Fuel system BMW 528i 1998 E39 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1998, Model line: 528i, Model: BMW 528i 1998 E39Pages: 1002
Page 901 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
Central Locking and Anti-Theft
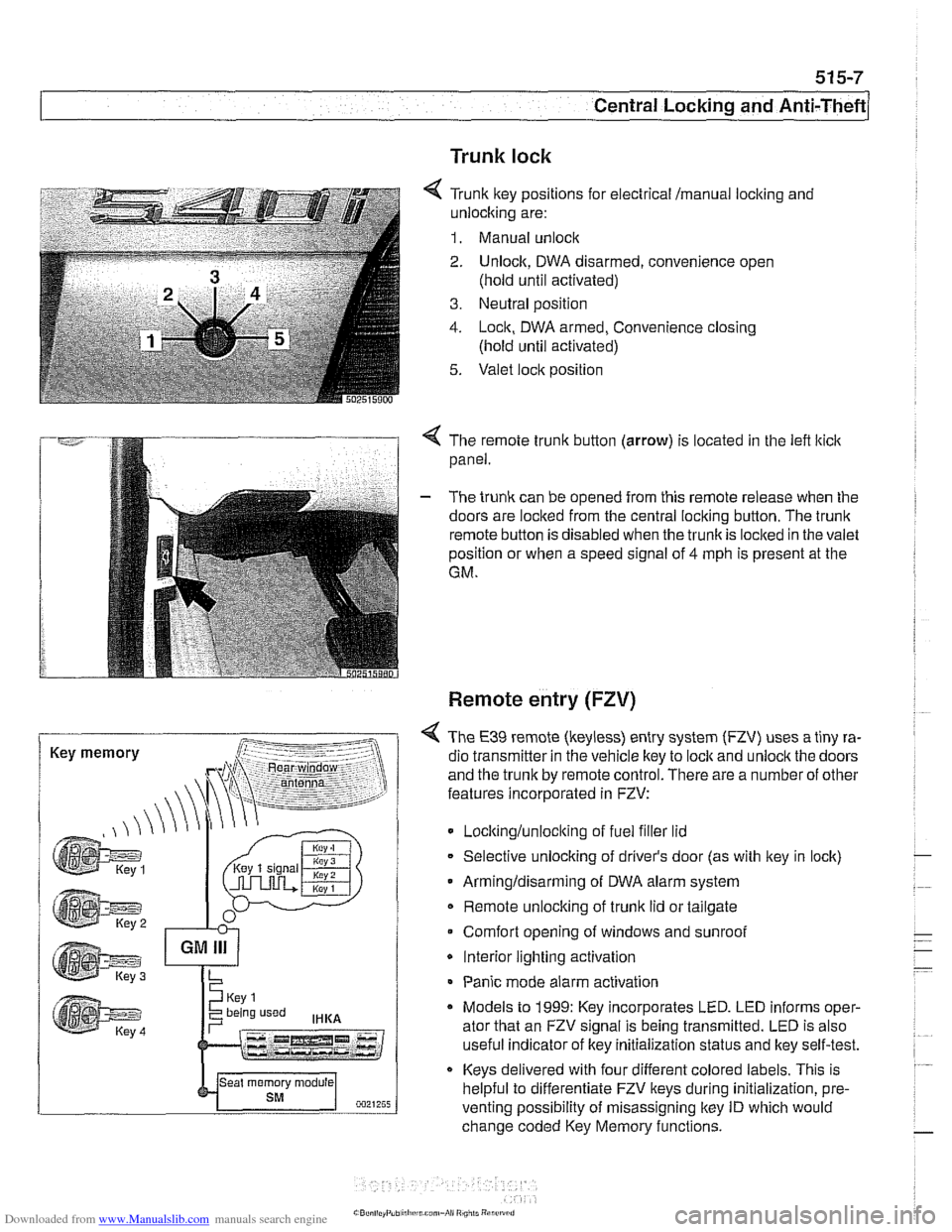
Trunk lock
6 Tr~nk ftey pos~rions for eecir'cal mama, locking and
-nlock~ng are:
1. Manual unock .. - - - ........ - ..- .- ................. s.=.=-- 2. Unlock. DWA oisarmed, conven:ence open
(nold
un1:l aclivaledj
3. Ne~tral posit'on
1. -ocn. DWA armeo, Convenience closng
(hold ~nti activated)
5. Valet .oc,t position
. -- .............-... .- . - -.....
