eco SUZUKI SWIFT 2006 2.G Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2006, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2006 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 256 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-206 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Troubleshooting
NOTE
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the
special tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors re ferring to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
• When A/C evaporator outlet air temp. is below 2.5 °C (36.5 °F), A/C remains OFF (“E23-47” terminal
voltage becomes 10 – 14 V). This condition is not abnormal.
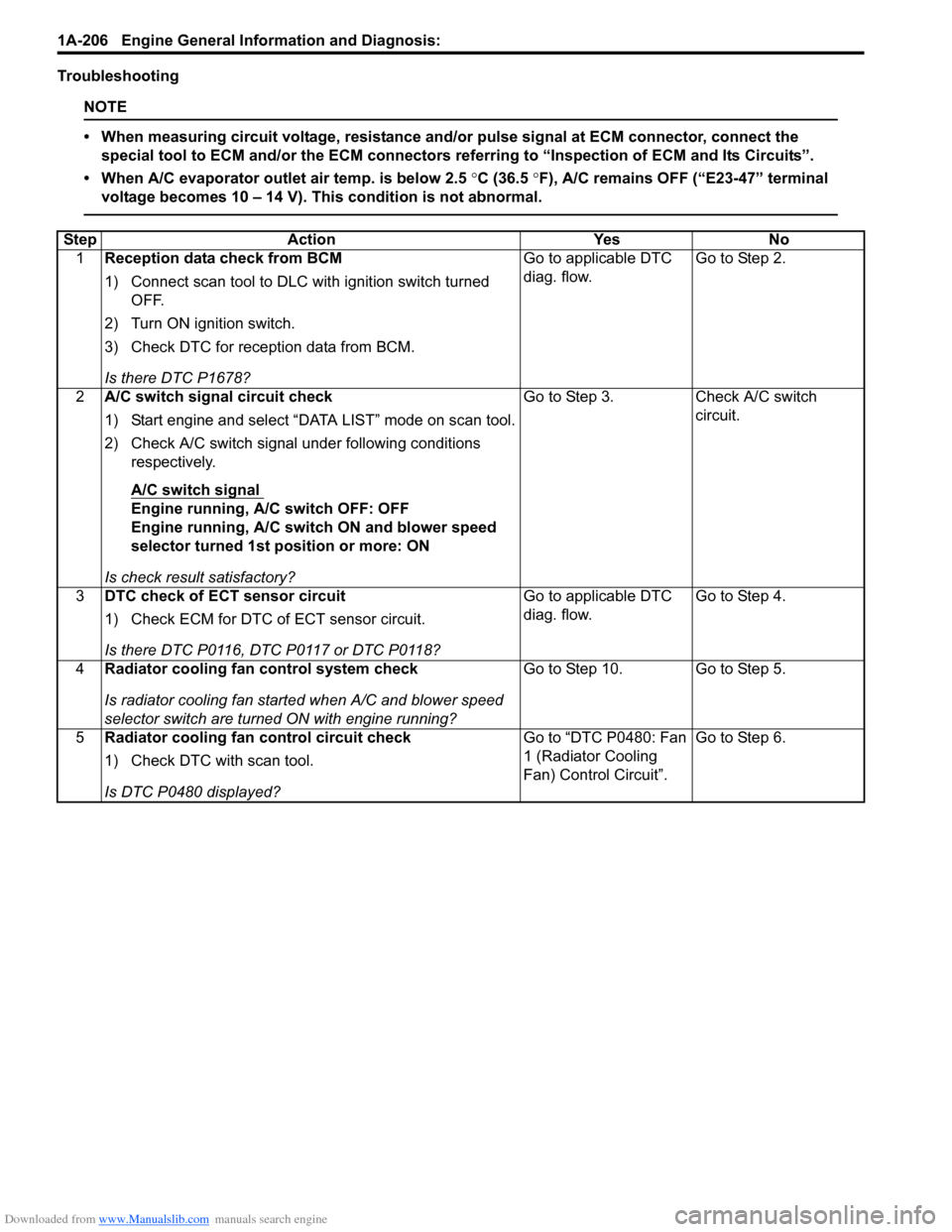
Step Action YesNo
1 Reception data check from BCM
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch turned
OFF.
2) Turn ON ignition switch.
3) Check DTC for reception data from BCM.
Is there DTC P1678? Go to applicable DTC
diag. flow.
Go to Step 2.
2 A/C switch signal circuit check
1) Start engine and select “DATA LIST” mode on scan tool.
2) Check A/C switch signal under following conditions
respectively.
A/C switch signal
Engine running, A/C switch OFF: OFF
Engine running, A/C switch ON and blower speed
selector turned 1st position or more: ON
Is check result satisfactory? Go to Step 3. Check A/C switch
circuit.
