sub ACURA INTEGRA 1998 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ACURA, Model Year: 1998, Model line: INTEGRA, Model: ACURA INTEGRA 1998Pages: 1680, PDF Size: 53.14 MB
Page 330 of 1680

F
I
Fuel Supply
PGM-Fl Main
System
Relay (cont'd)
\
lb
i
(From page 11 125)
- Reprir open or short in thewire between the PGM-FI mainrelay and the No. 31 STARTERSIGNAL {7.5 A} tuse.- RoDlace the No. 31 STARTERSIGNAL {7.5 A) fuse in theunder-dash luse/relav box,
Check for an open in the wire
{FLR line}:1. Turn the ignation switch OFF.2. Disconnect the ECM connector A (32P).
3. Check for continuity betweenthe PGM-FI main relay 7P con-nector terminal No. 1 and ECMconnector terminal A16-
Repair open in the wire betweenthe ECM (A161 and the PGM-FImein relay,ls there continuity?
Check for an open in the wires{lGPl, lGP2lines}:1. Reconnect the ECM connectorA (32P).
2. Reconnect the PGM-Fl mainrelay 7P connector.3. Turn the ignition switch ON {ll).4. Measure vo ltage betweenECM connector terminals A10and A11, and between A10and 424.
- Repaar open in lhe wir€ bet-ween the ECM 1A11, A24l andthe PGM-FI main relay.- Repldce the PGM-FI main relay.
ls there battery voltage?
Substitute a known-good ECMand recheck. It prescribed vohageis now available. roplace lhe o.ig-inalECM.
ls there 1.0 V or less?
Check the PGM-Fl main relaylsee page 11-124).
PGM.FI MAIN BELAY 7P CONNECTOR IC443I
FLR
FLR
Wire side of temale terminals
Check tor en open in the ECM:1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Measure voltage betlveen ECMconnector termanals A16 andA10 when the ignition switchis first turned ON (ll) for two
IGRN/BLU}
o
1,2!t5i6
:cM CONNEi)TOR A I32P)
I23sl6a9to11
1215lor 17 18t920/22232a
25262l12329
PGl(8LKI
IGP 1
{YEL/BLK}
(
t356I
t5161t la192022
25a
IGP 2{YEL/BLKI
12 15 15 17 18 19 20 .r 22 23
Page 340 of 1680
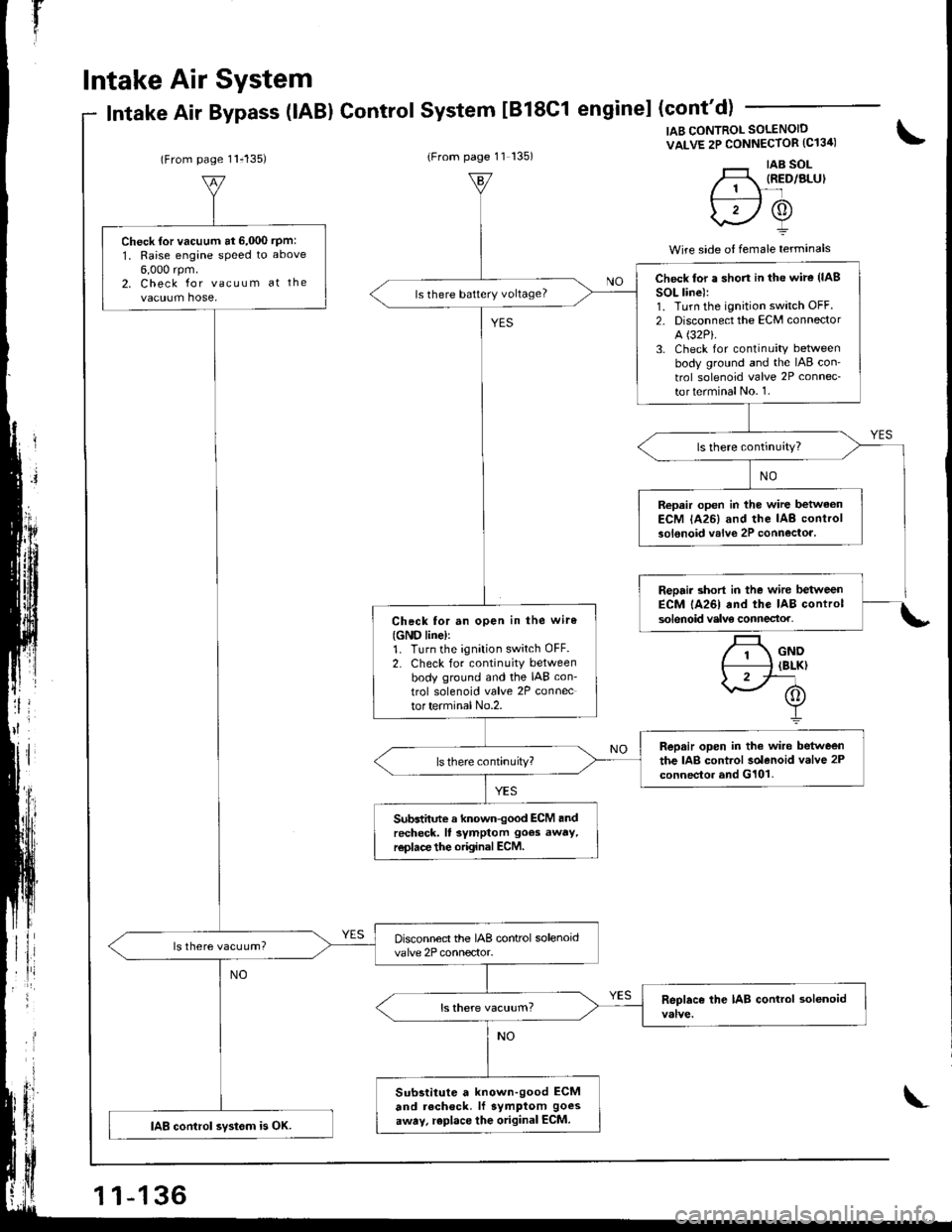
I
lntake
lntake
Air System
Air Bypass (lABl ControlSystem tB18C1 enginel (cont'd)
(From page 11i135)(From page 11 135)
IAB CONTROL SOLENOID
VALVE 2P CONNECTOR (C13ir)
'._r taB sol-H, IRED/ALUI// 1 \-'lf---:----l /A\
\2Y
Wire side o{ female terminals
\
.t
Check {or vacuum at 6,000 rpm:
1, Raise engane speed to above
6,000 rpm.2. Check for vacuum at the
vacuum hose,
Disconnect the IAB control solenoidvalve 2P connector.ls there vacuum?
