CHEVROLET BLAZER 1997 2.G Owner's Manual
Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1997, Model line: BLAZER, Model: CHEVROLET BLAZER 1997 2.GPages: 402, PDF Size: 21.93 MB
Page 21 of 402

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3. Pick up the latch plate and pull the belt across you.
Don't Ict it Sct twisted.
Make wrc thc t-clcw button on the buckle is
posiititmed 50 you would be able to unbuckle the
sat't'ty hclt quickly it' you ever had to.
5. To make the lap part tight. pull down on the buckle
end of the belt as you pull up on the shoulder belt.
Page 22 of 402
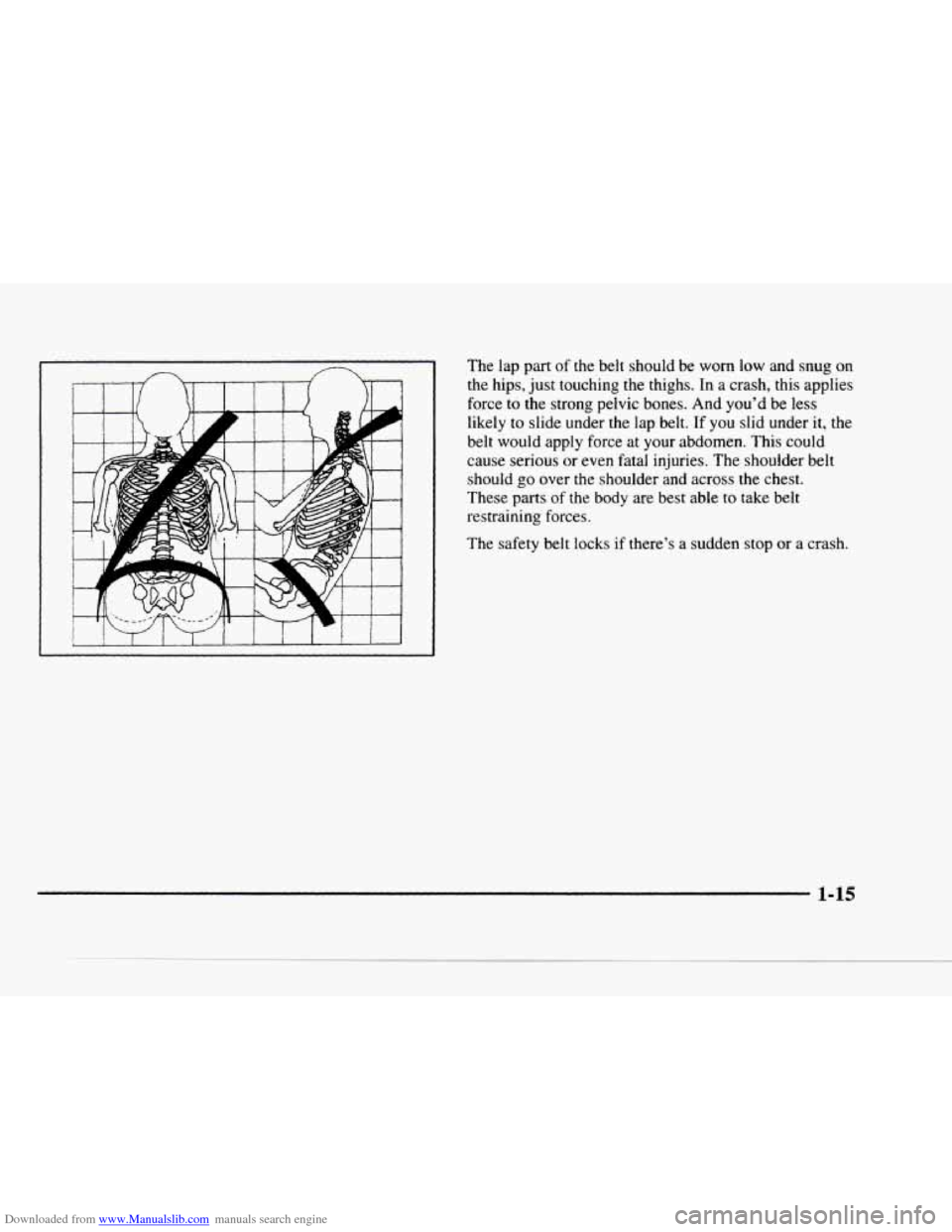
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine The lap part of the belt should be worn low and snug on
the hips, j'ust touching
the thighs. In a crash, this applies
force
to the strong pelvic bones. And you'd be less
likely to slide under
the lap belt. If you slid under it, the
belt would apply force at your abdomen. This could
cause serious or even fatal injuries. The shoulder belt should
go over the shoulder and across the chest.
