charging CHEVROLET CAMARO 1967 1.G Chassis User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1967, Model line: CAMARO, Model: CHEVROLET CAMARO 1967 1.GPages: 659, PDF Size: 114.24 MB
Page 69 of 659

HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONING 1A-46
MAKE ANGULAR CUT
FOR HOSE REMOVAL
LOCATING
BEAD
SEALING
BEADS
LOCATING
BEAD
not to nick or score the sealing beads when
cutting off the hose. Cutting the hose lengthwise
may result in this problem.
Fig.
58—Hose Clamp Connections
NOTE:
Where steel to aluminum connections
are being made, use torque for aluminum tubing.
Hose Clamps (Fig. 58)
When hose clamp connections are encountered special
procedures are necessary for both installation and
removal.
Installation
1.
Coat tube and hose with refrigeration oil.
2.
Carefully insert hose over the three beads on the
fitting and down as far as the fourth, or locating,
bead. Hose must butt against this fourth bead.
CAUTION: Use no sealer of any kind.
3.
Install clamps on hose, hooking the locating arms
over the cut end of the hose.
4.
Tighten the hose clamp screw to 35-42 lb. in.
(except Corvette) 30-38 lb. in. (Corvette). DO NOT
RETORQUE.
Removal
1.
Carefully, with a sharp knife, make an angle cut in
the hose as shown in Figure 58. This should loosen
the hose so that it may be worked off the fitting.
2.
Cut off slit end of hose when reinstalling. Reinstall
as described above.
CAUTION: Use only approved refrigeration
hose. Never use heater hose. Use extreme care
REPAIR OF REFRIGERANT LEAKS
Any refrigerant leaks found in the system should be
repaired in the manner given below:
Leaks at "O" Ring Connection
1.
Check the torque on the fitting and, if too loose,
tighten to the proper torque. Always use a backing
wrench to prevent twisting and damage to the "O"
ring. Do not overtighten. Again leak test the joint.
2.
If the leak is still present, discharge the refrigerant
from the system as described under "Evacuating
and Charging Procedures."
3.
Inspect the ''O" ring and the fitting and replace if
damaged in any way. Coat the "O". ring before re-
installed with refrigerati6n oil and install carefully.
4.
Retorque the fitting, using a backing wrench, and
then add 1/2 to 1 lb. of R-12 to the system and
recheck for leaks.
CAUTION: Do not operate the system with this
small refrigerant charge.
5. Purge the system, thus removing the 1/2 to 1 lb.
installed in Step 4 above.
6. Evacuate and charge the system.
Leaks at Hose Clamp Connection
1.
Check the tightness of the clamp itself and tighten
if necessary. Recheck for leak.
2.
If leak has not been corrected discharge the system
and loosen clamp and remove hose from connection.
Inspect condition of hose and connector. Replace
scored or damaged parts.
3.
Dip end of new hose in refrigerant oil and carefully
reinstall over connector. Never push end of hose
beyond the locating bead. Properly torque the clamp.
4.
Recheck the system for leaks by installing 1/2 to 1
lb.
of R-12 into the system. Do not run compressor.
5. Purge. the system, thus removing the 1/2 to 1 lb.
installed in Step 4 above.
6. Evacuate and charge the system.
Compressor Leaks
If leaks are located around the compressor shaft seal
or shell, replacement of necessary seals should be made
as outlined under "Compressor" in the Chassis Overhaul
Shop Manual.
REFRIGERANT HOSE FAILURE
After a leak or rupture has occurred in a refrigerant
