coolant level TOYOTA SIENNA 2007 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SIENNA, Model: TOYOTA SIENNA 2007Pages: 3000, PDF Size: 52.26 MB
Page 57 of 3000

IN–50INTRODUCTION – TERMS
IN
GLOSSARY OF SAE AND TOYOTA
TERMS
This glossary lists all SAE-J1930 terms and abbreviations
used in this manual in compliance with SAE
recommendations, as well as their TOYOTA equivalents.
SAE
ABBREVIATIONSSAE TERMSTOYOTA TERMS
( )-ABBREVIATIONS
A/C Air Conditioning Air Conditioner
ACL Air Cleaner Air Cleaner, A/CL
AIR Secondary Air Injection Air Injection (AI)
AP Accelerator Pedal -
B+ Battery Positive Voltage +B, Battery Voltage
BARO Barometric Pressure HAC
CAC Charge Air Cooler Intercooler
CARB Carburetor Carburetor
CFI Continuous Fuel Injection -
CKP Crankshaft Position Crank Angle
CL Closed Loop Closed Loop
CMP Camshaft Position Cam Angle
CPP Clutch Pedal Position -
CTOX Continuous Trap Oxidizer -
CTP Closed Throttle Position LL ON, Idle ON
DFI Direct Fuel Injection Direct Injection (DI./INJ)
DI Distributor Ignition -
DLC3 Data Link Connector 3 OBD II Diagnostic Connector
DTC Diagnostic Trouble Code Diagnostic Trouble Code
DTM Diagnostic Test Mode -
ECL Engine Coolant Level -
ECM Engine Control Module Engine Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
ECT Engine Coolant Temperature Coolant Temperature, Water Temperature (THW)
EEPROM Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only MemoryElectrically Erasable Programmable Read Only
Memory (EEPROM), Erasable Programmable Read
Only Memory (EPROM)
EFE Early Fuel Evaporation Cold Mixture Heater (CMH), Heat Control Valve (HCV)
EGR Exhaust Gas Recirculation Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
EI Electronic Ignition Distributorless Ignition (DLI)
EM Engine Modification Engine Modification (EM)
EPROM Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory Programmable Read Only Memory (PROM)
EVAP Evaporative Emission Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP)
FC Fan Control -
FEEPROMFlash Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only
Memory-
FEPROM Flash Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory -
FF Flexible Fuel -
FP Fuel Pump Fuel Pump
GEN Generator Alternator
GND Ground Ground (GND)
HO2S Heated Oxygen SensorHeated Oxygen Sensor (HO
2S)
IAC Idle Air Control Idle Speed Control (ISC)
IAT Intake Air Temperature Intake or Inlet Air Temperature
ICM Ignition Control Module -
Page 197 of 3000

SS–10SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS – 2GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL
SS
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
Part Tightened N*m kgf*cm ft.*lbf
Ignition coil assembly x Cylinder head cover sub-assembly 10 102 7
No. 1 engine hanger x Cylinder head sub-assembly RH 33 337 24
No. 2 engine hanger x Cylinder head sub-assembly LH 33 337 24
Engine mounting bracket RH x Cylinder block sub-assembly 54 551 40
No. 1 oil level gauge guide x Cylinder head sub-assembly 21 214 15
No. 2 oil level gauge guide x Cylinder block sub-assembly 21 214 15
No. 2 idler pulley sub-assembly x Timing chain cover sub-assembly 43 438 32
V-ribbed belt tensioner assembly x Cylinder block sub-assembly 43 438 32
Intake manifold x Cylinder head sub-assembly 21 214 15
Exhaust manifold sub-assembly RH x Cylinder head sub-assembly
RH21 214 15