Key memory
< The remote trunk button (arrow) is located in the lefl lticlc
panel.
- The trunk can be opened from this remote release when the
doors are locked from the central locking button. The
trunk
remote button is disabled when the trunkis loclted in the valet
position or when a speed signal of
4 mph is present at the
GM.
Remote entry (FZV)
< The €39 remote (keyless) entry system (FZV) uses a tiny ra-
dio transmitter in the vehicle key to
lock and unlock the doors
and the trunk by remote control. There are a number of other
features incorporated in FZV:
Locltinglunloclting of fuel filler lid
Selective unlocking of driver's door (as with key in lock)
Armingldisarming of DWA alarm system
Remote unlocking of
trunk lid or tailgate
Comfort opening of windows and sunroof
* Interior lighting activation
Panic mode alarm activation
* Models to 1999: Key incorporates LED. LED informs oper-
ator that an FZV signal is being transmitted. LED is also
useful indicator of key initialization status and lkey self-test.
Keys delivered with four different colored labels. This is
helpful to differentiate FZV keys during initialization,
pre.
venting possibility of misassigning key ID which would
change coded Key Memory functions.
Page 950 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
721 -2
l~irba~ System (SRS)
This repair group covers airbag components and replace-
ment.
Airbag system repairand fault diagnosis is not covered.
Diagnostics, component testing, and
airbag system repair
should be carried out by trained BMW service technicians.
Individual
airbag system components can only be tested elec-
tronically when installed in the car. BMW service testers
DIS
or MoDiC or equivalent must be used for diagnostic work.
WARNING-
Special test equipment is required to retrieve airbag fault
codes, diagnose system faults, and
reseffturn off the air-
bag indicator light. The indicator light will remain on until
any problem has been corrected and the fault memory has
been cleared.
Airbags are part of the BMW Multiple Restraint System
(MRS). Three versions of MRS are available in E39 models.
Multiple Restraint Systems
MRS and MRS II include the following restraint components:
311 996-811 997
911
997-311 999
311 999-2002
Driver and passenger front
airbags (MRSIMRS II)
MRS
MRS
II
MRS Ill
Passenger front two-stage airbag (cars manufactured
from
911998).
The seat occupancy sensor (SBE) is used for detection of
a passenger in the right front seat. MRS uses the SBE in-
put to determine seat belt tensioner
and/or front airbag de-
ployment thresholds.
Side impact
airbag for driver and front passenger
(MRSIMRS II)
Leftlright side impact crash sensors (MRSIMRS 11)
Side impact airbag for rear passenger (MRS II) (optional)
Head Protection System (HPS) for driver and front passen-
ger (MRS
II)
Battery Safety Terminal - BST (MRS II)
Hall Sensor seat belt switches (MRS II)
Front pyrotechnic seat belt tensioners
Fuel pump cut off message
Page 962 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
OED-2
On-Board Diagnostics
Specialized OED II scan tool equipment is needed to access
the fault memory and
OED I1 data.
The extra hardware needed to operate the OED
I1 system
consists mainly of the following:
* Additional oxygen sensors downstream of the catalytic
converters.
Fuel tank pressure sensor and device to pressurize
fuel
storage system.
Several engine and performance monitoring devices
Standardized 16-pin
OED II connector under the
dashboard.
Upgraded components for the federally required reliability
mandate.
Malfunction indicator light (MIL)
OED II software illuminates the malfunction indicator light
(MIL) when emission levels exceed 1.5 times Federal
standards.
4 For E34 cars covered by this manual, three different MIL
symbols were used, depending on year and model.
MIL illuminates under the following conditions:
Engine management system fault detected for
two
consecutive OED iI drive cycles. See Drive cycle in this
repair group.
- Catalyst damaging fault detected.
Component malfunction causes emissions to exceed 1.5
times OED
II standards.
Manufacturer-defined specifications exceeded. Implausible input signal.
Misfire
faults.
Leak in evaporative system,
Oxygen sensors observe no purge
flow from purge valve 1
evaporative system.
ECM fails to enter closed-loop operation within specified
time.