hose, or if a fitting has loosened and caused a consider-
able loss of refrigerant and oil, the entire system should
be flushed and recharged after repairs have been made.
Ji the system has been open to atmosphere for any pro-
longed period of time the receiver-dehydrator should be
replaced.
PREPARING SYSTEM FOR REPLACEMENT
OF COMPONENT PARTS
Air conditioning, like many other things, is farily
simple to service once it is understood. However, there
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 76 of 659
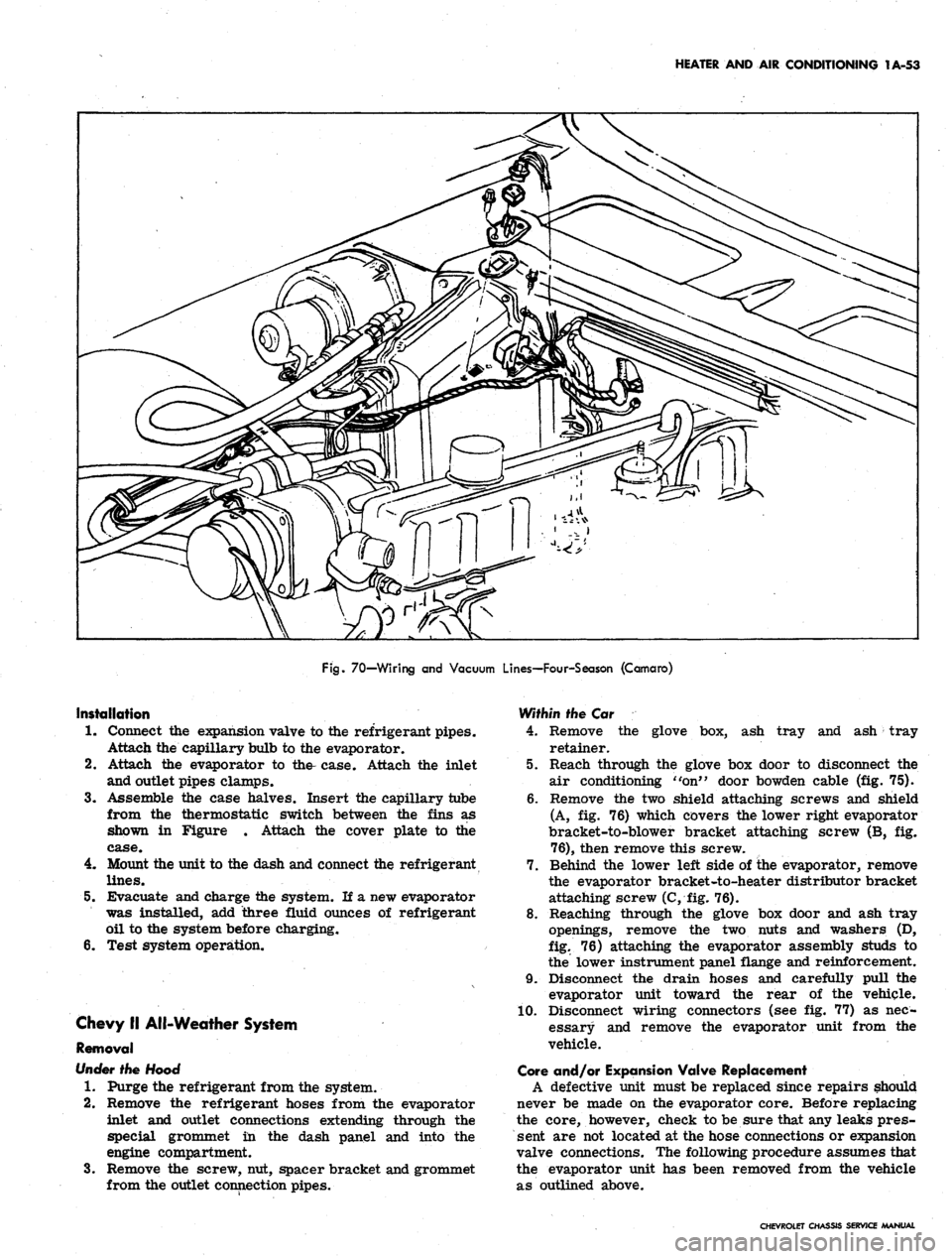
HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONING 1A-53
Fig.
70—Wiring and Vacuum Lines—Four-Season (Camaro)
Installation
1.
Connect the expansion valve to the refrigerant pipes.
Attach the capillary bulb to the evaporator.
2.
Attach the evaporator to the- case. Attach the inlet
and outlet pipes clamps.
3.
Assemble the case halves. Insert the capillary tube
from the thermostatic switch between the fins as
shown in Figure . Attach the cover plate to the
case.
4.
Mount the unit to the dash and connect the refrigerant
lines.
5.
Evacuate and charge the system. If a new evaporator
was installed, add three fluid ounces of refrigerant
oil to the system before charging.
6. Test system operation.
Chevy II All-Weather System
Removal
Under
the Hood
1.
Purge the refrigerant from the system.
2.
Remove the refrigerant hoses from the evaporator
inlet and outlet connections extending through the
special grommet in the dash panel and into the
engine compartment.
3.
Remove the screw, nut, spacer bracket and grommet
from the outlet connection pipes.
Within the Car
4.
Remove the glove box, ash tray and ash tray
retainer.
5.
Reach through the glove box door to disconnect the
air conditioning "on" door bowden cable (fig. 75).
6. Remove the two shield attaching screws and shield
(A, fig. 76) which covers the lower right evaporator
bracket-to-blower bracket attaching screw (B, fig.
76),
then remove this screw.
7.
Behind the lower left side of ihe evaporator, remove
the evaporator bracket-to-heater distributor bracket
attaching screw (C, fig. 76).
8. Reaching through the glove box door and ash tray
openings, remove the two nuts and washers (D,
fig.
76) attaching the evaporator assembly studs to
the lower instrument panel flange and reinforcement.
9. Disconnect the drain hoses and carefully pull the
evaporator unit toward the rear of the vehicle.
10.
Disconnect wiring connectors (see fig. 77) as nec-
essary and remove the evaporator unit from the
vehicle.
Gore and/or Expansion Valve Replacement
A defective unit must be replaced since repairs should
never be made on the evaporator core. Before replacing
the core, however, check to be sure that any leaks pres-
sent are not located at the hose connections or expansion
valve connections. The following procedure assumes that
the evaporator unit has been removed from the vehicle
as outlined above.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 107 of 659
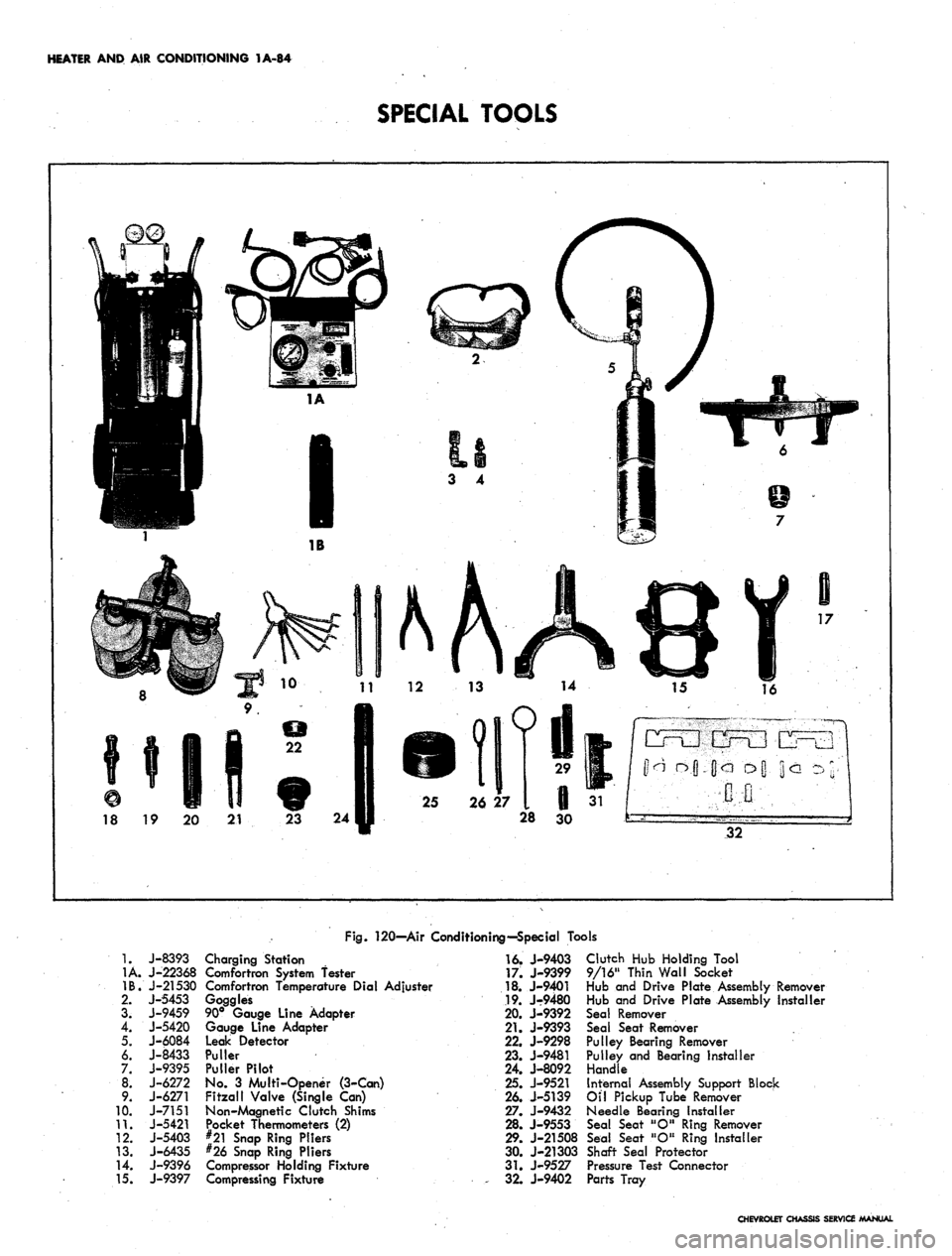
HEATER
AND AIR
CONDITIONING
1A-84
SPECIAL TOOLS
18
19 20 21 23 24
28
30
32
Fig.
120—Air Conditioning—Special Tools
1.
1A.
IB.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
00*
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
J-8393
J-22368
J-21530
J-5453
J-9459
J-5420
J-6084
J-8433
J-9395
J-6272
J-6271
J-7151
J-5421
J-5403
J-6435
J-9396
J-9397
Charging Station
Comfortron System fester
