BUICK CENTURY 1994 Owners Manual
Manufacturer: BUICK, Model Year: 1994, Model line: CENTURY, Model: BUICK CENTURY 1994Pages: 308, PDF Size: 16.3 MB
Page 141 of 308

Part 4 Your Driving and the Road
Here you’ll find information about driving on different kinds of roads and in varying weather conditions . We’ve
also included many other useful tips on driving
.
Part 4 includes:
DefensiveDriving .................................................................
DrunkenDriving ..................................................................
Control of a Vehicle ................................................................
Braking .....................................................................
Steering .....................................................................
Passing .....................................................................
LossofControl ....................................................................
DrivingatNight ...................................................................
DrivingintheRain .................................................................
CityDriving ......................................................................
HillandMountainRoads ............................................................
WinterDriving ....................................................................
TowingaTrailer ...................................................................
FreewayDriving ...................................................................
140
140
144
144
147 150
151
152
154
156 157
160
161
165
139
ProCarManuals.com
Page 142 of 308

Defensive Driving
The best advice anyone can give about driving is: Drive
defensively.
Please start with a very important safety device
in your
Buick: Buckle up. (See “Safety Belts”
in the Index.)
Defensive driving really means “be ready for anything.”
On city streets, rural roads, or freeways, it means
“always expect the unexpected.” Assume that pedestrians
or other drivers are going
to be
careless and make mistakes. Anticipate what they might
do. Be ready for their mistakes. -.
Rear-end collisions are about the most preventable of
accidents. Yet they are common. Allow enough
following distance. It’s the best defensive driving
maneuver,
in both city and rural driving. You never
know when the vehicle
in front of you is going to brake
or turn suddenly.
Drunken Driving
Death and injury associated with drinking and driving is
a national tragedy. It’s the number one contributor to the
highway death toll, claiming thousands of victims every
year. Alcohol takes away three things that anyone needs
to drive a vehicle:
Judgment
0 Muscular Coordination
Vision
Police records show that almost half of all motor
vehicle-related deaths involve alcohol
- a driver, a
passenger or someone else, such
as a pedestrian, had
140
ProCarManuals.com
Page 143 of 308

been drinking. In most cases, these deaths are the result
of someone who was drinking and driving. About
20,000 motor vehicle-related deaths occur each year
because
of alcohol, and thousands of people are injured.
Just how much alcohol
is too much if a person plans to
drive? Ideally, no one should drink alcohol and then
drive. But if one does, then what’s “too much”? It can be
a lot less than many might think. Although
it depends on
each person and situation, here
is some general
information on
the problem.
The Blood Alcohol Content (BAC) of someone who is
drinking depends upon four things:
How much alcohol is in the drink.
0 The drinker’s body weight.
0 The amount of food that is consumed before and
during drinking.
The length of time it has taken the drinker to
consume the alcohol. According
to the American Medical Association, a
180-pound (82 kg) person who drinks three 12-ounce
(355 ml) bottles of beer in an hour will end up with a
BAC of about
0.06 percent. The person would reach the
same BAC
by drinking three 4-ounce (120 ml) glasses
of wine or three mixed drinks if each had 1-1/2 ounces
(45 ml)
of a liquor like whiskey, gin or vodka.
1 A1
ProCarManuals.com
Page 144 of 308
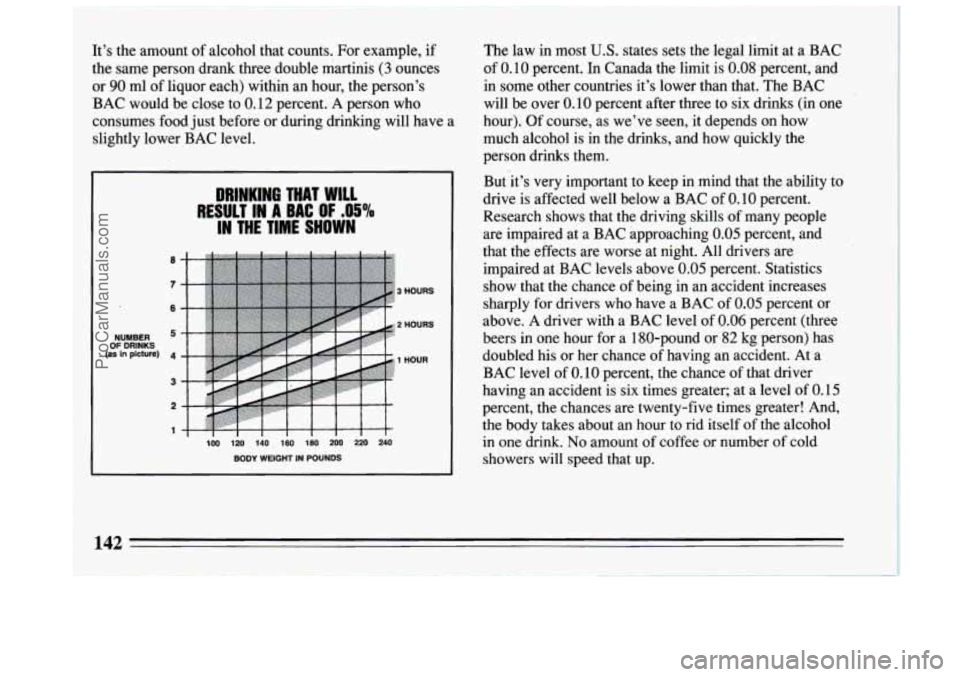
It’s the amount of alcohol that counts. For example, if
the same person drank three double martinis
(3 ounces
or
90 ml of liquor each) within an hour, the person’s
BAC would be close to 0.12 percent. A person who
consumes food just before or during drinking will have a
slightly lower BAC level.
DRINKING THAT WILL
RESULT IN A BAC nr 95%
IN THE TIM Sl., ...l
’ HOURS
OF DRINKS
NUMBER (as in plcture)
100 120 140 160 180 200 220 240
BODY WEIGHT IN POUNDS HOURS
HOUR
The
law in most U.S. states sets the legal limit at a BAC
of
0.10 percent. In Canada the limit is 0.08 percent, and
in
some other countries it’s lower than that. The BAC
will be over
0.10 percent after three to six drinks (in one
hour). Of course, as we’ve seen, it depends on how
much alcohol is
in the drinks, and how quickly the
person drinks them.
But it’s very important to keep in mind that the ability to
drive is affected well below
a BAC of 0.10 percent.
Research shows that the driving skills
of many people
are impaired at a BAC approaching
0.05 percent, and
that the effects are worse at night. All drivers are
impaired at BAC levels above
0.05 percent. Statistics
show that the chance of being in an accident increases
sharply for drivers who have a BAC
of 0.05 percent or
above. A driver with a BAC level of
0.06 percent (three
beers in one hour for a 180-pound
or 82 kg person) has
doubled his or her chance of having an accident. At a
BAC level of
0.10 percent, the chance of that driver
having an accident is six times greater; at a level of
0.15
percent, the chances are twenty-five times greater! And,
the body takes about an hour to rid itself of the alcohol
in one drink.
No amount of coffee or number of cold
showers will speed that up.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 145 of 308

