coolant TOYOTA SIENNA 2007 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SIENNA, Model: TOYOTA SIENNA 2007Pages: 3000, PDF Size: 52.26 MB
Page 376 of 3000

ES–702GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
P0172 System Too Rich
(Bank 1)1. Injector leakage or
blockage
2. MAF meter
3. ECT sensor
4. Ignition system
5. Fuel pressure
6. Gas leakage from
exhaust system
7. Open or short in A/
F sensor (bank 1, 2
sensor 1) circuit
8. A/F sensor (bank
1, 2 sensor 1)
9. A/F sensor heater
(bank 1, 2 sensor 1)
10. A/F sensor heater
relay
11. A/F sensor heater
and A/F sensor
heater relay circuits
12. ECMComes on DTC storedES-180
P0174 System Too Lean
(Bank 2)1. Intake system
2. Injector blockage
3. Mass Air Flow
(MAF) meter
4. Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT)
sensor
5. Fuel pressure
6. Gas leakage from
exhaust system
7. Open or short in A/
F sensor (bank 1, 2
sensor 1) circuit
8. A/F sensor (bank
1, 2 sensor 1)
9. A/F sensor heater
(bank 1, 2 sensor 1)
10. A/F sensor heater
relay
11. A/F sensor heater
and A/F sensor
heater relay circuits
12. PCV valve and
hose
13. PCV hose
connections
14. ECMComes on DTC storedES-180 DTC Code Detection Item Suspected Trouble
AreaMIL Memory See page
Page 378 of 3000

ES–722GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
P0300 Random / Multiple
Cylinder Misfire
Detected1. Open or short in
engine wire harness
2. Connector
connection
3. Vacuum hose
connections
4. Ignition system
5. Injector
6. Fuel pressure
7. Mass Air Flow
(MAF) meter
8. Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT)
sensor
9. Compression
pressure
10. Valve timing
11. Valve clearance
12. PCV valve and
hose
13. PCV hose
connections
14. Intake system
15. ECMComes on DTC storedES-196
P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire
DetectedSame as DTC P0300 Comes on DTC storedES-196
P0302 Cylinder 2 Misfire
DetectedSame as DTC P0300 Comes on DTC storedES-196
P0303 Cylinder 3 Misfire
DetectedSame as DTC P0300 Comes on DTC storedES-196
P0304 Cylinder 4 Misfire
DetectedSame as DTC P0300 Comes on DTC storedES-196