Substitute a known-good ECM
and recheck. lf symptom goes
away, replace the original ECM.IAB control svstom is OK.
Check lor a shon in the wire (lAB
SOL line):1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Disconnect the ECM connector
A (32P).
3. Check for continuity betweenbody ground and the IAB con'
trol solenoid valve 2P connec-
torterminalNo. 1.
ls there battery voltage?
Repair open in the wire betwaonECM lA26) and the IAB controlsolenoid valve 2P connectoa.
Check tor an open in the wiro
{GND line)r1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Check for continuity betweenbody ground and the IAB con-
trol solenoid valve 2P connector terminal No.2.
Repair open in the wire betweenthe IAB control solenoid valve 2Pconnector and G101.
Subdhnte a known-good ECM andrecheck. ll symptom goes away,r€place the original ECM.
\
Page 347 of 1680
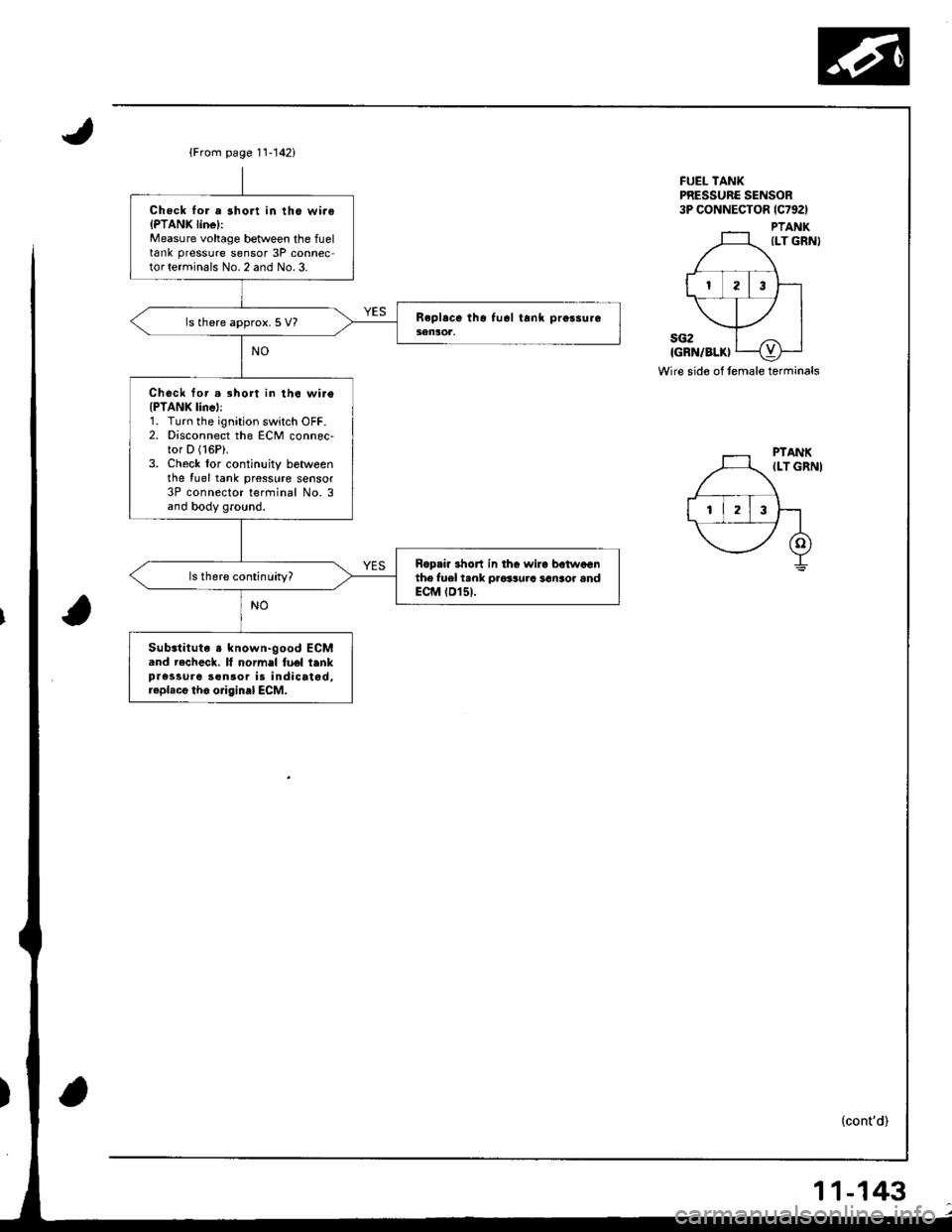
{From page 11-142i
Chock lor a short in tho wi.oIPTANK linel:Measure voltage between the fueltank pressure sensor 3P connec-tor terminals No. 2 and No. 3.
ls there approx. 5 V?
