engine TOYOTA RAV4 2006 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2006, Model line: RAV4, Model: TOYOTA RAV4 2006Pages: 2000, PDF Size: 45.84 MB
Page 1354 of 2000
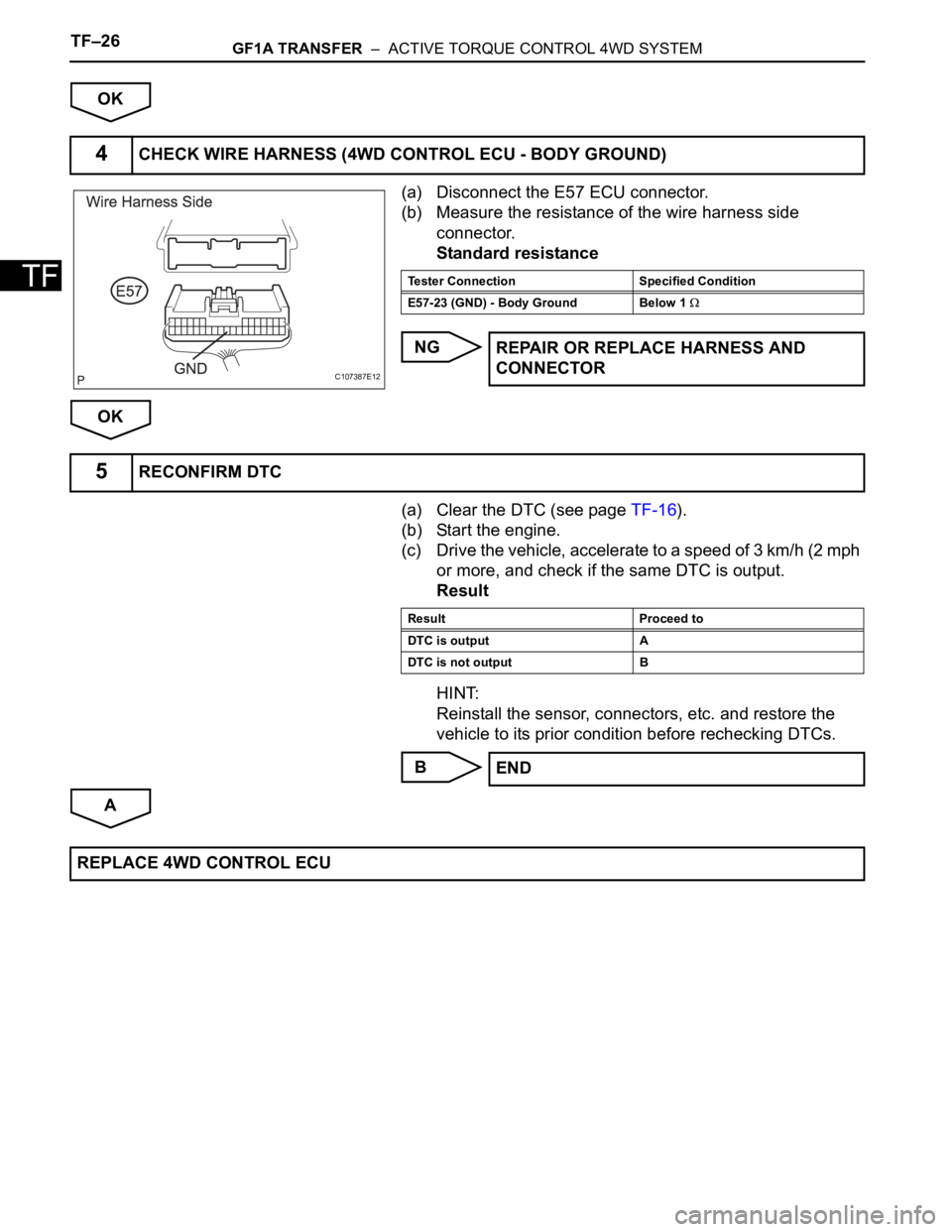
TF–26GF1A TRANSFER – ACTIVE TORQUE CONTROL 4WD SYSTEM
TF
OK
(a) Disconnect the E57 ECU connector.
(b) Measure the resistance of the wire harness side
connector.
Standard resistance
NG
OK
(a) Clear the DTC (see page TF-16).
(b) Start the engine.
(c) Drive the vehicle, accelerate to a speed of 3 km/h (2 mph
or more, and check if the same DTC is output.
