engine coolant TOYOTA RAV4 2006 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2006, Model line: RAV4, Model: TOYOTA RAV4 2006Pages: 2000, PDF Size: 45.84 MB
Page 5 of 2000
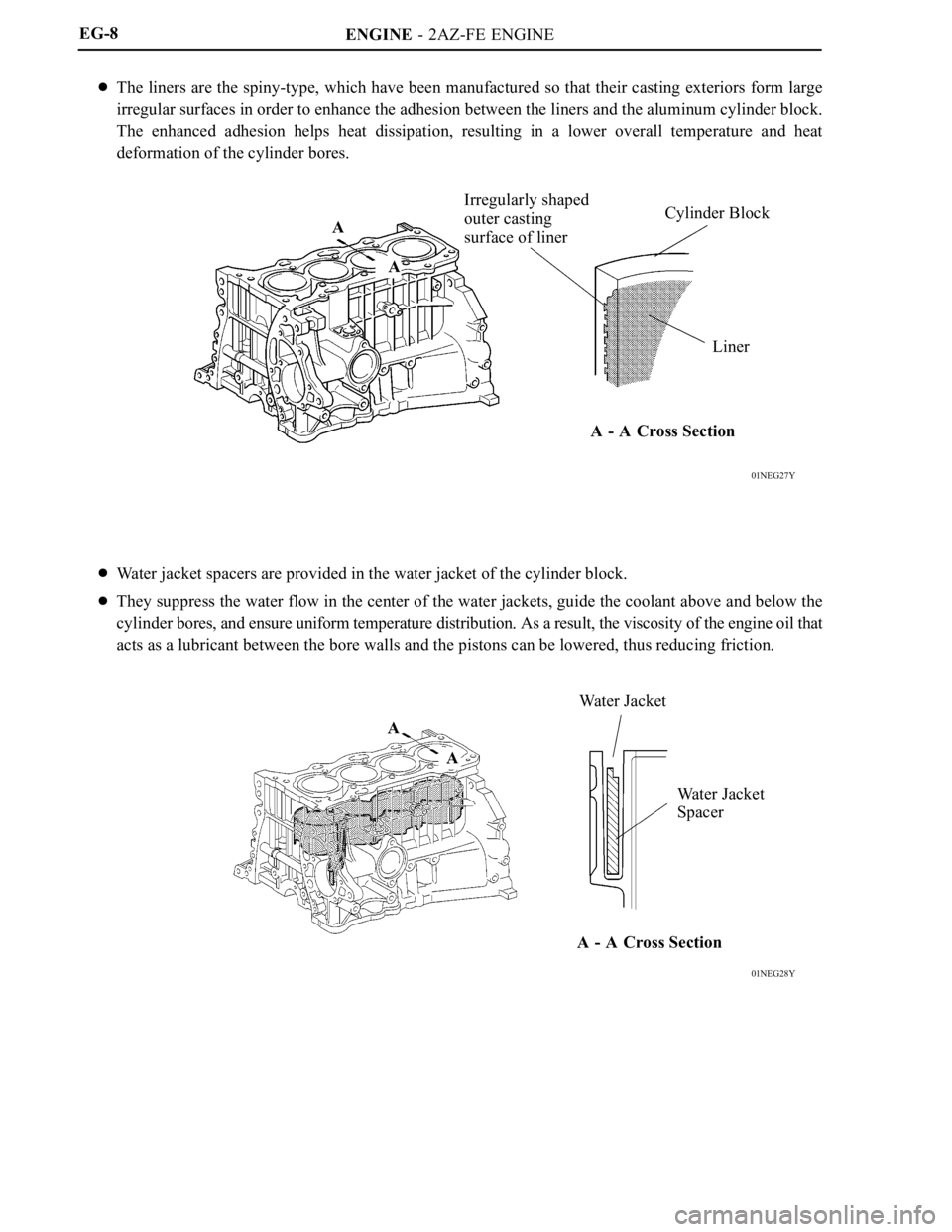
ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINE
01NEG27Y
Irregularly shaped
outer casting
surface of linerCylinder Block
Liner A
A
A - A Cross Section
01NEG28Y
Water Jacket
Spacer Water Jacket
A - A Cross Section A
A EG-8
The liners are the spiny-type, which have been manufactured so that their casting exteriors form large
irregular surfaces in order to enhance the adhesion between the liners and the aluminum cylinder block.
The enhanced adhesion helps heat dissipation, resulting in a lower overall temperature and heat
deformation of the cylinder bores.
Water jacket spacers are provided in the water jacket of the cylinder block.
They suppress the water flow in the center of the water jackets, guide the coolant above and below the
cylinder bores, and ensure uniform temperature distribution. As a result, the viscosity of the engine oil that
acts as a lubricant between the bore walls and the pistons can be lowered, thus reducing friction.
