engine TOYOTA RAV4 2006 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2006, Model line: RAV4, Model: TOYOTA RAV4 2006Pages: 2000, PDF Size: 45.84 MB
Page 1967 of 2000

2AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–79
ES
DESCRIPTION
In the VVT (Variable Valve Timing) system, the appropriate intake valve open and close timing is
controlled by the ECM. The ECM performs intake valve control by performing the following: 1) controlling
the camshaft and camshaft timing oil control valve, and operating the camshaft timing gear; and 2)
changing the relative positions of the gaps between the camshaft and crankshaft.
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The ECM optimizes the valve timing by using the VVT (Variable Valve Timing) system to control the intake
camshaft. The VVT system includes the ECM, the Oil Control Valve (OCV) and the VVT controller.
The ECM sends a target duty-cycle control signal to the OCV. This control signal regulates the oil
pressure supplied to the VVT controller. The VVT controller can advance or retard the intake camshaft.
The ECM calibrates the intake valve timing by setting the intake camshaft to the most retarded angle while
the engine is idling. The ECM closes the OCV to retard the cam. The ECM stores this value as the VVT
learning value. When the difference between the target and actual intake valve timings is 5
CA
(Crankshaft Angle) or less, the ECM stores it.
If the VVT learning value matches the following conditions, the ECM determines the existence of a
malfunction in the VVT system, and sets the DTC.
• VVT learning value: Less than 25
CA, or more than 51CA.
• Above condition continues for 18 seconds or more.
This DTC indicates that the angle between the intake camshaft and the crankshaft is incorrect due to
factors such as the timing chain having jumped a tooth.
This monitor begins to run after the engine has idled for 5 minutes.
MONITOR STRATEGY
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
DTC P0016Crankshaft Position - Camshaft Position Corre-
lation (Bank 1 Sensor A)
DTC No. DTC Detection Conditions Trouble Areas
P0016Deviation in crankshaft and camshaft position sensor signals
(2 trip detection logic)• Mechanical system (Timing chain has jumped tooth or
chain stretched)
•ECM
Related DTCs P0016: Camshaft timing misalignment at idling
Required Sensors/Components VVT actuator
Required Sensors/Components Camshaft position sensor, Crankshaft position sensor
Frequency of Operation Once per driving cycle
Duration Within 1 minute
MIL Operation 2 driving cycles
Sequence of Operation None
Monitor runs whenever following DTCs not presentP0011 (VVT system 1 - advance)
P0012 (VVT system 1 - retarded)
P0115 - P0118 (ECT sensor)
Engine RPM 550 to 1,000 rpm
One of following conditions met -
VVT learning value when camshaft maximum retarded Less than 27.8
CA
VVT learning value when camshaft maximum retarded More than 48
CA
Page 1968 of 2000
ES–802AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P0335 (see page ES-172).
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. Freeze frame data records the engine condition when
malfunctions are detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was
moving or stationary, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other
data from the time the malfunction occurred.
NG
OK
NEXT
NEXT
NOTICE:
After replacing the ECM or adjusting intake valve timing,
confirm that the DTC output does not recur.
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch ON.
(c) Turn the tester ON.
(d) Clear DTCs (see page ES-35).
(e) Switch the ECM from normal mode to check mode using
the tester (see page ES-38).
(f) Start the engine and warm it up.
(g) Allow the engine to idle for 1 minute or more, and then
drive the vehicle for 1 minute or more.
(h) Confirm that no DTC is set, using the tester.
OK:
No DTC output
NEXT
1CHECK VALVE TIMING (CHECK FOR LOOSE AND JUMPED TOOTH OF TIMING CHAIN)
(See page ES-77)
Go to step 3
2REPLACE ECM
Go to step 4
3ADJUST VALVE TIMING
4CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS
END
Page 1969 of 2000
2AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–81
ES
HINT:
• Although the DTC titles say oxygen sensor, these DTCs relate to the Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor.
• Sensor 1 refers to the sensor mounted in front of the Three-Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) and
located near the engine assembly.
DESCRIPTION
Refer to DTC P2195 (see page ES-292).