Result
HINT:
Reinstall the sensor, connectors, etc. and restore the
vehicle to its prior condition before rechecking DTCs.
B
A
4CHECK WIRE HARNESS (4WD CONTROL ECU - BODY GROUND)
C107387E12
Tester Connection Specified Condition
E57-23 (GND) - Body Ground Below 1
REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS AND
CONNECTOR
5RECONFIRM DTC
Result Proceed to
DTC is output A
DTC is not output B
END
REPLACE 4WD CONTROL ECU
Page 1355 of 2000
GF1A TRANSFER – ACTIVE TORQUE CONTROL 4WD SYSTEMTF–27
TF
DESCRIPTION
If a malfunction in the engine control ECU circuit occurs, the 4WD control ECU will output this DTC.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Check the condition of each related circuit connector before troubleshooting (see page IN-37).
(a) Clear the DTC (see page TF-16).
(b) Turn the ignition switch OFF.
(c) Turn the ignition switch ON and check that can
communication system DTC is not output.
Result
B
A
DTC C1280/82 Engine Circuit Malfunction
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
C1280/82 When the following continues for 5 seconds
or more:
- Communication with engine control ECU is
operating normally, but throttle position
sensor is malfunctioning.• Throttle position sensor
• Throttle position sensor wire harness and
connector
• CAN communication system
1CHECK FOR DTC
Result Proceed to
CAN communication system DTC is
outputA
Engine control DTC is output B
GO TO ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
GO TO CAN COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
Page 1358 of 2000
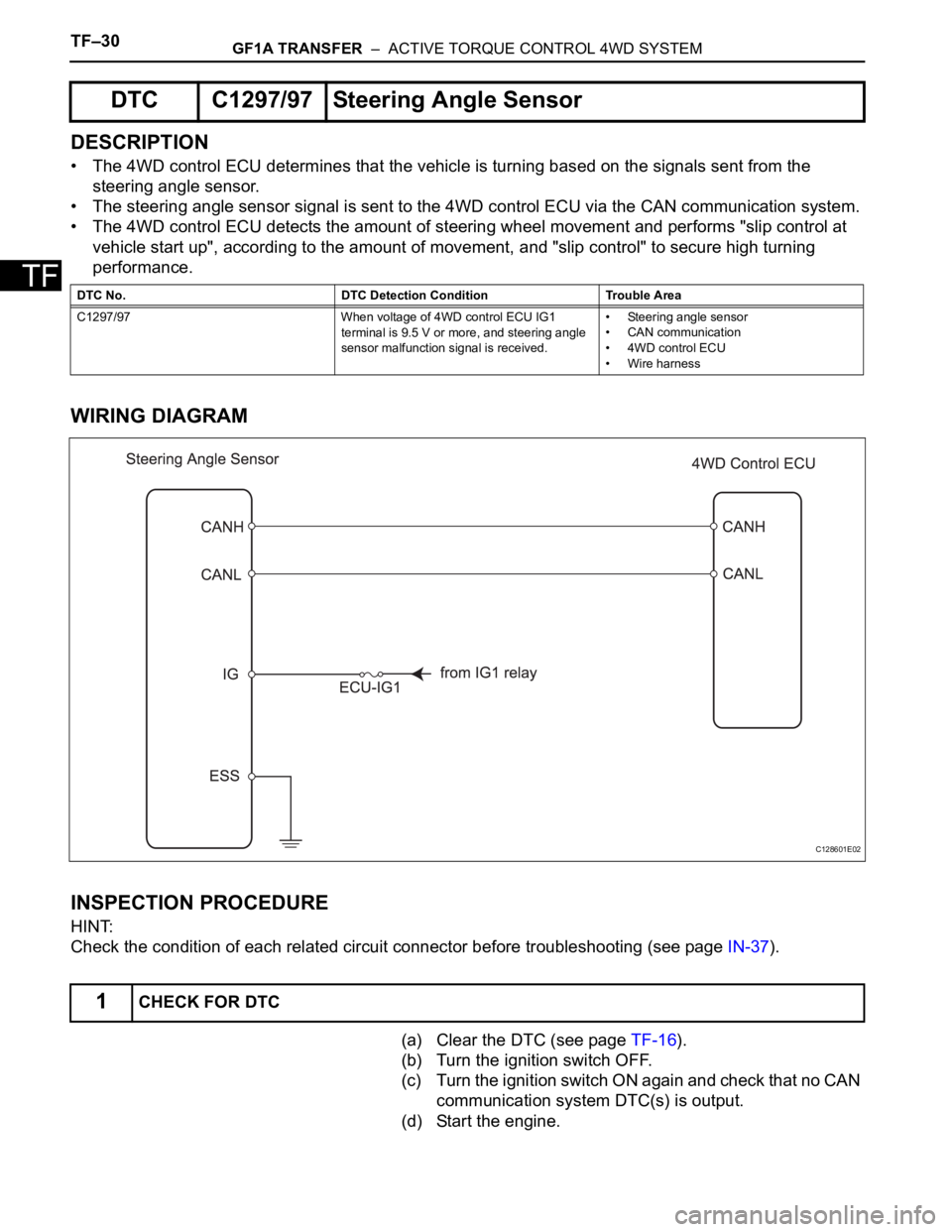
TF–30GF1A TRANSFER – ACTIVE TORQUE CONTROL 4WD SYSTEM
TF
DESCRIPTION
• The 4WD control ECU determines that the vehicle is turning based on the signals sent from the
steering angle sensor.