Comfortron Temperature Dial Adjuster
Goggles
90° Gauge Line Adapter
Gauge Line Adapter
Leak Detector
Puller
Puller Pilot
No.
3
Multi-Opener (3-Can)
Fitzall Valve (Single
Can)
Non-Magnetic Clutch Shims
Pocket Thermometers
(2)
#21 Snap Ring Pliers
#26 Snap Ring Pliers
Compressor Holding Fixture
Compressing Fixture
16.
J-9403
17.
J-9399
18.
J-9401
19.
J-9480
20.
J-9392
21.
J-9393
22.
J-9298
23.
J-9481
24.
J-8092
25.
J-9521
26.
J-5139
27.
J-9432
28.
J-9553
29.
J-21508
30.
J-21303
31.
J-9527
,
32.
J-9402
Clutch
Hub
Holding Tool
9/16" Thin Wall Socket
Hub
and
Drive Plate Assembly Remover
Hub
and
Drive Plate Assembly Installer
Seal Remover
Seal Seat Remover
Pulley Bearing Remover
Pulley and Bearing installer
Handle
Internal Assembly Support Block
Oil Pickup Tube Remover
Needle Bearing Installer
Seal Seat "O" Ring Remover
Seal Seat "O" Ring Installer
Shaft Seal Protector
Pressure Test Connector
Parts Tray
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 270 of 659

ENGINE
6-5
Service Battery and Battery Cables
1.
Measure the specific gravity of the electrolyte in
each cell (fig. 6). If it is below 1.230 (corrected to
80°F.) recharge with a slow rate charger, or if de-
sired, further check battery.
2.
Connect a voltmeter across the battery terminals and
measure the terminal voltage of the battery during
cranking (disconnect the coil primary lead at the
negative terminal during this check to prevent engine
from firing). If the terminal voltage is less than 9.0
volts at room temperature, approximately 80°
±
20°
F.,
the battery should be further checked. See
Section 6Y for further tests.
3.
Inspect for signs of corrosion on battery, cables and
surrounding area, loose or broken carriers, cracked
or bulged cases,- dirt and acid, electrolyte leakage
and low electrolyte level. !Fill cells to proper level
with distilled water or water passed through a
"demineralizer".
The top of the battery should be clean and the bat-
tery hold-down bolts properly tightened. Particular
care should be taken to see that the top of the battery
is kept clean of acid film and dirt. When cleaning
batteries, wash first with a dilute ammonia or soda
solution to neutralize any acid present and then flush
off with clean water. Keep vent plugs tight so that
the neutralizing solution does not enter the cell. The
hold-down bolts should be kept tight enough to prevent
the battery from shaking around in its holder, but
they should not be tightened to the point where the
battery case will be placed under a severe strain.
To insure good contact, the battery cables should
be tight on the battery posts. Oil battery terminal
felt washer. If the battery posts or cable terminals
are corroded, the cables should be cleaned separately
with a soda solution and wire brush. After cleaning
and before installing clamps, apply a thin coating of
petrolatum to the posts and cable clamps to help
retard corrosion.
If the battery has remained undercharged, check
for loose or defective fan belt, defective Delcotron,
high resistance in the charging circuit, oxidized
regulator contact points, or a low voltage setting.
If the battery has been using too much water, the
voltage output
is-
too high.
Service Deicotron and Regulator
The Delcotron and regulator tests during tune up con-
sist of the above battery tests; the condition of the battery
indicating further tests and adjustments as outlined in
Section 6Y.
