wheels SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.G Service Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2008, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 472 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2D-5 Wheels and Tires:
Radial Tire Lead / Pull DescriptionS7RS0B2401006
“Lead / Pull” is the deviation of the vehicle from a straight
path on a level road even with no pressure on the
steering wheel.
Lead is usually caused by the following conditions.
• Improper tire and wheel alignment.
• Uneven brake assemblies.
• Tire construction.
The way in which a tire is built can produce lead in a
vehicle. An example of this is placement of the belt. Off
center belts on radial tires can cause the tire to develop
a side force while rolling straight down the road. If one
side of the tire has a little larger diameter than the other,
the tire will tend to roll to one side. This will develop a
side force which can produce vehicle lead.
The procedure in the figure (Lead Diagnosis) should be
used to make sure that wheel alignment is not mistaken
for tire lead.
• Part of the lead diagnosis procedure is different from the proper tire rotation pattern currently in the owner
and service manuals. If a medium to high mileage tire
is moved to the other side of the vehicle, be sure to
check that ride roughness has not developed.
• Rear tires will not cause lead.
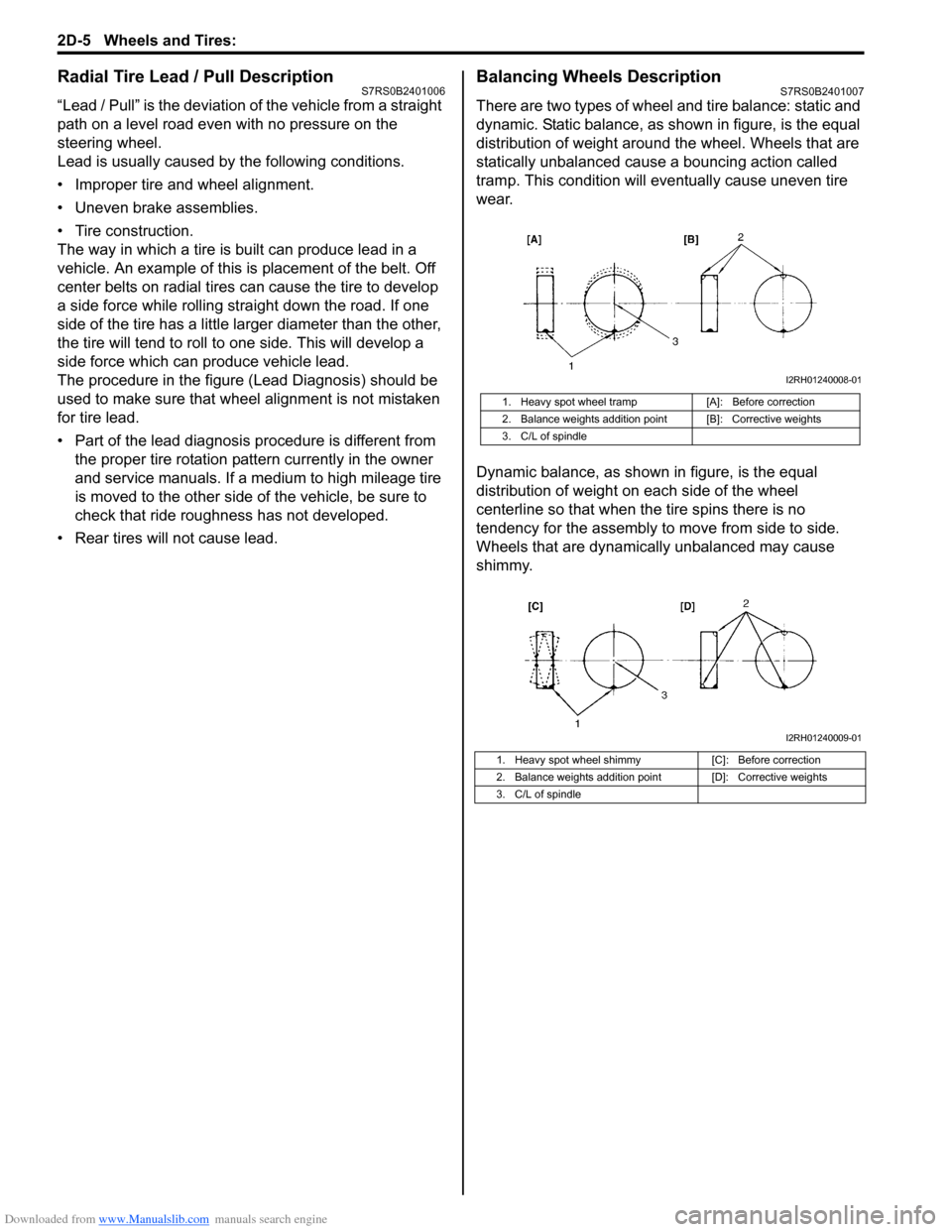
Balancing Wheels DescriptionS7RS0B2401007
There are two types of wheel an d tire balance: static and
dynamic. Static balance, as shown in figure, is the equal
distribution of weight around the wheel. Wheels that are
statically unbalanced cause a bouncing action called
tramp. This condition will eventually cause uneven tire
wear.
