heat SUZUKI SX4 2006 1.G Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2006, Model line: SX4, Model: SUZUKI SX4 2006 1.GPages: 1556, PDF Size: 37.31 MB
Page 392 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1G-15 Fuel System:
Fuel Tank Purging ProcedureS6RW0D1706013
WARNING!
• Before starting the following procedure, be
sure to observe “Precautions on Fuel
System Service” in order to reduce the risk
of fire and personal injury.
• This purging procedure will not remove all
fuel vapor.
Do not attempt any repair on tank using
heat of flame as an explosion resulting in
personal injury could occur.
CAUTION!
Never remain water in fuel tank after washing,
or fuel tank inside will get corrosion.
The following procedure are used for purging fuel tank.
1) After removing fuel tank, remove all hoses, pipes
and fuel pump assembly from fuel tank.
2) Drain all remaining fuel from tank.
3) Place fuel tank to flushing area.
4) Fill tank with warm water or tap water, and agitate
vigorously and drain. Repeat this washing until
inside of tank is clean. Replace tank if its inside is
rusty.
5) Completely flush out remaining water after washing.
6) Be sure to dry fuel tank assembly thoroughly out of
direct sunlight after washing.
Fuel Pump On-Vehicle InspectionS6RW0D1706014
WARNING!
Before starting the following procedure, be
sure to observe “Precautions on Fuel System
Service” in order to reduce the risk of fire and
personal injury.
NOTE
The fuel pressure regulator is incorporated
with the fuel pump assembly so individual
inspection of it is impossible.
1) Remove filler cap and turn ON ignition switch (2).
Then fuel pump operating sound should be heard
from fuel filler (1) for about 2 seconds and stop. Be
sure to reinstall fuel filler cap after checking.
If the check result is not satisfactory, go to “Fuel
Pump and Its Circuit Check in Section 1A”.2) Turn OFF ignition switch and leave over 10 minutes
as it is.
3) Fuel pressure should be felt at fuel feed hose (1) for
about 2 seconds after ignition switch ON.
If fuel pressure is not felt, go to “Fuel Pressure
Check in Section 1A”.
Fuel Pump Assembly Removal and InstallationS6RW0D1706015
WARNING!
Before starting the following procedure, be
sure to observe “Precautions on Fuel System
Service” in order to reduce the risk of fire and
personal injury.
Removal
1) Remove fuel tank from vehicle referring to “Fuel
Tank Removal and Installation”.
2) Disconnect fuel pipe (1) from fuel pump assembly (2)