Service Belts (Fig. 7)
Inspect belt condition.
Check and adjust if necessary for correct tension of
belt, as follows:
• Using a strand tension gauge, check the belt tension.
• Adjust belt until the specified tension is reached.
(See Tune Up Chart.)
Service Manifold Heat Valve (Figs. 8 or 9)
Check manifold heat control valve for freedom of oper-
ation. If shaft is sticking, free it up with GM Manifold
Heat Control Solvent or its equivalent.
NOTE: Tap shaft end to end to help free it up.
Tighten Manifold
Tighten intake manifold bolts to specifications in the
FLAME
ARRESTOR
FLAME
ARRESTOR
NON-VENTED\
CAP
V\ VALVE
CLOSED
POSITIVE (283 & 327)
POSITIVE
(IN LINE)
POSITIVE
(327)
POSITIVE
(396 & 427)
Fig.
10 -
Crank case
Ventilation Systems
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 326 of 659

SECTION 6Y
ENGINE ELECTRICAL
CONTENTS
OF
THIS SECTION
Page
System
6Y-19
6Y-32
6Y-34
BATTERY
INDEX
Page
General Description 6Y_i
Types of Batteries 6Y-1
Dry Charged Batteries 6Y-2
Activating Dry Charged Batteries 6Y-2
Wet Charged Batteries 6Y 2
Periodic Service 6Y-3
Common Causes of Failure 6Y-3
Delco Eye 6Y_3
Electrolyte Level
AY
3
Water Usage ] \ 6Y_3
Cleaning 6Y_4
Cables 6Y_4
Carrier and Holddown 6Y-4
Page
Safety Precautions 6Y-4
Charging Procedures . . gY_4
Slow Charging gY-4
Fast Charging . * 6Y-4
Emergency Boost Charging 6Y-4
Test Procedures QY-S
Visual Inspection 6Y-5
Instrument 6Y-5
Full Charge Hydrometer Test. 6Y-5
Specific Gravity Readings 6Y-5
Cell Comparison Test . 6Y-5
Installing Battery 6Y-5
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The battery (fig. lb) is made up of a number of separ-
ate elements, each located in an individual cell in a hard
rubber case. Each element consists of an assembly of
positive plates and negative plates containing dissimilar
active materials and kept apart by separators. Hie ele-
ments are immersed in an electrolyte composed of dilute
sulfuric acid. Plate straps located on the top of each ele-
ment connect all the positive plates and all the negative
plates into groups. The elements are connected in series
electrically by connectors that pass directly through the
case partitions between cells. The battery top is a one-
piece cover of hard rubber construction. Tfte cell con-
nectors, by-passing through the cell partitions, connect
the elements along the shortest practical path (fig. 2b).
With the length of the electrical circuit inside the
Battery reduced to a minimum, the internal voltage drop
is decreased resulting in improved performance, par-
ticularly during engine cranking at low temperatures.
The hard, smooth one-piece cover greatly reduces the
tendency for corrosion to form on the top of the Battery.
The cover is bonded to the case with sealing compound
that forms an air tight seal between the cover and case.
Protection for the Battery charging circuit (10 gage
wire) is provided by a pigtail lead which is a fusible Hnk
off the battery positive cable (14 gage wire). This lead is
an integral part of the Battery cable assembly and serv-
icing requires replacing the complete cable assembly.
TYPES
OF
BATTERIES
There are two types of Batteries—the "dry charge"
type and the "wet charge" type. The difference in types
depends on the method of manufacture.
ONE PIECE
CELL COVER
VENT PLUG
ELECTROLYTE LEVEL
INDICATOR
HOLD-DOWN SLOT
Fig.
lb—Battery
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 328 of 659

ENGINE-EIECTRICAI 6Y-3
PERIODIC SERVICING
Since the Battery is a perishable item which requires
periodic servicing, a good maintenance program will
insure the longest possible Battery life.
COMMON CAUSES OF FAILURE
If the Battery tests good but fails to perform satis-
factorily in service for no apparent reason, the following
are some of the more important factors that may point to
the cause of the trouble.
1.
Vehicle accessories inadvertently left on overnight to
cause a discharged condition.
2.
Slow speed driving of short duration, to cause an
3.
undercharged condition.
A vehicle
capacity.
electrical load exceeding the generator
4.
Defect in the charging system such as high resist-
ance, slipping fan belt, faulty generator or voltage
regulator.
5. Battery abuse, including failure to keep the Battery
top clean, cable clamps and posts clean and tight,
and improper addition of water to the cells.
LEVEL INDICATOR
The Battery features an electrolyte level indicator,
which is a specially designed vent plug with a transparent
rod extending through the center (fig. 5b). When the elec-
trolyte is at the proper level, the lower tip of the rod is
immersed, and the exposed top of the rod will appear
very dark; when the level falls below the tip of the rod,
the top will glow. ,
The Indicator reveals at a glance if water is needed,
without the necessity of removing the vent plugs (fig. 6b).
The Level Indicator is used in only one cell (second
cell cap from positive Battery post) because when the
electrolyte level is low in one cell, it is normally low in
all cells. Thus when the Indicator shows water is needed,
check the level in all six cells.
An alternate method of checking the electrolyte level is
to remove the vent plug and visually observe the electro-
lyte level in the vent well. The bottom of the vent well
features a split vent which will cause the surface of the
electrolyte to appear distorted when it makes contact.
The electrolyte level is. correct when the distortion first
appears at the bottom of the split vent (fig. 4b).
ELECTROLYTE LEVEL
The electrolyte level in the Battery should be checked
regularly. In hot weather, particularly during trip driv-
ing, checking should be more frequent because of more
rapid loss of water. If the electrolyte level is found to be
low, then colorless, odorless, drinking water should be
added to each cell until the liquid level rises to the split
vent located in the bottom of the vent well. DO NOT
OVERFILL because this will cause loss of electrolyte
resulting in poor performance, short life, and excessive
corrosion.