Dynamic balance, as shown in figure, is the equal
distribution of weight on each side of the wheel
centerline so that when the tire spins there is no
tendency for the assembly to move from side to side.
Wheels that are dynamically unbalanced may cause
shimmy.
1. Heavy spot wheel tramp [A]: Before correction
2. Balance weights addition point [B]: Corrective weights
3. C/L of spindle
1. Heavy spot wheel shimmy [C]: Before correction
2. Balance weights addition point [D]: Corrective weights
3. C/L of spindle
I2RH01240008-01
I2RH01240009-01
Page 473 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Wheels and Tires: 2D-6
Repair Instructions
General Balance ProceduresS7RS0B2406001
Deposits of mud, etc. must be cleaned from inside of rim.
WARNING!
Stones should be removed from the tread in
order to avoid operator injury during spin
balancing and to obtain good balance.
Each tire should be inspected for any damage, then
balanced according to equipment manufacturer’s
recommendation.
Off-Vehicle Balancing
Most electronic off-vehicle balancers are more accurate
than the on-vehicle spin balancers. They are easy to use
and give a dynamic (two plane) balance. Although they
do not correct for drum or disc unbalance as does on-
vehicle spin balancing, this is overcome by their
accuracy, usually to within 1/8 ounce.
On-Vehicle Balancing
On-vehicle balancing methods vary with equipment and
tool manufacturers. Be sure to follow each
manufacturer’s instructions during balancing operation.
WARNING!
Wheel spin should be limited to 55 km/h (35
mph) as indicated on speedometer.
This limit is necessary because speedometer
only indicates one-half of actual wheel speed
when one drive wheel is spinning and the
other drive wheel is stopped.
Unless care is taken in limiting drive wheel
spin, spinning wheel can reach excessive
speeds. This can result in possible tire
disintegration or differential failure, which
could cause serious personal injury or
extensive vehicle damage.
CAUTION!
Using on-vehicle balancing method with
ignition switch ON may set malfunction
diagnostic trouble code (DTC) of ESP® and
ABS even when system is in good condition.
Never turn ignition swit ch ON while spinning
wheel.
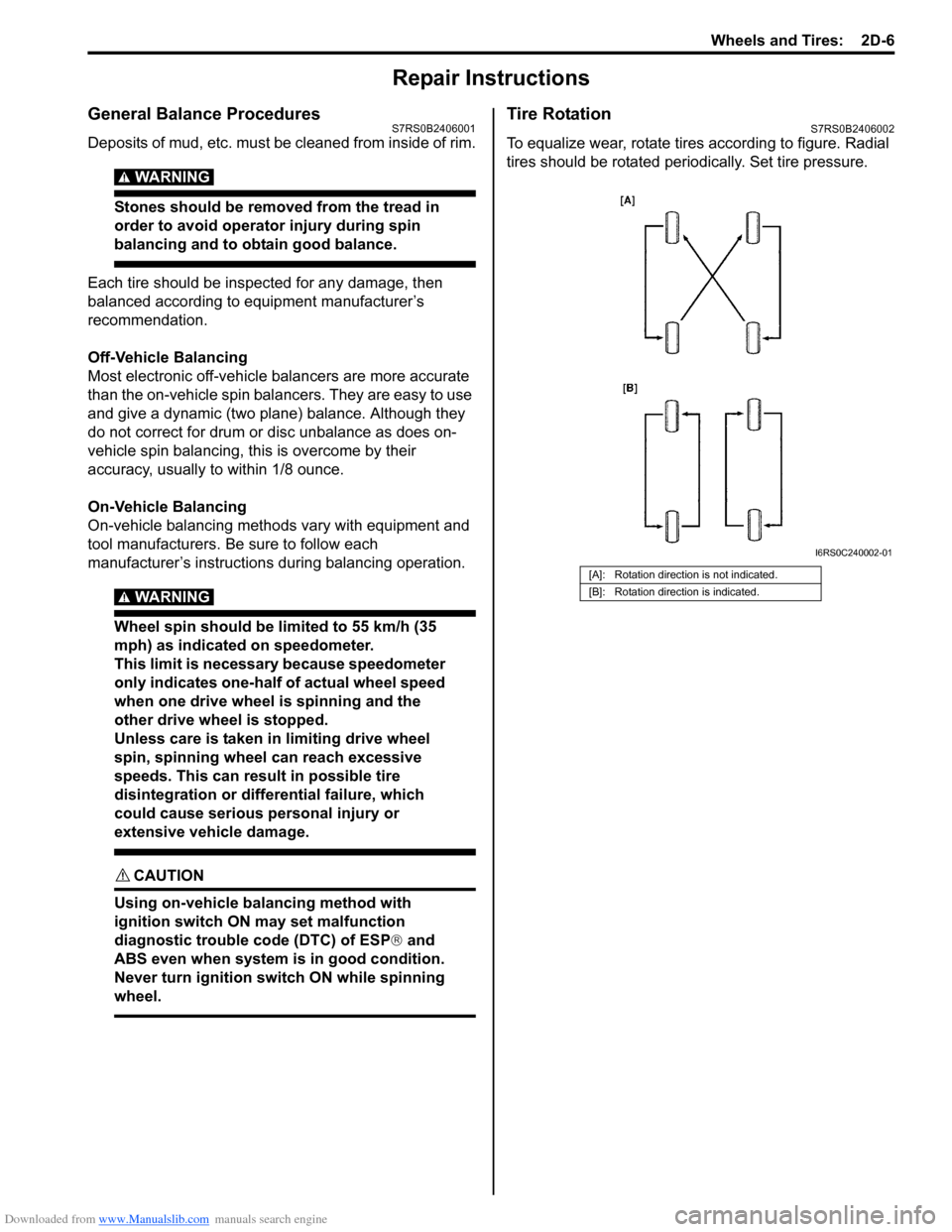
Tire RotationS7RS0B2406002
To equalize wear, rotate tires according to figure. Radial
tires should be rotated periodi cally. Set tire pressure.