Page 13 of 2000
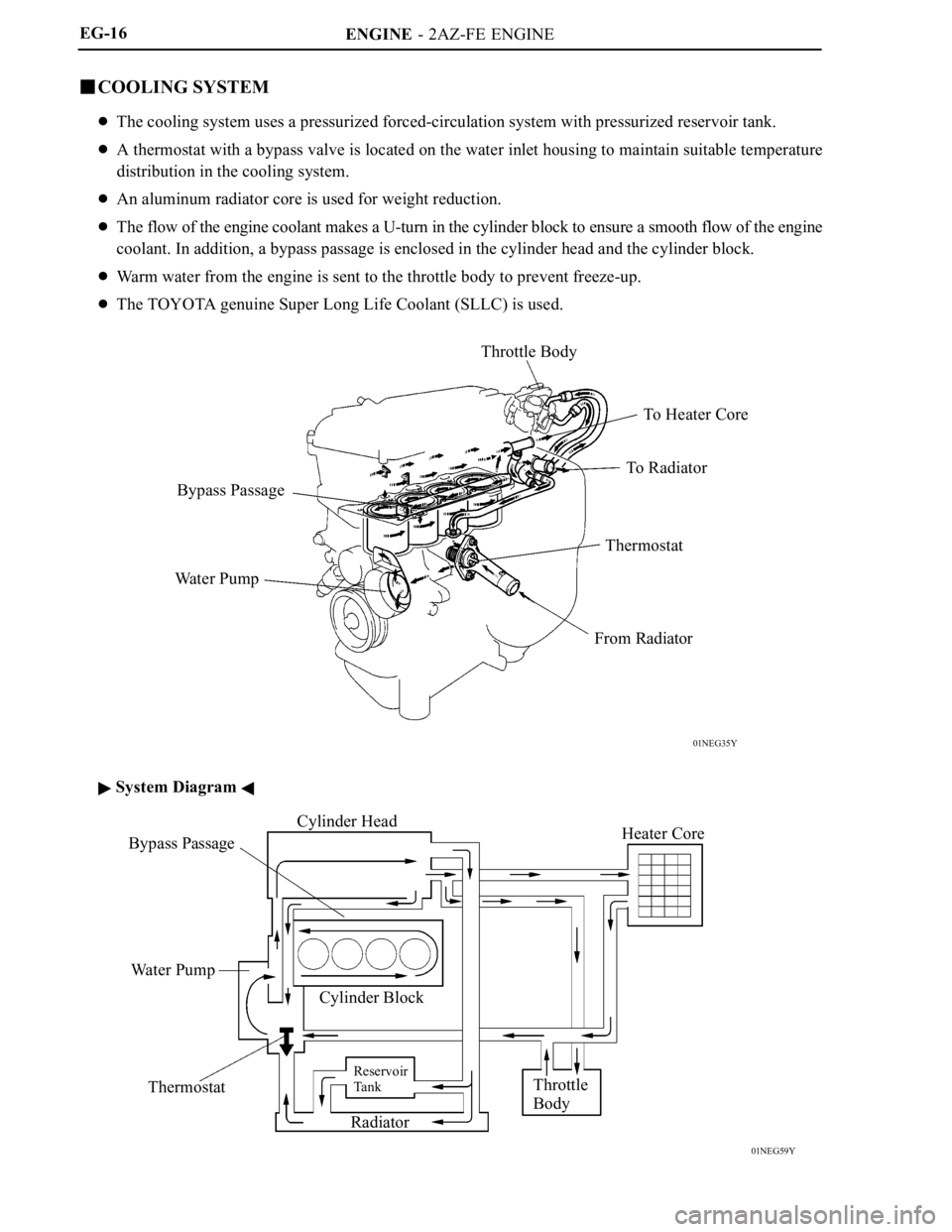
ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINE
01NEG35Y
Throttle Body
To H e a t e r C o r e
To R a d i a t o r
Thermostat
From Radiator Wa t e r P u m pBypass Passage
01NEG59Y
Bypass PassageCylinder Head
Wa t e r P u m p
Cylinder Block
Thermostat
Reservoir
Ta n k
RadiatorThrottle
BodyHeater Core EG-16
COOLING SYSTEM
The cooling system uses a pressurized forced-circulation system with pressurized reservoir tank.
A thermostat with a bypass valve is located on the water inlet housing to maintain suitable temperature
distribution in the cooling system.
An aluminum radiator core is used for weight reduction.
The flow of the engine coolant makes a U-turn in the cylinder block to ensure a smooth flow of the engine
coolant. In addition, a bypass passage is enclosed in the cylinder head and the cylinder block.
Warm water from the engine is sent to the throttle body to prevent freeze-up.
The TOYOTA genuine Super Long Life Coolant (SLLC) is used.
