prop shaft spec BMW 3 SERIES 1991 E30 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1991, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1991 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 71 of 228
16 Engine block- inspection
3
1Before the block is inspected, it should be
cleaned (see Section 15).
2Visually check the block for cracks, rust
and corrosion. Look for stripped threads in
the threaded holes. It’s also a good idea to
have the block checked for hidden cracks by
a machine shop that has the special
equipment to do this type of work. If defects
are found, have the block repaired, if possible;
otherwise, a new block will be required.
3Check the cylinder bores for scuffing and
scoring.
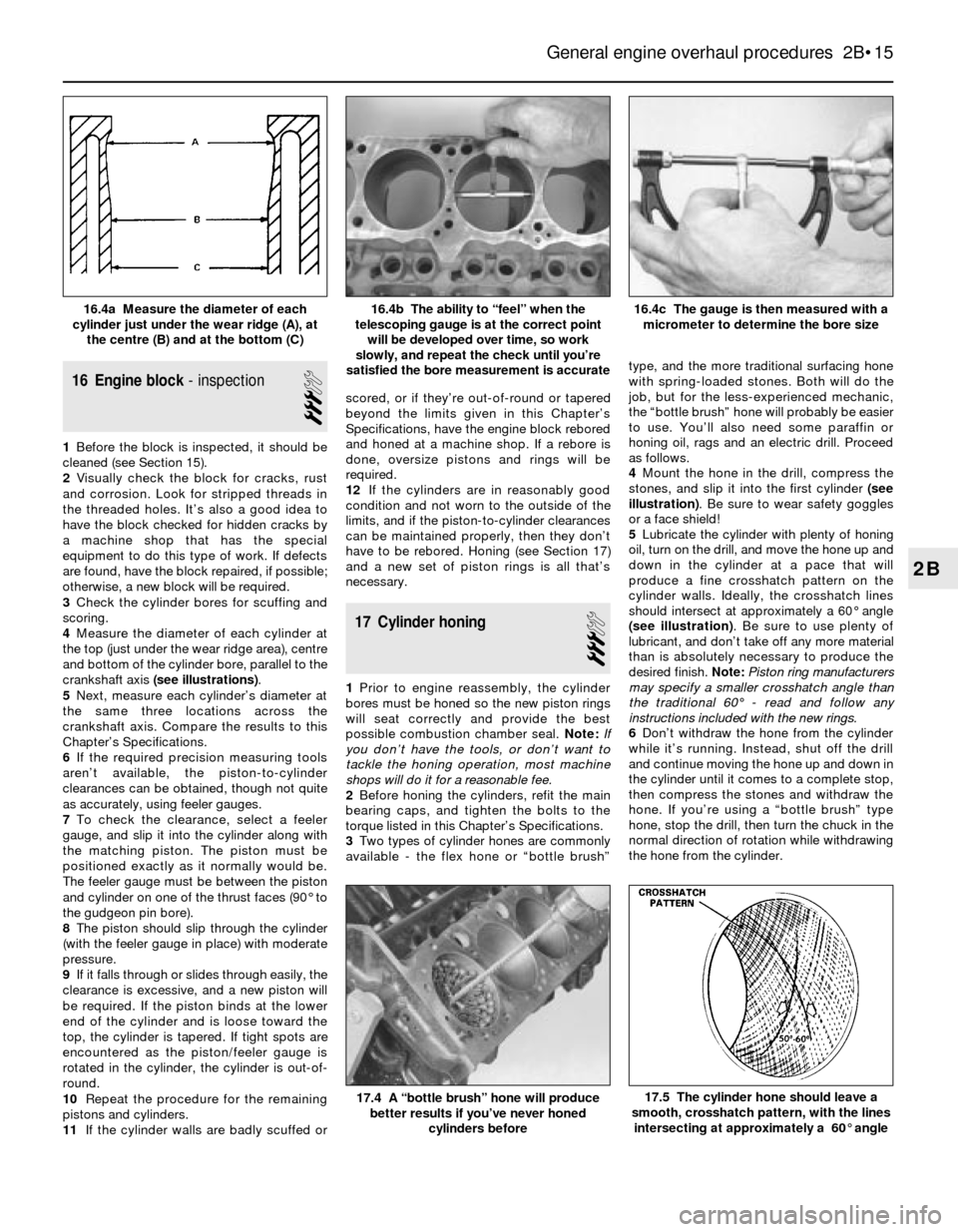
4Measure the diameter of each cylinder at
the top (just under the wear ridge area), centre
and bottom of the cylinder bore, parallel to the
crankshaft axis (see illustrations).
5Next, measure each cylinder’s diameter at
the same three locations across the
crankshaft axis. Compare the results to this
Chapter’s Specifications.
6If the required precision measuring tools
aren’t available, the piston-to-cylinder
clearances can be obtained, though not quite
as accurately, using feeler gauges.
7To check the clearance, select a feeler
gauge, and slip it into the cylinder along with
the matching piston. The piston must be
positioned exactly as it normally would be.
The feeler gauge must be between the piston
and cylinder on one of the thrust faces (90° to
the gudgeon pin bore).
8The piston should slip through the cylinder
(with the feeler gauge in place) with moderate
pressure.
9If it falls through or slides through easily, the
clearance is excessive, and a new piston will
be required. If the piston binds at the lower
end of the cylinder and is loose toward the
top, the cylinder is tapered. If tight spots are
encountered as the piston/feeler gauge is
rotated in the cylinder, the cylinder is out-of-
round.
10Repeat the procedure for the remaining
pistons and cylinders.
11If the cylinder walls are badly scuffed orscored, or if they’re out-of-round or tapered
beyond the limits given in this Chapter’s
Specifications, have the engine block rebored
and honed at a machine shop. If a rebore is
done, oversize pistons and rings will be
required.
12If the cylinders are in reasonably good
condition and not worn to the outside of the
limits, and if the piston-to-cylinder clearances
can be maintained properly, then they don’t
have to be rebored. Honing (see Section 17)
and a new set of piston rings is all that’s
necessary.
17 Cylinder honing
3
1Prior to engine reassembly, the cylinder
bores must be honed so the new piston rings
will seat correctly and provide the best
possible combustion chamber seal. Note:If
you don’t have the tools, or don’t want to
tackle the honing operation, most machine
shops will do it for a reasonable fee.
2Before honing the cylinders, refit the main
bearing caps, and tighten the bolts to the
torque listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
3Two types of cylinder hones are commonly
available - the flex hone or “bottle brush”type, and the more traditional surfacing hone
with spring-loaded stones. Both will do the
job, but for the less-experienced mechanic,
the “bottle brush” hone will probably be easier
to use. You’ll also need some paraffin or
honing oil, rags and an electric drill. Proceed
as follows.
4Mount the hone in the drill, compress the
stones, and slip it into the first cylinder (see
illustration). Be sure to wear safety goggles
or a face shield!
5Lubricate the cylinder with plenty of honing
oil, turn on the drill, and move the hone up and
down in the cylinder at a pace that will
produce a fine crosshatch pattern on the
cylinder walls. Ideally, the crosshatch lines
should intersect at approximately a 60° angle
(see illustration). Be sure to use plenty of
lubricant, and don’t take off any more material
than is absolutely necessary to produce the
desired finish. Note:Piston ring manufacturers
may specify a smaller crosshatch angle than
the traditional 60°- read and follow any
instructions included with the new rings.
6Don’t withdraw the hone from the cylinder
while it’s running. Instead, shut off the drill
and continue moving the hone up and down in
the cylinder until it comes to a complete stop,
then compress the stones and withdraw the
hone. If you’re using a “bottle brush” type
hone, stop the drill, then turn the chuck in the
normal direction of rotation while withdrawing
the hone from the cylinder.
General engine overhaul procedures 2B•15
16.4c The gauge is then measured with a
micrometer to determine the bore size16.4b The ability to “feel” when the
telescoping gauge is at the correct point
will be developed over time, so work
slowly, and repeat the check until you’re
satisfied the bore measurement is accurate16.4a Measure the diameter of each
cylinder just under the wear ridge (A), at
the centre (B) and at the bottom (C)
17.5 The cylinder hone should leave a
smooth, crosshatch pattern, with the lines
intersecting at approximately a 60° angle17.4 A “bottle brush” hone will produce
better results if you’ve never honed
cylinders before
2B
Page 73 of 228

12Check the piston-to-rod clearance by
twisting the piston and rod in opposite
directions. Any noticeable play indicates
excessive wear, which must be corrected. The
piston/connecting rod assemblies should be
taken to a machine shop for attention.
13If the pistons must be removed from the
connecting rods for any reason, they should
be taken to a machine shop. When this is
done, have the connecting rods checked for
bend and twist, since most machine shops
have special equipment for this purpose.
Note:Unless new pistons and/or connecting
rods must be fitted, do not dismantle the
pistons and connecting rods.
14Check the connecting rods for cracks and
other damage. Temporarily remove the rod
caps, lift out the old bearing shells, wipe the rod
and cap bearing surfaces clean, and inspect
them for nicks, gouges and scratches. After
checking the rods, fit new bearing shells, slip the
caps into place, and tighten the nuts finger-tight.
