MOUNT SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.G Service Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2008, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 309 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-24
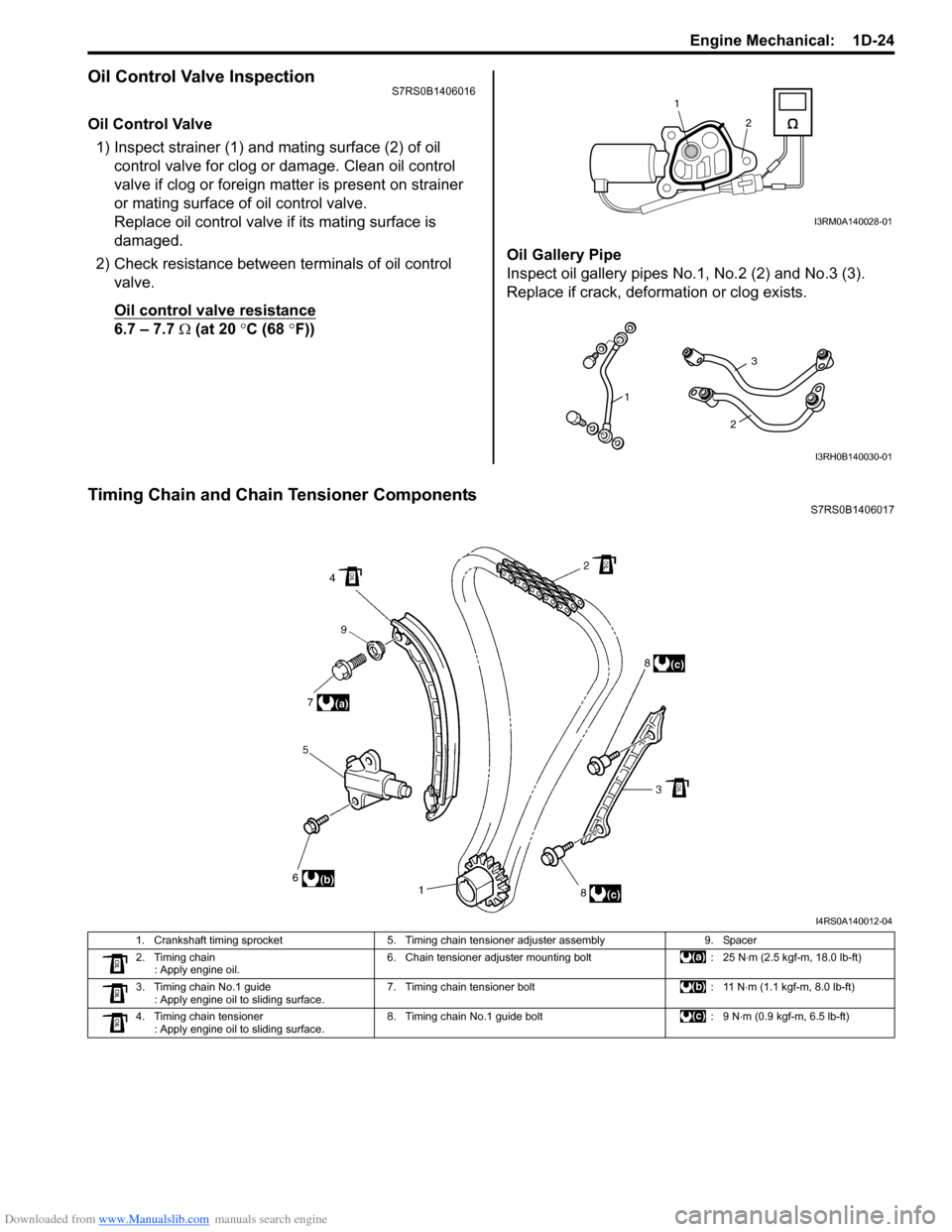
Oil Control Valve InspectionS7RS0B1406016
Oil Control Valve1) Inspect strainer (1) and mating surface (2) of oil control valve for clog or damage. Clean oil control
valve if clog or foreign matter is present on strainer
or mating surface of oil control valve.
Replace oil control valve if its mating surface is
damaged.
2) Check resistance between terminals of oil control
valve.
Oil control valve resistance
6.7 – 7.7 Ω (at 20 °C (68 °F)) Oil Gallery Pipe
Inspect oil gallery pipes No
.1, No.2 (2) and No.3 (3).
Replace if crack, deformation or clog exists.
Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner ComponentsS7RS0B1406017
1
2
I3RM0A140028-01
1
3
2
I3RH0B140030-01
I4RS0A140012-04
1. Crankshaft timing sprocket 5. Timing chain tensioner adjuster assembly 9. Spacer
2. Timing chain : Apply engine oil. 6. Chain tensioner adjuster mounting bolt
: 25 N⋅m (2.5 kgf-m, 18.0 lb-ft)
3. Timing chain No.1 guide : Apply engine oil to sliding surface. 7. Timing chain tensioner bolt
: 11 N⋅m (1.1 kgf-m, 8.0 lb-ft)
4. Timing chain tensioner : Apply engine oil to sliding surface. 8. Timing chain No.1 guide bolt
: 9 N⋅m (0.9 kgf-m, 6.5 lb-ft)
Page 314 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-29 Engine Mechanical:
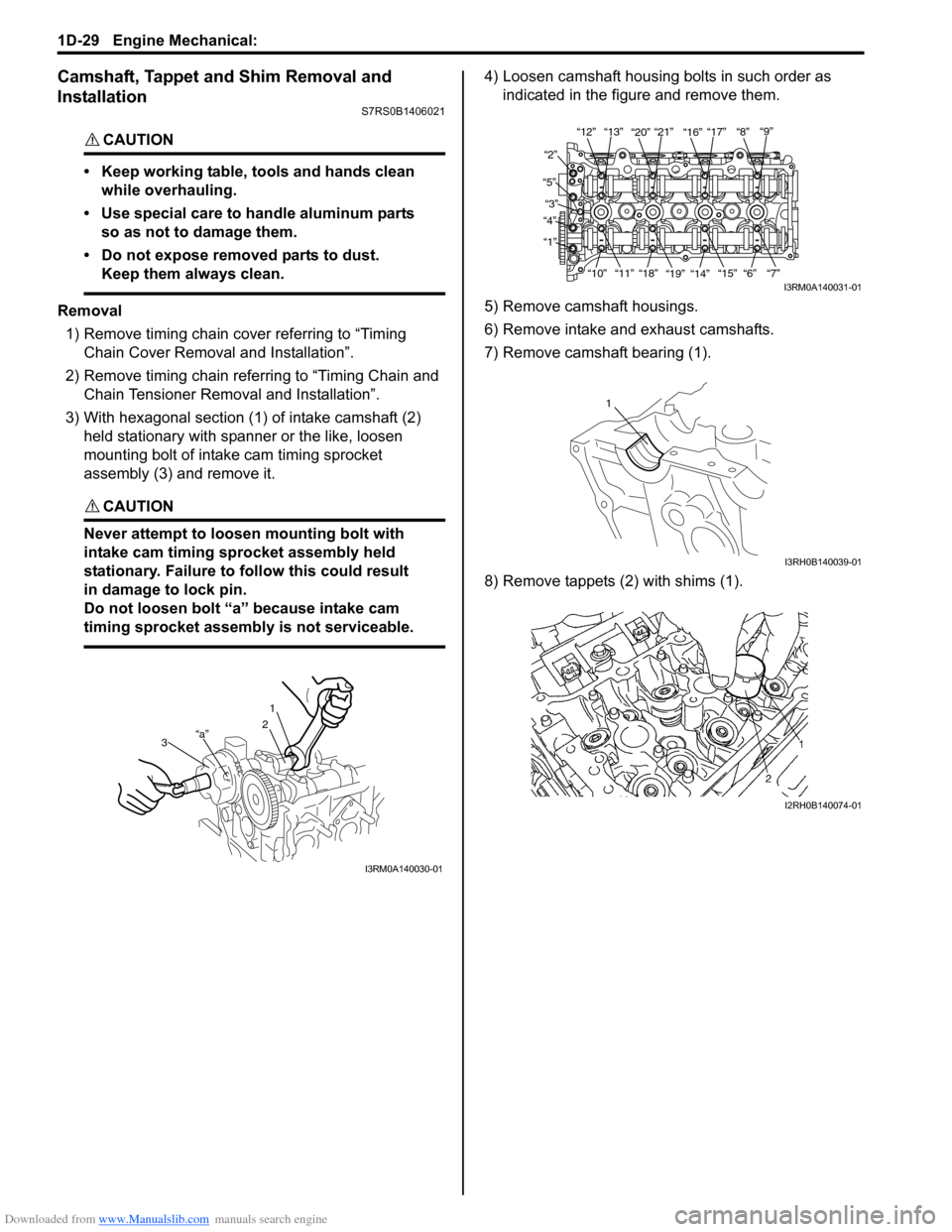
Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Removal and
Installation
S7RS0B1406021
CAUTION!