3 DTC check of ECT sensor circuit
1) Check ECM for DTC of ECT sensor circuit.
Is there DTC P0116, DTC P0117 or DTC P0118? Go to applicable DTC
diag. flow.
Go to Step 4.
4 Radiator cooling fan control system check
Is radiator cooling fan started when A/C and blower speed
selector switch are turned ON with engine running? Go to Step 10. Go to Step 5.
5 Radiator cooling fan control circuit check
1) Check DTC with scan tool.
Is DTC P0480 displayed? Go to “DTC P0480: Fan
1 (Radiator Cooling
Fan) Control Circuit”.
Go to Step 6.
Page 277 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Electrical Devices: 1C-5
Electric Throttle Body System CalibrationS7RS0B1306004
NOTE
If working the service described under the
“Precautions of Electric Throttle Body
System Calibration in Section 1A” perform
following steps for electric throttle body
system calibration.
1) If electric throttle body assembly and/or APP sensor
assembly are replaced, perform following steps.
a) Disconnect negative cable at battery for 20 seconds or more for the purpose of clearing
calibration data of closed throttle position from
memory in ECM.
b) Connect negative cable to battery.
2) Keep ignition switch at ON position for 5 seconds or more without running engine.
APP Sensor Assembly On-Vehicle InspectionS7RS0B1306005
1) Check that APP sensor a ssembly has been mounted
to vehicle body properly (no pinched floor carpet,
etc.).
If mounting is not pro perly, reinstall APP sensor
assembly properly refe rring to “APP Sensor
Assembly Removal and Installation”.
2) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch turned OFF.
3) Turn ON ignition switch and select “Data List” mode on scan tool.
4) Check that APP sensor voltage varies as the following graph.
If sensor voltage is out of specified value or does not
vary linearly as the fo llowing graph, check APP
sensor assembly referring to “APP Sensor Assembly
Inspection”.
APP Sensor Assembly Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1306006
CAUTION!
• Do not expose APP sensor assembly to
excessive shock like a dropping it. If APP
sensor assembly has been exposed to
excessive shock, it should be replaced.
• Be careful not to expose sensor section of APP sensor assembly to water.
NOTE
After replacing APP sensor assembly,
perform calibration of th rottle valve referring
to “Electric Throttle Body System
Calibration”.
Removal
1) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
2) Disconnect connector from APP sensor assembly.
3) Remove APP sensor asse mbly from its bracket.
Installation
Reverse removal procedure for installation noting the
following.
• Tighten APP sensor assembly upper nut (1) first and then lower nut (2) to specified torque.
Tightening torque
APP sensor assembly nut (a): 5.5 N·m (0.55 kgf-m,
4.0 lb-ft)
• Connect connector to APP sensor assembly securely.
[A]: APP sensor (main) voltage [D]: Idle position of accelerator pedal
[B]: APP sensor (sub) voltage [E]: Full depressed position of
accelerator pedal
[C]: Voltage
[C]
[B]
[D] [E] [A]
4.65 V
3.85 V
1.55 - 1.65 V
0.75 - 0.85 V
I4RS0B130010-02
1, (a)
2, (a)
I4RS0B130011-01
Page 291 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-6
6) Connect special tool (Vacuum gauge) to PCV hose (1).
Special tool
(A): 09915–67311
7) Blind PCV valve (2) using tape (3) or the like.
8) Install air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
9) Run engine at specified idle speed and read vacuum gauge. Vacuum should be within specification.
Vacuum specification (at sea level)
59 – 73 kPa (45 – 55 cmHg, 17.7 – 21.6 in.Hg) at
specified idle speed
10) Remove air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
11) Disconnect special tool (vacuum gage) from PCV valve.
12) Detach blind cap from PCV valve, and connect PCV hose to PCV valve.
13) Install air cleaner assembly and air suction hose referring to “Air Cleaner Components”.
14) Install engine cover.
Valve Lash (Clearance) InspectionS7RS0B1404003
1) Remove negative cable at battery.
2) Remove cylinder head cover referring to “Cylinder Head Cover Removal and Installation”.
3) Remove right side engine under cover, if necessary.
4) Using 17 mm wrench, turn crankshaft pulley (1) clockwise until cam lobes (2) become perpendicular
to shim faces (3) at valves “1” and “7” as shown in
the figure. 5) Check valve lashes with thickness gauge (4)
according to the following procedure.
a) Check valve lashes at valves “1” and “7”.
b) Turn camshafts by 90 ° (by turning crankshaft
with wrench).
c) Make sure that cam lobes are perpendicular to shim faces at valves to be checked (in this case,
“3” and “8”), if not, adjust it by turning crankshaft.
Check valve lashes.
d) In the same manner as b) – c), check valve
lashes at valves “4” and “6”.
e) In the same manner as b) – c) again, check valve lashes at valves “2” and “5”.