CAUTION: During service only water should be
added to the Battery, not electrolyte.
The liquid level in the cells should never be allowed to
drop below the top of the plates, as the portion of the
INDICATOR
ELECTROLYTE LEVEL
CORRECT
Fig.
5b—Cut-Away View Showing Electrolyte at Proper Level
with Indicator Having Dark Appearance
plates exposed to air may be permanently damaged with a
resulting loss in performance.
WATER USAGE
Excessive usage of water indicates the Battery is being
overcharged. The most common causes of overcharge
are high Battery operating temperatures, too high a volt-
age regulator setting, poor regulator ground wire con-
nection. Normal Battery water usage is approximately
one to two ounces per month per battery.
INDICATOR
Fig.
6b—Cut-Away View Showing Electrolyte at Low Level
with Indicator Having Light Appearance
CHASSIS SBtVKZ MANUAL
Page 329 of 659

ENGINE-ELECTRICAL
6Y-4
CLEANING
The external condition of the Battery should be checked
periodically for damage or for the presence of dirt and
corrosion. The top of the Battery should be kept clean.
An accumulation of acid film and dirt may permit current
to flow between the terminals, which will slowly dis-
charge the Battery. For best results when cleaning the
top of Batteries, wash first with a diluted ammonia or a
soda solution to neutralize any acid present; then flush
with clean water. Care must be taken to keep vent plugs
tight, so that the neutralizing solution does not enter the
cells.
CABLES
To insure good electrical contact, the cables should be
clean and tight on the Energizer posts. If the posts or
cable terminals are corroded, the cables should be dis-
connected and the terminals and clamps cleaned sepa-
rately with a soda solution and a wire brush. After
cleaning and installing clamps, apply a thin coating of
petroleum jelly on the cable clamps to retard corrosion.
CARRIER
AND
HOLD-DOWN
The Battery carrier and hold-down should be clean and
free from corrosion before installing the Battery. The
carrier should be in a sound mechanical condition so that
it will support the Battery securely and keep it level.
To prevent the Battery from shaking in its carrier,
the hold-down bolts should be tight (60-80 in. lbs.). How-
ever, the bolts should not be tightened to the point where
the Battery case or cover will be placed under a severe
strain.
BATTERY SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
When Batteries are being charged, an explosive gas
mixture forms in each cell. Part of this gas escapes
through the holes in the vent plugs and may form an
explosive atmosphere around the Battery itself if ventila-
tion is poor. This explosive gas may remain in or around
the Battery for several hours after it has been charged.
Sparks or flames can ignite this gas causing an internal
explosion which may shatter the Battery.
The following precautions should be observed to pre-
vent an explosion:
1.
Do not smoke near Batteries being charged or which
have been very recently charged.
2.
Do not break live circuits at the terminals- of Batr
teries because a spark usually occurs at the point
where a live circuit is broken. Care must always be
taken when connecting or disconnecting booster leads
or cable clamps on fast chargers. Poor connections
are a common cause of electrical arcs which cause
BATTERY CHARGING PROCEDURES
There are three methods of recharging Batteries.
They differ basically in the length of time the Battery is
charged and the rate at which charging current is sup-
plied. One is the Slow Charge method, the second is the
Fast Charge method, and the third is the Emergency
Boost Charge method.
Before recharging a Battery by any method, the elec-
trolyte level must be checked and adjusted if necessary.
SLOW CHARGING
The Slow Charge method supplies the Battery with a
relatively low current flow for a relatively long period of
time. This is the only method that will bring the Battery
to a full state of charge.
The Slow Charge method consists of charging at
approximately a 4 ampere rate for 24 hours or more if
necessary to bring the Battery to full charge. A fully
charged condition is reached when the cells are gassing
freely and three corrected specific gravity readings
taken at hourly intervals show no increase.
FAST CHARGING
The Fast Charge method supplies current to the Bat-
tery at a 40 to 50 ampere rate for a 1 1/2 hour period of
time. If the electrolyte temperature reaches 125°F before
the 1 1/2 hour period is completed, the Battery must be
taken off charge temporarily, or the charging rate
reduced to avoid damage to the Battery.
Although a Battery cannot be brought to a fully charged
condition during Fast Charge, it can be substantially
recharged or "boosted". In order to bring the Battery to
a fully charged condition, the charging cycle must be
finished by the Slow Charge method.
EMERGENCY BOOST CHARGING
In cases where the Battery is not sufficiently charged
to crank the engine, an emergency boost charge may be
applied as a temporary expedient in order to crank the
engine. The Emergency Boost Charge method consists of
charging at a 40 to 50 ampere rate for a period of one-
half hour.
It should be particularly noted that the Emergency
Boost Charge will not necessarily restore the Battery to
a useful state of. charge for continued service. After an
emergency boost charge, failure to charge the Battery
further, either by a long uninterrupted driving period or
by the Fast Charge or Slow Charge method, may result
in failure to crank the engine the next time cranking is
attempted. A Battery should never be condemned on the
basis of failure to crank the engine after an emergency
boost charge. Although an emergency boost charge may
put enough energy into the Battery to crank the engine
once, further charging usually is necessary in order to
create a sufficient reserve to crank a second and third
time.
12
VOLT BATTERY SUGGESTED
CHARGING RATES
(100 Amp/hr or Less Capacity)
TYPE OF
CHARGE
Boost Charge for
Light Load Test
Slow Charge
Fast Charge
Quick Boost .
Dry Charge
Warm-up Boost
LENGTH
OF TIME
20 Minutes
24 Hours
1-1/2 Hours
30 Minutes
10 Minutes
CHARGING
RATE
50 Amps
4 Amps
40-50 Amps
40-50 Amps
15 Amps
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 330 of 659

ENGINE—ELECTRICAL 6Y-5
BATTERY TESTING PROCEDURES
Testing procedures are used to determine whether the
Battery is (1) good and usable, (2) requires recharging or
(3) should be replaced. Analysis of Battery conditions can
be accomplished, by performing a visual inspection,
Instrument Test, and the full charge hydrometer test.
