meter connector SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.G Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2008, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 14 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 00-9 Precautions:
• Be careful not to touch the electrical terminals of parts which use microcomputers (e.g. electronic control unit
like as ECM, PCM, P/S controller, etc.). The static
electricity from your body can damage these parts.
• Never connect any tester (voltmeter, ohmmeter, or whatever) to electronic control unit when its coupler is
disconnected. Attempt to do it may cause damage to
it.
• Never connect an ohmmeter to electronic control unit with its coupler connected to it. Attempt to do it may
cause damage to electronic control unit and sensors.
• Be sure to use a specified voltmeter / ohmmeter. Otherwise, accurate measurements may not be
obtained or personal injury ma y result. If not specified,
use a voltmeter with high impedance (M Ω/V
minimum) or a digital type voltmeter.
• When taking measurements at electrical connectors using a tester probe, be sure to insert the probe (2)
from the wire harness side (backside) of the
connector (1). • When connecting meter probe (2) from terminal side
of coupler (1) because it can’t be connected from
harness side, use extra care not to bend male
terminal of coupler of force its female terminal open
for connection.
In case of such coupler as shown connect probe as
shown to avoid opening female terminal.
Never connect probe where male terminal is
supposed to fit.
• When checking connection of terminals, check its
male half for bend and female half for excessive
opening and both for locking (looseness), corrosion,
dust, etc.
• Before measuring voltage at each terminal, check to make sure that battery voltage is 11 V or higher. Such
terminal voltage check at lo w battery voltage will lead
to erroneous diagnosis.
I3RM0A000004-01
I2RH01010046-01
I2RH01010047-01
I2RH01010048-01
Page 16 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 00-11 Precautions:
Precaution for Vehicle Equipped with ESP®
System
S7RS0B0000015
• When testing with any of the following equipments
(when vehicle is tested by rotating wheels (tires)
under vehicle stop), be sure to deactivate ESP ®
system referring to “Precautions in Speedometer Test
or Other Tests in Section 4F” to obtain correct data.
– 2 or 4-wheel chassis dynamometer
– Speedometer tester
– Brake tester
–Etc.
ESP ® control module
• When ESP ® control module is removed / installed, do
not use impact wrenches which generate shock or
impact to avoid damaging sensors in ESP ® control
module.
• When any of the following operation is done, calibrate steering angle sensor referring to “Sensor Calibration
in Section 4F”.
– When battery or dome fuse is removed.
– When steering angle sensor is replaced.
Brake CautionS7RS0B0000014
CAUTION!
All brake fasteners are important attaching
parts in that they could affect the
performance of vital parts and systems, and/
or could result in major repair expense. They
must be replaced with one of same part
number or with an eq uivalent part if
replacement becomes necessary. Do not use
a replacement part of lesser quality or
substitute design. Torque values must be
used as specified during reassembly to
assure proper retention of all parts. There is
to be no welding as it may result in extensive
damage and weakening of the metal.
Repair Instructions
Electrical Circuit Inspection ProcedureS7RS0B0006001
While there are various electrical circuit inspection
methods, described here is a general method to check
its open and short circuit by using an ohmmeter and a
voltmeter.
Open Circuit Check
Possible causes for the open circuit are as follows. As
the cause is in the connector or terminal in many cases,
they need to be checked particularly carefully.
• Loose connection of connector
• Poor contact of terminal (due to dirt, corrosion or rust
on it, poor contact tension, entry of foreign object etc.)
• Wire harness being open
When checking system circuits including an electronic
control unit such as ECM, TCM, ABS control module,
etc., it is important to perfor m careful check, starting with
items which are easier to check.
1) Disconnect negative (–) cable from battery
2) Check each connector at both ends of the circuit being checked for loose connection. Also check lock
condition of connector if equipped with connector
lock. 3) Using a test male terminal
, check both terminals of
the circuit being checked for contact tension of its
female terminal. Check each terminal visually for
poor contact (possibly caused by dirt, corrosion, rust
entry of foreign object, etc.). At the same time, check
to make sure that each te rminal is locked in the
connector fully.
