VOLKSWAGEN CORRADO 1993 Repair Manual
Manufacturer: VOLKSWAGEN, Model Year: 1993, Model line: CORRADO, Model: VOLKSWAGEN CORRADO 1993Pages: 920, PDF Size: 6.92 MB
Page 511 of 920

E - THEORY/OPERATION
Article Text (p. 6)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:09PM
EMISSION SYSTEMS
AIR INJECTION SYSTEM
The air injection system consists of electrically operated
air pump, inlet valve, shut-off valve (mounted between intake ports
for cylinders No. 2 and 4), and air pump control relay.
The Electronic Control Module (ECM) control operation of air
injection system air pump by completing the ground circuit of the air
pump control relay (located above brake master cylinder). In addition,
the relay operates the secondary air injection inlet valve.
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM
The EGR system consist of EGR valve, EGR frequency valve, and
EGR temperature sensor. All Corrado SLC models are equipped with the
EGR system. The EGR system is switched on when engine coolant
temperature reaches 122øF (50øC). The system recirculates a small
portion of exhaust gas into the intake air/fuel mixture to reduce
nitrous oxide emissions (NOx).
EGR Frequency Valve
The EGR frequency valve is mounted on back of intake
manifold. The frequency valve controls the amount of vacuum supplied
to the EGR valve. The ECM, depending on engine speed and load,
controls the frequency valve's ground circuit. In doing so, the ECM
controls the amount of recirculated exhaust gas entering the engine.
EGR Temperature Sensor
Sensor is located in EGR valve exhaust gas recirculation
channel. The EGR temperature sensor measures exhaust gas temperature.
The electrical resistance of the sensor decreases as the temperature
of the exhaust gas increases. The signal generated by the EGR
temperature sensor is ONLY used for diagnosis of the EGR system.
FUEL EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS SYSTEM
Fuel Evaporative (Frequency) Valve
The ECM determines the duty cycle of the frequency valve to
regulate the flow of fuel vapors from fuel evaporative (carbon)
canister into engine. When no current is supplied to valve, it remains
in the open position. The valve is closed (100% duty cycle) when the
engine is started cold. A spring operated check valve inside the
frequency valve closes when the engine is off. This prevents fuel
vapors from entering intake manifold and causing a rich mixture during
engine restart.
Fuel Tank Venting
The engine speed, engine load, engine coolant temperature,
and throttle valve potentiometer input signals are used by the ECM to
control fuel tank venting. Fuel vapors from fuel tank are vented to
fuel evaporative (carbon) canister. When engine is warm and above idle
Page 512 of 920

E - THEORY/OPERATION
Article Text (p. 7)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:09PM
speed, the vapors will be drawn into intake manifold. Depending on
engine load and oxygen sensor signal, the fuel evaporative (frequency)
valve will regulate the amount of vapors entering the intake manifold.
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM
The Electronic Control Module (ECM) recognizes faults (open
circuits, short circuits, missing signals, or a continuously applied
signal voltage) in the following circuits/components.
* EGR Frequency Valve
* EGR Temperature Sensor
* Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
* Engine Speed (RPM)/Reference Sensor
* Fuel Evaporative (Frequency) Valve
* Hall Effect Sensor
* Idle Air Control/Stabilizer Valve
* Intake Air Temperature Sensor
* Knock Sensor(s)
* Throttle Valve Potentiometer
* Oxygen Sensor
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR (CHECK ENGINE) LIGHT
All California models are equipped with a malfunction
indicator (CHECK ENGINE) light. If CHECK ENGINE light comes on and
remains on during vehicle operation, cause of malfunction must be
determined. See the G - TESTS W/CODES article.
END OF ARTICLE
Page 513 of 920

ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE WARNING - BASIC INFORMATION
Article Text
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:09PM
ARTICLE BEGINNING
GENERAL INFORMATION
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Warning - Basic Information
All Makes amd Models
* PLEASE READ THIS FIRST *
NOTE: This article is intended for general information purposes
only.
INTRODUCTION
All Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) sensitive components
contain solid state circuits (transistors, diodes, semiconductors)
that may become damaged when contacted with an electrostatic charge.
The following information applies to all ESD sensitive devices. The
ESD symbol shown in Fig. 1 may be used on schematics to indicate which
components are ESD sensitive. See Fig. 1. Although different
manufactures may display different symbols to represent ESD sensitive
devices, the handling and measuring precautions and procedures are the
same.Fig. 1: Sample ESD Symbol
HANDLING STATIC-SENSITIVE CIRCUITS/DEVICES
When handling an electronic part that is ESD sensitive, the
technician should follow these guidelines to reduce any possible
electrostatic charge build-up on the technician's body and the
electronic part.
Page 514 of 920
ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE WARNING - BASIC INFORMATION
Article Text (p. 2)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:09PM
1) Always touch a known good ground source before handling
the part. This should be repeated while handling the part and more
frequently after sitting down from a standing position, sliding across
the seat or walking a distance.
2) Avoid touching electrical terminals of the part, unless
instructed by a diagnostic procedure.
3) DO NOT open the package of a new part until it is time to
install the part.