System Diagram
Page 14 of 2000
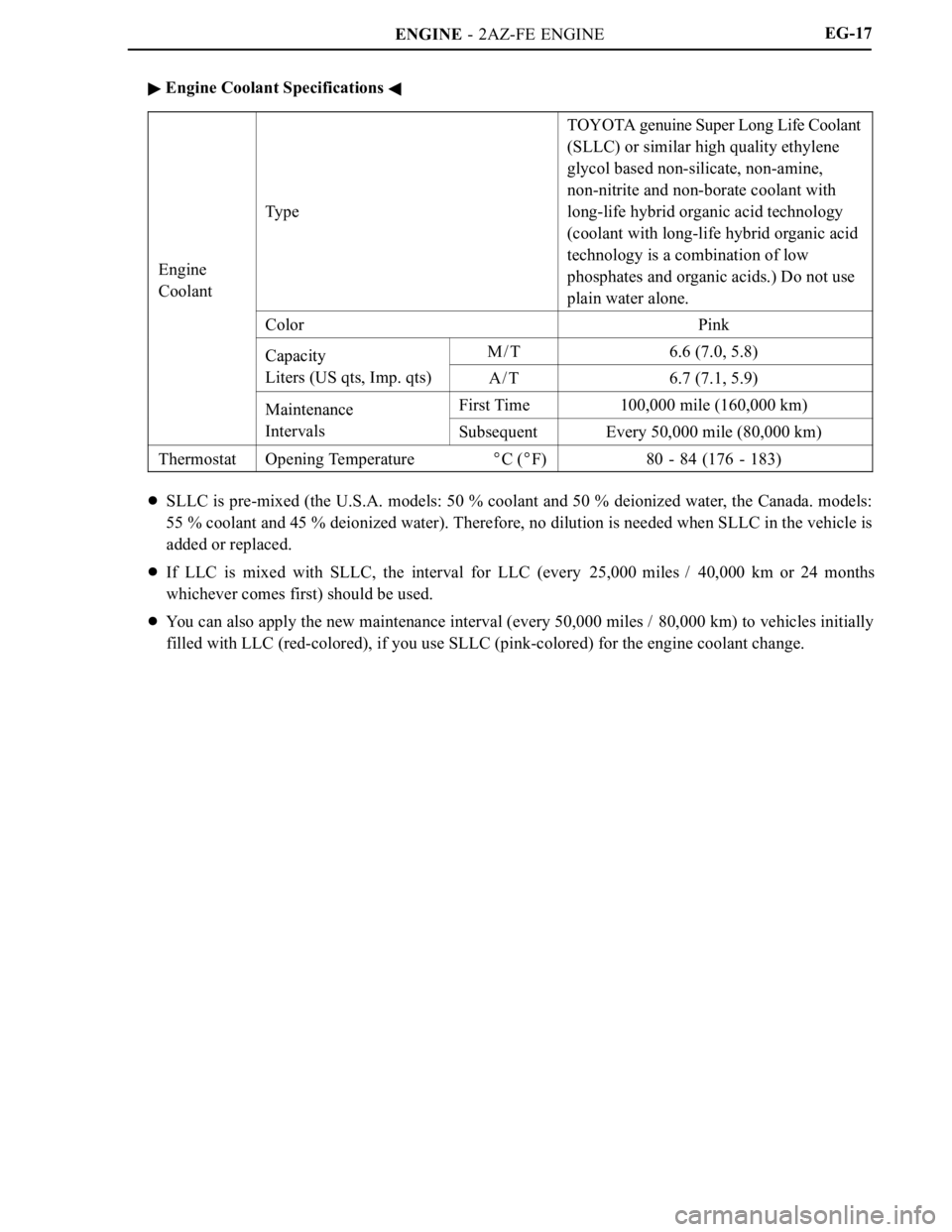
ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINEEG-17
Engine Coolant Specifications
Engine
Coolant
Ty p e
TOYOTA genuine Super Long Life Coolant
(SLLC) or similar high quality ethylene
glycol based non-silicate, non-amine,
non-nitrite and non-borate coolant with
long-life hybrid organic acid technology
(coolant with long-life hybrid organic acid
technology is a combination of low
phosphates and organic acids.) Do not use
plain water alone.
ColorPink
CapacityM/T6.6 (7.0, 5.8)Capacity
Liters (US qts, Imp. qts)A/T6.7 (7.1, 5.9)
MaintenanceFirst Time100,000 mile (160,000 km)Maintenance
IntervalsSubsequentEvery 50,000 mile (80,000 km)
ThermostatOpening TemperatureC (F)80 - 84 (176 - 183)
SLLC is pre-mixed (the U.S.A. models: 50 % coolant and 50 % deionized water, the Canada. models:
55 % coolant and 45 % deionized water). Therefore, no dilution is needed when SLLC in the vehicle is
added or replaced.
If LLC is mixed with SLLC, the interval for LLC (every 25,000 miles / 40,000 km or 24 months
whichever comes first) should be used.
You can also apply the new maintenance interval (every 50,000 miles / 80,000 km) to vehicles initially
filled with LLC (red-colored), if you use SLLC (pink-colored) for the engine coolant change.
Page 27 of 2000
ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINE EG-30
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
1. General
The engine control system for the 2AZ-FE engine has the following systems.
System
Outline
SFI
Sequential Multiport
Fuel InjectionAn L-type SFI system directly detects the intake air volume with a hot-wire
type mass air flow meter.
The fuel injection system is a sequential multiport fuel injection system.
ESA
Electronic Spark
AdvanceIgnition timing is determined by the ECM based on signals from various sensors.
The ECM corrects ignition timing in response to engine knocking.
ETCS-i
Electronic
Optimally controls the throttle valve opening in accordance with the amount of
accelerator pedal effort and the condition of the engine and the vehicle.