Chock for.3hort in th6 wi.e(PTANK lincl:1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Disconnect the ECM connec,tor D (16P).
3. Check lor continuity betweenthe {uel tank pr€sslrre sensor3P connector terfiinal No. 3and body ground.
Ropri. 3hon in tho wira betwaGnthe fuel t.nk prosaura san3or andECM tD15t.
Substituta s known-good ECM.nd recheck. It normel fuel tenkpressure son30r is indicatod,raplacg tho o.iginal ECM.
FUEL TANKPRESSURC SENSOR3P CONNECTOR lc792l
PTANKILT GRN}
sG2IGRN/BLKI
Wire sido of temale terminals
(cont'd)
11-143
Page 349 of 1680
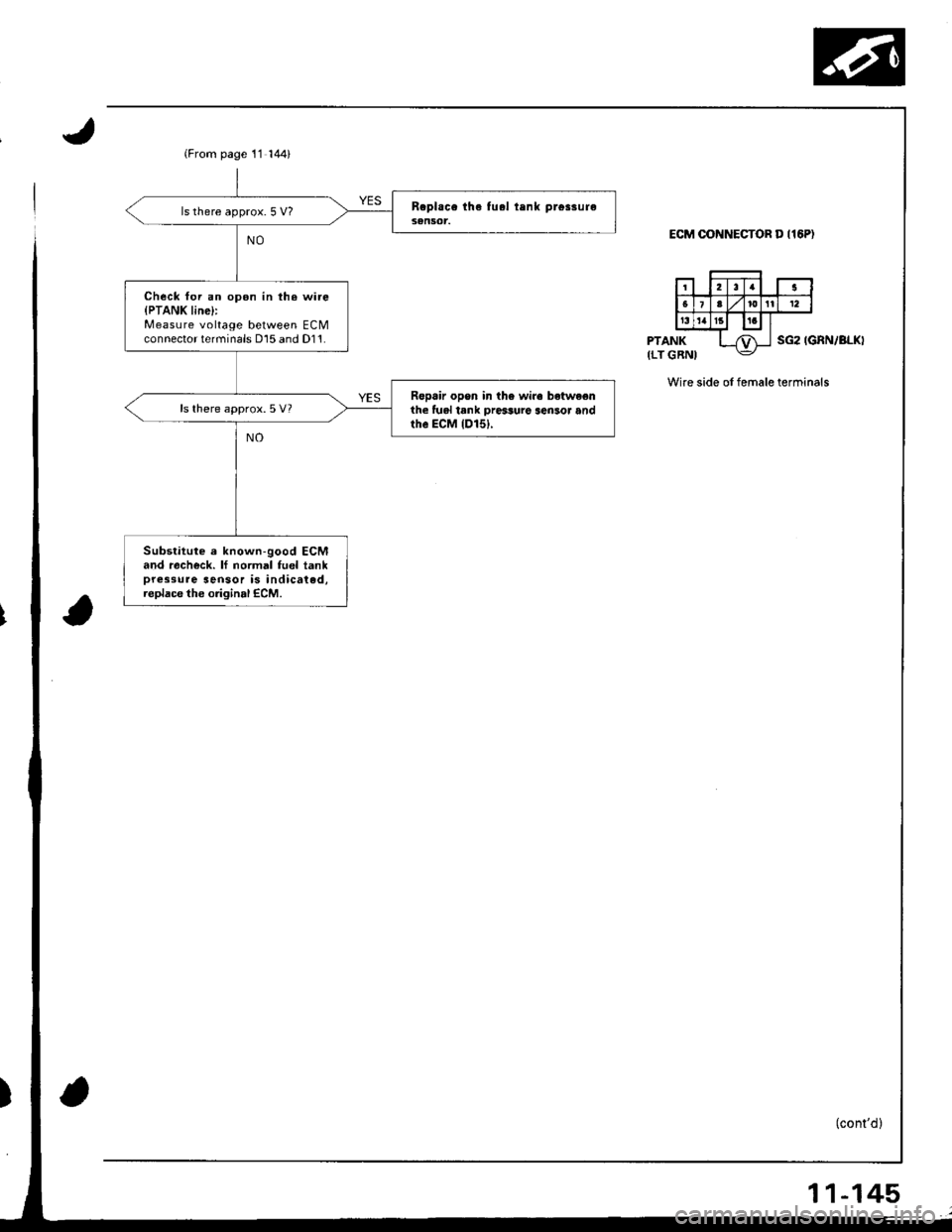
(From page 11 144)
ls there approx. 5 V?
Check foi an opon in th. wi.e{PTANK line}:Measure voltage between ECMconnector terminals D15 and D11.
Ropair opon in the wire betwe€nihe lual tank ore$ure sen3or andthe ECM {D151,
ls there approx.5 V?
Substitute e known-good ECMand racheck. lf normal fuel tankpressure sensor is indicated,replace the original ECM.