4) Before removing the part from its package, ground the
package to a known good ground source.
CHECKING STATIC-SENSITIVE CIRCUITS/DEVICES
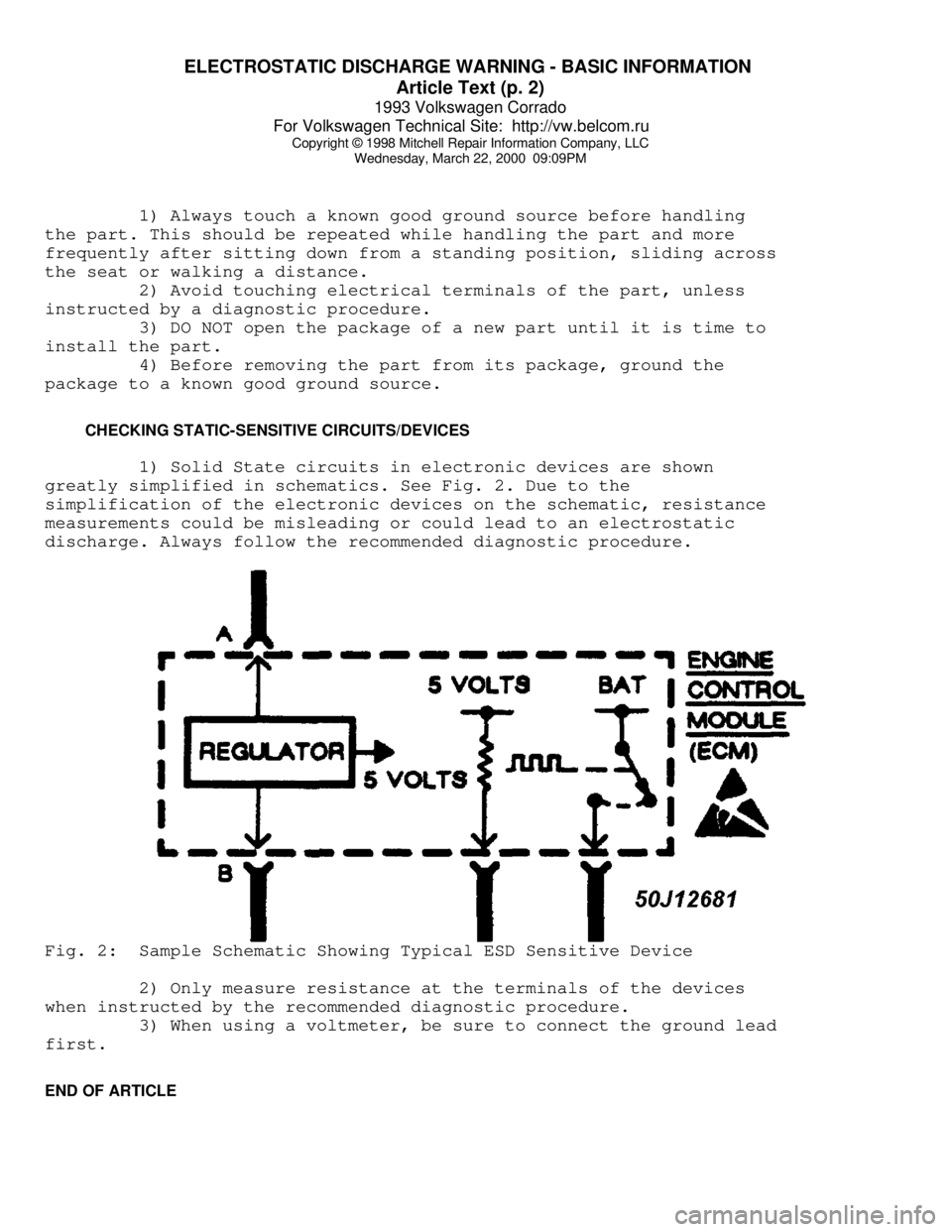
1) Solid State circuits in electronic devices are shown
greatly simplified in schematics. See Fig. 2. Due to the
simplification of the electronic devices on the schematic, resistance
measurements could be misleading or could lead to an electrostatic
discharge. Always follow the recommended diagnostic procedure.Fig. 2: Sample Schematic Showing Typical ESD Sensitive Device
2) Only measure resistance at the terminals of the devices
when instructed by the recommended diagnostic procedure.
3) When using a voltmeter, be sure to connect the ground lead
first.
END OF ARTICLE
Page 515 of 920
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES
Article Text
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:09PM
ARTICLE BEGINNING
GENERAL INFORMATION
All Makes Emission Control Visual Inspection Procedures
All Models
PLEASE READ THIS FIRST
This article is provided for general information only. Not
all information applies to all makes and models. For more complete
information, see appropriate article(s) in the ENGINE PERFORMANCE
Section.