• The steering angle sensor signal is sent to the 4WD control ECU via the CAN communication system.
• The 4WD control ECU detects the amount of steering wheel movement and performs "slip control at
vehicle start up", according to the amount of movement, and "slip control" to secure high turning
performance.
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Check the condition of each related circuit connector before troubleshooting (see page IN-37).
(a) Clear the DTC (see page TF-16).
(b) Turn the ignition switch OFF.
(c) Turn the ignition switch ON again and check that no CAN
communication system DTC(s) is output.
(d) Start the engine.
DTC C1297/97 Steering Angle Sensor
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
C1297/97 When voltage of 4WD control ECU IG1
terminal is 9.5 V or more, and steering angle
sensor malfunction signal is received.• Steering angle sensor
• CAN communication
• 4WD control ECU
• Wire harness
1CHECK FOR DTC
C128601E02
Page 1467 of 2000
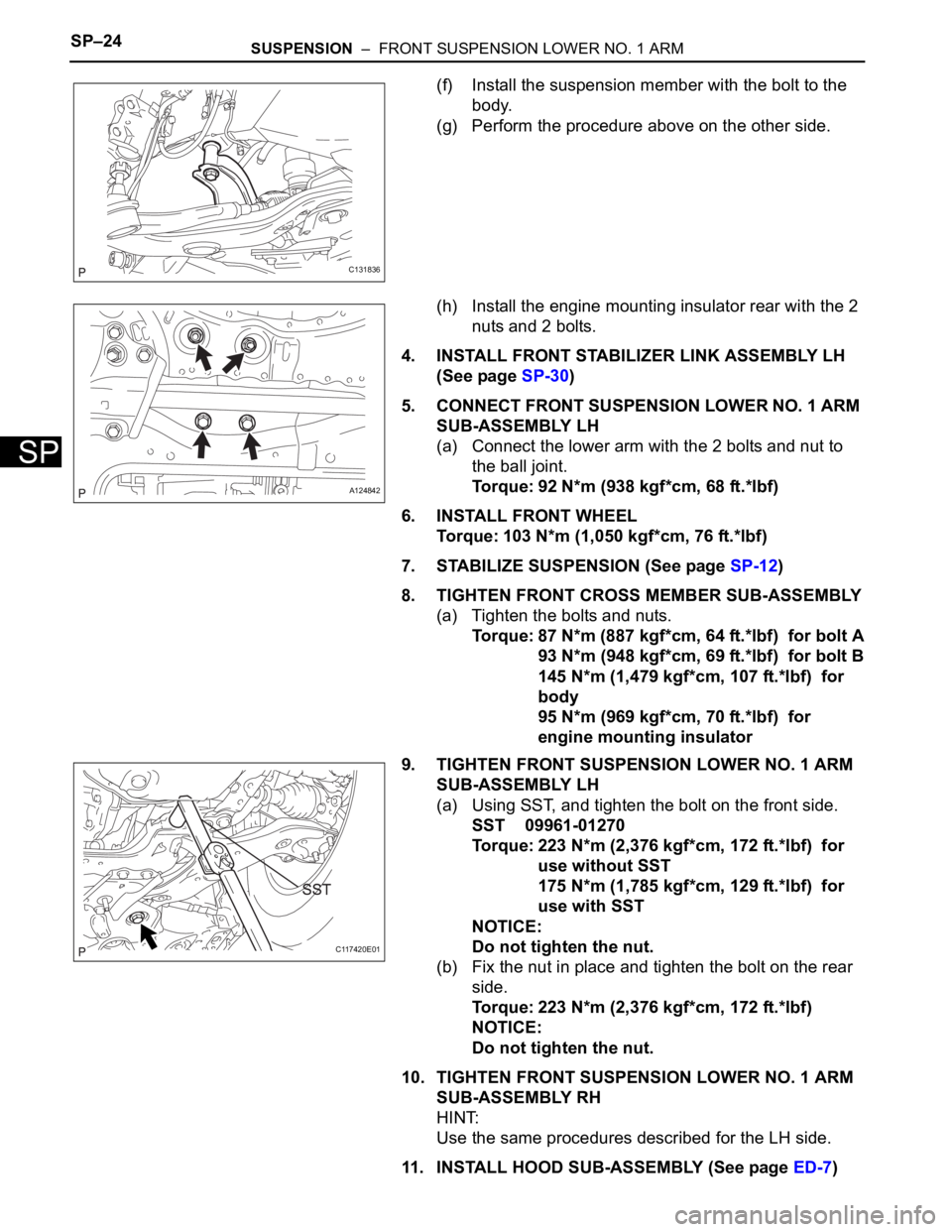
SP–24SUSPENSION – FRONT SUSPENSION LOWER NO. 1 ARM
SP
(f) Install the suspension member with the bolt to the
body.
(g) Perform the procedure above on the other side.
(h) Install the engine mounting insulator rear with the 2
nuts and 2 bolts.
4. INSTALL FRONT STABILIZER LINK ASSEMBLY LH
(See page SP-30)
5. CONNECT FRONT SUSPENSION LOWER NO. 1 ARM
SUB-ASSEMBLY LH
(a) Connect the lower arm with the 2 bolts and nut to
the ball joint.
Torque: 92 N*m (938 kgf*cm, 68 ft.*lbf)
6. INSTALL FRONT WHEEL
Torque: 103 N*m (1,050 kgf*cm, 76 ft.*lbf)