If valve lash is out of specification, record valve lash and
adjust it to specification by replacing shim.
Valve clearance specification
When cold (Coolant te mperature is 15 – 25 °C (59 –
77 °F)):
• Intake: 0.18 – 0.22 mm (0.007 – 0.009 in.)
• Exhaust: 0.28 – 0.32 mm (0.011 – 0.013 in.)
When hot (Coolant temperature is 60 – 68 °C (140 –
154 °F)):
• Intake: 0.21 – 0.27 mm (0.008 – 0.011 in.)
• Exhaust: 0.30 – 0.36 mm (0.012 – 0.014 in.)
(A)
13 2
I3RM0A140003-01
I3RM0A140004-01
Page 326 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-41 Engine Mechanical:
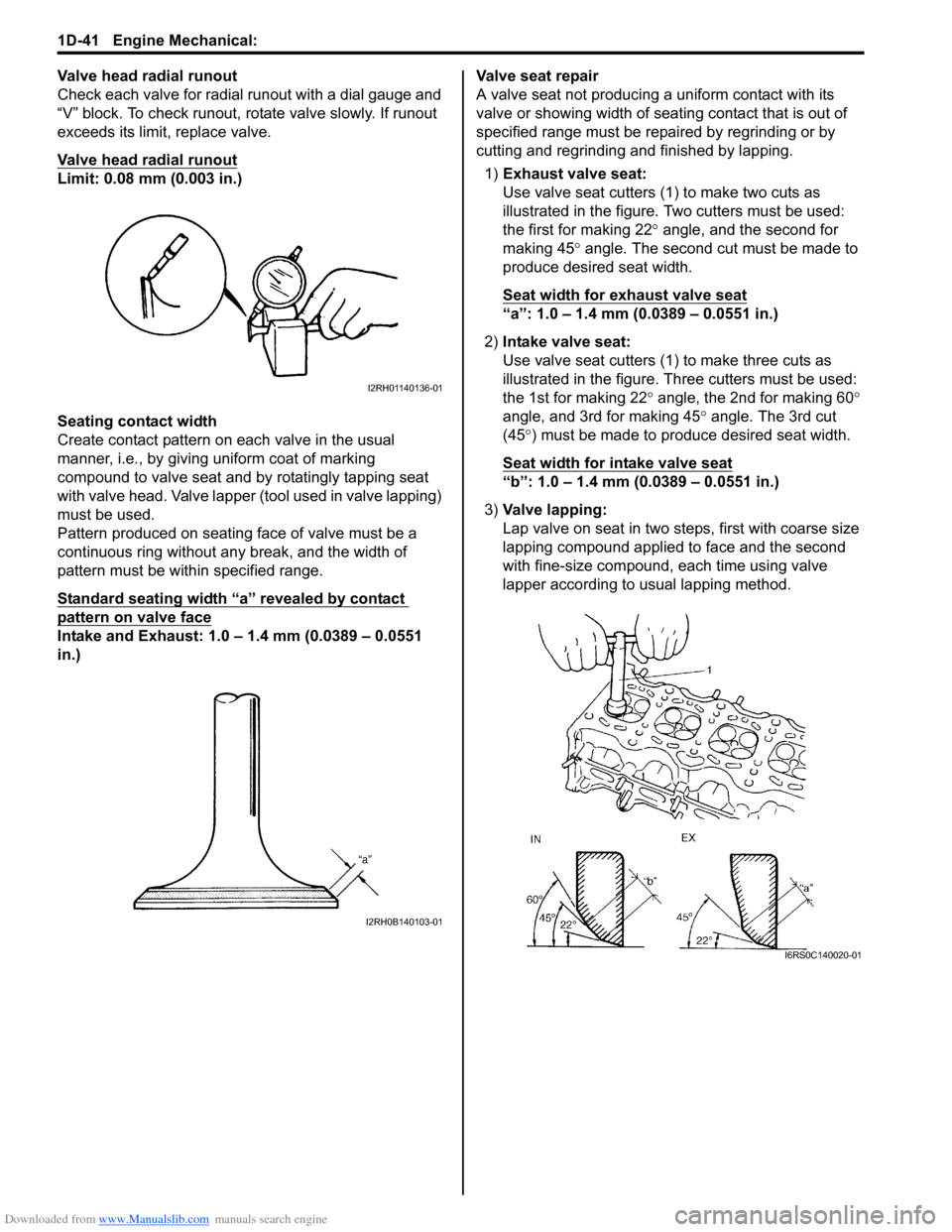
Valve head radial runout
Check each valve for radial runout with a dial gauge and
“V” block. To check runout, rotate valve slowly. If runout
exceeds its limit, replace valve.
Valve head radial runout
Limit: 0.08 mm (0.003 in.)