EMISSION CONTROL LABELS
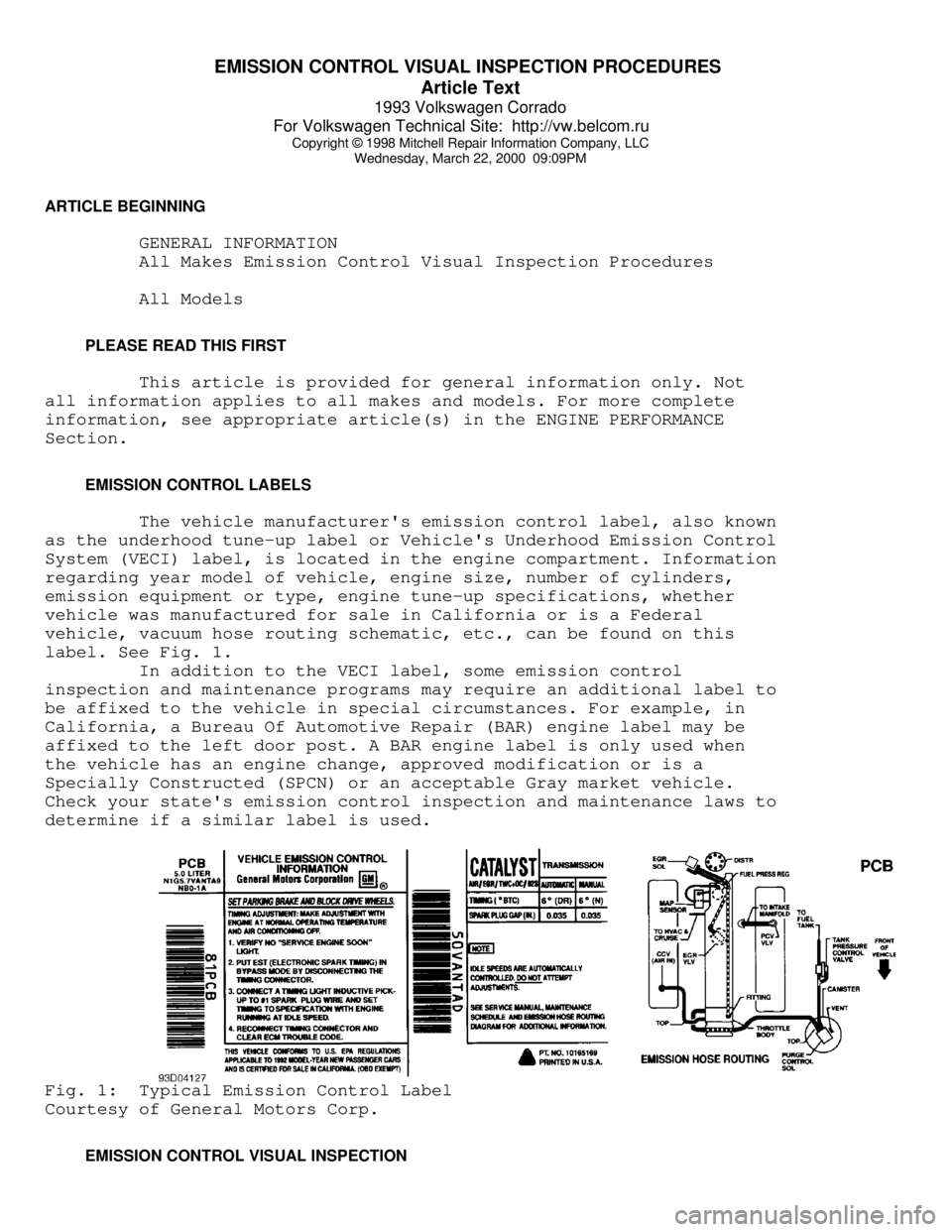
The vehicle manufacturer's emission control label, also known
as the underhood tune-up label or Vehicle's Underhood Emission Control
System (VECI) label, is located in the engine compartment. Information
regarding year model of vehicle, engine size, number of cylinders,
emission equipment or type, engine tune-up specifications, whether
vehicle was manufactured for sale in California or is a Federal
vehicle, vacuum hose routing schematic, etc., can be found on this
label. See Fig. 1.
In addition to the VECI label, some emission control
inspection and maintenance programs may require an additional label to
be affixed to the vehicle in special circumstances. For example, in
California, a Bureau Of Automotive Repair (BAR) engine label may be
affixed to the left door post. A BAR engine label is only used when
the vehicle has an engine change, approved modification or is a
Specially Constructed (SPCN) or an acceptable Gray market vehicle.
Check your state's emission control inspection and maintenance laws to
determine if a similar label is used.Fig. 1: Typical Emission Control Label
Courtesy of General Motors Corp.
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION
Page 516 of 920
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES
Article Text (p. 2)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:09PM
NOTE: The following emission control visual inspection procedures
should be used as a guide only. When performing a visual
inspection, always follow your state's recommended
inspection procedures.
A visual inspection is made to determine if any required
emission control devices are missing, modified or disconnected.
Missing, modified or disconnected systems must be made fully
operational before a vehicle can be certified.
POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION (PCV)
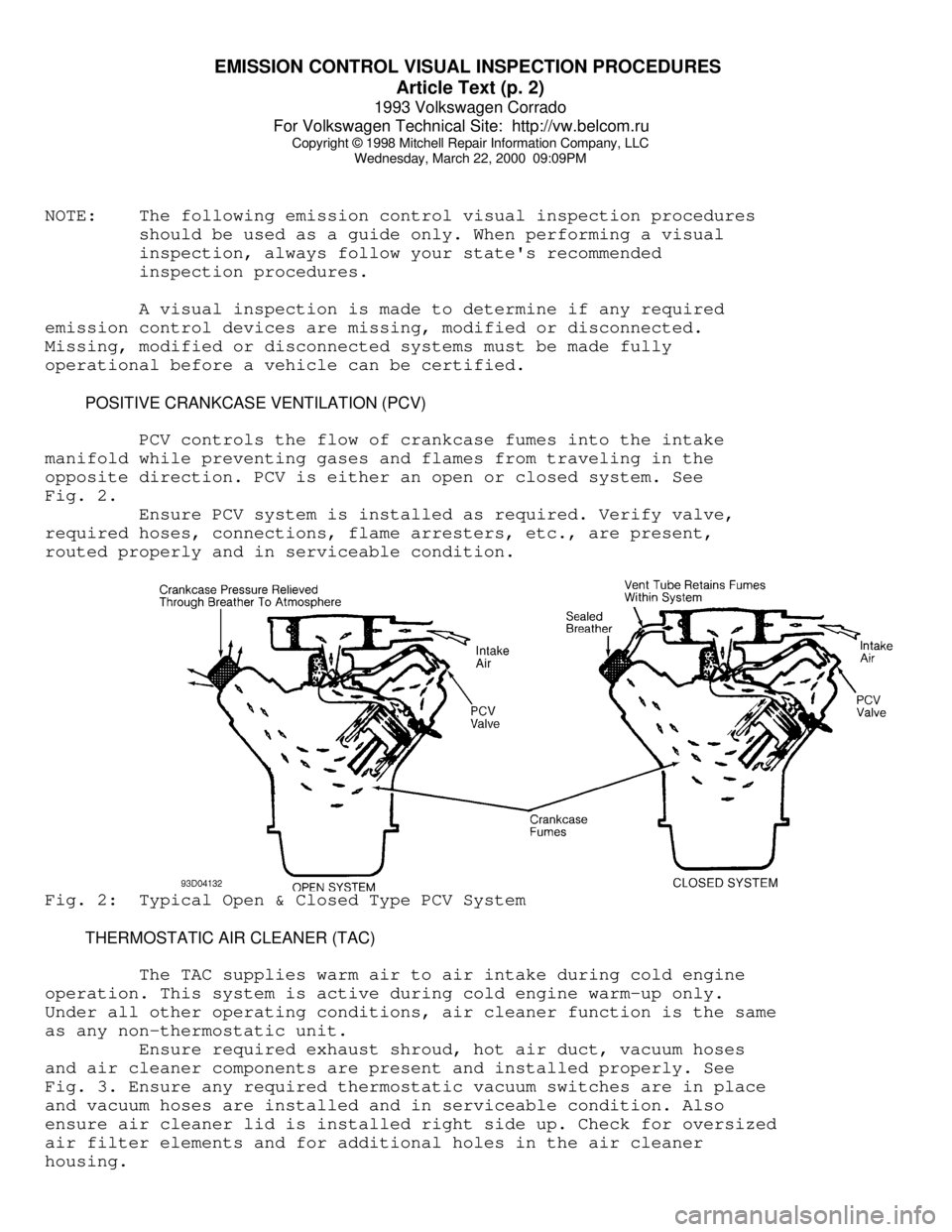
PCV controls the flow of crankcase fumes into the intake
manifold while preventing gases and flames from traveling in the
opposite direction. PCV is either an open or closed system. See
Fig. 2.