1. Check contact tension by inserting and removing just for once.
I2RH01010049-01
I2RH01010050-01
Page 22 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0A-1 General Information:
General Information
General Information
General Description
AbbreviationsS7RS0B0101001
A:
ABDC: After Bottom Dead Center
ABS: Anti-lock Brake System
AC: Alternating Current
A/C: Air Conditioning
A-ELR: Automatic-Emergency Locking Retractor
A/F: Air Fuel Mixture Ratio
ALR: Automatic Locking Retractor
API: American Petroleum Institute
APP sensor: Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
A/T: Automatic Transmission , Automatic Transaxle
AT D C : After Top Dead Center
ATF: Automatic Transmission Fluid, Automatic
Transaxle Fluid
B:
B+: Battery Positive Voltage
BBDC: Before Bottom Dead Center
BCM: Body Electrical Control Module
BDC: Bottom Dead Center
BTDC: Before Top Dead Center
C:
CAN: Controller Area Network
CKT: Circuit
CKP Sensor: Crankshaft Position Sensor
CMP Sensor: Camshaft Position Sensor
CO: Carbon Monoxide
CPP Switch: Clutch Pedal Position Switch (Clutch
Switch, Clutch Start Switch)
CPU: Central Processing Unit
CRS: Child Restraint System
D:
DC: Direct Current
DLC: Data Link Connector (Assembly Line Diag. Link,
ALDL, Serial Data Link, SDL)
DOHC: Double Over Head Camshaft
DOJ: Double Offset Joint
DRL: Daytime Running Light
DTC: Diagnostic Trouble Code (Diagnostic Code)
E:
EBCM: Electronic Brake Cont rol Module, ABS Control
Module
EBD: Electronic Brake Force Distribution
ECM: Engine Control Module
ECT Sensor: Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (Water Temp. Sensor, WTS)
EFE Heater: Early Fuel Evaporation Heater (Positive
Temperature Coefficient, PTC Heater)
EGR: Exhaust Gas Recirculation
EGRT Sensor: EGR Temperature Sensor (Recirculated
Exhaust Gas Temp. Sensor, REGTS)
ELR: Emergency Locking Retractor
ESP ®: Electronic Stability Program
EPS: Electronic Power Steering
EVAP: Evaporative Emission EVAP Canister:
Evaporative Emission Canister
(Charcoal Canister)
F:
4WD: 4 Wheel
Drive
G:
GEN: Generator
GND: Ground
GPS: Global Positioning System
H:
HVAC: Heating, Ventilating and Air Conditioning
HC: Hydrocarbons
HO2S: Heated Oxygen Sensor
I:
IAC Valve: Idle Air Control Valve (Idle Speed Control
Solenoid Valve, ISC Solenoid Valve)
IAT Sensor: Intake Air Temperature Sensor (Air
temperature Sensor, ATS)
ICM: Immobilizer Control Module
IG: Ignition
ISC Actuator: Idle Speed Control Actuator
L:
LH: Left Hand
LHD: Left Hand Drive Vehicle
LSPV: Load Sensing Proportioning Valve
M:
MAF Sensor: Mass Air Flow Sensor (Air Flow Sensor, AFS, Air Flow Meter, AFM)
MAP Sensor: Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
(Pressure Sensor, PS)
Max: Maximum
MFI: Multiport Fuel Injection (Mu ltipoint Fuel Injection)
Min: Minimum
MIL: Malfunction Indicator Lamp (“SERVICE ENGINE
SOON” Light)
M/T: Manual Transmission, Manual Transaxle
N:
NOx: Nitrogen Oxides
O:
OBD: On-Board Diagnostic System (Self-Diagnosis
Function)
O/D: Overdrive
OHC: Over Head Camshaft
O2S: Oxygen Sensor
P:
PCM: Powertrain Control Module
PCV: Positive Crankcase Ventilation
PNP: Park / Neutral Position
P/S: Power Steering
PSP Switch: Power Steering Pressure Switch (P/S
Pressure Switch)
R:
RH: Right Hand
RHD: Right Hand Drive Vehicle
S:
SAE: Society of Automotive Engineers
Page 52 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-2 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
• Be sure to read “Precautions for Electrical Circuit Service in Section 00” befo re inspection and observe
what is written there.
• ECM replacement: When substituting a known-good ECM, check for the
following conditions. Neglec ting this check may cause
damage to a known-good ECM.
– Resistance value of all relays, actuators is as specified respectively.
– MAP sensor, A/C refrigerant pressure sensor and TP sensor are in good condition and none of power
circuits of these sensors is shorted to ground.
• Communication of ECM, BCM, ABS/ESP ® control
module, combination meter, keyless start control
module, steering angle sensor (ESP ® model) and
TCM (A/T model), is esta blished by CAN (Controller
Area Network). (For more detail of CAN
communication for ECM, refer to “CAN
Communication System Description”). Therefore,
handle CAN communication line with care referring to
“Precaution for CAN Communication System in
Section 00”.
• Immobilizer transponder code registration after
replacing ECM
When ECM is replaced with new one or with another
one, make sure to register immobilizer transponder
code to ECM correctly according to “Procedure after
ECM Replacement in Section 10C”.Precautions of ECM Circuit InspectionS7RS0B1100003
• ECM connectors are waterproofed. Each terminal of the ECM connectors is sealed up with the grommet.
Therefore, when measuring ci rcuit voltage, resistance
and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, do not insert
the tester’s probe into th e sealed terminal at the
harness side. When measuring circuit voltage,
resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector,
connect the special tool to the ECM connectors. And,
insert the tester’s probe into the special tool’s
connectors at the harness side, and then measure
voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal. Or, ECM and
its circuits may be damaged by water.
• Wire colors of the special tool’s connectors are different from the ones of the ECM connectors.
However, the circuit arrangement of the special tool’s
connectors is same as the one of the ECM
connectors. Therefore, measure circuit voltage and
resistance by identifying the terminal location subject
to the measurement.
Precautions of Electric Throttle Body System
Calibration
S7RS0B1100004
After performing one of works described below, it is
necessary to re-register the completely closed throttle
valve reference position stored in memory of ECM. (For
detailed information, refer to “Description of Electric
Throttle Body System Calibration”.) For the procedure to
register such data in ECM, refer to “Electric Throttle
Body System Calibration in Section 1C”.