Seating contact width
Create contact pattern on each valve in the usual
manner, i.e., by giving uniform coat of marking
compound to valve seat and by rotatingly tapping seat
with valve head. Valve lapper (tool used in valve lapping)
must be used.
Pattern produced on seating face of valve must be a
continuous ring without any break, and the width of
pattern must be within specified range.
Standard seating width “a” revealed by contact
pattern on valve face
Intake and Exhaust: 1.0 – 1.4 mm (0.0389 – 0.0551
in.)Valve seat repair
A valve seat not producing
a uniform contact with its
valve or showing width of seating contact that is out of
specified range must be repaired by regrinding or by
cutting and regrinding and finished by lapping.
1) Exhaust valve seat:
Use valve seat cutters (1 ) to make two cuts as
illustrated in the figure. Two cutters must be used:
the first for making 22 ° angle, and the second for
making 45 ° angle. The second cut must be made to
produce desired seat width.
Seat width for exhaust valve seat
“a”: 1.0 – 1.4 mm (0.0389 – 0.0551 in.)
2) Intake valve seat:
Use valve seat cutters (1) to make three cuts as
illustrated in the figure. Th ree cutters must be used:
the 1st for making 22 ° angle, the 2nd for making 60 °
angle, and 3rd for making 45 ° angle. The 3rd cut
(45 °) must be made to produce desired seat width.
Seat width for intake valve seat
“b”: 1.0 – 1.4 mm (0.0389 – 0.0551 in.)
3) Valve lapping:
Lap valve on seat in two steps, first with coarse size
lapping compound applied to face and the second
with fine-size compound, each time using valve
lapper according to usual lapping method.
I2RH01140136-01
I2RH0B140103-01
I6RS0C140020-01
Page 351 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-66
Special Tools and Equipment
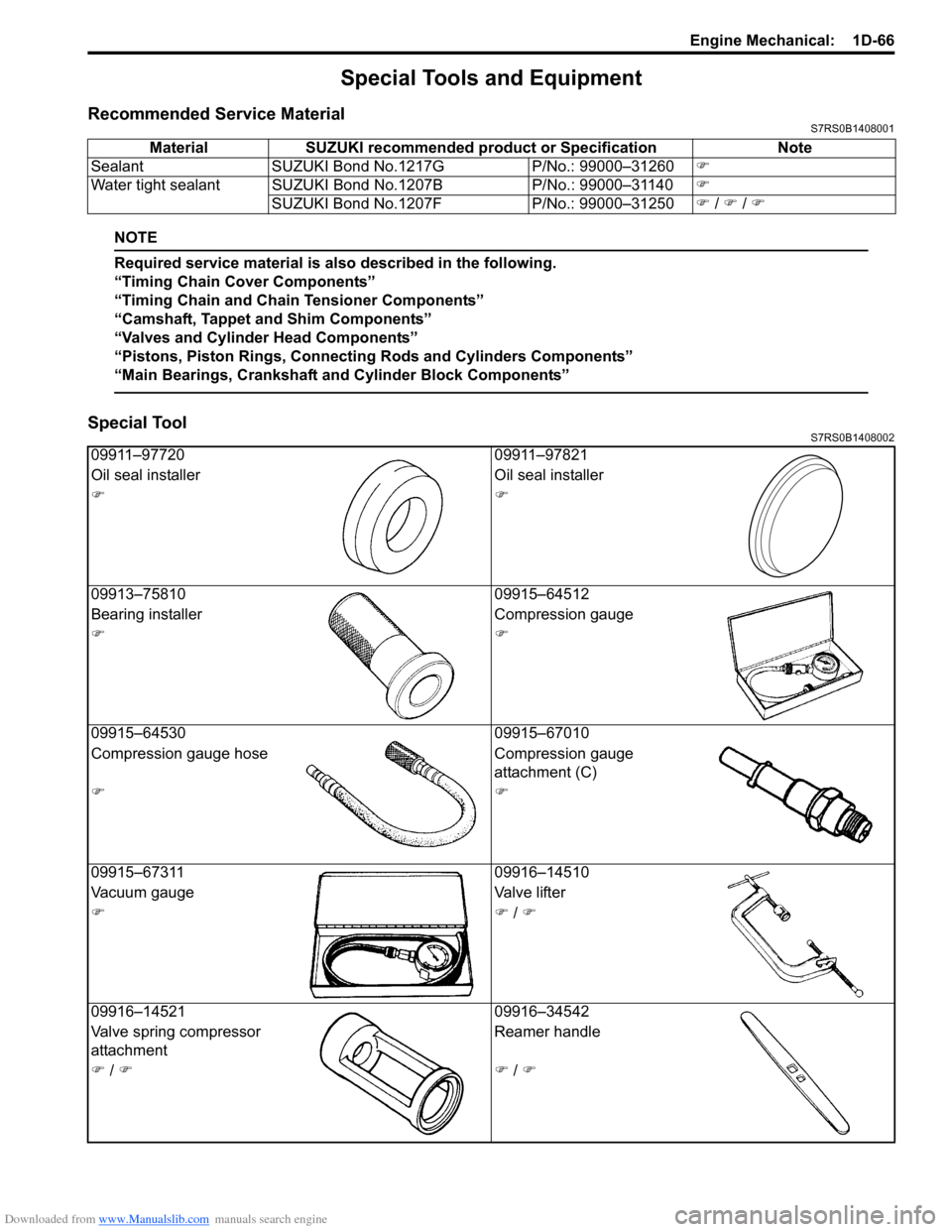
Recommended Service MaterialS7RS0B1408001
NOTE
Required service material is also described in the following.