Exhaust manifold sub-assembly LH x Cylinder head sub-assembly LH 21 214 15
Drive plate & ring gear sub-assembly x Crankshaft 83 850 61
Air cleaner case sub-assembly x Body 5.0 51 44 in.*lbf
Air cleaner case sub-assembly x Air cleaner bracket 5.0 51 44 in.*lbf
Engine coolant temperature x water by-pass joint RR 20 200 14
Engine assembly with Transaxle x Body A 85 867 63
B 32 329 24
No. 2 manifold stay x Exhaust manifold sub-assembly LH 34 347 25
No. 2 manifold stay x Cylinder block sub-assembly 34 347 25
No. 1 air cleaner inlet x Body 5.0 51 44 in.*lbf
No. 2 air cleaner inlet x Body 5.0 51 44 in.*lbf
Battery clamp x Body Bolt 5.5 56 49 in.*lbf
Nut 5.5 56 49 in.*lbf
Throttle body bracket x Intake air surge tank assembly 21 214 15
Throttle body bracket x Cylinder head cover sub-assembly RH 21 21415
No. 1 surge tank stay x Intake air surge tank assembly 21 214 15
No. 1 surge tank stay x Cylinder head cover sub-assembly RH 21 21415
No. 1 cowl top to cowl brace inner x Body 7.5 76 66 in.*lbf
No. 1 cowl top to cowl brace inner x Front outer cowl top panel sub-
assembly7.5 76 66 in.*lbf
Front outer cowl top panel sub-assembly x Body 7.5 76 66 in.*lbf
Fuel pump resistor x Front outer cowl top panel sub-assembly 7.576 66 in.*lbf
Radio setting condenser x Cylinder head cover sub-assembly RH 10102 7
Radio setting condense x Cylinder head cover sub-assembly LH 10 102 7
Intake air resonator sub-assembly x Body 5.0 51 44 in.*lbf
Air cleaner bracket x Body 7.8 80 69 in.*lbf
No. 1 vacuum switching valve assembly x Cylinder head cover sub-
assembly10 102 7
Engine mounting bracket RR x Cylinder block sub-assembly 64 650 47
Steering intermediate shaft x Steering gear 35 360 26
Stabilizer link x Shock absorber 74 755 55
Tie rod assembly x Steering gear 49 500 36
Front speed sensor x Front axle 8.0 85 71 in.*lbf
Front axle hub nut x Front drive shaft 294 2998 217
Cooler compressor assembly x V-ribbed belt tensioner 25 250 18
Cooler compressor assembly x Discharge hose sub-assembly 5.4 55 48 in.*lbf
Cooler compressor assembly x Suction hose sub-assembly 5.4 55 48 in.*lbf
Page 436 of 3000

ES–1302GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
DESCRIPTION
Refer to DTC P0100 (See page ES-116).
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The MAF meter is a sensor that measures the amount of air flowing through the throttle valve. The ECM
uses this information to determine the fuel injection time and to provide an appropriate air-fuel ratio.
Inside the MAF meter, there is a heated platinum wire which is exposed to the flow of intake air. By
applying a specific electrical current to the wire, the ECM heats it to a specific temperature. The flow of
incoming air cools both the wire and an internal thermistor, changing their resistance. To maintain a
constant current value, the ECM varies the voltage applied to these components of the MAF meter. The
voltage level is proportional to the air flow through the sensor, and the ECM uses it to calculate the intake
air volume.
If there is a defect in the sensor, or an open or short in the circuit, the voltage level deviates from the
normal operating range. The ECM interprets this deviation as a malfunction in the MAF meter and sets the
DTC.
Example:
If the voltage is more than 2.2 V, or less than 0.73 V while idling, the ECM determines that there is a
malfunction in the MAF meter and sets the DTC.