19 Crankshaft- inspection
3
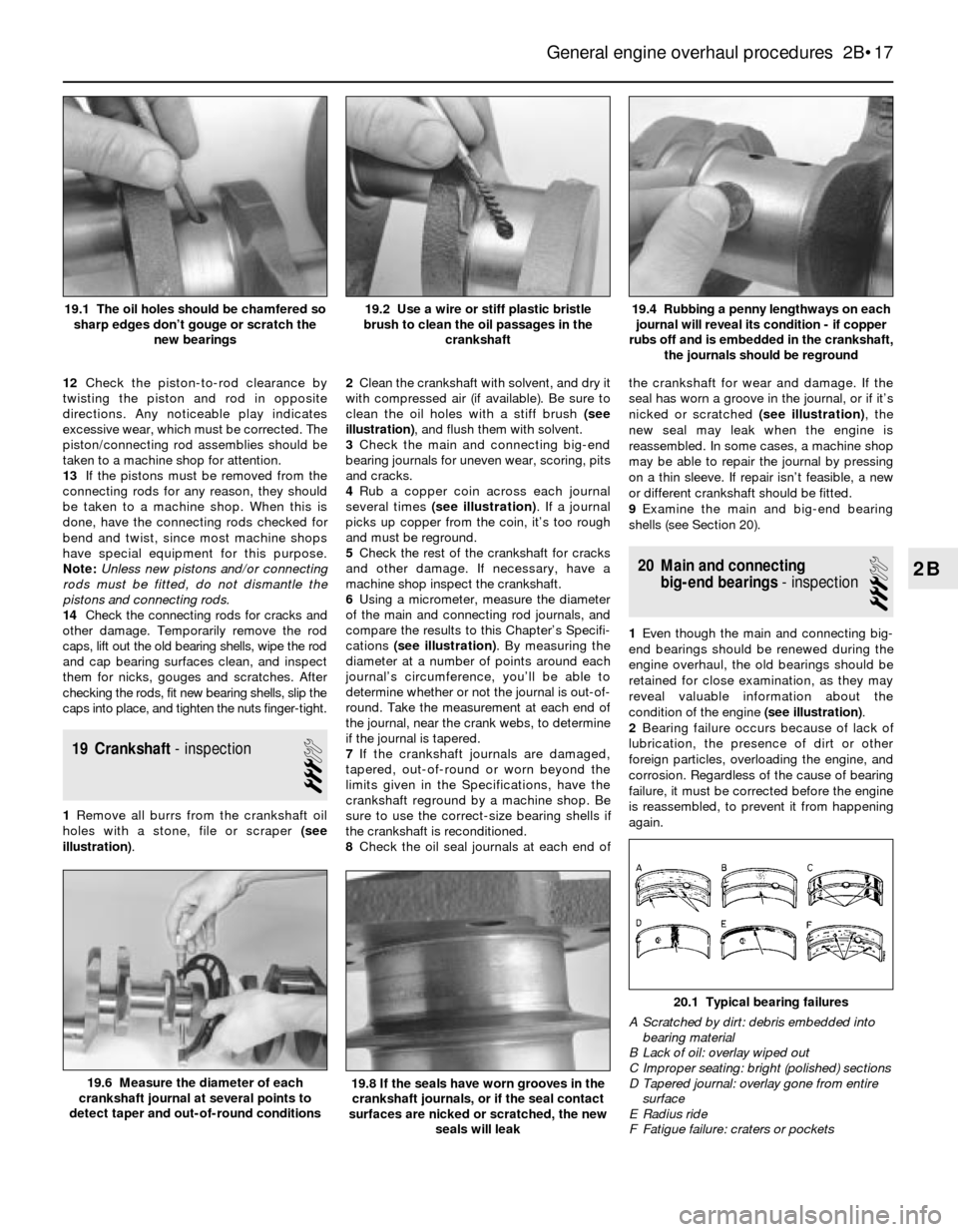
1Remove all burrs from the crankshaft oil
holes with a stone, file or scraper (see
illustration).2Clean the crankshaft with solvent, and dry it
with compressed air (if available). Be sure to
clean the oil holes with a stiff brush (see
illustration), and flush them with solvent.
3Check the main and connecting big-end
bearing journals for uneven wear, scoring, pits
and cracks.
4Rub a copper coin across each journal
several times (see illustration). If a journal
picks up copper from the coin, it’s too rough
and must be reground.
5Check the rest of the crankshaft for cracks
and other damage. If necessary, have a
machine shop inspect the crankshaft.
6Using a micrometer, measure the diameter
of the main and connecting rod journals, and
compare the results to this Chapter’s Specifi-
cations (see illustration). By measuring the
diameter at a number of points around each
journal’s circumference, you’ll be able to
determine whether or not the journal is out-of-
round. Take the measurement at each end of
the journal, near the crank webs, to determine
if the journal is tapered.
7If the crankshaft journals are damaged,
tapered, out-of-round or worn beyond the
limits given in the Specifications, have the
crankshaft reground by a machine shop. Be
sure to use the correct-size bearing shells if
the crankshaft is reconditioned.
8Check the oil seal journals at each end ofthe crankshaft for wear and damage. If the
seal has worn a groove in the journal, or if it’s
nicked or scratched (see illustration), the
new seal may leak when the engine is
reassembled. In some cases, a machine shop
may be able to repair the journal by pressing
on a thin sleeve. If repair isn’t feasible, a new
or different crankshaft should be fitted.
9Examine the main and big-end bearing
shells (see Section 20).
20 Main and connecting
big-end bearings- inspection
3
1Even though the main and connecting big-
end bearings should be renewed during the
engine overhaul, the old bearings should be
retained for close examination, as they may
reveal valuable information about the
condition of the engine (see illustration).
2Bearing failure occurs because of lack of
lubrication, the presence of dirt or other
foreign particles, overloading the engine, and
corrosion. Regardless of the cause of bearing
failure, it must be corrected before the engine
is reassembled, to prevent it from happening
again.
General engine overhaul procedures 2B•17
19.4 Rubbing a penny lengthways on each
journal will reveal its condition - if copper
rubs off and is embedded in the crankshaft,
the journals should be reground19.2 Use a wire or stiff plastic bristle
brush to clean the oil passages in the
crankshaft19.1 The oil holes should be chamfered so
sharp edges don’t gouge or scratch the
new bearings
20.1 Typical bearing failures
A Scratched by dirt: debris embedded into
bearing material
B Lack of oil: overlay wiped out
C Improper seating: bright (polished) sections
D Tapered journal: overlay gone from entire
surface
E Radius ride
F Fatigue failure: craters or pockets
19.8 If the seals have worn grooves in the
crankshaft journals, or if the seal contact
surfaces are nicked or scratched, the new
seals will leak19.6 Measure the diameter of each
crankshaft journal at several points to
detect taper and out-of-round conditions
2B
Page 74 of 228
3When examining the bearings, remove
them from the engine block, the main bearing
caps, the connecting rods and the rod caps,
and lay them out on a clean surface in the
same general position as their location in the
engine. This will enable you to match any
bearing problems with the corresponding
crankshaft journal.
4Dirt and other foreign particles get into the
engine in a variety of ways. It may be left in
the engine during assembly, or it may pass
through filters or the crankcase ventilation
(PCV) system. It may get into the oil, and from
there into the bearings. Metal chips from
machining operations and normal engine wear
are often present. Abrasives are sometimes
left in engine components after recondi-
tioning, especially when parts are not
thoroughly cleaned using the proper cleaning
methods. Whatever the source, these foreign
objects often end up embedded in the soft
bearing material, and are easily recognised.
Large particles will not embed in the bearing,
and will score or gouge the bearing and
journal. The best prevention for this cause of
bearing failure is to clean all parts thoroughly,
and to keep everything spotlessly-clean
during engine assembly. Frequent and regular
engine oil and filter changes are also
recommended.
5Lack of lubrication (or lubrication
breakdown) has a number of interrelated
causes. Excessive heat (which thins the oil),
overloading (which squeezes the oil from the
bearing face) and oil “leakage” or “throw off”
(from excessive bearing clearances, worn oil
pump, or high engine speeds) all contribute to
lubrication breakdown. Blocked oil passages,
which usually are the result of misaligned oil
holes in a bearing shell, will also oil-starve a
bearing and destroy it. When lack of
lubrication is the cause of bearing failure, the
bearing material is wiped or extruded from the
steel backing of the bearing. Temperatures
may increase to the point where the steel
backing turns blue from overheating.
6Driving habits can have a definite effect on
bearing life. Full-throttle, low-speed operation
(labouring the engine) puts very high loads onbearings, which tends to squeeze out the oil
film. These loads cause the bearings to flex,
which produces fine cracks in the bearing
face (fatigue failure). Eventually, the bearing
material will loosen in places, and tear away
from the steel backing. Short-trip driving
leads to corrosion of bearings, because
insufficient engine heat is produced to drive
off the condensation and corrosive gases.
These products collect in the engine oil,
forming acid and sludge. As the oil is carried
to the engine bearings, the acid attacks and
corrodes the bearing material.
7Incorrect bearing refitting during engine
assembly will lead to bearing failure as well.
Tight-fitting bearings leave insufficient bearing
oil clearance, and will result in oil starvation.