• Keep working table, tools and hands clean while overhauling.
• Use special care to handle aluminum parts so as not to damage them.
• Do not expose removed parts to dust. Keep them always clean.
Removal
1) Remove timing chain cover referring to “Timing Chain Cover Removal and Installation”.
2) Remove timing chain referring to “Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner Removal and Installation”.
3) With hexagonal section (1) of intake camshaft (2) held stationary with spanner or the like, loosen
mounting bolt of intake cam timing sprocket
assembly (3) and remove it.
CAUTION!
Never attempt to loosen mounting bolt with
intake cam timing sprocket assembly held
stationary. Failure to fo llow this could result
in damage to lock pin.
Do not loosen bolt “a” because intake cam
timing sprocket assembly is not serviceable.
4) Loosen camshaft housing bolts in such order as indicated in the figure and remove them.
5) Remove camshaft housings.
6) Remove intake and exhaust camshafts.
7) Remove camshaft bearing (1).
8) Remove tappets (2) with shims (1).
3“a”
1
2
I3RM0A140030-01
“12”“13” “20”“21”
“16”“17” “8” “9”
“2”
“5” “3”
“4”
“1”
“10”“11”“18”
“19” “14” “15” “6” “7”
I3RM0A140031-01
1
I3RH0B140039-01
I2RH0B140074-01
Page 334 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-49 Engine Mechanical:
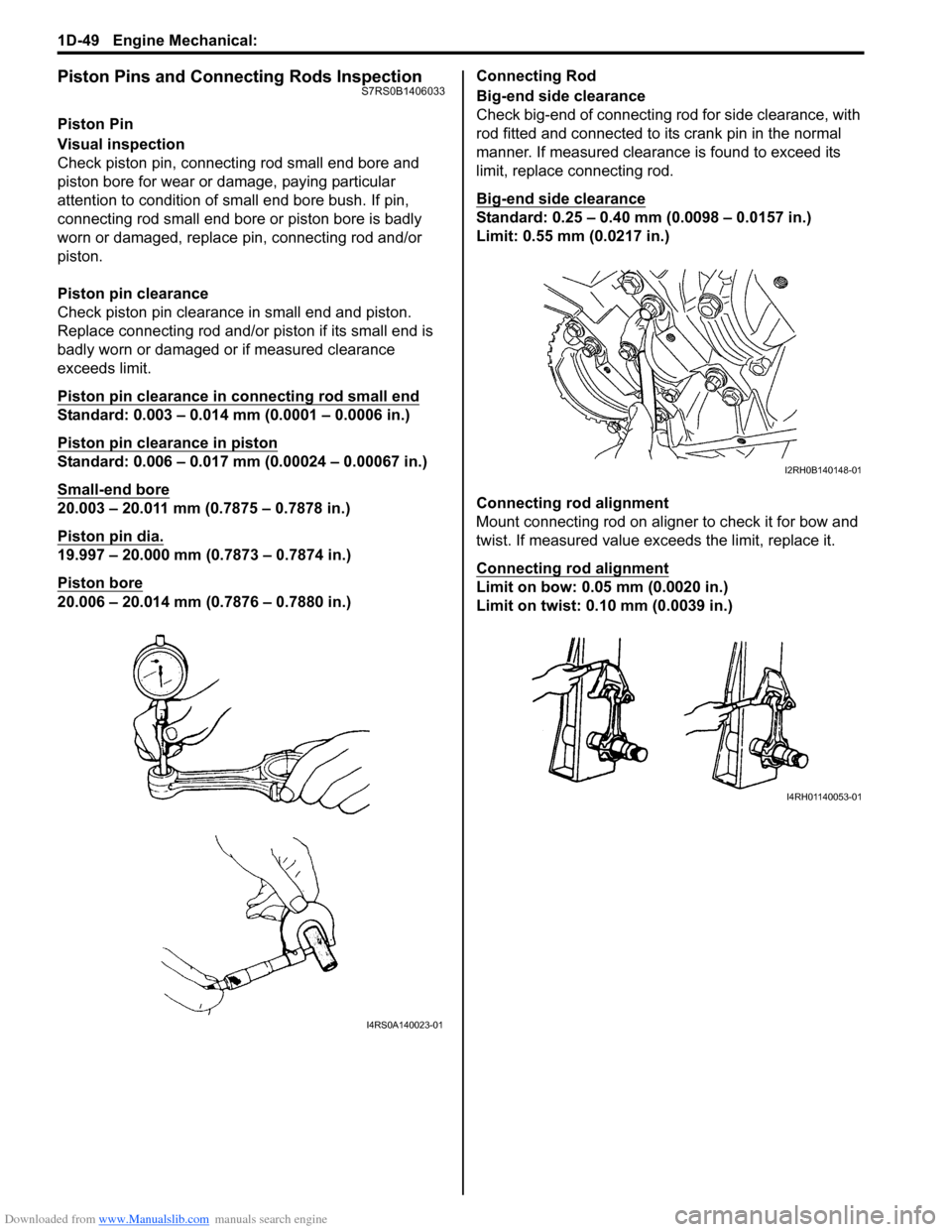
Piston Pins and Connecting Rods InspectionS7RS0B1406033
Piston Pin
Visual inspection
Check piston pin, connecting rod small end bore and
piston bore for wear or damage, paying particular
attention to condition of small end bore bush. If pin,
connecting rod small end bore or piston bore is badly
worn or damaged, replace pin, connecting rod and/or
piston.