MONITOR STRATEGY
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
DTC P0101Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit Range / Perfor-
mance Problem
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P01011. High voltage:
Conditions (a), (b) and (c) continue for more than
10 seconds (2 trip detection logic):
(a) Engine speed is less than 2000 rpm
(b) Engine coolant temperature is 70
C (158F) or
higher
(c) Voltage output of Mass Air Flow (MAF) meter is
more than 1.24 V (varies with Throttle Position [TP]
sensor voltage)
2. Low voltage:
Conditions (a) and (b) continue for more than 10
seconds (2 trip detection logic):
(a) Engine speed is more than 300 rpm
(b) Voltage output of MAF meter is less than 0.80 V
(varies with TP sensor voltage)MAF meter
Related DTCs P0101: Mass air flow meter rationality
Required Sensors / Components (Main) Mass air flow meter
Required Sensors / Components (Related)Crankshaft position sensor, engine coolant temperature sensor and throttle position
sensor
Frequency of Operation Continuous
Duration 10 times
MIL Operation 2 driving cycles
Sequence of Operation None
The monitor will run whenever these DTCs are not
presentP0115, P0116, P0117, P0118 (ECT Sensor), P0120, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0220,
P0222, P0223, P2135 (TP Sensor), P0125 (Insufficient ECT for Closed Loop),
P0335 (CKP Sensor), P0340 (CMP Sensor)
Throttle position (TP sensor voltage) 0.24 V or more
Page 494 of 3000

ES–1882GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
DESCRIPTION
The fuel trim is related to the feedback compensation value, not to the basic injection time. The fuel trim
consists of both the short-term and long-term fuel trims.
The short-term fuel trim is fuel compensation that is used to constantly maintain the air-fuel ratio at
stoichiometric levels. The signal from the Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor indicates whether the air-fuel ratio is
rich or lean compared to the stoichiometric ratio. This triggers a reduction in the fuel injection volume if the
air-fuel ratio is rich and an increase in the fuel injection volume if it is lean.
Factors such as individual engine differences, wear over time and changes in operating environment
cause short-term fuel trim to vary from the central value. The long-term fuel trim, which controls overall
fuel compensation, compensates for long-term deviations in the fuel trim from the central value caused by
the short-term fuel trim compensation.
If both the short-term and long-term fuel trims are lean or rich beyond predetermined values, it is
interpreted as a malfunction, and the ECM illuminates the MIL and sets a DTC.
HINT:
• When DTC P0171 or P0174 is set, the actual air-fuel ratio is on the lean side. When DTC P0172 or
P0175 is set, the actual air-fuel ratio is on the rich side.
• If the vehicle runs out of fuel, the air-fuel ratio is lean and DTC P0171 or P0174 may be set. The MIL is
then illuminated.
DTC P0171 System Too Lean (Bank 1)
DTC P0172 System Too Rich (Bank 1)
DTC P0174 System Too Lean (Bank 2)
DTC P0175 System Too Rich (Bank 2)
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P0171
P0174With warm engine and stable air-fuel ratio feedback,
fuel trim considerably in error to lean side (2 trip
detection logic)• Intake system
• Injector blockage
• Mass Air Flow (MAF) meter
• Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor
• Fuel pressure
• Gas leakage from exhaust system
• Open or short in A/F sensor (bank 1, 2 sensor 1)
circuit
• A/F sensor (bank 1, 2 sensor 1)
• A/F sensor heater (bank 1, 2 sensor 1)
• A/F sensor heater relay
• A/F sensor heater and A/F sensor heater relay
circuits
• PCV valve and hose
• PCV hose connections
•ECM
P0172
P0175With warm engine and stable air-fuel ratio feedback,
fuel trim considerably in error to rich side (2 trip
detection logic)• Injector leakage or blockage
• MAF meter
• ECT sensor
• Ignition system
• Fuel pressure
• Gas leakage from exhaust system
• Open or short in A/F sensor (bank 1, 2 sensor 1)
circuit
• A/F sensor (bank 1, 2 sensor 1)
• A/F sensor heater (bank 1, 2 sensor 1)
• A/F sensor heater relay
• A/F sensor heater and A/F sensor heater relay
circuits
•ECM
Page 510 of 3000
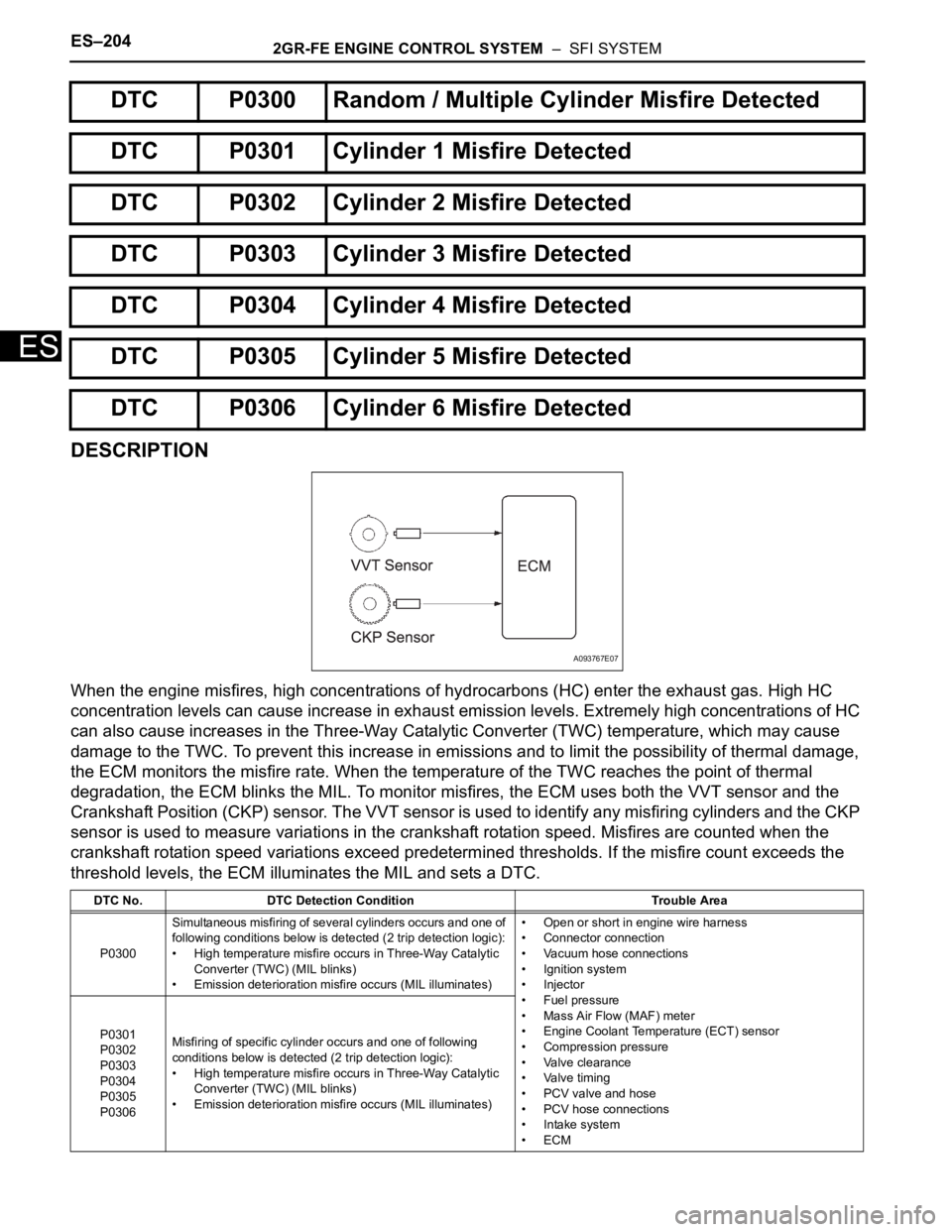
ES–2042GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
DESCRIPTION
When the engine misfires, high concentrations of hydrocarbons (HC) enter the exhaust gas. High HC
concentration levels can cause increase in exhaust emission levels. Extremely high concentrations of HC
can also cause increases in the Three-Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) temperature, which may cause
damage to the TWC. To prevent this increase in emissions and to limit the possibility of thermal damage,
the ECM monitors the misfire rate. When the temperature of the TWC reaches the point of thermal
degradation, the ECM blinks the MIL. To monitor misfires, the ECM uses both the VVT sensor and the
Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor. The VVT sensor is used to identify any misfiring cylinders and the CKP
sensor is used to measure variations in the crankshaft rotation speed. Misfires are counted when the
crankshaft rotation speed variations exceed predetermined thresholds. If the misfire count exceeds the
threshold levels, the ECM illuminates the MIL and sets a DTC.