7. STABILIZE SUSPENSION (See page SP-12)
8. TIGHTEN FRONT CROSS MEMBER SUB-ASSEMBLY
(a) Tighten the bolts and nuts.
Torque: 87 N*m (887 kgf*cm, 64 ft.*lbf) for bolt A
93 N*m (948 kgf*cm, 69 ft.*lbf) for bolt B
145 N*m (1,479 kgf*cm, 107 ft.*lbf) for
body
95 N*m (969 kgf*cm, 70 ft.*lbf) for
engine mounting insulator
9. TIGHTEN FRONT SUSPENSION LOWER NO. 1 ARM
SUB-ASSEMBLY LH
(a) Using SST, and tighten the bolt on the front side.
SST 09961-01270
Torque: 223 N*m (2,376 kgf*cm, 172 ft.*lbf) for
use without SST
175 N*m (1,785 kgf*cm, 129 ft.*lbf) for
use with SST
NOTICE:
Do not tighten the nut.
(b) Fix the nut in place and tighten the bolt on the rear
side.
Torque: 223 N*m (2,376 kgf*cm, 172 ft.*lbf)
NOTICE:
Do not tighten the nut.
10. TIGHTEN FRONT SUSPENSION LOWER NO. 1 ARM
SUB-ASSEMBLY RH
HINT:
Use the same procedures described for the LH side.
11. INSTALL HOOD SUB-ASSEMBLY (See page ED-7)
C131836
A124842
C117420E01
Page 1513 of 2000

BC–10BRAKE CONTROL – VEHICLE STABILITY CONTROL SYSTEM
BC
(1) Operation description:
The skid control ECU detects the vehicle's slip
condition by receiving signals from each speed
sensor and the ECM via CAN communication.
The skid control ECU controls engine torque
with the ECM via CAN communication and
brake fluid pressure through the pump and
solenoid valve. The slip indicator light blinks
when the system is operating.
for 4WD: The VSC warning light comes on when
the TRC system malfunctions.
for 2WD: The VSC warning light and SLIP
indicator light comes on when the TRC system
malfunctions.