[A]: Rotation direction is not indicated.
[B]: Rotation direction is indicated.
I6RS0C240002-01
Page 474 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2D-7 Wheels and Tires:
Wheel Removal and InstallationS7RS0B2406003
Removal
WARNING!
Do not removal all of the wheel nuts at once,
because all the wheels of this vehicle are
mounted by the wheel nuts.
Leave a nut at least not to drop the wheel.
Support the wheel and/or tire and then
remove the nut(s) left with the wheel.
1) Loosen wheel nuts by approximately 180° (half a
rotation).
2) Hoist vehicle.
3) Make sure that the vehicle will not fall off by trying to
move vehicle body in both ways.
4) Remove wheel nut except one.
5) Support the wheel and/or tire not to drop the wheel and then remove the nut left with the wheel.
CAUTION!
Never use heat to loosen tight wheel because
the application of heat to wheel causes the
wheel life shorter and the wheel bearing
damage.
Installation
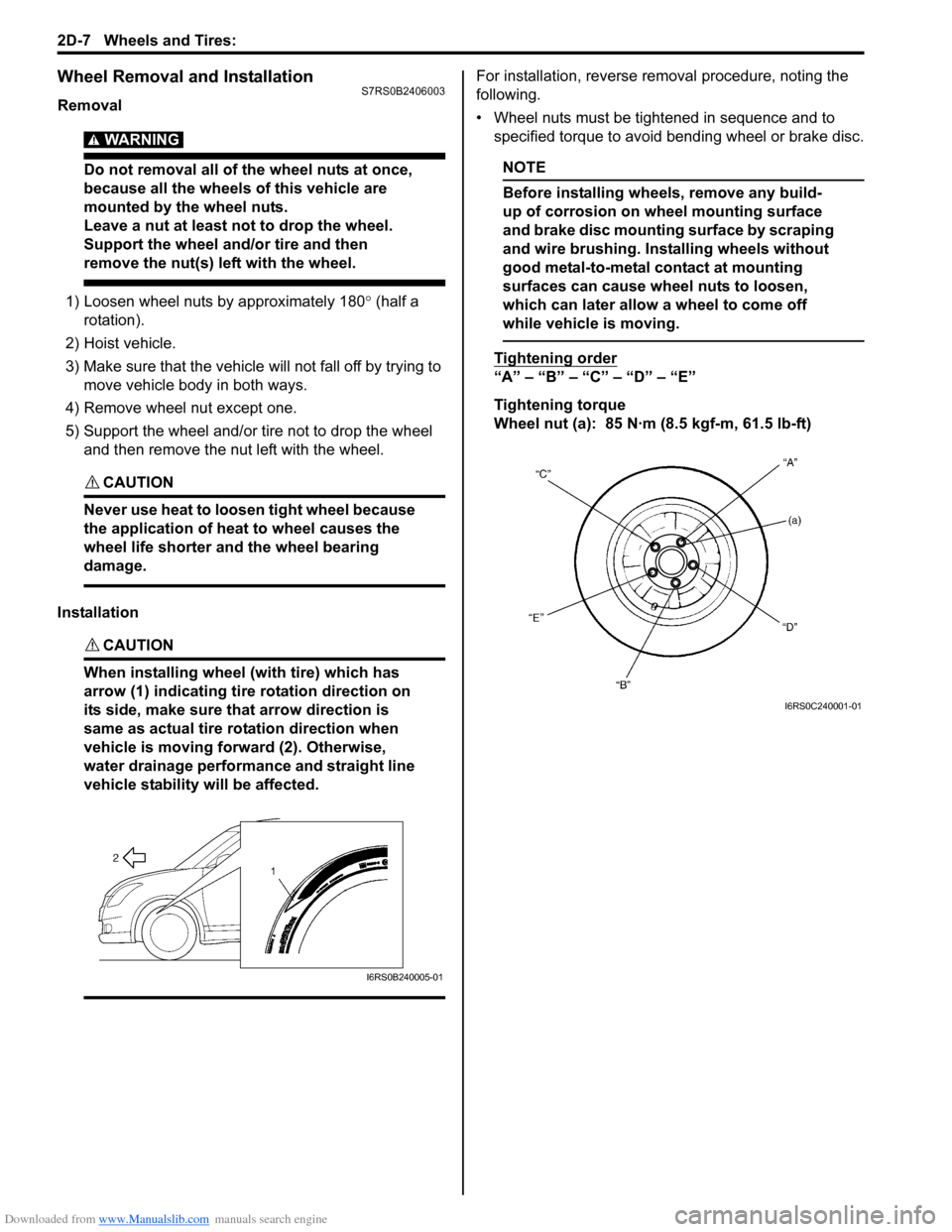
CAUTION!