ECM or automatic transmission control
module (TCM) in
"limp home" mode.
ignition key ON before cranking (bulb
check function).
OED
II fault memory (including the MIL) can only be reset
using a special scan tool. Removing the connector from the
ECM or disconnecting the battery does not erase the fault
memory.
Page 964 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
- -
On-Board Diagnostics
Professional diagnostic scan tools available atthe time of this
printing include the BMW factory tools
(DISplus, GTI,
MoDiC) and a small number of aftermarket BMW-specific
tools. See
020 Maintenance.
In addition to the professional line of scan tools, inexpensive
generic OBD
II scan tool software programs and handheld
units are readily available. Though limited, they are
nonetheless powerful diagnostic tools. These tools read live
data streams and freeze frame data as well as a host of other
valuable diagnostic data.
Diagnostic monitors
Diagnostic monitors run tests and checks on specific
emission control systems, components, and functions.
A complete drive cycle is requiredforthe tests to bevalid. See
Drive cycle in this repair group. The diagnostic monitor
signals the
ECM of the loss or impairment of the signal or
component and determines if a signal or sensor is faulty
based on
3 conditions:
* Signal or component shorted to ground
Signal or component shorted to
B+
Signal or component missing (open circuit)
The OBD
II system monitors all emission control systems that
are installed. Emission control systems vary by vehicle model
and year. For example, a vehicle may not be equipped with
secondary air injection, so no secondary air readiness code
would be present.
OBD
II software monitors the following:
Oxygen sensors
Catalysts
Engine misfire
- Fuel tank evaporative control system
Secondary air injection Fuel system
Oxygen sensor monitoring. When driving conditions allow,
response rate and switching time of each oxygen sensor is
monitored. The oxygen sensor heater function is also
monitored. The OBD
II system differentiates between
precataylst and post-catalyst oxygen sensors and reads each
one individually. In order
forthe oxygen sensor to be
effectively monitored, the system must be in closed loop
operation.
Page 966 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
OBD-6
On-Board Diagnostics
Fuel system monitoring. This monitor looks at the fuel
delivery needed (long
/short term fuel trim) for proper engine
operation based on programmed data. If too much or not
enough fuel is delivered over a predetermined time, a DTC is
set and the MIL illuminates.
Fuel trim refers to adiustments to base fuel schedule.
Lono- ., term fuel trim refers to gradual adjustments to the fuel
calibration adjustment as compared to short term fuel trim.
Long term fuel trim adjustments compensate for gradual
changes that occur over time.
Fuel system monitoring monitors the calculated injection time
(ti) in relation to enginespeed, load and precatalyticconverter
oxygen
sensor(s) signals.
Using this data, the system optimizes fuel delivery for all
engine operating conditions.
Evaporative system monitoring. This monitor checks the
the fuel storage system and related fuel lines for leaks. It can
detect very small leaks anywhere in the system.
A leak detection unit (LDP or DMTL) is used to pressurize the
evaporative control system on a continuous basis (as the
drive cycle allows) and to
check system integrity.
Drive cycle
The OED II drive cycle is an important concept in
understanding OBD
II requirements. The purpose of the drive
cycle is to run ail of the emission-related on-board diagnostics
over a broad range of driving conditions.
A drive cycle is considered complete when all of the
diagnostic monitors have run their tests without interruption.
~ora drive cycle to be initiated, the vehicle must be started
cold and brought up to
1 60°F and at least 40°F above its
original starting temperature.
Readiness codes
Inspection/maintenance (I/M) readiness codes are mandated
as part of OBD
II. The readiness code is stored aftercomplete
diagnostic monitoring of specified components and systems
is carried out. The readiness code function was designed to
prevent manipulating an
I/M emission test procedure by
clearing faults codes or disconnecting the ECM or battery.
Page 967 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
On-Board Diagnostics
Readiness codes indicate whether the OED Ii system is
actually ready to monitor the various emission control
systems on the vehicle. The vehicle must complete a drive
cycle to set readiness codes. The code is binary:
0 for ready
1 for not ready
f
4 The parameters which are monitored for readiness are:
llM readiness codes
1. Catalyst efficiency
2. Catalyst heating
3. Fuel tank evaporative control
4. Secondary air injection
5.