referring to “Fuel Hose Disconnecting and
Reconnecting”.
3) Remove fuel pump assembly and earth bracket from
fuel tank.
IVSY01170013-01
1I5RW0A170019-01
1
2
I7RW01170011-01
Page 419 of 1556
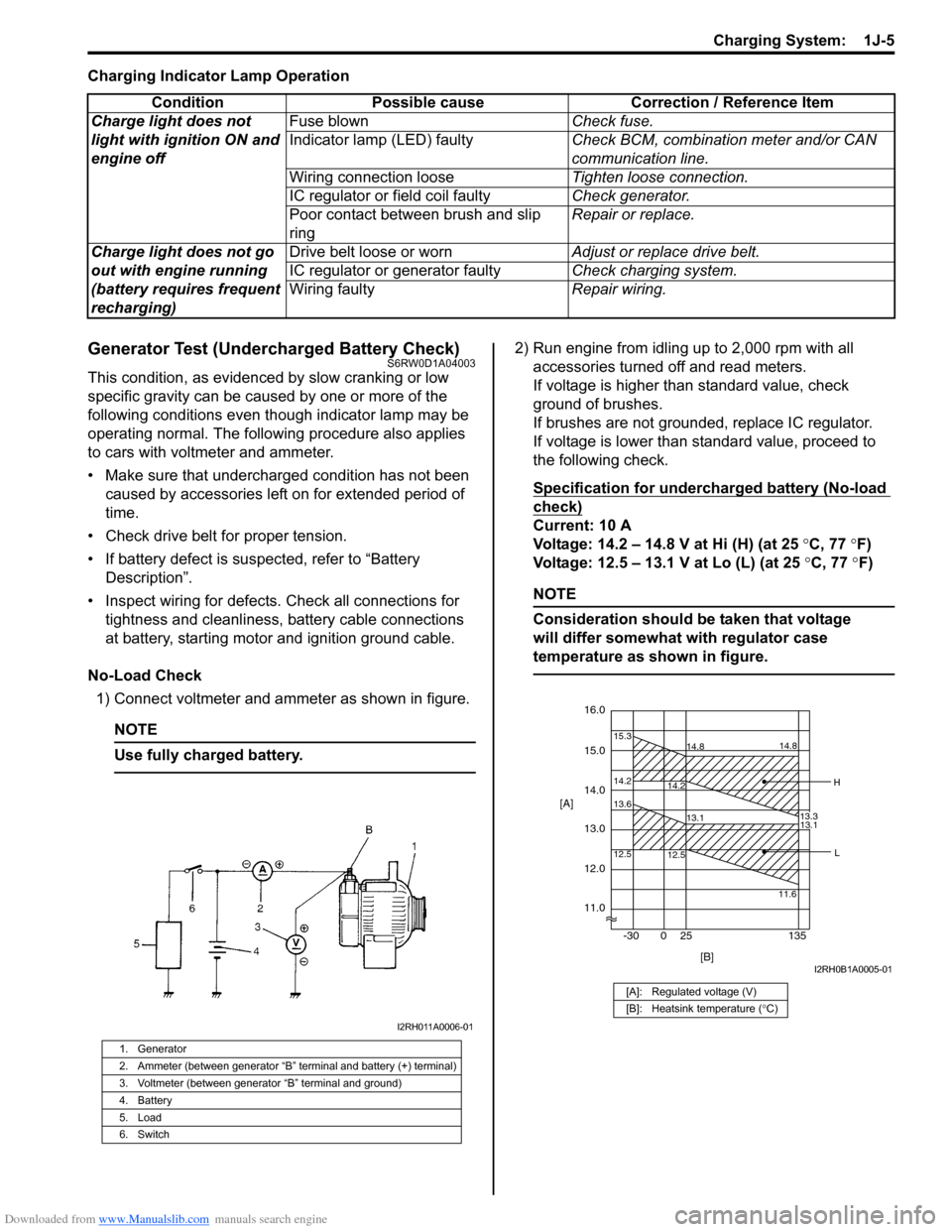
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Charging System: 1J-5
Charging Indicator Lamp Operation
Generator Test (Undercharged Battery Check)S6RW0D1A04003
This condition, as evidenced by slow cranking or low
specific gravity can be caused by one or more of the
following conditions even though indicator lamp may be
operating normal. The following procedure also applies
to cars with voltmeter and ammeter.
• Make sure that undercharged condition has not been
caused by accessories left on for extended period of
time.
• Check drive belt for proper tension.
• If battery defect is suspected, refer to “Battery
Description”.
• Inspect wiring for defects. Check all connections for
tightness and cleanliness, battery cable connections
at battery, starting motor and ignition ground cable.
No-Load Check
1) Connect voltmeter and ammeter as shown in figure.
NOTE
Use fully charged battery.
2) Run engine from idling up to 2,000 rpm with all
accessories turned off and read meters.
If voltage is higher than standard value, check
ground of brushes.
If brushes are not grounded, replace IC regulator.
If voltage is lower than standard value, proceed to
the following check.
Specification for undercharged battery (No-load
check)
Current: 10 A
Voltage: 14.2 – 14.8 V at Hi (H) (at 25 °C, 77 °F)
Voltage: 12.5 – 13.1 V at Lo (L) (at 25 °C, 77 °F)
NOTE
Consideration should be taken that voltage
will differ somewhat with regulator case
temperature as shown in figure.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Charge light does not
light with ignition ON and
engine offFuse blownCheck fuse.
Indicator lamp (LED) faultyCheck BCM, combination meter and/or CAN
communication line.
Wiring connection looseTighten loose connection.
IC regulator or field coil faultyCheck generator.
Poor contact between brush and slip
ringRepair or replace.
Charge light does not go
out with engine running
(battery requires frequent
recharging)Drive belt loose or wornAdjust or replace drive belt.
IC regulator or generator faultyCheck charging system.
Wiring faultyRepair wiring.
1. Generator
2. Ammeter (between generator “B” terminal and battery (+) terminal)
3. Voltmeter (between generator “B” terminal and ground)