“Timing Chain Cover Components”
“Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner Components”
“Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Components”
“Valves and Cylinder Head Components”
“Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and Cylinders Components”
“Main Bearings, Crankshaft and Cylinder Block Components”
Special ToolS7RS0B1408002
Material SUZUKI recommended product or Specification Note
Sealant SUZUKI Bond No.1217G P/No.: 99000–31260�)
Water tight sealant SUZUKI Bond No.1207B P/No.: 99000–31140�)
SUZUKI Bond No.1207F P/No.: 99000–31250�) / �) / �)
09911–97720 09911–97821
Oil seal installer Oil seal installer
�)�)
09913–75810 09915–64512
Bearing installer Compression gauge
�)�)
09915–64530 09915–67010
Compression gauge hose Compression gauge
attachment (C)
�)�)
09915–67311 09916–14510
Vacuum gauge Valve lifter
�)�) / �)
09916–14521 09916–34542
Valve spring compressor
attachment Reamer handle
�) / �)�) / �)
Page 363 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Lubrication System: 1E-11
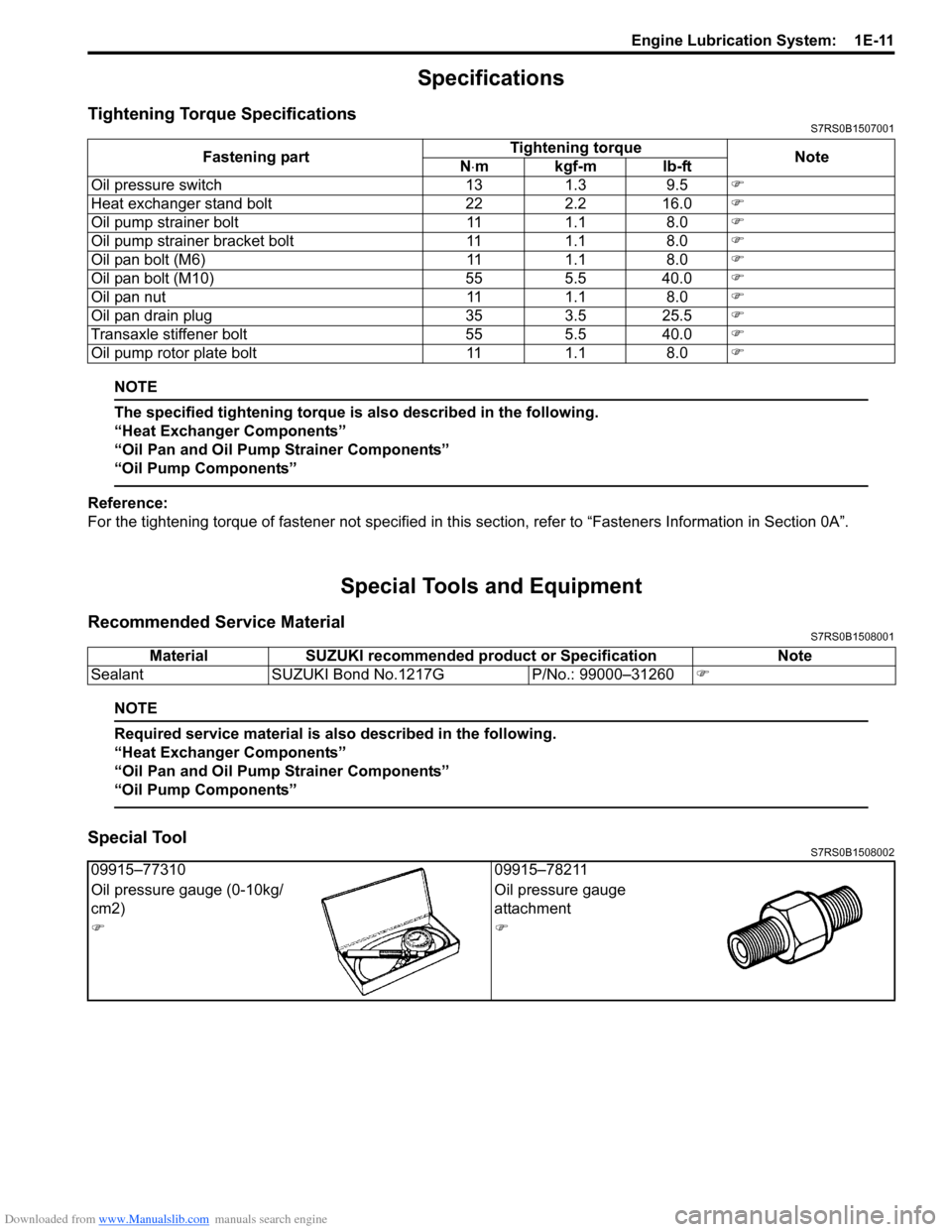
Specifications
Tightening Torque SpecificationsS7RS0B1507001
NOTE
The specified tightening torque is also described in the following.
