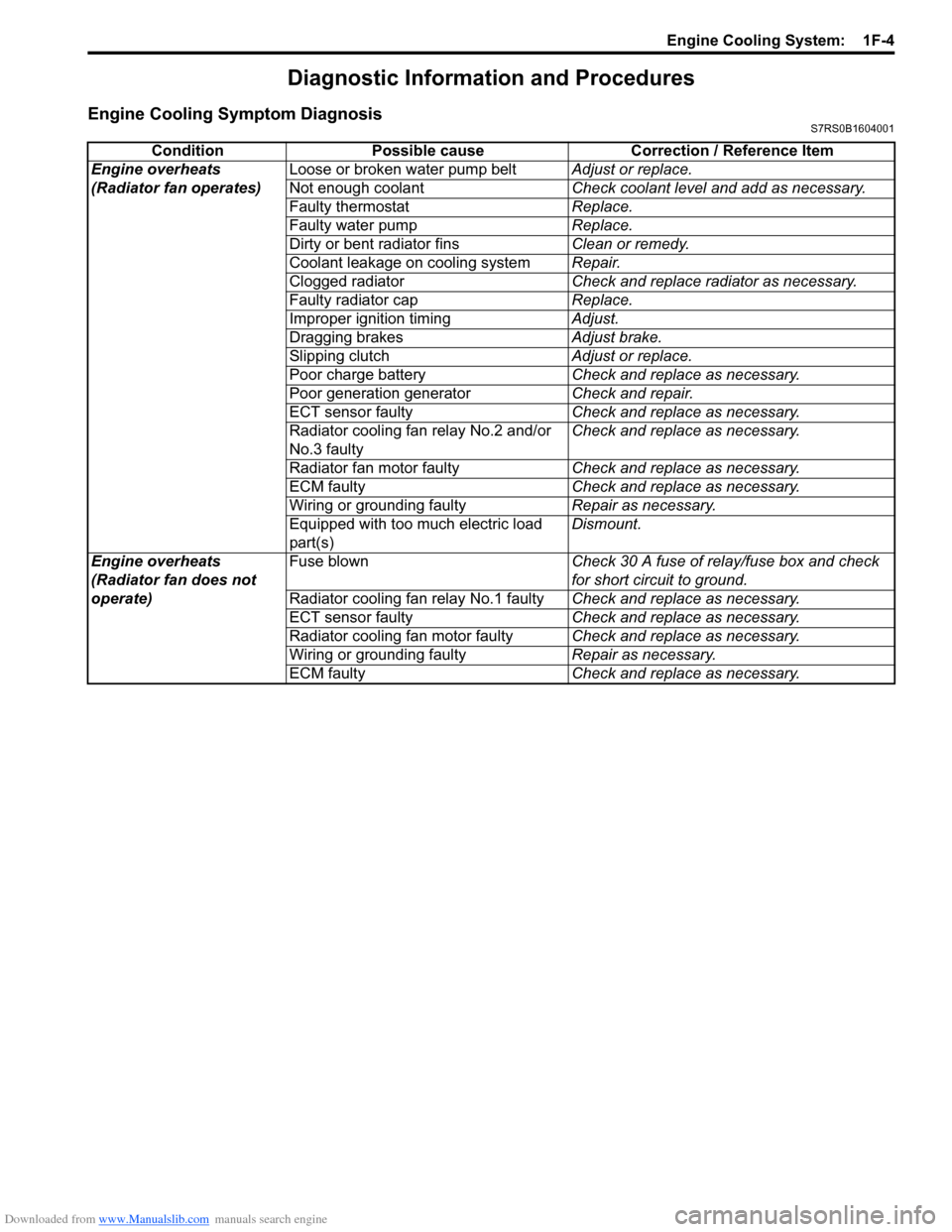
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Cooling System: 1F-4
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Engine Cooling Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B1604001
ConditionPossible cause Correction / Reference Item
Engine overheats
(Radiator fan operates) Loose or broken water pump belt
Adjust or replace.
Not enough coolant Check coolant level and add as necessary.
Faulty thermostat Replace.
Faulty water pump Replace.
Dirty or bent radiator fins Clean or remedy.