NC refrigerant
6. Oxygen sensors
7. Oxygen sensor heaters
8. Exhaust gas recirculation
Readiness codes are set to 1 (not ready) in the following
cases:
~9~~.f~[<+t~t~p:,~;:#j~~{]~y~ ,,... , , 8701Dbd001
The battery or ECM is disconnected.
When
all zeros are displayed, the system has established
DTCs are erased after completion of repairs and a drive
cycle is not completed.
readiness. Readiness codes
can be displayed using BMW
and aftermarket scan tools.
An
OED II scan tool can be used to determine IIM readiness.
Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)
SAE standard J2012 mandates a 5-digit diagnostic trouble
code (DTC) standard. Each digit represents a specific value.
Emission related DTCs
start with the letter P for power train.
When the engine service
light (MIL) is illuminated it indicates
that a DTC has been stored.
DTCs are stored as soon as they occur, whether or not the
engine service light illuminates.
DTCs store and display a time stamp.
DTCs record the current fault status: Present, not currently
present, or intermittent.
Page 968 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
OBD-8
I On-Board Diagnostics
DTC digit interpretation
1st digit
P powertrain
B body
C chassis
2nd digit
0 SAE
1 BMW
3rd digit
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
4th - 5th digits total
system
airlfuei induction
fuel injection
ignition system or misfire
auxiliary emission control
vehicle speed
& idle control
ECM
inputs/outputs
transmission
individual circuits or
components
DTC example: P 0 3 0 6
P: A powertrain problem
0: SAE sanctioned or 'generic'
a 3: Related to an ignition system / misfire
06 Misfire detected at cylinder #6
DTCs provide a freeze frame or snap-shot of a vehicle
performance or emissions fault at the moment that the fault
first occurs. This information is accessible through generic
OED I1 scan tools.
Freeze frame data contains, but is not limited to, the following
information:
Engine load (calculated)
Engine rpm
Short and
long term fuel trim
Vehicle speed
Coolant temperature Intake manifold pressure
Open/closed loop operation
Fuel pressure (if available)
DTC
Page 975 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
OBD-15
On-Board ~iagnosticsl
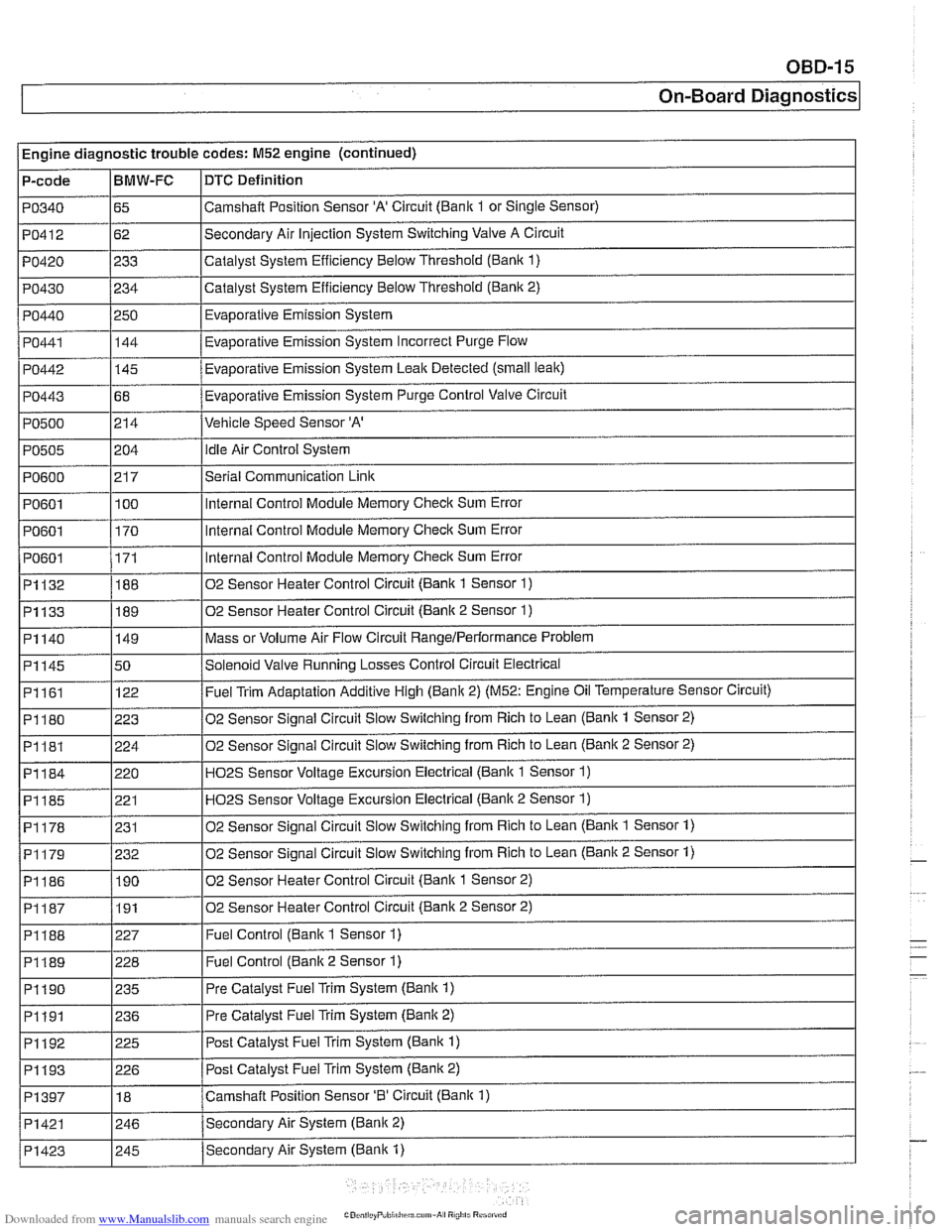
Engine diagnostic trouble codes: M52 engine (continued)
P-code
PO340
PO412
PO420
PO430
PO440
PO441
PO442
PO443
PO500
PO505
PO600
PO601
PO601
I PO601
~1132
~1133
BMW-FC
65
62
233
234
250 144
-
145
68
214
i I
DTC Definition
Camshalt Position Sensor 'A' Circuit (Bank 1 or Single Sensor)
Secondary Air Injection System Switching Valve A Circuit
Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold
(Bank 1)
Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
Evaporative Emission System
Eva~orative Emission Svstem Incorrect Purge Flow .
Evaporative Emission System Leak Detected (small leak)
Evaporative Emission System Purge Control Valve Circuit
Vehicle Speed Sensor 'A'
204
21 7
100
170
171
188
189
PI161
PI180
PI181
PI184
PI185
PI178
02 Sensor Heater Control Circuit (Bank 2 Sensor 2) I
idle Air Control System
Serial Communication
Link
Internal Control Module Memory Check Sum Error
Internal Control Module Memory
Check Sum Error
Internal Control Module Memory