Page 1515 of 2000

BC–12BRAKE CONTROL – VEHICLE STABILITY CONTROL SYSTEM
BC
(1) Operation description:
The skid control ECU determines the vehicle
condition by receiving signals from the speed
sensor, the yaw rate and deceleration sensor
and the steering sensor. The skid control ECU
controls engine torque with the ECM via CAN
communication and brake fluid pressure through
the pump and solenoid valve. The slip indicator
light blinks and the skid control buzzer sounds
when the system is operating.
for 4WD: The VSC warning light comes on when
the TRC system malfunctions.
for 2WD: The VSC warning light and slip
indicator light come on when the TRC system
malfunctions.
(f) Downhill Assist Control:
When the downhill assist control switch is pressed
with the shift lever on L or R range and the
accelerator and brake pedals not depressed,
downhill assist control is activated. When activated,
4-wheel hydraulic pressure control occurs in order
to maintain a constant low vehicle speed without
causing the wheels to become locked. Thus, the
vehicle can descend a steep hill in a stable manner.
HINT:
• Depressing the accelerator and brake pedal
cancels control of the downhill assist control.
• Downhill assist control begins operating when
driving down on a slope at a speed of 25 km/h
(16 mph) or less with the engine brake applied.
Page 1518 of 2000

BRAKE CONTROL – VEHICLE STABILITY CONTROL SYSTEMBC–15
BC
(1) Operation description:
When the system is in operation, the following
occurs: 1) the slip indicator light blinks; 2) the
VSC light comes on; and 3) when hill-start assist
control operation starts, the skid control buzzer
sounds once; when hill-start assist control
operation ends, the skid control buzzer sounds
twice.
The VSC warning light comes on when the hill-
start assist control is malfunctioning.
(h) AUTO LSD (Auto Limited Slip Differential) for 2WD:
The AUTO LSD achieves the equivalent functions of
an LSD (Limited Slip Differential) through the use of
a traction control system. When the driver presses
the AUTO LSD switch, this system achieves the
LSD effect by regulating the hydraulic pressure that
acts on the drive wheels and controlling the engine
output in accordance with the amount of pedal effort
applied on the accelerator. The AUTO LSD
operates with the AUTO LSD switch on and the
accelerator pedal depressed.
Auto LSD restrains brake pressure and reduces
differential movement, thus transmitting the drive
torque to the other drive wheel to ensure stability
under the following conditions:
• Wheels run off the road.
• Drive wheels spin in place when starting on a
slope with one wheel on snow/ice.
HINT:
Releasing the accelerator pedal cancels control of
the AUTO LSD system.
Page 1520 of 2000

BRAKE CONTROL – VEHICLE STABILITY CONTROL SYSTEMBC–17
BC
(1) Operation description:
The skid control ECU determines that the
vehicle is in a state in which the AUTO LSD can
operate by using various sensors and switches
to detect the operating conditions of the AUTO
LSD switch, shift position, accelerator pedal, and
brake pedal. When the vehicle is in a state in
which the AUTO LSD can operate, the skid
control ECU effects hydraulic pressure control of
the wheel cylinder at the wheel with the faster
wheel speed so that the wheel speeds of the
right and left drive wheels will become equal.
The slip indicator light blinks and the AUTO LSD
indicator light comes on when the system is
operating. Both the VSC warning light and SLIP
indicator light come on when the AUTO LSD
system malfunctions.
2. COOPERATIVE CONTROL FUNCTION
(a) Description
(1) Braking when Surface Resistance Differs
Between Left and Right Wheels
If the driver suddenly applies the brakes on a
road surface with a considerable difference in
friction coefficient between the right and left
wheels, the difference in the brake force
between the right and left wheels will cause the
vehicle posture to become unstable and create a
yaw movement. In this state, the skid control
ECU controls the VSC to stabilize the vehicle
posture. At the same time, it effects cooperative
control with the EPS to provide steering torque
assist, which facilitates the driver's steering
maneuvers to stabilize the vehicle posture.
(2) Accelerating when Surface Resistance Differs
Between Left and Right Wheels
If the driver suddenly starts off or accelerates on
a road surface with a considerable difference in
friction coefficient between the right and left
wheels, the slippage of a drive wheel will cause
the vehicle posture to become unstable and
negatively affect its acceleration performance. In
this state, the skid control ECU causes the TRC
to control the hydraulic brake of the slipping
drive wheel, and requests the engine ECU to
effect engine output control. At the same time, it
effects cooperative control with the EPS to
provide steering torque assist, which facilitates
the driver's steering maneuvers to stabilize the
vehicle posture.