When installing wheel (with tire) which has
arrow (1) indicating tire rotation direction on
its side, make sure that arrow direction is
same as actual tire ro tation direction when
vehicle is moving forw ard (2). Otherwise,
water drainage performance and straight line
vehicle stability will be affected.
For installation, reverse removal procedure, noting the
following.
• Wheel nuts must be tightened in sequence and to specified torque to avoid bending wheel or brake disc.
NOTE
Before installing wheels, remove any build-
up of corrosion on wheel mounting surface
and brake disc mounting surface by scraping
and wire brushing. Installing wheels without
good metal-to-metal contact at mounting
surfaces can cause wheel nuts to loosen,
which can later allow a wheel to come off
while vehicle is moving.
Tightening order
“A” – “B” – “C” – “D” – “E”
Tightening torque
Wheel nut (a): 85 N·m (8.5 kgf-m, 61.5 lb-ft)
I6RS0B240005-01
I6RS0C240001-01
Page 475 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Wheels and Tires: 2D-8
Tire Mounting and DismountingS7RS0B2406004
CAUTION!
When installing tire which has arrow
indicating tire rotation direction to wheel,
make sure that this tire rotation direction is
same as actual tire rotation direction when
vehicle is moving forward. Otherwise, it is
not possible to install wheel with tire to
vehicle in specified direction.
Use a tire changing machine to mount or dismount tires.
Follow equipment manufacturer’s instructions. Do not
use hand tools or tire irons al one to change tires as they
may damage tire beads or wheel rim.
Rim bead seats should be cleaned with a wire brush or
coarse steel wool to remove lubricants, old rubber and
light rust. Before mounting or dismounting a tire, bead
area should be well lubricated with approved tire
lubricant.
After mounting, inflate to specified pressure shown on
tire placard so that beads are completely seated.
WARNING!
Do not stand over tire when inflating. Bead
may break when bead snaps over rim’s safety
hump and cause serious personal injury.
Do not exceed 330 kpa (47.9 psi) pressure
when inflating. If 330 kpa (47.9 psi) pressure
will not seat beads, deflate, re-lubricate and
reinflate.
Over inflation may cause bead to break and
cause serious personal injury.
Install valve core and inflate to proper pressure.
Tire RepairS7RS0B2406005
There are many different materials and techniques on
the market to repair tires. As not all of these work on all
types of tires, tire manufacturers have published detailed
instructions on how and when to repair tires. These
instructions can be obtained from each tire
manufacturer.
Tire Repair for Emergency Repaired-Tire with
Sealant
S7RS0B2406006
WARNING!
Be sure to observe “Precaution for
Emergency Flat Tire Repair Kit”. Otherwise,
your health may be ruined.
1) Remove flat tire repair sealant from tire using plug (1), filler hose (2), sealant bottle (3) and extension
hose (4) in kit as follows.
a) Remove plug from fille r hose of sealant bottle.
Then connect ext ension hose to tip of filler hose.
b) Remove tire containing flat tire repair sealant from vehicle.
c) Loosen valve core carefully to release air.
WARNING!
Take care not to make sealant blast out from
valve. Otherwise, your health may be ruined.
d) Remove tire bead inside rim of wheel.
e) Make a clearance by inserting a tire lever (2) between tire bead and rim, and then insert hose
(1) thought clearance as shown in figure.
f) Press the bottle and suck out sealant (4), using bottle (3) as a pump.
NOTE
To make sealant easy to suck up from tire,
set bottle lower than sealant surface.
g) Change hose end position and repeat above step f) until sealant is not sucked out.
h) Put cap on bottle so that collected sealant does not leak.
4
1
2
3
I6RS0B240004-01
1 4
3 2
I6RS0C240003-01
Page 476 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2D-9 Wheels and Tires:
2) Check tire if it can be repaired, referring to “Tire
Repair”. If it cannot be repaired, replace it with new
one.
3) Replace valve core of flat tire with new one if tire is reused after repairing.CAUTION!
Be sure to use new valve core. Otherwise, air
leak may occur due to sealant attached to
valve core.
4) Install tire to ri m of wheel, check that there is no air
leakage and adjust it to specified pressure shown on
tire placard.
Specifications
Wheels and Tires SpecificationsS7RS0B2407001
Tire size (Standard)
: 195/50R16 87V
Wheel size (Standard)
: 16x 6 J
Tightening torque
Wheel nut: 85 N·m (8.5 kgf-m, 61.5 lb-ft)
NOTE
• Tire inflation pressure should be checked when tires are cool.
• Specified tire inflation pressure should be found on tire placard or in owner’s manual which came
with the vehicle.
Tightening Torque SpecificationsS7RS0B2407002
Reference:
For the tightening torque of fastener not specified in this section, refer to “Fasteners Information in Section 0A”.
Fastening part
Tightening torque
Note
N ⋅mkgf-mlb-ft
Wheel nut 858.5 61.5 �) / �)
Page 498 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4-1 Precautions:
Brakes
Precautions
Precautions
Precautions for BrakesS7RS0B4000001
Suspension Caution
Refer to “Suspension Caution in Section 00”.
Wheels and Tires Caution
Refer to “Wheels and Tires Caution in Section 00”.
Brake Caution
Refer to “Brake Caution in Section 00”.
ESP® System Precautions
Refer to “Precaution for Vehicle Equipped with ESP ® System in Section 00”.
General Precautions
Refer to “General Precautions in Section 00”.
Vehicle Lifting Points
Refer to “Vehicle Liftin g Points in Section 0A”.
Fastener Caution
Refer to “Fastener Caution in Section 00”.
Fastener Information
Refer to “Fasteners Information in Section 0A”.
Page 499 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Brake Control System and Diagnosis: 4A-1
Brakes
Brake Control System and Diagnosis
Precautions
Precautions on BrakeS7RS0B4100001
Air Bag Warning
Refer to “Air Bag System Service Warning in Section 00”.
Brakes Diagnosis Note
Refer to “Brakes Diagnosis Note”.
General Description
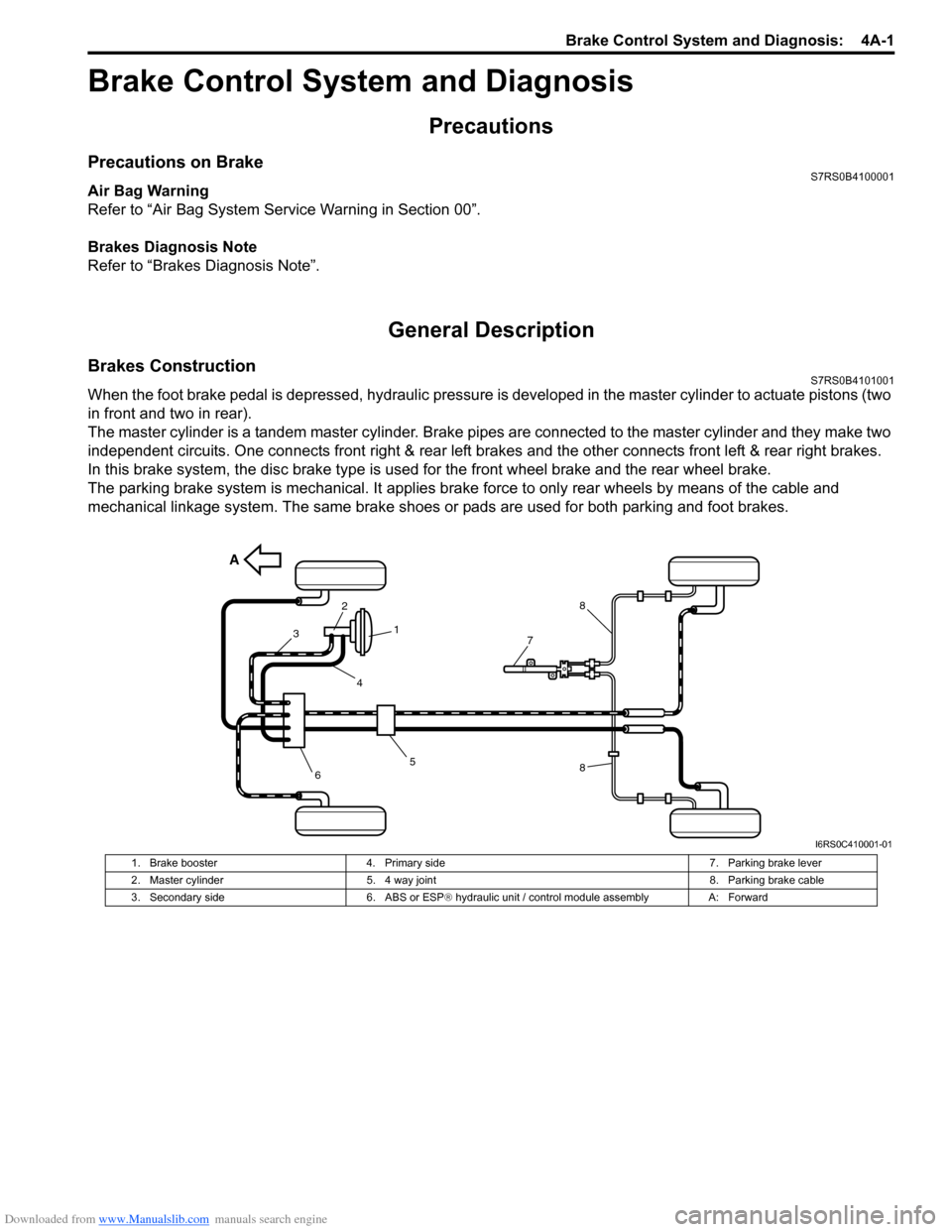
Brakes ConstructionS7RS0B4101001
When the foot brake pedal is depressed, hydraulic pressure is developed in the master cylinder to actuate pistons (two
in front and two in rear).