Electronic
Throttle Control
System-intelligent
(See page-43)A linkless-type is used, without an accelerator cable.
An accelerator pedal position sensor is provided on the accelerator pedal.
A non-contact type throttle position sensor and accelerator pedal position
sensor are used.
VVT-i
Va r i a b l e Va l v e
Timing-intelligent
(See page EG-48)
Controls the intake camshaft to an optimal valve timing in accordance with the
engine condition.
Air-fuel Ratio
Sensor, Oxygen
Sensor Heater
ControlMaintains the temperature of the air-fuel ratio sensor or oxygen sensor at an
appropriate level to realize accuracy of detection of the oxygen concentration in
the exhaust gas.
Air Conditioning
Cut-off ControlBy turning the air conditioning compressor ON or OFF in accordance with the
engine condition, drivability is maintained.
Cooling Fan Control
(See page EG-52)Radiator cooling fan operation is controlled by signals from ECM based on the
engine coolant temperature sensor signal and the condition of the air
conditioning operation.
Fuel Pump Control
(See page EG-53)Fuel pump operation is controlled by signal from the ECM.
The fuel pump is stopped when the SRS driver’s and front passenger’s airbags
are deployed.
Evapotative Emission
The ECM controls the purge flow of evaporative emissions (HC) in the canister
in accordance with engine conditions.
Evapotative Emission
Control
(See page EG-54)Approximately five hours after the ignition switch has been turned OFF, the
ECM operates the canister pump module to detect any evaporative emission
leakage occurring in the EVAP (evaporative emission) control system through
changes in the 0.02 in. leak pressure.
Charging Control
(See page EG-65)The ECM regulates the charging voltage of the generator in accordance with the
driving conditions and the charging state of the battery.
(Continued)
Page 29 of 2000
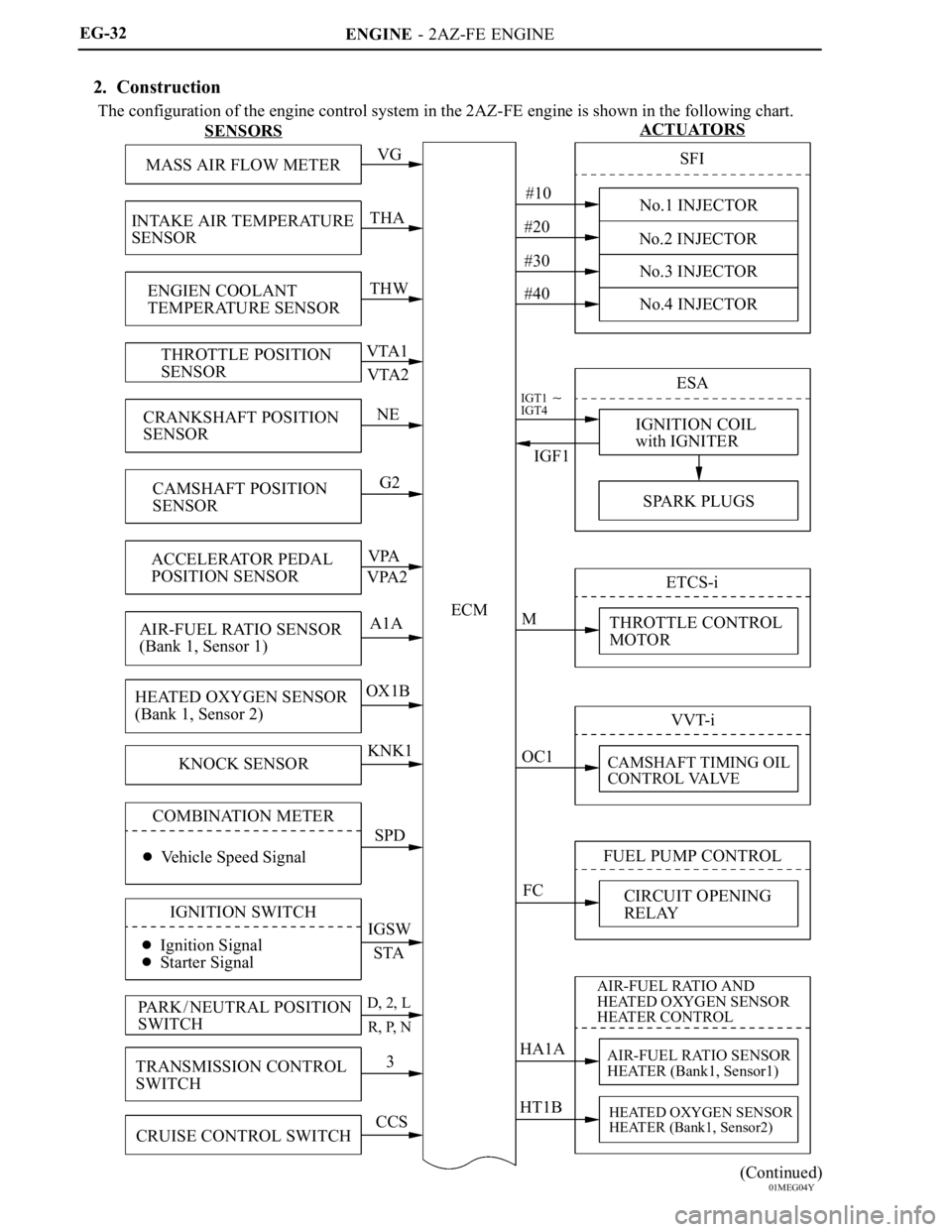
ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINE
01MEG04Y
SENSORSACTUATORS
MASS AIR FLOW METER
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
ENGIEN COOLANT
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
THROTTLE POSITION
SENSOR
CRANKSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR
CAMSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR
ACCELERATOR PEDAL
POSITION SENSOR
AIR-FUEL RATIO SENSOR
(Bank 1, Sensor 1)
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
(Bank 1, Sensor 2)
KNOCK SENSOR
COMBINATION METER
Vehicle Speed Signal
IGNITION SWITCH
Ignition Signal
Starter Signal
PA R K / N E U T R A L P O S I T I O N
SWITCH
TRANSMISSION CONTROL
SWITCH
CRUISE CONTROL SWITCHVG
THA
THW
VTA1
VTA2
NE
G2
VPA
VPA2
A1A
OX1B
KNK1
SPD
IGSW
STA
D, 2, L
R, P, N
3
CCSECM#10
#20
#30
#40
IGT1 IGT4
IGF1
M
OC1
FC
HA1A
HT1BSFI
No.1 INJECTOR
No.2 INJECTOR
No.3 INJECTOR
No.4 INJECTOR
ESA
IGNITION COIL
with IGNITER
SPARK PLUGS
ETCS-i
THROTTLE CONTROL
MOTOR
VVT-i
CAMSHAFT TIMING OIL
CONTROL VALVE
FUEL PUMP CONTROL
CIRCUIT OPENING
RELAY
AIR-FUEL RATIO AND
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
HEATER CONTROL
AIR-FUEL RATIO SENSOR
HEATER (Bank1, Sensor1)
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
HEATER (Bank1, Sensor2)
EG-32
2. Construction
The configuration of the engine control system in the 2AZ-FE engine is shown in the following chart.
(Continued)
Page 31 of 2000
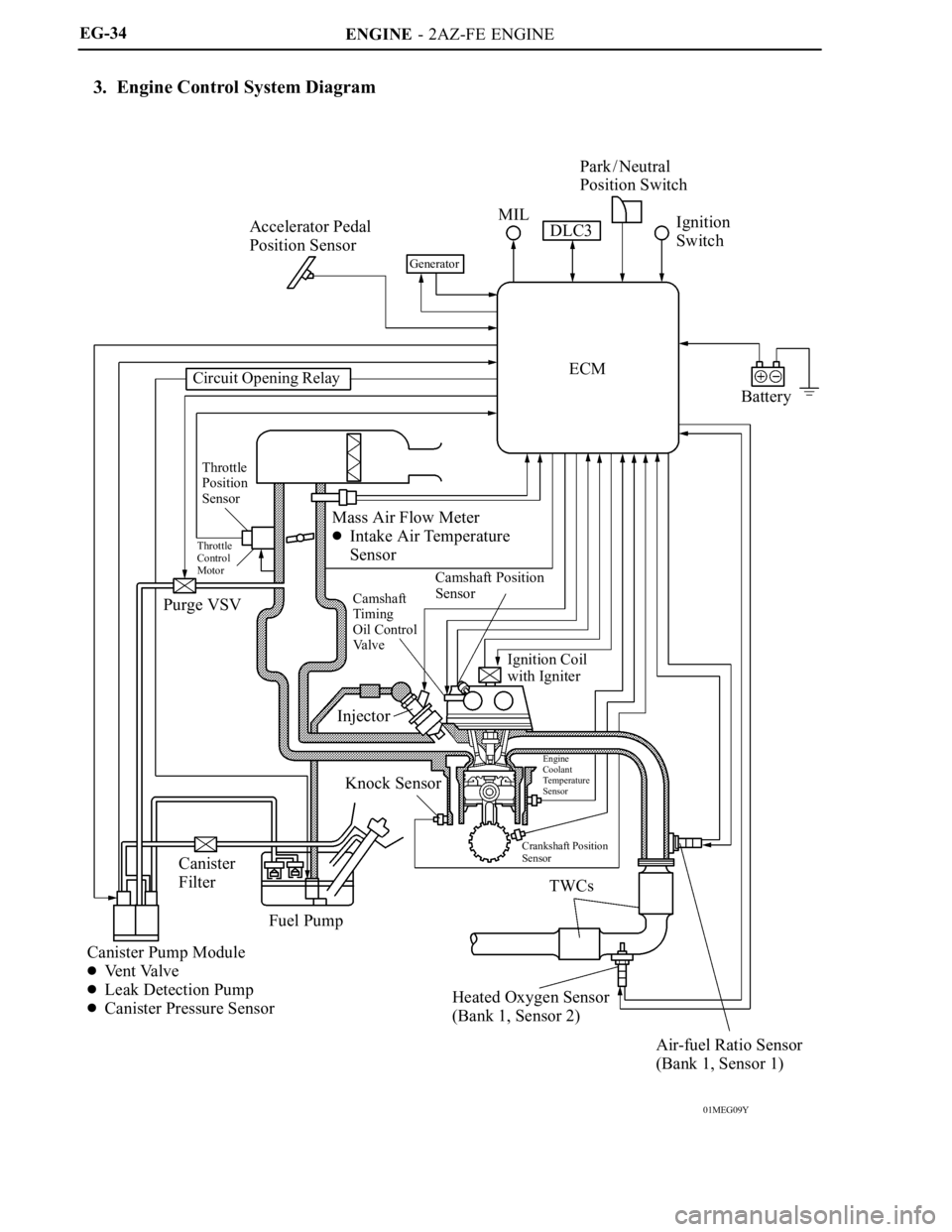
ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINE
01MEG09Y
Accelerator Pedal
Position Sensor
Generator
MIL
DLC3Park / Neutral
Position Switch
Ignition
Switch
Circuit Opening RelayECM
Battery
Throttle
Position
Sensor
Throttle
Control
Motor
Purge VSVMass Air Flow Meter
Intake Air Temperature
Sensor
Camshaft Position
Sensor
Camshaft
Timing
Oil Control
Va l v e
Ignition Coil
with Igniter
Injector
Knock Sensor
Engine
Coolant
Temperature
Sensor
Crankshaft Position
Sensor
Canister
Filter
Fuel Pump
Canister Pump Module
Ve n t Va l v e
Leak Detection Pump
Canister Pressure SensorTWCs
Heated Oxygen Sensor
(Bank 1, Sensor 2)
Air-fuel Ratio Sensor
(Bank 1, Sensor 1) EG-34
3. Engine Control System Diagram
Page 45 of 2000

ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINE
DR011EG25
Camshaft Position Sensor
Engine Coolant
Temperature Sensor
Crankshaft
Position Sensor
Camshaft Timing
Oil Control Valve
Throttle Position
Sensor
ECM
Mass Air Flow Meter Vehicle Speed Signal
221EG16
Crankshaft Position Sensor
Mass Air Flow Meter
Throttle Position Sensor