DTC P0300 Random / Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
DTC P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected
DTC P0302 Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected
DTC P0303 Cylinder 3 Misfire Detected
DTC P0304 Cylinder 4 Misfire Detected
DTC P0305 Cylinder 5 Misfire Detected
DTC P0306 Cylinder 6 Misfire Detected
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P0300Simultaneous misfiring of several cylinders occurs and one of
following conditions below is detected (2 trip detection logic):
• High temperature misfire occurs in Three-Way Catalytic
Converter (TWC) (MIL blinks)
• Emission deterioration misfire occurs (MIL illuminates)• Open or short in engine wire harness
• Connector connection
• Vacuum hose connections
• Ignition system
• Injector
• Fuel pressure
• Mass Air Flow (MAF) meter
• Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor
• Compression pressure
• Valve clearance
• Valve timing
• PCV valve and hose
• PCV hose connections
• Intake system
•ECM P0301
P0302
P0303
P0304
P0305
P0306Misfiring of specific cylinder occurs and one of following
conditions below is detected (2 trip detection logic):
• High temperature misfire occurs in Three-Way Catalytic
Converter (TWC) (MIL blinks)
• Emission deterioration misfire occurs (MIL illuminates)
A093767E07
Page 602 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–309
ES
NOTICE:
In this operation, the engine must be cold (the same level
as the engine coolant temperature recorded in the freeze
frame data).
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(c) Turn the tester on.
(d) Clear the DTCs (See page ES-39).
(e) Switch the ECM from normal mode to check mode using
the tester (See page ES-43).
(f) Start the engine to idle for a minute.
OK:
Stable fast idling.
(g) Read the DTCs.
OK:
No DTC output.
NEXT
15CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS (DTC P050A)
END
Page 608 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–315
ES
NEXT
NOTICE:
In this operation, the engine must be cold (the same level
as the engine coolant temperature recorded in the freeze
frame data).
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(c) Turn the tester on.
(d) Clear the DTCs.
(e) Switch the ECM from normal mode to check mode using
the tester.
(f) Start the engine to idle for a minute.
OK:
Stable fast idling.
(g) Read the DTCs.
OK:
No DTC output.
NEXT
14REPAIR OR REPLACE THROTTLE BODY ASSEMBLY
Go to step 15
15CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS (DTC P050B)
END
Page 1238 of 3000

2GR-FE COOLING – COOLING SYSTEMCO–1
CO
COOLING SYSTEM
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION
1. INSPECT FOR COOLANT LEAK
CAUTION:
Do not remove the radiator cap while the engine and
radiator are still hot. Pressurized, hot engine coolant
and steam may be released and cause serious
burns.
NOTICE:
Before performing each inspection, turn the A/C
switch OFF.
(a) Fill the radiator with coolant and attach a radiator
cap tester.
(b) Warm up the engine.
(c) Using a radiator cap tester, increase the pressure
inside the radiator to 118 kPa (1.2 kgf/cm
2, 17 psi),
and check that the pressure does not drop.
If the pressure drops, check the hoses, radiator and
water pump for leaks. If no external leaks are found,
check the heater core, cylinder block and cylinder
head.
2. INSPECT ENGINE COOLANT LEVEL IN RESERVOIR
(a) Check that the engine coolant level is between the
LOW and FULL lines when the engine is cold.
If the engine coolant level is low, check for leaks and
add "TOYOTA Super Long Life Coolant" or similar
high quality ethylene glycol based non-silicate, non-
amine, non-nitrite and non-borate coolant with long-
life hybrid organic acid technology to the FULL line.
NOTICE:
Do not substitute plain water for engine coolant.
3. INSPECT ENGINE COOLANT QUALITY
(a) Remove the radiator cap.
CAUTION:
Do not remove the radiator cap while the engine
and radiator are still hot. Pressurized, hot
engine coolant and steam may be released and
cause serious burns.
(b) Check if there are any excessive deposits of rust or
scales around the radiator cap and radiator filler
hole. Also, the coolant should be free of oil.
If excessively dirty, clean the coolant passage and
replace the coolant.
(c) Install the radiator cap.
A161453
Page 1253 of 3000

2GR-FE COOLING – COOLANTCO–7
CO
4. ADD ENGINE COOLANT
(a) Tighten the radiator drain cock plug by hand.
(b) Tighten the 2 cylinder block drain cock plugs.
Torque: 13 N*m (130 kgf*cm, 9 ft.*lbf) for
cylinder block drain cock plugs
(c) Remove the air drain cock plug from the water inlet
housing.
(d) Loosen the air drain plug at the top of the radiator 3
or 4 turns.
(e) Add TOYOTA Super Long Life Coolant (SLLC) to
the radiator inlet opening until coolant overflows
from the engine air drain cock hole. Then install the
air drain cock plug to the water inlet housing.
Torque: 13 N*m (130 kgf*cm, 9 ft.*lbf) for air
drain cock plug
(f) Continue to add TOYOTA Super Long Life Coolant
(SLLC) to the radiator inlet opening until coolant
overflows from the radiator air drain hole. Then
close the air drain plug at the top of the radiator.
HINT:
If the coolant level at the radiator inlet opening
drops after squeezing the No. 1 and No. 2 radiator
hoses, add coolant.
(g) Slowly fill the radiator with TOYOTA Super Long Life
Coolant (SLLC).
Standard capacity:
11.3 liters (12.0 US qts, 10.0 Imp. qts)
HINT:
• TOYOTA vehicles are filled with TOYOTA SLLC
at the factory. In order to avoid damage to the
engine cooling system and other technical
problems, only use TOYOTA SLLC or similar
high quality ethylene glycol based non-silicate,
non-amine, non-nitrite, non-borate coolant with
long-life hybrid organic acid technology (coolant
with long-life hybrid organic acid technology
consists of a combination of low phosphates and
organic acids).
• Contact your TOYOTA dealer for further details.
NOTICE:
Never use water as a substitute for engine
coolant.
(h) Slowly pour coolant into the radiator reservoir tank
until it reaches the FULL line.
(i) Squeeze the No. 1 and No. 2 radiator hoses several
times by hand, and then check the level of the
coolant.
If the coolant level is low, add coolant.
A162799E01
Page 1298 of 3000
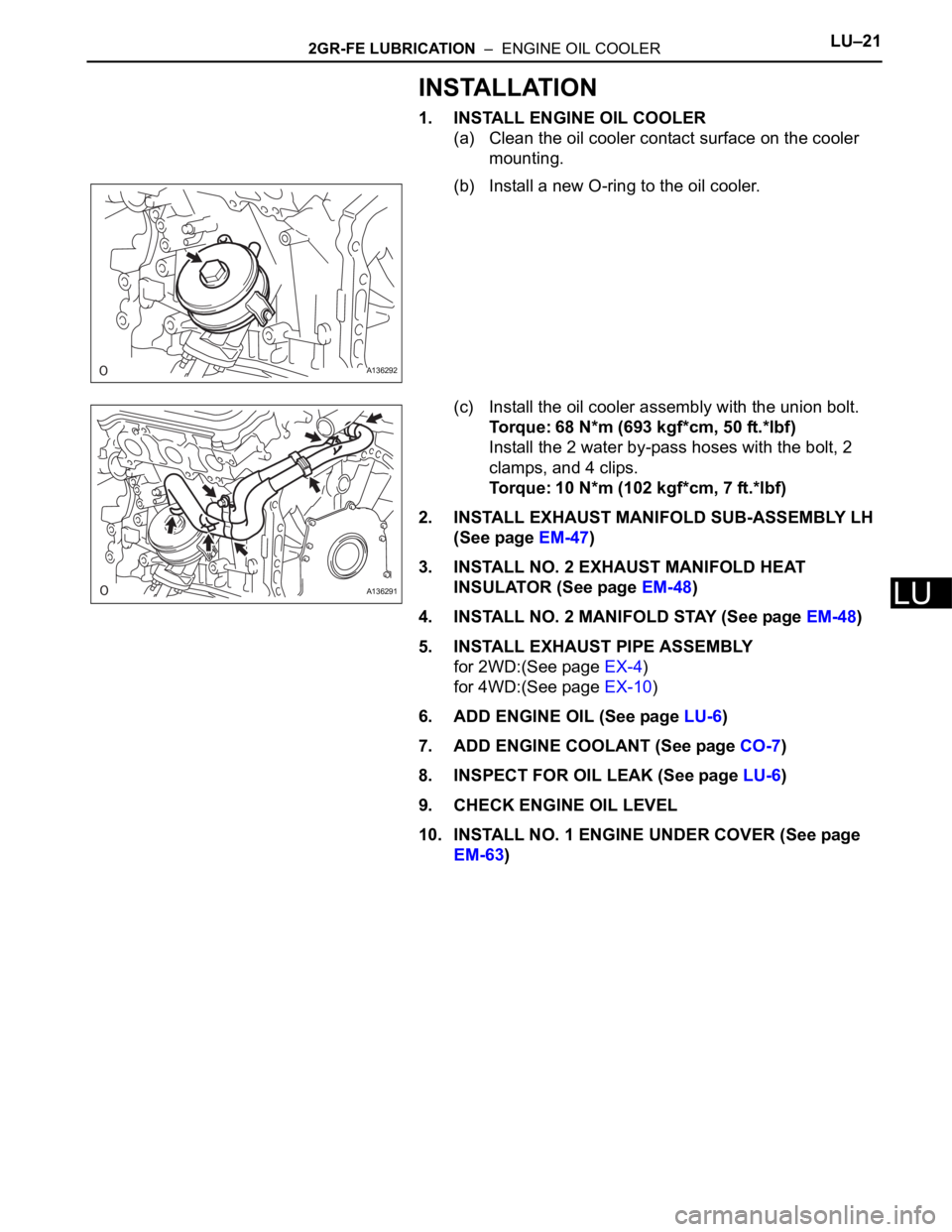
2GR-FE LUBRICATION – ENGINE OIL COOLERLU–21
LU
INSTALLATION
1. INSTALL ENGINE OIL COOLER
(a) Clean the oil cooler contact surface on the cooler
mounting.
(b) Install a new O-ring to the oil cooler.
(c) Install the oil cooler assembly with the union bolt.
Torque: 68 N*m (693 kgf*cm, 50 ft.*lbf)
Install the 2 water by-pass hoses with the bolt, 2
clamps, and 4 clips.
Torque: 10 N*m (102 kgf*cm, 7 ft.*lbf)
2. INSTALL EXHAUST MANIFOLD SUB-ASSEMBLY LH
(See page EM-47)
3. INSTALL NO. 2 EXHAUST MANIFOLD HEAT
INSULATOR (See page EM-48)
4. INSTALL NO. 2 MANIFOLD STAY (See page EM-48)
5. INSTALL EXHAUST PIPE ASSEMBLY
for 2WD:(See page EX-4)
for 4WD:(See page EX-10)
6. ADD ENGINE OIL (See page LU-6)
7. ADD ENGINE COOLANT (See page CO-7)
8. INSPECT FOR OIL LEAK (See page LU-6)
9. CHECK ENGINE OIL LEVEL
10. INSTALL NO. 1 ENGINE UNDER COVER (See page
EM-63)
A136292
A136291