• To shut off backup power of ECM for such purposes of battery replacement or “DOME” fuse removal
• To erase DTCs P0122, P01 23, P0222, P0223, P2101,
P2102, P2103, P2111, P2112, P2113, P2119, P2123,
P2127, P2128, P2135 and/or P2138
• To replace ECM
• To replace throttle body and/or accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor assembly
General Description
Statement on Cleanliness and CareS7RS0B1101001
An automobile engine is a combination of many
machined, honed, polished and lapped surfaces with
tolerances that are measured in the thousands of an
millimeter (ten thous ands of an inch).
Accordingly, when any internal engine parts are
serviced, care and cleanliness are important.
It should be understood that proper cleaning and
protection of machined surfaces and friction areas is part
of the repair procedure. This is considered standard
shop practice even if not specifically stated.
• A liberal coating of engine oil should be applied to friction areas during assembly to protect and lubricate
the surfaces on initial operation. • Whenever valve train components, pistons, piston
rings, connecting rods, rod bearings, and crankshaft
journal bearings are removed for service, they should
be retained in order.
At the time of installation, they should be installed in
the same locations and with the same mating
surfaces as when removed.
• Battery cables should be disconnected before any major work is performed on the engine.
Failure to disconnect cables may result in damage to
wire harness or other electrical parts.
Page 55 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-5
Freeze frame data clearance:
The freeze frame data is cleared at the same time as
clearance of DTC.
Non-Euro-OBD
ECM diagnosis troubles which may occur in the area
including the following parts w hen the ignition switch is
ON and the engine is running, and indicates the result by
turning on or flashing malfunction indicator lamp (1).
• Heated oxygen sensor
• ECT sensor
•TP sensor
• APP sensor
• MAF sensor
• IAT sensor
• MAP sensor
• CMP sensor
• CKP sensor
• Knock sensor
• Wheel speed sensor (VSS)
• CPU (Central Processing Unit) of ECM
• Oil control valve
• EGR valve
• EVAP canister purge valve
• Ignition coil
• Starter relay
• Radiator fan relay
• CAN communication
• Barometric pressure sensor
• ECM back up power supply
ECM and malfunction indicator lamp (1) operate as
follows.
• Malfunction indicator lamp (1) lights when the ignition switch is turned ON (but t he engine at stop) with the
diagnosis switch terminal ungrounded regardless of
the condition of Engine and Emission control system.
This is only to check the ma lfunction indicator lamp (1)
in the combination meter and its circuit.
• If the above areas of Engine and Emission control system is free from any trouble after the engine start
(while engine is running), malfunction indicator lamp
(1) turns OFF. • When ECM detects a trouble which has occurred in
the above areas, it makes malfunction indicator lamp
(1) turn ON while the engi ne is running to warn the
driver of such occurrence of trouble and at the same
time it stores the trouble area in ECM back-up
memory. (The memory is kept as it is even if the
trouble was only temporary and disappeared
immediately. And it is not erased unless the power to
ECM is shut off for specified time or it is cleared by
SUZUKI scan tool (2).)
For Hong Kong model, DTC can be read by not only
using SUZUKI scan tool but also displayed on
odometer (5) of the combination meter. (i.e. when
diagnosis switch terminal (3) is grounded with a
service wire (4) and ignition switch is turned ON.) For
further detail of the checking procedure, refer to “DTC