HINT:
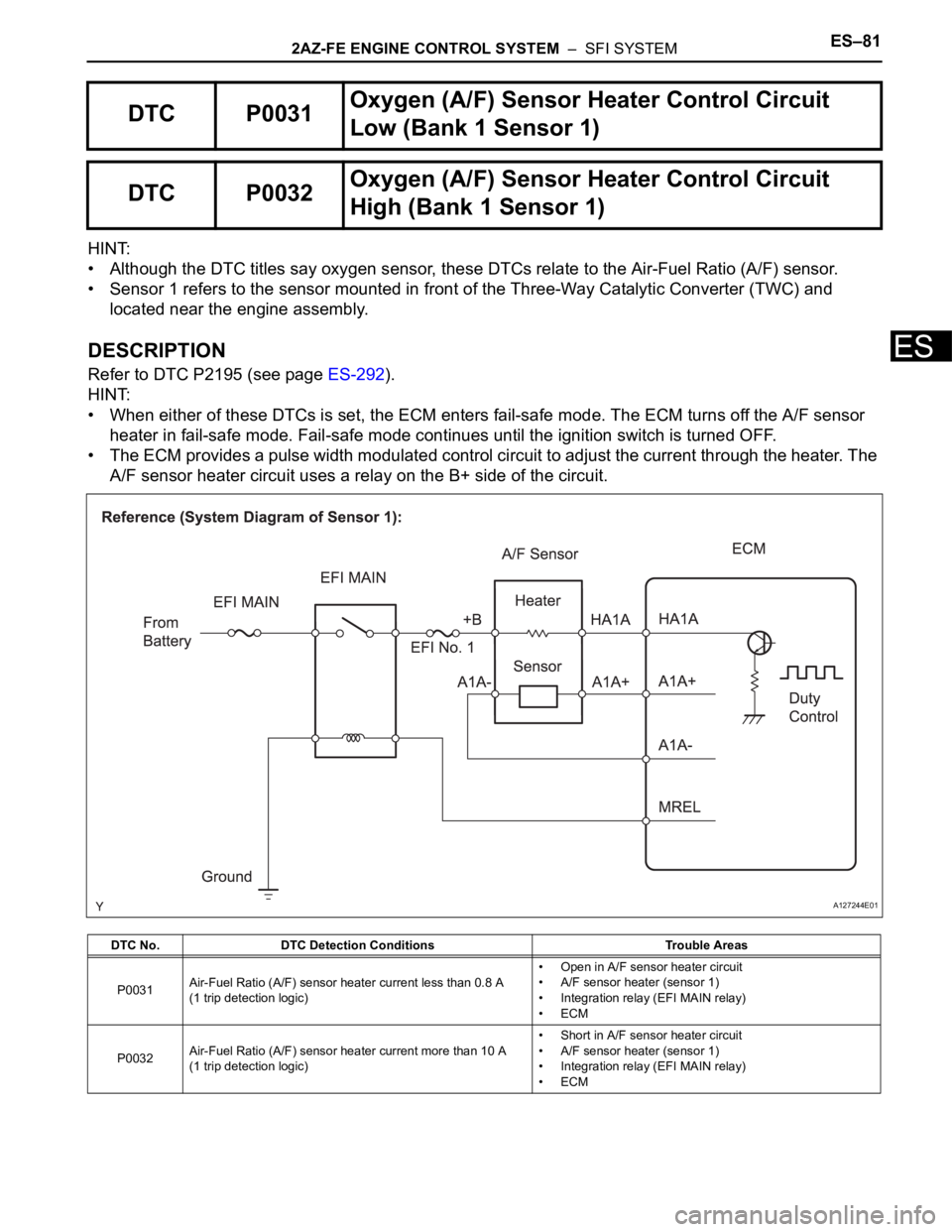
• When either of these DTCs is set, the ECM enters fail-safe mode. The ECM turns off the A/F sensor
heater in fail-safe mode. Fail-safe mode continues until the ignition switch is turned OFF.
• The ECM provides a pulse width modulated control circuit to adjust the current through the heater. The
A/F sensor heater circuit uses a relay on the B+ side of the circuit.
DTC P0031Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Heater Control Circuit
Low (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
DTC P0032Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Heater Control Circuit
High (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
DTC No. DTC Detection Conditions Trouble Areas
P0031Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor heater current less than 0.8 A
(1 trip detection logic)• Open in A/F sensor heater circuit
• A/F sensor heater (sensor 1)
• Integration relay (EFI MAIN relay)
•ECM
P0032Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor heater current more than 10 A
(1 trip detection logic)• Short in A/F sensor heater circuit
• A/F sensor heater (sensor 1)
• Integration relay (EFI MAIN relay)
•ECM
A127244E01
Page 1970 of 2000

ES–822AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The ECM uses information from the Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor to regulate the air-fuel ratio and keep it
close to the stoichiometric level. This maximizes the ability of the Three-Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) to
purify the exhaust gases.
The A/F sensor detects oxygen levels in the exhaust gas and transmits the information to the ECM. The
inner surface of the sensor element is exposed to the outside air. The outer surface of the sensor element
is exposed to the exhaust gas. The sensor element is made of platinum coated zirconia and includes an
integrated heating element.
The zirconia element generates a small voltage when there is a large difference in the oxygen
concentrations between the exhaust gas and outside air. The platinum coating amplifies this voltage
generation.