P0305 Cylinder 5 Misfire
DetectedSame as DTC P0300 Comes on DTC storedES-196
P0306 Cylinder 6 Misfire
DetectedSame as DTC P0300 Comes on DTC storedES-196
P0327 Knock Sensor 1
Circuit Low Input
(Bank 1 or Single
Sensor)1. Short in knock
sensor 1 or 2 circuit
2. Knock sensor 1 or
2
3. ECMComes on DTC storedES-213
P0328 Knock Sensor 1
Circuit High Input
(Bank 1 or Single
Sensor)1. Open in knock
sensor 1 or 2 circuit
2. Knock sensor 1 or
2
3. ECMComes on DTC storedES-213
P0332 Knock Sensor 2
Circuit Low Input
(Bank 2)1. Short in knock
sensor 1 or 2 circuit
2. Knock sensor 1 or
2
3. ECMComes on DTC storedES-213
P0333 Knock Sensor 2
Circuit High Input
(Bank 2)1. Open in knock
sensor 1 or 2 circuit
2. Knock sensor 1 or
2
3. ECMComes on DTC storedES-213
P0335 Crankshaft Position
Sensor "A" Circuit1. Open or short in
CKP sensor circuit
2. CKP sensor
3. Sensor plate (CKP
sensor plate)
4. ECMComes on DTC storedES-220 DTC Code Detection Item Suspected Trouble
AreaMIL Memory See page
Page 389 of 3000
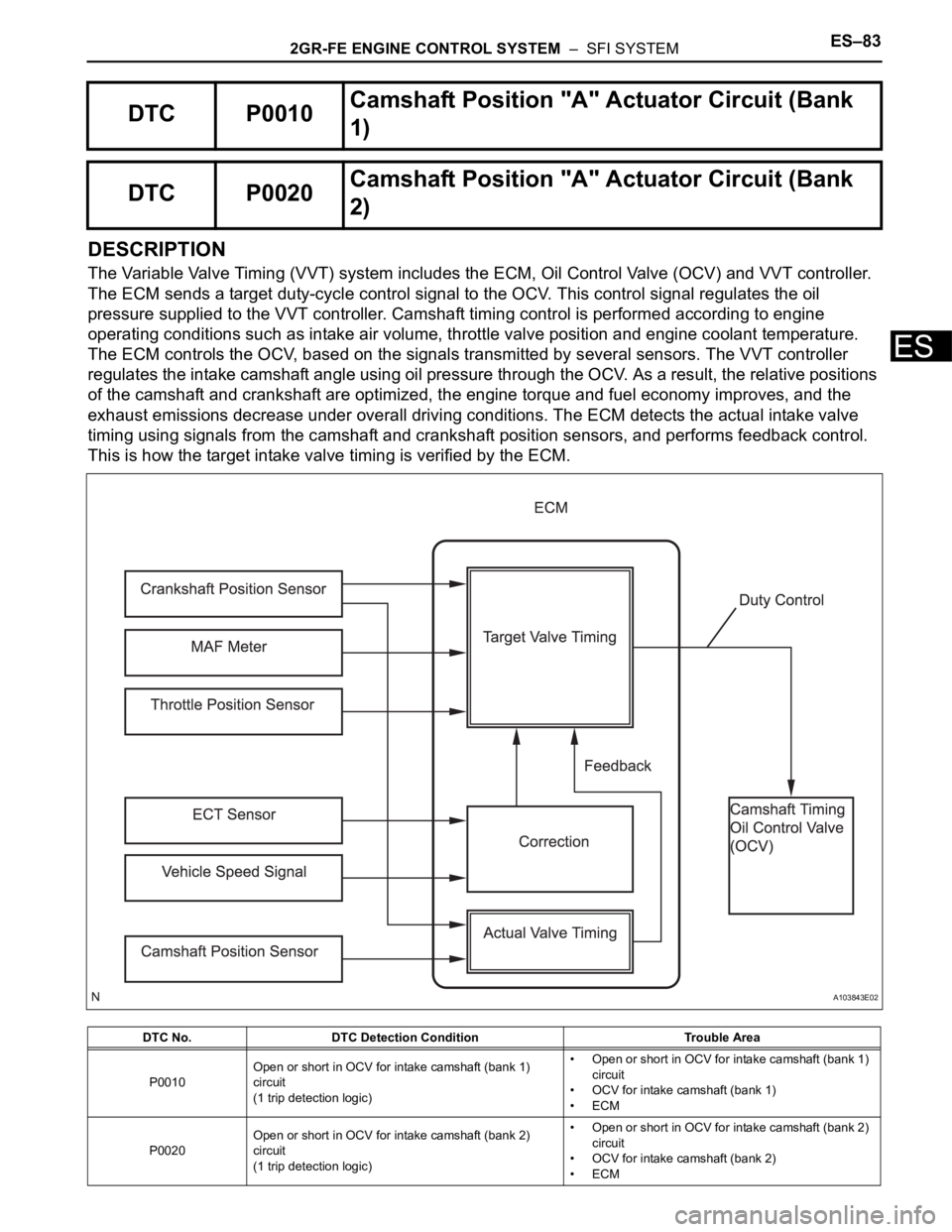
2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–83
ES
DESCRIPTION
The Variable Valve Timing (VVT) system includes the ECM, Oil Control Valve (OCV) and VVT controller.
The ECM sends a target duty-cycle control signal to the OCV. This control signal regulates the oil
pressure supplied to the VVT controller. Camshaft timing control is performed according to engine
operating conditions such as intake air volume, throttle valve position and engine coolant temperature.
The ECM controls the OCV, based on the signals transmitted by several sensors. The VVT controller
regulates the intake camshaft angle using oil pressure through the OCV. As a result, the relative positions
of the camshaft and crankshaft are optimized, the engine torque and fuel economy improves, and the
exhaust emissions decrease under overall driving conditions. The ECM detects the actual intake valve
timing using signals from the camshaft and crankshaft position sensors, and performs feedback control.
This is how the target intake valve timing is verified by the ECM.
DTC P0010Camshaft Position "A" Actuator Circuit (Bank
1)
DTC P0020Camshaft Position "A" Actuator Circuit (Bank
2)
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P0010Open or short in OCV for intake camshaft (bank 1)
circuit
(1 trip detection logic)• Open or short in OCV for intake camshaft (bank 1)
circuit
• OCV for intake camshaft (bank 1)
•ECM
P0020Open or short in OCV for intake camshaft (bank 2)
circuit
(1 trip detection logic)• Open or short in OCV for intake camshaft (bank 2)
circuit
• OCV for intake camshaft (bank 2)
•ECM
A103843E02
Page 395 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–89
ES
3) After above conditions 1) and 2) are met, the OCV is forcibly activated 63 times or more.
DTCs P0011 and P0021 (Advanced Cam Timing) are detected with 1 trip detection logic.
DTCs P0012 and P0022 (Retarded Cam Timing) are detected with 2 trip detection logic.
These DTCs indicate that the VVT controller cannot operate properly due to OCV malfunctions or the
presence of foreign objects in the OCV.
The monitor will not run unless the following conditions are met:
- The engine is warm (the engine coolant temperature is 75
C [167F] or more).
- The vehicle has been driven at more than 40 mph (64 km/h) for 3 minutes.
- The engine has idled for 3 minutes.
MONITOR STRATEGY
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
P0011, P0021:
P0012, P0022:
If the difference between the target and actual camshaft timings is greater than the specified value, the
ECM operates the VVT actuator.
Then, the ECM monitors the camshaft timing change for 5 seconds.
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P0010 (See page ES-77).
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
Related DTCsP0011: Advanced intake camshaft timing (bank 1)
P0012: Retarded intake camshaft timing (bank 1)
P0021: Advanced intake camshaft timing (bank 2)
P0022: Retarded intake camshaft timing (bank 2)
Required sensors / components (Main) VVT OCV, VVT Actuator
Required sensors / components (Related) Crankshaft position sensor, Camshaft position sensor, ECT sensor
Frequency of operation Once per driving cycles
Duration Less than 10 seconds
MIL operationP0011 and P0021: Immediate
P0012 and P0022: 2 driving cycles
Sequence operation None
The monitor will run whenever these DTCs are not
presentP0100, P0101, P0102, P0103 (MAF Sensor), P0115, P0116, P0117, P0118 (ECT
Sensor), P0125 (Insufficient ECT for Closed Loop), P0335 (CKP Sensor), P0340
(CMP Sensor), P0351, P0352, P0353, P0354, P0355, P0356 (Ignitor)
Battery voltage 11 V or more
Engine RPM 500 to 4000 rpm
ECT 75 to 100
C (167 to 212F)
Duration of actual valve timing and target valve timing More than 5
CA (Crankshaft angle)
Valve timing No change in advanced valve timing
Duration of actual valve timing and target valve timing More than 5
CA (Crankshaft angle)
Valve timing No change in retarded valve timing
Abnormal bankAdvanced timing over
(Valve timing is out of specified range)Retarded timing over
(Valve timing is out of specified range)
Bank 1 P0011 P0012
Bank 2 P0021 P0022
Page 401 of 3000
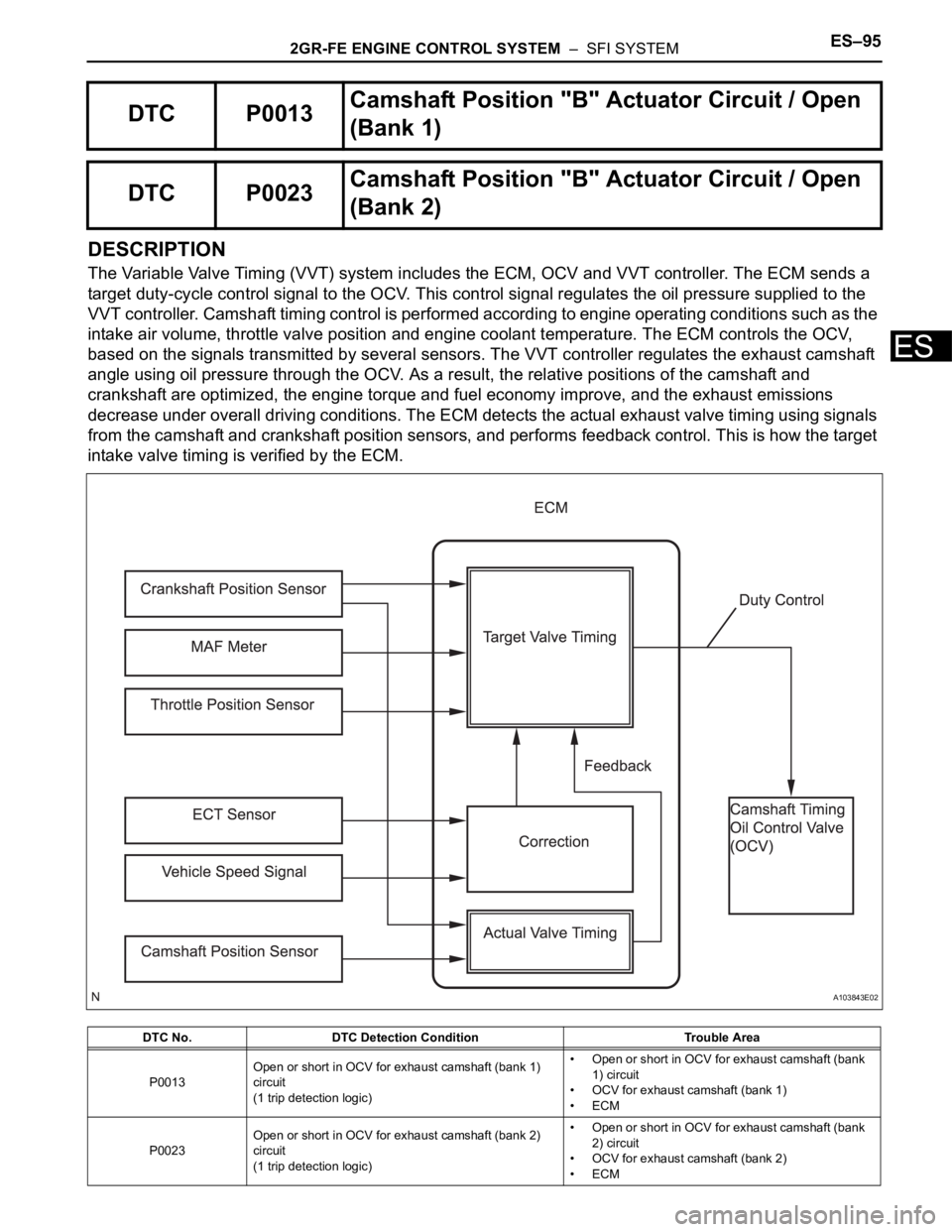
2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–95
ES
DESCRIPTION
The Variable Valve Timing (VVT) system includes the ECM, OCV and VVT controller. The ECM sends a
target duty-cycle control signal to the OCV. This control signal regulates the oil pressure supplied to the
VVT controller. Camshaft timing control is performed according to engine operating conditions such as the
intake air volume, throttle valve position and engine coolant temperature. The ECM controls the OCV,
based on the signals transmitted by several sensors. The VVT controller regulates the exhaust camshaft
angle using oil pressure through the OCV. As a result, the relative positions of the camshaft and
crankshaft are optimized, the engine torque and fuel economy improve, and the exhaust emissions
decrease under overall driving conditions. The ECM detects the actual exhaust valve timing using signals
from the camshaft and crankshaft position sensors, and performs feedback control. This is how the target
intake valve timing is verified by the ECM.
DTC P0013Camshaft Position "B" Actuator Circuit / Open
(Bank 1)
DTC P0023Camshaft Position "B" Actuator Circuit / Open
(Bank 2)
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P0013Open or short in OCV for exhaust camshaft (bank 1)
circuit
(1 trip detection logic)• Open or short in OCV for exhaust camshaft (bank
1) circuit
• OCV for exhaust camshaft (bank 1)
•ECM
P0023Open or short in OCV for exhaust camshaft (bank 2)
circuit
(1 trip detection logic)• Open or short in OCV for exhaust camshaft (bank
2) circuit
• OCV for exhaust camshaft (bank 2)
•ECM
A103843E02
Page 407 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–101
ES
MONITOR STRATEGY
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
Advanced camshaft timing:
Retarded camshaft timing:
If the difference between the target and actual camshaft timings is greater than the specified value, the
ECM operates the VVT actuator.
Then, the ECM monitors the camshaft timing change for 5 seconds.
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P0013 (See page ES-89).
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
• If DTC P0014 or P0015 is displayed, check the bank 1 VVT system circuit.
• Bank 1 refers to the bank that includes cylinder No. 1.
• If DTC P0024 or P0025 is displayed, check the bank 2 VVT system circuit.
• Bank 2 refers to the bank that does not include cylinder No. 1.
Related DTCsP0014: Advanced exhaust camshaft timing (bank 1)
P0015: Retarded exhaust camshaft timing (bank 1)
P0024: Advanced exhaust camshaft timing (bank 2)
P0025: Retarded exhaust camshaft timing (bank 2)
Required Sensors / Components (Main) VVT OCV and VVT Actuator
Required Sensors / Components (Related)P0014 and P0015:
Exhaust camshaft control actuator bank 1
Exhaust OCV bank 1
P0024 and P0025:
Exhaust camshaft control actuator bank 2
Exhaust OCV bank 2
Frequency of Operation Continuously
Duration Less than 10 seconds
MIL OperationP0014 and P0024: Immediate
P0015 and P0025: 2 driving cycles
Sequence of Operation None
The monitor will run whenever these DTCs are not
presentNone
Battery voltage 11 V or more
Engine RPM 500 to 4000 rpm
Engine coolant temperature 75 to 100
C (167 to 212F)
Valve timing No change
Valve timing Advanced position
Valve timing No change
Valve timing Retarded position
Abnormal bankAdvanced timing over
(Valve timing is out of specified range)Retarded timing over
(Valve timing is out of specified range)
Bank 1 P0014 P0015
Bank 2 P0024 P0025
Page 436 of 3000

ES–1302GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
DESCRIPTION
Refer to DTC P0100 (See page ES-116).
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The MAF meter is a sensor that measures the amount of air flowing through the throttle valve. The ECM
uses this information to determine the fuel injection time and to provide an appropriate air-fuel ratio.
Inside the MAF meter, there is a heated platinum wire which is exposed to the flow of intake air. By
applying a specific electrical current to the wire, the ECM heats it to a specific temperature. The flow of
incoming air cools both the wire and an internal thermistor, changing their resistance. To maintain a
constant current value, the ECM varies the voltage applied to these components of the MAF meter. The
voltage level is proportional to the air flow through the sensor, and the ECM uses it to calculate the intake
air volume.
If there is a defect in the sensor, or an open or short in the circuit, the voltage level deviates from the
normal operating range. The ECM interprets this deviation as a malfunction in the MAF meter and sets the
DTC.
Example:
If the voltage is more than 2.2 V, or less than 0.73 V while idling, the ECM determines that there is a
malfunction in the MAF meter and sets the DTC.
MONITOR STRATEGY
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
DTC P0101Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit Range / Perfor-
mance Problem
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P01011. High voltage:
Conditions (a), (b) and (c) continue for more than
10 seconds (2 trip detection logic):
(a) Engine speed is less than 2000 rpm
(b) Engine coolant temperature is 70
C (158F) or
higher
(c) Voltage output of Mass Air Flow (MAF) meter is
more than 1.24 V (varies with Throttle Position [TP]
sensor voltage)
2. Low voltage:
Conditions (a) and (b) continue for more than 10
seconds (2 trip detection logic):
(a) Engine speed is more than 300 rpm
(b) Voltage output of MAF meter is less than 0.80 V
(varies with TP sensor voltage)MAF meter
Related DTCs P0101: Mass air flow meter rationality
Required Sensors / Components (Main) Mass air flow meter
Required Sensors / Components (Related)Crankshaft position sensor, engine coolant temperature sensor and throttle position
sensor
Frequency of Operation Continuous
Duration 10 times
MIL Operation 2 driving cycles
Sequence of Operation None
The monitor will run whenever these DTCs are not
presentP0115, P0116, P0117, P0118 (ECT Sensor), P0120, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0220,
P0222, P0223, P2135 (TP Sensor), P0125 (Insufficient ECT for Closed Loop),
P0335 (CKP Sensor), P0340 (CMP Sensor)
Throttle position (TP sensor voltage) 0.24 V or more
Page 447 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–141
ES
DESCRIPTION
A thermistor is built into the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor, of which the resistance value
varies according to the ECT.
The structure of the sensor and its connection to the ECM are the same as those of the Intake Air
Temperature (IAT) sensor.
HINT:
When any of DTCs P0115, P0117 and P0118 are set, the ECM enters fail-safe mode. During fail-safe
mode, the ECT is estimated to be 80
C (176F) by the ECM. Fail-safe mode continues until a pass
condition is detected.
HINT:
When any of these DTCs are set, check the ECT by selecting the following menu items on the intelligent
tester: DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED OBD II / DATA LIST / PRIMARY / COOLANT TEMP.
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor is used to monitor the ECT. The ECT sensor has a
thermistor with a resistance that varies according to the temperature of the engine coolant. When the
coolant temperature becomes low, the resistance in the thermistor increases. When the temperature
becomes high, the resistance drops.
These variations in resistance are reflected in the voltage output from the sensor. The ECM monitors the
sensor voltage and uses this value to calculate the ECT. When the sensor output voltage deviates from
the normal operating range, the ECM interprets this as a fault in the ECT sensor and sets a DTC.
Example:
If the sensor voltage output is -40
C (-40F) for 0.5 seconds or more, the ECM determines that there is an
open in the ECT sensor circuit, and sets DTC P0118. Conversely, if the voltage output is more than 140
C
(284
F) for 0.5 seconds or more, the ECM determines that there is a short in the sensor circuit, and sets
DTC P0117.
If the malfunction is not repaired successfully, a DTC is set 0.5 seconds after the engine is next started.
MONITOR STRATEGY
DTC P0115 Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit
DTC P0117 Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit Low Input
DTC P0118 Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit High Input
DTC No. Proceed to DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P0115 Step 1Open or short in Engine Coolant Temperature
(ECT) sensor circuit for 0.5 seconds (1 trip
detection logic)• Open or short in ECT sensor circuit
• ECT sensor
•ECM
P0117 Step 4Short in Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT)
sensor circuit for 0.5 seconds (1 trip detection
logic)• Short in ECT sensor circuit
• ECT sensor
•ECM
P0118 Step 2Open in Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT)
sensor circuit for 0.5 seconds (1 trip detection
logic)• Open in ECT sensor circuit
• ECT sensor
•ECM
Temperature Displayed Malfunctions
-40
C (-40F) Open circuit
140
C (284F) or higher Short circuit
Related DTCsP0115: Engine coolant temperature sensor open/short (Fluctuating)
P0117: Engine coolant temperature sensor short (Low electrical voltage)
P0118: Engine coolant temperature sensor open (High electrical voltage)
Page 448 of 3000
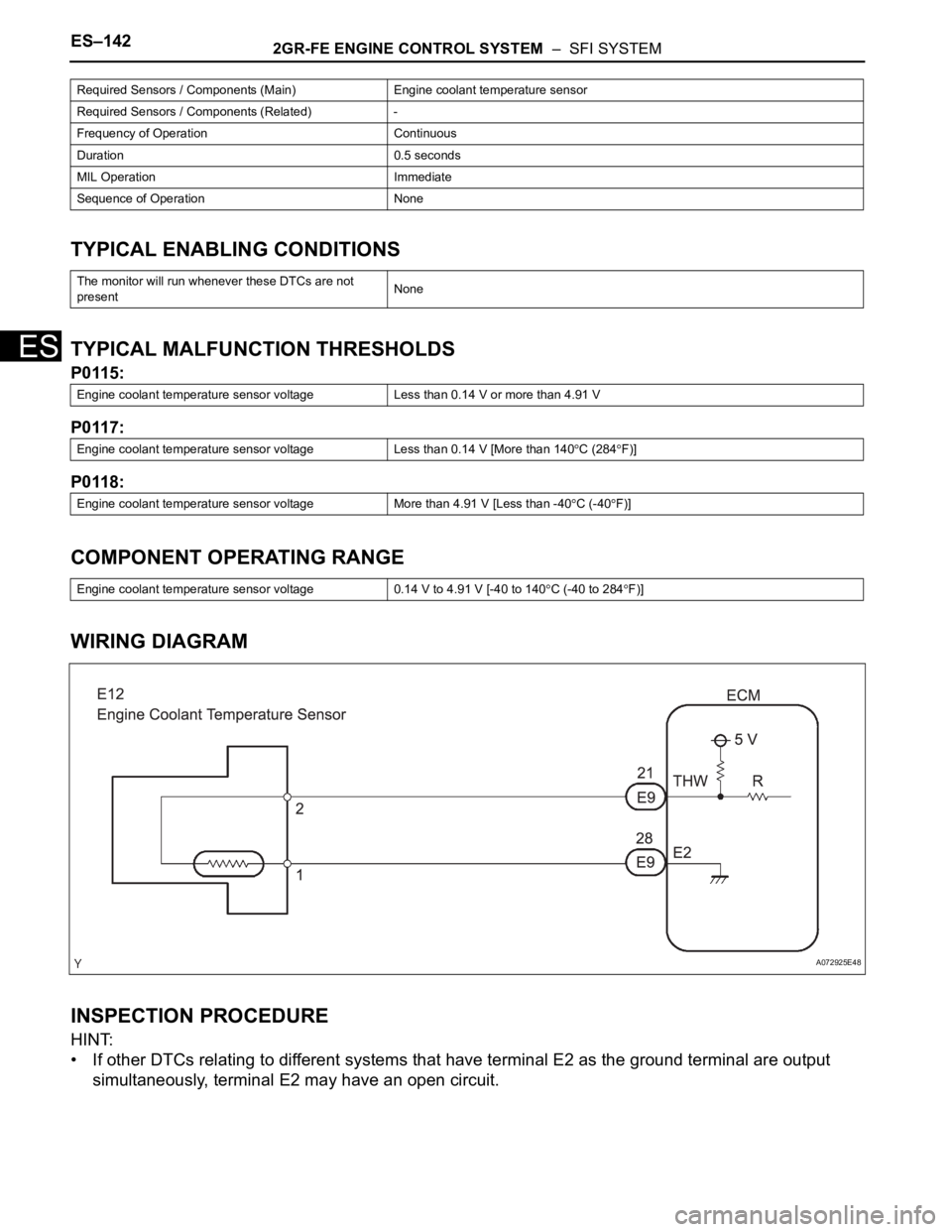
ES–1422GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
P0115:
P0117:
P0118:
COMPONENT OPERATING RANGE
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
• If other DTCs relating to different systems that have terminal E2 as the ground terminal are output
simultaneously, terminal E2 may have an open circuit.
Required Sensors / Components (Main) Engine coolant temperature sensor
Required Sensors / Components (Related) -
Frequency of Operation Continuous
Duration 0.5 seconds
MIL Operation Immediate
Sequence of Operation None
The monitor will run whenever these DTCs are not
presentNone
Engine coolant temperature sensor voltage Less than 0.14 V or more than 4.91 V
Engine coolant temperature sensor voltage Less than 0.14 V [More than 140
C (284F)]
Engine coolant temperature sensor voltage More than 4.91 V [Less than -40
C (-40F)]
Engine coolant temperature sensor voltage 0.14 V to 4.91 V [-40 to 140
C (-40 to 284F)]
A072925E48
Page 449 of 3000
2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–143
ES
• Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. The ECM records vehicle and driving condition
information as freeze frame data the moment a DTC is stored. When troubleshooting, freeze frame
data can be helpful in determining whether the vehicle was running or stopped, whether the engine
was warmed up or not, whether the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, as well as other data recorded at the
time of a malfunction.
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(c) Turn the tester on.
(d) Select the following menu items: DIAGNOSIS /
ENHANCED OBD II / DATA LIST / PRIMARY /
COOLANT TEMP.
(e) Read the value displayed on the tester.
Standard:
Between 80
C and 97C (176F and 207F) with
warm engine.
Result
HINT:
• If there is an open circuit, the intelligent tester
indicates -40
C (-40F).
• If there is a short circuit, the intelligent tester indicates
140
C (284F) or higher.
B
C
A
1READ VALUE OF INTELLIGENT TESTER (ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE)
Temperature Displayed Proceed to
-40
C (-40F) A
140
C (284F) or higher B
Between 80
C and 97C (176F and 207F) C
Go to step 4
CHECK FOR INTERMITTENT PROBLEMS