“Heat Exchanger Components”
“Oil Pan and Oil Pump Strainer Components”
“Oil Pump Components”
Reference:
For the tightening torque of fastener not specified in this section, refer to “Fasteners Information in Section 0A”.
Special Tools and Equipment
Recommended Service MaterialS7RS0B1508001
NOTE
Required service material is also described in the following.
“Heat Exchanger Components”
“Oil Pan and Oil Pump Strainer Components”
“Oil Pump Components”
Special ToolS7RS0B1508002
Fastening part Tightening torque
Note
N ⋅mkgf-mlb-ft
Oil pressure switch 13 1.3 9.5 �)
Heat exchanger stand bolt 22 2.2 16.0 �)
Oil pump strainer bolt 11 1.1 8.0 �)
Oil pump strainer bracket bolt 11 1.1 8.0 �)
Oil pan bolt (M6) 11 1.1 8.0 �)
Oil pan bolt (M10) 55 5.5 40.0 �)
Oil pan nut 11 1.1 8.0 �)
Oil pan drain plug 35 3.5 25.5 �)
Transaxle stiffener bolt 55 5.5 40.0 �)
Oil pump rotor plate bolt 11 1.1 8.0 �)
MaterialSUZUKI recommended product or Specification Note
Sealant SUZUKI Bond No.1217G P/No.: 99000–31260�)
09915–77310 09915–78211
Oil pressure gauge (0-10kg/
cm2) Oil pressure gauge
attachment
�)�)
Page 364 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1F-1 Engine Cooling System:
Engine
Engine Cooling System
General Description
Cooling System DescriptionS7RS0B1601001
The cooling system consists of the radiator cap, radiator, coolant reservoir, hoses, water pump, cooling fan and
thermostat. The radiator is of tube-and-fin type.
Coolant DescriptionS7RS0B1601002
WARNING!
• Do not remove radiator cap to check engine coolant level; check coolant visually at the see-through coolant reservoir. Coolant should be added only to reservoir as necessary.
• As long as there is pressure in the cooling system, the temperature can be considerably higher than the boiling temperature of the solution in the radiator without causing the solution to boil. Removal
of the radiator cap while engine is hot and pressure is high will cause the solution to boil
instantaneously and possibly with explosive force, spewing the solution over engine, fenders and
person removing cap. If the solution contains flammable anti-freeze such as alcohol (not
recommended for use at any time), there is also the possibility of causing a serious fire.
• Check to make sure that engine coolant temperature is cold before removing any part of cooling system.
• Also be sure to disconnect negative cable from battery terminal before removing any part.
The coolant recovery system is standard. The coolant in the radiator expands with heat, and the coolant is overflowed
to the reservoir.
When the system cools down, the coolant is drawn back into the radiator.
The cooling system has be en filled with a quality coolant that is a 50/50 mixture of water and ethylene glycol
antifreeze.
This 50/50 mixture coolant solution provides freezing protection to –36 °C (–33 °F).
• Maintain cooling system freeze protection at –36 °C (–33 °F) to ensure protection against corrosion and loss of
coolant from boiling. This should be done even if freezing temperatures are not expected.
• Add ethylene glycol base coolant when coolant has to be added because of coolant loss or to provide added protection against freezing at temperature lower than –36 °C (–33 °F).
NOTE
• Alcohol or methanol base coolant or plain water alone should not be used in cooling system at any
time as damage to cooling system could occur.
• Coolant must be mixed with deminerated water or distilled water.
Anti-freeze proportioning table
For M/T model For A/T model
Freezing temperature °
C –36 –36
° F –33 –33
Anti-freeze / Anti-corrosion coolant concentration % 50 50
Ratio of compound to cooling water ltr. 3.10/3.10 3.05/3.05
US pt. 6.55/6.55 6.44/6.44
Imp pt. 5.46/5.46 5.37/5.37
Page 371 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Cooling System: 1F-8
Thermostat Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1606007
Removal1) Drain coolant referring to “Cooling System Draining”.