“I‘ll be careful” isn’t the right answer. What if there’s an
emergency, a need to take sudden action, as when a
child darts into the street?
A person with a higher BAC
might not be able to react quickly enough to avoid the
collision.
There’s something else about drinking and driving that
many people don’t know. Medical research shows that
alcohol
in a person’s system can make crash injuries
worse. That’s especially true for brain, spinal cord and
heart injuries. That means that
if anyone who has been
drinking
-- driver or passenger -- is in a crash, the
chance of being killed or permanently disabled
is higher
than
if that person had not been drinking. And we’ve
already seen that the chance
of a crash itself is higher for
drinking drivers.
A CAUTION:
143
ProCarManuals.com
Page 146 of 308

Control of a Vehicle
You have three systems that make your vehicle go where
you want it to go. They are the brakes, the steering and
the accelerator. All three systems have to do their work
at the places where the tires meet the road. Sometimes,
as when you’re driving
on snow or ice, it’s
easy to ask more of those control systems than the tires
and road can provide. That means you can lose control
of your vehicle.
Braking
Braking action involves perception time and reaction
time.
First, you have
to decide to push on the brake pedal.
That’s perception time. Then
you have to bring up your
foot and do it. That’s reaction time.
Average reaction time is about
3/4 of a second. But
that’s only an average. It might be
less with one driver
and as long
as two or three seconds or more with
another. Age, physical condition, alertness,
coordination, and eyesight all play a part.
So do alcohol,
drugs and frustration. But even in
3/4 of a second, a
vehicle moving at
60 mph (100 km/h) travels 66 feet
(20 m). That could be a lot of distance in an emergency,
so keeping enough space between your vehicle and
others
is important.
144
ProCarManuals.com
Page 147 of 308