Coolant leakage on cooling system Repair.
Clogged radiator Check and replace radiator as necessary.
Faulty radiator cap Replace.
Improper ignition timing Adjust.
Dragging brakes Adjust brake.
Slipping clutch Adjust or replace.
Poor charge battery Check and replace as necessary.
Poor generation generator Check and repair.
ECT sensor faulty Check and replace as necessary.
Radiator cooling fan relay No.2 and/or
No.3 faulty Check and replace as necessary.
Radiator fan motor faulty Check and replace as necessary.
ECM faulty Check and replace as necessary.
Wiring or grounding faulty Repair as necessary.
Equipped with too much electric load
part(s) Dismount.
Engine overheats
(Radiator fan does not
operate) Fuse blown
Check 30 A fuse of relay/fuse box and check
for short circuit to ground.
Radiator cooling fan relay No.1 faulty Check and replace as necessary.
ECT sensor faulty Check and replace as necessary.
Radiator cooling fan motor faulty Check and replace as necessary.
Wiring or grounding faulty Repair as necessary.
ECM faulty Check and replace as necessary.
Page 389 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Fuel System: 1G-14
Fuel Tank Purging ProcedureS7RS0B1706015
WARNING!
• Before starting the following procedure, be sure to observe “Precautions on Fuel
System Service” in order to reduce the risk
or fire and personal injury.
• This purging procedure will not remove all fuel vapor.
Do not attempt any repair on tank using
heat of flame as an explosion resulting in
personal injury could occur.
CAUTION!
Never remain water in fu el tank after washing,
or fuel tank inside will get corrosion.
The following procedure are used for purging fuel tank.
1) After removing fuel tank, remove all hoses, pipes and fuel pump assembly from fuel tank.
2) Drain all remaining fuel from tank.
3) Place fuel tank to flushing area.
4) Fill tank with warm water or tap water, and agitate
vigorously and drain. Repeat this washing until
inside of tank is clean. Replace tank if its inside is
rusty.
5) Completely flush out rema ining water after washing.
Fuel Pump On-Vehicle InspectionS7RS0B1706016
WARNING!
Before starting the following procedure, be
sure to observe “Precautions on Fuel System
Service” in order to reduce the risk or fire
and personal injury.
NOTE
The fuel pressure regulator is incorporated
with the fuel pump assembly so individual
inspection of it is impossible.
1) Remove filler cap and turn ON ignition switch (2).
Then fuel pump operating sound should be heard
from fuel filler (1) for about 2 seconds and stop. Be
sure to reinstall fuel filler cap after checking.
If the check result is not satisfactory, go to “Fuel
Pump and Its Circuit Check in Section 1A”. 2) Turn OFF ignition switch and leave over 10 minutes
as it is.
3) Fuel pressure should be felt at fuel feed hose (1) for about 2 seconds after ignition switch ON.
If fuel pressure is not felt, go to “Fuel Pressure
Check in Section 1A”.
Fuel Pump Assembly Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1706017
WARNING!
Before starting the following procedure, be
sure to observe “Precautions on Fuel System
Service” in order to reduce the risk or fire
and personal injury.
Removal
1) Remove fuel tank from vehicle. Refer to “Fuel Tank Removal and Installation”.
2) Disconnect fuel feed pipe (1) from fuel pump assembly (2) referring to “Fuel Hose Disconnecting
and Reconnecting”.