2) Remove intake manifold referring to “Intake Manifold Removal and Installa tion in Section 1D”.
3) Remove generator referring to “Generator Dismounting and Remounting in Section 1J”.
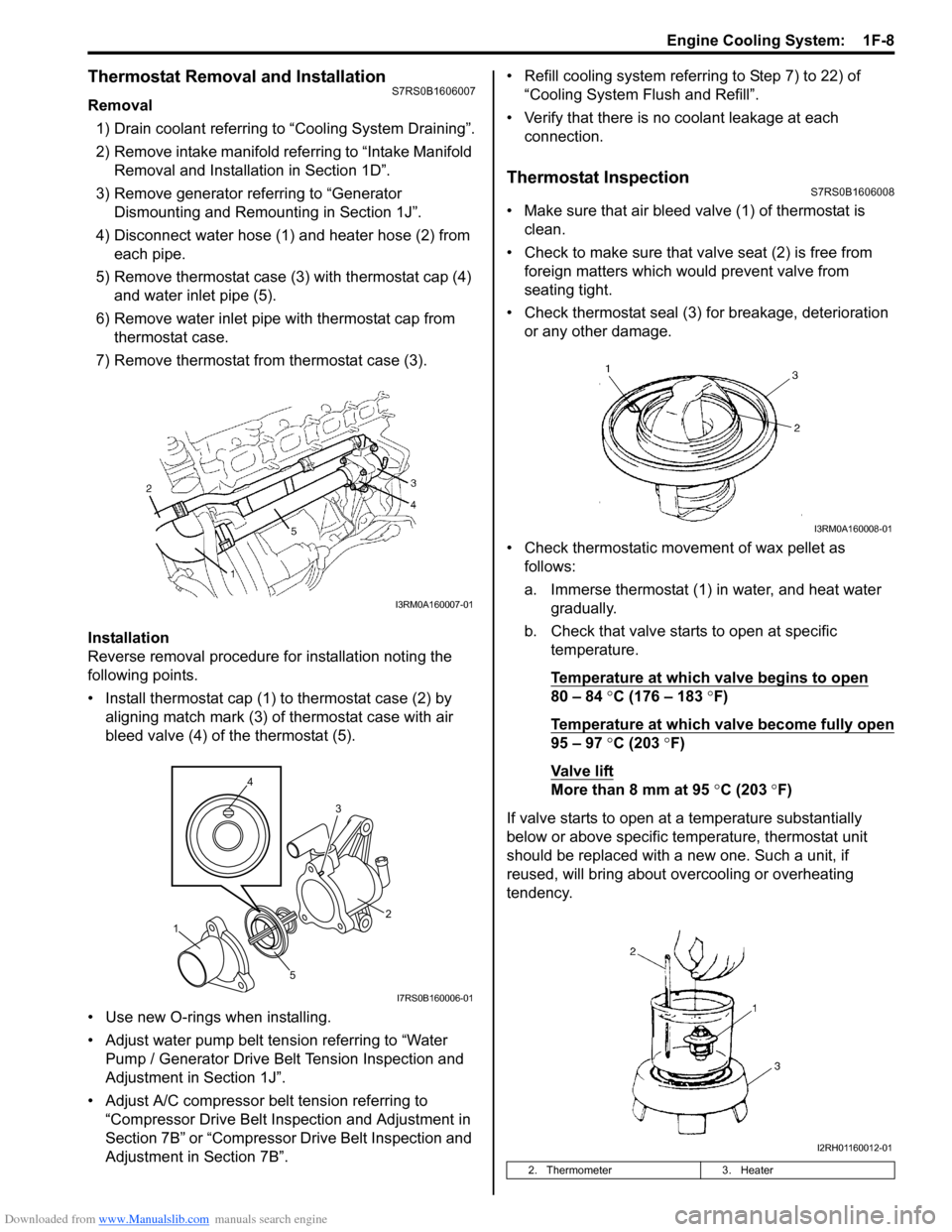
4) Disconnect water hose (1) and heater hose (2) from each pipe.
5) Remove thermostat case (3) with thermostat cap (4)
and water inlet pipe (5).
6) Remove water inlet pipe with thermostat cap from thermostat case.
7) Remove thermostat from thermostat case (3).
Installation
Reverse removal procedure for installation noting the
following points.
• Install thermostat cap (1) to thermostat case (2) by aligning match mark (3) of thermostat case with air
bleed valve (4) of the thermostat (5).
• Use new O-rings when installing.
• Adjust water pump belt tension referring to “Water Pump / Generator Drive Belt Tension Inspection and
Adjustment in Section 1J”.
• Adjust A/C compressor belt tension referring to “Compressor Drive Belt Inspection and Adjustment in
Section 7B” or “Compressor Drive Belt Inspection and
Adjustment in Section 7B”. • Refill cooling system referrin
g to Step 7) to 22) of
“Cooling System Flush and Refill”.
• Verify that there is no coolant leakage at each connection.
Thermostat InspectionS7RS0B1606008
• Make sure that air bleed valve (1) of thermostat is clean.
• Check to make sure that va lve seat (2) is free from
foreign matters which would prevent valve from
seating tight.
• Check thermostat seal (3) for breakage, deterioration or any other damage.
• Check thermostatic movement of wax pellet as follows:
a. Immerse thermostat (1) in water, and heat water gradually.
b. Check that valve starts to open at specific temperature.
Temperature at which valve begins to open
80 – 84 °C (176 – 183 °F)
Temperature at which valve become fully open
95 – 97 °C (203 °F)
Va l v e l i ft
More than 8 mm at 95 °C (203 ° F)
If valve starts to open at a temperature substantially
below or above specific temperature, thermostat unit
should be replaced with a new one. Such a unit, if
reused, will bring about ov ercooling or overheating
tendency.
I3RM0A160007-01
4
5 3
1 2
I7RS0B160006-01
2. Thermometer
3. Heater
I3RM0A160008-01
I2RH01160012-01
Page 375 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Cooling System: 1F-12
Specifications
Tightening Torque SpecificationsS7RS0B1607001
NOTE
The specified tightening torque is also described in the following.
“Cooling System Components”
Reference:
For the tightening torque of fastener not specified in this section, refer to “Fasteners Information in Section 0A”.
Special Tools and Equipment
Recommended Service MaterialS7RS0B1608001
Fastening part Tightening torque
Note
N ⋅mkgf-mlb-ft
Water pump bolt and nut 25 2.5 18.0 �)
MaterialSUZUKI recommended product or Specification Note
Water tight sealant SUZUKI Bond No.1207F P/No.: 99000–31250�)
Page 376 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1G-1 Fuel System:
Engine
Fuel System
Precautions
Precautions on Fuel System ServiceS7RS0B1700001
WARNING!
Before attempting service of any type on fuel system, the following should be always observed in
order to reduce the risk of fire and personal injury.
• Disconnect negative cable at battery.
• Do not smoke, and place no smoking signs near work area.
• Be sure to have CO
2 fire extinguisher handy.
• Be sure to perform work in a well-ventilated area and away from any open flames (such as gas hot heater).
• Wear safety glasses.
• To relieve fuel vapor pressure in fuel tank, remove fuel filler cap from fuel filler neck and then
reinstall it.
• As fuel feed line is still under high fuel pr essure even after stopping engine, loosening or
disconnecting fuel feed line directly may cause dangerous spout of fuel. Before loosening or
disconnecting fuel feed line, make sure to relieve fuel pressure referring to “Fuel Pressure Relief
Procedure”.
• A small amount of fuel may be released when the fuel line is disconnected. In order to reduce the risk of personal injury, cover a shop cloth to the fitting to be disconnected. Be sure to put that cloth
in an approved container after disconnecting.
• Never run engine with fuel pump relay disconnected when engine and exhaust system are hot.
• Note that fuel hose connection varies with each type of pipe. Be sure to connect and clamp each hose correctly referring to “Fuel Hose Disconnecting and Reconnecting”.
After connecting, make sure that it has no twist or kink.
• When installing inje ctor or fuel feed pipe, lubr icate its O-ring with gasoline.
General Description
Fuel System DescriptionS7RS0B1701001
CAUTION!
This engine requires the unleaded fuel only.
The leaded and/or low lead fuel can result in
engine damage and reduce the effectiveness
of the emission control system.
The main components of the fuel system are fuel tank,
fuel pump assembly (with fuel filter, fuel level gauge, fuel
pressure regulator, fuel feed line and fuel vapor line.
For the details of fuel flow, refer to “Fuel Delivery System
Diagram”.
Fuel Delivery System DescriptionS7RS0B1701002
The fuel delivery system consists of the fuel tank, fuel
pump assembly (with built-in f uel filter and fuel pressure
regulator), delivery pipe, injectors and fuel feed line.
The fuel in the fuel tank is pumped up by the fuel pump,
sent into delivery pipe and injected by the injectors.
As the fuel pump assembly is equipped with built-in fuel
filter and fuel pressure regulator, the fuel is filtered and
its pressure is regulated before being sent to the feed
pipe.
The excess fuel at fuel pressure regulation process is
returned back into the fuel tank.
Also, fuel vapor generated in fuel tank is led through the
fuel vapor line into the EVAP canister.
For system diagram, refer to “Fuel Delivery System
Diagram”.