heating CHERY TIGGO 2009 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHERY, Model Year: 2009, Model line: TIGGO, Model: CHERY TIGGO 2009Pages: 1903, PDF Size: 33.38 MB
Page 398 of 1903
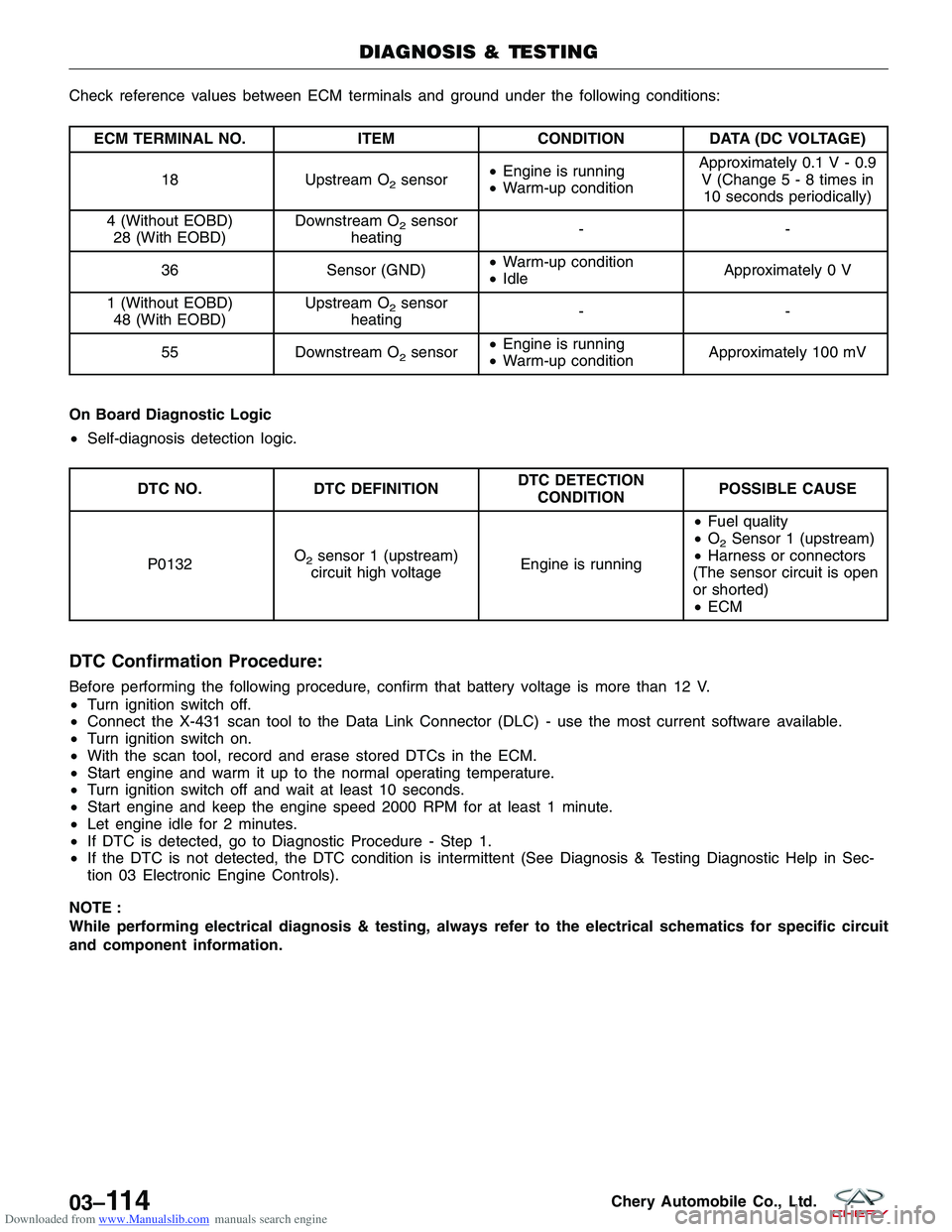
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Check reference values between ECM terminals and ground under the following conditions:
ECM TERMINAL NO.ITEMCONDITIONDATA (DC VOLTAGE)
18 Upstream O
2sensor•
Engine is running
• Warm-up condition Approximately 0.1 V - 0.9
V (Change5-8times in10 seconds periodically)
4 (Without EOBD) 28 (With EOBD) Downstream O
2sensor
heating --
36 Sensor (GND) •
Warm-up condition
• Idle Approximately 0 V
1 (Without EOBD) 48 (With EOBD) Upstream O
2sensor
heating --
55 Downstream O
2sensor•
Engine is running
• Warm-up condition Approximately 100 mV
On Board Diagnostic Logic
• Self-diagnosis detection logic.