Check”.
6. Diagnosis connector
2
1
6 3
5
4
I5RS0C110021-01
Page 57 of 1496
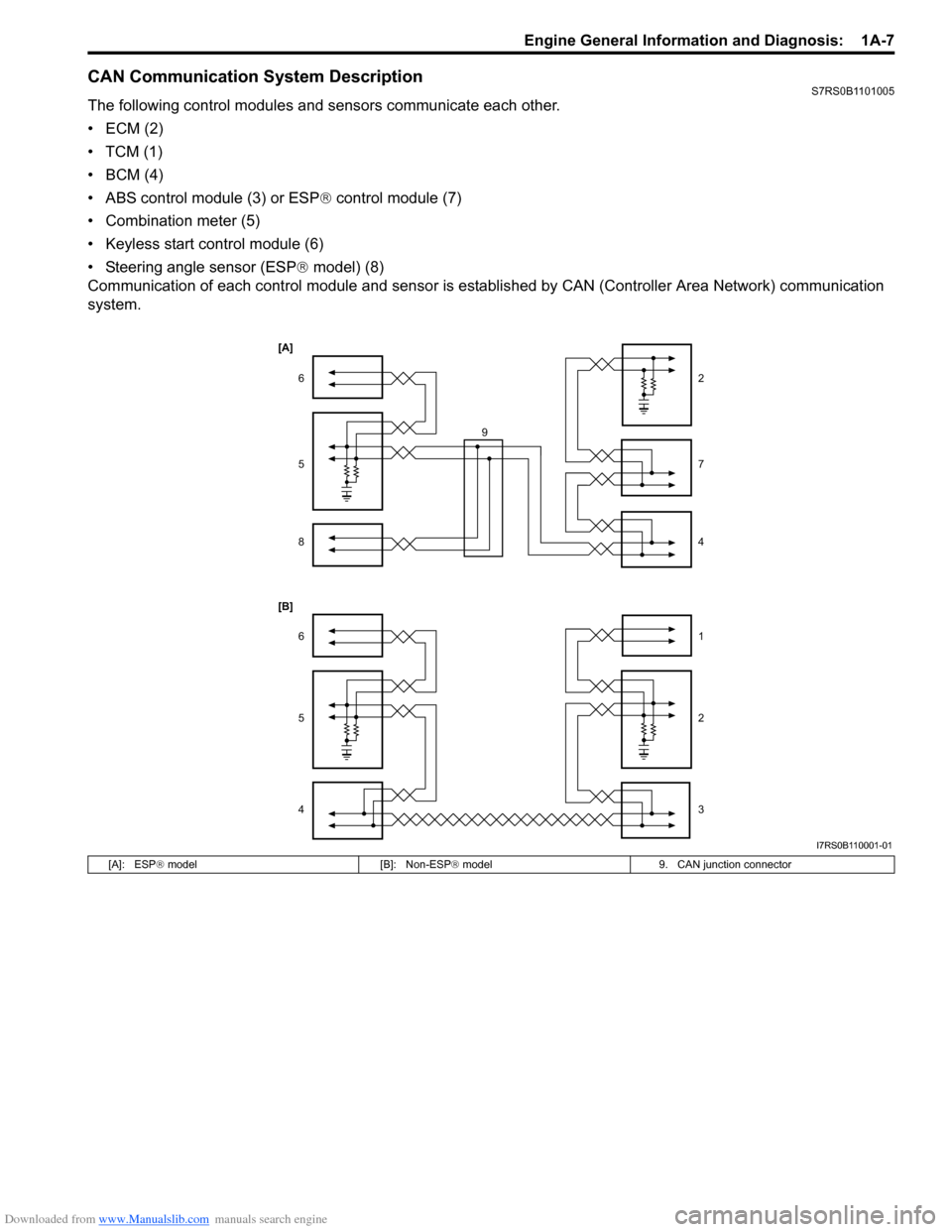
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-7
CAN Communication System DescriptionS7RS0B1101005
The following control modules and sensors communicate each other.
•ECM (2)
•TCM (1)
•BCM (4)
• ABS control module (3) or ESP® control module (7)
• Combination meter (5)
• Keyless start control module (6)
• Steering angle sensor (ESP ® model) (8)
Communication of each control module and sensor is es tablished by CAN (Controller Area Network) communication
system.
1
2
3
6
5
4
2
7
4
6
5
8
9
[A]
[B]
I7RS0B110001-01
[A]: ESP
® model [B]: Non-ESP ® model 9. CAN junction connector
Page 63 of 1496
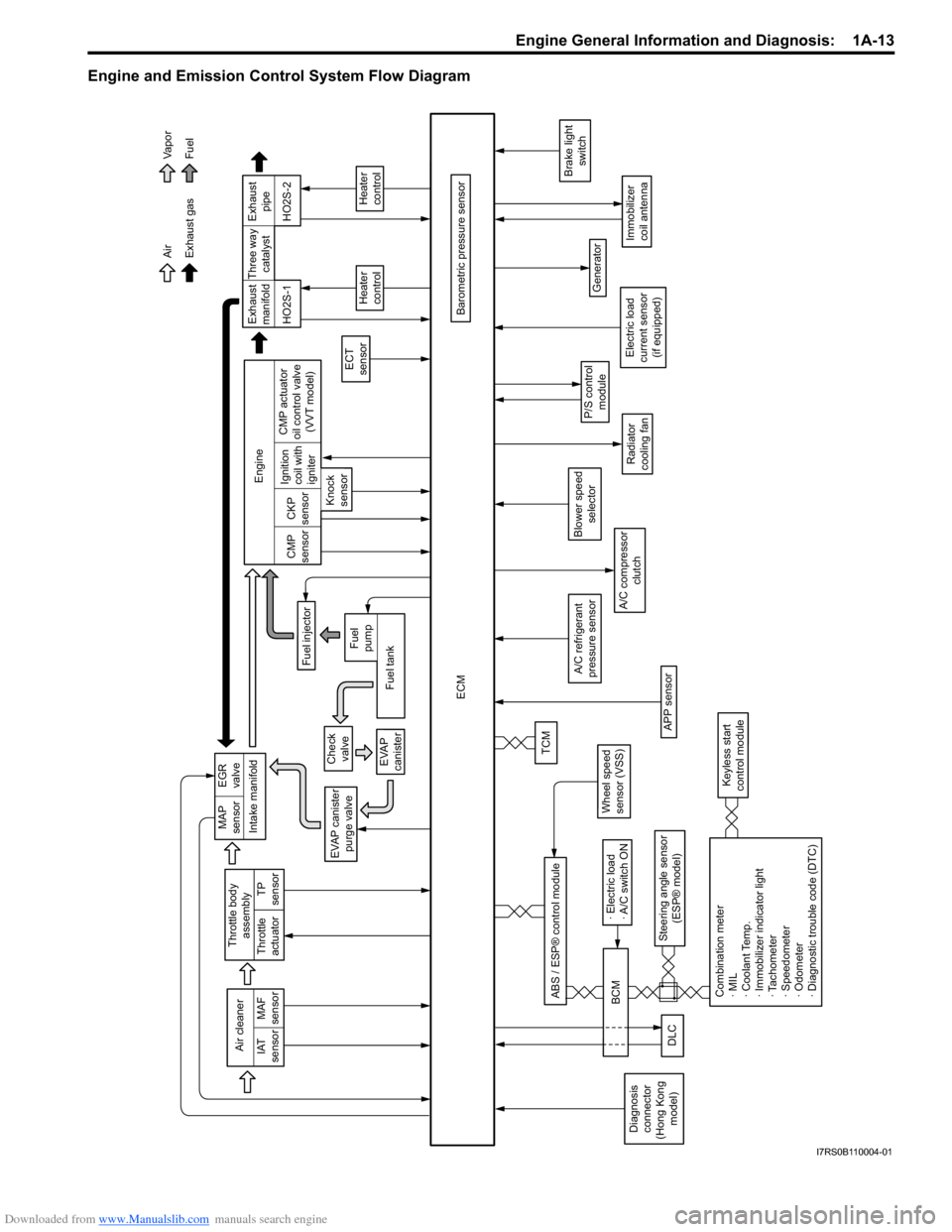
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-13
Engine and Emission Control System Flow Diagram
Intake manifold
Exhaust gas AirFuel
Va p o r
EVAP canister purge valve
ECM
Barometric pressure sensor
A/C compressor clutch
Generator
Immobilizer
coil antenna
P/S controlmodule
Brake light switch
Air cleaner
IAT
sensor MAF
sensor
A/C refrigerant
pressure sensor
TP
sensor
Throttle body
assembly
Throttle
actuator
Wheel speed
sensor (VSS)
Steering angle sensor (ESP® model)
ABS / ESP® control module
Blower speed
selector
MAP
sensor EGR
valve
Check valve
EVAP
canisterTCM
Exhaust
manifold Exhaust
pipe
Fuel injector
ECT
sensor
Heater
control
HO2S-1 HO2S-2
Engine
CMP
sensor CKP
sensor
Knock
sensor Ignition
coil with
igniter
Fuel tank
Fuel
pump CMP actuator
oil control valve (VVT model) Three way
catalyst
Heater
control
Radiator
cooling fan
Combination meter
· MIL
· Coolant Temp.
· Immobilizer indicator light
· Tachometer
· Speedometer
· Odometer
· Diagnostic trouble code (DTC)
Keyless start
control module
DLC
· Electric load
· A/C switch ON
BCM
Diagnosis
connector
(Hong Kong model) Electric load
current sensor (if equipped)
APP sensor
I7RS0B110004-01
Page 67 of 1496
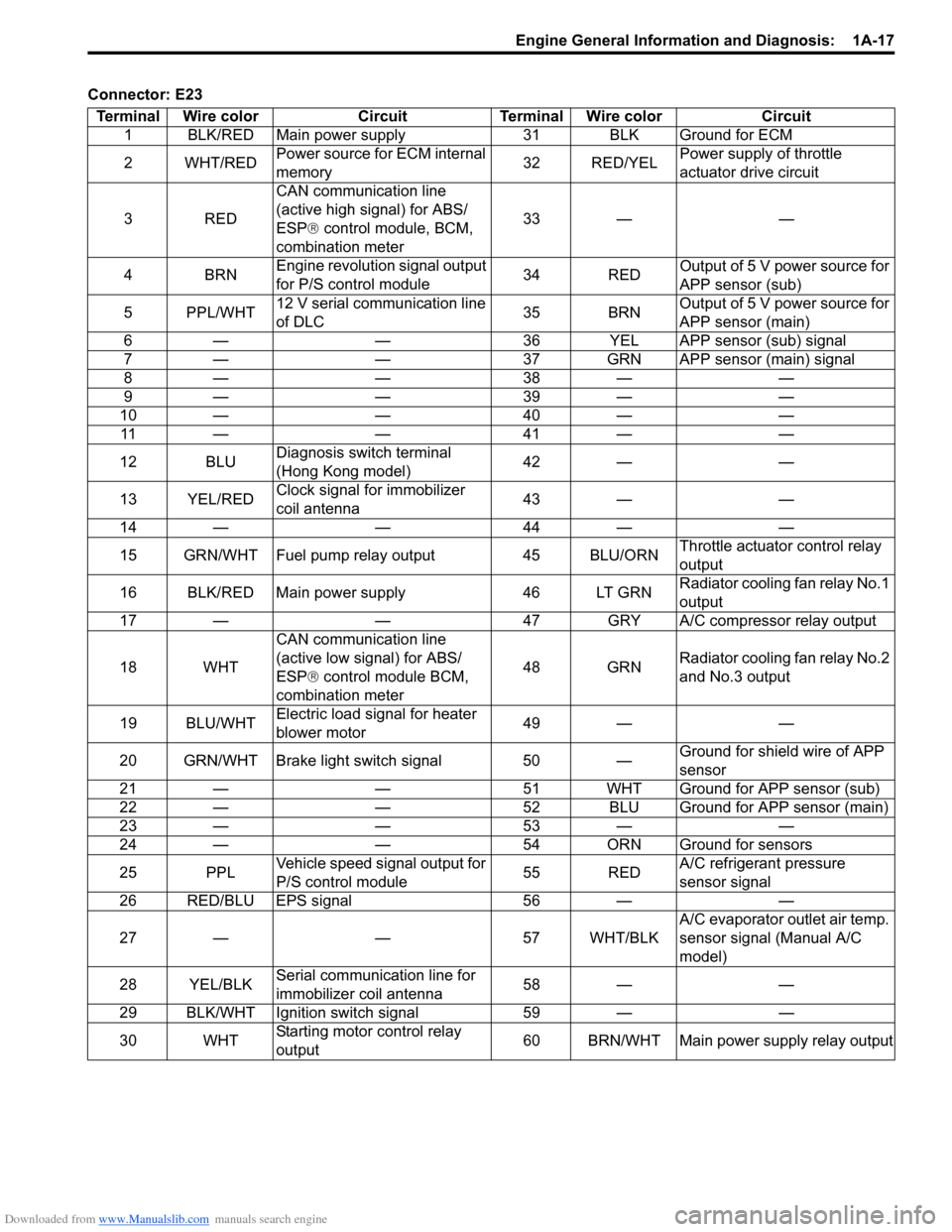
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-17
Connector: E23Terminal Wire color Circuit Terminal Wire color Circuit 1 BLK/RED Main power supply 31 BLK Ground for ECM
2WHT/RED Power source for ECM internal
memory 32 RED/YELPower supply of throttle
actuator drive circuit
3RED CAN communication line
(active high signal) for ABS/
ESP®
control module, BCM,
combination meter 33 — —
4BRN Engine revolution signal output
for P/S control module 34 REDOutput of 5 V power source for
APP sensor (sub)
5 PPL/WHT 12 V serial communication line
of DLC 35 BRNOutput of 5 V power source for
APP sensor (main)
6 — — 36 YEL APP sensor (sub) signal
7 — — 37 GRN APP sensor (main) signal
8— — 38— —
9— — 39— —
10——40—— 11——41——
12 BLU Diagnosis switch terminal
(Hong Kong model) 42 — —
13 YEL/RED Clock signal for immobilizer
coil antenna 43 — —
14——44——
15 GRN/WHT Fuel pump relay output 45 BLU/ORN Throttle actuator control relay
output
16 BLK/RED Main power supply 46 LT GRN Radiator cooling fan relay No.1
output
17 — — 47 GRY A/C compressor relay output
18 WHT CAN communication line
(active low signal) for ABS/
ESP®
control module BCM,
combination meter 48 GRN
Radiator cooling fan relay No.2
and No.3 output
19 BLU/WHT Electric load signal for heater
blower motor 49 — —
20 GRN/WHT Brake light switch signal 50 — Ground for shield wire of APP
sensor
21 — — 51 WHT Ground for APP sensor (sub)
22 — — 52 BLU Ground for APP sensor (main)
23——53——
24 — — 54 ORN Ground for sensors
25 PPL Vehicle speed signal output for
P/S control module 55 REDA/C refrigerant pressure
sensor signal
26 RED/BLU EPS signal 56 — —
27 — — 57 WHT/BLK A/C evaporator outlet air temp.
sensor signal (Manual A/C
model)
28 YEL/BLK Serial communication line for
immobilizer coil antenna 58 — —
29 BLK/WHT Ignition switch signal 59 — —
30 WHT Starting motor control relay
output 60 BRN/WHT Main power supply relay output
Page 71 of 1496
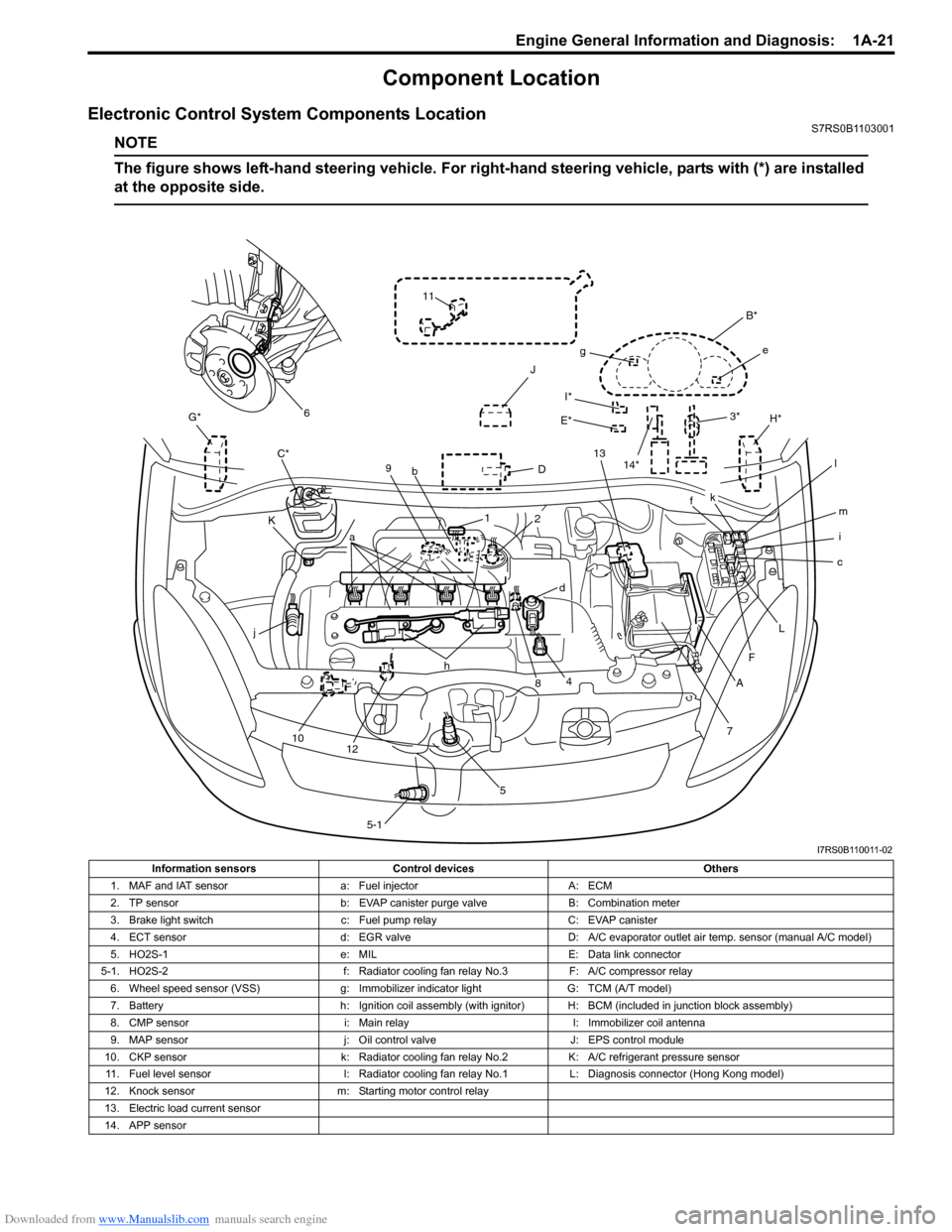
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-21
Component Location
Electronic Control System Components LocationS7RS0B1103001
NOTE
The figure shows left-hand steering vehicle. For right-hand steering vehicle, parts with (*) are installed
at the opposite side.
I*
E*
G*
D
K H*
J
C*
7
A
F
c
L
i m
f
B*
e
g
k
l
13
3*
4
j
10 12 h
58
a
9
b
1
5-1
d
2
11
6
14*
I7RS0B110011-02
Information sensors Control devices Others
1. MAF and IAT sensor a: Fuel injectorA: ECM
2. TP sensor b: EVAP canister purge valve B: Combination meter
3. Brake light switch c: Fuel pump relayC: EVAP canister
4. ECT sensor d: EGR valveD: A/C evaporator outlet air temp. sensor (manual A/C model)
5. HO2S-1 e: MILE: Data link connector
5-1. HO2S-2 f: Radiator cooling fan relay No.3F: A/C compressor relay
6. Wheel speed sensor (VSS) g: Immobilizer indicator lightG: TCM (A/T model)
7. Battery h: Ignition coil assembly (with ignitor) H: BCM (included in junction block assembly)
8. CMP sensor i: Main relayI: Immobilizer coil antenna
9. MAP sensor j: Oil control valveJ: EPS control module
10. CKP sensor k: Radiator cooling fan relay No.2K: A/C refrigerant pressure sensor
11. Fuel level sensor l: Radiator cooling fan relay No.1L: Diagnosis connector (Hong Kong model)
12. Knock sensor m: Starting motor control relay
13. Electric load current sensor
14. APP sensor
Page 76 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-26 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
DTC CheckS7RS0B1104003
NOTE
• There are two types of OBD system depending on the vehicle specification.
For details, refer to “Precaution on On-
Board Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
• The MIL is turned on when the ECM and/or TCM detect malfunction(s). Each ECM and
TCM stores diagnostic information as the
diagnostic trouble code (DTC) in its
memory and outputs th e DTC to the scan
tool.
Therefore, check both of the ECM and TCM
for any DTC with the SUZUKI scan tool
because the DTC stored in ECM and TCM
is not read and displayed at a time.
However, each of the ECM and TCM needs
not to be checked with the generic scan
tool because the DTC stored in ECM and
TCM is read and displayed at a time.
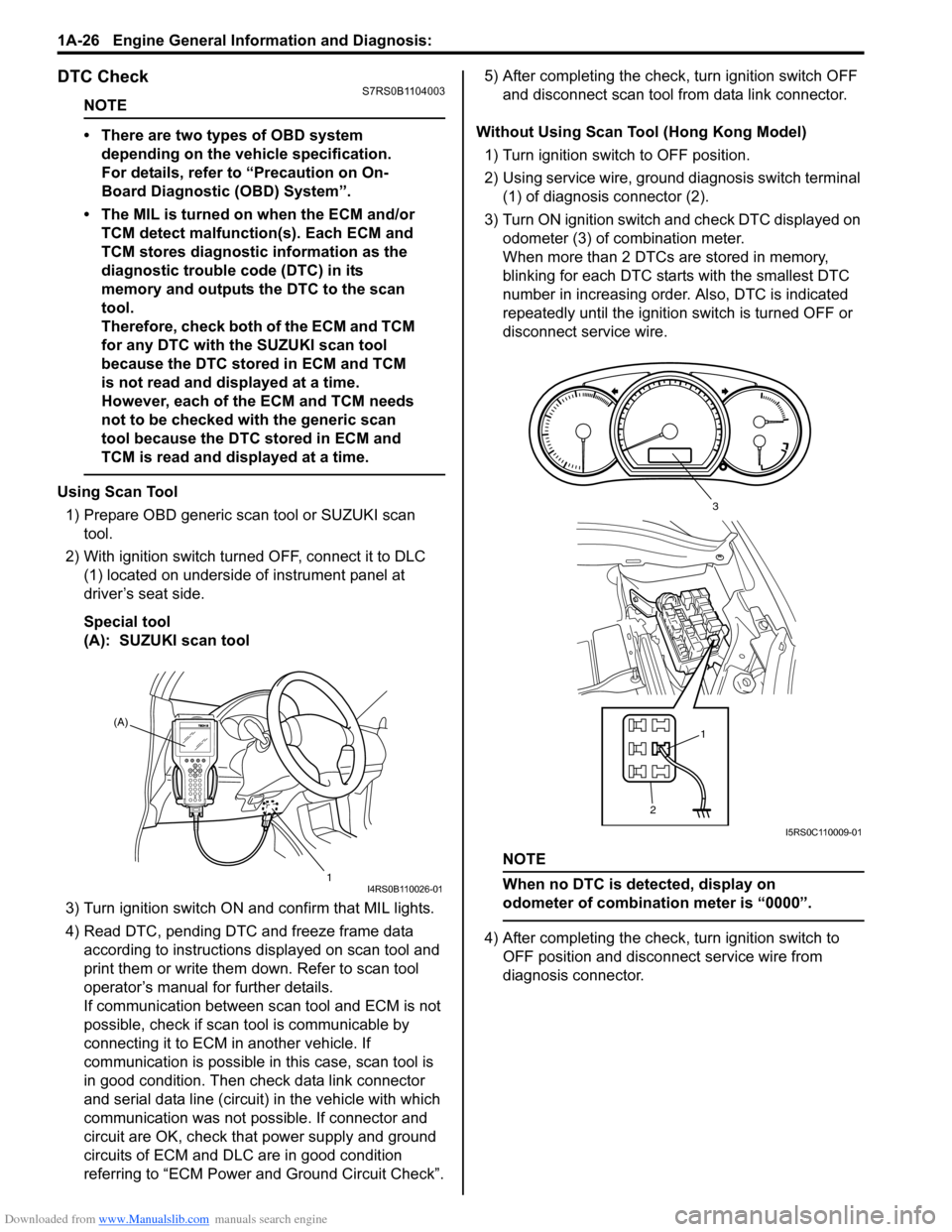
Using Scan Tool
1) Prepare OBD generic scan tool or SUZUKI scan tool.
2) With ignition switch turned OFF, connect it to DLC (1) located on underside of instrument panel at
driver’s seat side.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
3) Turn ignition switch ON and confirm that MIL lights.
4) Read DTC, pending DTC and freeze frame data according to instructions displayed on scan tool and
print them or write them down. Refer to scan tool
operator’s manual for further details.
If communication between scan tool and ECM is not
possible, check if scan tool is communicable by
connecting it to ECM in another vehicle. If
communication is possible in this case, scan tool is
in good condition. Then check data link connector
and serial data line (circuit) in the vehicle with which
communication was not possible. If connector and
circuit are OK, check that power supply and ground
circuits of ECM and DLC are in good condition
referring to “ECM Power and Ground Circuit Check”. 5) After completing the check,
turn ignition switch OFF
and disconnect scan tool from data link connector.
Without Using Scan Tool (Hong Kong Model) 1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Using service wire, ground diagnosis switch terminal (1) of diagnosis connector (2).
3) Turn ON ignition switch and check DTC displayed on
odometer (3) of combination meter.
When more than 2 DTCs are stored in memory,
blinking for each DTC star ts with the smallest DTC
number in increasing order. Also, DTC is indicated
repeatedly until the ignition switch is turned OFF or
disconnect service wire.
NOTE
When no DTC is detected, display on
odometer of combinatio n meter is “0000”.
4) After completing the check, turn ignition switch to
OFF position and disconnect service wire from
diagnosis connector.
(A)
1
I4RS0B110026-01
21
3
I5RS0C110009-01