IVSY01170013-01
1I3RM0A170019-01
1
2
I6RS0C170008-02
Page 397 of 1496
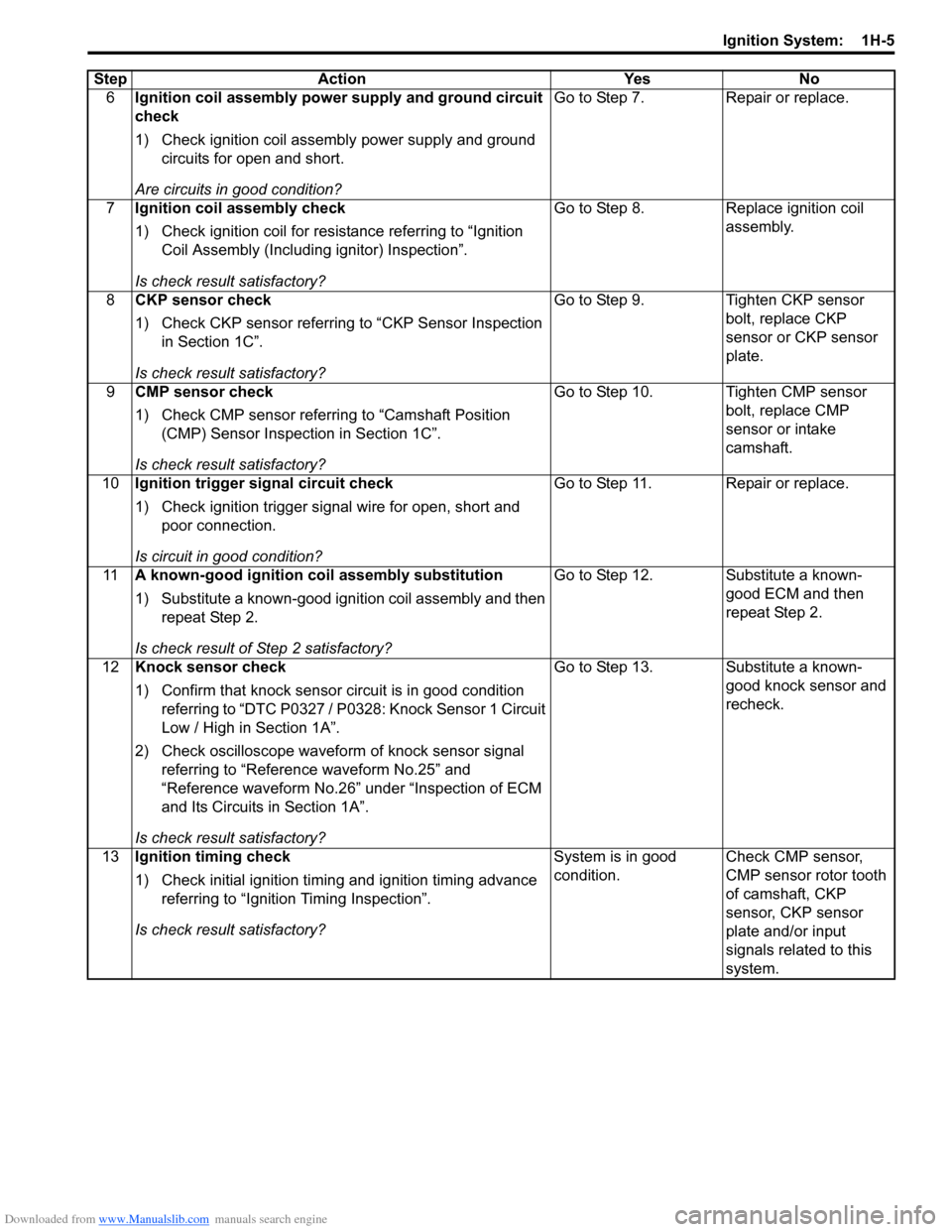
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Ignition System: 1H-5
6Ignition coil assembly power supply and ground circuit
check
1) Check ignition coil assembly power supply and ground
circuits for open and short.
Are circuits in good condition? Go to Step 7.
Repair or replace.
7 Ignition coil assembly check
1) Check ignition coil for resistance referring to “Ignition
Coil Assembly (Including ignitor) Inspection”.
Is check result satisfactory? Go to Step 8.
Replace ignition coil
assembly.
8 CKP sensor check
1) Check CKP sensor referring to “CKP Sensor Inspection
in Section 1C”.
Is check result satisfactory? Go to Step 9.
Tighten CKP sensor
bolt, replace CKP
sensor or CKP sensor
plate.
9 CMP sensor check
1) Check CMP sensor referring to “Camshaft Position
(CMP) Sensor Inspection in Section 1C”.
Is check result satisfactory? Go to Step 10. Tighten CMP sensor
bolt, replace CMP
sensor or intake
camshaft.
10 Ignition trigger signal circuit check
1) Check ignition trigger signal wire for open, short and
poor connection.
Is circuit in good condition? Go to Step 11. Repair or replace.
11 A known-good ignition coil assembly substitution
1) Substitute a known-good ignition coil assembly and then
repeat Step 2.
Is check result of Step 2 satisfactory? Go to Step 12. Substitute a known-
good ECM and then
repeat Step 2.
12 Knock sensor check
1) Confirm that knock sensor circuit is in good condition
referring to “DTC P0327 / P0328: Knock Sensor 1 Circuit
Low / High in Section 1A”.
2) Check oscilloscope waveform of knock sensor signal
referring to “Reference waveform No.25” and
“Reference waveform No.26” under “Inspection of ECM
and Its Circuits in Section 1A”.
Is check result satisfactory? Go to Step 13. Substitute a known-
good knock sensor and
recheck.
13 Ignition timing check
1) Check initial ignition timing and ignition timing advance
referring to “Ignition Timing Inspection”.
Is check result satisfactory? System is in good
condition.
Check CMP sensor,
CMP sensor rotor tooth
of camshaft, CKP
sensor, CKP sensor
plate and/or input
signals related to this
system.
Step
Action YesNo
Page 398 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1H-6 Ignition System:
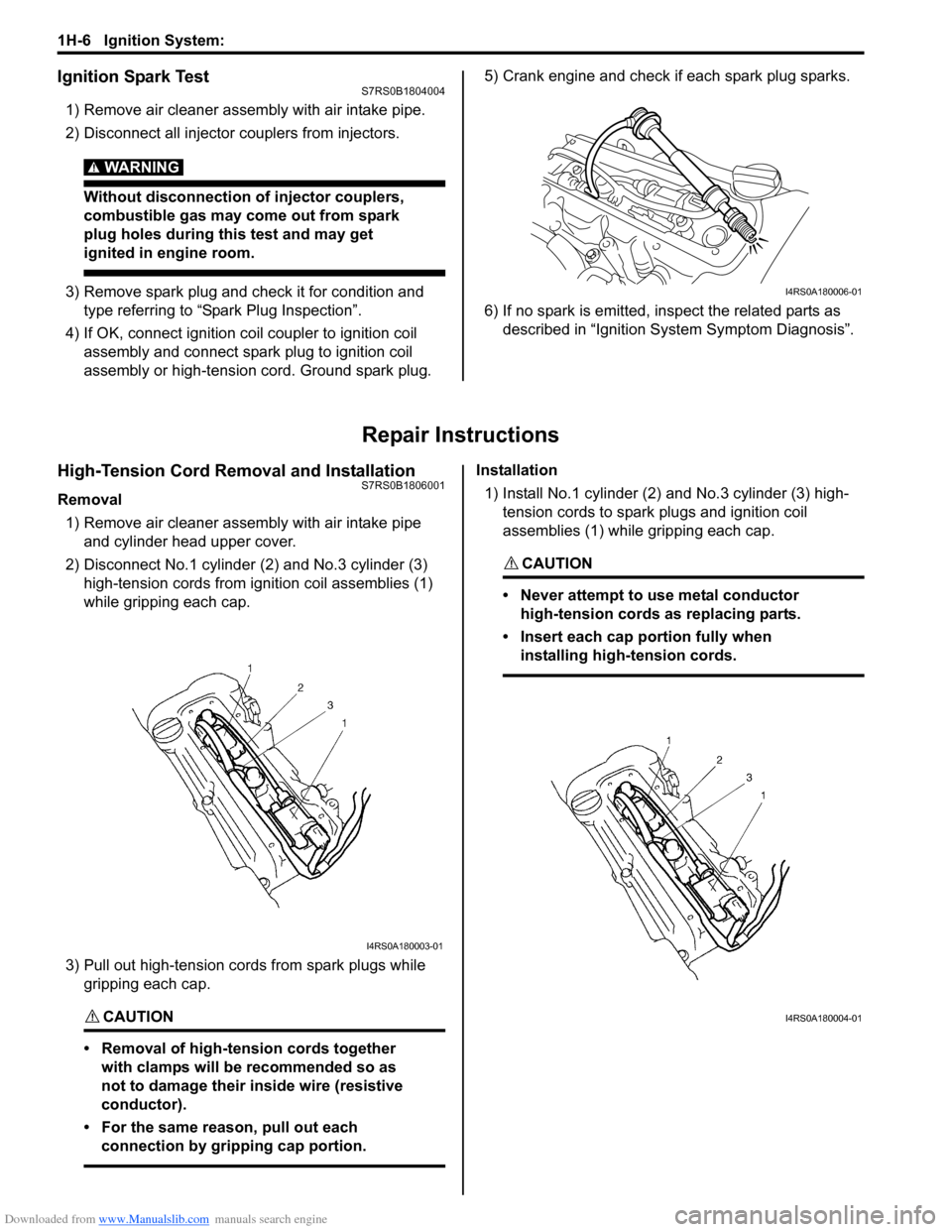
Ignition Spark TestS7RS0B1804004
1) Remove air cleaner assembly with air intake pipe.