Dirt or foreign particles trapped behind a
bearing shell result in high spots on the
bearing, which will lead to failure.
21 Engine overhaul-
reassembly sequence
1Before beginning engine reassembly, make
sure you have all the necessary new parts,
gaskets and seals, as well as the following
items on hand:
Common hand tools
A torque wrench
Piston ring refitting tool
Piston ring compressor
Vibration damper refitting tool
Short lengths of rubber or plastic hose to fit
over connecting rod bolts (where
applicable)
Plastigage
Feeler gauges
A fine-tooth file
New engine oil
Engine assembly oil or molybdenum
disulphide (“moly”) grease
Gasket sealant
Thread-locking compound
2In order to save time and avoid problems,
engine reassembly should be done in the
following general order:Piston rings
Crankshaft and main bearings
Piston/connecting rod assemblies
Oil pump
Sump
Cylinder head assembly
Timing belt or chain and tensioner
assemblies
Water pump
Timing belt or chain covers
Intake and exhaust manifolds
Valve cover
Engine rear plate
Flywheel/driveplate
22 Piston rings- refitting
2
1Before fitting the new piston rings, the ring
end gaps must be checked. It’s assumed that
the piston ring side clearance has been
checked and verified (see Section 18).
2Lay out the piston/connecting rod
assemblies and the new ring sets, so that the
ring sets will be matched with the same piston
and cylinder during the end gap measurement
and engine assembly.
3Insert the top ring into the first cylinder, and
square it up with the cylinder walls by pushing
it in with the top of the piston (see illustration).
The ring should be near the bottom of the
cylinder, at the lower limit of ring travel.
4To measure the end gap, slip feeler gauges
between the ends of the ring until a gauge equal
to the gap width is found(see illustration). The
feeler gauge should slide between the ring ends
with a slight amount of drag. Compare the
measurement to this Chapter’s Specifications.
If the gap is larger or smaller than specified,
double-check to make sure you have the
correct rings before proceeding.
5If the gap is too small, it must be enlarged,
or the ring ends may come in contact with
each other during engine operation, which
can cause serious damage to the engine. The
end gap can be increased by filing the ring
ends very carefully with a fine file. Mount the
2B•18 General engine overhaul procedures
22.5 If the end gap is too small, clamp a
file in a vice, and file the ring ends (from
the outside in only) to enlarge the gap
slightly22.4 With the ring square in the cylinder,
measure the end gap with a feeler gauge22.3 When checking piston ring end gap,
the ring must be square in the cylinder
bore (this is done by pushing the ring down
with the top of a piston as shown)
Page 75 of 228
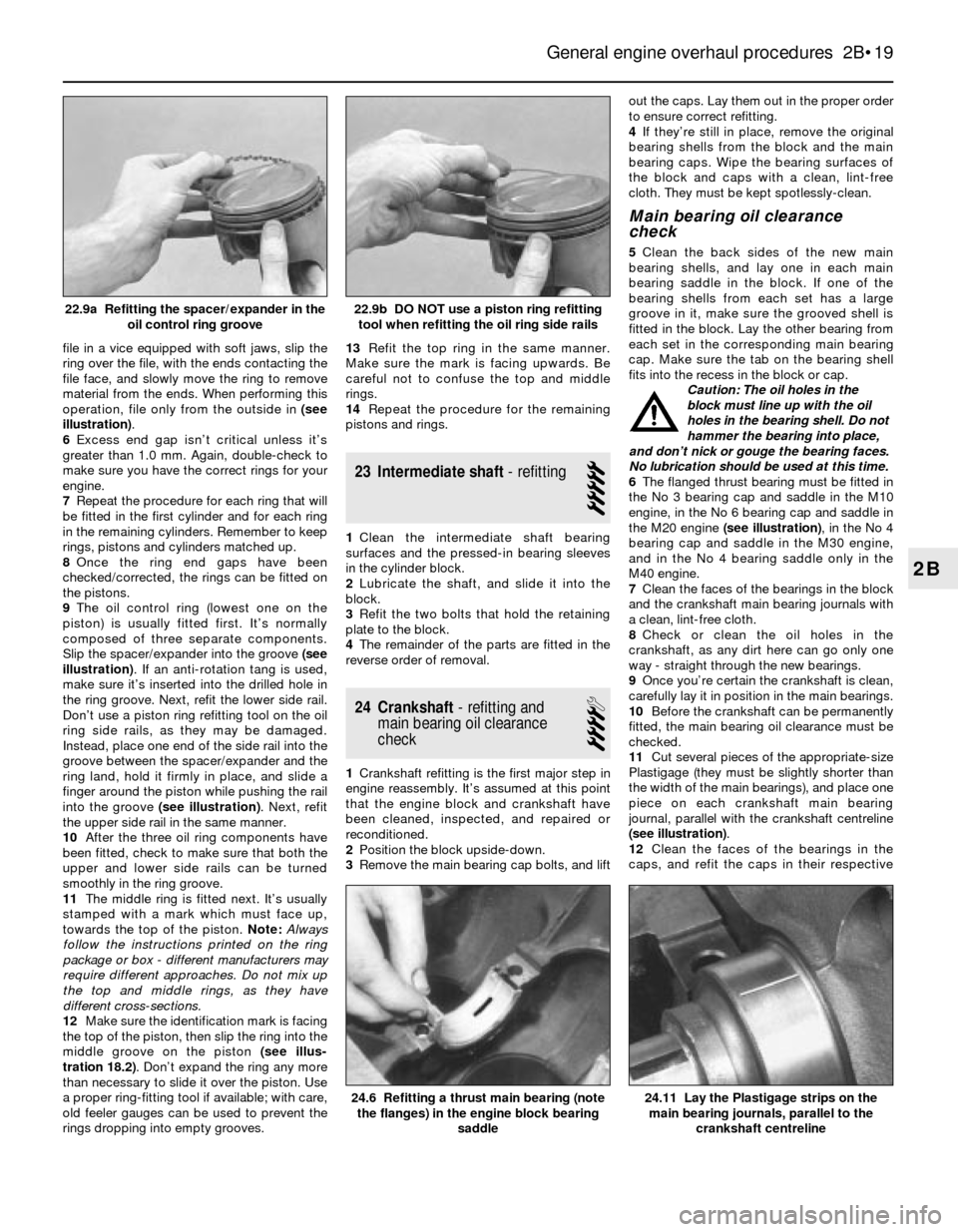
file in a vice equipped with soft jaws, slip the
ring over the file, with the ends contacting the
file face, and slowly move the ring to remove
material from the ends. When performing this
operation, file only from the outside in(see
illustration).
6Excess end gap isn’t critical unless it’s
greater than 1.0 mm. Again, double-check to
make sure you have the correct rings for your
engine.
7Repeat the procedure for each ring that will
be fitted in the first cylinder and for each ring
in the remaining cylinders. Remember to keep
rings, pistons and cylinders matched up.
8Once the ring end gaps have been
checked/corrected, the rings can be fitted on
the pistons.
9The oil control ring (lowest one on the
piston) is usually fitted first. It’s normally
composed of three separate components.
Slip the spacer/expander into the groove(see
illustration). If an anti-rotation tang is used,
make sure it’s inserted into the drilled hole in
the ring groove. Next, refit the lower side rail.
Don’t use a piston ring refitting tool on the oil
ring side rails, as they may be damaged.
Instead, place one end of the side rail into the
groove between the spacer/expander and the
ring land, hold it firmly in place, and slide a
finger around the piston while pushing the rail
into the groove(see illustration). Next, refit
the upper side rail in the same manner.
10After the three oil ring components have
been fitted, check to make sure that both the
upper and lower side rails can be turned
smoothly in the ring groove.
11The middle ring is fitted next. It’s usually
stamped with a mark which must face up,
towards the top of the piston. Note:Always
follow the instructions printed on the ring
package or box - different manufacturers may
require different approaches. Do not mix up
the top and middle rings, as they have
different cross-sections.
12Make sure the identification mark is facing
the top of the piston, then slip the ring into the
middle groove on the piston (see illus-
tration 18.2). Don’t expand the ring any more
than necessary to slide it over the piston. Use
a proper ring-fitting tool if available; with care,
old feeler gauges can be used to prevent the
rings dropping into empty grooves.13Refit the top ring in the same manner.
Make sure the mark is facing upwards. Be
careful not to confuse the top and middle
rings.
14Repeat the procedure for the remaining
pistons and rings.
23 Intermediate shaft- refitting
5
1Clean the intermediate shaft bearing
surfaces and the pressed-in bearing sleeves
in the cylinder block.
2Lubricate the shaft, and slide it into the
block.
3Refit the two bolts that hold the retaining
plate to the block.
4The remainder of the parts are fitted in the
reverse order of removal.
24 Crankshaft- refitting and
main bearing oil clearance
check
4
1Crankshaft refitting is the first major step in
engine reassembly. It’s assumed at this point
that the engine block and crankshaft have
been cleaned, inspected, and repaired or
reconditioned.
2Position the block upside-down.
3Remove the main bearing cap bolts, and liftout the caps. Lay them out in the proper order
to ensure correct refitting.