Piston pin clearance
Check piston pin clearance in small end and piston.
Replace connecting rod and/or piston if its small end is
badly worn or damaged or if measured clearance
exceeds limit.
Piston pin clearance in connecting rod small end
Standard: 0.003 – 0.014 mm (0.0001 – 0.0006 in.)
Piston pin clearance in piston
Standard: 0.006 – 0.017 mm (0.00024 – 0.00067 in.)
Small-end bore
20.003 – 20.011 mm (0.7875 – 0.7878 in.)
Piston pin dia.
19.997 – 20.000 mm (0.7873 – 0.7874 in.)
Piston bore
20.006 – 20.014 mm (0.7876 – 0.7880 in.)Connecting Rod
Big-end side clearance
Check big-end of connecting rod for side clearance, with
rod fitted and connected to its crank pin in the normal
manner. If measured clearance is found to exceed its
limit, replace connecting rod.
Big-end side clearance
Standard: 0.25 – 0.40 mm (0.0098 – 0.0157 in.)
Limit: 0.55 mm (0.0217 in.)
Connecting rod alignment
Mount connecting rod on aligner to check it for bow and
twist. If measured value exceeds the limit, replace it.
Connecting rod alignment
Limit on bow: 0.05 mm (0.0020 in.)
Limit on twist: 0.10 mm (0.0039 in.)
I4RS0A140023-01
I2RH0B140148-01
I4RH01140053-01
Page 335 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-50
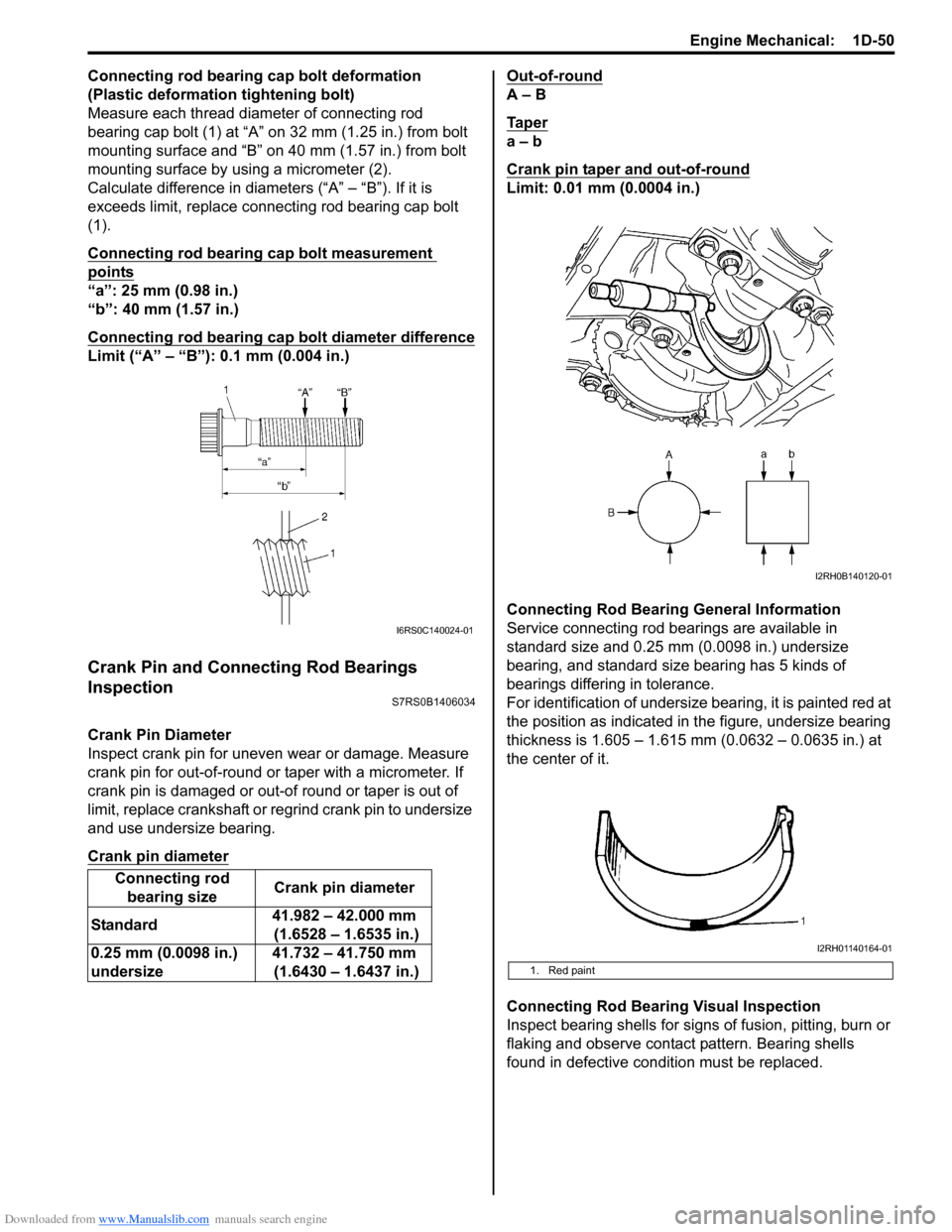
Connecting rod bearing cap bolt deformation
(Plastic deformation tightening bolt)
Measure each thread diameter of connecting rod
bearing cap bolt (1) at “A” on 32 mm (1.25 in.) from bolt
mounting surface and “B” on 40 mm (1.57 in.) from bolt
mounting surface by using a micrometer (2).