The A/F sensor is more efficient when heated. When the exhaust gas temperature is low, the sensor
cannot generate useful voltage signals without supplementary heating. The ECM regulates the
supplementary heating using a duty-cycle approach to adjust the average current in the sensor heater
element. If the heater current is outside the normal range, the signal transmitted by the A/F sensor
becomes inaccurate, as a result, the ECM is unable to regulate air-fuel ratio properly.
When the current in the A/F sensor heater is outside the normal operating range, the ECM interprets this
as a malfunction in the sensor heater and sets a DTC.
Example:
The ECM sets DTC P0032 when the current in the A/F sensor heater is more than 10 A. Conversely,
when the heater current is less than 0.8 A, DTC P0031 is set.
MONITOR STRATEGY
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
All:
P0031:
P0032:
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
P0031:
P0032:
Related DTCsP0031: A/F sensor heater open/short (Low electrical current)
P0032: A/F sensor heater open/short (High electrical current)
Required Sensors/Components (Main) A/F sensor heater
Required Sensors/Components (Related) -
Frequency of Operation Continuous
Duration 10 seconds
MIL Operation Immediate
Sequence of Operation None
Monitor runs whenever following DTCs not present None
Battery voltage 10.5 V or more
A/F sensor heater duty-cycle ratio 50 % or more
Time after engine start 10 seconds or more
Time after engine start 10 seconds or more
A/F sensor heater current Less than 0.8 A
A/F sensor heater current More than 10 A
Page 1971 of 2000
2AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–83
ES
COMPONENT OPERATING RANGE
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P2195 (see page ES-296).
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. Freeze frame data records the engine condition when
malfunctions are detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was
moving or stationary, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other
data from the time the malfunction occurred.
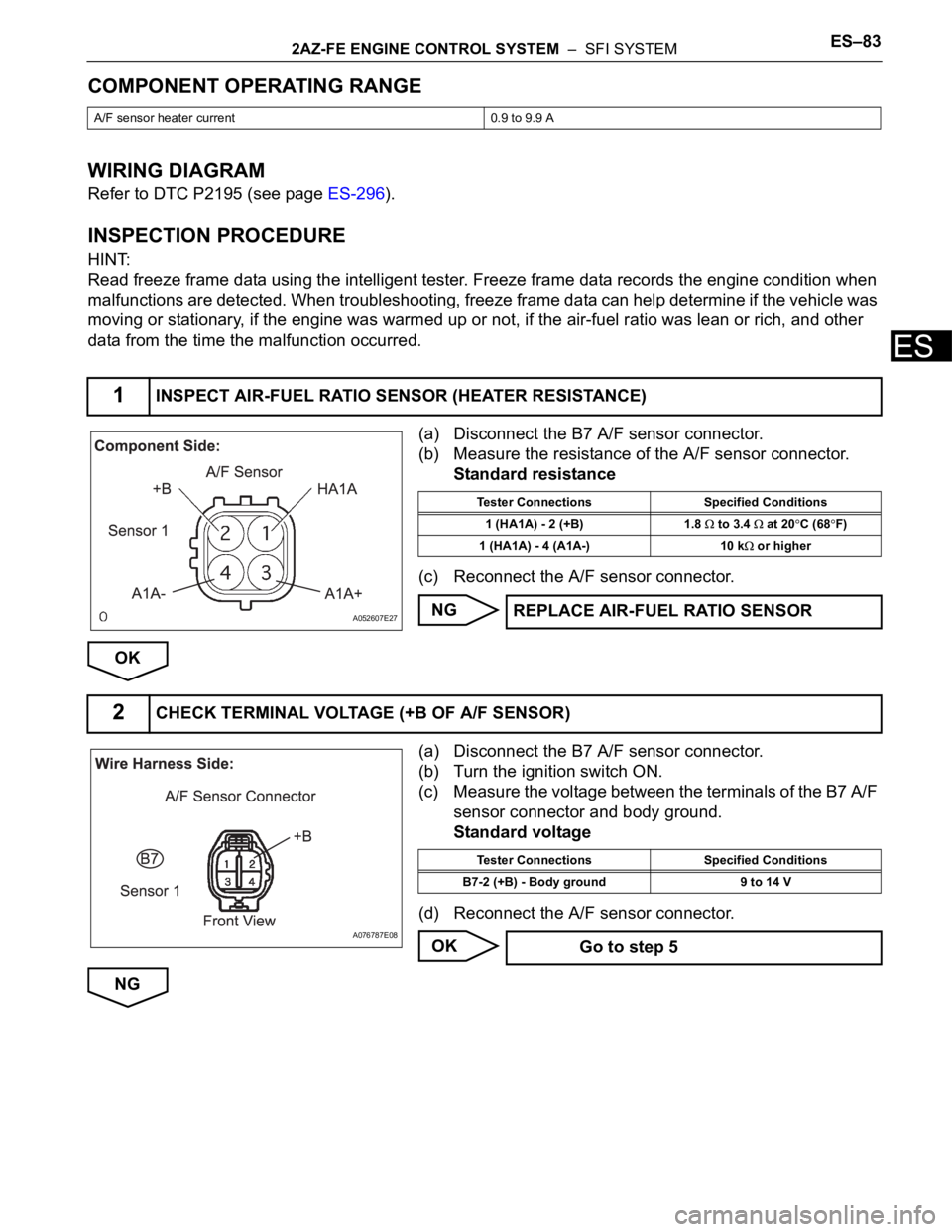
(a) Disconnect the B7 A/F sensor connector.