The master cylinder is a tandem master cylinder. Brake pipes are connected to the master cylinder and they make two
independent circuits. One connects front right & rear left brakes and the other connects front left & rear right brakes.
In this brake system, the disc brake type is used for the front wheel brake and the rear wheel brake.
The parking brake system is mechanical. It applies brake force to only rear wheels by means of the cable and
mechanical linkage system. The same brake shoes or pads are used for both parking and foot brakes.
A
5
3
2
1
4
8
8
6
7
I6RS0C410001-01
1. Brake booster 4. Primary side 7. Parking brake lever
2. Master cylinder 5. 4 way joint 8. Parking brake cable
3. Secondary side 6. ABS or ESP® hydraulic unit / control module assembly A: Forward
Page 518 of 1496
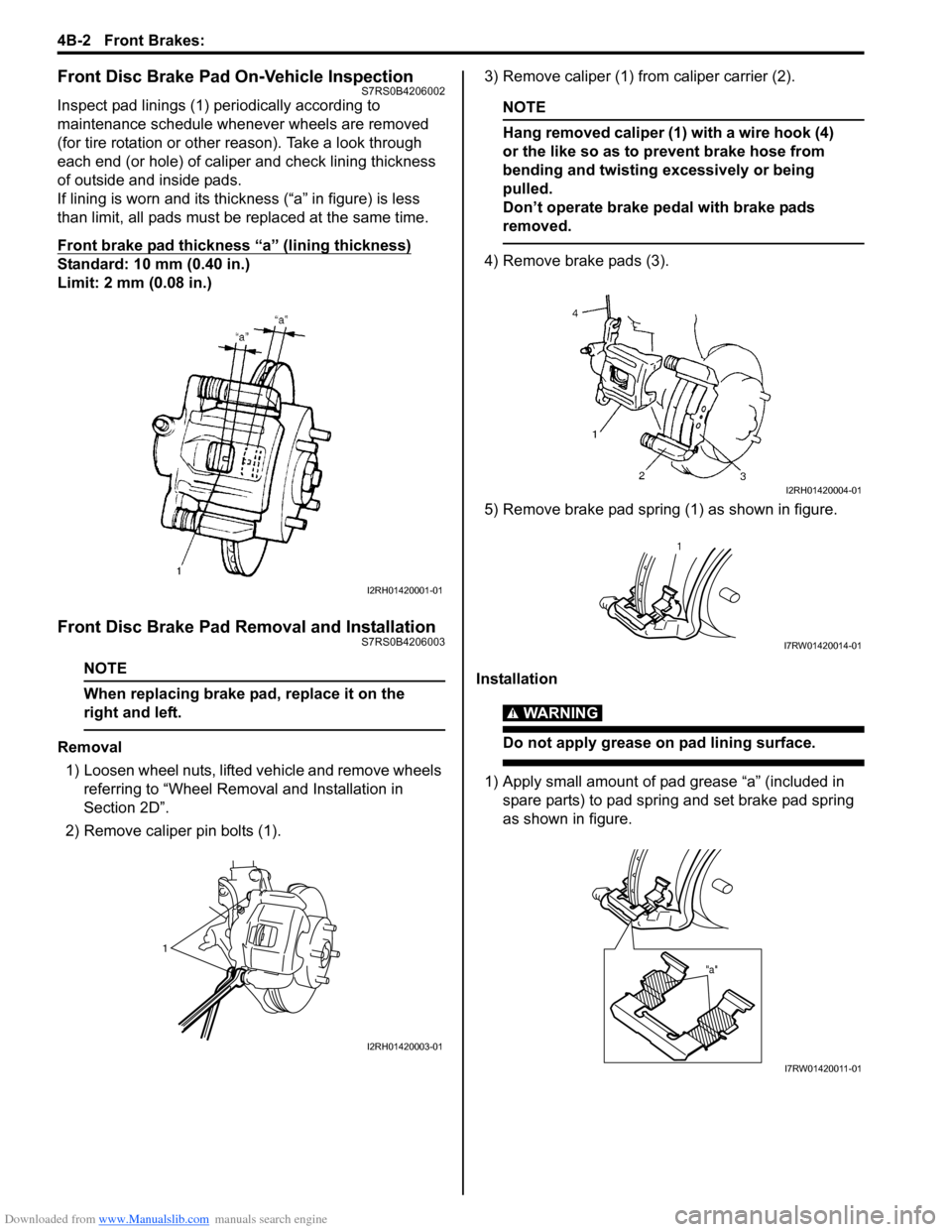
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4B-2 Front Brakes:
Front Disc Brake Pad On-Vehicle InspectionS7RS0B4206002
Inspect pad linings (1) periodically according to
maintenance schedule whenever wheels are removed
(for tire rotation or other reason). Take a look through
each end (or hole) of caliper and check lining thickness
of outside and inside pads.
If lining is worn and its thic kness (“a” in figure) is less
than limit, all pads must be replaced at the same time.
Front brake pad thickness “a” (lining thickness)
Standard: 10 mm (0.40 in.)
Limit: 2 mm (0.08 in.)
Front Disc Brake Pad Removal and InstallationS7RS0B4206003
NOTE
When replacing brake pad, replace it on the
right and left.
Removal
1) Loosen wheel nuts, lifted vehicle and remove wheels referring to “Wheel Remova l and Installation in
Section 2D”.
2) Remove caliper pin bolts (1). 3) Remove caliper (1) from caliper carrier (2).
NOTE
Hang removed caliper (1) with a wire hook (4)
or the like so as to prevent brake hose from
bending and twisting excessively or being
pulled.
Don’t operate brake pedal with brake pads
removed.
4) Remove brake pads (3).
5) Remove brake pad spring (1) as shown in figure.
Installation
WARNING!
Do not apply grease on pad lining surface.
1) Apply small amount of pad grease “a” (included in spare parts) to pad spring and set brake pad spring
as shown in figure.
I2RH01420001-01
1
I2RH01420003-01
I2RH01420004-01
1
I7RW01420014-01
"a"
I7RW01420011-01
Page 537 of 1496
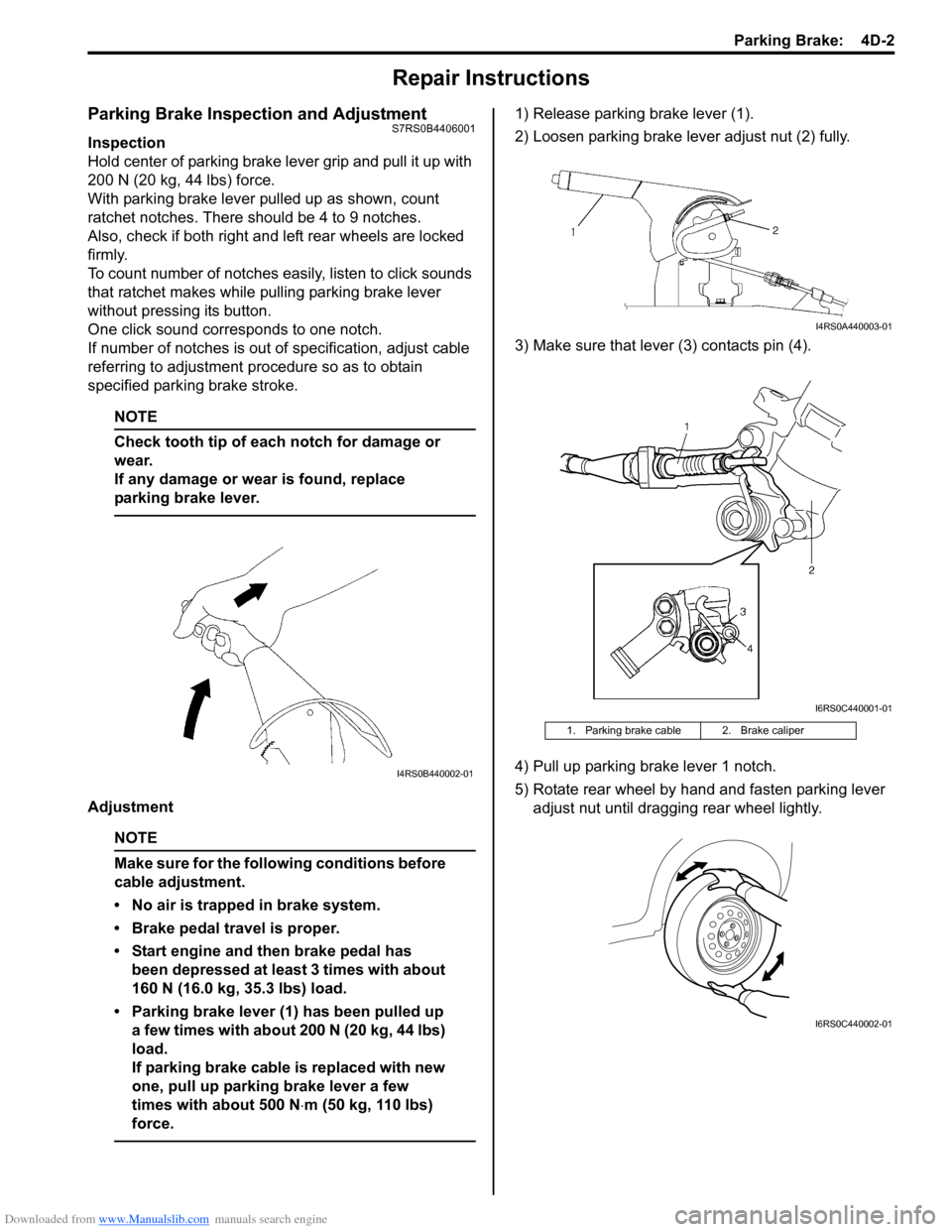
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Parking Brake: 4D-2
Repair Instructions
Parking Brake Inspection and AdjustmentS7RS0B4406001
Inspection
Hold center of parking brake lever grip and pull it up with
200 N (20 kg, 44 lbs) force.
With parking brake lever pulled up as shown, count
ratchet notches. There should be 4 to 9 notches.
Also, check if both right and left rear wheels are locked
firmly.
To count number of notches easily, listen to click sounds
that ratchet makes while pulling parking brake lever
without pressing its button.
One click sound corresponds to one notch.
If number of notches is out of specification, adjust cable
referring to adjustment procedure so as to obtain
specified parking brake stroke.
NOTE
Check tooth tip of each notch for damage or
wear.
If any damage or wear is found, replace
parking brake lever.
Adjustment
NOTE
Make sure for the following conditions before
cable adjustment.
• No air is trapped in brake system.
• Brake pedal travel is proper.
• Start engine and then brake pedal has been depressed at least 3 times with about
160 N (16.0 kg, 35.3 lbs) load.
• Parking brake lever (1) has been pulled up a few times with about 200 N (20 kg, 44 lbs)
load.
If parking brake cable is replaced with new
one, pull up parking brake lever a few
times with about 500 N ⋅m (50 kg, 110 lbs)
force.