Engine Coolant Temp. Sensor
Camshaft Position Sensor
Vehicle Speed SignalECM
Target Valve Timing
Feedback
Correction
Actual Valve Timing
Duty-cycle
Control
Camshaft Timing
Oil Control Valve
EG-48
7. VVT-i (Variable Valve Timing-intelligent) System
General
The VVT-i system is designed to control the intake camshaft within a range of 40 (of Crankshaft Angle)
to provide valve timing that is optimally suited to the engine condition. This realizes proper torque in
all the speed ranges as well as realizing excellent fuel economy, and reducing exhaust emissions.
Using the engine speed signal, vehicle speed signal, and the signals from mass air flow meter, throttle
position sensor and engine coolant temperature sensor, the ECM can calculate optimal valve timing for
each driving condition and controls the camshaft timing oil control valve. In addition, the ECM uses
signals from the camshaft position sensor and crankshaft position sensor to detect the actual valve timing,
thus providing feedback control to achieve the target valve timing.
Page 49 of 2000
ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINE
01NEG09Y
01NEG10Y
Air
Conditioning
ECU
Engine Coolant
Temperature SensorFANL
ECM
FA N HCooling Fan
Relay No.3
Cooling Fan
Motor No.2
Cooling Fan
Relay No.1
Cooling Fan
Motor No.1
Low Speed (Series Connection)
High Speed (Parallel Connection) Air
Conditioning
ECU
Engine Coolant
Temperature SensorFA N L
ECM
FA N HCooling Fan
Relay No.3
Cooling Fan
Motor No.2
Cooling Fan
Relay No.1
Cooling Fan
Relay No.2
Cooling Fan
Motor No.1 : CAN
Cooling Fan
Relay No.2
EG-52
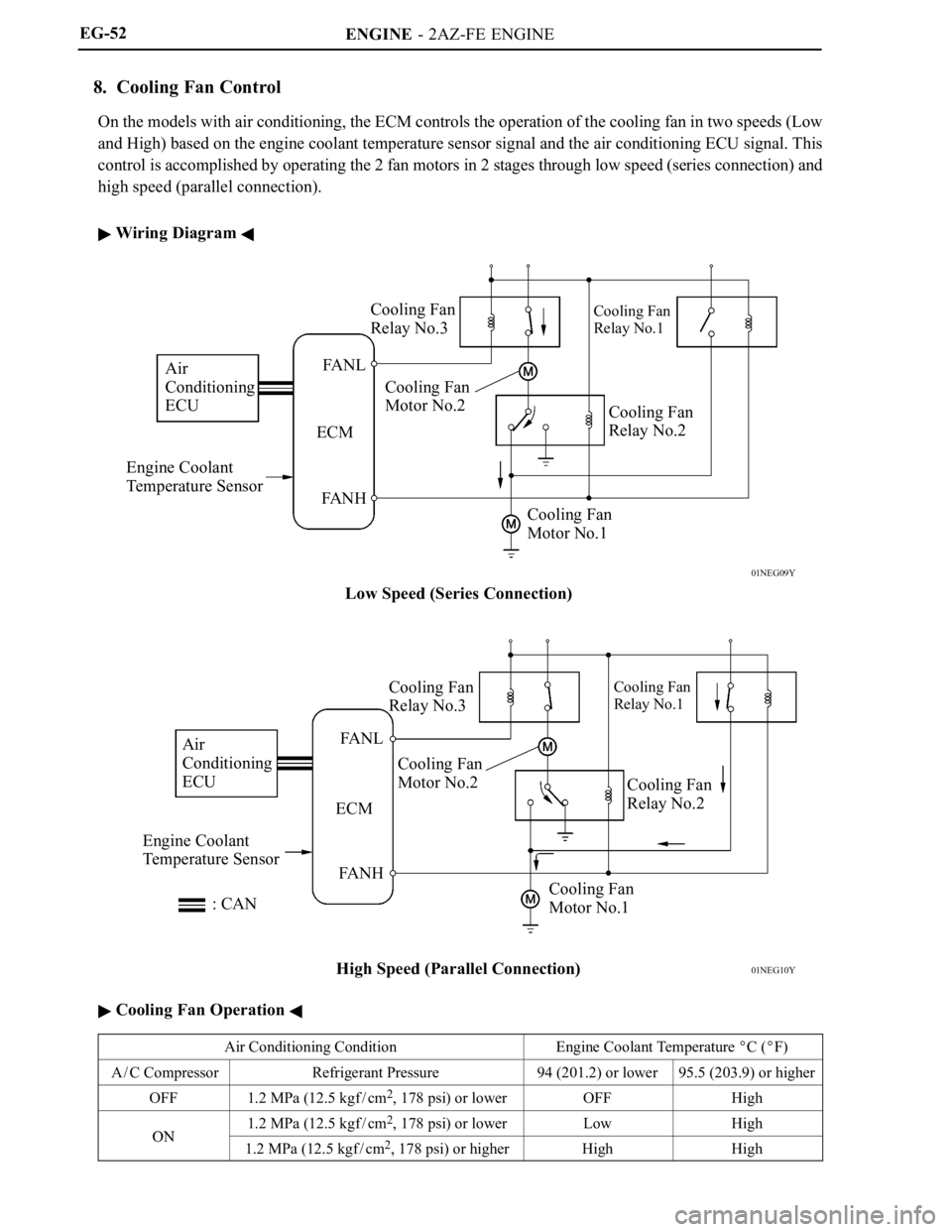
8. Cooling Fan Control
On the models with air conditioning, the ECM controls the operation of the cooling fan in two speeds (Low
and High) based on the engine coolant temperature sensor signal and the air conditioning ECU signal. This
control is accomplished by operating the 2 fan motors in 2 stages through low speed (series connection) and
high speed (parallel connection).
Wiring Diagram
Cooling Fan Operation
Air Conditioning ConditionEngine Coolant Temperature C (F)
A / C CompressorRefrigerant Pressure94 (201.2) or lower95.5 (203.9) or higher
OFF1.2 MPa (12.5 kgf / cm2, 178 psi) or lowerOFFHigh
ON1.2 MPa (12.5 kgf / cm2, 178 psi) or lowerLowHighON1.2 MPa (12.5 kgf / cm2, 178 psi) or higherHighHigh
Page 51 of 2000

ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINE
Service Tip
The canister pump module performs the EVAP leak check. This check is done approximately five
hours after the engine is turned off. So you may hear sound coming from underneath the luggage
compartment for several minutes. It does not indicate a malfunction.
The pinpoint pressure test procedure is carried out by pressurizing the fresh air line that runs from
the pump module to the air filler neck. For details, refer to the 2006 RAV4 Repair Manual (Pub.
No. RM01M1U).
EG-54
10. EVAP (evaporative Emission) Control System
General
The EVAP (evaporative emission) control system prevents the vapor gas that is created in the fuel tank from
being released directly into the atmosphere.
The canister stores the vapor gas that has been created in the fuel tank.
The ECM controls the purge VSV in accordance with the driving conditions in order to direct the vapor
gas into the engine, where it is burned.
In this system, the ECM checks the evaporative emission leak and outputs DTC (Diagnostic Trouble
Code) in the event of a malfunction. An EVAP (evaporative emission) leak check consists of an
application of a vacuum pressure to the system and monitoring the changes in the system pressure in order
to detect a leakage.
This system consists of the purge VSV, canister, refueling valve, canister pump module, and ECM.
The ORVR (Onboard Refueling Vapor Recovery) function is provided in the refueling valve.
The canister pressure sensor has been included to the canister pump module.
The canister filter has been provided on the fresh air line. This canister filter is maintenance-free.
The followings are the typical conditions for enabling an EVAP leak check:
Typical Enabling
Condition
Five hours have elapsed after the engine has been turned OFF*.
Altitude: Below 2400 m (8000 feet)
Battery voltage: 10.5 V or more
Ignition switch: OFF
Engine coolant temperature: 4.4 to 35C (40 to 95F)
Intake air temperature: 4.4 to 35C (40 to 95F)
*: If engine coolant temperature does not drop below 35C (95F), this time should be extended to 7hours.
Even after that, if the temperature is not less than 35
C (95F), the time should be extended to 9.5 hours.
Page 55 of 2000
ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINE
00REG23Y
To Intake Manifold
Atmosphere
Purge VSV
(Open)
ECM
00REG24Y
CloseOpen EG-58
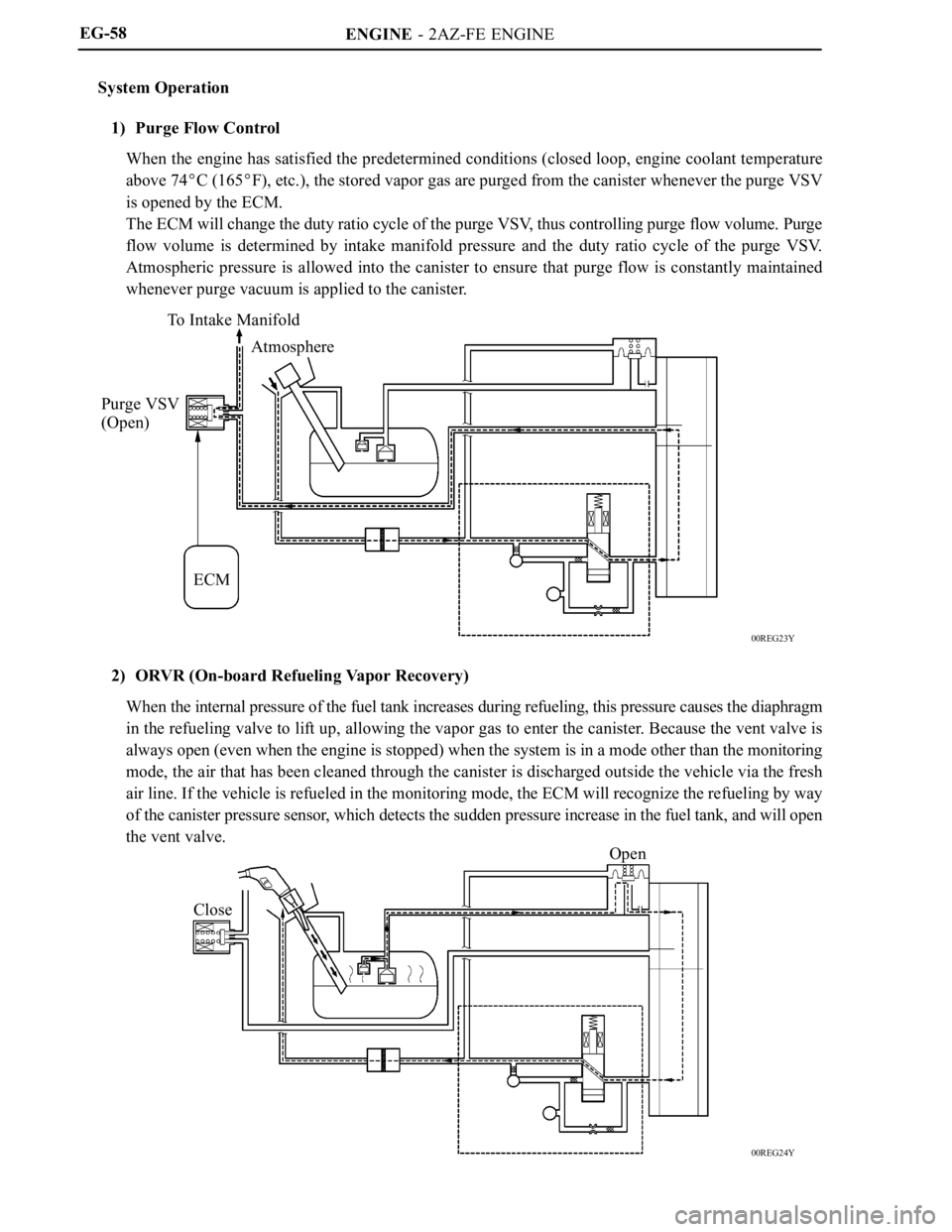
System Operation
1) Purge Flow Control
When the engine has satisfied the predetermined conditions (closed loop, engine coolant temperature
above 74
C (165F), etc.), the stored vapor gas are purged from the canister whenever the purge VSV
is opened by the ECM.
The ECM will change the duty ratio cycle of the purge VSV, thus controlling purge flow volume. Purge
flow volume is determined by intake manifold pressure and the duty ratio cycle of the purge VSV.
Atmospheric pressure is allowed into the canister to ensure that purge flow is constantly maintained
whenever purge vacuum is applied to the canister.
2) ORVR (On-board Refueling Vapor Recovery)
When the internal pressure of the fuel tank increases during refueling, this pressure causes the diaphragm
in the refueling valve to lift up, allowing the vapor gas to enter the canister. Because the vent valve is
always open (even when the engine is stopped) when the system is in a mode other than the monitoring
mode, the air that has been cleaned through the canister is discharged outside the vehicle via the fresh
air line. If the vehicle is refueled in the monitoring mode, the ECM will recognize the refueling by way
of the canister pressure sensor, which detects the sudden pressure increase in the fuel tank, and will open
the vent valve.