Ensure PCV system is installed as required. Verify valve,
required hoses, connections, flame arresters, etc., are present,
routed properly and in serviceable condition.Fig. 2: Typical Open & Closed Type PCV System
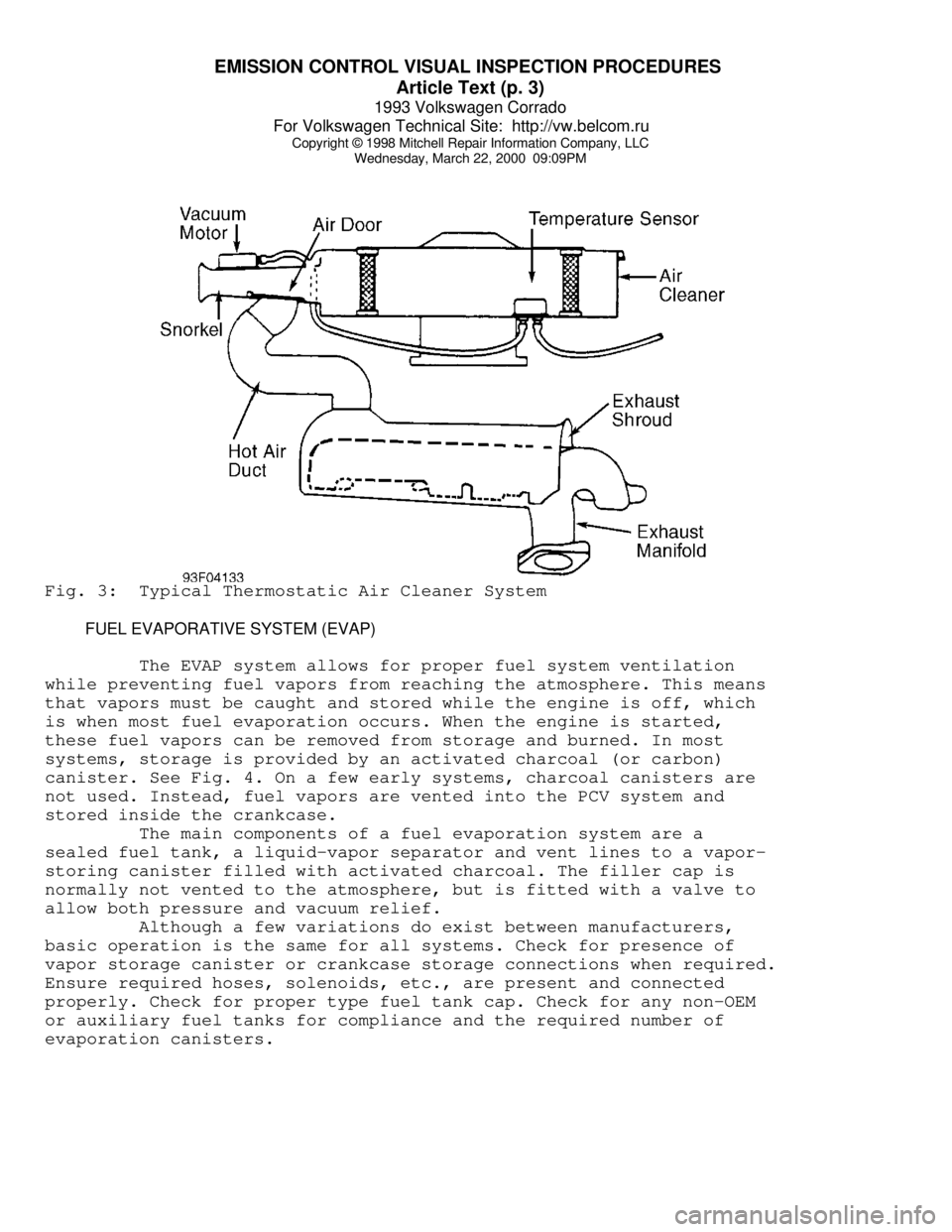
THERMOSTATIC AIR CLEANER (TAC)
The TAC supplies warm air to air intake during cold engine
operation. This system is active during cold engine warm-up only.
Under all other operating conditions, air cleaner function is the same
as any non-thermostatic unit.
Ensure required exhaust shroud, hot air duct, vacuum hoses
and air cleaner components are present and installed properly. See
Fig. 3. Ensure any required thermostatic vacuum switches are in place
and vacuum hoses are installed and in serviceable condition. Also
ensure air cleaner lid is installed right side up. Check for oversized
air filter elements and for additional holes in the air cleaner
housing.
Page 517 of 920
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES
Article Text (p. 3)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:09PMFig. 3: Typical Thermostatic Air Cleaner System
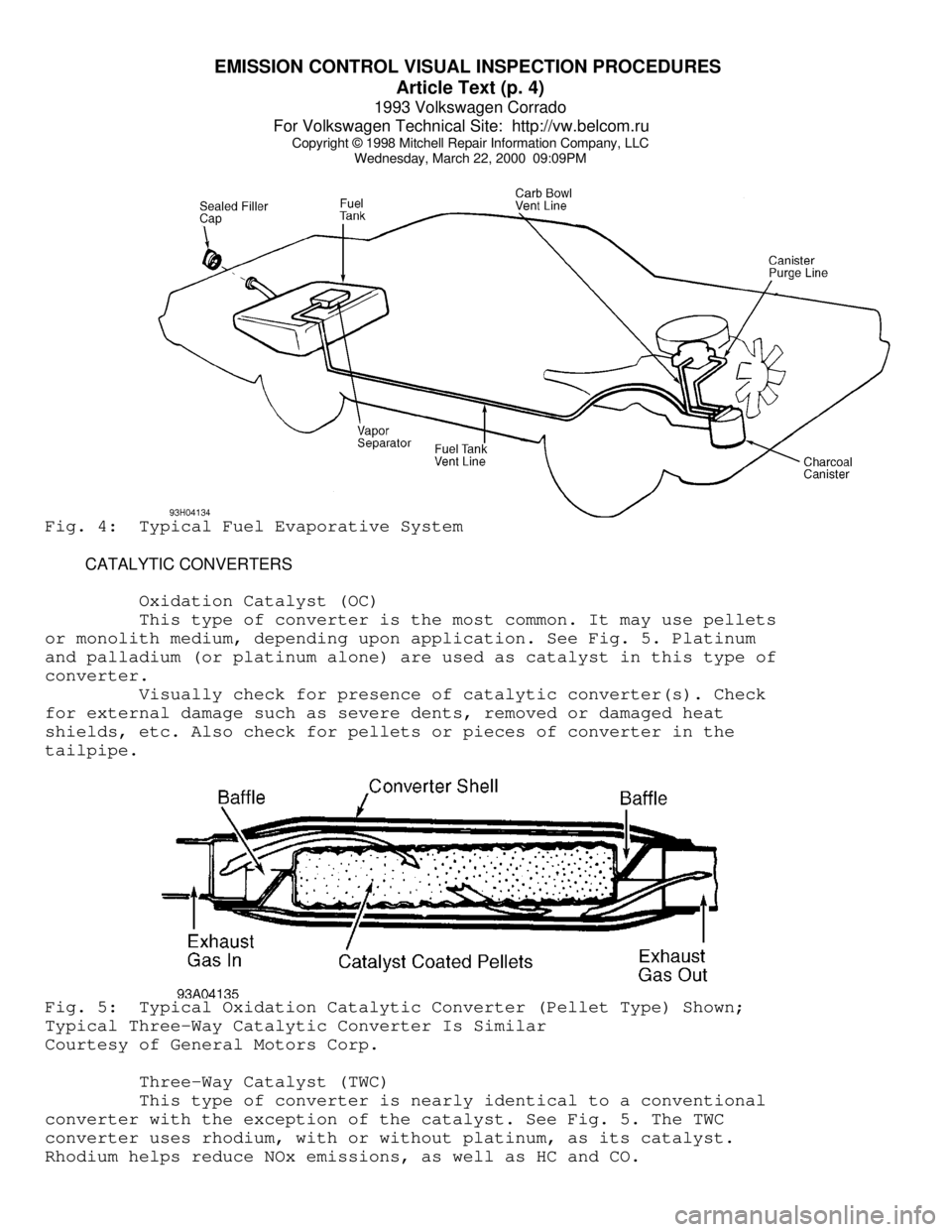
FUEL EVAPORATIVE SYSTEM (EVAP)
The EVAP system allows for proper fuel system ventilation
while preventing fuel vapors from reaching the atmosphere. This means
that vapors must be caught and stored while the engine is off, which
is when most fuel evaporation occurs. When the engine is started,
these fuel vapors can be removed from storage and burned. In most
systems, storage is provided by an activated charcoal (or carbon)
canister. See Fig. 4. On a few early systems, charcoal canisters are
not used. Instead, fuel vapors are vented into the PCV system and
stored inside the crankcase.
The main components of a fuel evaporation system are a