These parts
of the body are best able to take belt
restraining forces.
The safety belt
locks if there's a sudden stop or a crash.
1-15
Page 23 of 402
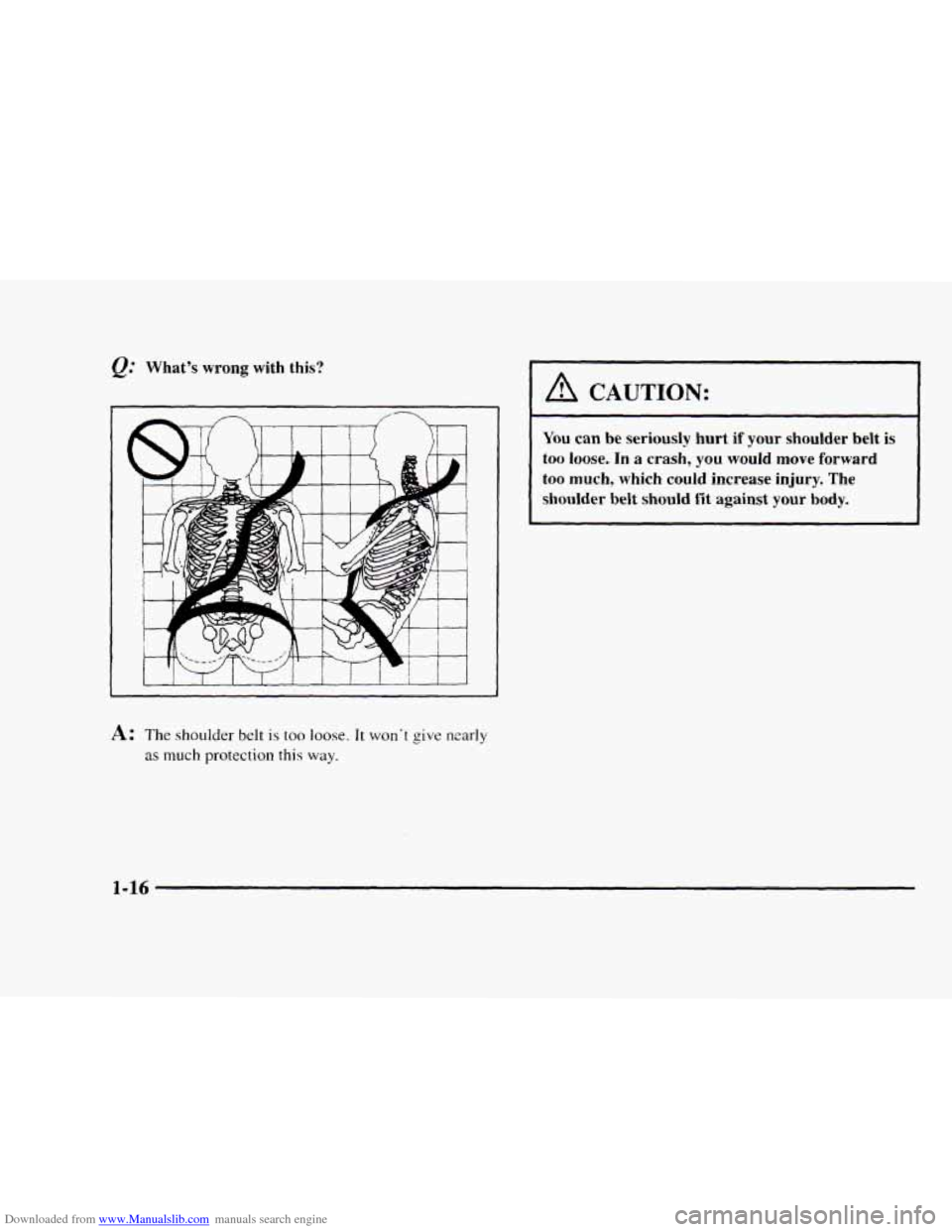
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine @ What’s wrong with this?