1.
VISUAL INSPECTION
The first step in testing the Battery should be a visual
inspection, which very often will save time and expense
in determining Battery condition.
• Check the outside of the Battery for a broken or
cracked case or a broken or cracked cover. If any
damage is evident, the Battery should be replaced.
« Note the electrolyte level. Levels that are too low or
too high may cause poor performance, as covered in
the section entitled "Periodic Servicing".
o Check for loose cable connections, and for evidence
of corrosion as covered in section entitled ' 'Periodic
Servicing". Correct as required before proceeding
with tests.
2.
INSTRUMENT TEST
A number of suppliers have approved testing equipment
available. These testers have a programmed test proce-
dure consisting of a series of timed discharge and
charge events, requiring approximately 2 to 3 minutes,
that will determine the condition of the Battery with a
high degree of accuracy. When using these testers, the
procedure recommended by the tester manufacturer
should be followed. Batteries should not be charged prior
to testing as doing so may alter the test results. If a
tester is not available for testing, the "Specific Gravity
Cell Comparison Test" may be used or an alternate
method, but with a sacrifice in testing accuracy.
3. FULL CHARGE HYDROMETER TEST
This test should be used only on Batteries which test
good with testing equipment or "Specific Gravity Cell
Comparison Test" but which subsequently fail in service.
• Remove the Battery from the vehicle, and adjust the
electrolyte level as necessary, by adding colorless,
odorless, drinking water.
• Fully charge the Battery at the Slow Charging rate
as covered in the section entitled "Battery Charg-
ing".
• Measure the specific gravity of the electrolyte in
each cell and interpret as follows:
Hydrometer Reading Less Than
1.230—Full
charge
hydrometer readings less than 1.230 corrected for
temperature indicate the Battery is defective and
should be replaced.
Hydrometer Readings Above
1.310—Full
charge hy-
drometer readings above 1.310 corrected for tem-
perature indicate that the cells have been improperly
filled (activation) or improperly serviced. Poor
service and short Battery life will result.
SPECIFIC GRAVITY READINGS
A hydrometer can be used to measure the specific
gravity of the electrolyte in each cell.
The hydrometer measures the percentage of sulphuric
acid in the battery electrolyte in terms of specific
gravity. As a battery drops from a charged to a dis-
charged condition, the acid leaves the solution and enters
the plates, causing a decrease in specific gravity of
electrolyte. An indication of the concentration of the
electrolyte is obtained with a hydrometer.
When using a hydrometer, observe the following points:
1.
Hydrometer must be clean, inside and out, to insure
an accurate reading.
2.
Hydrometer readings must never be taken immedi-
ately after water has been added. The water must be
thoroughly mixed with the electrolyte by charging for
at least 15 minutes at a rate high enough to cause
vigorous gassing.
3.
If hydrometer has built-in thermometer, draw liquid
into it several times to insure correct temperature
before taking reading.
4.
Hold hydrometer vertically and draw in just enough
liquid from battery cell so that float is free floating.
Hold hydrometer at eye level so that float is vertical
and free of outer tube, then take reading at surface of
liquid. Disregard the curvature where the liquid
rises against float stem due to surface tension.
5.
Avoid dropping battery fluid on car or clothing as it
is extremely corrosive. Any fluid that drops should
be washed off immediately with baking soda solution.
The specific gravity of the electrolyte varies not only
with the percentage of acid in the liquid but also with
temperature. As temperature increases, the electrolyte
expands so that the specific gravity is reduced. As
temperature drops, the electrolyte contracts so that the
specific gravity increases. Unless these variations in
specific gravity are taken into account, the specific
gravity obtained by the hydrometer may not give a true
indication of the concentration of acid in the electrolyte.
A fully charged Battery will have a specific gravity
reading of approximately 1.270 at an electrolyte temper-
ature of 80°F. If the electrolyte temperature is above or
below 80°F, additions or subtractions must be made in
order to obtain a hydrometer reading corrected to the
80°F standard. For every 10° above 80°F, add four
specific gravity points (.004) to the hydrometer reading.
Example: A hydrometer reading of 1.260 at 110°F would
be 1.272 corrected to 80°F, indicating a fully charged
Battery. For every 10° below 80°F, subtract four points
(.004) from the reading. Example: A hydrometer reading
of 1.272 at 0°F would be 1.240 corrected to 80°F, indi-
cating a partially charged Battery.
Specific Gravity Cell Comparison Test—This test may
be used when a instrument tester is not available. To
perform this test measure the specific gravity of each
cell, regardless of state of charge, and interpret the
results as follows:
• If specific gravity readings show a difference be-
tween the highest and lowest cell of .050 (50 points)
or more, the Battery is defective and should be
replaced.
INSTALLING BATTERIES
To install a Battery properly, it is important to ob-
serve the following precautions:
• Connect grounded terminal of Battery last to avoid
short circuits which may damage the electrical
system.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 332 of 659
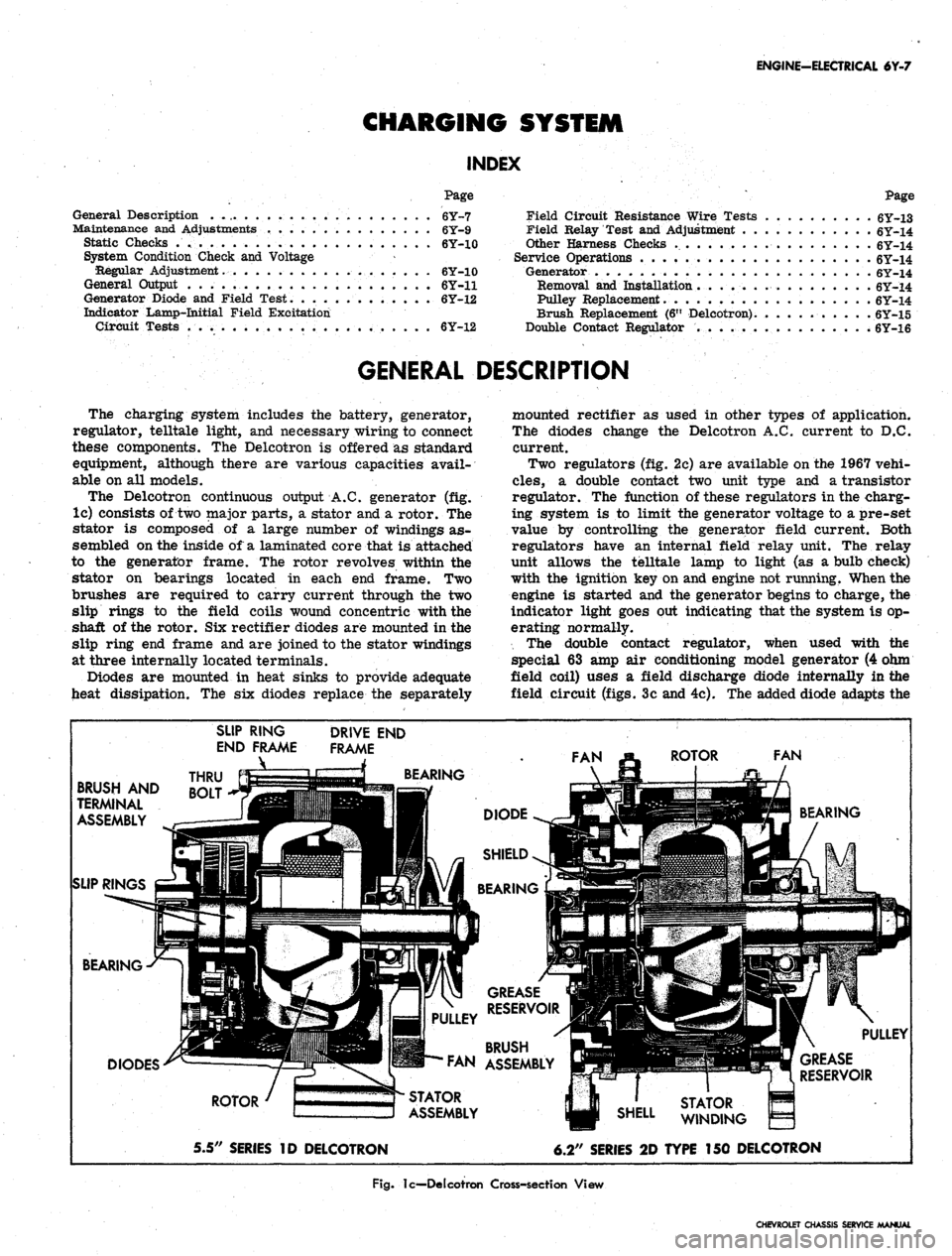
ENGINE-ELECTRICAL 6Y-7
CHARGING SYSTEM
INDEX
Page
General Description . 6Y-7
Maintenance and Adjustments 6Y-9
Static Checks . 6Y-10
System Condition Check and Voltage
•Regular Adjustment. 6Y-10
General Output 6Y-11
Generator Diode and Field Test 6Y-12
Indicator Lamp-Initial Field Excitation
Circuit Tests . 6Y-12
Page
Field Circuit Resistance Wire Tests 6Y-13
Field Relay Test and Adjustment 6Y-14
Other Harness Checks 6Y-14
Service Operations 6Y-14
Generator 6Y-14
Removal and Installation 6Y-14
Pulley Replacement. 6Y-14
Brush Replacement (6" Delcotron). 6Y-15
Double Contact Regulator . . . . . . 6Y-16
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The charging system includes the battery, generator,
regulator, telltale light, and necessary wiring to connect
these components. The Delcotron is offered as standard
equipment, although there are various capacities avail-
able on all models.
The Delcotron continuous output A.C. generator (fig.
lc) consists of two major parts, a stator and a rotor. The
stator is composed of a large number of windings as-
sembled on the inside of a laminated core that is attached
to the generator frame. The rotor revolves within the
stator on bearings located in each end frame. Two
brushes are required to carry current through the two
slip rings to the field coils wound concentric with the
shaft of the rotor. Six rectifier diodes are mounted in the
slip ring end frame and are joined to the stator windings
at three internally located terminals.
Diodes are mounted in heat sinks to provide adequate
heat dissipation. The six diodes replace the separately
mounted rectifier as used in other types of application.
The diodes change the Delcotron A.C. current to D.C.
current.
Two regulators (fig. 2c) are available on the 1967 vehi-
cles,
a double contact two unit type and a transistor
regulator. The function of these regulators in the charg-
ing system is to limit the generator voltage to a pre-set
value by controlling the generator field current. Both
regulators have an internal field relay unit. The relay
unit allows the telltale lamp to light (as a bulb check)
with the ignition key on and engine not running. When the
engine is started and the generator begins to charge, the
indicator light goes out indicating that the system is op-
erating normally.
The double contact regulator, when used with the
special 63 amp air conditioning model generator (4 ohm
field coil) uses a field discharge diode internally in the
field circuit (figs. 3c and 4c). The added diode adapts the
BRUSH AND
TERMINAL
ASSEMBLY
SLIP RINGS
SLIP RING
END FRAME
_\
THRU
BOLT
DRIVE END
FRAME
BEARING
BEARING
DIODES
ROTOR
5.5" SERIES ID DELCOTRON
STATOR
ASSEMBLY
GREASE
RESERVOIR
BRUSH
FAN ASSEMBLY
6.2" SERIES 2D TYPE 150 DELCOTRON
Fig.
lc—Delcotron Cross-section View
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 333 of 659
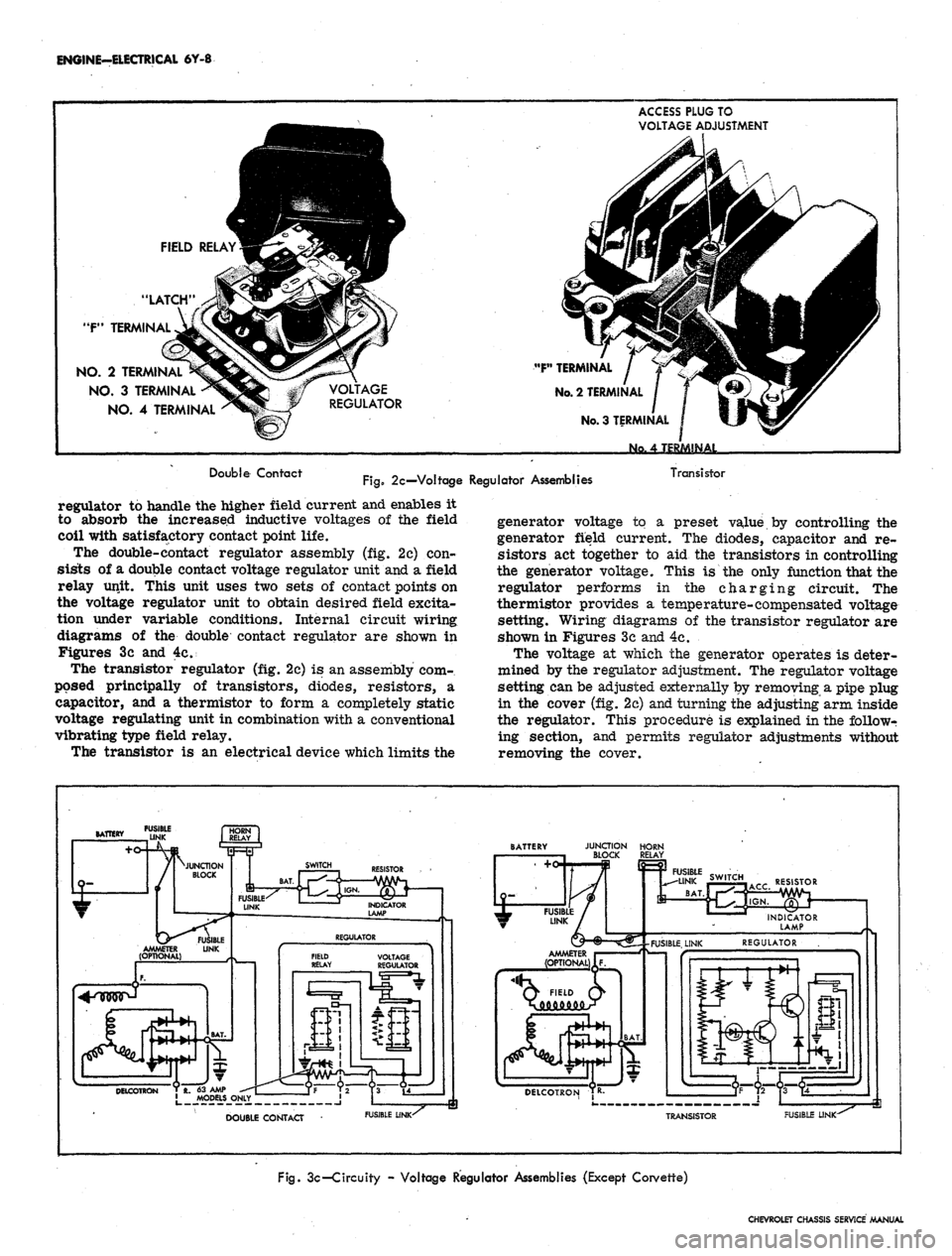
ENGINE-ELECTRICAL 6Y-8
1
FIELD RELAY^I^p2
"LATCH"
^PFN?^
"P1
TERMINAL
JyJvJCTl^
NO. 2 TERMINAD^5^^^«
NO.
3 TERMINAL ^S5«£
NO.
4 TERMINAL ^^^
m
# / VOLTAGE
¥ REGULATOR
1
ACCESS PLUG TO
VOLTAGE ADJUSTMENT
No 4 TERMINAL
Double Contact
Fig.
2c—Voltage Regulator Assemblies
Transistor
regulator to handle the higher field current and enables it
to absorb the increased inductive voltages of the field
coil with satisfactory contact point life.
The double-contact regulator assembly (fig. 2c) con-
sists of a double contact voltage regulator unit and a field
relay unit. This unit uses two sets of contact points on
the voltage regulator unit to obtain desired field excita-
tion under variable conditions. Internal circuit wiring
diagrams of the double contact regulator are shown in
Figures 3c and 4c.
The transistor regulator (fig. 2c) is an assembly com-
posed principally of transistors, diodes, resistors, a
capacitor, and a thermistor to form a completely static
voltage regulating unit in combination with a conventional
vibrating type field relay.
The transistor is an electrical device which limits the
generator voltage to a preset value by controlling the
generator field current. The diodes, capacitor and re-
sistors act together to aid the transistors in controlling
the generator voltage. This is the only function that the
regulator performs in the charging circuit. The
thermistor provides a temperature-compensated voltage
setting. Wiring diagrams of the transistor regulator are
shown in Figures 3c and 4c.
The voltage at which the generator operates is deter-
mined by the regulator adjustment. The regulator voltage
setting can be adjusted externally by removing a pipe plug
in the cover (fig. 2c) and turning the adjusting arm inside
the regulator. This procedure is explained in the followr
ing section, and permits regulator adjustments without
removing the cover.
FUSIBLE
DOUBLE CONTACT
FUSIBLE LINK-^
JUNCTION HORN
BLOCK RELAY
RESISTOR
Q FIELD Q>
DELCOTRON TR-
TRANSISTOR
FUSIBLE LINK-
Fig.
3c-Circuity - Voltage Regulator Assemblies (Except Corvette)
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL