Engine parts SUZUKI SWIFT 2006 2.G Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2006, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2006 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 40 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0B-10 Maintenance and Lubrication:
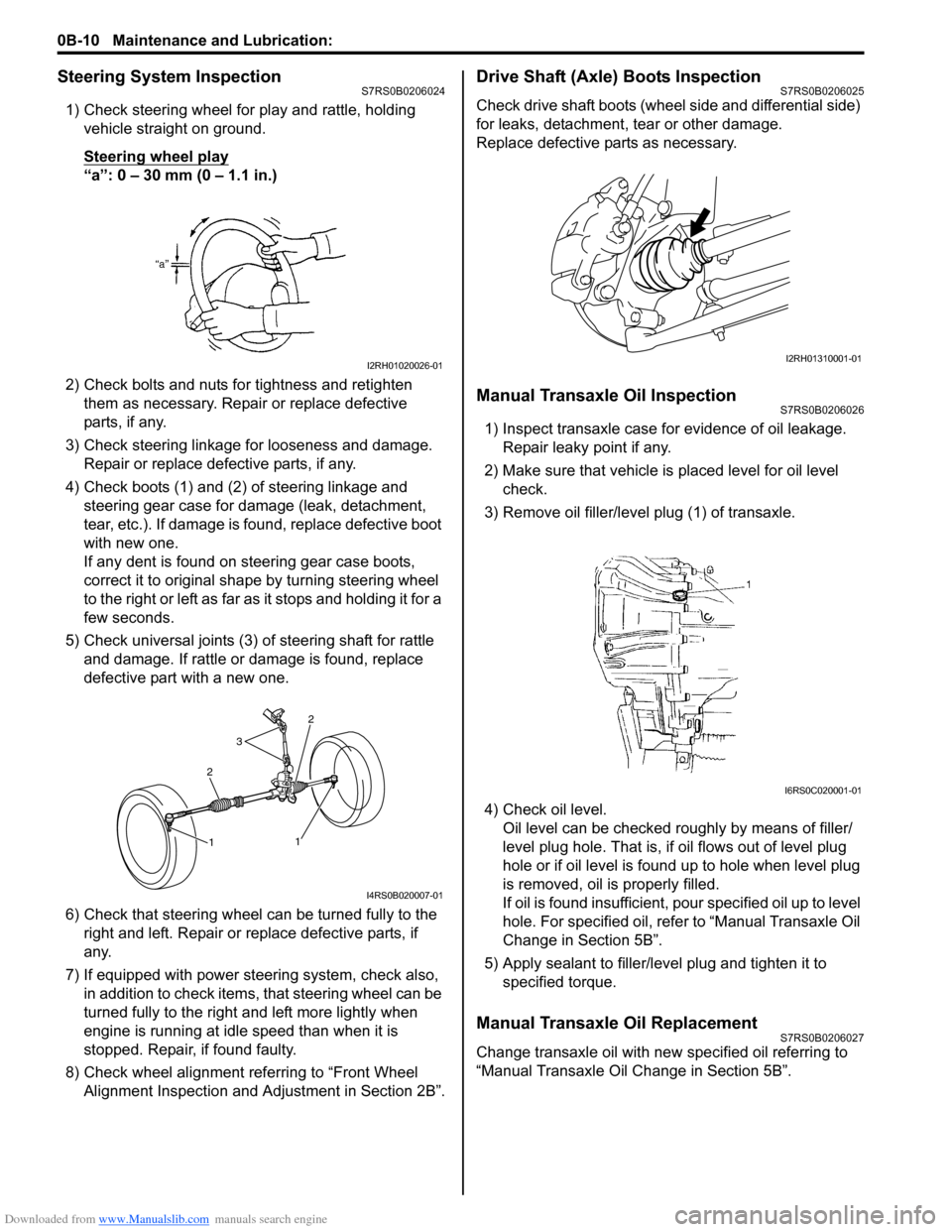
Steering System InspectionS7RS0B0206024
1) Check steering wheel for play and rattle, holding vehicle straight on ground.
Steering wheel play
“a”: 0 – 30 mm (0 – 1.1 in.)
2) Check bolts and nuts for tightness and retighten them as necessary. Repair or replace defective
parts, if any.
3) Check steering linkage for looseness and damage. Repair or replace defective parts, if any.
4) Check boots (1) and (2) of steering linkage and steering gear case for damage (leak, detachment,
tear, etc.). If damage is fo und, replace defective boot
with new one.
If any dent is found on steering gear case boots,
correct it to original shape by turning steering wheel
to the right or left as far as it stops and holding it for a
few seconds.
5) Check universal joints (3) of steering shaft for rattle and damage. If rattle or damage is found, replace
defective part with a new one.
6) Check that steering wheel can be turned fully to the
right and left. Repair or replace defective parts, if
any.
7) If equipped with power steering system, check also, in addition to check items, that steering wheel can be
turned fully to the right and left more lightly when
engine is running at idle speed than when it is
stopped. Repair, if found faulty.
8) Check wheel alignment referring to “Front Wheel Alignment Inspection and Adjustment in Section 2B”.
Drive Shaft (Axle) Boots InspectionS7RS0B0206025
Check drive shaft boots (wheel side and differential side)
for leaks, detachment, tear or other damage.
Replace defective parts as necessary.
Manual Transaxle Oil InspectionS7RS0B0206026
1) Inspect transaxle case for evidence of oil leakage. Repair leaky point if any.
2) Make sure that vehicle is placed level for oil level
check.
3) Remove oil filler/leve l plug (1) of transaxle.
4) Check oil level. Oil level can be checked roughly by means of filler/
level plug hole. That is, if oil flows out of level plug
hole or if oil level is found up to hole when level plug
is removed, oil is properly filled.
If oil is found insufficient, po ur specified oil up to level
hole. For specified oil, refe r to “Manual Transaxle Oil
Change in Section 5B”.
5) Apply sealant to filler/leve l plug and tighten it to
specified torque.
Manual Transaxle Oil ReplacementS7RS0B0206027
Change transaxle oil with new specified oil referring to
“Manual Transaxle Oil Change in Section 5B”.
I2RH01020026-01
2
3
2
1
1
I4RS0B020007-01
I2RH01310001-01
I6RS0C020001-01
Page 52 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-2 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
• Be sure to read “Precautions for Electrical Circuit Service in Section 00” befo re inspection and observe
what is written there.
• ECM replacement: When substituting a known-good ECM, check for the
following conditions. Neglec ting this check may cause
damage to a known-good ECM.
– Resistance value of all relays, actuators is as specified respectively.
– MAP sensor, A/C refrigerant pressure sensor and TP sensor are in good condition and none of power
circuits of these sensors is shorted to ground.
• Communication of ECM, BCM, ABS/ESP ® control
module, combination meter, keyless start control
module, steering angle sensor (ESP ® model) and
TCM (A/T model), is esta blished by CAN (Controller
Area Network). (For more detail of CAN
communication for ECM, refer to “CAN
Communication System Description”). Therefore,
handle CAN communication line with care referring to
“Precaution for CAN Communication System in
Section 00”.
• Immobilizer transponder code registration after
replacing ECM
When ECM is replaced with new one or with another
one, make sure to register immobilizer transponder
code to ECM correctly according to “Procedure after
ECM Replacement in Section 10C”.Precautions of ECM Circuit InspectionS7RS0B1100003
• ECM connectors are waterproofed. Each terminal of the ECM connectors is sealed up with the grommet.
Therefore, when measuring ci rcuit voltage, resistance
and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, do not insert
the tester’s probe into th e sealed terminal at the
harness side. When measuring circuit voltage,
resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector,
connect the special tool to the ECM connectors. And,
insert the tester’s probe into the special tool’s
connectors at the harness side, and then measure
voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal. Or, ECM and
its circuits may be damaged by water.
• Wire colors of the special tool’s connectors are different from the ones of the ECM connectors.
However, the circuit arrangement of the special tool’s
connectors is same as the one of the ECM
connectors. Therefore, measure circuit voltage and
resistance by identifying the terminal location subject
to the measurement.
Precautions of Electric Throttle Body System
Calibration
S7RS0B1100004
After performing one of works described below, it is
necessary to re-register the completely closed throttle
valve reference position stored in memory of ECM. (For
detailed information, refer to “Description of Electric
Throttle Body System Calibration”.) For the procedure to
register such data in ECM, refer to “Electric Throttle
Body System Calibration in Section 1C”.
• To shut off backup power of ECM for such purposes of battery replacement or “DOME” fuse removal
• To erase DTCs P0122, P01 23, P0222, P0223, P2101,
P2102, P2103, P2111, P2112, P2113, P2119, P2123,
P2127, P2128, P2135 and/or P2138
• To replace ECM
• To replace throttle body and/or accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor assembly
General Description
Statement on Cleanliness and CareS7RS0B1101001
An automobile engine is a combination of many
machined, honed, polished and lapped surfaces with
tolerances that are measured in the thousands of an
millimeter (ten thous ands of an inch).
Accordingly, when any internal engine parts are
serviced, care and cleanliness are important.
It should be understood that proper cleaning and
protection of machined surfaces and friction areas is part
of the repair procedure. This is considered standard
shop practice even if not specifically stated.
• A liberal coating of engine oil should be applied to friction areas during assembly to protect and lubricate
the surfaces on initial operation. • Whenever valve train components, pistons, piston
rings, connecting rods, rod bearings, and crankshaft
journal bearings are removed for service, they should
be retained in order.
At the time of installation, they should be installed in
the same locations and with the same mating
surfaces as when removed.
• Battery cables should be disconnected before any major work is performed on the engine.
Failure to disconnect cables may result in damage to
wire harness or other electrical parts.
Page 53 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-3
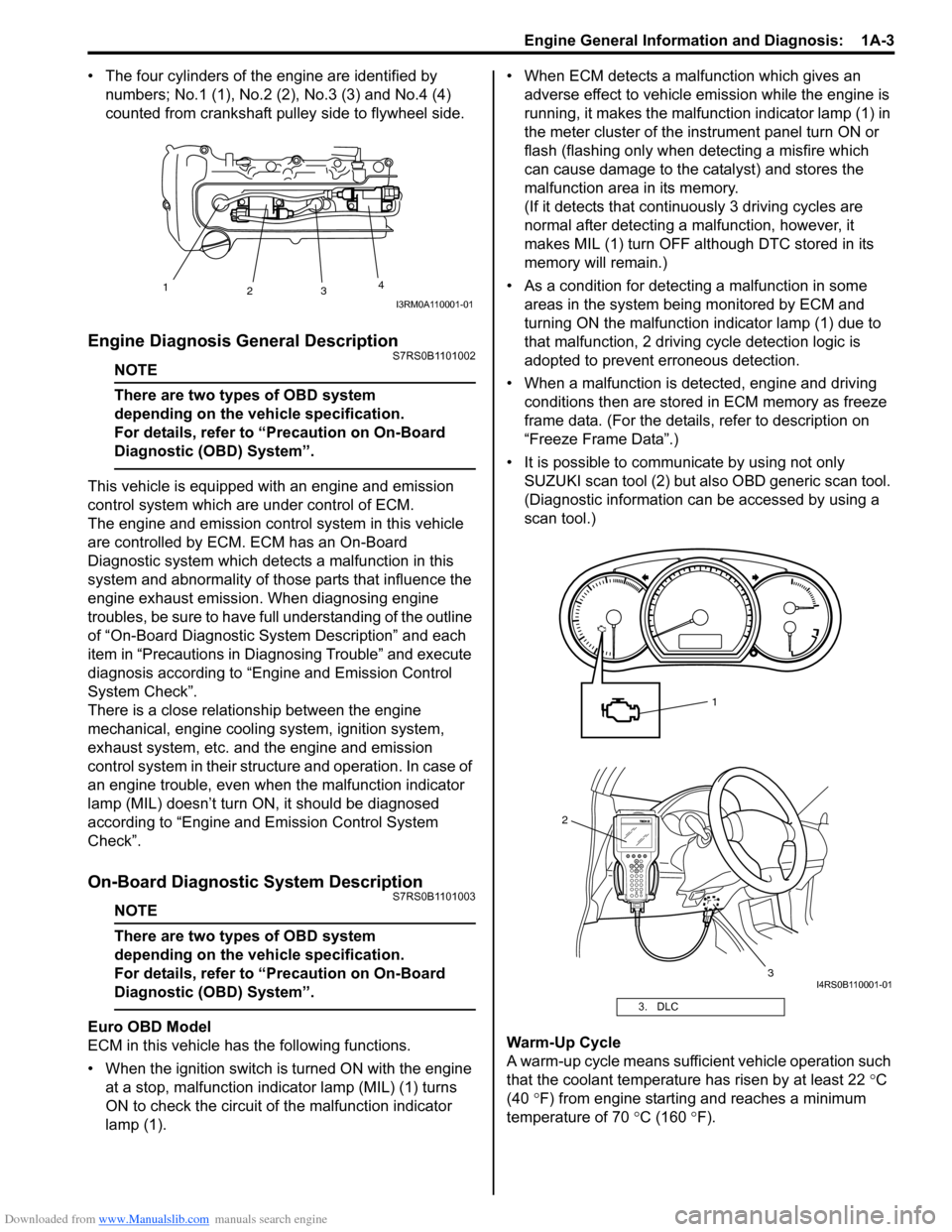
• The four cylinders of the engine are identified by numbers; No.1 (1), No.2 (2 ), No.3 (3) and No.4 (4)
counted from crankshaft pulley side to flywheel side.
Engine Diagnosis General DescriptionS7RS0B1101002
NOTE
There are two types of OBD system
depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
This vehicle is equipped with an engine and emission
control system which are under control of ECM.
The engine and emission control system in this vehicle
are controlled by ECM. ECM has an On-Board
Diagnostic system which detects a malfunction in this
system and abnormality of those parts that influence the
engine exhaust emission. When diagnosing engine
troubles, be sure to have full understanding of the outline
of “On-Board Diagnostic System Description” and each
item in “Precautions in Diagnosing Trouble” and execute
diagnosis according to “Engine and Emission Control
System Check”.
There is a close relationship between the engine
mechanical, engine cooling system, ignition system,
exhaust system, etc. and the engine and emission
control system in their structure and operation. In case of
an engine trouble, even when the malfunction indicator
lamp (MIL) doesn’t turn ON, it should be diagnosed
according to “Engine and Emission Control System
Check”.
On-Board Diagnostic System DescriptionS7RS0B1101003
NOTE
There are two types of OBD system
depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
Euro OBD Model
ECM in this vehicle has the following functions.
• When the ignition switch is turned ON with the engine at a stop, malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) (1) turns
ON to check the circuit of the malfunction indicator
lamp (1). • When ECM detects a malfunction which gives an
adverse effect to vehicle emission while the engine is
running, it makes the malfunction indicator lamp (1) in
the meter cluster of the inst rument panel turn ON or
flash (flashing only when detecting a misfire which
can cause damage to the catalyst) and stores the
malfunction area in its memory.
(If it detects that contin uously 3 driving cycles are
normal after detecting a malfunction, however, it
makes MIL (1) turn OFF although DTC stored in its
memory will remain.)
• As a condition for detecting a malfunction in some areas in the system being monitored by ECM and
turning ON the malfunction indicator lamp (1) due to
that malfunction, 2 driving cycle detection logic is
adopted to prevent erroneous detection.
• When a malfunction is detected, engine and driving conditions then are stored in ECM memory as freeze
frame data. (For the details, refer to description on
“Freeze Frame Data”.)
• It is possible to communicate by using not only SUZUKI scan tool (2) but also OBD generic scan tool.
(Diagnostic information can be accessed by using a
scan tool.)
Warm-Up Cycle
A warm-up cycle means sufficie nt vehicle operation such
that the coolant temperature has risen by at least 22 °C
(40 °F) from engine starting and reaches a minimum
temperature of 70 °C (160 ° F).
1
23 4
I3RM0A110001-01
3. DLC
2
3
1
I4RS0B110001-01
Page 55 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-5
Freeze frame data clearance:
The freeze frame data is cleared at the same time as
clearance of DTC.
Non-Euro-OBD
ECM diagnosis troubles which may occur in the area
including the following parts w hen the ignition switch is
ON and the engine is running, and indicates the result by
turning on or flashing malfunction indicator lamp (1).
• Heated oxygen sensor
• ECT sensor
•TP sensor
• APP sensor
• MAF sensor
• IAT sensor
• MAP sensor
• CMP sensor
• CKP sensor
• Knock sensor
• Wheel speed sensor (VSS)
• CPU (Central Processing Unit) of ECM
• Oil control valve
• EGR valve
• EVAP canister purge valve
• Ignition coil
• Starter relay
• Radiator fan relay
• CAN communication
• Barometric pressure sensor
• ECM back up power supply
ECM and malfunction indicator lamp (1) operate as
follows.
• Malfunction indicator lamp (1) lights when the ignition switch is turned ON (but t he engine at stop) with the
diagnosis switch terminal ungrounded regardless of
the condition of Engine and Emission control system.
This is only to check the ma lfunction indicator lamp (1)
in the combination meter and its circuit.
• If the above areas of Engine and Emission control system is free from any trouble after the engine start
(while engine is running), malfunction indicator lamp
(1) turns OFF. • When ECM detects a trouble which has occurred in
the above areas, it makes malfunction indicator lamp
(1) turn ON while the engi ne is running to warn the
driver of such occurrence of trouble and at the same
time it stores the trouble area in ECM back-up
memory. (The memory is kept as it is even if the
trouble was only temporary and disappeared
immediately. And it is not erased unless the power to
ECM is shut off for specified time or it is cleared by
SUZUKI scan tool (2).)
For Hong Kong model, DTC can be read by not only
using SUZUKI scan tool but also displayed on
odometer (5) of the combination meter. (i.e. when
diagnosis switch terminal (3) is grounded with a
service wire (4) and ignition switch is turned ON.) For
further detail of the checking procedure, refer to “DTC
Check”.
6. Diagnosis connector
2
1
6 3
5
4
I5RS0C110021-01
Page 71 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-21
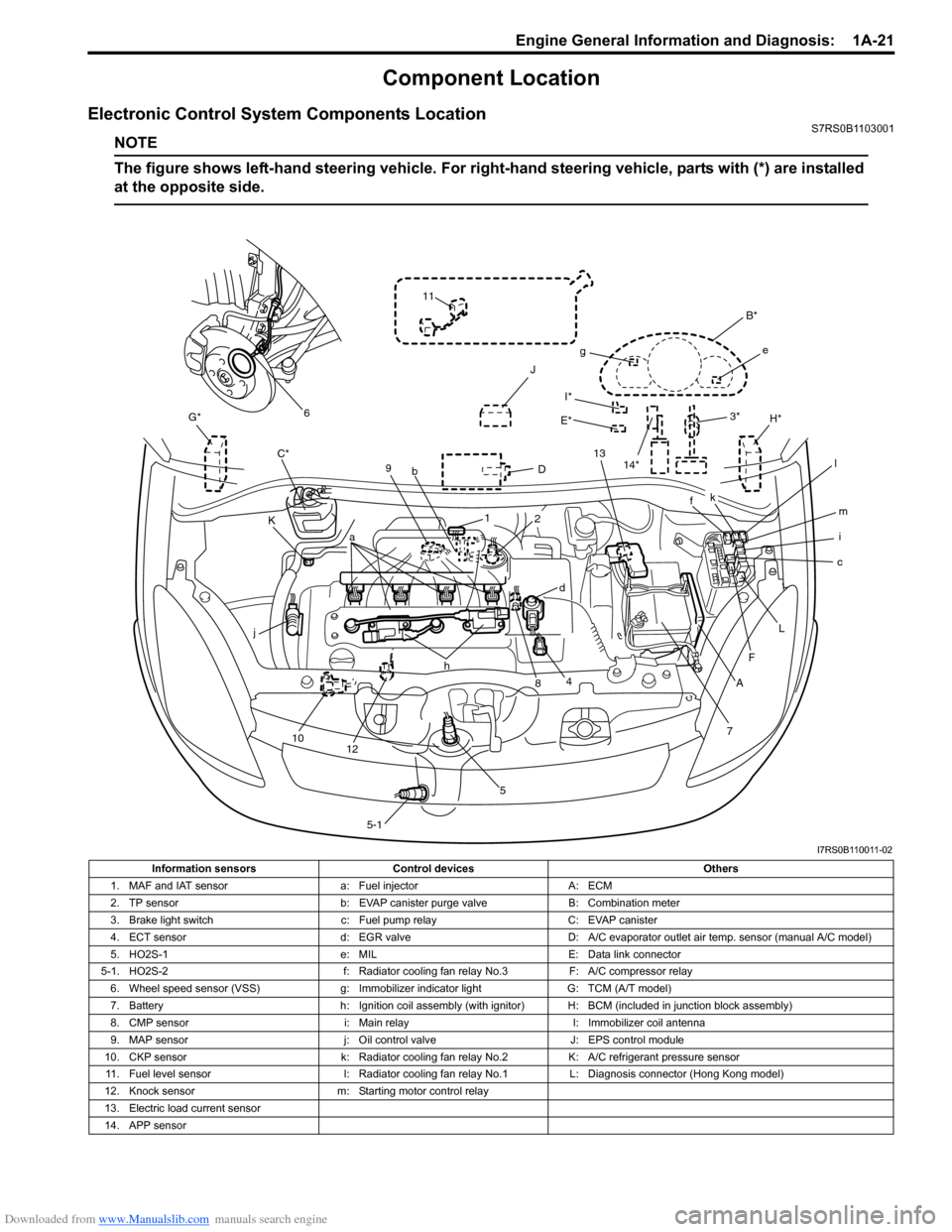
Component Location
Electronic Control System Components LocationS7RS0B1103001
NOTE
The figure shows left-hand steering vehicle. For right-hand steering vehicle, parts with (*) are installed
at the opposite side.
I*
E*
G*
D
K H*
J
C*
7
A
F
c
L
i m
f
B*
e
g
k
l
13
3*
4
j
10 12 h
58
a
9
b
1
5-1
d
2
11
6
14*
I7RS0B110011-02
Information sensors Control devices Others
1. MAF and IAT sensor a: Fuel injectorA: ECM
2. TP sensor b: EVAP canister purge valve B: Combination meter
3. Brake light switch c: Fuel pump relayC: EVAP canister
4. ECT sensor d: EGR valveD: A/C evaporator outlet air temp. sensor (manual A/C model)
5. HO2S-1 e: MILE: Data link connector
5-1. HO2S-2 f: Radiator cooling fan relay No.3F: A/C compressor relay
6. Wheel speed sensor (VSS) g: Immobilizer indicator lightG: TCM (A/T model)
7. Battery h: Ignition coil assembly (with ignitor) H: BCM (included in junction block assembly)
8. CMP sensor i: Main relayI: Immobilizer coil antenna
9. MAP sensor j: Oil control valveJ: EPS control module
10. CKP sensor k: Radiator cooling fan relay No.2K: A/C refrigerant pressure sensor
11. Fuel level sensor l: Radiator cooling fan relay No.1L: Diagnosis connector (Hong Kong model)
12. Knock sensor m: Starting motor control relay
13. Electric load current sensor
14. APP sensor
Page 75 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-25
Step 2: DTC / Freeze Frame Data Check, Record and
Clearance
First, check DTC (including pending DTC), referring to
“DTC Check”. If DTC is indicated, print it and freeze
frame data or write them down and then clear them by
referring to “DTC Clearance”. DTC indicates malfunction
that occurred in the system but does not indicate
whether it exists now or it occurred in the past and the
normal condition has been restored now. To check which
case applies, check the sy mptom in question according
to Step 5 and recheck DTC according to Step 6 and 7.
Attempt to diagnose a trouble based on DTC in this step
only or failure to clear the DTC in this step will lead to
incorrect diagnosis, trouble diagnosis of a normal circuit
or difficulty in troubleshooting.
Step 3 and 4: Visual Inspection
As a preliminary step, be sure to perform visual check of
the items that support proper function of the engine
referring to “Visual Inspection”.
Step 5: Trouble Symptom Confirmation
Based on information obtained in “Step 1: Customer
Complaint Analysis: ” and “Step 2: DTC / Freeze Frame
Data Check, Record and Clearance: ”, confirm trouble
symptoms. Also, reconfirm DTC according to “DTC
Confirmation Procedure” described in each DTC diag.
flow.
Step 6 and 7: Rechecking and Record of DTC /
Freeze Frame Data
Refer to “DTC Check” for checking procedure.
Step 8: Engine Basic Inspection and Engine
Symptom Diagnosis
Perform basic engine check according to “Engine Basic
Inspection” first. When the end of the flow has been
reached, check the parts of the system suspected as a
possible cause referring to “Engine Symptom Diagnosis”
and based on symptoms appearing on the vehicle
(symptoms obtained through steps of customer
complaint analysis, trouble symptom confirmation and/or
basic engine check) and repair or replace faulty parts, if
any.
Step 9: Troubleshooting for DTC (See each DTC
Diag. Flow)
Based on the DTC indicated in Step 6 or 7 and referring
to the applicable DTC diag. flow, locate the cause of the
trouble, namely in a sensor, switch, wire harness,
connector, actuator, ECM or other part and repair or
replace faulty parts. Step 10: Intermittent Problems Check
Check parts where an intermit
tent trouble is easy to
occur (e.g., wire harness, connector, etc.), referring to
“Intermittent and Poor Connec tion Inspection in Section
00” and related circuit of DTC recorded in Step 2.
Step 11: Final Confirmation Test
Confirm that the problem symptom has gone and the
engine is free from any abnormal conditions. If what has
been repaired is re lated to the DTC, clear the DTC once,
perform DTC confirmation procedure and confirm that no
DTC is indicated.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) CheckS7RS0B1104002
1) Turn ON ignition switch (with engine at stop) and check that MIL (1) lights.
If MIL does not light up (or MIL dims) but engine can
be starting, go to “MIL Does Not Come ON with
Ignition Switch ON and Engine Stop (but Engine Can
Be Started)” for troubleshooting.
If MIL does not light with ignition switch ON and
engine does not start though it is cranked up, go to
“ECM Power and Ground Circuit Check”.
2) Start engine and check that MIL turns OFF. If MIL remains ON and no DTC is stored in ECM, go
to “Malfunction Indicator Lamp Remains ON after
Engine Starts” for troubleshooting.
1
I4RS0A110012-01
Page 83 of 1496
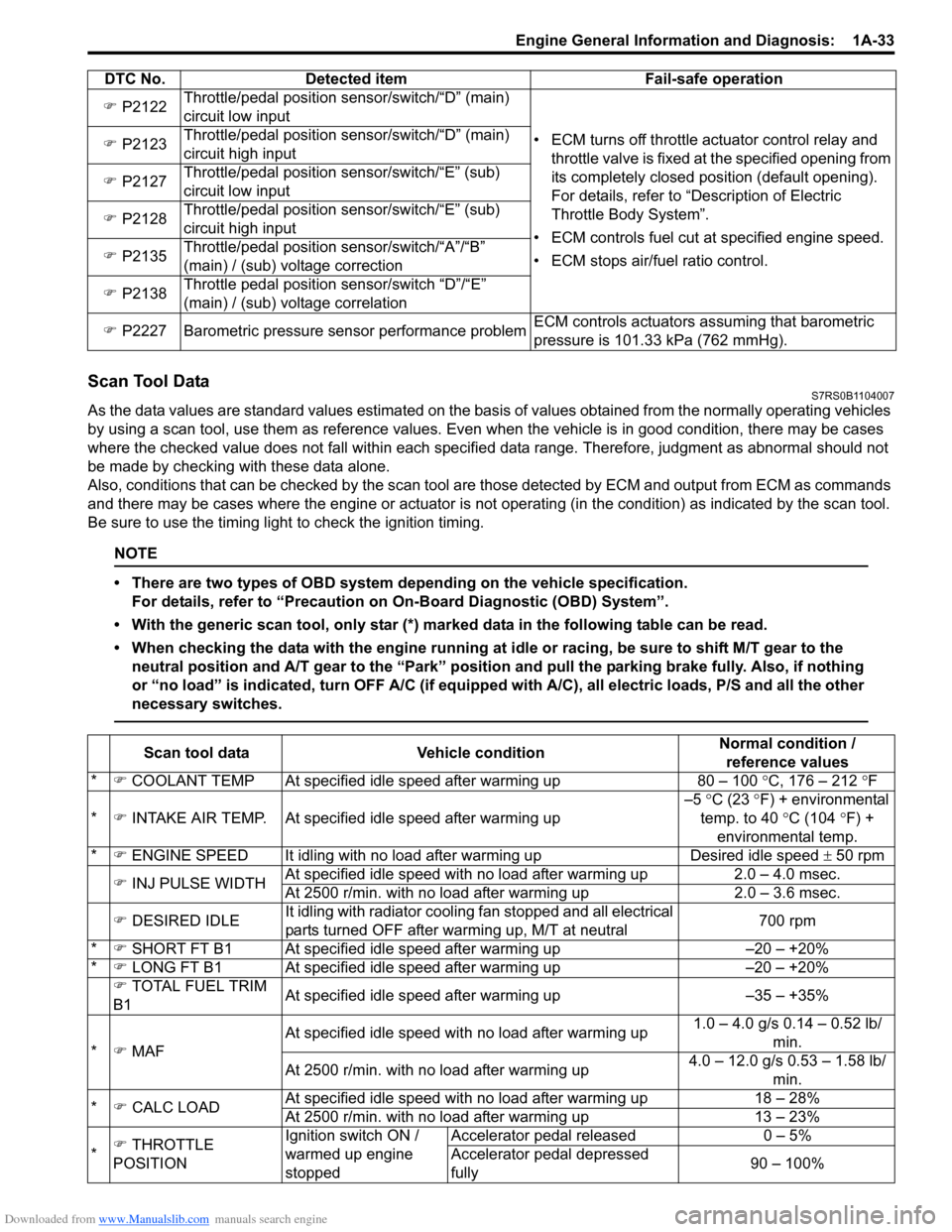
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-33
Scan Tool DataS7RS0B1104007
As the data values are standard values estimated on the basis of values obtained from the normally operating vehicles
by using a scan tool, use them as re ference values. Even when the vehicle is in good condition, there may be cases
where the checked value does not fall within each specified data range. Therefore, judgment as abnormal should not
be made by checking with these data alone.
Also, conditions that can be checked by the scan tool are those detected by ECM and output from ECM as commands
and there may be cases where the engine or actuator is not operating (in the condition) as indicated by the scan tool.
Be sure to use the timing light to check the ignition timing.
NOTE
• There are two types of OBD system depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
• With the generic scan tool, only star (*) marked data in the following table can be read.
• When checking the data with the engine running at idle or racing, be sure to shift M/T gear to the neutral position and A/T gear to the “Park” position and pull the parking brake fully. Also, if nothing
or “no load” is indicated, turn O FF A/C (if equipped with A/C), all electric loads, P/S and all the other
necessary switches.
�) P2122 Throttle/pedal position sensor/switch/“D” (main)
circuit low input
• ECM turns off throttle actuator control relay and throttle valve is fixed at the specified opening from
its completely closed position (default opening).
For details, refer to “Description of Electric
Throttle Body System”.
• ECM controls fuel cut at specified engine speed.
• ECM stops air/fuel ratio control.
�)
P2123 Throttle/pedal position sensor/switch/“D” (main)
circuit high input
�) P2127 Throttle/pedal position sensor/switch/“E” (sub)
circuit low input
�) P2128 Throttle/pedal position sensor/switch/“E” (sub)
circuit high input
�) P2135 Throttle/pedal position sensor/switch/“A”/“B”
(main) / (sub) voltage correction
�) P2138 Throttle pedal position sensor/switch “D”/“E”
(main) / (sub) voltage correlation
�) P2227 Barometric pressure sensor performance problem ECM controls actuators assuming that barometric
pressure is 101.33 kPa (762 mmHg).
DTC No. Detected item Fail-safe operation
Scan tool data
Vehicle condition Normal condition /
reference values
* �) COOLANT TEMP At specified idle speed after warming up 80 – 100 °C, 176 – 212 °F
* �) INTAKE AIR TEMP. At specifie d idle speed after warming up –5
°C (23 °F) + environmental
temp. to 40 °C (104 °F) +
environmental temp.
* �) ENGINE SPEED It idling with no load after warming upDesired idle speed ± 50 rpm
�) INJ PULSE WIDTH At specified idle speed with no load after warming up
2.0 – 4.0 msec.
At 2500 r/min. with no load after warming up 2.0 – 3.6 msec.
�) DESIRED IDLE It idling with radiator cooling fan stopped and all electrical
parts turned OFF after warming up, M/T at neutral 700 rpm
* �) SHORT FT B1 At specified idle speed after warming up –20 – +20%
* �) LONG FT B1 At specified idle speed after warming up –20 – +20%
�) TOTAL FUEL TRIM
B1 At specified idle speed after warming up
–35 – +35%
* �) MAF At specified idle speed wit
h no load after warming up 1.0 – 4.0 g/s 0.14 – 0.52 lb/
min.
At 2500 r/min. with no load after warming up 4.0 – 12.0 g/s 0.53 – 1.58 lb/
min.
* �) CALC LOAD At specified idle speed with no load after warming up
18 – 28%
At 2500 r/min. with no load after warming up 13 – 23%
* �)
THROTTLE
POSITION Ignition switch ON /
warmed up engine
stoppedAccelerator pedal released
0 – 5%
Accelerator pedal depressed
fully 90 – 100%
Page 87 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-37
TP SENSOR 2 VOLT (THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
(SUB) OUTPUT VOLTAGE, V)
The TP sensor (sub) reading provides throttle valve
opening information in the form of voltage.
APP SENSOR 1 VOLT (ACCELERATOR PEDAL
POSITION (APP) SENSOR (MAIN) OUTPUT
VOLTAGE, V)
The APP sensor (main) read ing provides accelerator
pedal opening information in the form of voltage.
APP SENSOR 2 VOLT (ACCELERATOR PEDAL
POSITION (APP) SENSOR (S UB) OUTPUT VOLTAGE,
V)
The APP sensor (sub) reading provides accelerator
pedal opening information in the form of voltage.
ACCEL POSITION (ABSOLUTE ACCELERATOR
PEDAL POSITION, %)
When accelerator pedal is at fully released position,
accelerator pedal is indicated as 0 – 5% and 90 – 100%
fully depressed position. THROTTLE TARGET POSI (TARGET THROTTLE
VALVE POSITION, %)
Target throttle valve position is ECM internal parameter
which indicates the ECM requested throttle valve
position.
BATTERY CURRENT (A)
This parameter indicates elec
tric load value (current
consumption) that detected by electric load current
sensor.
GENERATOR CONT DUTY (GENERATOR CONTROL
DUTY, %)
This parameter indicates generator control duty ratio that
controls production electricity of generator by ECM.
100%: No limitation for the generating
0%: Maximum limitation for the generating
GENERATOR FIELD DUTY (GENERATOR FIELD
COIL DUTY, %)
This parameter indicates ope rating rate (status of
production electricity) for gen erator by field coil duty
ratio.
100%: maximum operation.
0%: minimum operation.
Visual InspectionS7RS0B1104008
Visually check the following parts and systems.
Inspection item Reference section
• Engine oil – level, leakage “Engine Oil and Filter Change in Section 0B”
• Engine coolant – level, leakage “Co olant Level Check in Section 1F”
• Fuel – level, leakage “Fuel Lines and Connections Inspection in Section 0B”
• Air cleaner element – dirt, clogging “Air Cleaner Filter Inspection in Section 0B”
• Battery – fluid level, corrosion of terminal “Battery Description in Section 1J”
• Water pump belt – tension damage “Accessory Drive Belt Inspection in Section 0B”
• Throttle valve – operating sound “Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle Inspection in Section 1C”
• Vacuum hoses of air intake system – disconnection, looseness,
deterioration, bend “Vacuum Hose and Purge Valve Chamber
Inspection in Section 1B”
• Connectors of electric wire harness – disconnection, friction
• Fuses – burning
• Parts – installation, bolt – looseness
• Parts – deformation
• Other parts that can be checked visually
Also check the following items at engine start, if possible
• Malfunction indicator lamp – Operation “Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Check”
• Charge warning lamp – Operation “Genera tor Symptom Diagnosis in Section 1J”
• Engine oil pressure warning lamp – Operation “O il Pressure Switch Inspection in Section 9C”
• Engine coolant temp. meter – Operation “ECT Sensor Inspection in Section 1C”
• Fuel level meter – Operation “Fuel Level Sensor Inspection in Section 9C”
• Tachometer – Operation
• Abnormal air being inhaled from air intake system
• Exhaust system – leakage of exhaust gas, noise
• Other parts that can be checked visually
Page 89 of 1496
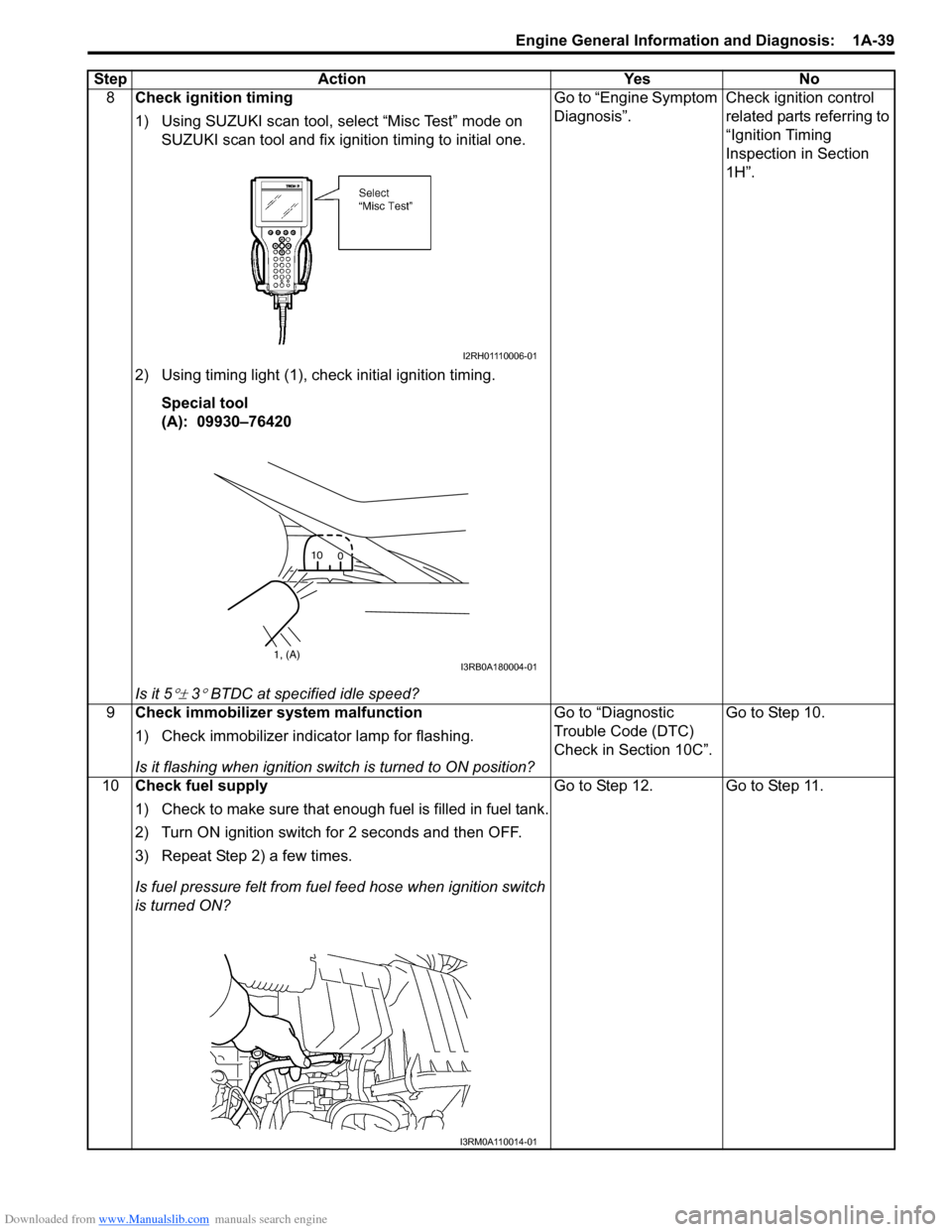
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-39
8Check ignition timing
1) Using SUZUKI scan tool, select “Misc Test” mode on
SUZUKI scan tool and fix ignition timing to initial one.
2) Using timing light (1), check initial ignition timing. Special tool
(A): 09930–76420
Is it 5
°± 3° BTDC at specif ied idle speed? Go to “Engine Symptom
Diagnosis”.
Check ignition control
related parts referring to
“Ignition Timing
Inspection in Section
1H”.
9 Check immobilizer system malfunction
1) Check immobilizer indica tor lamp for flashing.
Is it flashing when ignition switch is turned to ON position? Go to “Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC)
Check in Section 10C”.
Go to Step 10.
10 Check fuel supply
1) Check to make sure that enough fuel is filled in fuel tank.
2) Turn ON ignition switch for 2 seconds and then OFF.
3) Repeat Step 2) a few times.
Is fuel pressure felt from fuel feed hose when ignition switch
is turned ON? Go to Step 12. Go to Step 11.
Step Action Yes No
I2RH01110006-01
1, (A)
10
0I3RB0A180004-01
I3RM0A110014-01
Page 91 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-41
Engine Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B1104010
Perform troubleshooting referring to the followings when ECM has detected no DTC and no abnormality has been
found in “Visual Inspection” and “Engine Basic Inspection”.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Hard starting (Engine
cranks OK) Faulty spark plug
“Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Leaky high-tension cord “High-Tension Cord Inspection in Section 1H”
Loose connection or disconnection of
high-tension cord(s) or lead wire(s) “High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
in Section 1H”
Faulty ignition coil “Ignition Coil Assembly (Including ignitor)
Inspection in Section 1H”
Dirty or clogged fuel hose or pipe “Fuel Pressure Check”
Malfunctioning fuel pump “Fuel Pressure Check”
Air drawn in through intake manifold
gasket or throttle body gasket
Faulty electric throttle body assembly “Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly “APP Sensor Assembly Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty ECT sensor or MAF sensor “ECT Sensor Inspection in Section 1C” or
“MAF and IAT Sensor Inspection in Section
1C”
Faulty ECM
Low compression “Compression Check in Section 1D”
Poor spark plug tightening or faulty
gasket “Spark Plug Removal and Installation in
Section 1H”
Compression leak from valve seat “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Sticky valve stem “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Weak or damaged valve springs “Valve Spring Inspection in Section 1D”
Compression leak at cylinder head
gasket “Cylinder Head Inspection in Section 1D”
Sticking or damaged piston ring “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Worn piston, ring or cylinder “Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection in Section 1D”
Malfunctioning PCV valve “PCV Valve Inspection in Section 1B”
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order “Oil Control Valve Inspection in Section 1D”
Faulty EGR system “EGR System Inspection in Section 1B”
Low oil pressure Improper oil viscosity “Engine Oil and Filter Change in Section 0B”
Malfunctioning oil pressure switch “Oil Pressure Switch Inspection in Section 9C”
Clogged oil strainer “Oil Pan and Oil Pump Strainer Cleaning in
Section 1E”
Functional deterioration of oil pump “Oil Pump Inspection in Section 1E”
Worn oil pump relief valve “Oil Pump Inspection in Section 1E”
Excessive clearance in various sliding
parts
Engine noise – Valve
noise
NOTE
Before checking
mechanical noise, make
sure that:
• Specified spark plug is used.
• Specified fuel is used.
Improper valve lash “Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Inspection in
Section 1D”
Worn valve stem and guide “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”
Weak or broken valve spring “Valve Spring Inspection in Section 1D”
Warped or bent valve “Valves and Valve Guides Inspection in
Section 1D”