ECM OONNECTOR D I16P)
PTANK(LT GRNISG2 IGRN/BLKI
Wire side of female terminals
11-145
Page 352 of 1680
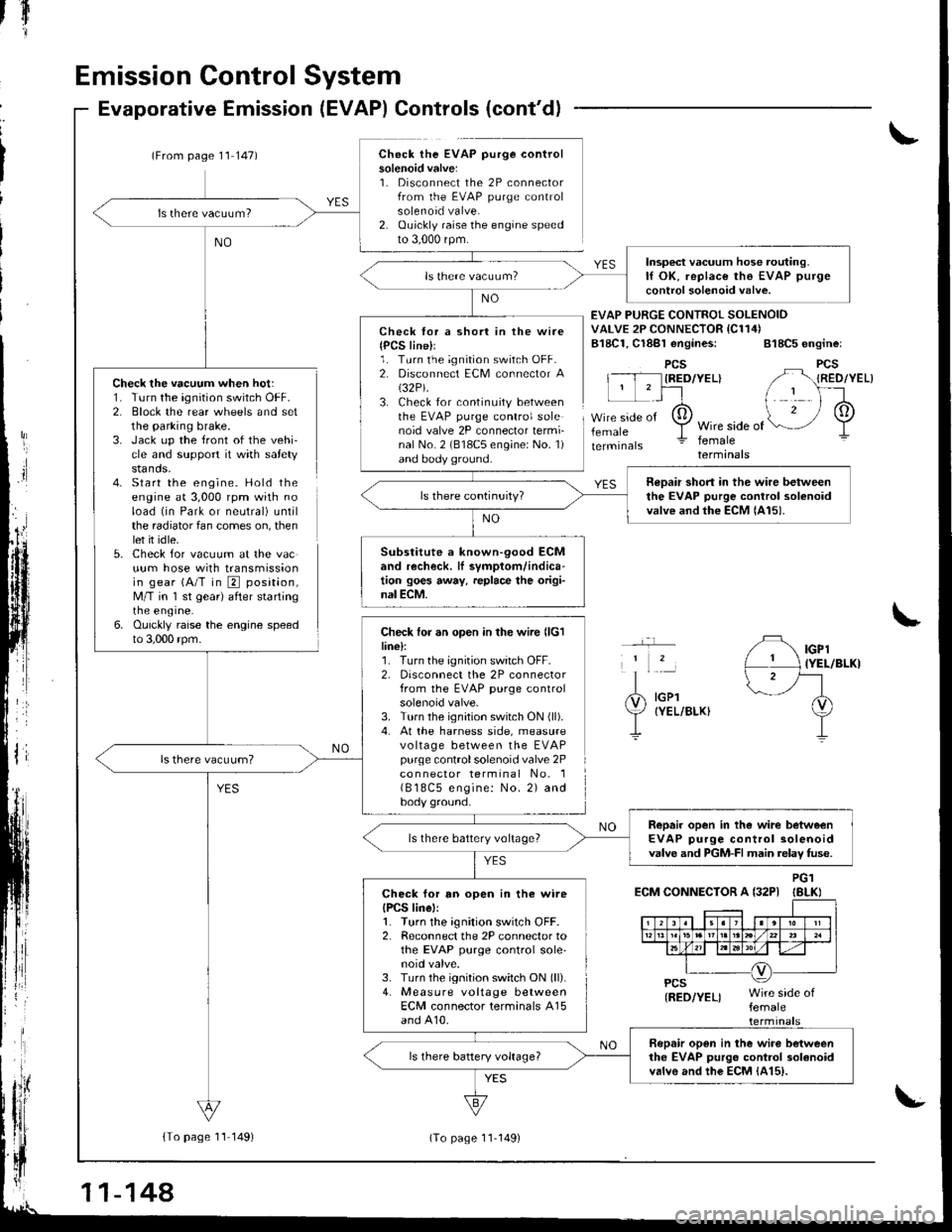
Emission Control System
Check the vacuum when hot:1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Block the rear wheels and setthe parking brake.3. Jack up the front of the vehi-cle and support it with safetystands.4- Start the engine. Hold theengine at 3,000 rpm with noload (in Park or neutral) untilthe radiator fan comes on, thenlet it idle.5. Check for vacuum at the vacuum hose with transmissionin gear (A/T in E position,M/T in 'l st gear) after startingrne engrne.6. Ouickly raise the engine speedto 3,000 rpm.
Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Controls (cont'd)
(From page 1'l 147)Check the EVAP purge controlsolenoid valve:1. Disconnect the 2P connectorfrom the EVAP purge controlsolenoid valve.2. Ouickly raise the engine speedto 3,000 rpm.
{To page 11 149)
tfl'I
Check lor a short in the wire{PCS line}l1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Disconnect ECM connector A(32P).
3. Check for continuity betweenthe EVAP purge control solenoid valve 2P connector termi-nal No. 2 (818C5 engine: No. 1)and body ground.
Check for an open in the wire llclline):1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2, Disconnect the 2P connectorfrom the EVAP purge controlsolenoid valve.3. Turn the ignition switch ON (ll).
4. At the harness side, measurevo ltage between the EVAPpurge controlsolenoid valve 2Pco n nector terminal No. 1( B 18C5 engine: No. 2) andbody ground.
EVAP PURGE CONTROI SOLENOIDVALVE 2P CONNECTOR IC114)B18C1, Cl8Bl engines: 818C5 engine:
PCSIRED/YEL}
femaleWire side offemaleterminals
YES
IGPl{YEL/BLKI
IGPlIYEL/BLKI
ECM CONNECTOR A {32PIPG1IBLKI
Insp€ct vacuum hose routing.lf OK, replace the EVAP purge
control solenoid valve.
neDair short in the wire betweenthe EVAP purge control solenoidvalve and the ECM lAl5).