2) Disconnect all injector couplers from injectors.
WARNING!
Without disconnection of injector couplers,
combustible gas may come out from spark
plug holes during this test and may get
ignited in engine room.
3) Remove spark plug and check it for condition and
type referring to “Spark Plug Inspection”.
4) If OK, connect ignition coil coupler to ignition coil assembly and connect spark plug to ignition coil
assembly or high-tension cord. Ground spark plug. 5) Crank engine and check if each spark plug sparks.
6) If no spark is emitted, inspect the related parts as
described in “Ignition System Symptom Diagnosis”.
Repair Instructions
High-Tension Cord Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1806001
Removal
1) Remove air cleaner assembly with air intake pipe and cylinder head upper cover.
2) Disconnect No.1 cylinder (2) and No.3 cylinder (3)
high-tension cords from ignition coil assemblies (1)
while gripping each cap.
3) Pull out high-tension cords from spark plugs while gripping each cap.
CAUTION!
• Removal of high-tension cords together with clamps will be recommended so as
not to damage their inside wire (resistive
conductor).
• For the same reason, pull out each connection by gripping cap portion.
Installation
1) Install No.1 cylinder (2) and No.3 cylinder (3) high-
tension cords to spark plugs and ignition coil
assemblies (1) while gripping each cap.
CAUTION!
• Never attempt to use metal conductor high-tension cords as replacing parts.
• Insert each cap portion fully when installing high-tension cords.
I4RS0A180006-01
I4RS0A180003-01
I4RS0A180004-01
Page 400 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1H-8 Ignition System:
Ignition Coil Assembly (Including ignitor)
Removal and Installation
S7RS0B1806005
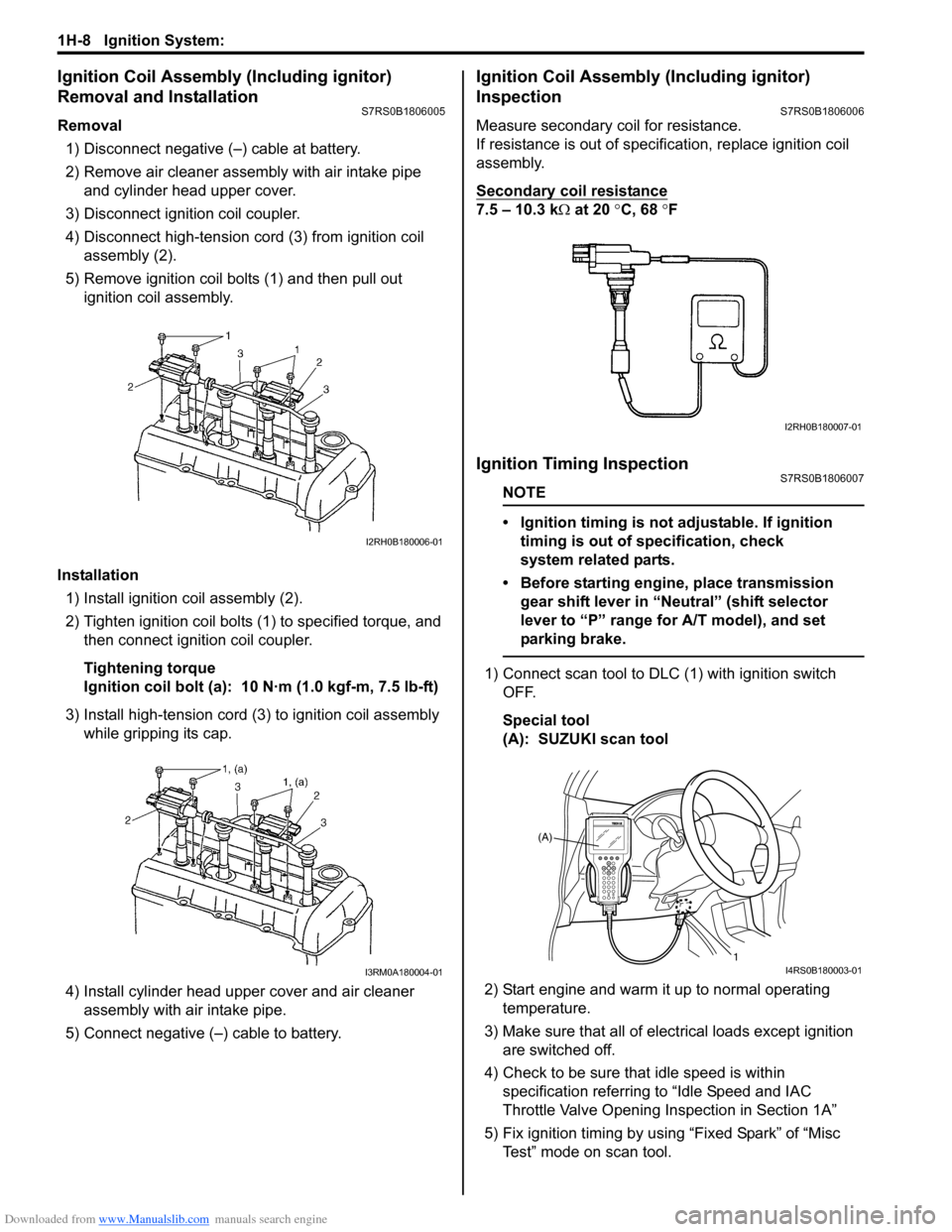
Removal1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Remove air cleaner assembly with air intake pipe and cylinder head upper cover.
3) Disconnect ignition coil coupler.
4) Disconnect high-tension cord (3) from ignition coil assembly (2).
5) Remove ignition coil bolts (1) and then pull out ignition coil assembly.
Installation 1) Install ignition coil assembly (2).
2) Tighten ignition coil bolts (1) to specified torque, and then connect igni tion coil coupler.
Tightening torque
Ignition coil bolt (a): 10 N·m (1.0 kgf-m, 7.5 lb-ft)
3) Install high-tension cord (3) to ignition coil assembly while gripping its cap.
4) Install cylinder head upper cover and air cleaner assembly with air intake pipe.
5) Connect negative (–) cable to battery.
Ignition Coil Assembly (Including ignitor)
Inspection
S7RS0B1806006
Measure secondary coil for resistance.
If resistance is out of specification, replace ignition coil
assembly.
Secondary coil resistance
7.5 – 10.3 k Ω at 20 °C, 68 ° F
Ignition Timing InspectionS7RS0B1806007
NOTE
• Ignition timing is not adjustable. If ignition
timing is out of specification, check
system related parts.
• Before starting engine, place transmission gear shift lever in “Neutral” (shift selector
lever to “P” range for A/T model), and set
parking brake.
1) Connect scan tool to DLC (1) with ignition switch OFF.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
2) Start engine and warm it up to normal operating temperature.
3) Make sure that all of electrical loads except ignition are switched off.
4) Check to be sure that idle speed is within specification referring to “Idle Speed and IAC
Throttle Valve Opening Inspection in Section 1A”
5) Fix ignition timing by using “Fixed Spark” of “Misc Test” mode on scan tool.
I2RH0B180006-01
I3RM0A180004-01
I2RH0B180007-01
(A)
1
I4RS0B180003-01