(b) Measure the resistance of the A/F sensor connector.
Standard resistance
(c) Reconnect the A/F sensor connector.
NG
OK
(a) Disconnect the B7 A/F sensor connector.
(b) Turn the ignition switch ON.
(c) Measure the voltage between the terminals of the B7 A/F
sensor connector and body ground.
Standard voltage
(d) Reconnect the A/F sensor connector.
OK
NG
A/F sensor heater current 0.9 to 9.9 A
1INSPECT AIR-FUEL RATIO SENSOR (HEATER RESISTANCE)
A052607E27
Tester Connections Specified Conditions
1 (HA1A) - 2 (+B) 1.8
to 3.4 at 20C (68F)
1 (HA1A) - 4 (A1A-) 10 k
or higher
REPLACE AIR-FUEL RATIO SENSOR
2CHECK TERMINAL VOLTAGE (+B OF A/F SENSOR)
A076787E08
Tester Connections Specified Conditions
B7-2 (+B) - Body ground 9 to 14 V
Go to step 5
Page 1972 of 2000
ES–842AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
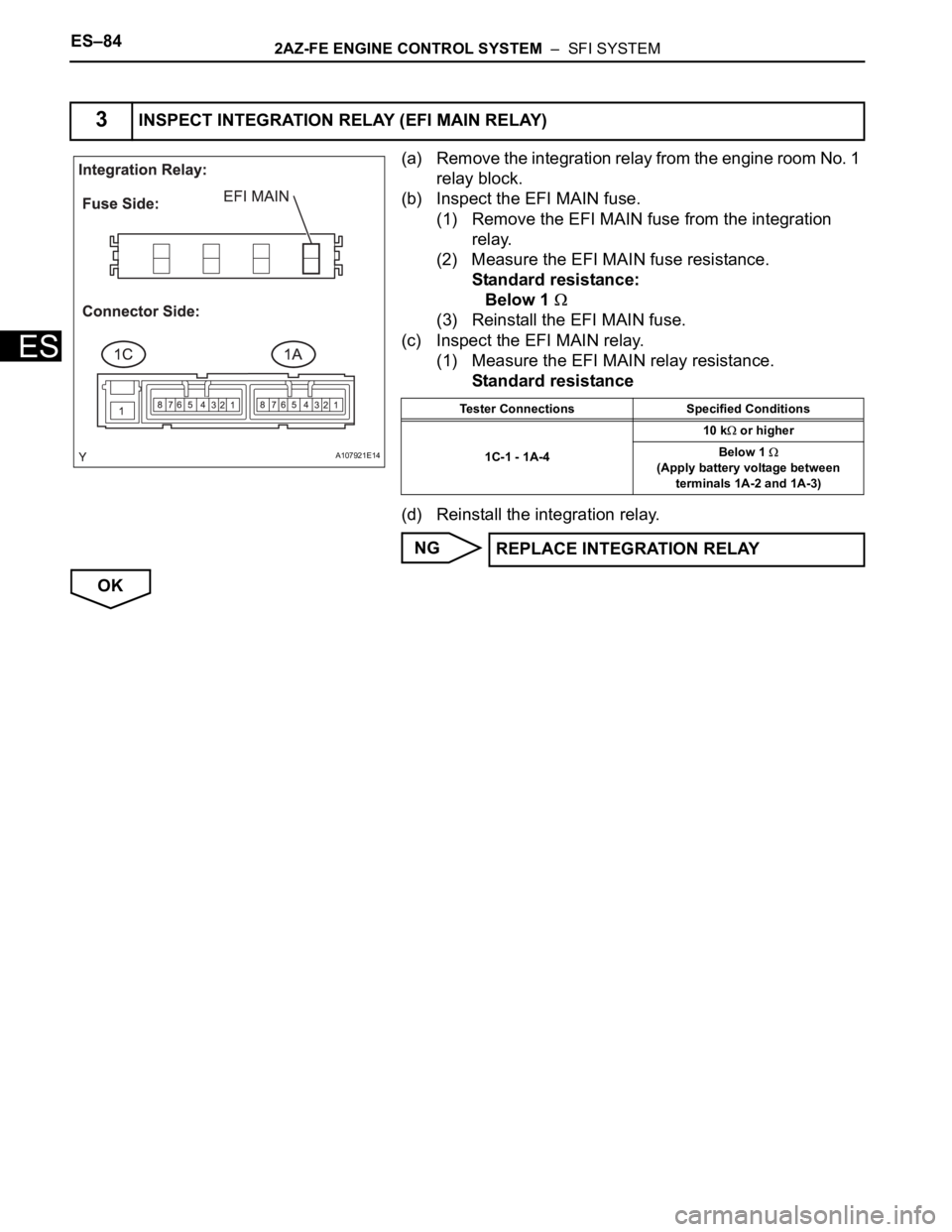
(a) Remove the integration relay from the engine room No. 1
relay block.
