tire type CHEVROLET CAMARO 1967 1.G Chassis User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1967, Model line: CAMARO, Model: CHEVROLET CAMARO 1967 1.GPages: 659, PDF Size: 114.24 MB
Page 352 of 659

ENGINE-ELECTRICAL 6Y-27
timing mark on pulley lines up with timing tab.
2.
Position distributor to opening in block in normal
installed attitude (fig. 15i), noting position of vacuum
control unit.
3.
Position rotor to point toward front of engine (with
distributor housing held in installed attitude), then
turn rotor counter-clockwise approximately 1/8 turn
more toward left cylinder bank and push distributor
down to engine camshaft. It may be necessary to ro-
tate rotor slightly until camshaft engagement is felt.
4.
While pressing firmly down on distributor housing,
kick starter over a few times to make sure oil pump
shaft is engaged. Install hold-down clamp and bolt
and snug up bolt.
5. Turn distributor body slightly until points just open
and tighten distributor clamp bolt.
6. Place distributor cap in position and check to see
that rotor lines up with terminal for No. 1 spark
plug.
7. Install cap, check all high tension wire connections
and connect spark plug wires if they have been re-
moved. It is important that the wires be installed in
their location in the supports.
NOTE:
The brackets are numbered to show the
correct installation. Wires must be installed as
indicated to prevent cross firing.
8. Connect vacuum line to distributor and distributor
primary wire to coil terminal.
9. Start engine and set timing as described under Turn-
Up in Section 6.
BREAKERLESS (MAGNETIC PULSE)
DISTRIBUTOR
REMOVAL (CORVETTE)
1.
If vehicle is equipped with radio, remove three bolts
securing ignition shield over distributor and coil.
One bolt is accessible from the top of shield, the
other two are at rear of shield, facing firewall.
2.
Disconnect tachometer drive cables from distributor
housing.
3.
Disconnect pickup coil leads at connector.
4.
Remove distributor cap.
5. Crank engine so rotor is in position to fire No. 1
cylinder and timing mark on harmonic balancer is
indexed with pointer.
6. Remove vacuum line from distributor.
7. Remove distributor clamping screw and hold-down
clamp.
8. Remove distributor and distributor-to-block gasket.
It will be noted that the rotor will rotate as the
distributor is pulled out of the block. Mark the re-
lationship of the rotor and the distributor housing
after removal so that the rotor can be set in the
same position when the distributor is being installed.
DISASSEMBLY (Fig. 16i)
NOTE:
If a distributor is being disassembled
for replacement of the stationary magnetic
pickup assembly only, it will be necessary to
perform only Steps 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, and 12 of the
service procedure listed below.
1.
Remove screws securing rotor and remove rotor.
2.
Remove centrifugal weight springs and weights.
3.
Remove the tachometer drive gear from the distribu-
tor (Corvette only).
4.
Remove roll pin, then remove distributor drive gear
and washer.
CAUTION: To prevent
magnet, support drive gear
;e to the permanent
?n
driving out roll
pin.
5. Remove drive shaft assembly.
6. Remove centrifugal weight support and timer core
from drive shaft.
7. Remove connector from pickup coil leads.
8. Remove retaining ring which secures magnetic
core support plate to distributor shaft bushing in
housing.
9. As a unit, remove the entire magnetic pickup assem-
bly from the distributor housing.
10.
Remove brass washer and felt pad.
11.
Remove vacuum advance unit.
12.
To reassemble distributor, perform the above steps
in reverse order.
INSTALLATION (CORVETTE)
1.
Check to see that the engine is at firing position for
No.
1 cylinder (timing mark on harmonic balancer
indexed with pointer).
2.
Position a new distributor-to-block gasket on the
block.
3.
Before installing distributor, index rotor with hous-
ing as noted when distributor was removed. Install
distributor in block so that vacuum diaphragm faces
approximately 45° forward on the right side of the
engine and the rotor points toward contact in cap for
No.
1 cylinder.
4.
Replace distributor clamp leaving screw loose
enough to allow distributor to be turned for timing
adjustment.
5. Install spark plug wires in distributor cap. Place
wire for No. 1 cylinder in tower (marked on old cap
during disassembly) then install remaining wires
clockwise around the cap according to the firing
order (1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2).
6. Attach distributor to coil primary wires.
7. Replace distributor cap.
8. Adjust timing and then fully tighten distributor clamp
screw.
9. Attach vacuum line to distributor.
10.
Connect tachometer drive cables to distributor body.
11.
Replace ignition shields.
DISTRIBUTOR OFF-ENGINE TEST
The distributor's centrifugal and vacuum advance can
be checked in a distributor testing machine or synchro-
scope specially adapted or designed to accommodate this
type distributor. However, since this involves removing
the distributor from the engine, this test may be post-
poned until other system checks have been made. A dwell
reading cannot be obtained on this distributor and it is not
likely that the centrifugal or vacuum advance will be a
cause of trouble.
COIL REPLACEMENT
1.
