engine TOYOTA SIENNA 2007 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SIENNA, Model: TOYOTA SIENNA 2007Pages: 3000, PDF Size: 52.26 MB
Page 453 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–147
ES
DESCRIPTION
Refer to DTC P0115 (See page ES-133).
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The ECT sensor is used to monitor the ECT. The ECT sensor has a built-in thermistor with a resistance
that varies according to the temperature of the engine coolant. When the ECT becomes low, the
resistance of the thermistor increases. When the temperature becomes high, the resistance drops. These
variations in the resistance are reflected in the voltage output from the ECT sensor.
The ECM monitors the sensor voltage and uses this value to calculate the ECT. If the sensor voltage
output deviates from the normal operating range, the ECM interprets this deviation as a malfunction in the
ECT sensor and sets the DTC.
Examples:
• Upon starting the engine, the ECT is between 35
C and 60C (95F and 140F). If the ECT remains
within 3
C (5.4F) of the stating temperature after driving for 250 seconds, the DTC is set (2 trip
detection logic).
• Upon starting the engine, the ECT is over 60
C (140F). If the ECT remains within 1C (1.8F) of the
starting temperature after driving for 250 seconds, the DTC is set (6 trip detection logic).
MONITOR STRATEGY
DTC P0116Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit Range /
Performance Problem
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P0116ECTs as listed below are nearly same (2 trip detection
logic):
– ECT when engine is started at lower than 60
C
(140
F) of ECT
– ECT when engine is warmed up
•Thermostat
• ECT sensor ECTs as listed below are nearly same when engine is
started at higher than 60
C (140F) of ECT (2 trip
detection logic)
– ECT when engine is stopped after driving
– ECT when engine is started at lower than 60
C
(140F) of ECT
When either of following conditions is met (2 trip
detection logic):
• When cold engine started and engine warmed up,
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor value
does not change
• After engine is warmed up, ECT sensor value does
not change when engine stopped and then next
cold engine start is performed
Related DTCsP0116: Engine coolant temperature sensor output stuck at low engine coolant
temperature
P0116: Engine coolant temperature sensor output stuck at high engine coolant
temperature
Required Sensors / Components (Main) Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor
Required Sensors / Components (Related) Crankshaft position sensor, intake air temperature sensor and mass air flow meter
Frequency of Operation Continuous
Duration 5 hours
MIL Operation 2 driving cycles
Sequence of Operation None
Page 454 of 3000

ES–1482GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
All:
ECT sensor cold start monitor:
ECT sensor soak monitor:
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
ECT sensor cold start monitor:
ECT sensor soak monitor:
COMPONENT OPERATING RANGE
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
• If any of DTC P0115, P0117, P0118 or P0125 are set simultaneously with DTC P0116, the ECT sensor
may have an open or a short circuit. Troubleshoot those DTCs first.
• Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. The ECM records vehicle and driving condition
information as freeze frame data the moment a DTC is stored. When troubleshooting, freeze frame
data can be helpful in determining whether the vehicle was running or stopped, whether the engine
was warmed up or not, whether the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, as well as other data recorded at the
time of a malfunction.
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(c) Turn the tester on.
(d) Enter the following menus: DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED II
/ DTC INFO / CURRENT CODES.
(e) Read the DTC.
Monitor will run whenever these DTCs are not present. P0100, P0102, P0103 (MAF Sensor)
Battery voltage 10.5 V or more
Time after engine start 1 second or more
ECT at engine start Less than 60
C (140F)
IAT sensor circuit OK
Soak time 5 hours or more
Accumulated MAF 1421.2 g or more
Engine Running
Fuel cut OFF
Difference between ECT at engine start and IAT Less than 40
C (72F)
Battery voltage 10.5 V or more
Engine Running
Soak time 5 hours or more
ECT at engine start 60
C (140F) or more
Accumulated MAF 3298.1 g or more
ECT sensor value change Less than 5
C (9F)
ECT sensor value change Less than 5
C (9F)
Engine coolant temperature Varies with actual engine coolant temperature
1CHECK ANY OTHER DTCS OUTPUT (IN ADDITION TO DTC P0166)
Page 455 of 3000
2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–149
ES
Result
B
A
(a) Remove the thermostat (See page CO-16).
(b) Check the valve opening temperature of the thermostat.
Standard:
80 to 84
C (176 to 183F)
HINT:
In addition to the above check, confirm that the valve is
completely closed when the temperature is below the
standard.
(c) Reinstall the thermostat (See page CO-17).
NG
OK
Display (DTC output) Proceed to
P0116 A
P0116 and other DTCs B
GO TO DTC CHART
2INSPECT THERMOSTAT
REPLACE THERMOSTAT
REPLACE ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
Page 456 of 3000
ES–1502GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
DESCRIPTION
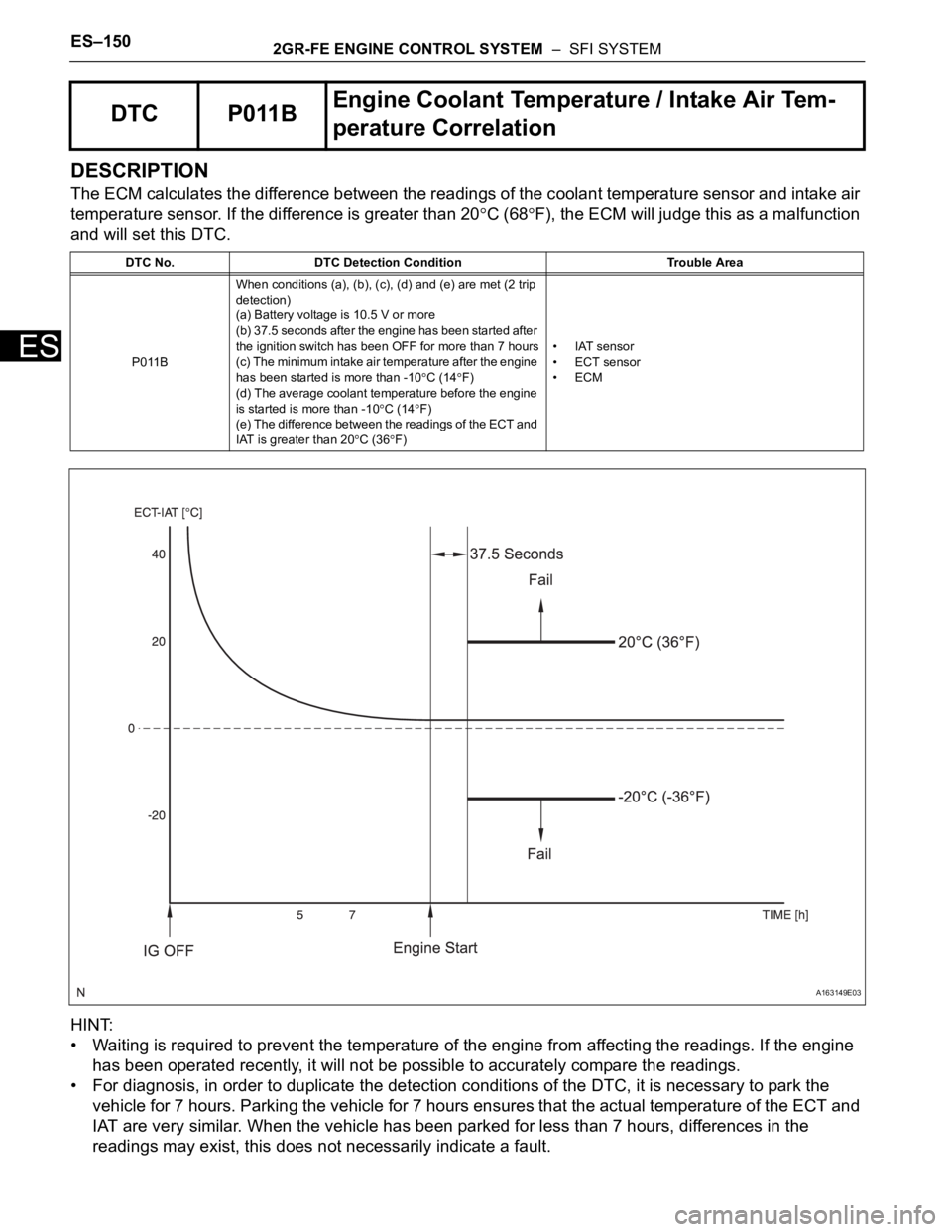
The ECM calculates the difference between the readings of the coolant temperature sensor and intake air
temperature sensor. If the difference is greater than 20
C (68F), the ECM will judge this as a malfunction
and will set this DTC.
HINT:
• Waiting is required to prevent the temperature of the engine from affecting the readings. If the engine
has been operated recently, it will not be possible to accurately compare the readings.
• For diagnosis, in order to duplicate the detection conditions of the DTC, it is necessary to park the
vehicle for 7 hours. Parking the vehicle for 7 hours ensures that the actual temperature of the ECT and
IAT are very similar. When the vehicle has been parked for less than 7 hours, differences in the
readings may exist, this does not necessarily indicate a fault.
DTC P011BEngine Coolant Temperature / Intake Air Tem-
perature Correlation
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P011BWhen conditions (a), (b), (c), (d) and (e) are met (2 trip
detection)
(a) Battery voltage is 10.5 V or more
(b) 37.5 seconds after the engine has been started after
the ignition switch has been OFF for more than 7 hours
(c) The minimum intake air temperature after the engine
has been started is more than -10
C (14F)
(d) The average coolant temperature before the engine
is started is more than -10
C (14F)
(e) The difference between the readings of the ECT and
IAT is greater than 20
C (36F)•IAT sensor
• ECT sensor
•ECM
A163149E03
Page 457 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–151
ES
MONITOR STRATEGY
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(c) Turn the tester on.
(d) Enter the following menus: DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED
OBD ll / DTC INFO / CURRENT CODES.
(e) Read the DTCs.
Result
HINT:
If any DTCs other than P011B are output, troubleshoot
those DTCs first.
B
A
Related DTCs P011B: ECT / IAT sensor correlation
Required Sensors / Components (Main) ECT / IAT sensor
Required Sensors / Components (Related) -
Frequency of Operation Continuous
Duration 2 driving cycles
MIL Operation 2 driving cycles
Sequence of Operation None
The monitor will run whenever these DTCs are not present None
All of following conditions is met Condition 1 and 2
1. All of following conditions is met Condition (a), (b), (c) and (d)
(a) After ignition switch ON and engine not running time More than 20 seconds
(b) Soak Time 7 hours or more
(c) Battery voltage 10.5 V or more
(d) Time after engine start 37.5 seconds or more
2. Either of the following conditions are met Condition (a) and (b)
(a) After engine start minimum IAT -10
C (14F) or more
(b) Before engine start ECT -10
C (14F) or more
Deviated ECT minus Deviated IAT Less than -20
C (-36F) or more than 20C (36F)
1CHECK ANY OTHER DTCS OUTPUT (IN ADDITION P011B)
Display (DTC Output) Proceed to
P011BA
P011B and other DTCsB
GO TO DTC CHART
Page 458 of 3000

ES–1522GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
(a) Leave the vehicle for 7 hours or more.
HINT:
It is necessary leave the vehicle for 7 hours or more to
allow conditions similar to the DTC detection conditions.
(b) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(c) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(d) Turn the tester ON.
(e) Enter the following menus: DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED
OBD ll / DATA LIST / PRIMARY / INTAKE AIR.
(f) Read the value displayed on the tester.
OK:
The intake air temperature and the outside air
temperature are within 10
C (50F) of each other.
HINT:
Temperature readings on the vehicle's outside
temperature gauge (if equipped) are not suitable for
comparing to the IAT reading. The outside temperature
gauge has a significant delay built in to prevent
temperature swings from being displayed on its display.
Use an accurate thermometer to determine the outside
air temperature.
NG
OK
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(c) Turn the tester ON.
(d) Enter the following menus: DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED
OBD ll / DATA LIST / PRIMARY / COOLANT TEMP.
OK:
The coolant temperature and the outside air
temperature are within 10
C (50F) of each other.
HINT:
If the result is not as specified, check that there are heat
sources such as a block heater in the engine
compartment.
NG
OK
2READ VALUE OF INTELLIGENT TESTER (INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE)
REPLACE MASS AIR FLOW METER (See
page ES-504)
3READ VALUE OF INTELLIGENT TESTER (COOLANT TEMPERATURE)
REPLACE ENGINE COOLANT
TEMPERATURE SENSOR (See page ES-516)
REPLACE ECM (See page ES-498)
Page 459 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–153
ES
HINT:
These DTCs relate to the Throttle Position (TP) sensor.
DESCRIPTION
HINT:
This ETC (Electrical Throttle Control System) does not use a throttle cable.
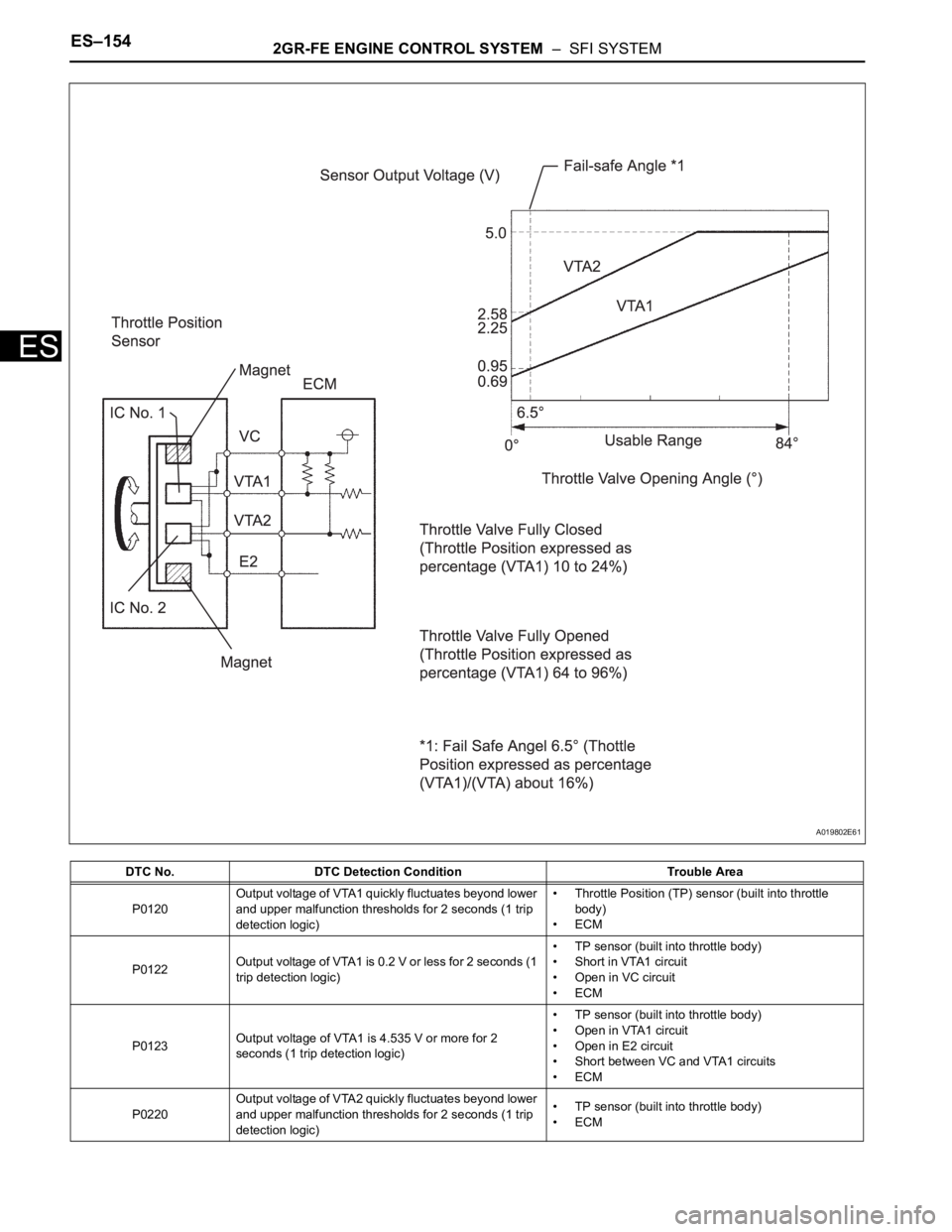
The Throttle Position (TP) sensor is mounted on the throttle body, and detects the opening angle of the
throttle valve. This sensor is a non-contact type, and uses Hall-effect elements, in order to yield accurate
signals, even in extreme driving conditions, such as at high speeds as well as very low speeds.
The TP sensor has two sensor circuits which each transmits a signal, VTA1 and VTA2. VTA1 is used to
detect the throttle valve angle and VTA2 is used to detect malfunctions in VTA1. The sensor signal
voltages vary between 0 V and 5 V in proportion to the throttle valve opening angle, and are transmitted to
the VTA terminals of the ECM.
As the valve closes, the sensor output voltage decreases and as the valve opens, the sensor output
voltage increases. The ECM calculates the throttle valve opening angle according to these signals and
controls the throttle actuator in response to driver inputs. These signals are also used in calculations such
as air-fuel ratio correction, power increase correction and fuel-cut control.
DTC P0120Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "A"
Circuit
DTC P0122Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "A"
Circuit Low Input
DTC P0123Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "A"
Circuit High Input
DTC P0220Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "B"
Circuit
DTC P0222Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "B"
Circuit Low Input
DTC P0223Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "B"
Circuit High Input
DTC P2135Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "A" /
"B" Voltage Correlation
Page 460 of 3000
ES–1542GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P0120Output voltage of VTA1 quickly fluctuates beyond lower
and upper malfunction thresholds for 2 seconds (1 trip
detection logic)• Throttle Position (TP) sensor (built into throttle
body)
•ECM
P0122Output voltage of VTA1 is 0.2 V or less for 2 seconds (1
trip detection logic)• TP sensor (built into throttle body)
• Short in VTA1 circuit
• Open in VC circuit
•ECM
P0123Output voltage of VTA1 is 4.535 V or more for 2
seconds (1 trip detection logic)• TP sensor (built into throttle body)
• Open in VTA1 circuit
• Open in E2 circuit
• Short between VC and VTA1 circuits
•ECM
P0220Output voltage of VTA2 quickly fluctuates beyond lower
and upper malfunction thresholds for 2 seconds (1 trip
detection logic)• TP sensor (built into throttle body)
•ECM
A019802E61
Page 461 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–155
ESHINT:
• When any of these DTCs are set, check the throttle valve opening angle by selecting the following
menu items on the intelligent tester: DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED OBD II / DATA LIST / ETCS /
THROTTLE POS AND THROTTLE POS #2.
• THROTTLE POS denotes the VTA1 signal (expressed in percentages), and THROTTLE POS #2
denotes the VTA2 signal (expressed in voltages).
Reference (Normal Condition)
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The ECM uses the Throttle Position (TP) sensor to monitor the throttle valve opening angle. There are
several checks that the ECM performs to confirm the proper operation of the TP sensor.
• A specific voltage difference is expected between the sensor terminals, VTA1 and VTA2, for each
throttle valve opening angle. If the difference between VTA1 and VTA2 is incorrect, the ECM interprets
this as a malfunction in the sensor, and sets a DTC.
• VTA1 and VTA2 each have a specific voltage range. If VTA1 or VTA2 is outside the normal operating
range, the ECM interprets this as a malfunction in the sensor, and sets a DTC.
• VTA1 and VTA2 should never be close to the same voltage level. If VTA1 is within 0.02 V of VTA2, the
ECM determines that there is a short circuit in the sensor, and sets a DTC.
If the malfunction is not repaired successfully, a DTC is set 2 seconds after the engine is next started.
MONITOR STRATEGY
P0222Output voltage of VTA2 is 1.75 V or less for 2 seconds
(1 trip detection logic)• TP sensor (built into throttle body)
• Short in VTA2 circuit
• Open in VC circuit
•ECM
P0223Output voltage of VTA2 is 4.8 V or more, and VTA1 is
between 0.2 V and 2.02 V, for 2 seconds (1 trip
detection logic)• TP sensor (built into throttle body)
• Open in VTA2 circuit
• Open in E2 circuit
• Short between VC and VTA2 circuits
•ECM
P2135Either condition (a) or (b) is met (1 trip detection logic):
(a) Difference between output voltages of VTA1 and
VTA2 is 0.02 V or less for 0.5 seconds or more
(b) Output voltage of VTA1 is 0.2 V or less, and VTA2 is
0.5 V or less, for 0.4 seconds or more• Short between VTA1 and VTA2 circuits
• TP sensor (built into throttle body)
•ECM
Tester Display Accelerator Pedal Fully Released Accelerator Pedal Fully Depressed
THROTTLE POS 10 to 24% 64 to 96%
THROTTLE POS #2 2.1 to 3.1 V 4.5 to 5.0 V
Related DTCsP0120: Throttle position sensor 1 range check (Fluctuating)
P0122: Throttle position sensor 1 range check (Low voltage)
P0123: Throttle position sensor 1 range check (High voltage)
P0220: Throttle position sensor 2 range check (Fluctuating)
P0222: Throttle position sensor 2 range check (Low voltage)
P0223: Throttle position sensor 2 range check (High voltage)
P2135: Throttle position sensor range check (Correlation)
Required Sensors / Components (Main) Throttle position sensor
Required Sensors / Components (Related) -
Frequency of Operation Continuous
Duration2 seconds: P0120, P0122, P0123, P0220, P0222 and P0223 (Accelerator pedal ON)
10 seconds: P0120, P0122, P0123, P0220, P0222 and P0223 (Accelerator pedal
OFF)
0.5 seconds: P2135
MIL Operation Immediate
Sequence of Operation NoneDTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
Page 462 of 3000

ES–1562GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
P0120:
P0122:
P0123:
P0220:
P0222:
P0223:
P2135:
COMPONENT OPERATING RANGE
FA I L - S A F E
When any of these DTCs, as well as other DTCs relating to ETCS (Electronic Throttle Control System)
malfunctions, are set, the ECM enters fail-safe mode. During fail-safe mode, the ECM cuts the current to
the throttle actuator off, and the throttle valve is returned to a 6.5
throttle angle by the return spring. The
ECM then adjusts the engine output by controlling the fuel injection (intermittent fuel-cut) and ignition
timing, in accordance with the accelerator pedal opening angle, to allow the vehicle to continue at a
minimal speed. If the accelerator pedal is depressed slowly, the vehicle can be driven slowly.
Fail-safe mode continues until a pass condition is detected, and the ignition switch is turned off.
The monitor will run whenever these DTCs are not
presentNone
VTA1 voltage 0.2 V or less, or 4.535 V or more
VTA1 voltage 0.2 V or less
VTA1 voltage 4.535 V or more
VTA2 voltage 1.75 V or less, or 4.8 V or more
VTA2 voltage 1.75 V or less
VTA2 voltage when VTA1 0.2 V to 2.02 V 4.8 V or more
Either of following conditions A or B is met: -
Condition A -
Difference between VTA1 and VTA2 voltages 0.02 V or less
Condition B -
Both of the following conditions are met (a) or (b)
(a) VTA1 voltage 0.2 V or less
(b) VTA2 voltage 1.75 V or less
VTA1 voltage 0.2 to 4.535 V
VTA2 voltage 1.75 to 4.8 V