(b) Inspect the EFI MAIN fuse.
(1) Remove the EFI MAIN fuse from the integration
relay.
(2) Measure the EFI MAIN fuse resistance.
Standard resistance:
Below 1
(3) Reinstall the EFI MAIN fuse.
(c) Inspect the EFI MAIN relay.
(1) Measure the EFI MAIN relay resistance.
Standard resistance
(d) Reinstall the integration relay.
NG
OK
3INSPECT INTEGRATION RELAY (EFI MAIN RELAY)
A107921E14
Tester Connections Specified Conditions
1C-1 - 1A-410 k
or higher
Below 1
(Apply battery voltage between
terminals 1A-2 and 1A-3)
REPLACE INTEGRATION RELAY
Page 1973 of 2000
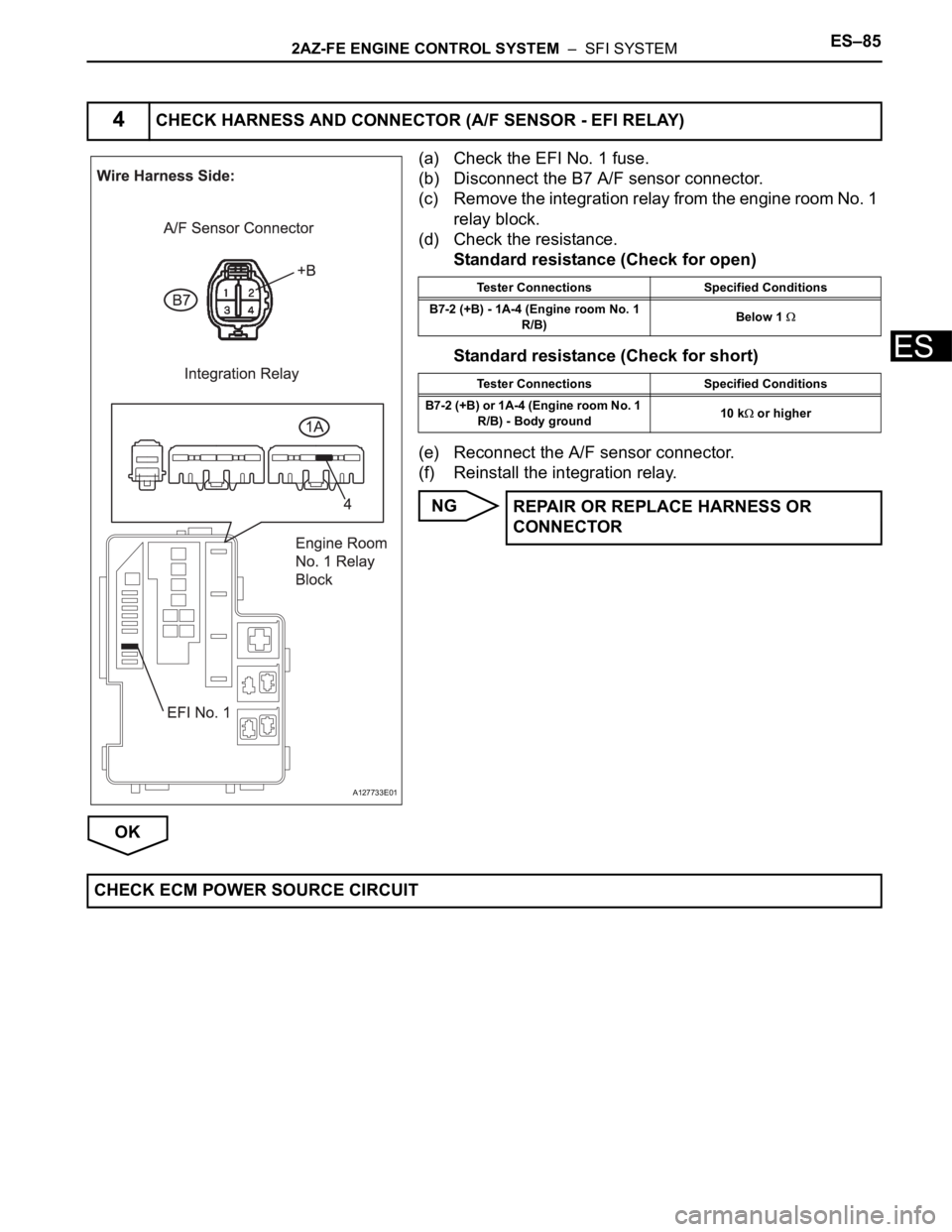
2AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–85
ES
(a) Check the EFI No. 1 fuse.