Disconnect ignition switch and distributor leads from
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 357 of 659
ENGINE-ELECTRICAL 6Y-32
STARTER CIRCUIT
INDEX
Page
General Description 6Y-32
Maintenance and Adjustments . '. . 6Y-32
Resistance Checks 6Y-32
Starting Motor and Solenoid Check 6Y-33
Page
Service Operations 6Y-33
Starter Motor 6Y-33
Removal and Installation 6Y-33
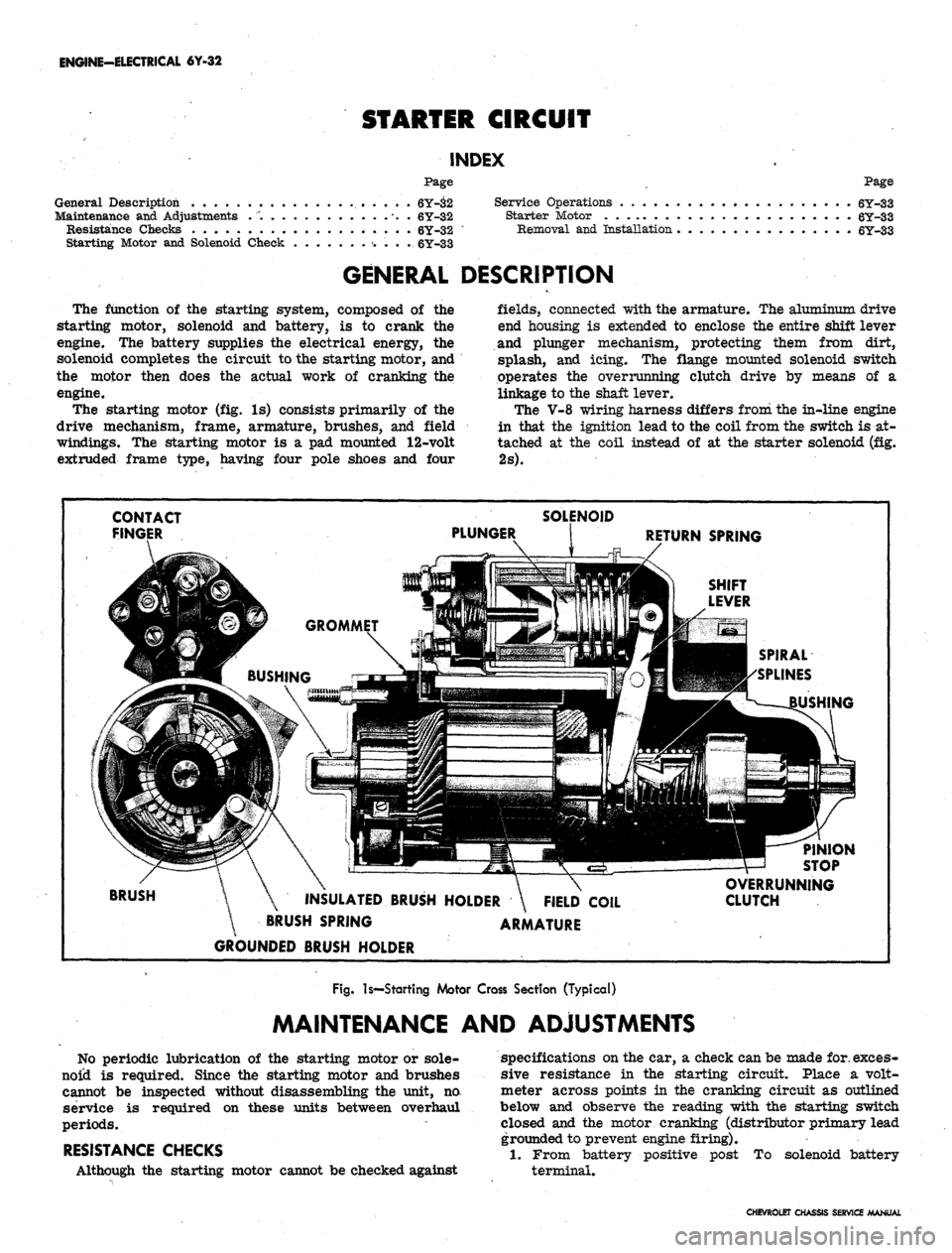
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The function of the starting system, composed of the
starting motor, solenoid and battery, is to crank the
engine. The battery supplies the electrical energy, the
solenoid completes the circuit to the starting motor, and
the motor then does the actual work of cranking the
engine.
The starting motor (fig. Is) consists primarily of the
drive mechanism, frame, armature, brushes, and field
windings. The starting motor is a pad mounted 12-volt
extruded frame type, having four pole shoes and four
fields,
connected with the armature. The aluminum drive
end housing is extended to enclose the entire shift lever
and plunger mechanism, protecting them from dirt,
splash, and icing. The flange mounted solenoid switch
operates the overrunning clutch drive by means of a
linkage to the shaft lever.
The V-8 wiring harness differs from the in-line engine
in that the ignition lead to the coil from the switch is at-
tached at the coil instead of at the starter solenoid (fig.
2s).
CONTACT
FINGER
PINION
STOP
BRUSH
INSULATED BRUSH HOLDER \ FIELD COIL
BRUSH SPRING ARMATURE
GROUNDED BRUSH HOLDER
OVERRUNNING
CLUTCH
Fig.
Is—Starting Motor Cross Section (Typical)
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS
No periodic lubrication of the starting motor or sole-
noid is required. Since the starting motor and brushes
cannot be inspected without disassembling the unit, no.
service is required on these units between overhaul
periods.