L
L I I I 1 I I I I I 1 I
A: The shoulder belt is too loose. It won‘t give nzarly
as much protection this way.
I A CAUTION:
You can be seriously hurt if your shoulder belt is
too loose. In a crash, you would move forward
too much, which could increase injury. The
shoulder
belt should fit against your body.
1-16
Page 24 of 402
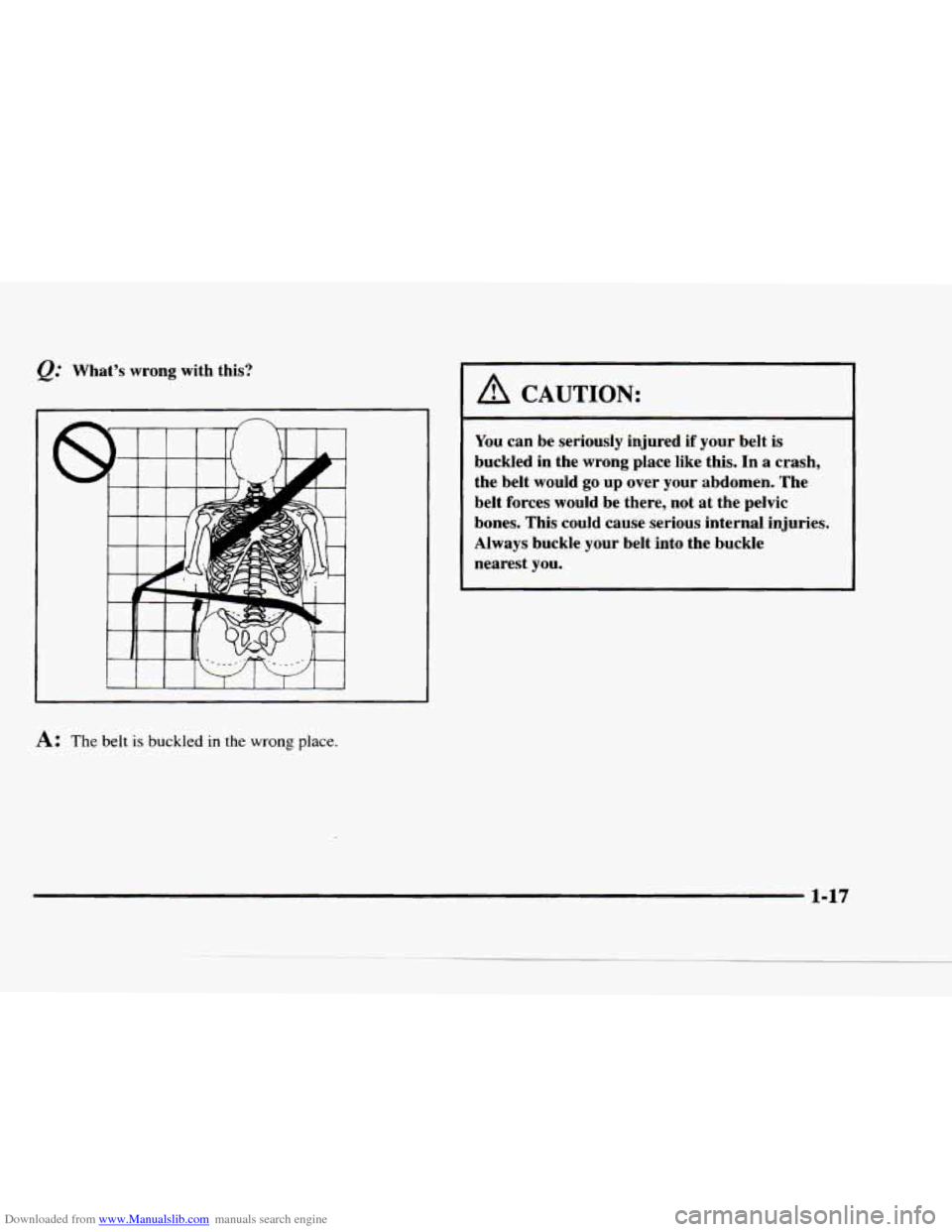
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine What’s wrong with this?
1
A: The belt is buckled in the wrong place.
A CAUTION:
You can be seriously injured if your belt is
buckled in the wrong place like this. In a crash,
the belt would
go up over your abdomen. The
belt forces would be there, not at the pelvic
bones. This could cause serious internal injuries.
Always buckle your belt into the buckle
nearest you.
1-17
Page 25 of 402
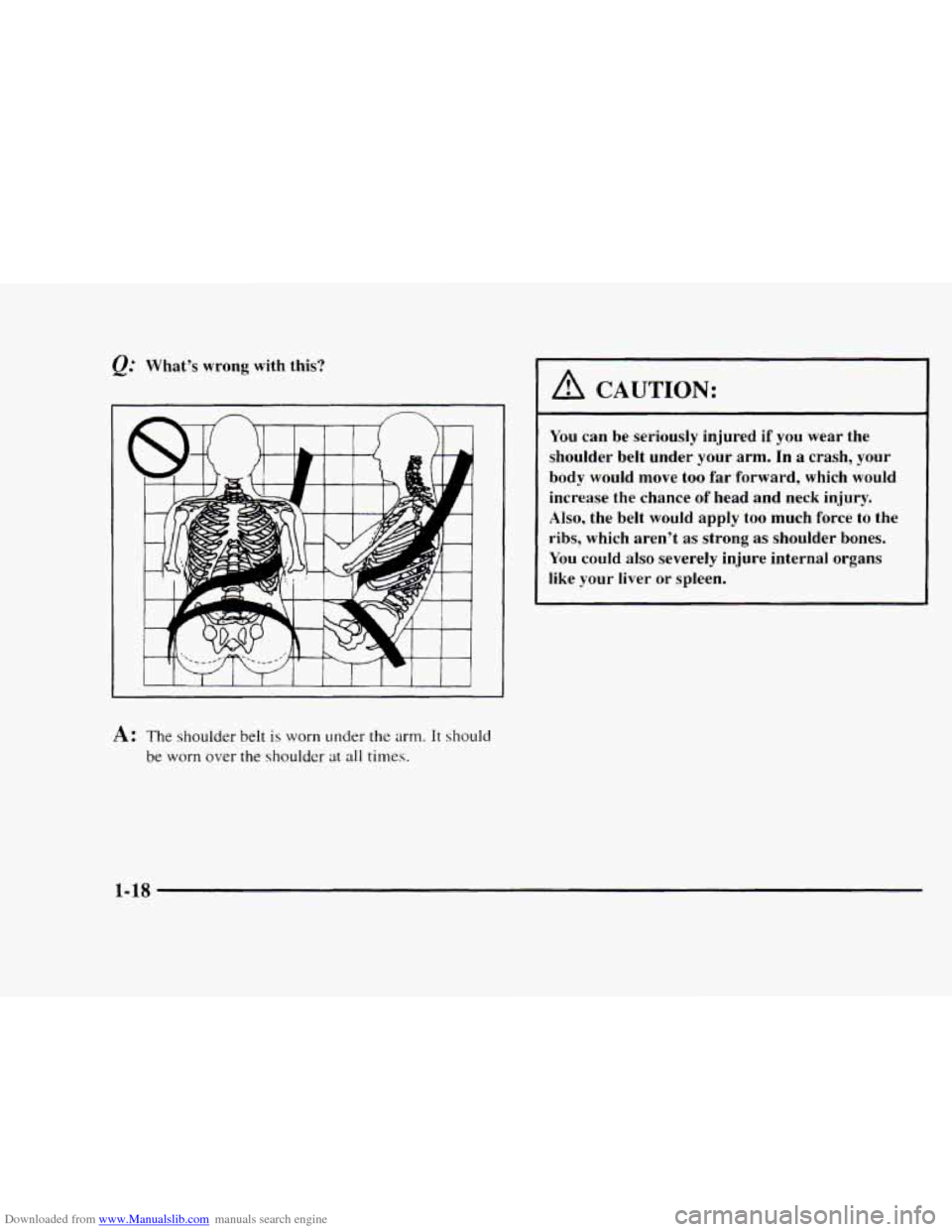
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine e.'' What's wrong with this?
A: The shoulder belt is worn under the arm. It should
be worn over the shoulder at all times.
A CAUTION:
You can be seriously injured if you wear the
shoulder belt under your arm. In
a crash, your
body would move too far forward, which would
increase the chance
of head and neck injury.
Also, the belt would apply too much force to the
ribs, which aren't
as strong as shoulder bones.
You could also severely injure internal organs
like your liver or spleen.
1-18
Page 26 of 402
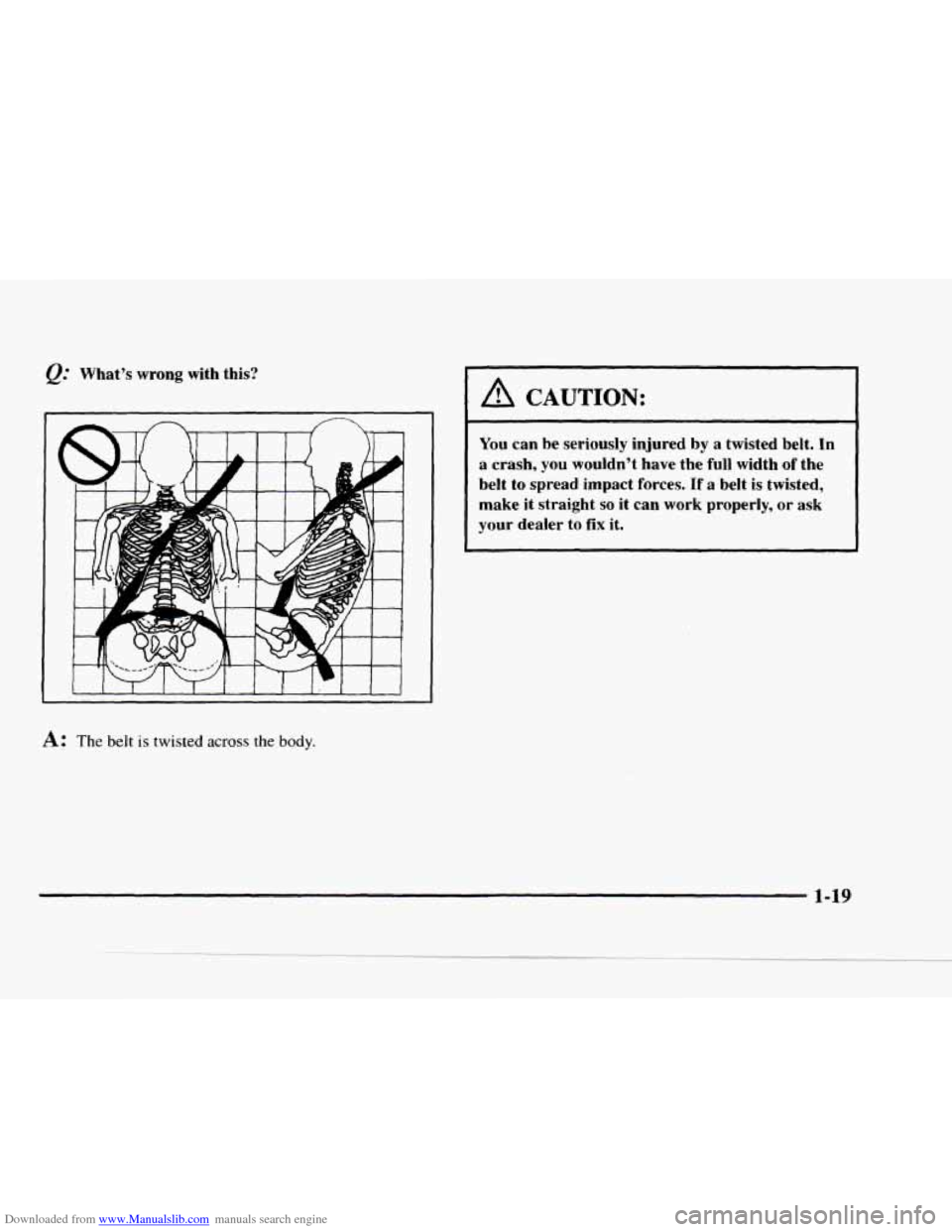
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine What’s wrong with this?
A CAUTION:
~~
You can be seriously injured by a twisted belt. In
a crash, you wouldn’t have the full width of the
belt
to spread impact forces. If a belt is twisted,
make it straight
so it can work properly, or ask
your dealer
to fix it.
A: The belt is twisted across the body.
1-19
Page 27 of 402

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ‘i
To unlatch the belt, just push the button on the buckle.
The belt should go back out of the way.
Before you close the
door, be sure the belt is out of the
way.
If you slam the door on it, you can damage both the
belt and your vehicle.
Supplemental Inflatable Restraint
(SIR) System
This part explains the Supplemental Inflatable Restraint
(SIR) system or air bag system.
Your vehicle has an air bag for the driver.
Here are
the most important things to know about the
air bag system:
A CAUTION:
You can be severely injured or killed in a crash if
you aren’t wearing your safety belt -- even if you
have an air bag. Wearing your safety belt during
a crash helps reduce your chance of hitting things
inside the vehicle or being ejected from it. Air
bags are “supplemental restraints”
to the safety
belts.
All air bags are designed to work with
safety belts, but don’t replace them. Air bags are
designed to work only in moderate to severe
crashes where the front
of your vehicle hits
something. They aren’t designed to inflate at all
CAUTION: (Continued)
1-20
Page 28 of 402

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine CAUTION: (Continued)
in rollover, rear, side or low-speed frontal crashes.
Everyone in your vehicle should wear a safety belt
properly
-- whether or not there’s an air bag for
that person.
A CAUTION:
Air bags inflate with great force, faster than the
blink of an eye.
If you’re too close to an inflating
air bag, it could seriously injure you. Safety belts
help keep you in position before and during a
crash. Always wear your safety belt, even with an
air
bag, and sit as far back as you can while still
maintaining control
of your vehicle. There is
an air bag readiness
light on
the instrument
panel, which shows
AIR
BAG
AIR BAG.
The system checks the air bag electrical system for
malfunctions. The light tells you if there is an electrical
problem. See “Air Bag Readiness Light” in the Index
for more information.
1-21
Page 29 of 402

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine How the Air Bag System Works
Where is the air bag?
The driver's air bag is in the middle of the steering wheel.
A CAUTION:
If something is between the driver and the air
bag, the bag might not inflate properly or it
might force the object into that person. The path
of' an inflating air bag must be kept clear. Don't
put anything between an occupant and the air
bag, and don't attach
or put anything on or near
the steering wheel
hub.
1-22
Page 30 of 402

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine When should an air bag inflate?
An air bag is designed to inflate in a moderate to severe
frontal or near-frontal crash. The air bag will inflate
only
if the impact speed is above the system’s designed
“threshold level.” If your vehicle goes straight into a
wall that doesn’t move or deform, the threshold level
is
about 14 to 18 mph (23 to 29 kmh). The threshold level
can
vary, however, with specific vehicle design, so that
it can be somewhat above or below this range. If your
vehicle strikes something
that will move or deform, such
as a parked car, the threshold level will be higher. The
air bag is not designed to inflate
in rollovers, side
impacts or rear impacts, because inflation would not
help
the occupant.
In any particular crash, no one can say whether an air
bag should have inflated simply because of the damage to a vehicle or because of what the repair costs were.
Inflation is determined
by the angle of the impact and
how quickly the vehicle slows down in frontal and
near-frontal impacts.
What makes an air bag inflate?
In an impact of sufficient severity, the air bag sensing
system detects that the vehicle is
in a crash. The sensing
system triggers a release of gas from the inflator, which
inflates the air bag. The inflator, air bag and related
hardware are all part of the air bag module inside the
steering wheel.
How does an air bag restrain?
In moderate to severe frontal or near-frontal collisions,
even belted occupants can contact the steering wheel.
The air bag supplements the protection provided by
safety belts. Air bags distribute the force of the impact
more evenly over the occupant’s upper body, stopping
the occupant more gradually. But air bags would not
help you in many types
of collisions, including
rollovers, rear impacts and side impacts, primarily
because an occupant’s motion is not toward the air bag.
Air bags should never be regarded
as anything more
than
a supplement to safety belts, and then only in
moderate to severe frontal or near-frontal collisions.
The air bag system
is designed to work properly under a
wide range of conditions, including off-road usage.
Observe safe driving speeds, especially on rough terrain.
As always, wear your safety belt. See “Off-Road
Driving”
in the Index for more tips on off-road driving.
1-23