4. Battery
5. Load
6. Switch
I2RH011A0006-01
[A]: Regulated voltage (V)
[B]: Heatsink temperature (°C)
16.0
12.0
14.2 15.3
14.8
14.2
13.3 14.8
15.0
11.0 14.0
13.0 [A]
12.5 13.6
13.1
12.5
11.613.1
[B] -30 0 25 135
H
L
I2RH0B1A0005-01
Page 420 of 1556
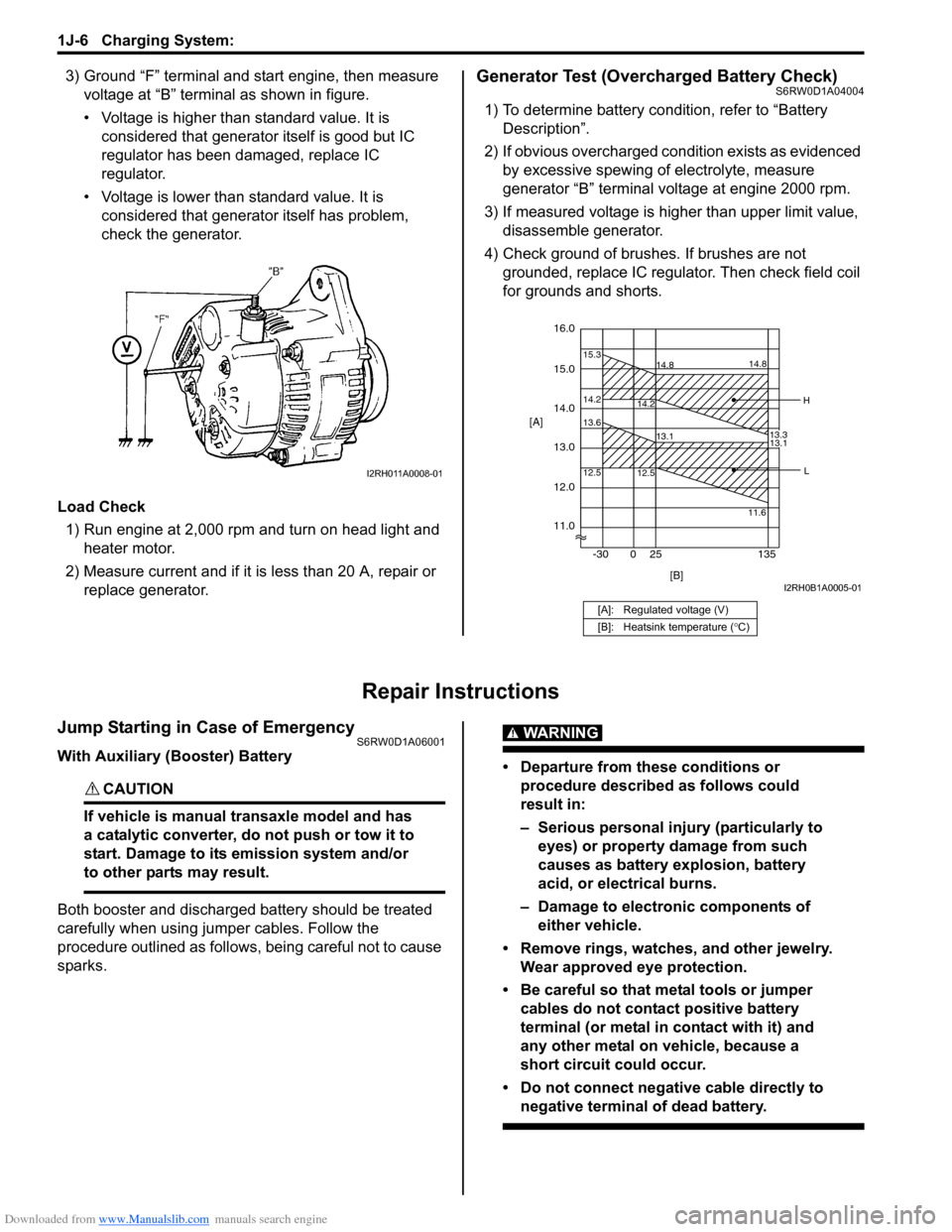
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1J-6 Charging System:
3) Ground “F” terminal and start engine, then measure
voltage at “B” terminal as shown in figure.
• Voltage is higher than standard value. It is
considered that generator itself is good but IC
regulator has been damaged, replace IC
regulator.
• Voltage is lower than standard value. It is
considered that generator itself has problem,
check the generator.
Load Check
1) Run engine at 2,000 rpm and turn on head light and
heater motor.
2) Measure current and if it is less than 20 A, repair or
replace generator.Generator Test (Overcharged Battery Check)S6RW0D1A04004
1) To determine battery condition, refer to “Battery
Description”.
2) If obvious overcharged condition exists as evidenced
by excessive spewing of electrolyte, measure
generator “B” terminal voltage at engine 2000 rpm.
3) If measured voltage is higher than upper limit value,
disassemble generator.
4) Check ground of brushes. If brushes are not
grounded, replace IC regulator. Then check field coil
for grounds and shorts.
Repair Instructions
Jump Starting in Case of EmergencyS6RW0D1A06001
With Auxiliary (Booster) Battery
CAUTION!
If vehicle is manual transaxle model and has
a catalytic converter, do not push or tow it to
start. Damage to its emission system and/or
to other parts may result.
Both booster and discharged battery should be treated
carefully when using jumper cables. Follow the
procedure outlined as follows, being careful not to cause
sparks.
WARNING!
• Departure from these conditions or
procedure described as follows could
result in:
– Serious personal injury (particularly to
eyes) or property damage from such
causes as battery explosion, battery
acid, or electrical burns.
– Damage to electronic components of
either vehicle.
• Remove rings, watches, and other jewelry.
Wear approved eye protection.
• Be careful so that metal tools or jumper
cables do not contact positive battery
terminal (or metal in contact with it) and
any other metal on vehicle, because a
short circuit could occur.
• Do not connect negative cable directly to
negative terminal of dead battery.