RESISTANCE CHECKS
Although the starting motor cannot be checked against
specifications on the car, a check can be made for. exces-
sive resistance in the starting circuit. Place a volt-
meter across points in the cranking circuit as outlined
below and observe the reading with the starting switch
closed and the motor cranking (distributor primary lead
grounded to prevent engine firing).
1.
From battery positive post To solenoid battery
terminal.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 424 of 659
FUEL TANK
AND
EXHAUST SYSTEMS
8-18
CORVETTE
FUEL TANK
INDEX
Page
General Description.
. 8-18
Service Operations
8-18
Fuel Tank
8-18
Gauge Sending Unit
8-20
Fuel Lines.
8-20
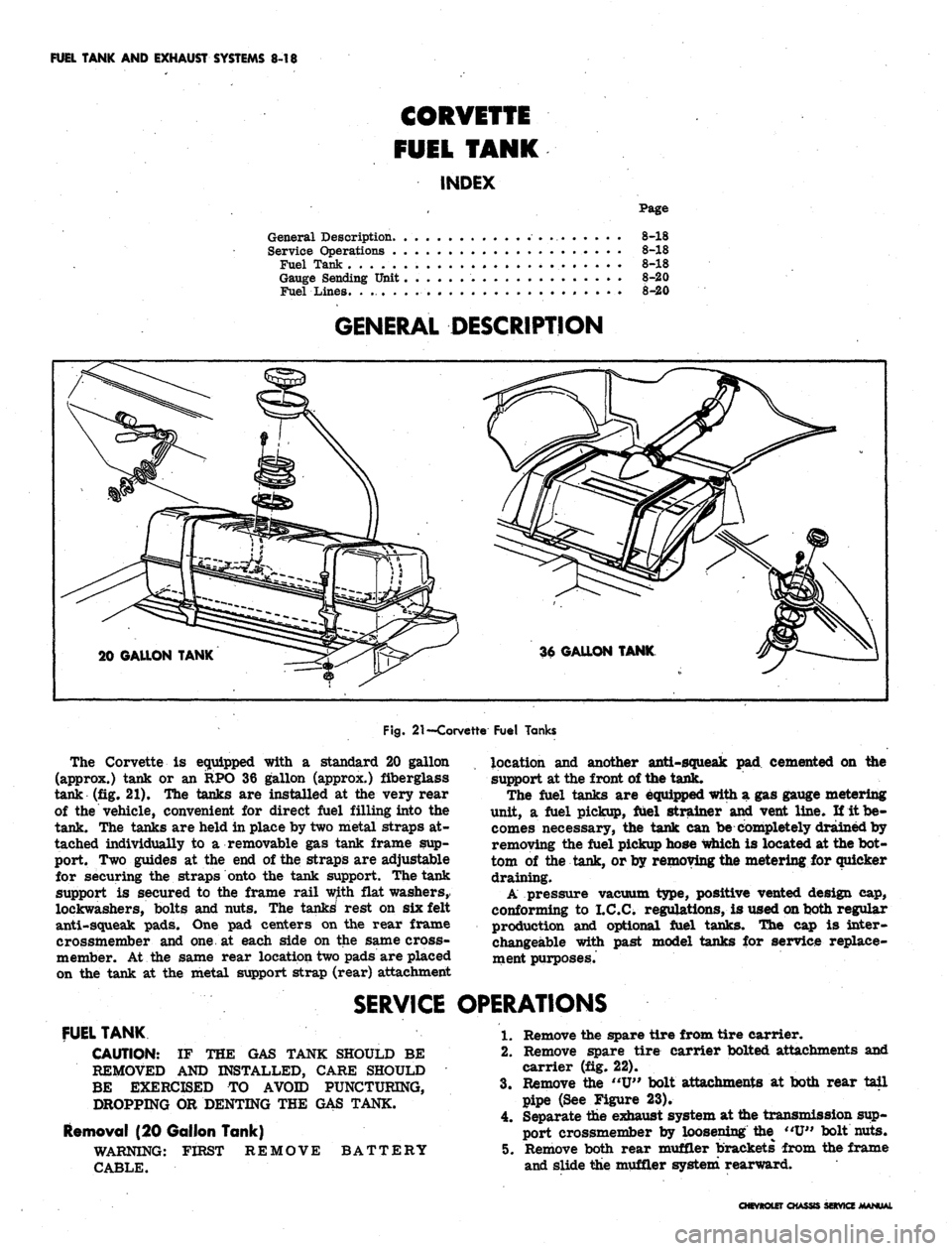
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
20 GALLON TANK
Fig.
21
—Corvette Fuel Tanks
The Corvette
is
equipped with
a
standard
20
gallon
(approx.) tank
or an RPO 36
gallon (approx.) fiberglass
tank
(fig. 21). The
tanks
are
installed
at the
very rear
of
the
vehicle, convenient
for
direct fuel filling into
the
tank.
The
tanks
are
held
in
place
by
two metal straps
at-
tached individually
to a
removable
gas
tank frame
sup-
port.
Two
guides
at the end of
the straps
are
adjustable
for securing
the
straps onto
the
tank support. The tank
support
is
secured
to the
frame rail with flat washers,
lockwashers, bolts
and
nuts.
The
tanks' rest
on six
felt
anti-squeak pads.
One pad
centers
on the
rear frame
crossmember
and one at
each side
on the
same cross-
member.
At the
same rear location two pads
are
placed
on
the
tank
at the
metal support strap (rear) attachment
location
and
another anti-squeak
pad
cemented
on the
support
at
the front
of
the tank.
The fuel tanks
are
equipped with
a gas
gauge metering
unit,
a
fuel pickup, fuel strainer
and
vent line.
If it be-
comes necessary,
the
tank
can be
completely drained
by
removing
the
fuel pickup hose which
is
located
at
the
bot-
tom
of the
tank,
or
by removing the metering
for
quicker
draining.
A pressure vacuum type, positive vented design
cap,
conforming
to
I.C.C. regulations,
is
used on both regular
production
and
optional fuel tanks.
The cap is
inter-
changeable with past model tanks
for
service replace-
ment purposes.
SERVICE OPERATIONS
FUEL TANK
CAUTION:
IF THE GAS
TANK SHOULD
BE
REMOVED
AND
INSTALLED, CARE SHOULD
BE EXERCISED
TO
AVOID PUNCTURING,
DROPPING
OR
DENTING
THE GAS
TANK.
Removal
(20
Gallon Tank)
WARNING: FIRST REMOVE BATTERY
CABLE.
1.
Remove
the
spare tire from tire carrier.
2.
Remove spare tire carrier bolted attachments
and
carrier
(fig. 22).
3.
Remove
the "U"
bolt attachments
at
both rear tail
pipe
(See
Figure
23).
4.
Separate
the
exhaust system
at
the transmission sup-
port crossmember
by
loosening
the "U"
bolt nuts.
5. Remove both rear muffler brackets from
the
frame
and slide
the
muffler system rearward.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 426 of 659
FUEL TANK AND EXHAUST SYSTEMS 8-20
4.
Attach the retaining straps with strap guide attached
to the fuel tank support, and secure with-the nut and
lockwasher assembly.
5. Connect the filler neck boot to the drain hose of the
tank and install boot around filler neck,
6. Connect the fuel pickup line, ground wire and make
certain that the fuel drain line is flush to 1/2" in-
board of the rear bumper opening.
7. Attach tank metering unit wires (fig. 25).
8. Replace fuel in tank. Replace gas cap.
9. Check for possible leaks.
10.
Reconnect the exhaust system by reversing the above
removal procedures (see "Exhaust System").
11.
Install spare tire carrier by securing the bolt
attachment.
12.
Install the spare tire in the tire carrier.
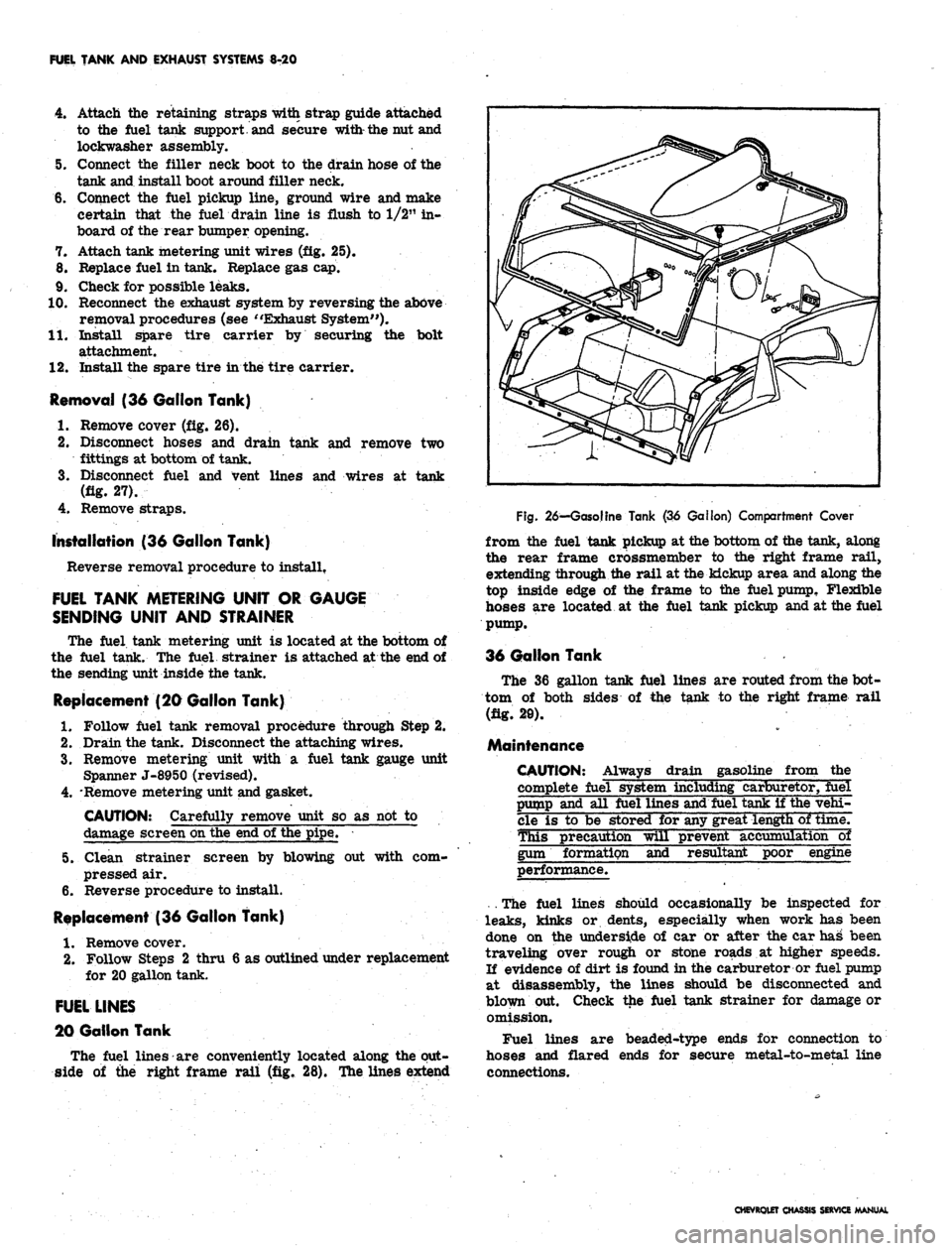
Removal (36 Gallon Tank)
1.
Remove cover (fig. 26).
2.
Disconnect hoses and drain tank and remove two
fittings at bottom of tank.
3.
Disconnect fuel and vent lines and wires at tank
(fig. 27).
4.
Remove straps.
installation (36 Gallon Tank)
Reverse removal procedure to install.
FUEL TANK METERING UNIT OR GAUGE
SENDING UNIT AND STRAINER
The fuel tank metering unit is located at the bottom of
the fuel tank. The fuel strainer is attached at the end of
the sending unit inside the tank.
Replacement (20 Gallon Tank)
1.
Follow fuel tank removal procedure through Step 2.
2.
Drain the tank. Disconnect the attaching wires.
3.
Remove metering unit with a fuel tank gauge unit
Spanner J-8950 (revised).
4.
'Remove metering unit and gasket.
CAUTION: Carefully remove unit so as not to
damage screen on the end of the pipe.
5. Clean strainer screen by blowing out with com-
pressed air.
6. Reverse procedure to install.
Replacement (36 Gallon Tank)
1.
Remove cover.
2.
Follow Steps 2 thru 6 as outlined under replacement
for 20 gallon tank.
FUEL LINES
20 Gallon Tank
The fuel lines are conveniently located along the out-
side of the right frame rail (fig. 28). The lines extend
Fig.
26—Gasoline Tank (36 Gallon) Compartment Cover
from the fuel tank pickup at the bottom of the tank, along
the rear frame crossmember to the right frame rail,
extending through the rail at the kickup area and along the
top inside edge of the frame to the fuel pump, Flexible
hoses are located at the fuel tank pickup and at the fuel
pump.
36 Gallon Tank
The 36 gallon tank fuel lines are routed from the bot-
tom of both sides of the tank to the right frame rail
(fig. 20).
Maintenance
CAUTION: Always drain gasoline from the
complete fuel system including carburetor, fuel
pump and all fuel lines and fuel tank if the vehi-
cle is to be stored for any great length of time.
This precaution will prevent accumulation~ol
gum formation and resultant poor engine
performance.
. The fuel lines should occasionally be inspected for
leaks,
kinks or dents, especially when work has been
done on the underside of car or after the car has been
traveling over rough or stone roads at higher speeds.
If evidence of dirt is found in the carburetor or fuel pump
at disassembly, the lines should be disconnected and
blown put. Check the fuel tank strainer for damage or
omission.
Fuel lines are beaded-type ends for connection to
hoses and flared ends for secure metal-to-metal line
connections.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 474 of 659

STEERING 9-34
Fig.
64-Over Center Adjustment
transmission fluid "Type A" bearing the mark
"AQ-ATF" followed by a number and the suffix
letter "A".
ADJUSTMENTS
POWER STEERING GEAR
Chevrolet, Chevelle, and Camaro
The over-center adjustment (fig. 64) is the only power
steering gear adjustment which can be made on the car.
However, in order to make this adjustment, it is also
necessary to check the combined ball and thrust bearing
preload.
If the vehicle is equipped with a tilt column it will be
necessary to disconnect the steering coupling to obtain a
torque reading of the column. This torque should then be
subtracted from any reading taken on the gear.
1.
Disconnect the pitman arm from the relay rod.
2.
Loosen the pitman shaft adjusting screw loeknut and
thread the adjusting screw out to the limit of its
travel through the side cover. '. •
3.
Disconnect steering column harness at chassis wir-
ing connector plug.
4.
Remove horn button.
5.
Turn the steering wheel through its full travel, then
locate the wheel at its center of travel.
6. Gheck the combined ball and thrust bearing preload
with an inch-pound torque wrench on the steering
shaft nut by rotating through the center of travel
(approximately 1/4 turn in each direction). Note the
highest reading.
7.
Tighten the pitman shaft adjusting screw and check
torque at steering shaft nut until over center preload
and total steering gear preload falls within speci-
fications. Refer to torque specifications at rear of
manual for correct torque values.
8. Install horn button. Connect steering column harness
at wiring connector plug.
Chevy II and Corvette
The steering gear used with power steering is adjusted
in the same manner as the manual steering gear.
PUMP BELT TENSION
1.
Loosen nut on pivot bolt and pump brace adjusting
nut.
CAUTION: Do not move pump by prying against
reservoir or by pulling on filler neck.
2.
Move pump, with belt in place until belt is tensioned
to specifications as indicated by Tool J-7316 (Fig-.
65).
3.
Tighten pump brace adjusting nut. Then tighten pivot
bolt nut.