Check Sum Error
02 Sensor Heater Control Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor
1)
02 Sensor Heater Control Circuit (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit RangeIPerlormance Problem PI140
I
I I
P1188 1227 I Fuel Control (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
PI145 150 /Solenoid Valve Running Losses Control Circuit Electrical
149
122
223
224
220 221
231
I I
P1189 1228 I Fuel Control (Banlc 2 Sensor 1)
Fuel Trim Adaptation Additive High (Bank 2) (M52: Engine Oil Temperature Sensor Circuit)
02 Sensor Signal Circuit Slow Switching from Rich to Lean
(Bank 1 Sensor 2)
02 Sensor Signal Circuit Slow Switching from Rich to Lean
(Bank 2 Sensor 2)
H02S Sensor Voltage Excursion Electrical (Banlc 1 Sensor 1)
HO2S Sensor Voltage Excursion Electrical (Banlc 2 Sensor 1)
02 Sensor Sianai Circuit Slow Switchina from Rich to Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
02 Sensor Signal Circuit Slow Switching from Rich to Lean (Bank 2 Sensor 1) PI179
I I
PI190 1235 I Pre Catalyst Fuel Trim System (Banlc 1)
PI186 1190 102 Sensor Heater Control Circuit (Banlc 1 Sensor 2)
232
I I
PI191 1236 I Pre
Catalyst Fuel Trim System (Banlc 2)
PI192
. . -- - i Pi193 1226 I Post Catalvst Fuel Trim Svstem (Bank 2)
225
PI397
I I
Post Catalyst Fuel Trim System (Bank 1)
PI421 1246 /Secondarv Air System (Bank 2)
18
Secondary Air System (Bank
1) PI423
Camshaft Position Sensor '0' Circuit (Bank 1)
I 245
Page 979 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
On-Board ~ia~nosticsl
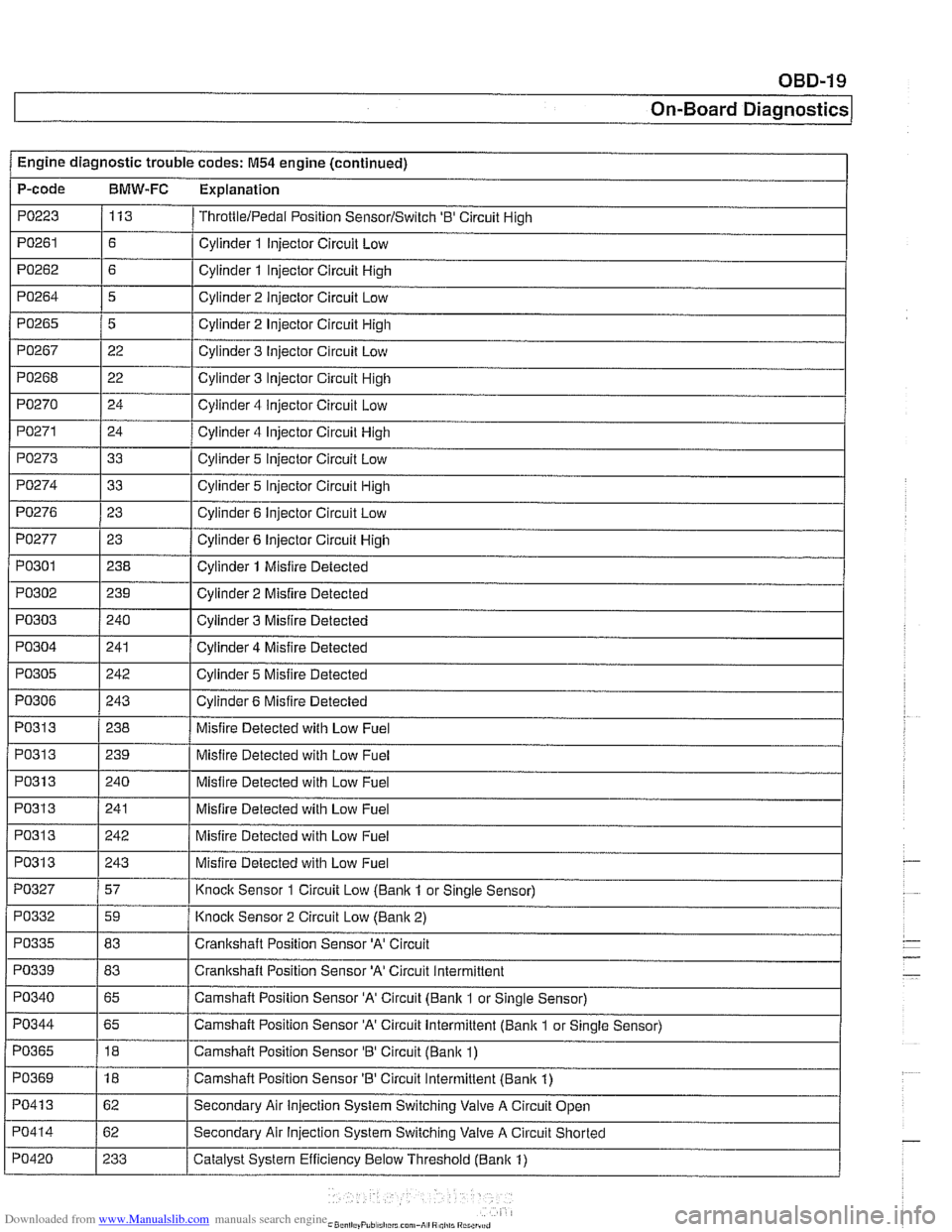
Engine diagnostic trouble codes: M54 engine (continued) I -.