DTC NO. DTC DEFINITION DTC DETECTION
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
P0132 O
2sensor 1 (upstream)
circuit high voltage Engine is running•
Fuel quality
• O2Sensor 1 (upstream)
• Harness or connectors
(The sensor circuit is open
or shorted)
• ECM
DTC Confirmation Procedure:
Before performing the following procedure, confirm that battery voltage is more than 12 V.
• Turn ignition switch off.
• Connect the X-431 scan tool to the Data Link Connector (DLC) - use the most current software available.
• Turn ignition switch on.
• With the scan tool, record and erase stored DTCs in the ECM.
• Start engine and warm it up to the normal operating temperature.
• Turn ignition switch off and wait at least 10 seconds.
• Start engine and keep the engine speed 2000 RPM for at least 1 minute.
• Let engine idle for 2 minutes.
• If DTC is detected, go to Diagnostic Procedure - Step 1.
• If the DTC is not detected, the DTC condition is intermittent (See Diagnosis & Testing Diagnostic Help in Sec-
tion 03 Electronic Engine Controls).
NOTE :
While performing electrical diagnosis & testing, always refer to the electrical schematics for specific circuit
and component information.
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING
03–11 4Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 502 of 1903
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6. Installation is in the reverse order of removal.
NOTE :
After installed the engine coolant temperature sensor, check the coolant level.
Knock Sensor
Description
The knock sensor is attached to the cylinder block. The knock sensor is designed to detect engine vibration that is
caused by detonation.
Operation
When the knock sensor detects a knock in one of the cylinders, it sends an input signal to the Engine Control Module
(ECM). In response, the ECM retards ignition timing for all cylinders by a specified amount.
Knock sensors contain a piezoelectric material which constantly vibrates and sends an input voltage (signal) to the
ECM while the engine operates. As the intensity of the crystal’s vibration increases, the knock sensor output voltage
also increases.
The ECM ignores knock sensor input during engine idle conditions. Once the engine speed exceeds a specified
value, knock retard is allowed.
Removal & Installation
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the knock sensor electrical connector.