And, of course, actual stopping distances vary greatly
with the surface of
the road (whether it’s pavement or
gravel); the condition
of the road (wet, dry, icy); tire
tread; and the condition
of your brakes.
Avoid needless heavy braking. Some people drive
in
spurts -- heavy acceleration followed by heavy braking
-- rather than keeping pace with traffic. This is a
mistake. Your brakes may not have time to cool between
hard stops. Your brakes will wear out much faster if you
do a
lot of heavy braking. If you keep pace with the
traffic and allow realistic following distances, you will
eliminate a lot
of unnecessary braking. That means
better braking and longer brake life.
If your engine ever stops while you’re driving, brake
normally but don’t pump your brakes.
If you do, the
pedal may get harder to push down. If your engine
stops,
you will still have some power brake assist. But
you will use it when you brake. Once the power assist is
used up, it may take longer
to stop and the brake pedal
will be harder to push.
Anti-Lock Brakes (ABS)
Your Buick has an advanced electronic braking system
that will help prevent skidding.
ANTI-
LOCK
This light on the
instrument panel will
go on when
you start
your vehicle.
When you start your vehicle, or when you begin to drive
away,
you may hear a momentary motor or clicking
noise. And you may even notice that your brake pedal
moves a little while this is going on. This
is the ABS
system testing itself. If there’s a problem with the
anti-lock brake system, the anti-lock brake system warning light
will stqy on or flash.
See “Anti-lock Brake System Warning Light” in
the
Index.
145
ProCarManuals.com
Page 148 of 308

/-
Here’s how anti-lock works. Let’s say the road is wet.
You’re driving safely. Suddenly an animal jumps out
in
front of you.
You slam on the brakes. Here’s what happens with ABS.
A computer senses that wheels are slowing down. If one
of the wheels is about to stop rolling, the computer will
separately work the brakes at each front wheel and at the
rear wheels. The
anti-lock system can change the brake pressure
faster than any driver could. The computer
is
programmed to make the most of available tire and road
conditions.
You can steer around the obstacle while braking hard.
As you brake, your computer keeps receiving updates on
wheel speed and controls braking pressure accordingly.
146
ProCarManuals.com
Page 149 of 308

Remember: Anti-lock doesn’t change the time you need
to get your foot up to the brake pedal. If you get too
close
to the vehicle in front of you, you won’t have time
to apply your brakes
if that vehicle suddenly slows or
stops. Always leave enough room up ahead to stop, even
though you have anti-lock brakes.
Steering
Power Steering
If you lose power steering assist because the engine
stops or the system is not functioning, you can steer but
it will take much more effort.
To Use Anti-Lock
Don’t pump the brakes. Just hold the brake pedal down
and let anti-lock
work for you. You may feel the system
working, or
you may notice some noise, but this is
normal. When your anti-lock system is adjusting brake
pressure to help avoid a braking skid, the
“LOW
TRACTION” light will come on. See “Anti-Lock Brake
System Active Light”
in the Index.
Braking in Emergencies
Use your anti-lock braking system when you need to.
With anti-lock, you can steer and brake at the same
time. In many emergencies, steering can help
you more
than even
the very best braking.
Steering Tips
Driving on Curves
It’s important to take curves at a reasonable speed.
A lot of the “driver lost control” accidents mentioned on
the news happen on curves. Here’s why:
Experienced driver or beginner, each of us is subject to
the same laws
of physics when driving on curves. The
traction of the tires against the road surface makes
it
possible for the vehicle to change its path when you turn
the front wheels. If there’s no traction, inertia will keep
the vehicle going
in the same direction. If you’ve ever
tried to steer
a vehicle on wet ice, you’ll understand this.
The traction
you can get in a curve depends on the
condition of your tires and the road surface, the angle at
which
the curve is banked, and your speed. While
you’re
in a curve, speed is the one factor you can
control.
147
ProCarManuals.com
Page 150 of 308

Suppose you’re steering through a sharp curve. Then
you suddenly accelerate. Both control systems --
steering and acceleration -- have to do their work where
the tires meet the road. Adding the sudden acceleration
can demand too much of those places. You can lose
control.
What should you do
if this ever happens? Ease up on the
accelerator pedal, steer the vehicle the way you want
it
to go, and slow down.
Speed limit signs near curves warn that you should
adjust your speed. Of course, the posted speeds are
based on good weather and road conditions. Under less
favorable conditions
you’ll want to go slower.
If you need to reduce your speed as you approach a
curve, do
it before you enter the curve, while your front
wheels are straight ahead.
Try to adjust your speed
so you can “drive” through the
curve. Maintain a reasonable, steady speed. Wait to
accelerate until you are
out of the curve, and then
accelerate gently into the straightaway.
Steering in Emergencies
There are times when steering can be more effective than
braking.
For example, you come over a hill and find a
truck stopped in your lane, or a car suddenly pulls out
from nowhere, or a child darts out from between parked
cars and stops right
in front of you. You can avoid these
problems by braking
-- if you can stop in time. But
sometimes you can’t; there isn’t room. That’s
the time for
evasive action
-- steering around the problem.
Your Buick can perform very well
in emergencies like
these. First apply your brakes. It is better to remove as
much speed as you can from a possible collision. Then
steer around the problem, to the left or right depending
on the space available.
An emergency like this requires close attention and a
quick decision. If you are holding the steering wheel at
the recommended 9 and 3 o’clock positions, you can
turn
it a full 180 degrees very quickly without removing
either hand. But you have
to act fast, steer quickly, and
just as quickly straighten the wheel once you have
avoided the object.
148
ProCarManuals.com