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM CHECKS
The following procedure outlines methods to identify
and isolate power steering hydraulic circuit difficulties.
This test is divided into two parts. Test number one
provides means of determining whether power steering
system hydraulic parts are actually faulty. If test number
one results in readings indicating faulty hydraulic opera-
tion, test number two will identify the faulty part. Be-
fore performing hydraulic circuit test, carefully check
belt tension and condition of driving pulley. Strand
tension of belt should be 125 lbs. on new belts and 75 lbs.
on old belts, as indicated by Tool J-7316 (Fig. 65).
Test Number One—Oil Circuit Open
Engine must be at normal operating temperature. In-
flate front, tires to correct pressure. All tests are made
with engine idling, so adjust engine idle speed to correct
specifications listed in Section 6 and proceed as follows:
a. With engine not running, disconnect flexible pres-
sure line from pump and install Tool J-5176 as
Fig.
65— Checking Belt Tension with Tool J-7316
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 483 of 659

WHEELS AND TIRES 10-3
Fig.
3 - Spof Wear
to cautioning the owner of his driving habits, is to inter-
change tires regularly.
Side
This may be caused by incorrect wheel camber, under-
inflation, high cambered roads or taking corners at too
high a rate of speed.
The first two causes are the most common. Camber
wear can be readily identified because it occurs only on
one side of the treads, whereas underinflation causes
wear on both sides (fig. 2).
There is, of course, no correction for high cambered
roads.
Cornering wear is discussed further on.
Center
This is caused primarily by overinflation pf the tire
(fig. 2). Invisible fabric damage can also be caused by
overinflation.
Uneven
Uneven or spotty wear (fig. 3) is due to such irregu-
larities as unequal caster or camber, bent front or rear
suspension parts, out-of-balance wheels, brake drums
Fig.
4 - Cornering Wear
out-of-round, brakes out-of-adjustment, or other me-
chanical conditions. The remedy in each case consists
of locating the mechanical defect and correcting it.
Cornering
Since the introduction of independent spring front and
rear wheels, improvements in spring suspension have
enabled drivers to negotiate curves at higher rates of
speed with the same feeling of security that they had
with the older cars at lower speeds. Consequently,
curves are being taken at higher speeds with the result
that a type of tire wear called "Cornering Wear" (fig. 4),
frequently appears.
When a car makes an extremely fast turn, the weight
is shifted from a normal loading on all four wheels to an
abnormal load on the tires on the outside of the curve
and a very light load on the inside tires due to centrifugal
force. This unequal loading may have two unfavorable
results.
First, the rear tire on the inside of the curve may be
relieved of so much load that it is no longer geared to
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 484 of 659

WHEELS AND TIRES 10-4
the road and it slips, grinding off the tread on the inside
half of the tire at an excessive rate. This type of tire
shows much the same appearance of tread wear as tire
wear caused by negative camber.
Second, the transfer of weight may also over-load the
outside tires so much that they are laterally distorted
resulting in excessive wear on the outside half of the
tire producing a type of wear like that caused by ex-
cessive positive camber.
Cornering wear can be most easily distinguished from
abnormal camber wear by the rounding of the outside
shoulder or edge of the tire and by the roughening of the
tread surface which denotes abrasion.
Cornering wear often produces a fin or raised portion
along the inside edge of each row in the tread pattern.
In some cases this fin is almost as pronounced as a
toe-in fin, and in others, it tapers into a row of tread
blocks to such an extent that the tire has a definite step
wear appearance.
The only remedy for cornering wear is proper in-
struction of owners.
Fig.
5 - Tire Rotatidh
Rotation
To minimize the possibility of tire noise and to equal-
ize tire wear, it is recommended that tires be inter-
changed every 6000 miles as shown in Figure 5 or more
frequently in the case of extremely heavy wear.
NOTE:
Rotate Corvette tires at 4000 miles or
sooner.
Interchanging tires will effectively prevent undue wear
on any particular tire. II tire interchanging is followed
as recommended above, all tires will have the same
number of miles in each wheel position at the end of the
fourth change. When interchanging tires, inspect for
signs of abnormal wear, bulging, etc., stones, glass, and
nails should be removed before reinstallation.
Noise
Noise caused by the normal action of tire treads on
various road surfaces is often confused with rear axle
gears or other noises in the car.
The determination of whether tires are causing the
noise complained of is relatively simple. The car should
be driven at various speeds and note taken of part
throttle, and sudden acceleration and deceleration. Axle
and exhaust noises show definite variations under these
conditions, while tire noise will remain constant. Tire
noise is, however, most pronounced at speeds of approx-
imately twenty or thirty miles per hour.
The tires may be further checked by driving the ear
over smooth pavement with the tires at normal pressure
and again over the same stretch of pavement when the
tires have been inflated to fifty pounds pressure. Reduce
the tires to normal pressure one at a time to determine
the faulty tire or tires. This high inflation pressure
should immediately be reduced to normal after test. If
the noise for which the test is being made is caused by
tires,.
it will noticeably decrease when the tire pressure
is increased, whereas axle noise should show no change
in volume.
If, on inspection, the tires on the front wheels are
found to be creating most of the noise the alignment of
the front wheels should be checked. Excessive tire noise
usually results from lower than recommended tire pres-
sure, incorrect alignment, uneven tire wear, or defective
(thumper) tire.
Cleaning
A great deal of ordinary road dirt which collects on
white sidewall tires may be sponged off with clear water
or a mild soap solution.
A good brand of whitewall tire cleaner, however, is
a quicker and more effective cleaner for removing dirt
and stains from whitewall tires and in many cases it
will remove stains and discoloration that the simpler
method of soap and water will not remove.
Under no circumstances should gasoline, kerosene or
any cleaning fluid containing a solvent derived from oil
be used to clean whitewall tires. Oil in any form is
detrimental to tire rubber and a cleaner with an oil base
will discolor or injure whitewall tires.
Change (W/Wheels)
To change the road wheels using the jack that comes
with the car, observe the following procedure:
1.
Set hand brake and block front wheels if rear wheel
is being changed.
2.
Remove hub cap or wheel disc and break wheel
mounting nuts loose.
3.
Place the jack as directed tinder, General Informa-
tion,
Section 0 and raise car until wheel clears
ground.
4.
Remove wheel mounting nuts and remove wheel from
hub or drum.
5. To replace road wheel, reverse the above instrue-
. tions. Proper torque on nuts is 55-75 ft. lbs.
torque (70-85 ft. lbs. for Corvette aluminum wheel
nuts).
CAUTION: On models equipped with discs, in-
dex the pilot hole in the disc on the valve stem.
(To insure that the anti-rotation notches in wheel
disc register on lugs in wheel rim.)
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 486 of 659

WHEELS AND TIRES
10-6
lifted on the rim to force the top tire bead
against the top rim flange. The weight of the
tire will seat the bottom bead.
Repair
When a tire loses all or most of its air pressure,
particularly when driving at high legal speeds on today1 s
super-highways, recommended procedure is to remove it
from the wheel for complete inspection to be sure no
tire damage has occurred. Punctured tires should be
removed from the wheel and permanently repaired from
the inside.
Externally applied plug type repairs should be con-?
sidered temporary and the tire should be permanently
repaired as soon as possible.
Hot Patch Method
It is essential to thoroughly clean and remove all
foreign matter from the hole left by the puncturing-object
without enlarging the injury and then follow the manu-
facturer's instructions for vulcanizing the patch.
Rubber Plug Methods
There are several types of rubber plugs--some are
inserted from the inside of the tire; others are inserted
from the outside of the tire without demounting the tire
from the rim.
When using the plug method be sure to clean and
lubricate the hole with repair cement before inserting
the plug. Your tire supplier has available complete kits
containing materials, tools and detailed instructions for
making repairs with plugs. Follow instructions in the kit
you use.
Cold Patch Method
(Self Vulcanizing Type)
In this method it is essential to thoroughly clean and
remove all foreign matter from the hole left by the
puncturing object without enlarging the injury; also on
the inside of the tire, buff an area large enough for the
patch. Follow the manufacturer1 s instructions for appli-
cation of the special cement and self-vulcanizing cold
patch.
Pressure Gun Method
Several types of pressure guns are available. Consult
your tire supplier for materials and instructions.
Tire Installation Safety Precautions
When tires are mounted on dirty or corroded rims, or
when they are not properly centered on rims, the tire
bead may "bind" on the rim, and refuse to seat. Allowing
pressure to continue to build up within the assembly in
an attempt to seat the tire bead is a DANGEROUS PRAC-
TICE which can result in a broken tire bead, and serious
injury to the serviceman.
1.
Make sure that rim flanges and bead ledge (espe-
cially hump and radius) areas are smooth and clean.
Remove any oxidized rubber, dried soap solution,
rust, heavy paint, etc. with a wire brush, or, in ex-
treme cases, a file.
2.
Lubricate tire beads, rim flanges, and bead ledge
areas with a liberal amount of thin vegetable oil
soap solution, or approved rubber lubricant,
3.
Insure that air pressure build-up during the bead
seating process is not allowed to exceed 40 pounds
pressure. If beads have not seated by the time pres-
sure reaches 40 pounds, assembly should be deflated,
re-positioned on rim, re-lubricated and re-inflated.
4.
Make sure valve core is inserted in valve stem
prior to inflating.
5.
Use an extension gauge with clip on chuck so air
pressure build-up can be closely watched and so
that you can stand well back from the assembly
during the bead seating process.
WHEELS
Valve Assembly
Replace
NOTE: Always use new valve assembly when
replacing.
1.
Cut or drive old valve assembly out of rim.
2.
Clean valve hole and surrounding area on inside of
flange with steel wool.
Fig. 6 - Installing Valve
Fig. 7 - Rim Inspection
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 515 of 659
ELECTRICAL-BODY AND CHASSIS 12-3
Fig.
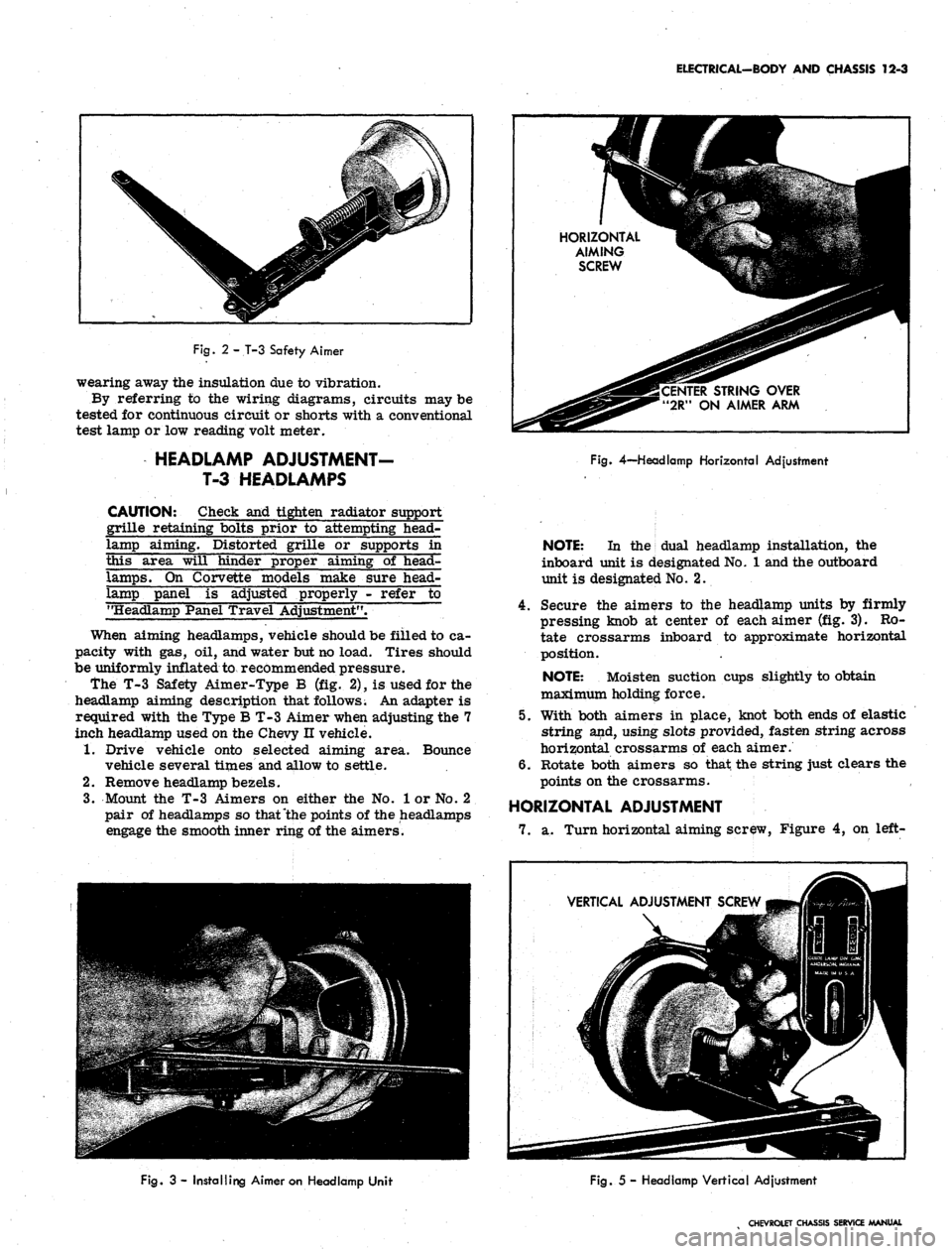
2 - T-3 Safety Aimer
wearing away the insulation due to vibration.
By referring to the wiring diagrams, circuits may be
tested for continuous circuit or shorts with a conventional
test lamp or low reading volt meter.
HEADLAMP ADJUSTMENT-
T-3 HEADLAMPS
CAUTION: Check and tighten radiator support
grille retaining bolts prior to attempting head-
lamp aiming. Distorted grille or supports in
this area will hinder proper aiming of head-
lamps. On Corvette models make sure head-
lamp panel is adjusted properly - refer to
"Headlamp Panel Travel Adjustment".
When aiming headlamps, vehicle should be filled to ca-
pacity with gas, oil, and water but no load. Tires should
be uniformly inflated to recommended pressure.
the T-3 Safety Aimer-Type B (fig. 2), is used for the
headlamp aiming description that follows. An adapter is
required with the Type B T-3 Aimer when adjusting the 7
inch headlamp used on the Chevy n vehicle.
1.
Drive vehicle onto selected aiming area. Bounce
vehicle several times and allow to settle.
2.
Remove headlamp bezels.
3.
Mount the T-3 Aimers on either the No. 1 or No. 2
pair of headlamps so that "the points of the headlamps
engage the smooth inner ring of the aimers.
HORIZONTAL
AIMING
SCREW
STRING OVER
"2R" ON AIMER ARM
Fig.
4—-Headlamp Horizontal Adjustment
NOTE:
In the dual headlamp installation, the
inboard unit is designated No. 1 and the outboard
unit is designated No. 2.
4.
Secure the aimers to the headlamp units by firmly
pressing knob at center of each aimer (fig. 3). Ro-
tate crossarms inboard to approximate horizontal
position.
NOTE:
Moisten suction cups slightly to obtain
maximum holding force.
5. With both aimers in place, knot both ends of elastic
string and, using slots provided, fasten string across
horizontal crossarms of each aimer.
6. Rotate both aimers so that the string just clears the
points on the crossarms.
HORIZONTAL ADJUSTMENT
7. a. Turn horizontal aiming screw, Figure 4, on left-
VERTICAL ADJUSTMENT SCREW
Fig.
3 - Installing Aimer on Headlamp Unit
Fig.
5 - Headlamp Vertical Adjustment
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL