Vin SUZUKI SWIFT 2006 2.G Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2006, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2006 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 413 of 1496
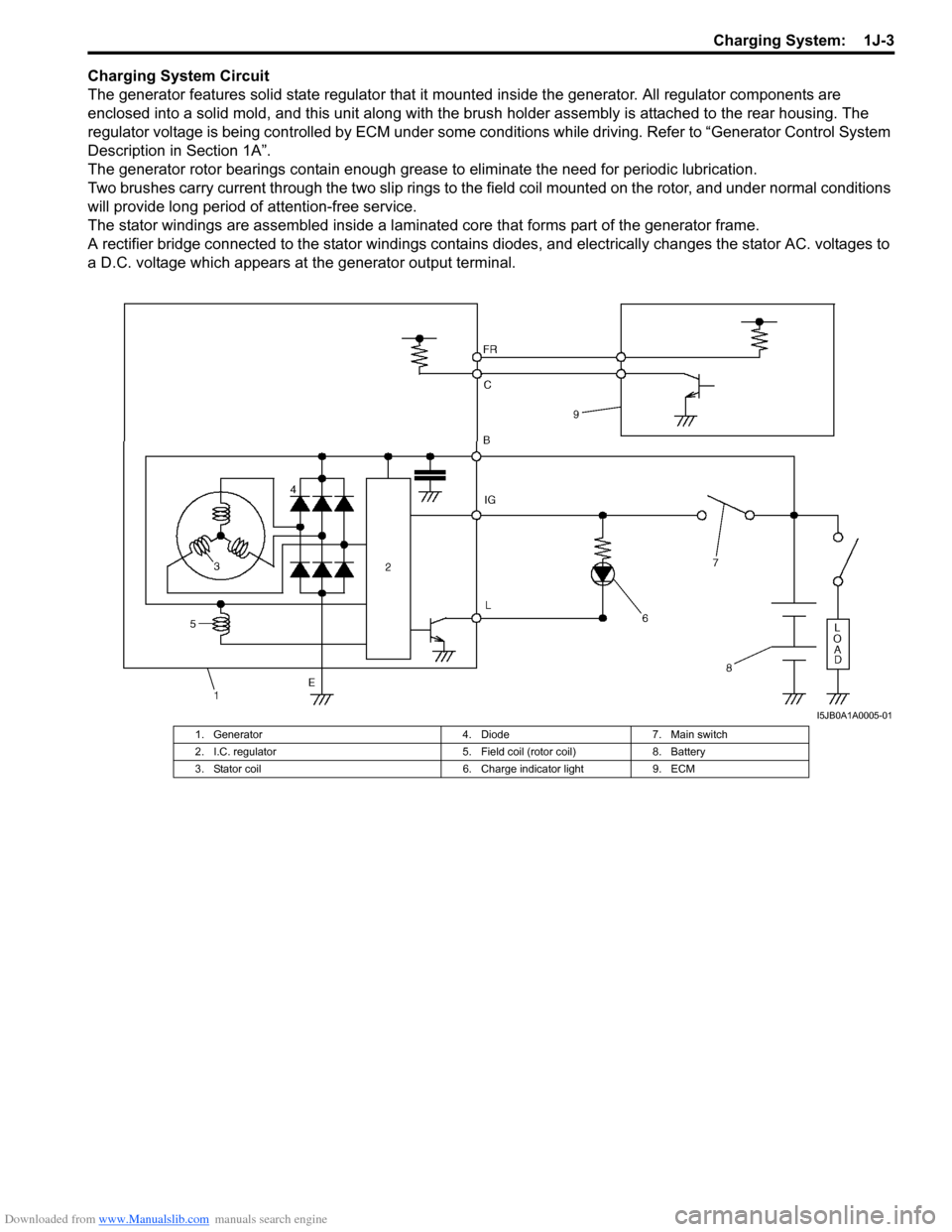
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Charging System: 1J-3
Charging System Circuit
The generator features solid state regulator that it mounted inside the generator. All regulator components are
enclosed into a solid mold, and this unit along with the brus h holder assembly is attached to the rear housing. The
regulator voltage is being controlled by ECM under some cond itions while driving. Refer to “Generator Control System
Description in Section 1A”.
The generator rotor bearings contain enough grease to eliminate the need for periodic lubrication.
Two brushes carry current through the two slip rings to the field coil mounted on the rotor, and under normal conditions
will provide long period of attention-free service.
The stator windings are assembled inside a laminate d core that forms part of the generator frame.
A rectifier bridge connected to the stator windings contains diodes, and electrically changes the stator AC. voltages to
a D.C. voltage which appears at the generator output terminal.
I5JB0A1A0005-01
1. Generator 4. Diode7. Main switch
2. I.C. regulator 5. Field coil (rotor coil)8. Battery
3. Stator coil 6. Charge indicator light9. ECM
Page 414 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1J-4 Charging System:
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Battery InspectionS7RS0B1A04001
Common Causes of Failure
A battery is not designed to last indefinitely; however, with proper care, it will provide many years of service. If the
battery performs satisfactorily during te st but fails to operate properly for no apparent reason, the following are some
factors that may point to the cause of trouble:
• Accessories left on overnight or for an extended period without the generator operating.
• Slow average driving speeds for short periods.
• Electrical load exceeding generator output partic ularly with addition of aftermarket equipment.
• Defects in charging system such as high resistance, s lipping drive belt, loose generator output terminal, faulty
generator or voltage regulator, Refer to “Generator Symptom Diagnosis”.
• Battery abuse, including failure to keep battery cable terminals clean and tight or loose battery hold down.
• Mechanical problems in electrical sys tem such as shorted or pinched wires.
Visual Inspection
Check for obvious damage, such as cracked or broken case or cover, that could permit loss of electrolyte. If obvious
damage is noted, replace battery. Determine cause of damage and correct as needed.
Generator Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B1A04002
CAUTION!
• Do not mistake polarities of “IG” terminal and “L” terminal.
• Do not create short circuit between “IG” and “L” terminals. Always connect these terminals through a lamp.
• Do not connect any load between “L” and “E” terminals.
• When connecting charger or booster battery to vehicle battery, refer to “Jump Starting in Case of Emergency”.
Trouble in charging system will show up as one or more of the following conditions:
1) Faulty indicator lamp operation.
2) An undercharged battery as evidenced by slow cranking or indicator dark.
3) An overcharged battery as evidenced by ex cessive spewing of electrolyte from vents.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Noisy generator Loose drive belt Adjust or replace drive belt.
Loose drive belt pulley Tighten by specified torque.
Loose mounting bolts Tighten by specified torque.
Worn or dirty bearings Replace.
Defective diode or stator Replace.
Charge light does not
light with ignition ON and
engine off Fuse blown
Replace fuse and check for shorted circuit.
Indicator lamp (LED) faulty Replace combination meter.
Wiring connection loose Tighten loose connection.
IC regulator or field coil faulty Replace.
Poor contact between brush and slip
ring Repair or replace.
Charge light does not go
out with engine running
(battery requires frequent
recharging) Drive belt loose or worn
Adjust or replace drive belt.
IC regulator or generator faulty Replace.
Wiring faulty Repair wiring.
Page 418 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1J-8 Charging System:
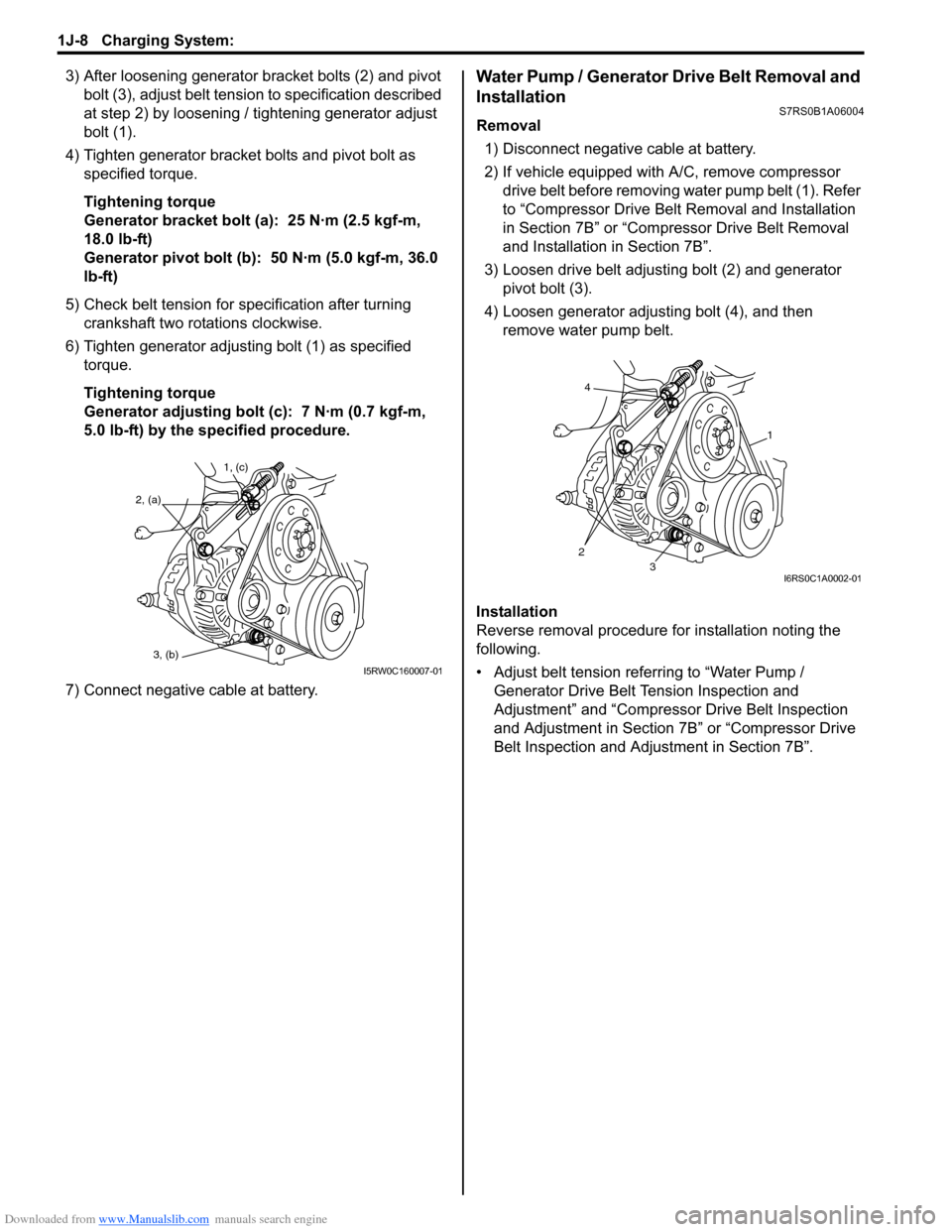
3) After loosening generator bracket bolts (2) and pivot bolt (3), adjust belt tensio n to specification described
at step 2) by loosening / tightening generator adjust
bolt (1).
4) Tighten generator bracket bolts and pivot bolt as specified torque.
Tightening torque
Generator bracket bolt (a): 25 N·m (2.5 kgf-m,
18.0 lb-ft)
Generator pivot bolt (b): 50 N·m (5.0 kgf-m, 36.0
lb-ft)
5) Check belt tension for specification after turning crankshaft two rotations clockwise.
6) Tighten generator adjusting bolt (1) as specified torque.
Tightening torque
Generator adjusting bolt (c): 7 N·m (0.7 kgf-m,
5.0 lb-ft) by the specified procedure.
7) Connect negative cable at battery.Water Pump / Generator Drive Belt Removal and
Installation
S7RS0B1A06004
Removal 1) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
2) If vehicle equipped with A/C, remove compressor drive belt before removing water pump belt (1). Refer
to “Compressor Drive Belt Removal and Installation
in Section 7B” or “Compr essor Drive Belt Removal
and Installation in Section 7B”.
3) Loosen drive belt adjusting bolt (2) and generator pivot bolt (3).
4) Loosen generator adjusting bolt (4), and then remove water pump belt.
Installation
Reverse removal procedure for installation noting the
following.
• Adjust belt tension referring to “Water Pump / Generator Drive Belt Tension Inspection and
Adjustment” and “Compressor Drive Belt Inspection
and Adjustment in Section 7B” or “Compressor Drive
Belt Inspection and Adjustment in Section 7B”.
1, (c)
2, (a)
3, (b)
I5RW0C160007-01
4
23
1
I6RS0C1A0002-01
Page 432 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2A-1 Suspension General Diagnosis:
Suspension
Suspension General Diagnosis
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Suspension, Wheels and Tires Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B2104001
ConditionPossible cause Correction / Reference Item
Vehicle pulls (Leads) Mismatched or uneven tires Replace tires.
Tires not adequately inflated Adjust tire pressure.
Broken or sagging coil springs Replace coil springs.
Radial tire lateral force Replace tire.
Disturbed wheel alignment Check and adjust wheel alignment.
Brake dragging in one road wheel Repair brake.
Loose, bent or broken front or rear
suspension parts Tighten or replace related suspension parts.
Abnormal or excessive
tire wear Sagging or broken coil spring
Replace coil spring.
Tire out of balance Adjust balance or replace tire.
Disturbed wheel alignment Check and adjust wheel alignment.
Faulty strut (shock absorber) Replace strut (shock absorber).
Hard driving Replace tires.
Overloaded vehicle Replace tires and check suspension parts.
Not rotated tires Replace or rotate tires.
Worn or loose wheel bearing Replace wheel bearing.
Wobbly wheel or tire Replace wheel or tire.
Tires not adequately inflated Adjust tire pressure.
Wheel tramp Blister or bump on tire Replace tire.
Improper strut (shock absorber) action Replace strut (shock absorber).
Shimmy, shake or
vibration Tire or wheel out of balance
Balance wheel or replace tire and/or wheel.
Loosen wheel bearings Replace wheel bearings.
Worn tie-rod ends Replace tie-rod ends.
Worn lower ball joints Replace front suspension control arm.
Excessive wheel runout Repair or replace wheel and/or tire.
Blister or bump on tire Replace tire.
Excessively loaded radial runout of tire /
wheel assembly Replace tire or wheel.
Disturbed wheel alignment Check and adjust wheel alignment.
Loose or worn steering linkage Tighten or replace steering linkage.
Loose steering gear case bolts Tighten steering gear case bolts.
Abnormal noise, front end Worn, sticky or loose tie-rod ends, lower
ball joints, tie-rod in side ball joints or
drive shaft joints Replace tie-rod end, su
spension arm, tie-rod
or drive shaft joint.
Damaged struts or mountings Repair or replace struts or mountings.
Worn suspension arm bushings Replace suspension arm bushings.
Loose stabilizer bar Tighten bolts or nuts and/or replace bushes.
Loose wheel nuts Tighten wheel nuts.
Loose suspension bolts or nuts Tighten suspension bolts or nuts.
Broken or damaged wheel bearings Replace wheel bearings.
Broken suspension springs Replace suspension springs.
Poorly lubricated or worn strut bearings Replace strut bearing.
Malfunction of Power Steering System Check and correct malfunction.
Low or uneven trim height
NOTE
See NOTE *1.
Broken or sagging coil springs Replace coil springs.
Over loaded Check loading.
Incorrect coil springs Replace coil spring.
Tires not adequately inflated Adjust tire pressure.
Ride too soft Faulty strut (shock absorber) Replace strut (shock absorber).
Suspension bottoms Overloaded Check loading.
Faulty strut (shock absorber) Replace strut (shock absorber).
Incorrect, broken or sagging coil springs Replace coil spring.
Page 437 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Front Suspension: 2B-4
Reference Information
Side slip
When checked with side slip tester, side slip should
satisfy following specification.Side slip
0 to IN 3.0 mm/m (0 to IN 0.118 in/3.3 ft)
If side slip is greatly di
fferent, toe or front wheel
alignment may not be correct.
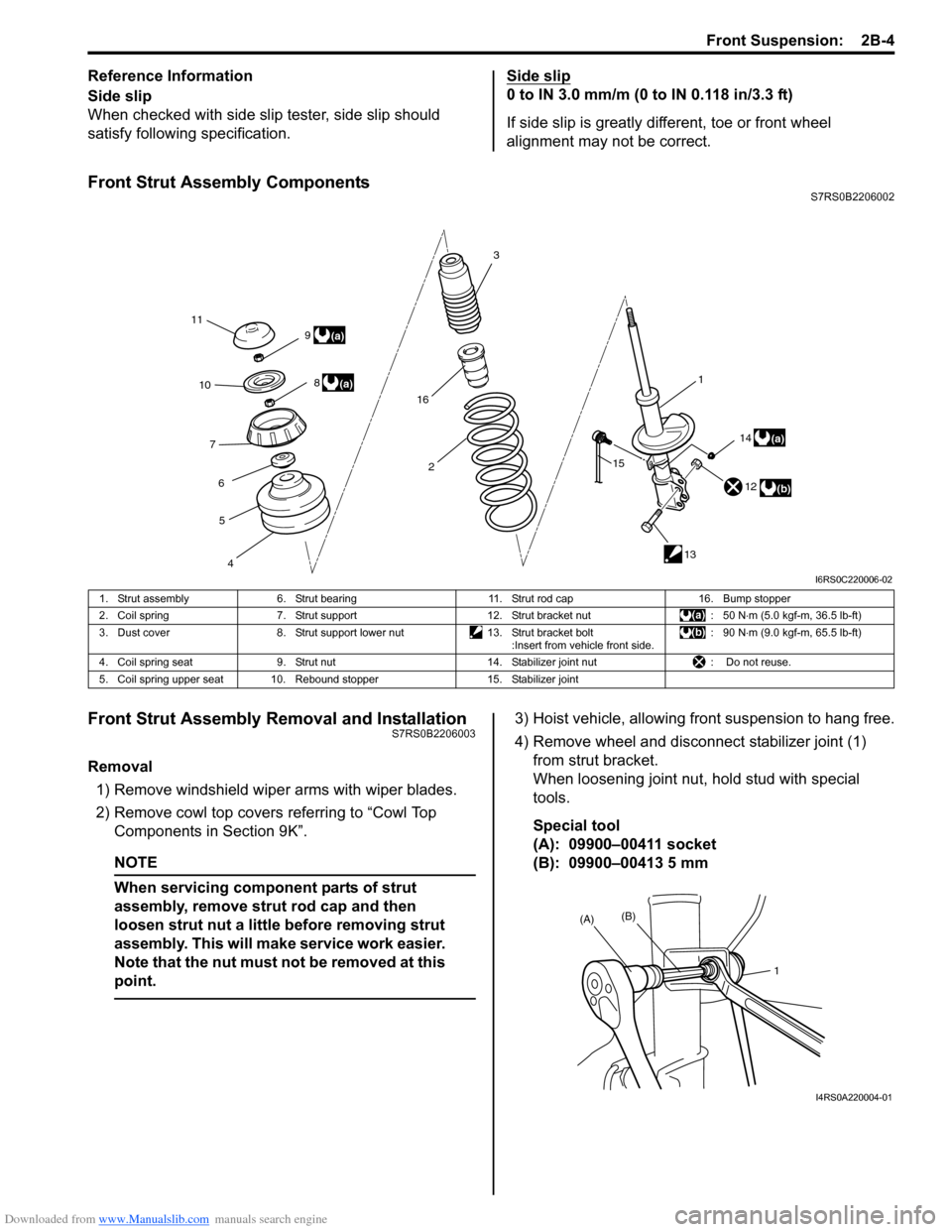
Front Strut Assembly ComponentsS7RS0B2206002
Front Strut Assembly Removal and InstallationS7RS0B2206003
Removal
1) Remove windshield wipe r arms with wiper blades.
2) Remove cowl top covers referring to “Cowl Top
Components in Section 9K”.
NOTE
When servicing component parts of strut
assembly, remove stru t rod cap and then
loosen strut nut a little before removing strut
assembly. This will make service work easier.
Note that the nut must not be removed at this
point.
3) Hoist vehicle, allowing front suspension to hang free.
4) Remove wheel and disconn ect stabilizer joint (1)
from strut bracket.
When loosening joint nu t, hold stud with special
tools.
Special tool
(A): 09900–00411 socket
(B): 09900–00413 5 mm
11 3
2 1
12
13
4
5
6
7
10
8(a)
(b)
9
(a)
14
15(a)
16
I6RS0C220006-02
1. Strut assembly
6. Strut bearing 11. Strut rod cap16. Bump stopper
2. Coil spring 7. Strut support 12. Strut bracket nut : 50 N⋅m (5.0 kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft)
3. Dust cover 8. Strut support lower nut 13. Strut bracket bolt
:Insert from vehicle front side. : 90 N
⋅m (9.0 kgf-m, 65.5 lb-ft)
4. Coil spring seat 9. Strut nut 14. Stabilizer joint nut : Do not reuse.
5. Coil spring upper seat 10. Rebound stopper 15. Stabilizer joint
1
(A)
(B)
I4RS0A220004-01
Page 441 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Front Suspension: 2B-8
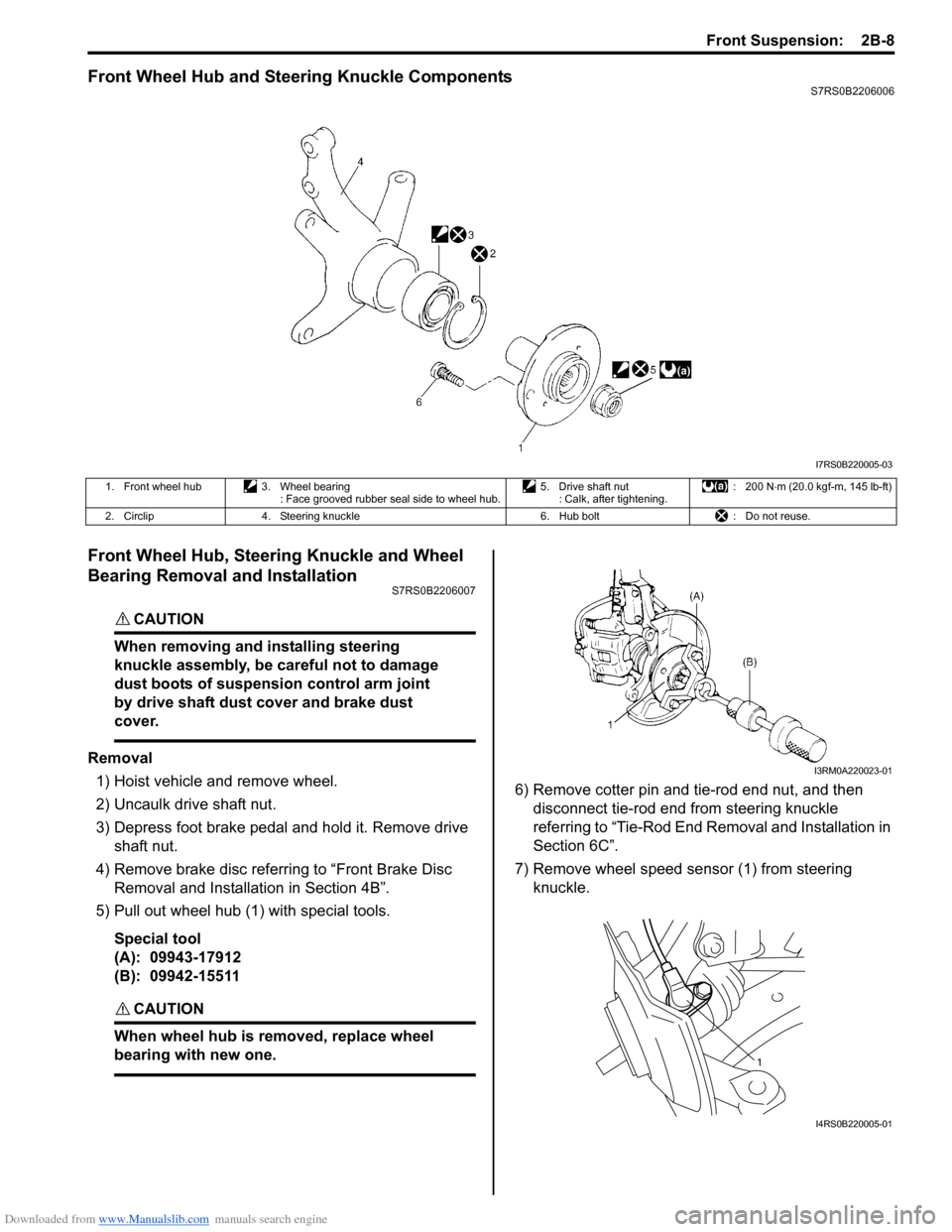
Front Wheel Hub and Steering Knuckle ComponentsS7RS0B2206006
Front Wheel Hub, Steering Knuckle and Wheel
Bearing Removal and Installation
S7RS0B2206007
CAUTION!
When removing and installing steering
knuckle assembly, be careful not to damage
dust boots of suspension control arm joint
by drive shaft dust cover and brake dust
cover.
Removal1) Hoist vehicle and remove wheel.
2) Uncaulk drive shaft nut.
3) Depress foot brake pedal and hold it. Remove drive shaft nut.
4) Remove brake disc referring to “Front Brake Disc Removal and Installa tion in Section 4B”.
5) Pull out wheel hub (1) with special tools.
Special tool
(A): 09943-17912
(B): 09942-15511
CAUTION!
When wheel hub is removed, replace wheel
bearing with new one.
6) Remove cotter pin and tie-rod end nut, and then disconnect tie-rod end from steering knuckle
referring to “Tie-Rod End Removal and Installation in
Section 6C”.
7) Remove wheel speed sensor (1) from steering knuckle.
I7RS0B220005-03
1. Front wheel hub 3. Wheel bearing
: Face grooved rubber seal side to wheel hub. 5. Drive shaft nut
: Calk, after tightening. : 200 N
⋅m (20.0 kgf-m, 145 lb-ft)
2. Circlip 4. Steering knuckle 6. Hub bolt: Do not reuse.
I3RM0A220023-01
1
I4RS0B220005-01
Page 445 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Front Suspension: 2B-12
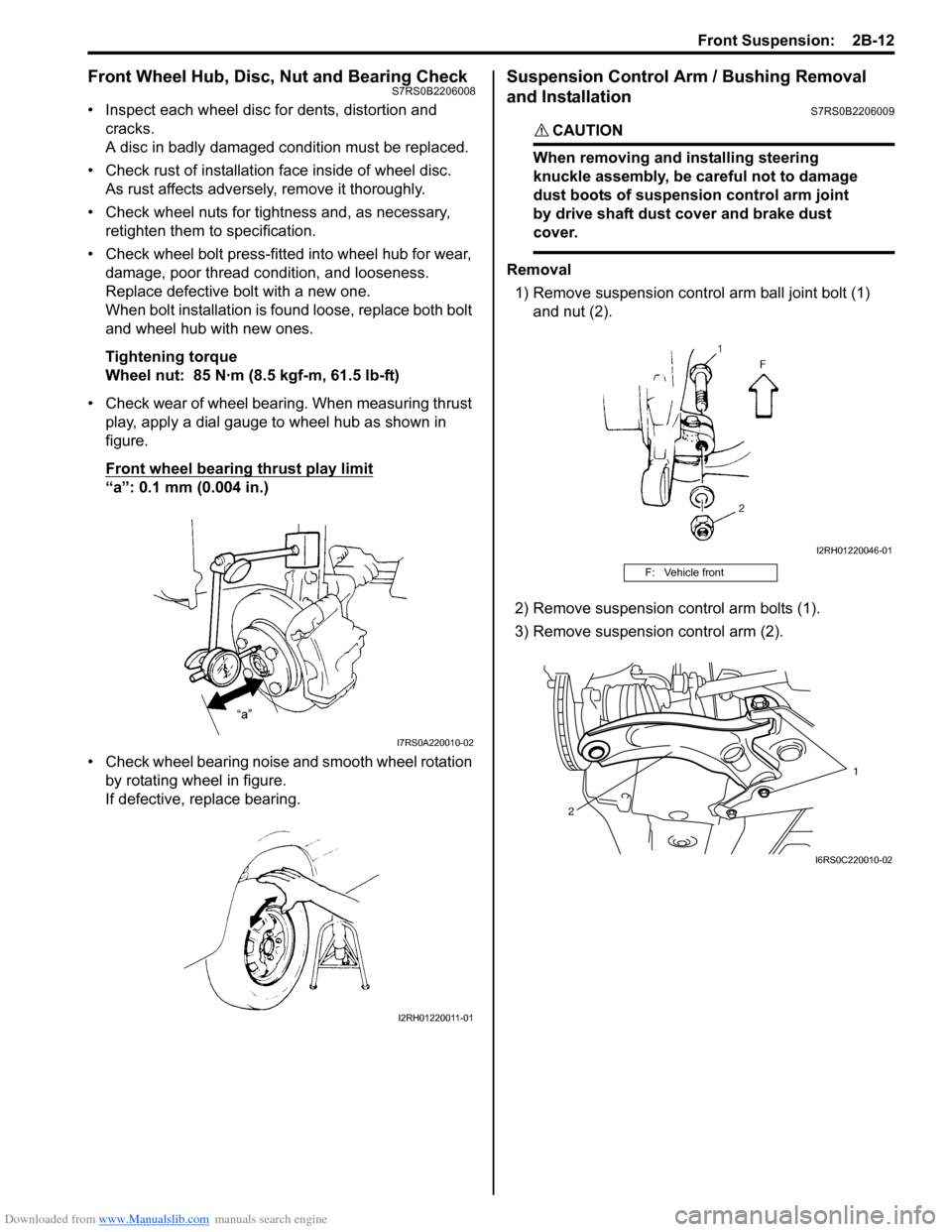
Front Wheel Hub, Disc, Nut and Bearing CheckS7RS0B2206008
• Inspect each wheel disc for dents, distortion and cracks.
A disc in badly damaged condition must be replaced.
• Check rust of installation face inside of wheel disc.
As rust affects adversely, remove it thoroughly.
• Check wheel nuts for tightness and, as necessary, retighten them to specification.
• Check wheel bolt press-fitted into wheel hub for wear, damage, poor thread condition, and looseness.
Replace defective bolt with a new one.
When bolt installation is found loose, replace both bolt
and wheel hub with new ones.
Tightening torque
Wheel nut: 85 N·m (8.5 kgf-m, 61.5 lb-ft)
• Check wear of wheel bearing. When measuring thrust play, apply a dial gauge to wheel hub as shown in
figure.
Front wheel bearing thrust play limit
“a”: 0.1 mm (0.004 in.)
• Check wheel bearing noise and smooth wheel rotation by rotating wheel in figure.
If defective, replace bearing.
Suspension Control Arm / Bushing Removal
and Installation
S7RS0B2206009
CAUTION!
When removing and installing steering
knuckle assembly, be ca reful not to damage
dust boots of suspension control arm joint
by drive shaft dust cover and brake dust
cover.
Removal
1) Remove suspension contro l arm ball joint bolt (1)
and nut (2).
2) Remove suspension control arm bolts (1).
3) Remove suspension control arm (2).
I7RS0A220010-02
I2RH01220011-01
F: Vehicle front
I2RH01220046-01
1
2
I6RS0C220010-02
Page 448 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2B-15 Front Suspension:
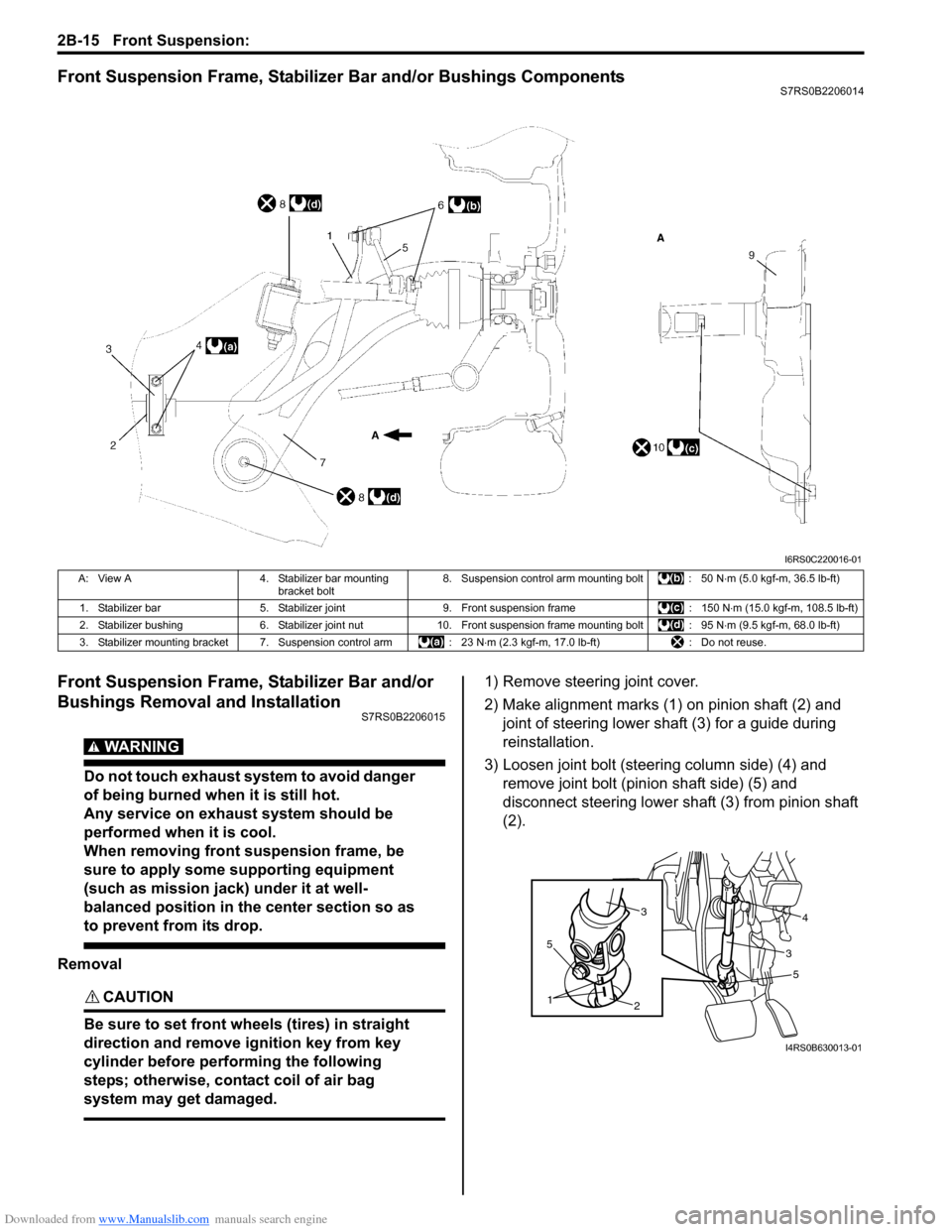
Front Suspension Frame, Stabilizer Bar and/or Bushings ComponentsS7RS0B2206014
Front Suspension Frame, Stabilizer Bar and/or
Bushings Removal and Installation
S7RS0B2206015
WARNING!
Do not touch exhaust system to avoid danger
of being burned when it is still hot.
Any service on exhaust system should be
performed when it is cool.
When removing front suspension frame, be
sure to apply some supporting equipment
(such as mission jack) under it at well-
balanced position in the center section so as
to prevent from its drop.
Removal
CAUTION!
Be sure to set front wheels (tires) in straight
direction and remove ignition key from key
cylinder before performing the following
steps; otherwise, contact coil of air bag
system may get damaged.
1) Remove steering joint cover.
2) Make alignment marks (1) on pinion shaft (2) and joint of steering lower shaft (3) for a guide during
reinstallation.
3) Loosen joint bolt (steering column side) (4) and remove joint bolt (pin ion shaft side) (5) and
disconnect steering lower shaft (3) from pinion shaft
(2).
I6RS0C220016-01
A: View A 4. Stabilizer bar mounting
bracket bolt 8. Suspension control arm mounting bolt : 50 N
⋅m (5.0 kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft)
1. Stabilizer bar 5. Stabilizer joint 9. Front suspension frame : 150 N⋅m (15.0 kgf-m, 108.5 lb-ft)
2. Stabilizer bushing 6. Stabilizer joint nut10. Front suspension frame mounting bolt : 95 N ⋅m (9.5 kgf-m, 68.0 lb-ft)
3. Stabilizer mounting bracket 7. Suspension control arm : 23 N⋅m (2.3 kgf-m, 17.0 lb-ft) : Do not reuse.
5
2
1
5
34
3
I4RS0B630013-01
Page 468 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2D-1 Wheels and Tires:
Suspension
Wheels and Tires
Precautions
Precaution for Emergency Flat Tire Repair KitS7RS0B2400001
WARNING!
Flat tire repair sealant including in kit is
harmful. Be sure to observe the following.
Otherwise, your health may be ruined.
• If swallowed, get medical attention immediately.
• Keep out of reach of children.
• Select place where there is good ventilation for this work.
• If it enters eye or contacts skin, wash thoroughly with water. If anything
abnormal still rema ins, get medical
attention immediately.
• Do not discard tire containing sealant as it is. Make sure to remove sealant from tire,
referring to “Tire Repair for Emergency
Repaired-Tire with Sealant”.
• Dispose of sealant as waste oil.
CAUTION!
• When tire repaired with Emergency Flat Tire Repair Kit is brought in, remove flat
tire repair sealant from tire and repair flat
tire referring to “Tire Repair for Emergency
Repaired-Tire with Sealant”.
• Sealant expiration date is printed on bottle label. if it expires, sealant should be
replaced with a new one to ensure
emergency flat tire repair.
General Description
Tires DescriptionS7RS0B2401001
The tire is of tubeless type. The tire is designed to
operate satisfactorily with loads up to the full rated load
capacity when inflated to the recommended inflation
pressures.
Correct tire pressures and driving habits have an
important influence on tire life. Heavy cornering,
excessively rapid acceleration, and unnecessary sharp
braking increase tire wear.
Tire Placard
The “Tire Placard” is located on the left or right door lock
pillar and should be referred to tire information.
The placard lists the maximum load, tire size and cold
tire pressure where applicable.
NOTE
Whether rim size and/or maximum load are
listed or not depends on regulations of each
country.
Inflation of Tires
The pressure recommended for any model is carefully
calculated to give a satisfacto ry ride, stability, steering,
tread wear, tire life and resistance to bruises.
Tire pressure, with tires cold, (after vehicle has set for 3
hours or more, or driven less than one mile) should be
checked monthly or before any extended trip. Set to the
specifications on the “Tire Placard” located on the left
door lock pillar.
It is normal for tire pressure to increase when the tires
become hot during driving.
Do not bleed or reduce tire pressure after driving.
Bleeding reduces the “Cold Inflation Pressure”.
Higher than recommended pressure can cause:
• Hard ride
• Tire bruising or carcass damage
• Rapid tread wear at center of tire
Unequal pressure on same axle can cause:
• Uneven braking
• Steering lead
• Reduced handling
• Swerve on acceleration
Page 469 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Wheels and Tires: 2D-2
Lower than recommended pressure can cause:
• Tire squeal on turns
• Hard Steering
• Rapid and uneven wear on the edges of the tread
• Tire rim bruises and rupture
• Tire cord breakage
• High tire temperature
• Reduced handling
• High fuel consumption
Replacement Tires
When replacement is necessary, the original equipment
type tire should be used. Refer to the Tire Placard.
Replacement tires should be of the same size, load
range and construction as those originally on the vehicle.
Use of any other size or type tire may affect ride,
handling, speedometer / odometer calibration, vehicle
ground clearance and tire or snow chain clearance to the
body and chassis.
It is recommended that new tires be installed in pairs on
the same axle. If necessary to replace only one tire, it
should be paired with the tire having the most tread, to
equalize braking traction.
WARNING!
Do not mix different types of tires on the
same vehicle such as radial, bias and bias-
belted tires except in emergencies, because
handling may be seriously affected and may
result in loss of control.
The metric term for tire infl ation pressure is the kilo
pascal (kPa). Tire pressures is usually printed in both
kPa and kgf/cm
2 on the “Tire Placard”.
Metric tire gauges are available from tool suppliers.
The chart, shown the table, converts commonly used
inflation pressures from kPa to kgf/cm
2 and psi.
Wheels DescriptionS7RS0B2401002
Wheel Maintenance
Wheel repairs that use welding, heating, or peening are
not approved. All damaged wheels should be replaced.
Replacement Wheels
Wheels must be replaced if they are bent, dented, have
excessive lateral or radial runout, air leak through welds,
have elongated bolt holes, if lug wheel bolts won’t stay
tight, or if they are heavily rusted. Wheels with greater
runout than shown in the following may cause
objectional vibrations.
Replacement wheels must be equivalent to the original
equipment wheels in load capacity, diameter, rim with
offset and mounting configuration. A wheel of improper
size or type may affect wheel and bearing life, brake
cooling, speedometer / odometer calibration, vehicle
ground clearance and tire clearance to body and
chassis.
How to Measure Wheel Runout
To measure the wheel runout, it is necessary to use an
accurate dial indicator. The tire may be on or off the
wheel. The wheel should be installed to the wheel
balancer of the like for proper measurement.
Take measurements of both lateral runout “a” and radial
runout “b” at both inside an d outside of the rim flange.
With the dial indicator set in place securely, turn the
wheel one full revolution slowly and record every reading
of the indicator.
When the measured runout exceeds the specification
and correction by the balancer adjustment is impossible,
replace the wheel. If the reading is affected by welding,
paint or scratch, it should be ignored.
Lateral runout limit “a”
: 0.3 mm (0.012 in.)
Radial runout limit “b”
: 0.3 mm (0.012 in.)
kPa kgf/cm2psi
Conversion: 1 psi =
6.895 kPa 1 kgf/cm
2 =
98.066 kPa 160 1.6 23
180 1.8 26
200 2.0 29
220 2.2 32
240 2.4 35
260 2.6 38
280 2.8 41
300 3.0 44
I4RS0A240001-01