I2RH011A0008-01
[A]: Regulated voltage (V)
[B]: Heatsink temperature (°C)
16.0
12.0
14.2 15.3
14.8
14.2
13.3 14.8
15.0
11.0 14.0
13.0 [A]
12.5 13.6
13.1
12.5
11.613.1
[B] -30 0 25 135
H
L
I2RH0B1A0005-01
Page 428 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1K-1 Exhaust System:
Engine
Exhaust System
General Description
Exhaust System DescriptionS6RW0D1B01001
The exhaust system consists of an exhaust manifold, three-way catalytic converter (TWC) in catalyst case, exhaust
pipes, a muffler and seals, gasket and etc.
The three-way catalytic converter is an emission control device added to the exhaust system to lower the levels of
Hydrocarbon (HC), Carbon Monoxide (CO), and Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) pollutants in the exhaust gas.
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Exhaust System CheckS6RW0D1B04001
WARNING!
To avoid the danger of being burned, do not touch the exhaust system when the system is hot. Any
service on the exhaust system should be performed when the system is cool.
At every interval of periodic maintenance service, and when vehicle is raised for other service, check exhaust system
as follows:
• Check rubber mountings for damage, deterioration, and out of position.
• Check exhaust system for leakage, loose connection, dent and damage.
• If bolts or nuts are loosened, tighten them to specified torque referring to “Exhaust System Components”.
• Check nearby body areas damaged, missing, or mispositioned part, open seam, hole connection or any other
defect which could permit exhaust fumes to seep into vehicle.
• Make sure that exhaust system components have enough clearance from underbody to avoid overheating and
possible damage to vehicle underbody.
• Any defect should be fixed at once.
IYSY011B0003-01
Page 429 of 1556
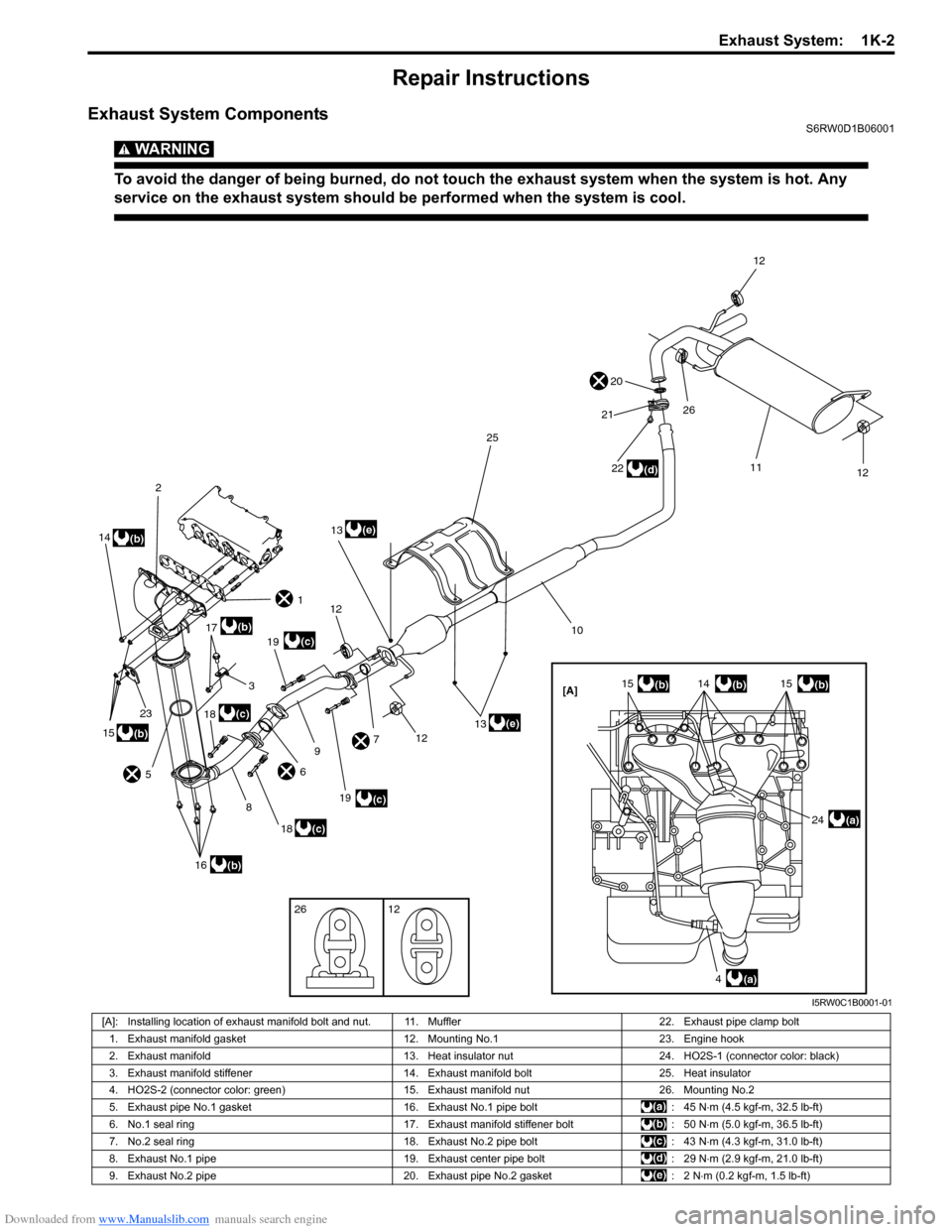
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Exhaust System: 1K-2
Repair Instructions
Exhaust System ComponentsS6RW0D1B06001
WARNING!
To avoid the danger of being burned, do not touch the exhaust system when the system is hot. Any
service on the exhaust system should be performed when the system is cool.
[A]
1
2
3
4
56
7
8
9
10
11
12
12
26
12
12
141515
16
26 12
17
18
18
19
19
20
21
23
22
24
25
(a)(c)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(b)
(a)
(b)(b)
(c)
(c)
(b)
(b)
14(b)
15(b)13
(e)
13
I5RW0C1B0001-01
[A]: Installing location of exhaust manifold bolt and nut. 11. Muffler 22. Exhaust pipe clamp bolt
1. Exhaust manifold gasket 12. Mounting No.1 23. Engine hook
2. Exhaust manifold 13. Heat insulator nut 24. HO2S-1 (connector color: black)
3. Exhaust manifold stiffener 14. Exhaust manifold bolt 25. Heat insulator
4. HO2S-2 (connector color: green) 15. Exhaust manifold nut 26. Mounting No.2
5. Exhaust pipe No.1 gasket 16. Exhaust No.1 pipe bolt : 45 N⋅m (4.5 kgf-m, 32.5 lb-ft)
6. No.1 seal ring 17. Exhaust manifold stiffener bolt : 50 N⋅m (5.0 kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft)
7. No.2 seal ring 18. Exhaust No.2 pipe bolt : 43 N⋅m (4.3 kgf-m, 31.0 lb-ft)
8. Exhaust No.1 pipe 19. Exhaust center pipe bolt : 29 N⋅m (2.9 kgf-m, 21.0 lb-ft)
9. Exhaust No.2 pipe 20. Exhaust pipe No.2 gasket : 2 N⋅m (0.2 kgf-m, 1.5 lb-ft)
Page 471 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Wheels and Tires: 2D-2
Replacement Tires
When replacement is necessary, the original equipment
type tire should be used. Refer to the Tire Placard.
Replacement tires should be of the same size, load
range and construction as those originally on the vehicle.
Use of any other size or type tire may affect ride,
handling, speedometer / odometer calibration, vehicle
ground clearance and tire or snow chain clearance to the
body and chassis.
It is recommended that new tires be installed in pairs on
the same axle. If necessary to replace only one tire, it
should be paired with the tire having the most tread, to
equalize braking traction.
WARNING!
Do not mix different types of tires on the
same vehicle such as radial, bias and bias-
belted tires except in emergencies, because
handling may be seriously affected and may
result in loss of control.
The metric term for tire inflation pressure is the kilo
pascal (kPa). Tire pressures is usually printed in both
kPa and kgf/cm
2 on the “Tire Placard”.
Metric tire gauges are available from tool suppliers.
The chart, shown in the table, converts commonly used
inflation pressures from kPa to kgf/cm
2 and psi.
Wheels DescriptionS6RW0D2401002
Wheel Maintenance
Wheel repairs that use welding, heating, or peening are
not approved. All damaged wheels should be replaced.
Replacement Wheels
Wheels must be replaced if they are bent, dented, have
excessive lateral or radial runout, air leak through welds,
have elongated bolt holes, if lug wheel bolts won’t stay
tight, or if they are heavily rusted. Wheels with greater
runout than shown in the following may cause
objectional vibrations.
Replacement wheels must be equivalent to the original
equipment wheels in load capacity, diameter, rim with
offset and mounting configuration. A wheel of improper
size or type may affect wheel and bearing life, brake
cooling, speedometer / odometer calibration, vehicle
ground clearance and tire clearance to body and
chassis.How to Measure Wheel Runout
To measure the wheel runout, it is necessary to use an
accurate dial indicator. The tire may be on or off the
wheel. The wheel should be installed to the wheel
balancer of the like for proper measurement.
Take measurements of both lateral runout “a” and radial
runout “b” at both inside and outside of the rim flange.
With the dial indicator set in place securely, turn the
wheel one full revolution slowly and record every reading
of the indicator.
When the measured runout exceeds the specification
and correction by the balancer adjustment is impossible,
replace the wheel. If the reading is affected by welding,
paint or scratch, it should be ignored.
Lateral runout limit “a”
Aluminum wheel: 0.3 mm (0.012 in.)
Steel wheel: 0.9 mm (0.035 in.)
Radial runout limit “b”
Aluminum wheel: 0.3 mm (0.012 in.)
Steel wheel: 0.7 mm (0.028 in.)
Metric Lug Nuts and Wheel Studs
All models use metric lug nuts and wheel studs.
Metric lug nuts and wheel studs size
M12 x 1.25
If a broken stud is found, see “Front Wheel Hub, Disc,
Bolt and Bearing Check in Section 2B”, “Front Wheel
Hub, Steering Knuckle and Wheel Bearing Removal and
Installation in Section 2B”, “Rear Wheel Hub Assembly
Removal and Installation in Section 2C”. kPa kgf/cm
2psi
Conversion: 1 psi =
6.895 kPa 1 kgf/cm
2 =
98.066 kPa160 1.6 23
180 1.8 26
200 2.0 29
220 2.2 32
240 2.4 35
260 2.6 38
280 2.8 41
300 3.0 44
320 3.2 47
340 3.4 50I4RS0A240001-01
I2RH01240003-01
Page 475 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Wheels and Tires: 2D-6
Wheel (with Tire) Removal and InstallationS6RW0D2406003
Removal
CAUTION!
Never use heat to loosen tight wheel because
the application of heat to wheel causes the
wheel life shorter and the wheel bearing
damage.
1) Loosen wheel nuts by approximately 180° (half a
rotation).
2) Hoist vehicle.
3) Make sure that the vehicle will not fall off by trying to
move vehicle body in both ways.
4) Remove wheel nuts except one.
5) Support the wheel and/or tire not to drop the wheel
and then remove the nut left with the wheel.
Installation
For installation, reverse removal procedure, noting the
following.
• Wheel nuts must be tightened in sequence and to
specified torque to avoid bending wheel or brake disc
or drum as shown in the figure.
NOTE
Before installing wheels, remove any build-
up of corrosion on wheel mounting surface
and brake disc or drum mounting surface by
scraping and wire brushing. Installing wheels
without good metal-to-metal contact at
mounting surfaces can cause wheel bolts to
loosen, which can later allow a wheel to
come off while vehicle is moving.
Tightening order
“1” – “2” – “3” – “4” – “5”
Tightening torque
Wheel nut (a): 85 N·m (8.5 kgf-m, 61.5 lb-ft)
Tire Mounting and DismountingS6RW0D2406004
WARNING!
Do not stand over tire when inflating. Bead
may break when bead snaps over rim’s safety
hump and cause serious personal injury.
Do not exceed specified pressure when
inflating. If specified pressure will not seat
beads, deflate, re-lubricate and reinflate.
Over inflation may cause bead to break and
cause serious personal injury.
Use a tire changing machine to mount or dismount tires.
Follow equipment manufacturer’s instructions. Do not
use hand tools or tire irons alone to change tires as they
may damage tire beads or wheel rim.
Rim bead seats should be cleaned with a wire brush or
coarse steel wool to remove lubricants, old rubber and
light rust. Before mounting or dismounting a tire, bead
area should be well lubricated with approved tire
lubricant.
After mounting, inflate 330 kPa (47.9 psi) pressure so
that beads are completely seated. Then adjust pressure
to specified shown in the tire placard.
Tire RepairS6RW0D2406005
There are many different materials and techniques on
the market to repair tires. As not all of these work on all
types of tires, tire manufacturers have published detailed
instructions on how and when to repair tires. These
instructions can be obtained from each tire
manufacturer.
IYSQ01240008-01
Page 506 of 1556
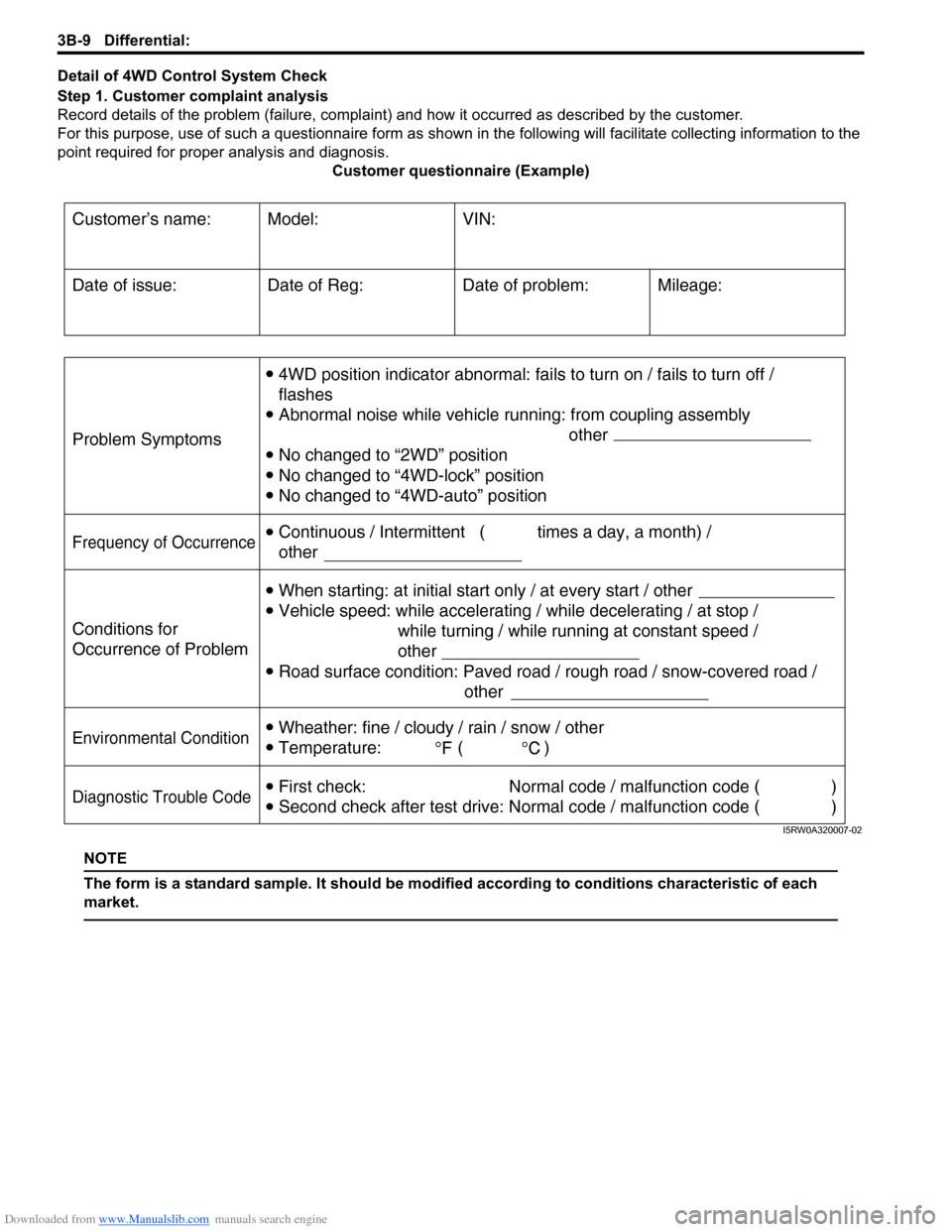
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3B-9 Differential:
Detail of 4WD Control System Check
Step 1. Customer complaint analysis
Record details of the problem (failure, complaint) and how it occurred as described by the customer.
For this purpose, use of such a questionnaire form as shown in the following will facilitate collecting information to the
point required for proper analysis and diagnosis.
Customer questionnaire (Example)
NOTE
The form is a standard sample. It should be modified according to conditions characteristic of each
market.
Customer’s name: Model: VIN:
Problem Symptoms
Frequency of Occurrence
Conditions for
Occurrence of Problem
Environmental Condition
Diagnostic Trouble Code
Date of Reg:
4WD position indicator abnormal: fails to turn on / fails to turn off /
flashes
Abnormal noise while vehicle running: from coupling assembly
other
No changed to “2WD” position
No changed to “4WD-lock” position
No changed to “4WD-auto” position
When starting: at initial start only / at every start / other
Vehicle speed: while accelerating / while decelerating / at stop /
while turning / while running at constant speed /
other
Road surface condition: Paved road / rough road / snow-covered road /
other
Wheather: fine / cloudy / rain / snow / other
Temperature: ( )
First check: Normal code / malfunction code ( )
Second check after test drive: Normal code / malfunction code ( ) Continuous / Intermittent ( times a day, a month) /
otherDate of problem: Mileage: Date of issue:
I5RW0A320007-02
Page 529 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Differential: 3B-32
Coupling Air Temperature Sensor InspectionS6RW0D3206007
CAUTION!
Do not heat up coupling air temperature
sensor more than 100 °C (212 °F). Otherwise,
coupling air temperature sensor will be
damaged.
• Blow hot air to temperature sensing part (2) of
coupling air temperature sensor (3) using hot air drier
(4) and measure resistance between sensor terminals
while heating air gradually.
If measured resistance does not show such
characteristic as shown, replace air temperature
sensor.
Coupling Assembly InspectionS6RW0D3206008
• Check coupling assembly for oil leakage. If leakage
exists, replace it.
• Measure resistance between “a” terminal and “b”
terminal of coupling connector (1).
If measured resistance is out of specification, check
harness for open or short.
If OK, replace coupling assembly.
Coupling assembly resistance
: 2 – 3 Ω
[A]: Lower limit [D]: Resistance
[B]: Normal [E]: Temperature
[C]: Upper limit 1. Temperature gauge
020
32 68 17680 (6.00)
(0.34) (2.56)
1
4
23
[D]
[C]
[B]
[A]
[E]
I5RW0A320021-01
1
“a” “b”I5RW0A320064-01
Page 566 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3D-1 Propeller Shafts:
Driveline / Axle
Propeller Shafts
Precautions
Propeller Shaft CautionS6RW0D3400001
CAUTION!
• All propeller shaft fasteners are an important attaching part in that it could affect the performance of
vital parts and systems, and/or could result in major repair expense. They must be replaced with one
of the same part number or with an equivalent part if replacement becomes necessary. Do not use a
replacement part of lesser quality or substitute design. Torque values must be used as specified
during reassembly to assure proper retention of this part.
• Never attempt to heat, quench or straighten any propeller shaft part. Replace it with a new part, or
damage to the part may result.
General Description
Propeller Shaft ConstructionS6RW0D3401001
Universal joints and ball joint require no maintenance. They are lubricated for life and can not be lubricated on the
vehicle. If a universal joint becomes noisy or worn, it must be replaced.
The propeller shaft is a balanced unit. Handle it carefully so that balance can be maintained.
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Propeller Shaft Symptom DiagnosisS6RW0D3404001
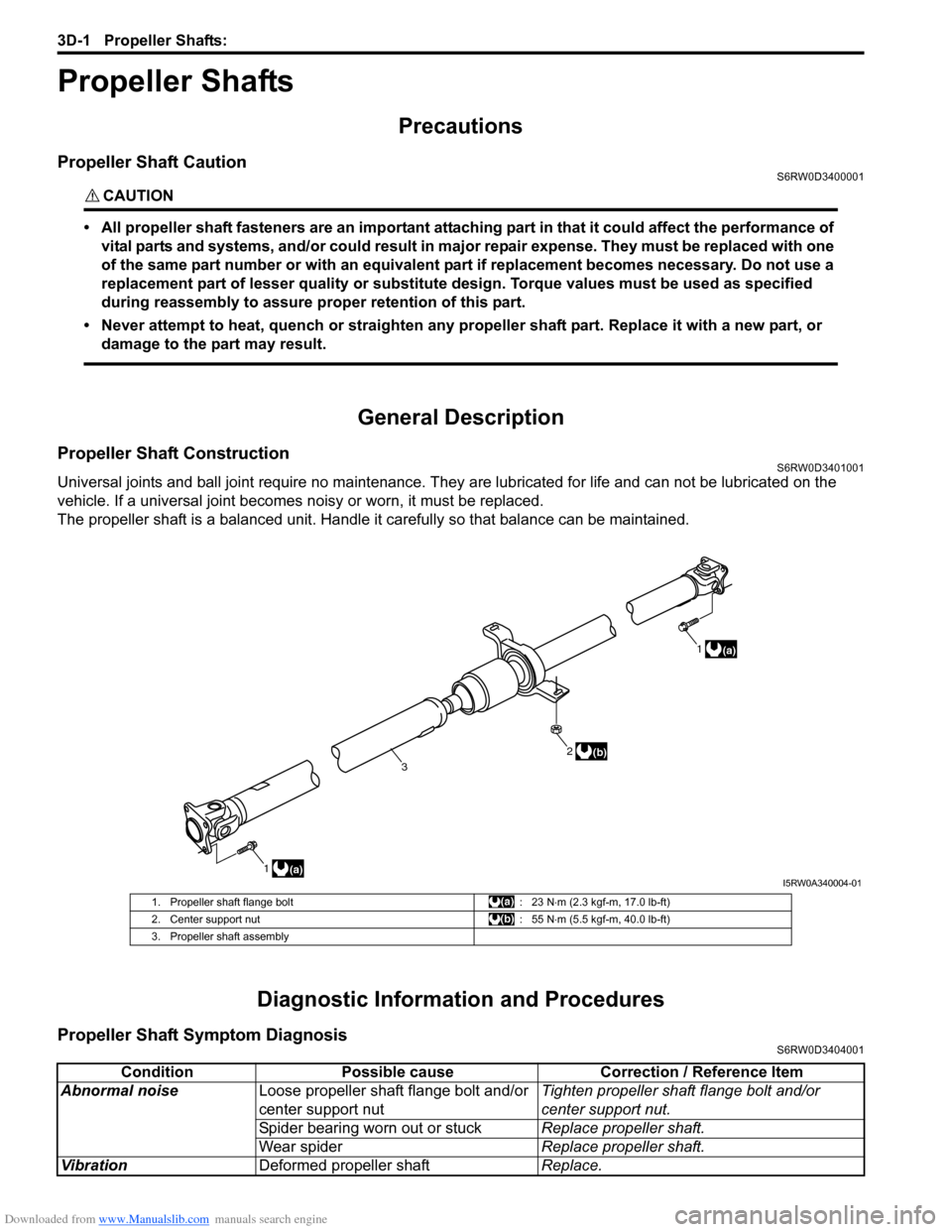
1(a)1
(a)
2
3(b)
I5RW0A340004-01
1. Propeller shaft flange bolt : 23 N⋅m (2.3 kgf-m, 17.0 lb-ft)
2. Center support nut : 55 N⋅m (5.5 kgf-m, 40.0 lb-ft)
3. Propeller shaft assembly
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Abnormal noiseLoose propeller shaft flange bolt and/or
center support nutTighten propeller shaft flange bolt and/or
center support nut.
Spider bearing worn out or stuckReplace propeller shaft.
Wear spiderReplace propeller shaft.
VibrationDeformed propeller shaftReplace.