P-code BMW-FC Explanation
PO223 113 ThrottlelPedal Position SensorlSwitch '0' Circuit High
PO261 / Cylinder 1 Injector Circuit Low
PO271 Cylinder 4 Injector Circuit High
PO273 Cylinder 5 Injector Circuit Low
Cylinder 2 Injector Circuit High
Cylinder 3 Injector Circuit
Low
Cylinder 3 Injector Circuit High
Cylinder 4
iniector Circuit Low
PO265
PO267
PO268
PO270
, I
PO277 1 23 1 Cylinder 6 Injector Circuit High
5
22
22
24
I I
PO274
PO301
PO302
PO303
PO304
PO276 1 23 I Cylinder 6 Injector Circuit Low
33
I
I -
I I
PO31 3 1 240 I Misfire Detected with Low Fuel Cylinder 5 Injector Circuit High
238
239
240
241
PO305
I I
Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected
Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected
Cylinder 3 Misfire Detected
Cylinder 4 Misfire Detected
PO313
PO306 1 243 I Cylinder 6 Misfire Detected
242
PO313
PO313
PO31 3
PO327
Cylinder 5 Misfire
Detected
PO31 3 1239 I Misfire Detected with Low Fuel
238
PO332
PO335
PO339 - PO340
Misfire Detected with Low Fuel
241
242
243
57
PO344
PO365
PO369
PO41 3
PO414
PO420
Misfire Detected with Low Fuel
Misfire Detected with Low Fuel
Misfire Detected with Low Fuel
Knock Sensor 1 Circuit Low
(Banlc 1 or Sinale Sensor)
59
83
83
65
-
Knoclc Sensor 2 Circuit Low (Banlc 2)
Crankshaft Position Sensor
'A' Circuit
Crankshaft Position Sensor
'A' Circuit Intermittent
Camshaft Position Sensor 'A' Circuit (Bank 1 or Single Sensor)
65
18
18
62
62
233 Camshaft Position Sensor
'A' Circuit Intermittent (Bank 1
or Single Sensor)
Camshaft Position Sensor
'B' Circuit (Banlc 1)
Camshaft Position Sensor 'B' Circuit Intermittent (Bank 1)
Secondary Air Injection System Switching Valve A Circuit Open
Secondary Air
Injection System Switching Valve A Circuit Shorted
Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
Page 980 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
I On-Board Diagnostics
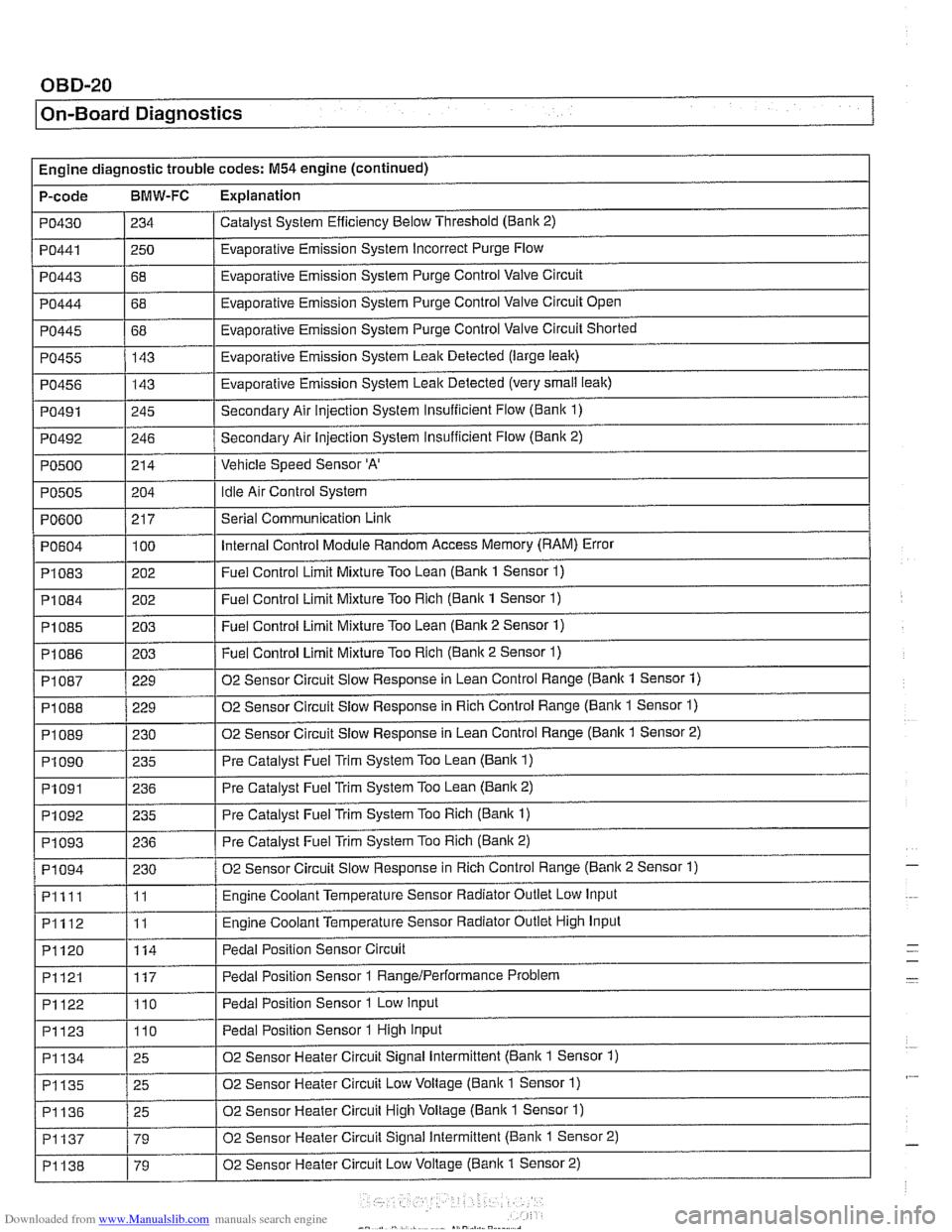
Engine diagnostic trouble codes: M54 engine (continued)
P-code
BMW-FC Explanation
Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
PO430
PO443
PO444
PO445
PO455
PO456
PO491
PO492
PO500
PO441 1250 / Evaporative Emission System Incorrect Purge Flow
234
I I
68
68
68 143
143
245
246
214
PO604
PI083
PI084
PI085
PI086
Evaporative Emission System Purge Control Valve Circuit