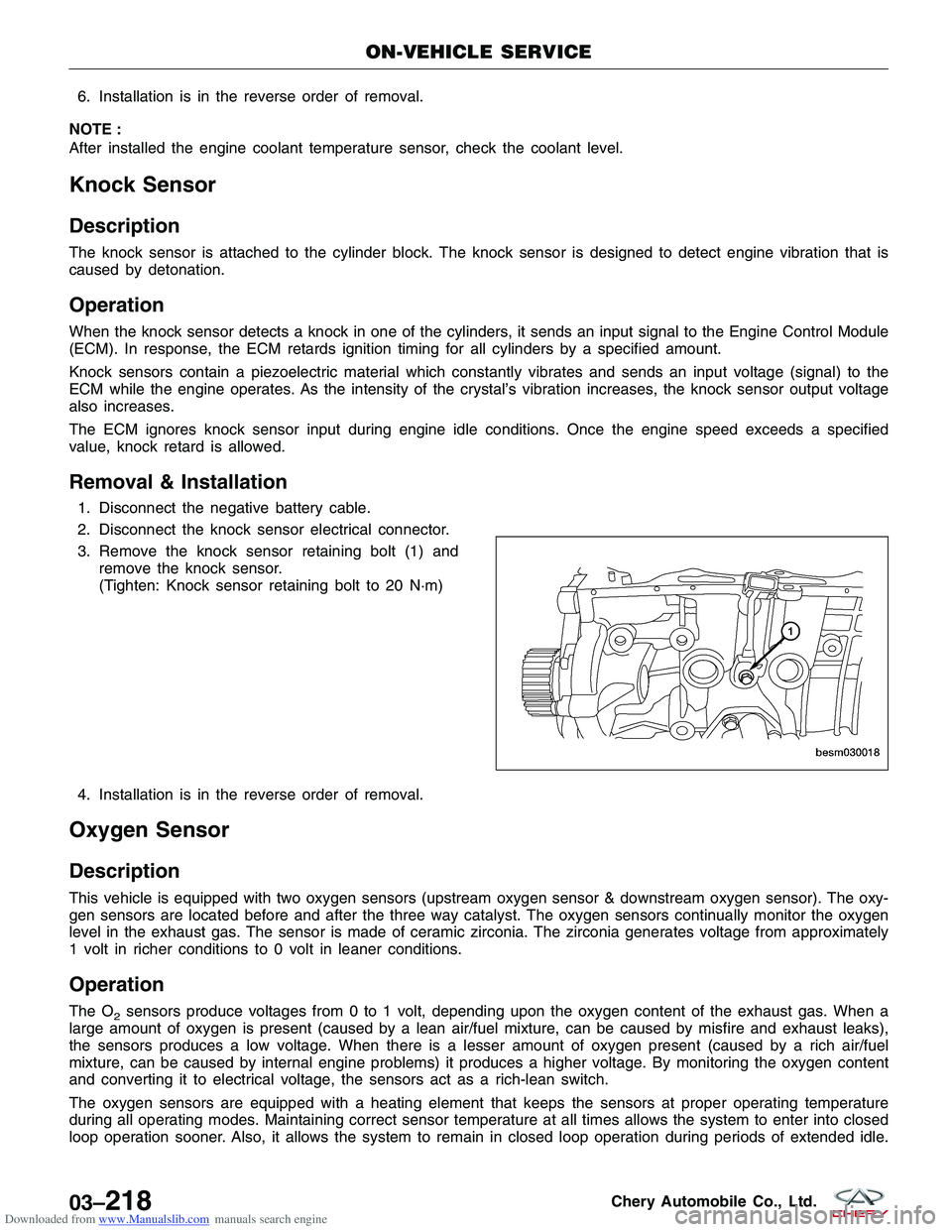
3. Remove the knock sensor retaining bolt (1) and remove the knock sensor.
(Tighten: Knock sensor retaining bolt to 20 N·m)
4. Installation is in the reverse order of removal.
Oxygen Sensor
Description
This vehicle is equipped with two oxygen sensors (upstream oxygen sensor & downstream oxygen sensor). The oxy-
gen sensors are located before and after the three way catalyst. The oxygen sensors continually monitor the oxygen
level in the exhaust gas. The sensor is made of ceramic zirconia. The zirconia generates voltage from approximately
1 volt in richer conditions to 0 volt in leaner conditions.
Operation
The O2sensors produce voltages from 0 to 1 volt, depending upon the oxygen content of the exhaust gas. When a
large amount of oxygen is present (caused by a lean air/fuel mixture, can be caused by misfire and exhaust leaks),
the sensors produces a low voltage. When there is a lesser amount of oxygen present (caused by a rich air/fuel
mixture, can be caused by internal engine problems) it produces a higher voltage. By monitoring the oxygen content
and converting it to electrical voltage, the sensors act as a rich-lean switch.
The oxygen sensors are equipped with a heating element that keeps the sensors at proper operating temperature
during all operating modes. Maintaining correct sensor temperature at all times allows the system to enter into closed
loop operation sooner. Also, it allows the system to remain in closed loop operation during periods of extended idle.
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
BESM030018
03–218Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 513 of 1903

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GENERAL INFORMATION
Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) utilizes integrated circuitry and information carried on the Controller Area Network
(CAN) data bus along with many hard wired inputs to monitor many sensors and switches inputs throughout the
vehicle. In response to those inputs, the internal circuitry and programming of the ECM allow it to control and inte-
grate many electronic functions and features of the vehicle through both hard wired outputs and the transmission of
electronic message outputs to other electronic modules in the vehicle over the CAN data bus.
The following are the input and output components monitored by the ECM. The monitored functions include compo-
nents from the engine, ignition, transaxle, air conditioning, or any other ECM supported subsystem.
ECM Inputs
•Brake Switch Sensor
• A/C Pressure Switch
• Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
• Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
• Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
• Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
• Air Flow Sensor
• Throttle Position Sensor (integral with Electronic Throttle Control Actuator)
• Power Steering Switch
• Accelerator Pedal Position (APP) Sensor
• Knock Sensor
• Oxygen Sensor (Upstream & Downstream)
• Clutch Pedal Switch (manual transaxle only)
ECM Outputs
• Canister Control Valve
• Fuel Injectors
• Fuel Pump Relay
• Electronic Throttle Control Actuator
• Ignition Coil
• A/C Compressor
• Cooling Fan
• Oxygen Sensor heating coil (Upstream & Downstream)
Operation
The ECM monitors components and circuits and tests them in various ways depending on the hardware, function,
and type of signal. For example, analog inputs such as throttle position or engine coolant temperature are typically
checked for opens, shorts and out-of-range values. This type of monitoring is carried out continuously. Some digital
inputs like vehicle speed or crankshaft position rely on rationality checks - checking to see if the input value makes
sense at the current engine operating conditions. These types of tests may require monitoring several components
and can only be carried out under appropriate test conditions.
The ECM is a pre-programmed, microprocessor-based digital computer. It regulates ignition timing, air-fuel ratio,
emission control devices, charging system, certain transmission features, speed control, air conditioning compressor
clutch engagement and idle speed. The ECM can adapt its programming to meet changing operating conditions.
03
03–229Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 557 of 1903
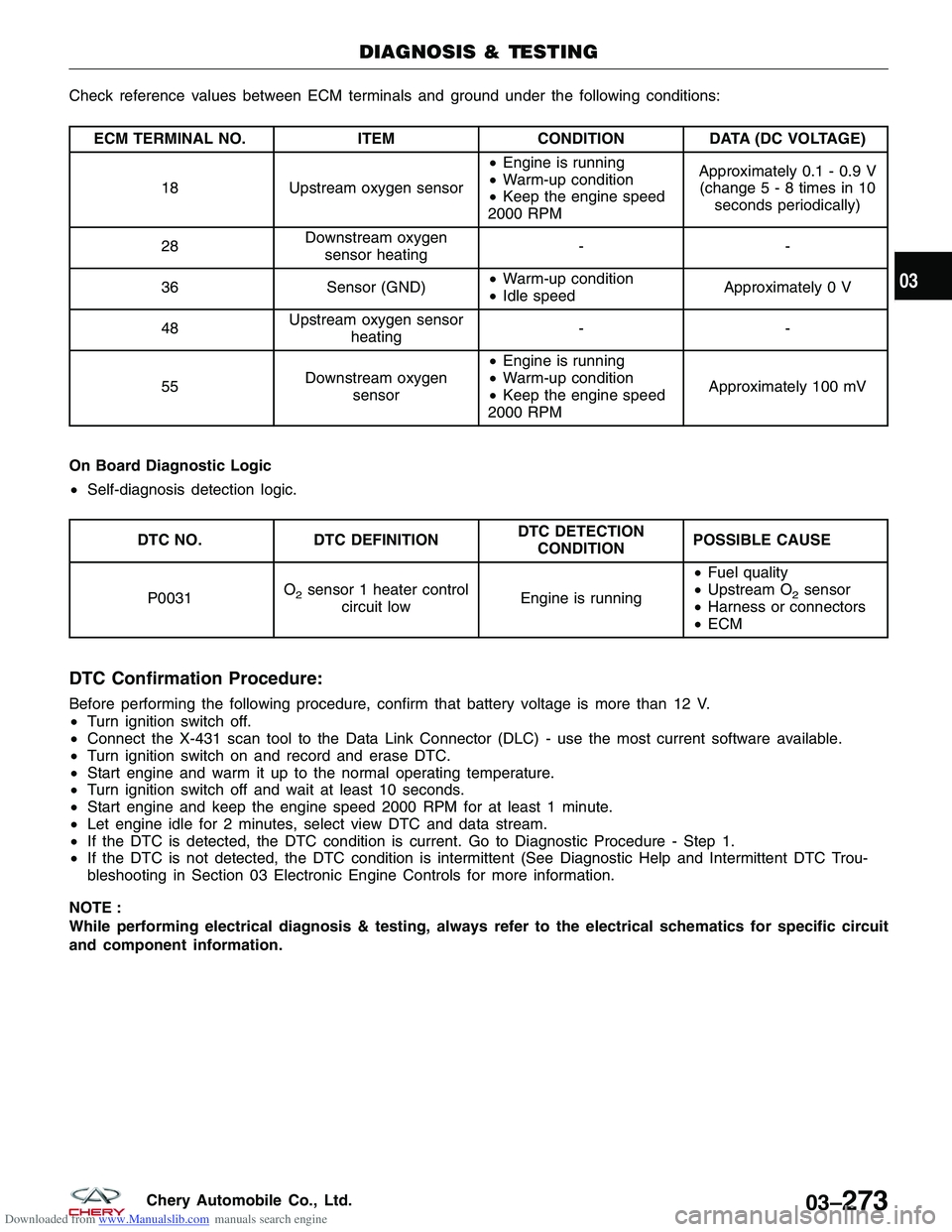
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Check reference values between ECM terminals and ground under the following conditions:
ECM TERMINAL NO.ITEMCONDITIONDATA (DC VOLTAGE)
18 Upstream oxygen sensor •
Engine is running
• Warm-up condition
• Keep the engine speed
2000 RPM Approximately 0.1 - 0.9 V
(change5-8times in 10 seconds periodically)
28 Downstream oxygen
sensor heating --
36 Sensor (GND)•
Warm-up condition
• Idle speed Approximately 0 V
48 Upstream oxygen sensor
heating --
55 Downstream oxygen
sensor •
Engine is running
• Warm-up condition
• Keep the engine speed
2000 RPM Approximately 100 mV
On Board Diagnostic Logic
• Self-diagnosis detection logic.
DTC NO. DTC DEFINITION DTC DETECTION
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
P0031 O
2sensor 1 heater control
circuit low Engine is running•
Fuel quality
• Upstream O2sensor
• Harness or connectors
• ECM
DTC Confirmation Procedure:
Before performing the following procedure, confirm that battery voltage is more than 12 V.
• Turn ignition switch off.
• Connect the X-431 scan tool to the Data Link Connector (DLC) - use the most current software available.
• Turn ignition switch on and record and erase DTC.
• Start engine and warm it up to the normal operating temperature.
• Turn ignition switch off and wait at least 10 seconds.
• Start engine and keep the engine speed 2000 RPM for at least 1 minute.
• Let engine idle for 2 minutes, select view DTC and data stream.
• If the DTC is detected, the DTC condition is current. Go to Diagnostic Procedure - Step 1.
• If the DTC is not detected, the DTC condition is intermittent (See Diagnostic Help and Intermittent DTC Trou-
bleshooting in Section 03 Electronic Engine Controls for more information.
NOTE :
While performing electrical diagnosis & testing, always refer to the electrical schematics for specific circuit
and component information.
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING
03
03–273Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 562 of 1903
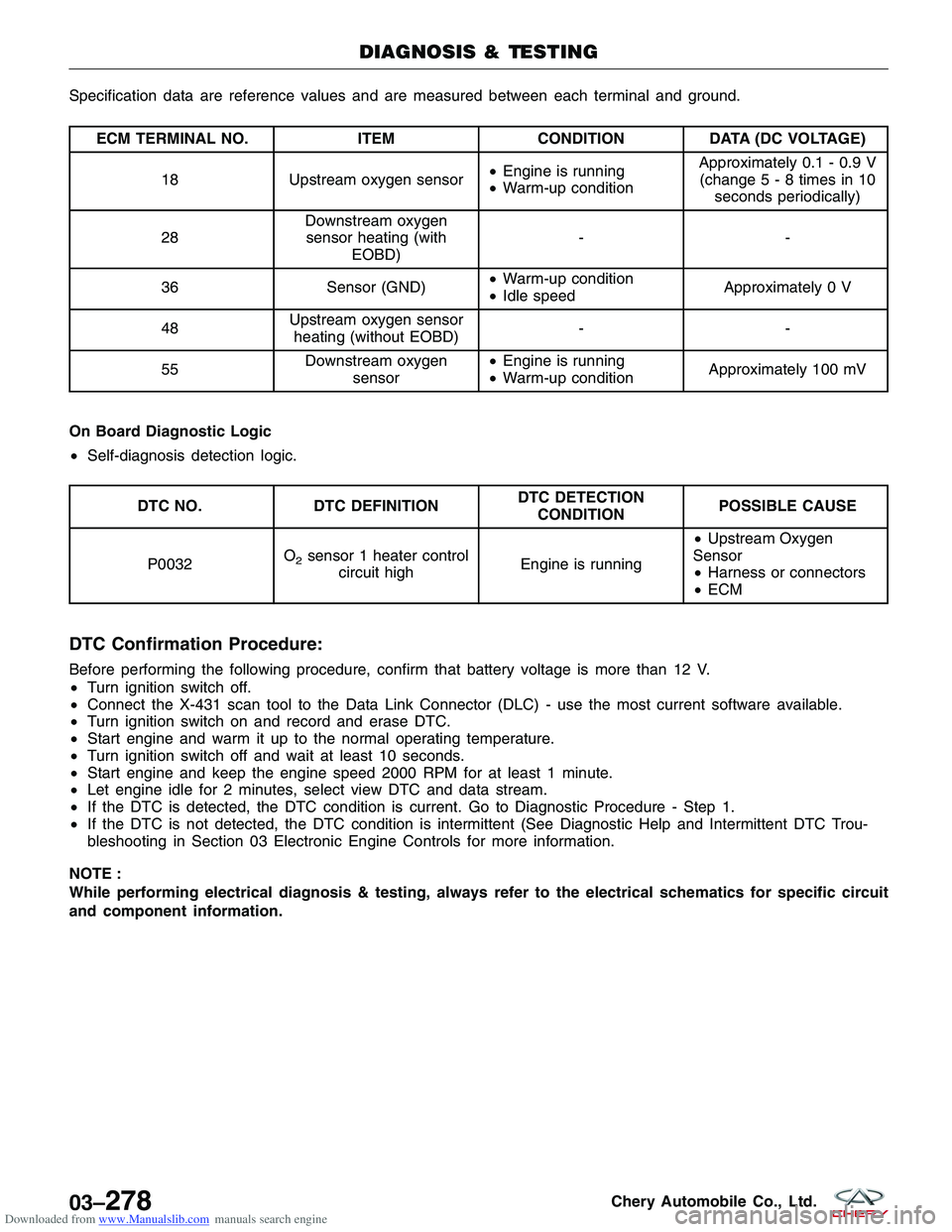
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Specification data are reference values and are measured between each terminal and ground.
ECM TERMINAL NO.ITEMCONDITIONDATA (DC VOLTAGE)
18 Upstream oxygen sensor •
Engine is running
• Warm-up condition Approximately 0.1 - 0.9 V
(change5-8times in 10 seconds periodically)
28 Downstream oxygen
sensor heating (with EOBD) --
36 Sensor (GND)•
Warm-up condition
• Idle speed Approximately 0 V
48 Upstream oxygen sensor
heating (without EOBD) --
55 Downstream oxygen
sensor •
Engine is running
• Warm-up condition Approximately 100 mV
On Board Diagnostic Logic
• Self-diagnosis detection logic.
DTC NO. DTC DEFINITION DTC DETECTION
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
P0032 O
2sensor 1 heater control
circuit high Engine is running•
Upstream Oxygen
Sensor
• Harness or connectors
• ECM
DTC Confirmation Procedure:
Before performing the following procedure, confirm that battery voltage is more than 12 V.
• Turn ignition switch off.
• Connect the X-431 scan tool to the Data Link Connector (DLC) - use the most current software available.
• Turn ignition switch on and record and erase DTC.
• Start engine and warm it up to the normal operating temperature.
• Turn ignition switch off and wait at least 10 seconds.
• Start engine and keep the engine speed 2000 RPM for at least 1 minute.
• Let engine idle for 2 minutes, select view DTC and data stream.
• If the DTC is detected, the DTC condition is current. Go to Diagnostic Procedure - Step 1.
• If the DTC is not detected, the DTC condition is intermittent (See Diagnostic Help and Intermittent DTC Trou-
bleshooting in Section 03 Electronic Engine Controls for more information.
NOTE :
While performing electrical diagnosis & testing, always refer to the electrical schematics for specific circuit
and component information.
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING
03–278Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 607 of 1903
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Check reference values between ECM terminals and ground under the following conditions:
ECM TERMINAL NO.ITEMCONDITIONDATA (DC VOLTAGE)
18 Upstream oxygen sensor •
Engine is running
• Warm-up condition Approximately 0.1 - 0.9 V
(change5-8times in 10 seconds periodically)
28 Downstream oxygen
sensor heating (with EOBD) --
36 Oxygen sensor signal
ground •
Warm-up condition
• Idle Approximately 0 V
48 Upstream oxygen sensor
heating (with EOBD) --
55 Downstream oxygen
sensor •
Engine is running
• Warm-up condition Approximately 100 mV
On Board Diagnostic Logic
• Self-diagnosis detection logic.
DTC NO. DTC DEFINITION DTC DETECTION
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
P0132 O
2sensor 1 (upstream)
circuit high voltage Engine is running•
Fuel quality
• Oxygen Sensor 1
(upstream)
• Harness or connectors
• ECM
DTC Confirmation Procedure:
Before performing the following procedure, confirm that battery voltage is more than 12 V.
• Turn ignition switch off.
• Connect the X-431 scan tool to the Data Link Connector (DLC) - use the most current software available.
• Turn ignition switch on.
• With the scan tool, record and erase stored DTCs in the ECM.
• Start engine and warm it up to the normal operating temperature.
• Turn ignition switch off and wait at least 10 seconds.
• Start engine and keep the engine speed 2000 RPM for at least 1 minute.
• Let engine idle for 2 minutes.
• Select view data stream and DTC.
• If DTC is detected, go to Diagnostic Procedure - Step 1.
• If the DTC is not detected, the DTC condition is intermittent (See Diagnosis & Testing Diagnostic Help in Sec-
tion 03 Electronic Engine Controls).
NOTE :
While performing electrical diagnosis & testing, always refer to the electrical schematics for specific circuit
and component information.
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING
03
03–323Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 712 of 1903
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6. Installation is in the reverse order of removal.
NOTE :
After installing the engine coolant temperature sensor, check the coolant level.
Knock Sensor
Description
The knock sensor is attached to the cylinder block. The knock sensor is designed to detect engine vibration that is
caused by detonation.
Operation
When the knock sensor detects a knock in one of the cylinders, it sends an input signal to the Engine Control Module
(ECM). In response, the ECM retards ignition timing for all cylinders by a specified amount.
The knock sensor contains a piezoelectric material which constantly vibrates and sends an input voltage (signal) to
the ECM while the engine operates. As the intensity of the vibration increases, the knock sensor output voltage also
increases.
The ECM ignores knock sensor input during engine idle conditions. Once the engine speed exceeds a specified
value, knock retard is allowed.
Removal & Installation
1. Disconnect and isolate the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the knock sensor electrical connector.
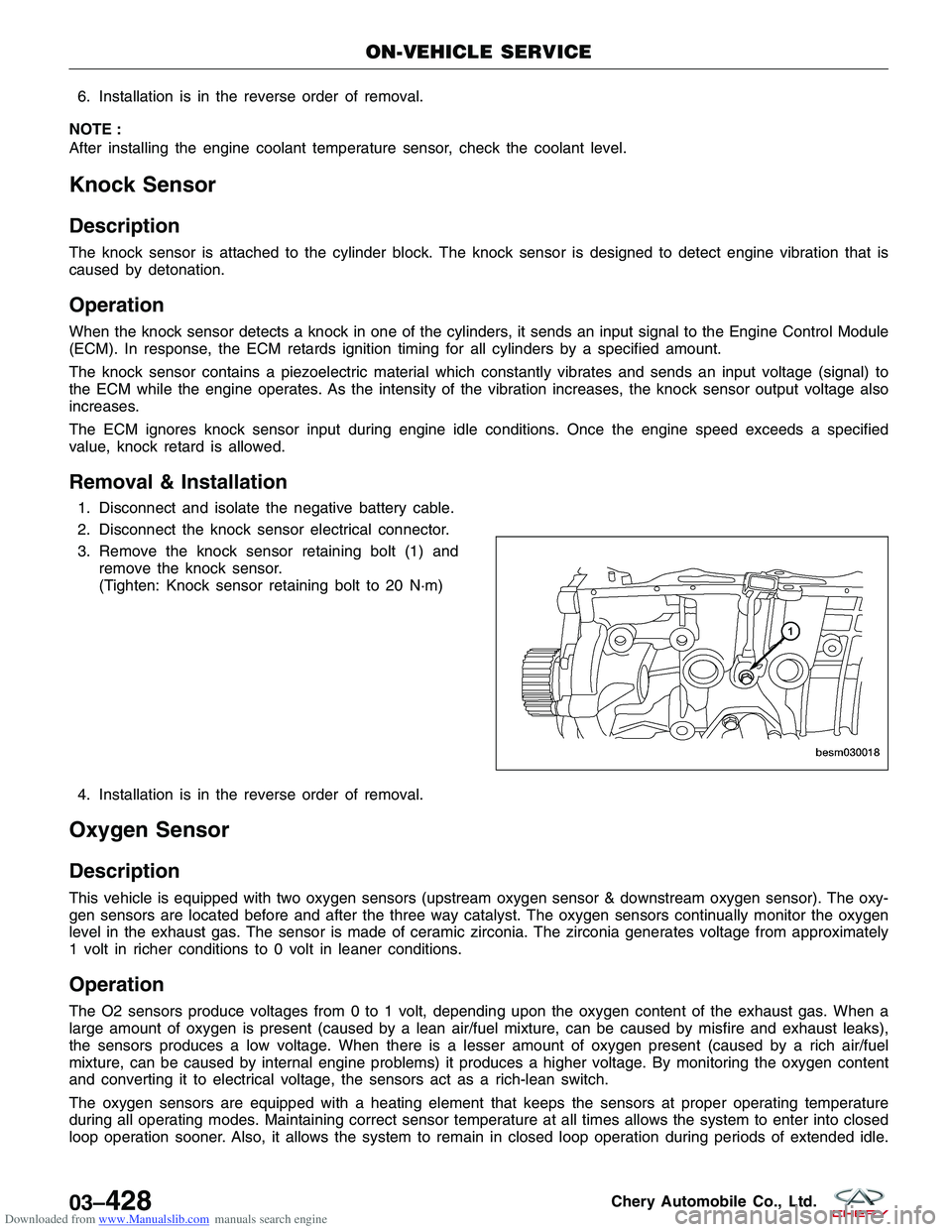
3. Remove the knock sensor retaining bolt (1) and
remove the knock sensor.
(Tighten: Knock sensor retaining bolt to 20 N·m)
4. Installation is in the reverse order of removal.
Oxygen Sensor
Description
This vehicle is equipped with two oxygen sensors (upstream oxygen sensor & downstream oxygen sensor). The oxy-
gen sensors are located before and after the three way catalyst. The oxygen sensors continually monitor the oxygen
level in the exhaust gas. The sensor is made of ceramic zirconia. The zirconia generates voltage from approximately
1 volt in richer conditions to 0 volt in leaner conditions.
Operation
The O2 sensors produce voltages from 0 to 1 volt, depending upon the oxygen content of the exhaust gas. When a
large amount of oxygen is present (caused by a lean air/fuel mixture, can be caused by misfire and exhaust leaks),
the sensors produces a low voltage. When there is a lesser amount of oxygen present (caused by a rich air/fuel
mixture, can be caused by internal engine problems) it produces a higher voltage. By monitoring the oxygen content
and converting it to electrical voltage, the sensors act as a rich-lean switch.
The oxygen sensors are equipped with a heating element that keeps the sensors at proper operating temperature
during all operating modes. Maintaining correct sensor temperature at all times allows the system to enter into closed
loop operation sooner. Also, it allows the system to remain in closed loop operation during periods of extended idle.
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
BESM030018
03–428Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 726 of 1903

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GENERAL INFORMATION
Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) consists of a microcomputer and connectors for signal input and output and for
power supply. The ECM controls the engine.
The following are the input and output components monitored by the ECM. The monitored functions include compo-
nents from the engine, ignition, transaxle, air conditioning, or any other ECM supported subsystem.
ECM Inputs
•Brake Switch Sensor
• Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
• Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
• Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
• Air Flow Sensor
• Coolant Temperature Sensor (For Instrument Cluster)
• Throttle Position Sensor (Integral with Electronic Throttle Control Actuator)
• Power Steering Switch
• Knock Sensor
• Oxygen Sensor (Upstream & Downstream)
• Clutch Pedal Switch (Manual transmission only)
ECM Outputs
• Canister Control Valve
• Fuel Injectors
• Fuel Pump Relay
• Electronic Throttle Control Actuator
• Ignition Coil
• A/C Compressor
• Cooling Fan
• Oxygen Sensor heating coil (Upstream & Downstream)
Operation
The ECM monitors components and circuits and tests them in various ways depending on the hardware, function,
and type of signal. For example, analog inputs such as throttle position or engine coolant temperature are typically
checked for opens, shorts and out-of-range values. This type of monitoring is carried out continuously. Some digital
inputs like vehicle speed or crankshaft position rely on rationality checks - checking to see if the input value makes
sense at the current engine operating conditions. These types of tests may require monitoring several components
and can only be carried out under appropriate test conditions.
The ECM is a pre-programmed, microprocessor-based digital computer. It regulates ignition timing, air-fuel ratio,
emission control devices, charging system, certain transmission features, speed control, air conditioning compressor
clutch engagement and idle speed. The ECM can adapt its programming to meet changing operating conditions.
03–442Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 755 of 1903

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ECM TERMINAL NO.ITEMCONDITIONDATA (DC VOLTAGE)
52 Upstream oxygen sensor
heating •
Warm-up condition
• Idle 0-3V
• Engine is running
• Keep the engine speed
5000 RPM System voltage
59 Downstream oxygen
sensor •
Engine is running
• Warm-up condition
• Keep the engine speed
2000 RPM 0 - 0.8 V (recycle)
60 Upstream oxygen sensor •
Engine is running
• Warm-up condition
• Keep the engine speed
2000 RPM 0 - 0.8 V (recycle)
76 Sensor (GND)•
Warm-up condition
• Idle Approximately 0 V
On Board Diagnostic Logic
• Self-diagnosis detection logic.
DTC NO. DTC DEFINITION DTC DETECTION
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
11 Oxygen sensor Engine is running•
Fuel quality
• Oxygen sensor
• Harness or connectors
• ECM
DTC Confirmation Procedure:
Before performing the following procedure, confirm that battery voltage is more than 12 V.
• Turn ignition switch off.
• Connect the X-431 scan tool to the Data Link Connector (DLC) - use the most current software available.
• Turn ignition switch on.
• With the scan tool, record and erase stored DTCs in the ECM.
• Start engine and warm it up to the normal operating temperature.
• Turn ignition switch off and wait at least 10 seconds.
• Start engine and keep the engine speed 2000 RPM for at least 1 minute.
• Let engine idle for 2 minutes and select view DTC.
• If DTC is detected, go to Diagnostic Procedure - Step 1.
• If the DTC is not detected, the DTC condition is intermittent (See Diagnosis & Testing Diagnostic Help in Sec-
tion 03 Electronic Engine Controls).
NOTE :
Before performing the following procedure, make sure that ECM ground connections are in good condition.
NOTE :
While performing electrical diagnosis & testing, always refer to the electrical schematics for specific circuit
and component information.
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING
03
03–471Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 818 of 1903

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine The oxygen sensors are equipped with a heating element that keeps the sensors at proper operating temperature
during all operating modes. Maintaining correct sensor temperature at all times allows the system to enter into closed
loop operation sooner. Also, it allows the system to remain in closed loop operation during periods of extended idle.
Upstream Oxygen Sensor
The input from the upstream heated oxygen sensor tells the Engine Control Module (ECM) the oxygen content of the
exhaust gas. Based on this input, the ECM fine tunes the air-fuel ratio by adjusting injector pulse width.
Downstream Oxygen Sensor
The downstream heated oxygen sensor signal is used to detect catalytic convertor deterioration. As the convertor
deteriorates, the signal from the downstream sensor begins to match the upstream sensor signal except for a slight
time delay. By comparing the downstream heated oxygen sensor signal to the signal from the upstream sensor, the
ECM calculates catalytic convertor efficiency. This calculation is also used to establish the upstream O2 goal voltage
(switching point).
Removal & Installation - Upstream Oxygen Sensor
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the oxygen sensor electrical connector.
CAUTION:
Remove the oxygen sensor after the exhaust pipe has cooled.
3. Remove the upstream oxygen sensor (1).(Tighten: Upstream oxygen sensor to 45 N·m)
4. Installation is in the reverse order of removal.
Installation Notes:
• Before installing the oxygen sensor, coat the threads with rust inhibiting lubricant.
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
LTSM030004
03–534Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.