(b) Disconnect the B7 A/F sensor connector.
(c) Remove the integration relay from the engine room No. 1
relay block.
(d) Check the resistance.
Standard resistance (Check for open)
Standard resistance (Check for short)
(e) Reconnect the A/F sensor connector.
(f) Reinstall the integration relay.
NG
OK
4CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (A/F SENSOR - EFI RELAY)
A127733E01
Tester Connections Specified Conditions
B7-2 (+B) - 1A-4 (Engine room No. 1
R/B)Below 1
Tester Connections Specified Conditions
B7-2 (+B) or 1A-4 (Engine room No. 1
R/B) - Body ground10 k
or higher
REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR
CONNECTOR
CHECK ECM POWER SOURCE CIRCUIT
Page 1974 of 2000
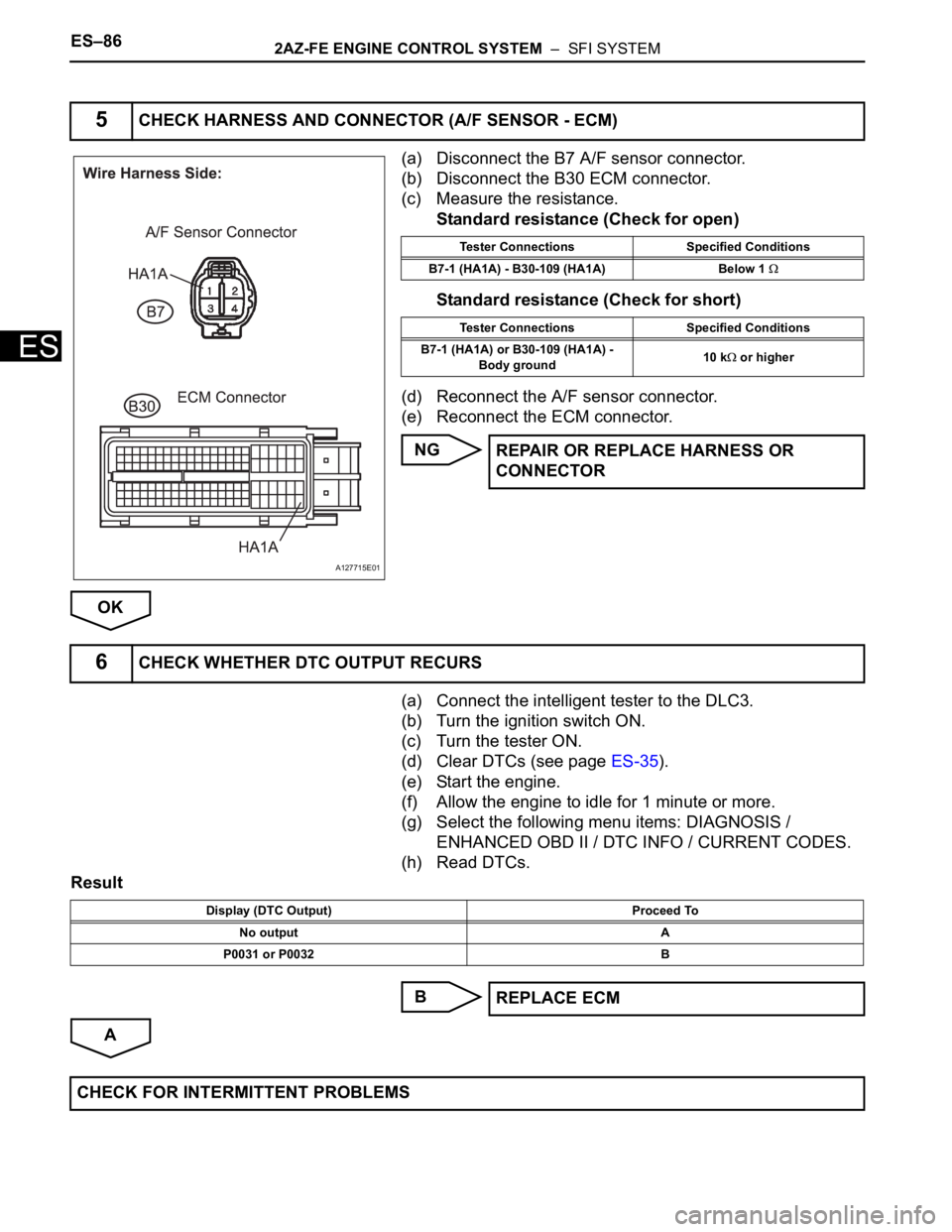
ES–862AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
(a) Disconnect the B7 A/F sensor connector.