Substitute a known-90od ECMand recheck. lI symptom/indica-tion goes away, replace the origi-nal ECM.
Repair open in the wirc betweenEVAP purge control solenoidvalve and PGM-FI main relav fuse.ls there battery voltage?
Check for an open in the wireIPCS linel:1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Reconnect the 2P connector tothe EVAP purge control sole'noid valve.3. Turn the ignition switch ON (ll).
4. Measure voltage betweenECM connector terminals A15and A10.
Bopair open in the wiro betweenthe EVAP purgo control 3olanoidvalvo and the EcM {415).
11-144
(To page 11-149)
Page 353 of 1680
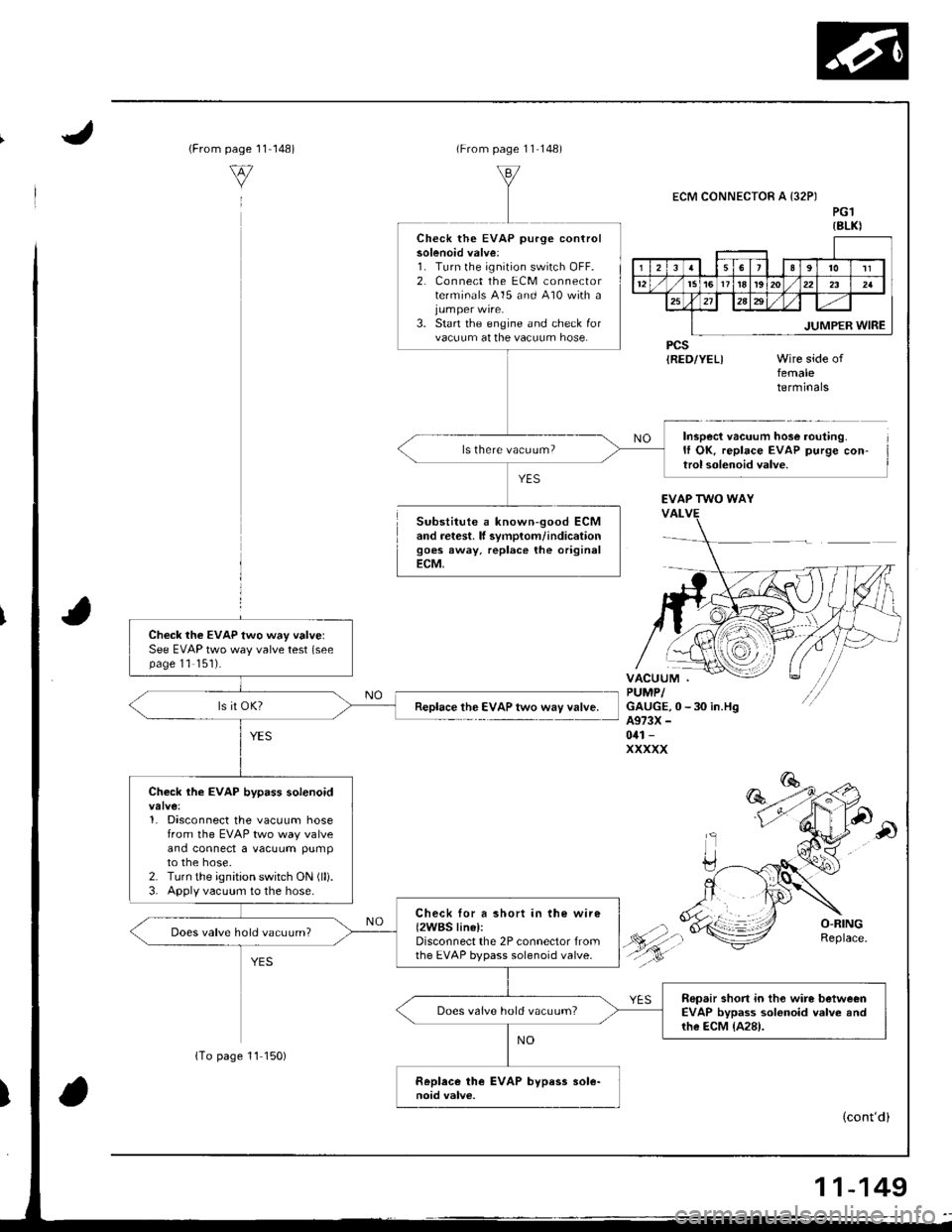
{From1 1-148)page
v
(From page 11 148)
Substitute a known-good ECMand retest. lf svmplom/indicationgoes away, replace the originalECM,
ECM CONNECTOR A {32PIPG1{8LKI
PCSIRED/YEL)femaletermrnars
Inspect vacuum hose routing.It OK, replace EVAP purge con-trol solenoid valve.
Check the EVAP purge controlsolenoid valve:1. Turn lhe ignition switch OFF.2, Connect the ECM connectorterminals 415 and 410 with a
3. Start the engine and check forvacuum at the vacuum hose.
ls there vacuum?
EVAP TWO WAY
Check the EVAP two way valvelSee EVAP two way valve test (seepage 11 '151).
Replace the EVAP two way valve.
Check the EVAP bypass solenoid
1. Disconnect the vacuum hosefrom the EVAP two way valveand connect a vacuum pumpto the hose.2. Turn the ignition switch ON (lli.
3. Apply vacuum to the hose.
Check lor a short in the wire{2WBS linel:Disconnect the 2P connector fromthe EVAP bypass solenoid valve.
Does valve hold vacuum?
Repair short in tho wire betweenEVAP bypass solonoid valve andrhe ECM {A28).
Does valve hold vacuum?
(cont'd)
{To page 11 150)
11-149
Page 403 of 1680
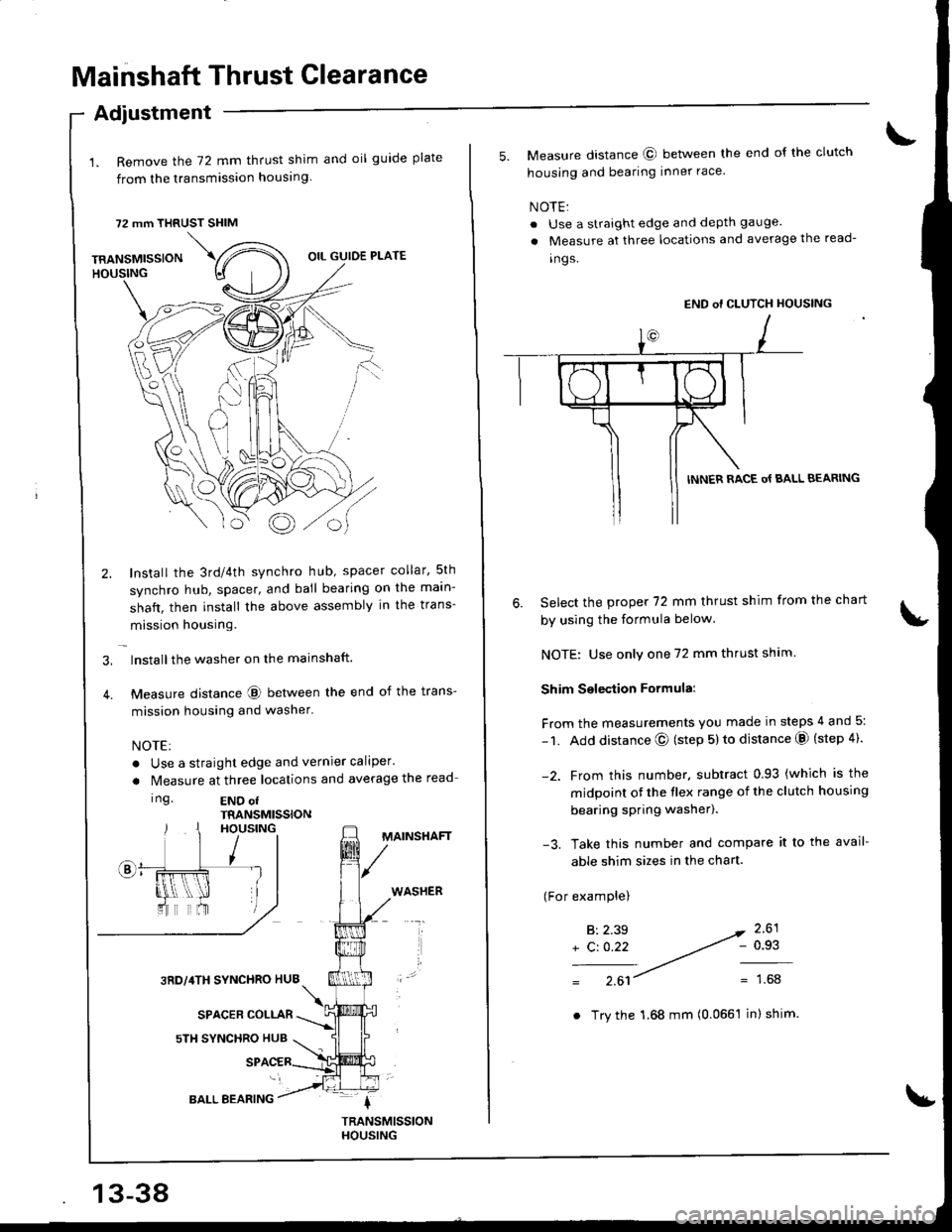
Mainshaft Thrust Glearance
1. Remove the 72 mm thrust shim and oil guide plate
from the transmission housing
72 mm THRUST SHIM
Adiustment
TRANSMISSIONHOUSING
\,
Bo
OIL GUIDE PLATE
Install the 3rd/4th synchro hub, spacer collar,5th
synchro hub, spacer, and ball bearing on the maln-
shaft, then install the above assembly in the trans-
mission housing.
lnstallthe washer on the mainshaft.
Measure distance @ between the end of the trans-
mission housing and washer'
NOTE:
. Use a straight edge and vernier caliper'
a N4easure at three locations and average the read
Ing.END ofTRANSMISSIONHOUSING
3RD,/4TH SYNCHRO HUB
SPACER COLLAR
sTH SYNCHRO HUB
MAINSHAFT
WASHER
BALL BEARING
. Try the 1.68 mm (0.0661 inI shim.
5. Measure distance @ between the end of the clutch
housing and bearing inner race
NOTE:
. Use a straight edge and depth gauge
a Measure at three locations and average the read-
ings.
Select the prcpe( 72 mm thrust shim from the chart
by using the formula below.
NOTE: Use only one 72 mm thrust shim
Shim Selection Formula:
From the measurements you made in steps 4 and 5:
- 1. Add distance @ (step 5) to distance @ (step 4).
-2. Frcm this number. subtract 0.93 (which is the
midpoint ot the flex range of the clutch housing
bearing spring washer).
-3. Take this number and compare it to the avail-
able shim sizes in the chart.
(For examplel
6.
B:2.39
+ C: 0.22- 0.93
1.68
END of CLUTCH HOUSING
INNER RACE o{ BALL BEARING
Page 417 of 1680

Automatic Transmission
Special Tools ................ '14-2
Descraption .................... 14-3
Clutches ............ ...... 14-6
Power Flow ..,........... 14-8
Electronic Control System ..................... 1 4-1 8
Hydraulic Control ...... 14-23
Hydraulic Flow .........- 14-28
Lock-up System ........ 14-38
Electrical System
Component Location -................................ 1 4-45
Circuit Diagram ............. 14-46
TCM Terminal Voltage/
Measuring Conditions ......,.................... 1 4-48
Troubleshooting Procedures .. . ... ........ ...... ... 14-50
Symptom-to-Component Chart
Electrical System ...... 14-54
Electrical Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Flowcharts .......... ... ...,.. 14-56
Lock-up Control Solenoid Valve A/B Assembly
Test .................. ...... 14-A7
Replacement ............. 14-a7
Shilt Control Solenoid Valve A/B Assembly
Test .................. ...... '14-88
Replacement .,..,........ 14-88
lvlainshaf t/Countershaft Speed Sensors
Replacement ....-......,. 14-89
Transmission Control Module (TCM)
Replacement ............. 14-89
Hydraulic System
Symptom-to-Component Chart
Hydraulic System ...... 14-90
Road Test ,................... 14-94
Stall Speed
Test .................. ...... 14-97
Fluid Level
Checking/Changing .... 14-98
Pressure Testing ........... 14-99
Transmission
Transmission
Removal ............. ...... 14-10�4
lllustrated lndex
Transmission/Right Side Cover ............... 1 4-1 08
Transmission Housin9 ................,..,....... 1 4-1'1 O
Torque Converter Housing/ValveBody .................. .. 14-112
Right Side Cover
Removal ............. ...... 14-114
Transmission Housing
Removal ............. ...... 14-1 l6
Torque Converter Housing/Valve Body
Removal ............. ...... l4-1 18
Valve Caps
Description ...........-... 14-120
Valve Body
Repair ................ ...... 14-12'l
Valve
Assembly
ATF Pump
Inspeclton
Main Valve Body
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassembly
Regulator Valve Body
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassembly
Lock-up Valve Body
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassembly
Secondary Valve Body
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassembly
Servo Body
....... 14-124
....... 14-126
....... 14-127
....... 14 124
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassembly .......
1st-hold Accumulator/Right Side Cover
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassembly .......
Mainsha{t
14-130
14-132
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassembly ....... 14-133
Inspection ................. 14-134
Countershaft
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassembly,..,.., l4-136
Disassembly/Reassembly ..,...,..,.........,,.. 1 4-1 37
Inspection ......,...,..,... 14-138
One-way Clutch
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassembly ....,.. 14-141
Sub-shaft
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassembly ...,,..'14-142
Disassembly/Reassembly ....................... 1 4- l 43
Sub-shaft Bearings
Replacement ,..,,.,,..,.. 14-144
Clutch
lllustrated Index ................................... I 4-1 45
Disassembly ............. 14-144
Reassembly .............. 14-150
Torque Converter Housing Bearings
Mainshaft Bearing/Oil Seal
Replacement ......... 14-154
Countershaft Bearing Replacement ......... 1 4- 1 55
Transmission Housing Bearings
Mainshaft/Countershaft BearingReplacement ......,.. 14-'156
Sub-shaft Bearing Replacement .,............ 1 4-1 57
Reverse ldler Gear
Installation .........-..... 14-158
Parking Brake Stop
Inspection/Adjustment .......................... 1 4-1 58
Transmission
Reassembly .............. 14-160
Torque Converler/Drive Plate ..............,.,,.,, 1 4-1 67
Transmission
Installation ............... 14-168
Cooler Flushing ......... 14-172
ATF Cooler Hoses
Connection ,..,,,....,,.,, '14-'174
*shift cable
Removal/lnstallation . . .. .... ... .... ... .... .. . ... .. 14-'l75
Adjustment ,..,...,,,,.,, 14-'116*Shilt lever
Disassembly/Reassembly ....................... 1 4-'17 7'Shift Indicator Panel
Adjustment .............. 14-178
\l
)g
Page 419 of 1680
Description
\J
t{
{
14-3
The automatic transmission is a combination of a 3-element torque converter and triple-shalt electronically controlled
automatic transmission which provides 4 speeds forward and 1 speed reverse. The entire unit is positioned in line with
the engrne.
Torque Converter, Gears, and Clutches
The torque converter consists of a pump, turbine, and stator, assembled in sigle unit. The torque converter is connected to
the engine crankshaft so they turn torether as a unit as the engine turns. Around the outside of the torque convener is a
ring gear which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is being started. The entire torque converter assembly
serves as a flywheel while transmitting power to the transmission mainshaft.
The transmission has three parallel shafts; the mainshaft. the countershaft, and the sub shaft. The mainshaft is in-line with
the engine crankshaft.
The mainshaft includes the 1st, and 2ndl4th clutches,and gear for 3rd, 2nd, 4th, reverse, and 1st. (3rd gear is integral with
the mainshaft, while reverse gear is integral with the 4th gear.)