1) Release parking brake lever (1).
2) Loosen parking brake lever adjust nut (2) fully.
3) Make sure that lever (3) contacts pin (4).
4) Pull up parking brake lever 1 notch.
5) Rotate rear wheel by hand and fasten parking lever adjust nut until dragging rear wheel lightly.
I4RS0B440002-01
1. Parking brake cable 2. Brake caliper
I4RS0A440003-01
I6RS0C440001-01
I6RS0C440002-01
Page 538 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4D-3 Parking Brake:
6) Release parking brake lever and then make sure that there is no drag in rear wheel.
If there is, repeats go to step 2).
7) Make sure that the number of notch is between 4 and 9 when operating parking brake lever.
8) If the number of notch is not between 4 and 9, replace parking brake cable and/or inspect rear
brake caliper.
Parking brake stroke
When lever is pulled up at 200 N (20kg, 44lbs) : 4
to 9 notches
Parking Brake Cable Removal and InstallationS7RS0B4406002
Removal
NOTE
When it is necessary to remove both right
and left parking brake cables, repeat below
steps 2) and 5) on right and left wheels.
1) Hoist vehicle.
2) Remove wheel.
3) Disconnect parking brake cable from equalizer (parking brake lever) and clamps.
4) Disconnect parking brake cable from lever referring to “Rear Disc Brake Caliper Removal and Installation
in Section 4C”.
5) Remove parking brake cable and parking cable bracket.
Installation
Install it by reversing removal procedure, noting the
following points.
• Install clamps properly referring to “Parking Brake Cable Construction”.
• Tighten bolts and nuts to specified torque referring to “Parking Brake Cable Construction”.
Tightening torque
Parking brake lever bolt: 25 N·m (2.5 kgf-m, 18.0
lb-ft)
Parking cable clamp bolt: 11 N·m (1.1 kgf-m, 8.0
lb-ft)
Parking cable bracket bolt: 25 N·m (2.5 kgf-m,
18.0 lb-ft)
• Adjust parking brake cable. Refer to “Parking Brake Inspection and Adjustment”.
• Check brake disc for dragging and brake system for proper performance. Brake test should be performed.
Parking Brake Lever Removal and InstallationS7RS0B4406003
Removal
1) Remove console box.
2) Block vehicle wheels and release parking brake lever.
3) Disconnect lead wire of parking brake switch at coupler.
4) Loosen parking brake cable adjusting nut (1).
5) Remove parking brake lever bolts (1) and then remove parking brake lever assembly (2) with
equalizer (3).
NOTE
Don’t disassemble parking brake lever
switch. It must be removed and installed as a
complete switch assembly.
I4RS0A440004-01
I4RS0A440005-01