sealed fuel tank, a liquid-vapor separator and vent lines to a vapor-
storing canister filled with activated charcoal. The filler cap is
normally not vented to the atmosphere, but is fitted with a valve to
allow both pressure and vacuum relief.
Although a few variations do exist between manufacturers,
basic operation is the same for all systems. Check for presence of
vapor storage canister or crankcase storage connections when required.
Ensure required hoses, solenoids, etc., are present and connected
properly. Check for proper type fuel tank cap. Check for any non-OEM
or auxiliary fuel tanks for compliance and the required number of
evaporation canisters.
Page 518 of 920
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES
Article Text (p. 4)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:09PMFig. 4: Typical Fuel Evaporative System
CATALYTIC CONVERTERS
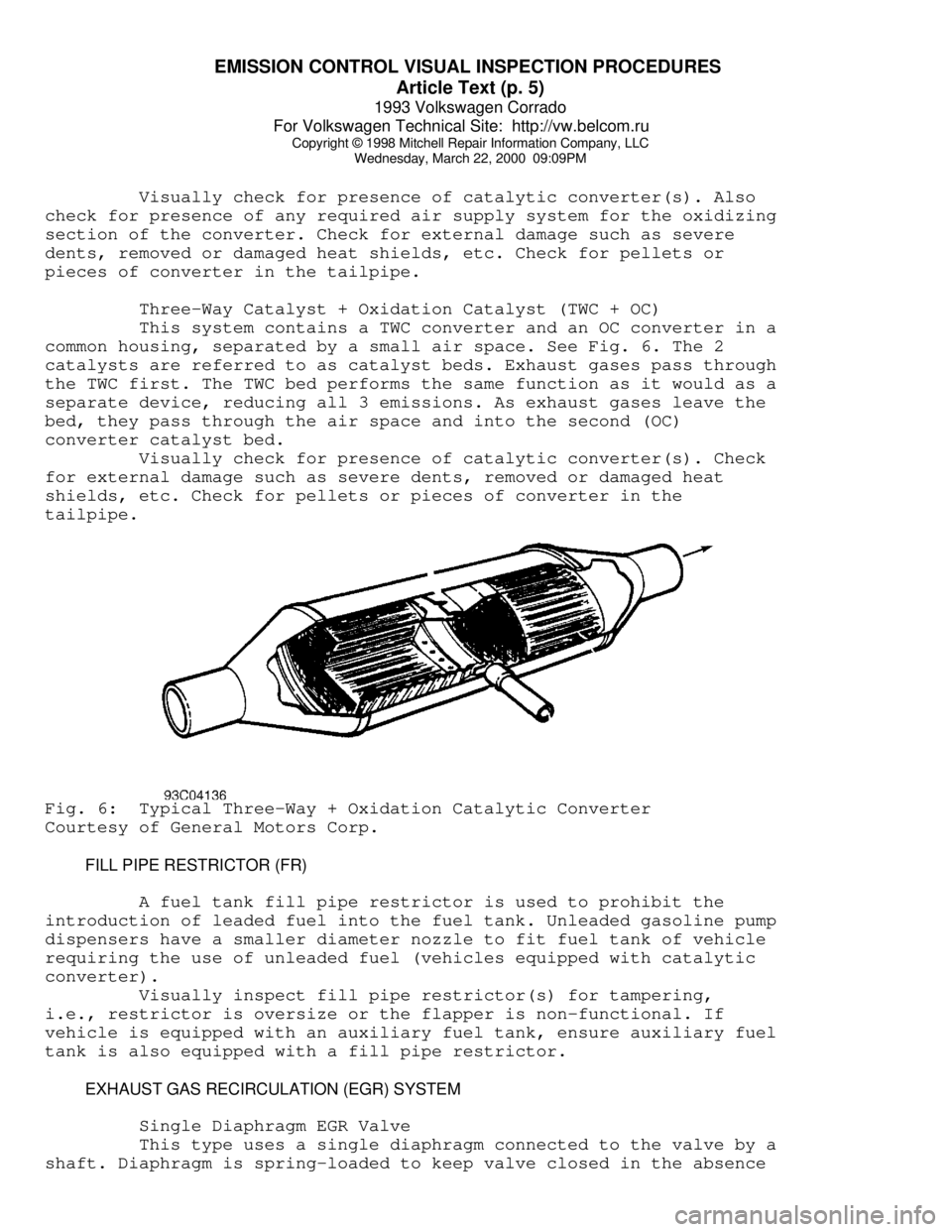
Oxidation Catalyst (OC)
This type of converter is the most common. It may use pellets
or monolith medium, depending upon application. See Fig. 5. Platinum
and palladium (or platinum alone) are used as catalyst in this type of
converter.
Visually check for presence of catalytic converter(s). Check
for external damage such as severe dents, removed or damaged heat
shields, etc. Also check for pellets or pieces of converter in the
tailpipe.Fig. 5: Typical Oxidation Catalytic Converter (Pellet Type) Shown;
Typical Three-Way Catalytic Converter Is Similar
Courtesy of General Motors Corp.
Three-Way Catalyst (TWC)
This type of converter is nearly identical to a conventional
converter with the exception of the catalyst. See Fig. 5. The TWC
converter uses rhodium, with or without platinum, as its catalyst.
Rhodium helps reduce NOx emissions, as well as HC and CO.
Page 519 of 920
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES
Article Text (p. 5)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:09PM
Visually check for presence of catalytic converter(s). Also
check for presence of any required air supply system for the oxidizing
section of the converter. Check for external damage such as severe
dents, removed or damaged heat shields, etc. Check for pellets or
pieces of converter in the tailpipe.
Three-Way Catalyst + Oxidation Catalyst (TWC + OC)
This system contains a TWC converter and an OC converter in a
common housing, separated by a small air space. See Fig. 6. The 2
catalysts are referred to as catalyst beds. Exhaust gases pass through
the TWC first. The TWC bed performs the same function as it would as a
separate device, reducing all 3 emissions. As exhaust gases leave the
bed, they pass through the air space and into the second (OC)
converter catalyst bed.
Visually check for presence of catalytic converter(s). Check
for external damage such as severe dents, removed or damaged heat
shields, etc. Check for pellets or pieces of converter in the
tailpipe.Fig. 6: Typical Three-Way + Oxidation Catalytic Converter
Courtesy of General Motors Corp.
FILL PIPE RESTRICTOR (FR)
A fuel tank fill pipe restrictor is used to prohibit the
introduction of leaded fuel into the fuel tank. Unleaded gasoline pump
dispensers have a smaller diameter nozzle to fit fuel tank of vehicle
requiring the use of unleaded fuel (vehicles equipped with catalytic
converter).
Visually inspect fill pipe restrictor(s) for tampering,
i.e., restrictor is oversize or the flapper is non-functional. If
vehicle is equipped with an auxiliary fuel tank, ensure auxiliary fuel
tank is also equipped with a fill pipe restrictor.
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM
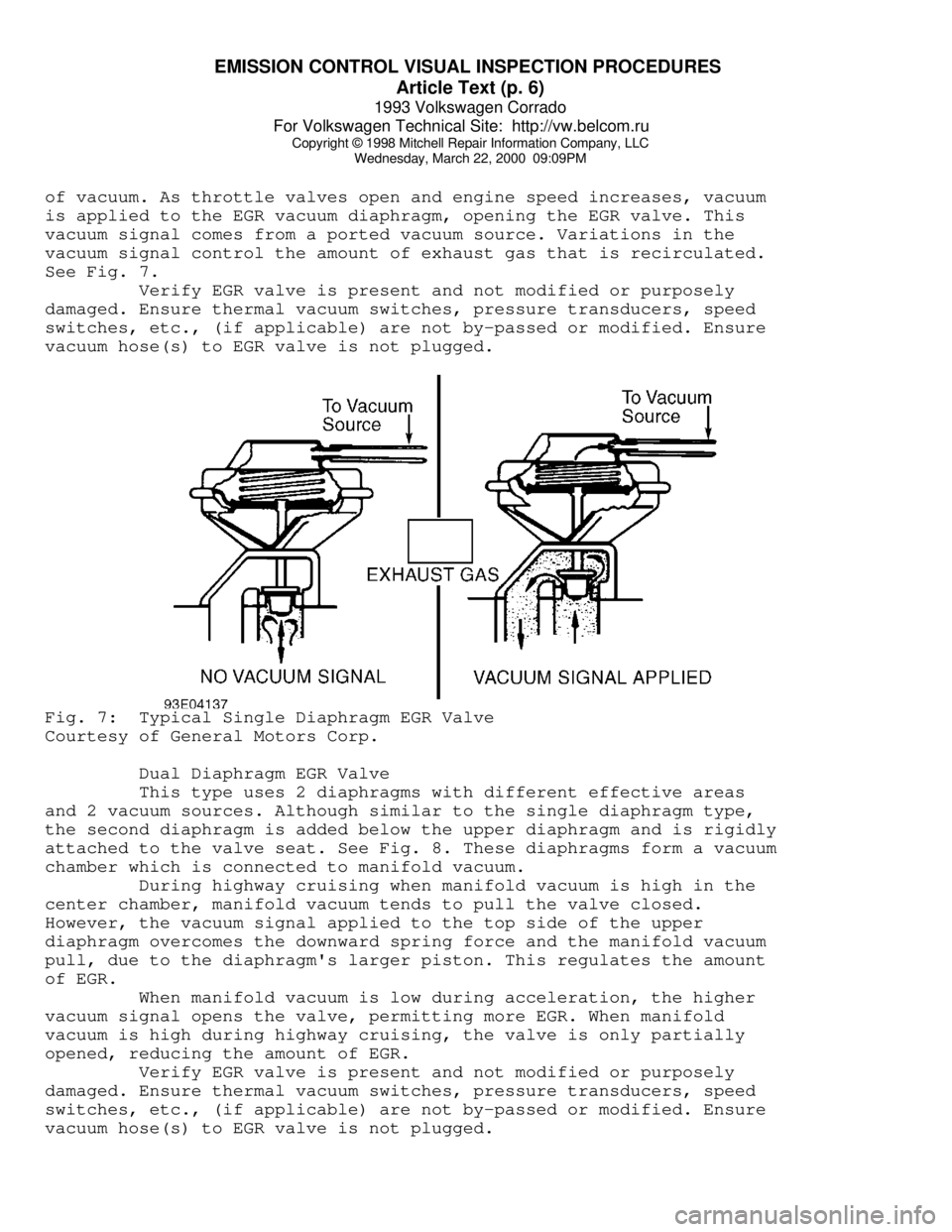
Single Diaphragm EGR Valve
This type uses a single diaphragm connected to the valve by a
shaft. Diaphragm is spring-loaded to keep valve closed in the absence
Page 520 of 920
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES
Article Text (p. 6)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:09PM
of vacuum. As throttle valves open and engine speed increases, vacuum
is applied to the EGR vacuum diaphragm, opening the EGR valve. This
vacuum signal comes from a ported vacuum source. Variations in the
vacuum signal control the amount of exhaust gas that is recirculated.
See Fig. 7.
Verify EGR valve is present and not modified or purposely
damaged. Ensure thermal vacuum switches, pressure transducers, speed
switches, etc., (if applicable) are not by-passed or modified. Ensure
vacuum hose(s) to EGR valve is not plugged.Fig. 7: Typical Single Diaphragm EGR Valve
Courtesy of General Motors Corp.
Dual Diaphragm EGR Valve
This type uses 2 diaphragms with different effective areas
and 2 vacuum sources. Although similar to the single diaphragm type,
the second diaphragm is added below the upper diaphragm and is rigidly
attached to the valve seat. See Fig. 8. These diaphragms form a vacuum
chamber which is connected to manifold vacuum.
During highway cruising when manifold vacuum is high in the
center chamber, manifold vacuum tends to pull the valve closed.
However, the vacuum signal applied to the top side of the upper
diaphragm overcomes the downward spring force and the manifold vacuum
pull, due to the diaphragm's larger piston. This regulates the amount
of EGR.
When manifold vacuum is low during acceleration, the higher
vacuum signal opens the valve, permitting more EGR. When manifold
vacuum is high during highway cruising, the valve is only partially
opened, reducing the amount of EGR.
Verify EGR valve is present and not modified or purposely
damaged. Ensure thermal vacuum switches, pressure transducers, speed
switches, etc., (if applicable) are not by-passed or modified. Ensure
vacuum hose(s) to EGR valve is not plugged.