The countershaft includes the 3rd clutch and gears for 3rd,2nd, 4th, reverse, 1st, and parking. Reverse and 4th gears can
be loched to the countershaft at its center,providing 4th gear or reverse, depending on which way the selector is moved.
The sub-shaft includes the 1st-hold clutch and gears fo 1st and 4th.
The gears on the mainshaft are in constant mesh with those on the countersahft and sub-shaft.When certain combinations
of gears in the transmission are engaged by clutches. power in transmitted from the mainshaft to the countershaft via the
sub-shaft to orovude oil, lo'1. E, E. and E.
Electronic Control
The electronic control svstem consists of the Transmission Control Module (TCM), sensors, and four solenoid valves.
Shilting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comfortable driving under all conditions.
The TCM is located below the dashboard, behind the lelt side kick panel on the driver's side.
Hydraulic Control
The valve bodies include the main valve body, the secondary valve body, the regulator valve body, the serbvo body, and
the lock-up valve body, through the respective separator plates, They are bolted to the torque converter housing,
The main valve body contains the manual valve, the 1-2 shift valve, the 2-3 shitt valve, the Clutch Pressure Control
lCPC) valve, the 4th exhaust valve, the reliel valve, and the ATF pump gears.
The secondary valve body contains the 4-3 kick-down valve, the 3-2 kick-down valve, the 2-3 orifice control valve, the
3-4 shift valve, the orilice control valve, the modulator valve, and the servo control valve.
The regulator valve body contains the pressure regulator valve, the lock-up control valve, the torque converter check
valve, and the cooler check valve.
The servo body contains the servo valve, which is integrated with shift fork shaft, the throttle valve B, and the accumula-
tors.
The lock-up valve body contains the lock-up shift valve and the lock-up timing B valve, and is bolted to the regulator valve
ooqy.
Fluid from the regulator passes through the manual valve to the various control valves.
Shift Control Mechanism
Input to the TCM from various sensors located throughout the car determines which shift control solenoid valve should
be activated. Activating a shitt control solenoid valve changes modulator pressure, causing a shift valve to move. This
pressurizes a line to one ol the clutches, engaging that clutch and its corresponding gear.
Lock-uD Mechanism
In @ position, in 2nd, 3rd and 4th, and @ position in 3rd, pressurized fluid can be drained lrom the back oI the tor-
que converter through a fluid passage, causing the lock-up piston to be held against the torque converter cover. As this
takes place, the mainshaft rotates at the same speed as the engine crankshaft. Together with hydraulic control, the TCM
optimizes the timing of the lock-up mechanism.
The lock-up valves controlthe range of lock-up according to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B, and throttle valve B.
When lock-up control solenoid valves A and B activate, modulator pressure changes. Lock-up control solenoid valves
A and B are mounted on the torque converter housing, and are controlled by the TCM.
(cont'd)
Page 422 of 1680

Description
Clutches
t
{
The four-speed automatic transmission uses hydraulically-actuated clutches to engage or disengage the transmission gears.
When hydraulic pressure is introduced into the clutch drum. the clutch piston is applied. This presses the friction discs
and steel plates together, locking them so they don't slip. Power is then transmitted through the engaged clutch pack
to its hub-mounted gear.
Likewise, when hydraulic pressure is bled from the clutch pack, the piston releases the friction discs and steel plates,
and they are free to slide past each other while disengaged. This allows the gear to spin independently on its shaft, trans-
mrrrng no power.
lsr Clutch
The 1 st clutch engages/disengages 1st gear, and is located at the end of the msinshaft, just behind the right side cover.
The 1st clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure by its ATF feed pipe within the mainshaft.
l st-hold clurch
The '1 st-hold clutch engages/disengages 'lst-hold or E] position, and is located at the middle of the sub-shaft. The 1st-
hold clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure by its ATF feed pipe within the sub-shaft.
2nd Clutch
The 2nd clutch engages/disengages 2nd gear, and is located at the middle of the mainshaft. The 2nd clutch is joined
back-to-back to the 4th clutch. The 2nd clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure through the mainshaft by a circuit connected
to the internal hydraulic circuit.
3rd ClutchThe 3rd clutch engages/disengages 3rd gear, and is located at the end of the counte.shaft, opposite the right side cover.
The 3rd clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure by its ATF feed pipe within the countershaft.
4th Clutch
The 4th clutch engages/disengages 4th gear, as well as reverse gear, and is located at the middle of the mainshaft.
The 4th clutch is joined back-to-back to the 2nd clutch. The 4th clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure by its ATF feed
oiDe within the mainshaft.
One-way Clutch
The one-way clutch is positioned between the parking gear and the countershaft 1st gear. with the parking gear splined
to the countershalt. The countershaft 1st gear provides the outer race, and the parking gear provides the inner race sur-
face. The one-way clutch locks up when power is transmitted from the msinshaft 1st gear to the countershaft I st gear.
The 1st clutch and gears remain engaged in the 1st, 2nd. 3rd, and 4th gear ranges in the Lqd, Lq9.l or La position.
However, the one-way clutch disengages when the 2nd, 3rd, or 4th clutches/gears are applied in the E, lDll o, Eposition. This is because the increased rotational speed of the gears on the countershatt over-ride the locking "speed
range" ot the one-way clutch. Thereatter, the one-way clutch free-wheels with the lst clutch still engaged.
COUiITERSHAFT lST GEAR
FREE
-".--)
LOCKS
F
LOCKS FREE
PARKING GEAR
NOTE:View from right side cover side.
14-6