4If they’re still in place, remove the original
bearing shells from the block and the main
bearing caps. Wipe the bearing surfaces of
the block and caps with a clean, lint-free
cloth. They must be kept spotlessly-clean.
Main bearing oil clearance
check
5Clean the back sides of the new main
bearing shells, and lay one in each main
bearing saddle in the block. If one of the
bearing shells from each set has a large
groove in it, make sure the grooved shell is
fitted in the block. Lay the other bearing from
each set in the corresponding main bearing
cap. Make sure the tab on the bearing shell
fits into the recess in the block or cap.
Caution: The oil holes in the
block must line up with the oil
holes in the bearing shell. Do not
hammer the bearing into place,
and don’t nick or gouge the bearing faces.
No lubrication should be used at this time.
6The flanged thrust bearing must be fitted in
the No 3 bearing cap and saddle in the M10
engine, in the No 6 bearing cap and saddle in
the M20 engine (see illustration), in the No 4
bearing cap and saddle in the M30 engine,
and in the No 4 bearing saddle only in the
M40 engine.
7Clean the faces of the bearings in the block
and the crankshaft main bearing journals with
a clean, lint-free cloth.
8Check or clean the oil holes in the
crankshaft, as any dirt here can go only one
way - straight through the new bearings.
9Once you’re certain the crankshaft is clean,
carefully lay it in position in the main bearings.
10Before the crankshaft can be permanently
fitted, the main bearing oil clearance must be
checked.
11Cut several pieces of the appropriate-size
Plastigage (they must be slightly shorter than
the width of the main bearings), and place one
piece on each crankshaft main bearing
journal, parallel with the crankshaft centreline
(see illustration).
12Clean the faces of the bearings in the
caps, and refit the caps in their respective
General engine overhaul procedures 2B•19
22.9b DO NOT use a piston ring refitting
tool when refitting the oil ring side rails22.9a Refitting the spacer/expander in the
oil control ring groove
24.11 Lay the Plastigage strips on the
main bearing journals, parallel to the
crankshaft centreline24.6 Refitting a thrust main bearing (note
the flanges) in the engine block bearing
saddle
2B
Page 77 of 228
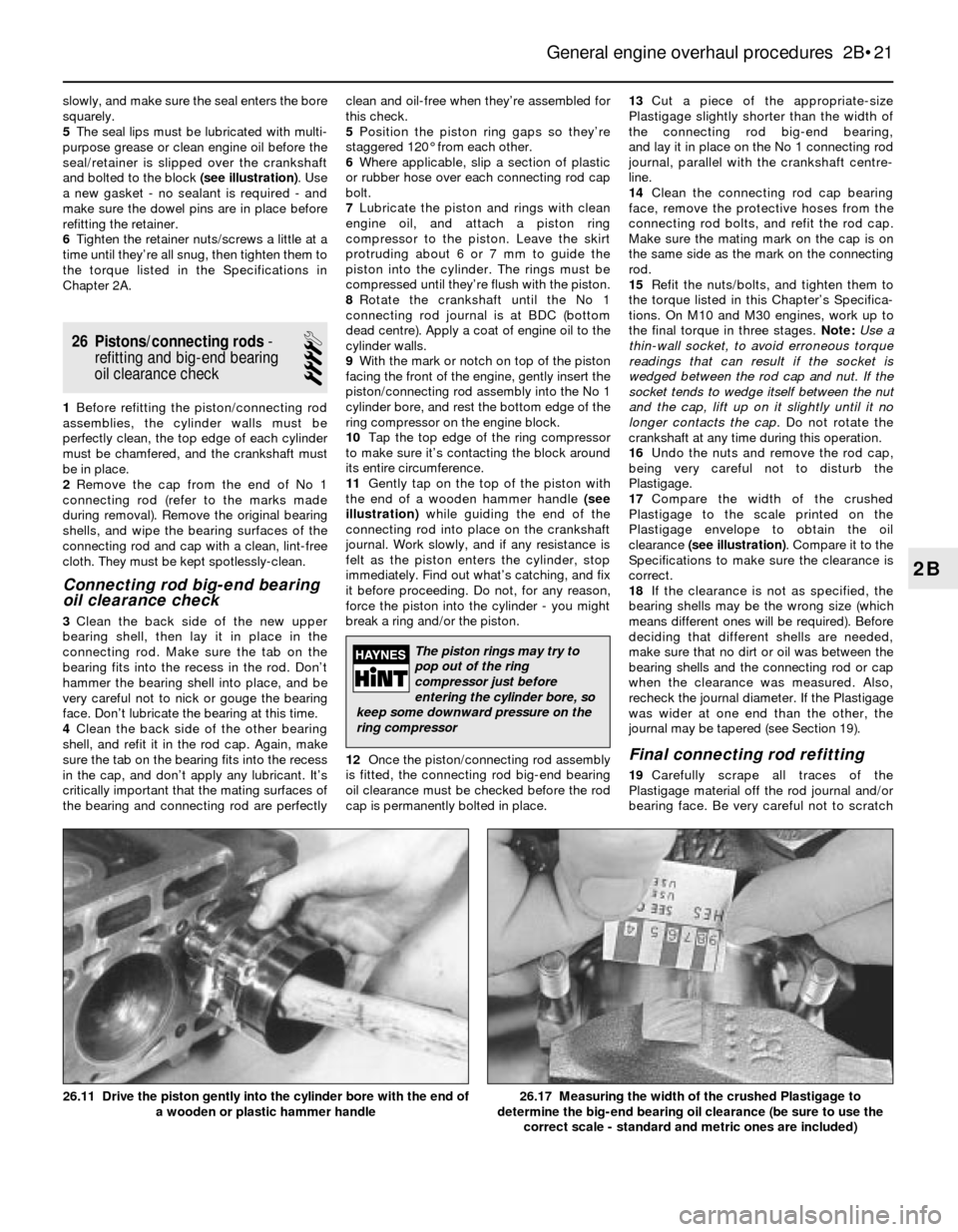
slowly, and make sure the seal enters the bore
squarely.
5The seal lips must be lubricated with multi-
purpose grease or clean engine oil before the
seal/retainer is slipped over the crankshaft
and bolted to the block (see illustration). Use
a new gasket - no sealant is required - and
make sure the dowel pins are in place before
refitting the retainer.
6Tighten the retainer nuts/screws a little at a
time until they’re all snug, then tighten them to
the torque listed in the Specifications in
Chapter 2A.
26 Pistons/connecting rods-
refitting and big-end bearing
oil clearance check
4
1Before refitting the piston/connecting rod
assemblies, the cylinder walls must be
perfectly clean, the top edge of each cylinder
must be chamfered, and the crankshaft must
be in place.
2Remove the cap from the end of No 1
connecting rod (refer to the marks made
during removal). Remove the original bearing
shells, and wipe the bearing surfaces of the
connecting rod and cap with a clean, lint-free
cloth. They must be kept spotlessly-clean.
Connecting rod big-end bearing
oil clearance check
3Clean the back side of the new upper
bearing shell, then lay it in place in the
connecting rod. Make sure the tab on the
bearing fits into the recess in the rod. Don’t
hammer the bearing shell into place, and be
very careful not to nick or gouge the bearing
face. Don’t lubricate the bearing at this time.
4Clean the back side of the other bearing
shell, and refit it in the rod cap. Again, make
sure the tab on the bearing fits into the recess
in the cap, and don’t apply any lubricant. It’s
critically important that the mating surfaces of
the bearing and connecting rod are perfectlyclean and oil-free when they’re assembled for
this check.
5Position the piston ring gaps so they’re
staggered 120° from each other.
6Where applicable, slip a section of plastic
or rubber hose over each connecting rod cap
bolt.
7Lubricate the piston and rings with clean
engine oil, and attach a piston ring
compressor to the piston. Leave the skirt
protruding about 6 or 7 mm to guide the
piston into the cylinder. The rings must be
compressed until they’re flush with the piston.
8Rotate the crankshaft until the No 1
connecting rod journal is at BDC (bottom
dead centre). Apply a coat of engine oil to the
cylinder walls.
9With the mark or notch on top of the piston
facing the front of the engine, gently insert the
piston/connecting rod assembly into the No 1
cylinder bore, and rest the bottom edge of the
ring compressor on the engine block.
10Tap the top edge of the ring compressor
to make sure it’s contacting the block around
its entire circumference.
11Gently tap on the top of the piston with
the end of a wooden hammer handle (see
illustration)while guiding the end of the
connecting rod into place on the crankshaft
journal. Work slowly, and if any resistance is
felt as the piston enters the cylinder, stop
immediately. Find out what’s catching, and fix
it before proceeding. Do not, for any reason,
force the piston into the cylinder - you might
break a ring and/or the piston.
12Once the piston/connecting rod assembly
is fitted, the connecting rod big-end bearing
oil clearance must be checked before the rod
cap is permanently bolted in place.13Cut a piece of the appropriate-size
Plastigage slightly shorter than the width of
the connecting rod big-end bearing,
and lay it in place on the No 1 connecting rod
journal, parallel with the crankshaft centre-
line.
14Clean the connecting rod cap bearing
face, remove the protective hoses from the
connecting rod bolts, and refit the rod cap.
Make sure the mating mark on the cap is on
the same side as the mark on the connecting
rod.