Page 1521 of 2000

BC–18BRAKE CONTROL – VEHICLE STABILITY CONTROL SYSTEM
BC
(3) Front Wheel Skid Tendency
When the skid control ECU determines that
there is a front wheel skid tendency, it controls
the VSC to dampen the front wheel skid. At the
same time, it effects cooperative control with the
EPS to provide steering torque assist, which
facilitates the driver's steering maneuvers to
stabilize the vehicle posture. To prevent
excessive steering maneuvers, it provides a
steering torque assist. This assist increases the
resistance to counter the driver's steering effort,
if the driver turns the steering wheel excessively.
(4) Rear Wheel Skid Tendency
When the skid control ECU determines that
there is a rear wheel skid tendency, it controls
the VSC to dampen the rear wheel skid. At the
same time, it effects cooperative control with the
EPS to provide steering torque assist, which
facilitates the driver's steering maneuvers in the
direction to correct the rear wheel skid.
(5) Acceleration During Cornering
A sudden acceleration of the vehicle during
cornering may cause a drive wheel to freewheel,
which could cause the front wheels or rear
wheels to skid. If the skid control ECU
determines that there is freewheeling of a drive
wheel, a front wheel skid tendency, or a rear
wheel skid tendency, it effects cooperative
control with the 4WD system to optimally control
the drive torque distribution to the front and rear
wheels. Furthermore, it controls the TRC and
the VSC as needed to ensure driving stability
and acceleration performance.
(b) Operation
The operation of the solenoid valves under the
cooperative control is the same as the TRC or VSC
operation.
3. ABS WITH EBD, BA, TRC AND VSC OPERATION
(a) The skid control ECU calculates vehicle stability
tendency based on the signals from the 4 wheel
speed sensors, the yaw rate and deceleration
sensor and the steering sensor. In addition, it
evaluates the results of the calculations to
determine whether any control actions (control of
the engine output torque by electronic throttle
control and of the brake fluid pressure by the ABS
and TRACTION actuator) should be implemented.
(b) The slip indicator blinks and the skid control buzzer
sounds to inform the driver that the VSC system is
operating. The slip indicator also blinks when
traction control is operating, and the operation being
performed is displayed.
Page 1522 of 2000

BRAKE CONTROL – VEHICLE STABILITY CONTROL SYSTEMBC–19
BC
4. FAIL SAFE FUNCTION
(a) When a failure occurs in the ABS with BA, TRC and
VSC systems, the ABS and VSC warning lights
illuminate, the slip indicator light comes on*1 or
remains off*2, and the operations of those systems
are prohibited. In addition to this, when a failure
which disables the EBD operation occurs, the brake
warning light comes on and its operation is
prohibited.
HINT:
*1: for 2WD
*2: for 4WD
(b) If control is prohibited due to a malfunction during
operation, control is disabled gradually to avoid
sudden vehicle instability.
5. INITIAL CHECK
(a) When the vehicle speed first reaches approximately
6 km/h (4 mph) or more after the ignition switch is
turned ON, each solenoid valve and the motor of the
ABS and TRACTION actuator are sequentially
activated to perform electrical checks. During the
initial check, the operating sound of the solenoid
valve and motor can be heard from the engine
compartment, but this does not indicate a
malfunction.
6. SERVICE MODE
(a) VSC operation can be disabled by operating the
intelligent tester.
HINT:
Refer to the intelligent tester operator's manual for
further details.
7. FUNCTION OF COMPONENTS
Components Functions
Speed Sensor
(Semiconductor Type)Detects the wheel speed and sends the signal to skid
control ECU
Skid Control ECU
(Housed in ABS and TRACTION Actuator)• Processes the signals from each sensor to control the
ABS, BA, TRC, and VSC
• Sends and receives control signals to and from the
ECM, yaw rate and deceleration sensor, steering
sensor, etc. via CAN communication.
ABS and TRACTION Actuator • Consists of the master cylinder cut solenoid valve,
holding solenoid valve, pressure reduction solenoid
valve, pump motor, and reservoir, and adjusts the brake
fluid pressure applied to each wheel cylinder
• Houses the skid control ECU
Solenoid Relay • Supplies power to each solenoid
• Housed in the skid control ECU
Motor Relay (VSC MTR Relay) • Supplies power to the pump motor
• Installed in engine room No. 1 relay block
Fail-safe Relay (VSC FAIL Relay) • Cuts off power to the motor when the pump motor circuit
malfunctions
• Installed in engine room No. 1 relay block