Evaporative Emission System Purge Control Valve Circuit Open
Evaporative Emission System Purge Control Valve Circuit Shorted
Evaporative Emission System Leak Detected (large leak)
Evaporative Emission System Leak Detected (very
small leak)
Secondary Air injection System Insufficient Flow (Bani( 1)
Secondary Air Injection System insufficient Flow
(Banic 2)
Vehicle Speed Sensor
'A'
Idle Air Control System PO505
.
PI 087
PI 088
PI089
PI090
PO600 / 217 I Serial Communication Link
204
100
202
202
203
203
PI091
PI092
PI093
PI094
Pllll
PI112
PI120
Internal Control Module Random Access Memory (RAM) Error
Fuel Control Limit Mixture Too Lean (Bank 1 Sensor
1)
Fuel Control Limit Mixture Too Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
Fuel Control Limit Mixture Too Lean (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
Fuel Control Limit Mixture Too Rich (Banic 2 Sensor 1) ~ ~
229
229
230 235
PI121
PI122
PI123
02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response in Lean Control Range (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response in Rich Control Range (Bank 1 Sensor
1)
02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response in Lean Control Range (Banlc 1 Sensor 2)
Pre Catalyst Fuel Trim System Too Lean
(Bank 1)
236
235
236
230
11
11
114
PI134
PI135
PI136
PI137
PI138
Pre Catalyst Fuel Trim System Too Lean (Banic 2)
Pre Catalyst Fuel Trim System Too Rich
(Bank 1)
Pre Catalyst Fuel Trim System Too Rich (Bank 2)
02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response in Rich Control Range (Banic 2 Sensor 1)
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Radiator Outlet Low Input
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Radiator Outlet High Input
Pedal Position Sensor Circuit
117
110
110
25
25
25
79
79 Pedal Position Sensor 1
RangeIPerformance Problem
Pedal Position Sensor 1 Low Input
Pedal Position Sensor 1 High Input
02 Sensor Heater Circuit Signal Intermittent (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
02 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor
1)
02 Sensor Heater Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
02 Sensor Heater Circuit Signal Intermittent (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
02 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Voltage
(Banic 1 Sensor 2)
-
-