15Refit the nuts/bolts, and tighten them to
the torque listed in this Chapter’s Specifica-
tions. On M10 and M30 engines, work up to
the final torque in three stages. Note:Use a
thin-wall socket, to avoid erroneous torque
readings that can result if the socket is
wedged between the rod cap and nut. If the
socket tends to wedge itself between the nut
and the cap, lift up on it slightly until it no
longer contacts the cap. Do not rotate the
crankshaft at any time during this operation.
16Undo the nuts and remove the rod cap,
being very careful not to disturb the
Plastigage.
17Compare the width of the crushed
Plastigage to the scale printed on the
Plastigage envelope to obtain the oil
clearance (see illustration). Compare it to the
Specifications to make sure the clearance is
correct.
18If the clearance is not as specified, the
bearing shells may be the wrong size (which
means different ones will be required). Before
deciding that different shells are needed,
make sure that no dirt or oil was between the
bearing shells and the connecting rod or cap
when the clearance was measured. Also,
recheck the journal diameter. If the Plastigage
was wider at one end than the other, the
journal may be tapered (see Section 19).
Final connecting rod refitting
19Carefully scrape all traces of the
Plastigage material off the rod journal and/or
bearing face. Be very careful not to scratch
General engine overhaul procedures 2B•21
26.17 Measuring the width of the crushed Plastigage to
determine the big-end bearing oil clearance (be sure to use the
correct scale - standard and metric ones are included)26.11 Drive the piston gently into the cylinder bore with the end of
a wooden or plastic hammer handle
2B
The piston rings may try to
pop out of the ring
compressor just before
entering the cylinder bore, so
keep some downward pressure on the
ring compressor
Page 78 of 228
the bearing - use your fingernail or the edge of
a credit card.
20Make sure the bearing faces are perfectly
clean, then apply a uniform layer of
molybdenum disulphide (“moly”) grease or
engine assembly oil to both of them. You’ll
have to push the piston into the cylinder to
expose the face of the bearing shell in the
connecting rod - be sure to slip the protective
hoses over the rod bolts first, where
applicable.
21Slide the connecting rod back into place
on the journal, and remove the protective
hoses from the rod cap bolts. Refit the rod
cap, and tighten the nuts/bolts to the
specified torque.
22Repeat the entire procedure for the
remaining pistons/connecting rods.
23The important points to remember are:
a) Keep the back sides of the bearing shells
and the insides of the connecting rods
and caps perfectly clean when
assembling them.
b) Make sure you have the correct
piston/rod assembly for each cylinder.
c) The notch or mark on the piston must
face the front of the engine.
d) Lubricate the cylinder walls with clean oil.
e) Lubricate the bearing faces when refitting
the rod caps after the oil clearance has
been checked.
24After all the piston/connecting rod
assemblies have been properly fitted, rotate
the crankshaft a number of times by hand to
check for any obvious binding.25Check the connecting rod side play (see
Section 13).
26Compare the measured side play to the
Specifications to make sure it’s correct. If it
was correct before dismantling, and the
original crankshaft and rods were refitted, it
should still be right. If new rods or a new
crankshaft were fitted, the side play may be
incorrect. If so, the rods will have to be
removed and taken to a machine shop for
attention.
27 Initial start-up and running-
in after overhaul
1
Warning:Have a fire extinguisher
handy when starting the engine
for the first time.
1Once the engine has been refitted in the
vehicle, double-check the engine oil and
coolant levels.
2With the spark plugs removed and the
ignition system disabled (see Section 3), crank
the engine until oil pressure registers on the
gauge, or until the oil pressure warning light
goes out.
3Refit the spark plugs, connect the HT leads,
and restore the ignition system functions (see
Section 3).
4Start the engine. It may take a few
moments for the fuel system to build uppressure, but the engine should start without
a great deal of effort. Note: If backfiring
occurs through the throttle body or
carburettor, check the valve timing (check that
the timing chain/belt has been correctly fitted),
the firing order (check the fitted order of the
spark plug HT leads), and the ignition timing.
5After the engine starts, it should be allowed
to warm up to normal operating temperature.
While the engine is warming up, make a
thorough check for fuel, oil and coolant leaks.
6Shut the engine off and recheck the engine
oil and coolant levels.
7Drive the vehicle to an area with minimum
traffic, accelerate at full throttle from 30 to
50 mph, then lift off the throttle completely,
and allow the vehicle to slow to 30 mph with
the throttle closed. Repeat the procedure
10 or 12 times. This will load the piston rings,
and cause them to seat properly against the
cylinder walls. Check again for oil and coolant
leaks.
8Drive the vehicle gently for the first
500 miles (no sustained high speeds) and
keep a constant check on the oil level. It is not
unusual for an engine to use oil during the
running-in period.
9At approximately 500 to 600 miles, change
the oil and filter.
10For the next few hundred miles, drive the
vehicle normally - don’t nurse it, but don’t
abuse it, either.
11After 2000 miles, change the oil and filter
again. The engine may now be considered to
be fully run-in.
2B•22 General engine overhaul procedures
Page 95 of 228
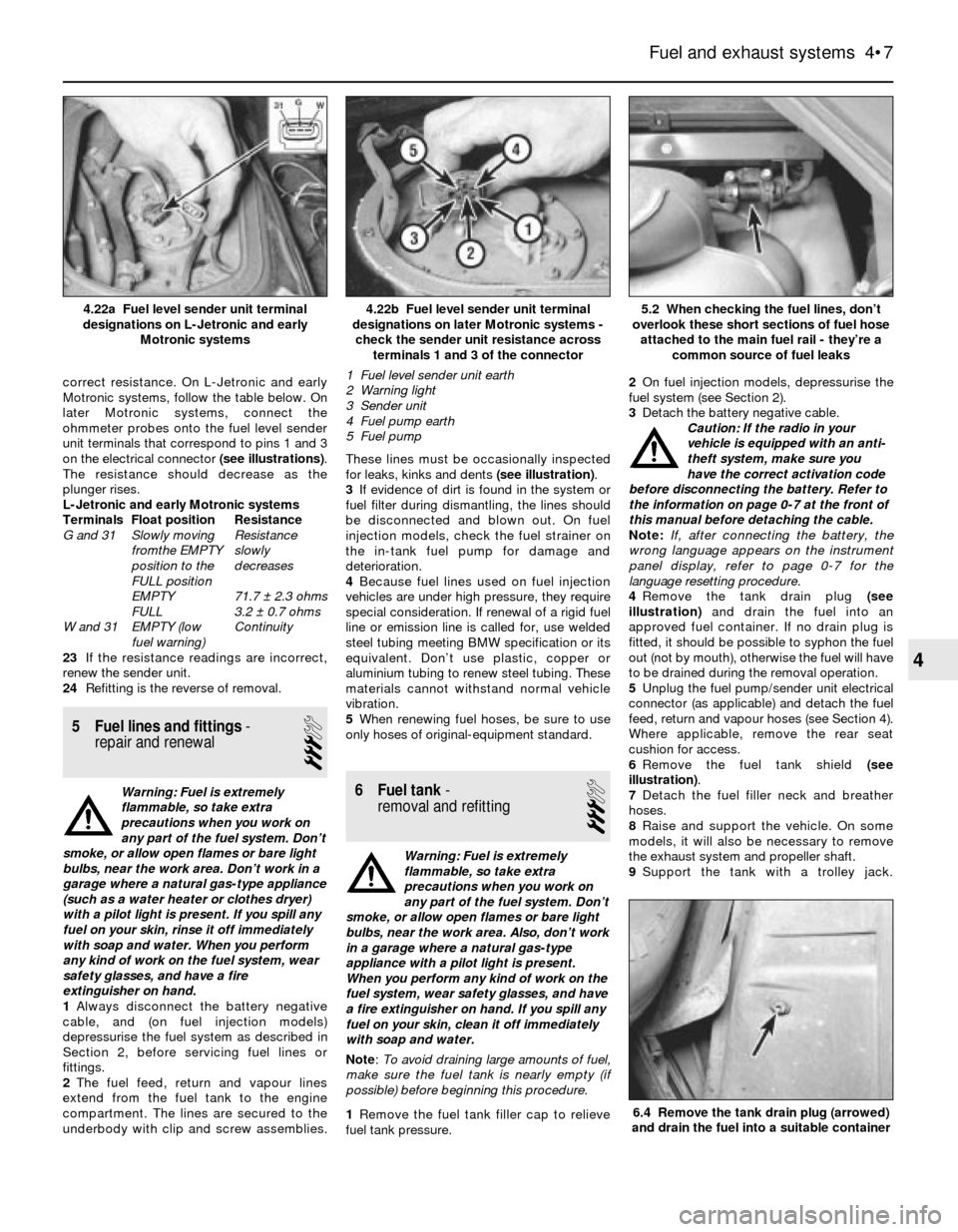
correct resistance. On L-Jetronic and early
Motronic systems, follow the table below. On
later Motronic systems, connect the
ohmmeter probes onto the fuel level sender
unit terminals that correspond to pins 1 and 3
on the electrical connector (see illustrations).
The resistance should decrease as the
plunger rises.
L-Jetronic and early Motronic systems
Terminals Float position Resistance
G and 31 Slowly moving Resistance
fromthe EMPTY slowly
position to the decreases
FULL position
EMPTY 71.7 ± 2.3 ohms
FULL 3.2 ± 0.7 ohms
W and 31 EMPTY (low Continuity
fuel warning)
23If the resistance readings are incorrect,
renew the sender unit.
24Refitting is the reverse of removal.
5 Fuel lines and fittings-
repair and renewal
3
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Don’t work in a
garage where a natural gas-type appliance
(such as a water heater or clothes dryer)
with a pilot light is present. If you spill any
fuel on your skin, rinse it off immediately
with soap and water. When you perform
any kind of work on the fuel system, wear
safety glasses, and have a fire
extinguisher on hand.
1Always disconnect the battery negative
cable, and (on fuel injection models)
depressurise the fuel system as described in
Section 2, before servicing fuel lines or
fittings.
2The fuel feed, return and vapour lines
extend from the fuel tank to the engine
compartment. The lines are secured to the
underbody with clip and screw assemblies.These lines must be occasionally inspected
for leaks, kinks and dents (see illustration).
3If evidence of dirt is found in the system or
fuel filter during dismantling, the lines should
be disconnected and blown out. On fuel
injection models, check the fuel strainer on
the in-tank fuel pump for damage and
deterioration.
4Because fuel lines used on fuel injection
vehicles are under high pressure, they require
special consideration. If renewal of a rigid fuel
line or emission line is called for, use welded
steel tubing meeting BMW specification or its
equivalent. Don’t use plastic, copper or
aluminium tubing to renew steel tubing. These
materials cannot withstand normal vehicle
vibration.
5When renewing fuel hoses, be sure to use
only hoses of original-equipment standard.6 Fuel tank-
removal and refitting
3
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Also, don’t work
in a garage where a natural gas-type
appliance with a pilot light is present.
When you perform any kind of work on the
fuel system, wear safety glasses, and have
a fire extinguisher on hand. If you spill any
fuel on your skin, clean it off immediately
with soap and water.
Note: To avoid draining large amounts of fuel,
make sure the fuel tank is nearly empty (if
possible) before beginning this procedure.
1Remove the fuel tank filler cap to relieve
fuel tank pressure.2On fuel injection models, depressurise the
fuel system (see Section 2).
3Detach the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
4Remove the tank drain plug (see
illustration)and drain the fuel into an
approved fuel container. If no drain plug is
fitted, it should be possible to syphon the fuel
out (not by mouth), otherwise the fuel will have
to be drained during the removal operation.
5Unplug the fuel pump/sender unit electrical
connector (as applicable) and detach the fuel
feed, return and vapour hoses (see Section 4).
Where applicable, remove the rear seat
cushion for access.
6Remove the fuel tank shield (see
illustration).
7Detach the fuel filler neck and breather
hoses.
8Raise and support the vehicle. On some
models, it will also be necessary to remove
the exhaust system and propeller shaft.
9Support the tank with a trolley jack.
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•7
4.22b Fuel level sender unit terminal
designations on later Motronic systems -
check the sender unit resistance across
terminals 1 and 3 of the connector
1 Fuel level sender unit earth
2 Warning light
3 Sender unit
4 Fuel pump earth
5 Fuel pump4.22a Fuel level sender unit terminal
designations on L-Jetronic and early
Motronic systems
6.4 Remove the tank drain plug (arrowed)
and drain the fuel into a suitable container
5.2 When checking the fuel lines, don’t
overlook these short sections of fuel hose
attached to the main fuel rail - they’re a
common source of fuel leaks
4
Page 126 of 228
slightly by hand. Release the throttle slowly
until it reaches 0.2 to 0.6 mm from the throttle
stop. There should be continuity.
29Check the resistance between terminals 3
and 18 as the throttle is opened. There should
be continuity when the throttle switch is within
8 to 12 degrees of fully-open. If the readings
are incorrect, adjust the TPS.
30If all the resistance readings are correct
and the TPS is properly adjusted, check for
power (5 volts) at the sensor, and if necessary
trace any wiring circuit problems between the
sensor and ECU (see Chapter 12).
Adjustment
31If the adjustment is not as specified
(paragraphs 28 to 30), loosen the screws on
the TPS, and rotate the sensor into the correct
adjustment. Follow the procedure for
checking the TPS given above, and tighten
the screws when the setting is correct.
32Recheck the TPS once more; if the
readings are correct, reconnect the TPS
harness connector.
Early 535i models with automatic
transmission
Check
33First test the continuity of the TPS. Follow
paragraphs 28 to 30 and check for continuity.
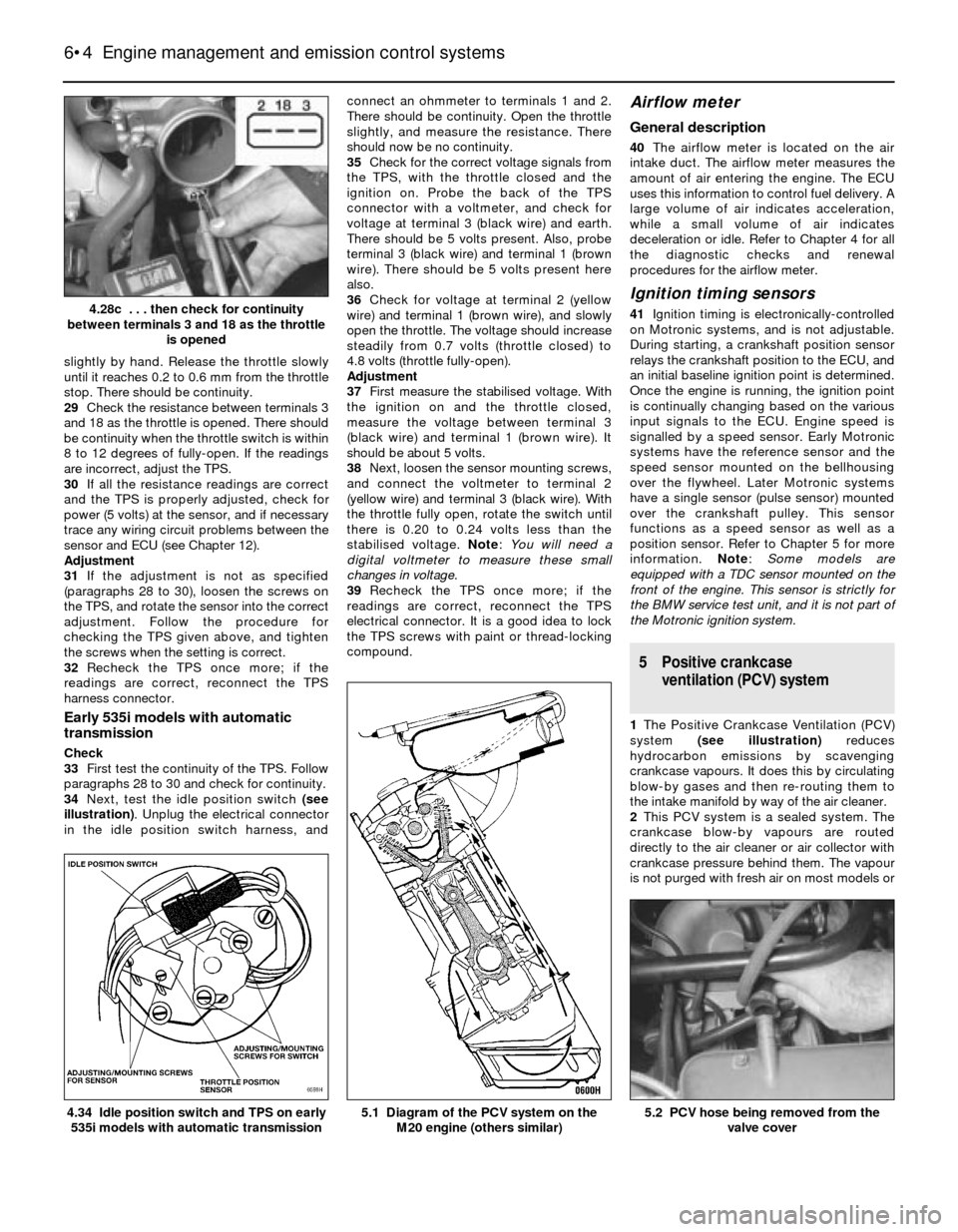
34Next, test the idle position switch (see
illustration). Unplug the electrical connector
in the idle position switch harness, andconnect an ohmmeter to terminals 1 and 2.
There should be continuity. Open the throttle
slightly, and measure the resistance. There
should now be no continuity.
35Check for the correct voltage signals from
the TPS, with the throttle closed and the
ignition on. Probe the back of the TPS
connector with a voltmeter, and check for
voltage at terminal 3 (black wire) and earth.
There should be 5 volts present. Also, probe
terminal 3 (black wire) and terminal 1 (brown
wire). There should be 5 volts present here
also.
36Check for voltage at terminal 2 (yellow
wire) and terminal 1 (brown wire), and slowly
open the throttle. The voltage should increase
steadily from 0.7 volts (throttle closed) to
4.8 volts (throttle fully-open).
Adjustment
37First measure the stabilised voltage. With
the ignition on and the throttle closed,
measure the voltage between terminal 3
(black wire) and terminal 1 (brown wire). It
should be about 5 volts.
38Next, loosen the sensor mounting screws,
and connect the voltmeter to terminal 2
(yellow wire) and terminal 3 (black wire). With
the throttle fully open, rotate the switch until
there is 0.20 to 0.24 volts less than the
stabilised voltage. Note: You will need a
digital voltmeter to measure these small
changes in voltage.
39Recheck the TPS once more; if the
readings are correct, reconnect the TPS
electrical connector. It is a good idea to lock
the TPS screws with paint or thread-locking
compound.
Airflow meter
General description
40The airflow meter is located on the air
intake duct. The airflow meter measures the
amount of air entering the engine. The ECU
uses this information to control fuel delivery. A
large volume of air indicates acceleration,
while a small volume of air indicates
deceleration or idle. Refer to Chapter 4 for all
the diagnostic checks and renewal
procedures for the airflow meter.
Ignition timing sensors
41Ignition timing is electronically-controlled
on Motronic systems, and is not adjustable.
During starting, a crankshaft position sensor
relays the crankshaft position to the ECU, and
an initial baseline ignition point is determined.
Once the engine is running, the ignition point
is continually changing based on the various
input signals to the ECU. Engine speed is
signalled by a speed sensor. Early Motronic
systems have the reference sensor and the
speed sensor mounted on the bellhousing
over the flywheel. Later Motronic systems
have a single sensor (pulse sensor) mounted
over the crankshaft pulley. This sensor
functions as a speed sensor as well as a
position sensor. Refer to Chapter 5 for more
information. Note: Some models are
equipped with a TDC sensor mounted on the
front of the engine. This sensor is strictly for
the BMW service test unit, and it is not part of
the Motronic ignition system.
5 Positive crankcase
ventilation (PCV) system
1The Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV)
system (see illustration)reduces
hydrocarbon emissions by scavenging
crankcase vapours. It does this by circulating
blow-by gases and then re-routing them to
the intake manifold by way of the air cleaner.
2This PCV system is a sealed system. The
crankcase blow-by vapours are routed
directly to the air cleaner or air collector with
crankcase pressure behind them. The vapour
is not purged with fresh air on most models or
6•4 Engine management and emission control systems
5.2 PCV hose being removed from the
valve cover5.1 Diagram of the PCV system on the
M20 engine (others similar)4.34 Idle position switch and TPS on early
535i models with automatic transmission
4.28c . . . then check for continuity
between terminals 3 and 18 as the throttle
is opened
Page 139 of 228
the stop-light switch (see Section 13). Note:
On right-hand-drive models, the brake pedal
in on the right-hand side of the vehicle, and is
connected to the left-hand side by a cross-
shaft. The adjustment is carried out on the
pushrod at the left-hand side, but the
dimension is measured at the pedal on the
right-hand side.
14On 5-Series models, adjust the brake
pedal height and the stop-light switch (see
Section 13).
15Refit the master cylinder (see Section 7)
and attach the vacuum hose.
16Carefully test the operation of the brakes
before returning the vehicle to normal use
9 Hydraulic brake servo-
description, removal and
refitting
3
Warning: Brake fluid is
poisonous. It is also an effective
paint stripper. Refer to the
warning at the start of Section 16.
Description
1On 5-Series E28 (“old-shape”) models, a
hydraulic brake servo system is fitted. The
servo unit, located between the brake pedal
(left-hand-drive) or cross-shaft lever (right-
hand-drive) and the master cylinder, is
operated by hydraulic pressure generated by
the power steering pump. When the engine is
running, the power steering pump supplies
hydraulic pressure to a power flow regulator/
accumulator. The regulator/accumulator
stores and regulates the pressure to the
hydraulic brake servo. When you press the
brake pedal, the pressure in the servo helps
actuate the master cylinder, reducing pedal
effort.
2The hydraulic brake servo cannot be
overhauled; if it fails, a new one must be fitted.
Testing the system requires special tools, so
even fault diagnosis is beyond the scope of
the home mechanic. If the system fails, take it
to a dealer service department or other
qualified garage for repairs.
Removal and refitting
3With the engine off, discharge the hydraulic
accumulator by depressing the brake pedal
20 times or more.
4Remove the master cylinder (see Section 7).
5Clean the area around the return and
supply line fittings, then disconnect them.
Plug the lines, to prevent dirt from entering the
system, and to prevent further fluid loss.
Caution: Even a particle of dirt
can damage the servo, so be
extremely careful to prevent dirt
from entering the system while
the lines are disconnected.
6Working from inside the passenger
compartment, remove the lower left trim
panels above the brake pedal (left-hand-drive
models) or glovebox and trim (right-hand-drive models). On left-hand-drive models, also
disconnect the pedal return spring.
7Prise off the retaining clip, and disconnect
the pushrod from the brake pedal (see
illustration 8.9) or cross-shaft lever.
8Remove the four mounting nuts and
remove the brake servo (see illus-
tration 8.10).
9Refitting is the reverse of removal. Tighten
the hydraulic lines to the torque listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications. Note:Don’t try to
tighten these fittings without a torque wrench.
If they’re loose, they can leak, which can affect
system operation; if they’re tight, they can be
damaged, and they’ll also leak. You’ll need a
crowfoot-type split ring (“brake”) attachment
for your torque wrench to tighten the fittings
properly.
10When you’re done, bleed the brake
hydraulic system (Section 16) and adjust the
brake pedal travel and the stop-light switch
(see Section 13).
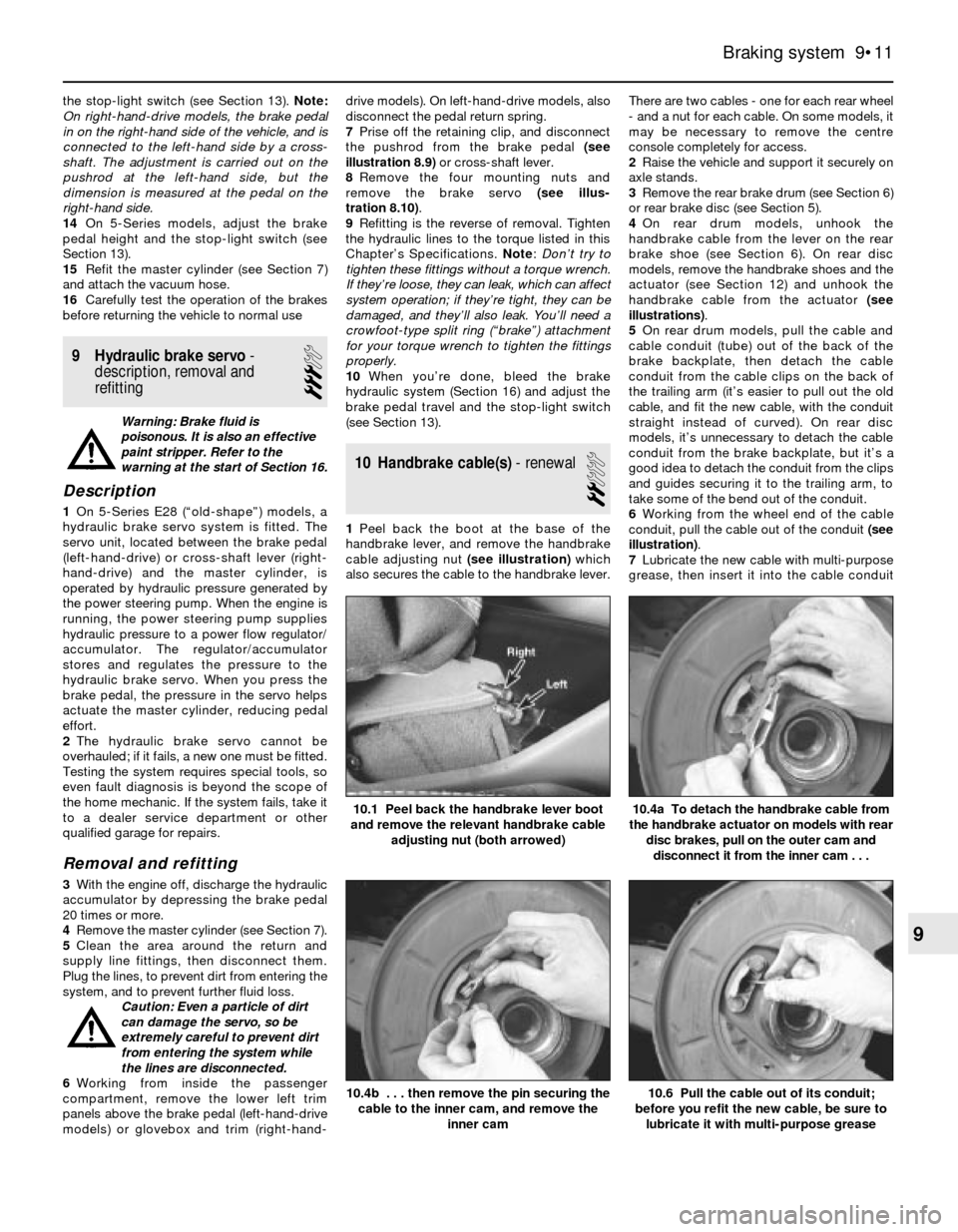
10 Handbrake cable(s)- renewal
2
1Peel back the boot at the base of the
handbrake lever, and remove the handbrake
cable adjusting nut (see illustration)which
also secures the cable to the handbrake lever.There are two cables - one for each rear wheel
- and a nut for each cable. On some models, it
may be necessary to remove the centre
console completely for access.
2Raise the vehicle and support it securely on
axle stands.
3Remove the rear brake drum (see Section 6)
or rear brake disc (see Section 5).
4On rear drum models, unhook the
handbrake cable from the lever on the rear
brake shoe (see Section 6). On rear disc
models, remove the handbrake shoes and the
actuator (see Section 12) and unhook the
handbrake cable from the actuator (see
illustrations).
5On rear drum models, pull the cable and
cable conduit (tube) out of the back of the
brake backplate, then detach the cable
conduit from the cable clips on the back of
the trailing arm (it’s easier to pull out the old
cable, and fit the new cable, with the conduit
straight instead of curved). On rear disc
models, it’s unnecessary to detach the cable
conduit from the brake backplate, but it’s a
good idea to detach the conduit from the clips
and guides securing it to the trailing arm, to
take some of the bend out of the conduit.
6Working from the wheel end of the cable
conduit, pull the cable out of the conduit (see
illustration).
7Lubricate the new cable with multi-purpose
grease, then insert it into the cable conduit
Braking system 9•11
10.1 Peel back the handbrake lever boot
and remove the relevant handbrake cable
adjusting nut (both arrowed)
10.6 Pull the cable out of its conduit;
before you refit the new cable, be sure to
lubricate it with multi-purpose grease10.4b . . . then remove the pin securing the
cable to the inner cam, and remove the
inner cam
10.4a To detach the handbrake cable from
the handbrake actuator on models with rear
disc brakes, pull on the outer cam and
disconnect it from the inner cam . . .
9
Page 141 of 228
then back off the adjuster until the shoes
don’t drag (see Section 11). Refit the wheel
bolts, and tighten them to the torque given in
Chapter 1 Specifications.
13 Brake pedal- adjustment
1
Note:You should always adjust brake pedal
height after the master cylinder or brake servo
has been removed or renewed. You should
also adjust the stop-light switch (see Sec-
tion 14).
1Measure the distance between the lower
edge of the brake pedal footpad (ie the edge
furthest from the bulkhead) and the bulkhead
(see illustration), and compare your
measurement with the dimension listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications. If it’s not as listed,
loosen the locknut on the pushrod, and rotatethe pushrod while holding the clevis stationary
until the distance is correct. Note:On right-
hand-drive models, the adjustment is carried
out at the left-hand side of the cross-shaft,
after removing the glovebox, but the
dimension is still measured at the pedal.
14 Stop-light switch-
check and adjustment
1
Note:The stop-light switch should be
checked and, if necessary, adjusted after the
master cylinder or brake servo has been
removed or renewed.
1The stop-light switch is located on a
bracket at the top of the brake pedal. The
switch activates the brake lights whenever the
pedal is depressed.
2With the brake pedal in the rest position,
measure the distance between the switch
contact point on the brake pedal and the
switch housing (see illustration)and
compare your measurement with dimension A
listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
3If your measurement is outside theindicated dimension, disconnect the wires
from the switch. Loosen the locknuts, screw
the switch in or out until the plunger
dimension is correct, and retighten the
locknuts. Reconnect the wires and check for
correct operation.
15 Brake hoses and lines-
inspection and renewal
4
Warning: Brake fluid is
poisonous. It is also an effective
paint stripper. Refer to the
warning at the start of Section 16.
Inspection
1At the intervals specified in Chapter 1, the
brake hoses and lines should be inspected.
With the vehicle raised and placed securely
on axle stands, the flexible hoses should be
checked for cracks, chafing of the outer
cover, leaks, blisters and other damage.
These are important and vulnerable parts of
the brake system, and inspection should be
thorough. The metal pipes should be checked
for excessive pitting and corrosion. If a hose
or pipe exhibits any of the conditions
described, renew it.
Flexible hose renewal
2Clean all dirt away from the ends of the
hose. Have ready a suitable container to catch
spilled brake fluid when the hose is
disconnected.
3To disconnect the hose at the chassis end,
use a spanner to hold the hex-shaped fitting
on the end of the flexible hose, and loosen the
nut on the metal brake line (see illustration).
If the nut is stuck, soak it with penetrating oil.
After the hose is disconnected from the metal
line, remove the spring clip from the bracket
and detach the hose from the bracket.
4To detach the flexible hose from the caliper,
Braking system 9•13
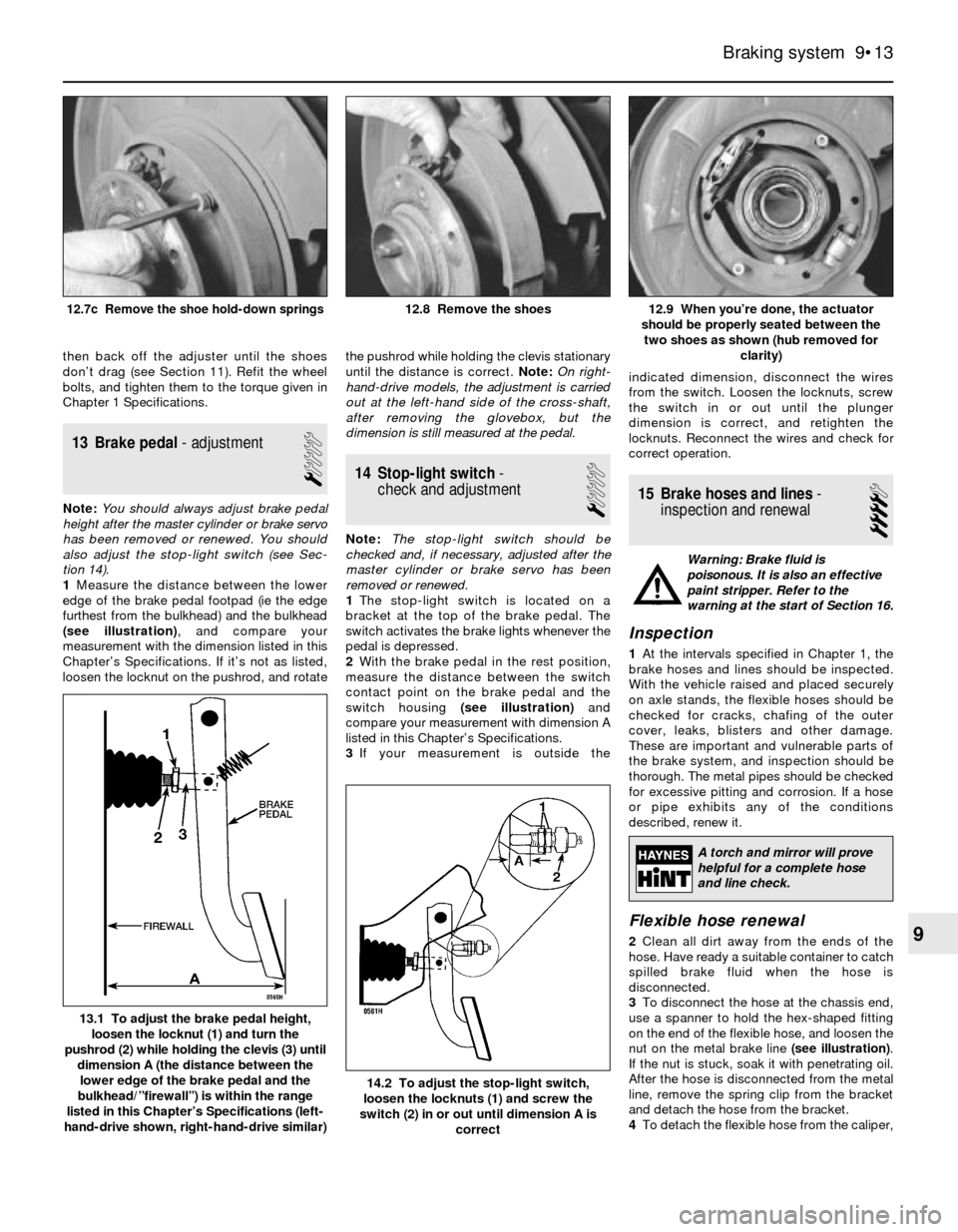
12.9 When you’re done, the actuator
should be properly seated between the
two shoes as shown (hub removed for
clarity)12.8 Remove the shoes12.7c Remove the shoe hold-down springs
14.2 To adjust the stop-light switch,
loosen the locknuts (1) and screw the
switch (2) in or out until dimension A is
correct
13.1 To adjust the brake pedal height,
loosen the locknut (1) and turn the
pushrod (2) while holding the clevis (3) until
dimension A (the distance between the
lower edge of the brake pedal and the
bulkhead/”firewall”) is within the range
listed in this Chapter’s Specifications (left-
hand-drive shown, right-hand-drive similar)
9
A torch and mirror will prove
helpful for a complete hose
and line check.