(b) Disconnect the B30 ECM connector.
(c) Measure the resistance.
Standard resistance (Check for open)
Standard resistance (Check for short)
(d) Reconnect the A/F sensor connector.
(e) Reconnect the ECM connector.
NG
OK
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch ON.
(c) Turn the tester ON.
(d) Clear DTCs (see page ES-35).
(e) Start the engine.
(f) Allow the engine to idle for 1 minute or more.
(g) Select the following menu items: DIAGNOSIS /
ENHANCED OBD II / DTC INFO / CURRENT CODES.
(h) Read DTCs.
Result
B
A
5CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (A/F SENSOR - ECM)
A127715E01
Tester Connections Specified Conditions
B7-1 (HA1A) - B30-109 (HA1A) Below 1
Tester Connections Specified Conditions
B7-1 (HA1A) or B30-109 (HA1A) -
Body ground10 k
or higher
REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR
CONNECTOR
6CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS
Display (DTC Output) Proceed To
No output A
P0031 or P0032 B
REPLACE ECM
CHECK FOR INTERMITTENT PROBLEMS
Page 1975 of 2000
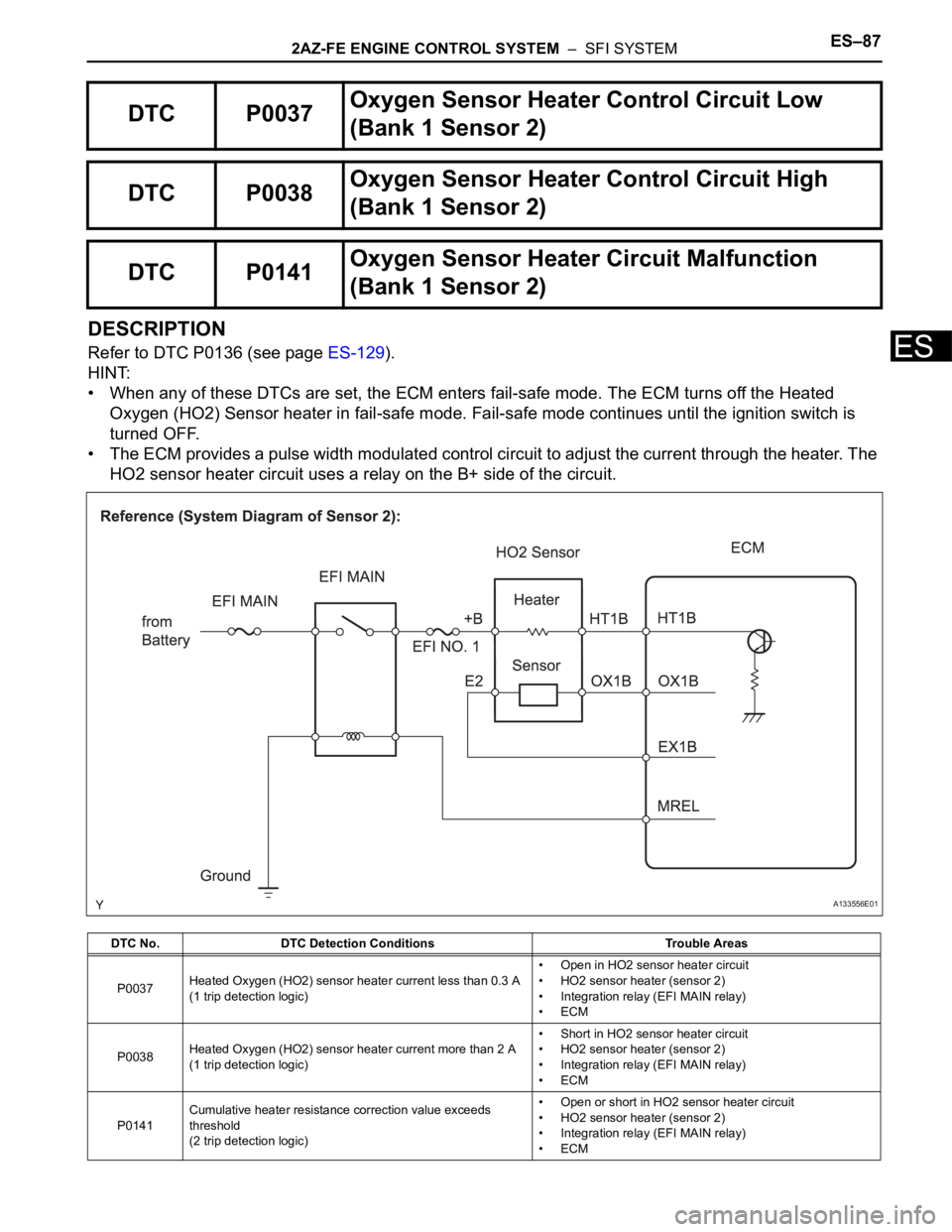
2AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–87
ES
DESCRIPTION
Refer to DTC P0136 (see page ES-129).