Calculate difference in diameters (“A” – “B”). If it is
exceeds limit, replace connecting rod bearing cap bolt
(1).
Connecting rod bearing cap bolt measurement
points
“a”: 25 mm (0.98 in.)
“b”: 40 mm (1.57 in.)
Connecting rod bearing cap bolt diameter difference
Limit (“A” – “B”): 0.1 mm (0.004 in.)
Crank Pin and Connecting Rod Bearings
Inspection
S7RS0B1406034
Crank Pin Diameter
Inspect crank pin for uneven wear or damage. Measure
crank pin for out-of-round or taper with a micrometer. If
crank pin is damaged or out-of round or taper is out of
limit, replace crankshaft or regrind crank pin to undersize
and use undersize bearing.
Crank pin diameter
Out-of-round
A – B
Ta p e r
a – b
Crank pin taper and out-of-round
Limit: 0.01 mm (0.0004 in.)
Connecting Rod Bearing General Information
Service connecting rod be arings are available in
standard size and 0.25 mm (0.0098 in.) undersize
bearing, and standard size bearing has 5 kinds of
bearings differing in tolerance.
For identification of undersize bearing, it is painted red at
the position as indicated in the figure, undersize bearing
thickness is 1.605 – 1.615 mm (0.0632 – 0.0635 in.) at
the center of it.
Connecting Rod Bearing Visual Inspection
Inspect bearing shells for signs of fusion, pitting, burn or
flaking and observe contact pattern. Bearing shells
found in defective condition must be replaced.
Connecting rod
bearing size Crank pin diameter
Standard 41.982 – 42.000 mm
(1.6528 – 1.6535 in.)
0.25 mm (0.0098 in.)
undersize 41.732 – 41.750 mm
(1.6430 – 1.6437 in.)
I6RS0C140024-01
1. Red paint
I2RH0B140120-01
I2RH01140164-01
Page 338 of 1496
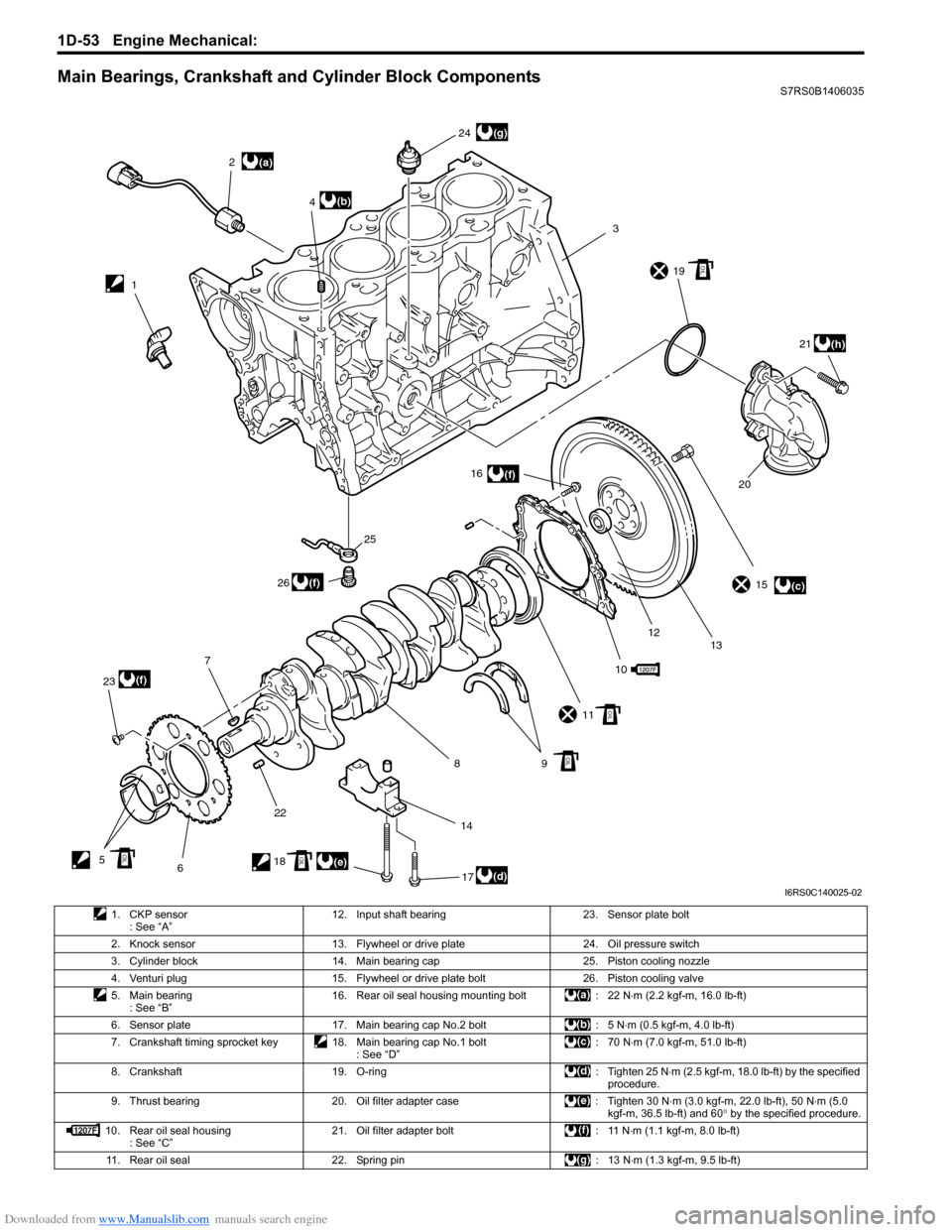
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-53 Engine Mechanical:
Main Bearings, Crankshaft and Cylinder Block ComponentsS7RS0B1406035
(a)
(c)
(d)(e)
(b)
(f)
(f)
(f)
(g)
(h)
12
3
4
5 67
8910
11 15
12 13
14 16
17
18 19
2021
22
23 24
25
26
OIL
OIL
OIL
OILOIL
I6RS0C140025-02
1. CKP sensor : See “A” 12. Input shaft bearing 23. Sensor plate bolt
2. Knock sensor 13. Flywheel or drive plate 24. Oil pressure switch 3. Cylinder block 14. Main bearing cap 25. Piston cooling nozzle
4. Venturi plug 15. Flywheel or drive plate bolt 26. Piston cooling valve
5. Main bearing : See “B” 16. Rear oil seal housing mounting bolt : 22 N
⋅m (2.2 kgf-m, 16.0 lb-ft)
6. Sensor plate 17. Main bearing cap No.2 bolt : 5 N ⋅m (0.5 kgf-m, 4.0 lb-ft)
7. Crankshaft timing sprocket key 18. Main bearing cap No.1 bolt : See “D”:70 N
⋅m (7.0 kgf-m, 51.0 lb-ft)
8. Crankshaft 19. O-ring : Tighten 25 N ⋅m (2.5 kgf-m, 18.0 lb-ft) by the specified
procedure.
9. Thrust bearing 20. Oil filter adapter case : Tighten 30 N ⋅m (3.0 kgf-m, 22.0 lb-ft), 50 N⋅m (5.0
kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft) and 60 ° by the specified procedure.
10. Rear oil seal housing : See “C” 21. Oil filter adapter bolt : 11 N
⋅m (1.1 kgf-m, 8.0 lb-ft)
11. Rear oil seal 22. Spring pin : 13 N ⋅m (1.3 kgf-m, 9.5 lb-ft)
Page 341 of 1496
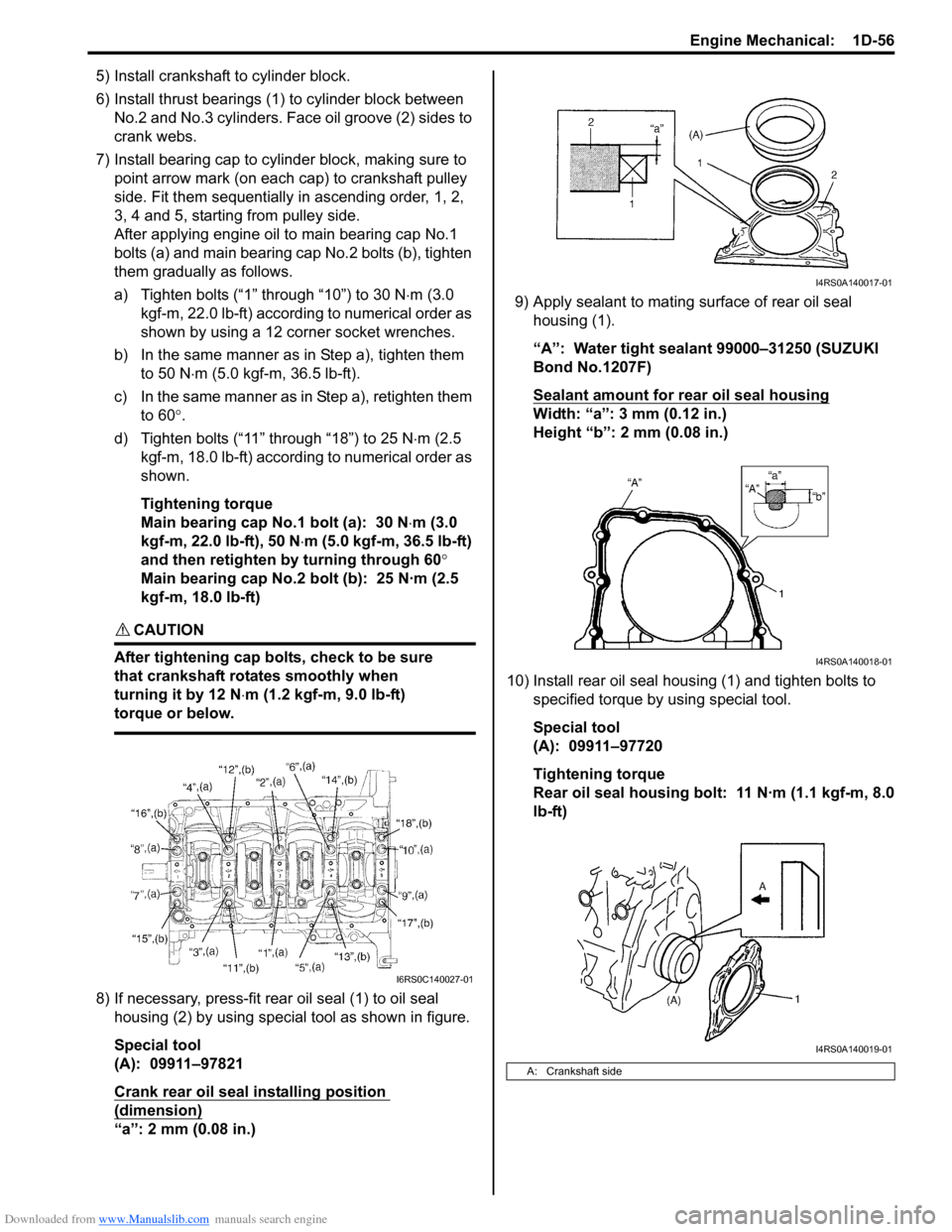
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-56
5) Install crankshaft to cylinder block.
6) Install thrust bearings (1) to cylinder block between No.2 and No.3 cylinders. Face oil groove (2) sides to
crank webs.
7) Install bearing cap to cylinder block, making sure to point arrow mark (on each cap) to crankshaft pulley
side. Fit them sequentially in ascending order, 1, 2,
3, 4 and 5, starting from pulley side.
After applying engine oil to main bearing cap No.1
bolts (a) and main bearing cap No.2 bolts (b), tighten
them gradually as follows.
a) Tighten bolts (“1” through “10”) to 30 N ⋅m (3.0
kgf-m, 22.0 lb-ft) according to numerical order as
shown by using a 12 corner socket wrenches.
b) In the same manner as in Step a), tighten them to 50 N ⋅m (5.0 kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft).
c) In the same manner as in Step a), retighten them to 60 °.
d) Tighten bolts (“11” through “18”) to 25 N ⋅m (2.5
kgf-m, 18.0 lb-ft) according to numerical order as
shown.
Tightening torque
Main bearing cap No.1 bolt (a): 30 N ⋅m (3.0
kgf-m, 22.0 lb-ft), 50 N ⋅m (5.0 kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft)
and then retighten by turning through 60 °
Main bearing cap No.2 bolt (b): 25 N·m (2.5
kgf-m, 18.0 lb-ft)
CAUTION!
After tightening cap bolts, check to be sure
that crankshaft rotates smoothly when
turning it by 12 N ⋅m (1.2 kgf-m, 9.0 lb-ft)
torque or below.
8) If necessary, press-fit rear oil seal (1) to oil seal housing (2) by using special tool as shown in figure.
Special tool
(A): 09911–97821
Crank rear oil seal installing position
(dimension)
“a”: 2 mm (0.08 in.) 9) Apply sealant to mating surface of rear oil seal
housing (1).
“A”: Water tight sealant 99000–31250 (SUZUKI
Bond No.1207F)
Sealant amount for rear oil seal housing
Width: “a”: 3 mm (0.12 in.)
Height “b”: 2 mm (0.08 in.)
10) Install rear oil seal housing (1) and tighten bolts to specified torque by using special tool.
Special tool
(A): 09911–97720
Tightening torque
Rear oil seal housing bolt: 11 N·m (1.1 kgf-m, 8.0
lb-ft)
I6RS0C140027-01
A: Crankshaft side
I4RS0A140017-01
I4RS0A140018-01
I4RS0A140019-01
Page 343 of 1496
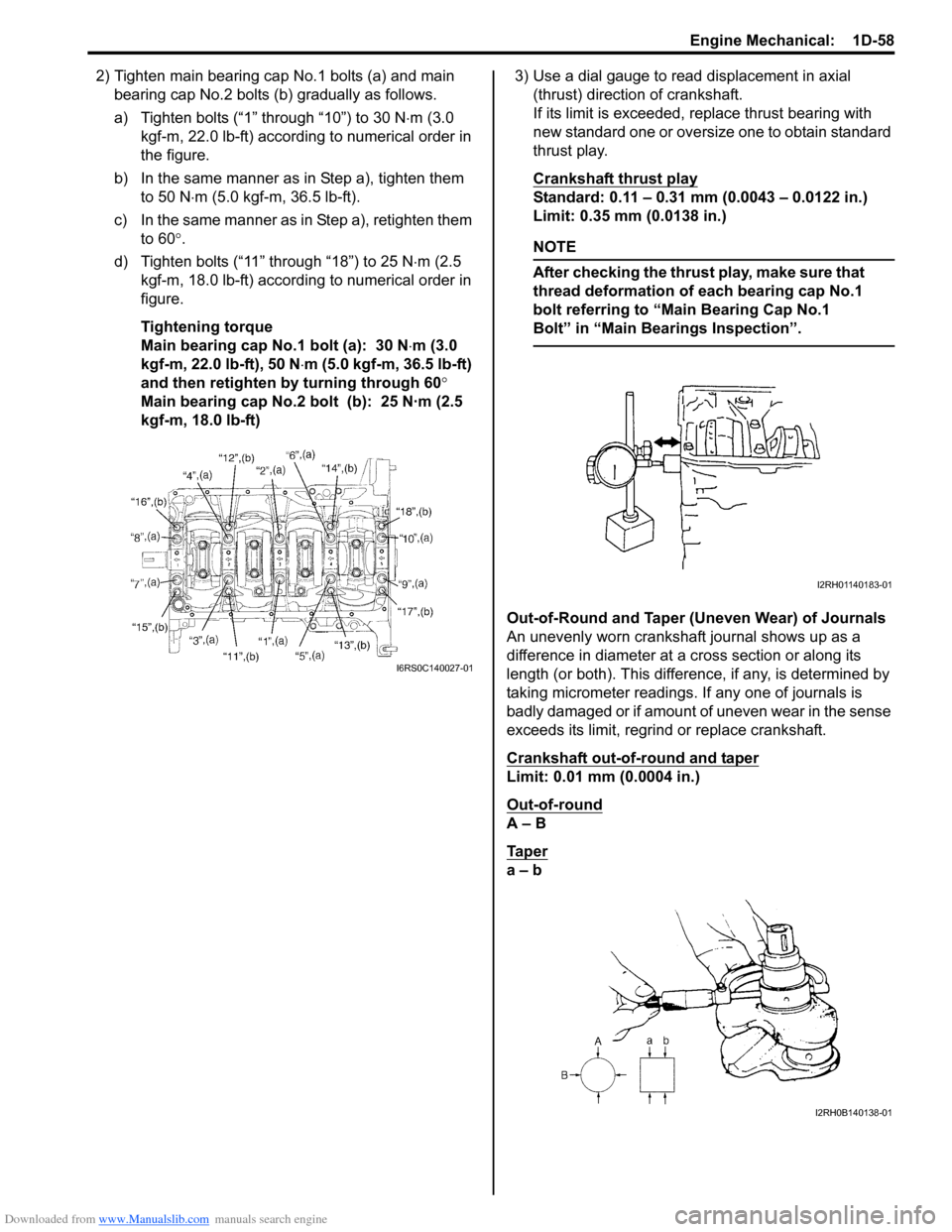
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-58
2) Tighten main bearing cap No.1 bolts (a) and main bearing cap No.2 bolts (b ) gradually as follows.
a) Tighten bolts (“1” through “10”) to 30 N ⋅m (3.0
kgf-m, 22.0 lb-ft) according to numerical order in
the figure.
b) In the same manner as in Step a), tighten them to 50 N ⋅m (5.0 kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft).
c) In the same manner as in Step a), retighten them to 60 °.
d) Tighten bolts (“11” through “18”) to 25 N ⋅m (2.5
kgf-m, 18.0 lb-ft) according to numerical order in
figure.
Tightening torque
Main bearing cap No.1 bolt (a): 30 N ⋅m (3.0
kgf-m, 22.0 lb-ft), 50 N ⋅m (5.0 kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft)
and then retighten by turning through 60 °
Main bearing cap No.2 bolt (b): 25 N·m (2.5
kgf-m, 18.0 lb-ft) 3) Use a dial gauge to read displacement in axial
(thrust) direction of crankshaft.
If its limit is exceeded, replace thrust bearing with
new standard one or oversize one to obtain standard
thrust play.
Crankshaft thrust play
Standard: 0.11 – 0.31 mm (0.0043 – 0.0122 in.)
Limit: 0.35 mm (0.0138 in.)
NOTE
After checking the thrust play, make sure that
thread deformation of each bearing cap No.1
bolt referring to “Main Bearing Cap No.1
Bolt” in “Main Bear ings Inspection”.
Out-of-Round and Taper (Uneven Wear) of Journals
An unevenly worn crankshaft journal shows up as a
difference in diameter at a cross section or along its
length (or both). This difference, if any, is determined by
taking micrometer readings. If any one of journals is
badly damaged or if amount of uneven wear in the sense
exceeds its limit, regrind or replace crankshaft.
Crankshaft out-of-round and taper
Limit: 0.01 mm (0.0004 in.)
Out-of-round
A – B
Ta p e r
a – b
I6RS0C140027-01
I2RH01140183-01
I2RH0B140138-01
Page 349 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-64
Honing or Reboring Cylinders1) When any cylinder needs reboring, all other cylinders must also be rebored at the same time.
2) Select oversized piston according to amount of cylinder wear.
Oversize piston specification
Oversize 0.50: 78.453 – 78.468 mm (3.0887 –
3.0893 in.)
3) Using micrometer, measure piston diameter. Measurement position for piston diameter
“a”: 7.0 mm (0.28 in.) 4) Rebore and hone cylinder to the following
dimension.
NOTE
Before reboring, install all main bearing caps
in place and tighten to specification to avoid
distortion of bearing bores.
Cylinder bore diameter to be rebored
Oversize 0.50: 78.500 – 78.514 mm (3.0906 –
3.0911 in.)
5) Measure piston clearance after honing. Piston clearance
0.032 – 0.061 mm (0.0013 – 0.0024 in.)
Specifications
Tightening Torque SpecificationsS7RS0B1407001
I2RH01140157-01
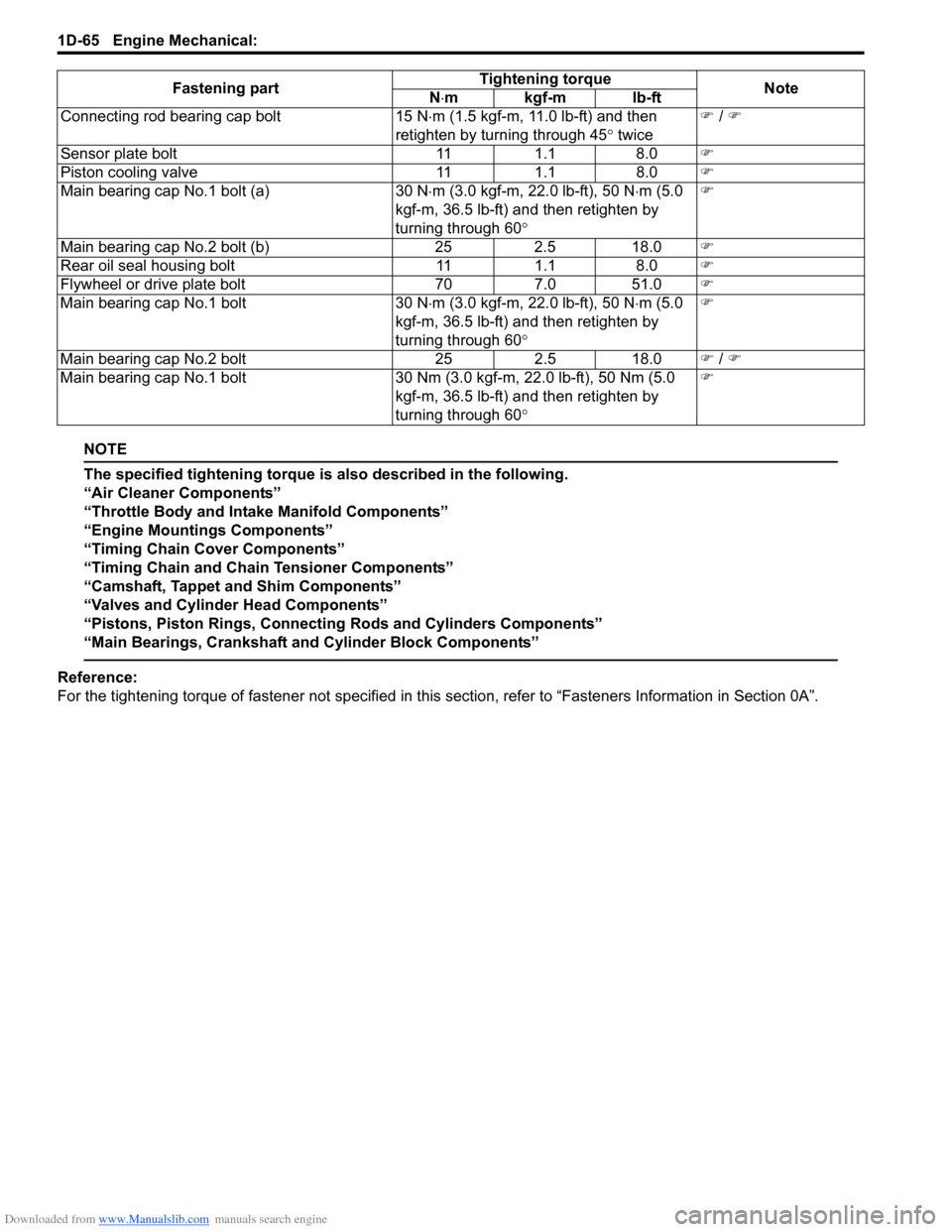
Fastening part Tightening torque
Note
N ⋅mkgf-mlb-ft
Camshaft housing bolt 11 1.1 8.0 �)
Cylinder head cover bolt Tighten 3 N ⋅m (0.3 kgf-m, 2.5 lb-ft), 5 N ⋅m
(0.5 kgf-m, 4.0 lb-ft) and 8 N ⋅m (0.8 kgf-m,
6.0 lb-ft) by the specified procedure �)
Intake manifold bolt 23 2.3 17.0 �)
Intake manifold nut 23 2.3 17.0 �)
Intake manifold ground terminal bolt 11 1.1 8.0 �)
Engine left mounting bracket nut 55 5.5 40.0 �)
Engine right mounting nut 65 6.5 47.0 �)
Engine rear mounting bush bolt 55 5.5 40.0 �)
Starting motor terminal nut 11 1.1 8.0 �)
Generator terminal nut 6 0.6 4.5 �)
Intake manifold ground terminal bolt 11 1.1 18.0 �)
Timing chain cover bolt 25 2.5 18.0 �)
Timing chain cover nut 25 2.5 18.0 �)
Cap bolt 25 2.5 18.0 �)
Oil gallery pipe No.2 and No.3 bolt 11 1.1 8.0 �)
Crankshaft pulley bolt 150 15.0 108.5 �)
Oil control valve mounting nut 11 1.1 8.0 �)
Oil gallery pipe No.1 bolt 30 3.0 21.5 �)
Timing chain No.1 guide bolt 9 0.9 6.5 �)
Timing chain tensioner bolt 25 2.5 18.0 �)
Timing chain tensioner adjuster bolt 11 1.1 8.0 �)
Camshaft housing bolt 5 N ⋅m (0.5 kgf-m, 4.0 lb-ft) and 11 N ⋅m (1.1
kgf-m, 8.0 lb-ft) by the specified procedure �)
/ �)
Intake cam timing sprocket bolt 60 6.0 43.5 �)
Venturi plug 3.5 0.35 3.0 �)
Cylinder head bolt for M8 25 2.5 18.0 �)
Cylinder head bolt for M10 20 N ⋅m (2.0 kgf-m, 14.5 lb-ft), 40 N ⋅m (4.0
kgf-m, 29.0 lb-ft) and then retighten by
turning through to 60 ° twice �)
Page 350 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-65 Engine Mechanical:
NOTE
The specified tightening torque is also described in the following.
“Air Cleaner Components”
“Throttle Body and Intake Manifold Components”
“Engine Mountings Components”
“Timing Chain Cover Components”
“Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner Components”
“Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Components”
“Valves and Cylinder Head Components”
“Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and Cylinders Components”
“Main Bearings, Crankshaft and Cylinder Block Components”
Reference:
For the tightening torque of fastener not specified in this section, refer to “Fasteners Information in Section 0A”.
Connecting rod bearing cap bolt
15 N⋅m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft) and then
retighten by turning through 45 ° twice �)
/ �)
Sensor plate bolt 111.1 8.0 �)
Piston cooling valve 111.1 8.0 �)
Main bearing cap No.1 bolt (a) 30 N⋅m (3.0 kgf-m, 22.0 lb-ft), 50 N ⋅m (5.0
kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft) and then retighten by
turning through 60 ° �)
Main bearing cap No.2 bolt (b) 252.5 18.0 �)
Rear oil seal housing bolt 111.1 8.0 �)
Flywheel or drive plate bolt 707.0 51.0 �)
Main bearing cap No.1 bolt 30 N⋅m (3.0 kgf-m, 22.0 lb-ft), 50 N ⋅m (5.0
kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft) and then retighten by
turning through 60 ° �)
Main bearing cap No.2 bolt 252.5 18.0 �) / �)
Main bearing cap No.1 bolt 30 Nm (3.0 kgf-m, 22.0 lb-ft), 50 Nm (5.0
kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft) and then retighten by
turning through 60 ° �)
Fastening part
Tightening torque
Note
N ⋅mkgf-mlb-ft
Page 353 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Lubrication System: 1E-1
Engine
Engine Lubrication System
General Description
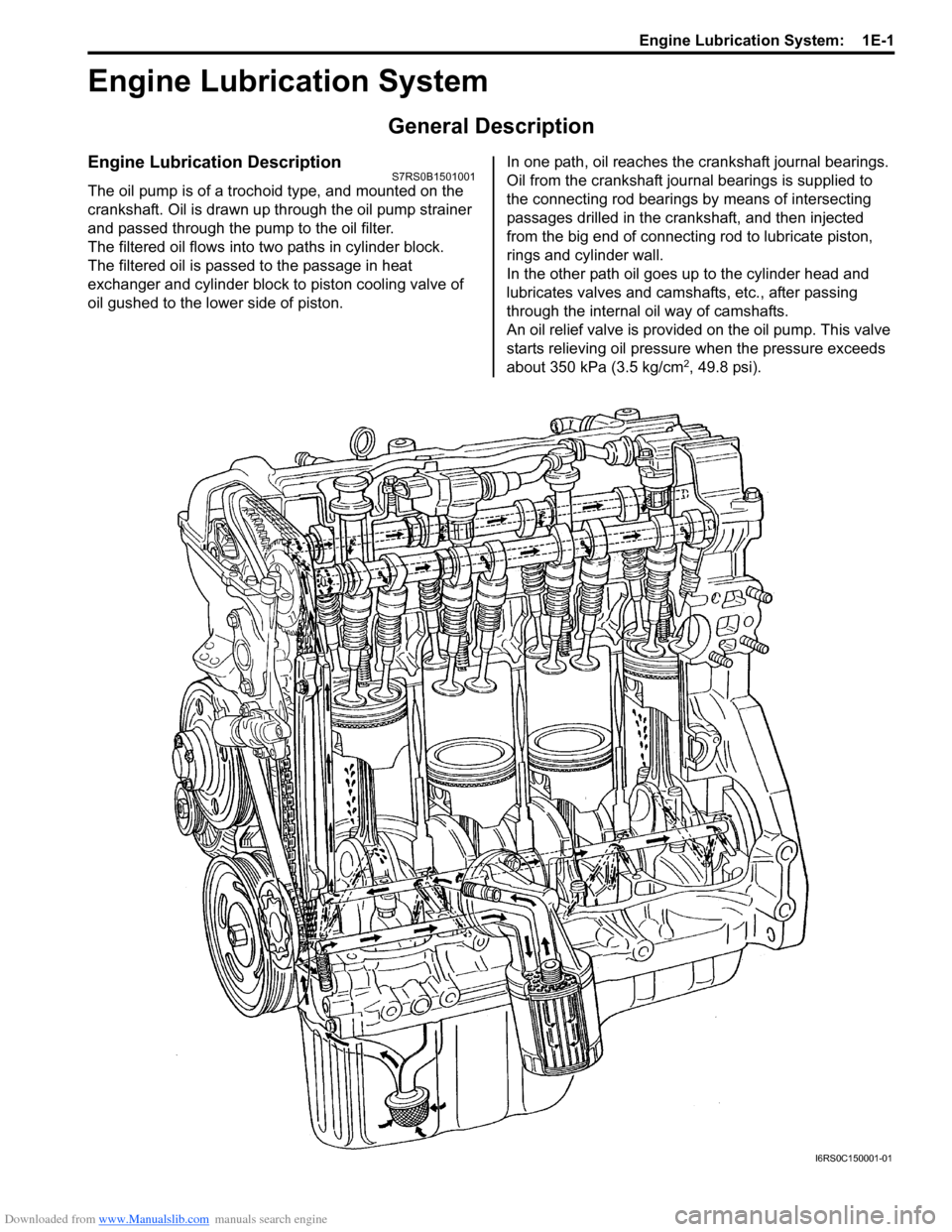
Engine Lubrication DescriptionS7RS0B1501001
The oil pump is of a trochoid type, and mounted on the
crankshaft. Oil is drawn up through the oil pump strainer
and passed through the pump to the oil filter.
The filtered oil flows into two paths in cylinder block.
The filtered oil is passed to the passage in heat
exchanger and cylinder block to piston cooling valve of
oil gushed to the lower side of piston. In one path, oil reaches the crankshaft journal bearings.
Oil from the crankshaft journal bearings is supplied to
the connecting rod bearings by means of intersecting
passages drilled in the cran
kshaft, and then injected
from the big end of connecting rod to lubricate piston,
rings and cylinder wall.
In the other path oil goes up to the cylinder head and
lubricates valves and camshafts, etc., after passing
through the internal oil way of camshafts.
An oil relief valve is provided on the oil pump. This valve
starts relieving oil pressure when the pressure exceeds
about 350 kPa (3.5 kg/cm
2, 49.8 psi).
I6RS0C150001-01