HINT:
• When any of these DTCs are set, the ECM enters fail-safe mode. The ECM turns off the Heated
Oxygen (HO2) Sensor heater in fail-safe mode. Fail-safe mode continues until the ignition switch is
turned OFF.
• The ECM provides a pulse width modulated control circuit to adjust the current through the heater. The
HO2 sensor heater circuit uses a relay on the B+ side of the circuit.
DTC P0037Oxygen Sensor Heater Control Circuit Low
(Bank 1 Sensor 2)
DTC P0038Oxygen Sensor Heater Control Circuit High
(Bank 1 Sensor 2)
DTC P0141Oxygen Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction
(Bank 1 Sensor 2)
DTC No. DTC Detection Conditions Trouble Areas
P0037Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor heater current less than 0.3 A
(1 trip detection logic)• Open in HO2 sensor heater circuit
• HO2 sensor heater (sensor 2)
• Integration relay (EFI MAIN relay)
•ECM
P0038Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor heater current more than 2 A
(1 trip detection logic)• Short in HO2 sensor heater circuit
• HO2 sensor heater (sensor 2)
• Integration relay (EFI MAIN relay)
•ECM
P0141Cumulative heater resistance correction value exceeds
threshold
(2 trip detection logic)• Open or short in HO2 sensor heater circuit
• HO2 sensor heater (sensor 2)
• Integration relay (EFI MAIN relay)
•ECM
A133556E01
Page 1976 of 2000

ES–882AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The sensing position of the Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor has a zirconia element which is used to detect
the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas. If the zirconia element is at the appropriate temperature,
and the difference between the oxygen concentrations surrounding the inside and outside surfaces of the
sensor is large, the zirconia element generates voltage signals. In order to increase the oxygen
concentration detecting capacity of the zirconia element, the ECM supplements the heat from the exhaust
with heat from a heating element inside the sensor.
Heated oxygen sensor heater range check (P0037 and P0038):
The ECM monitors the current applied to the O2 sensor heater to check the heater for malfunctions. If the
current is below the threshold value, the ECM determines that there is an open circuit in the heater. If the
current is above the threshold value, the ECM determines that there is a short circuit in the heater.
The ECM constantly monitors the current applied to the heater. If the ECM detects an open or short
circuit, the ECM turns the MIL on and sets a DTC.
If a malfunction is detected, the ECM cuts off the current applied to the heater.
Example:
The ECM sets DTC P0038 when the current in the HO2 sensor heater is more than 2 A. Conversely,
when the heater current is less than 0.3 A, DTC P0037 is set.
Heated oxygen sensor heater performance (P0141):
After the accumulated heater ON time exceeds 100 seconds, the ECM calculates the heater resistance
using the battery voltage and the current applied to the heater.
If the resistance is above the threshold value, the ECM determines that there is a malfunction in the HO2
sensor heater and set DTC P0141.
MONITOR STRATEGY
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
All:
P0037:
P0038:
P0141 (Heater performance monitor check):
Related DTCsP0037: Heated oxygen sensor heater range check (Low electrical
current)
P0038: Heated oxygen sensor heater range check (High electrical
current)
P0141: Heated oxygen sensor heater performance
Required Sensors/Components (Main) Heated oxygen sensor heater
Required Sensors/Components (Related) -
Frequency of OperationContinuous: P0037 and P0038
Once per driving cycle: P0141
Duration1 second: P0037 and P0038
10 seconds: P0141
MIL OperationImmediate: P0037 and P0038
2 driving cycles: P0141
Sequence of Operation None
Monitor runs whenever following DTCs not present None
Battery voltage 10.5 to 20 V
Battery voltage 10.5 to 20 V
All of following conditions met: -
Battery voltage 10.5 V or more
Fuel cut OFF
Time after fuel cut ON to OFF 30 seconds or more