sensor CHEVROLET CAMARO 1982 Repair Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1982, Model line: CAMARO, Model: CHEVROLET CAMARO 1982Pages: 875, PDF Size: 88.64 MB
Page 581 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 581
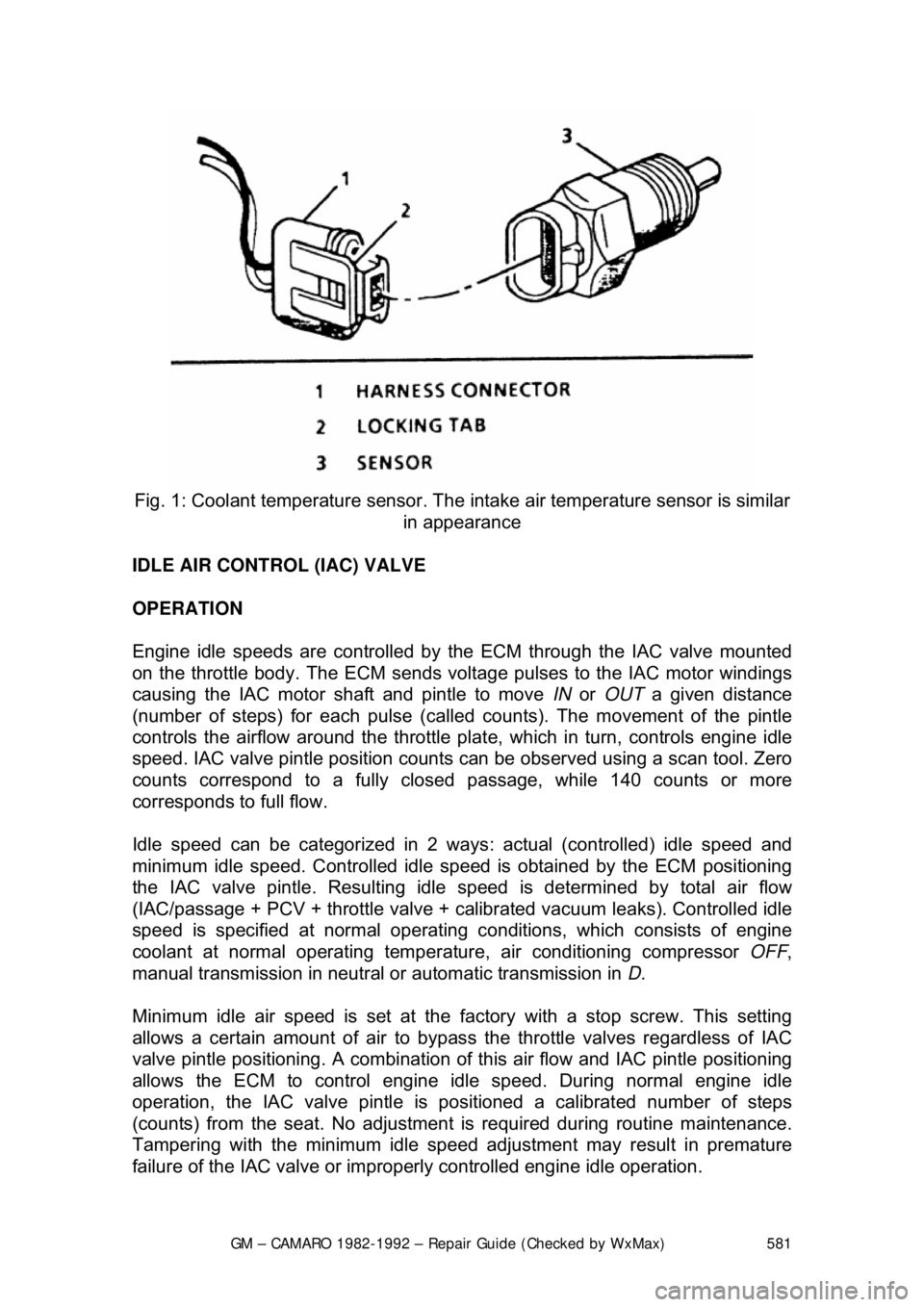
Fig. 1: Coolant temperature sensor. The in take air temperature sensor is similar
in appearance
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) VALVE
OPERATION
Engine idle speeds are controlled by the ECM through the IAC valve mounted
on the throttle body. The ECM sends volt age pulses to the IAC motor windings
causing the IAC motor shaft and pintle to move IN or OUT a given distance
(number of steps) for each pulse (called counts). The movement of the pintle
controls the airflow around the throttle plat e, which in turn, controls engine idle
speed. IAC valve pintle position counts ca n be observed using a scan tool. Zero
counts correspond to a fully closed passage, while 140 counts or more
corresponds to full flow.
Idle speed can be categorized in 2 ways : actual (controlled) idle speed and
minimum idle speed. Contro lled idle speed is obtained by the ECM positioning
the IAC valve pintle. Resulting idle speed is determined by total air fl\
ow
(IAC/passage + PCV + throttle valve + ca librated vacuum leaks). Controlled idle
speed is specified at normal operating c onditions, which consists of engine
coolant at normal operating temper ature, air conditioning compressor OFF,
manual transmission in neutral or automatic transmission in D.
Minimum idle air speed is set at t he factory with a stop screw. This setting
allows a certain amount of air to bypas s the throttle valves regardless of IAC
valve pintle positioning. A co mbination of this air flow and IAC pintle positioning
allows the ECM to control engine idle speed. During normal engine idle
operation, the IAC valve pintle is positioned a calibrated number of steps
(counts) from the seat. No adjustment is required during routine maintenance.
Tampering with the minimum idle speed adjustment may result in premature
failure of the IAC valve or imprope rly controlled engine idle operation.
Page 585 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 585
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR
OPERATION
The MAP sensor measures the changes in
intake manifold pressure, which
result from engine load/ speed changes and converts this information to a
voltage output. The MAP sensor reading is the opposite of a vacuum gauge
reading: when manifold pressu re is high, MAP sensor value is high and vacuum
is low. A MAP sensor will produce a low output on engine coast-down with a
closed throttle while a wide open throttle will produce a high output. The high
output is produced because the pressure inside the manifold is the same as
outside the manifold, so 100 percent of t he outside air pressure is measured.
The MAP sensor is also used to meas ure barometric pressure under certain
conditions, which allows the ECM to autom atically adjust for different altitudes.
The MAP sensor changes the 5 volt signal supplied by the ECM, which reads
the change and uses the information to cont rol fuel delivery and ignition timing.
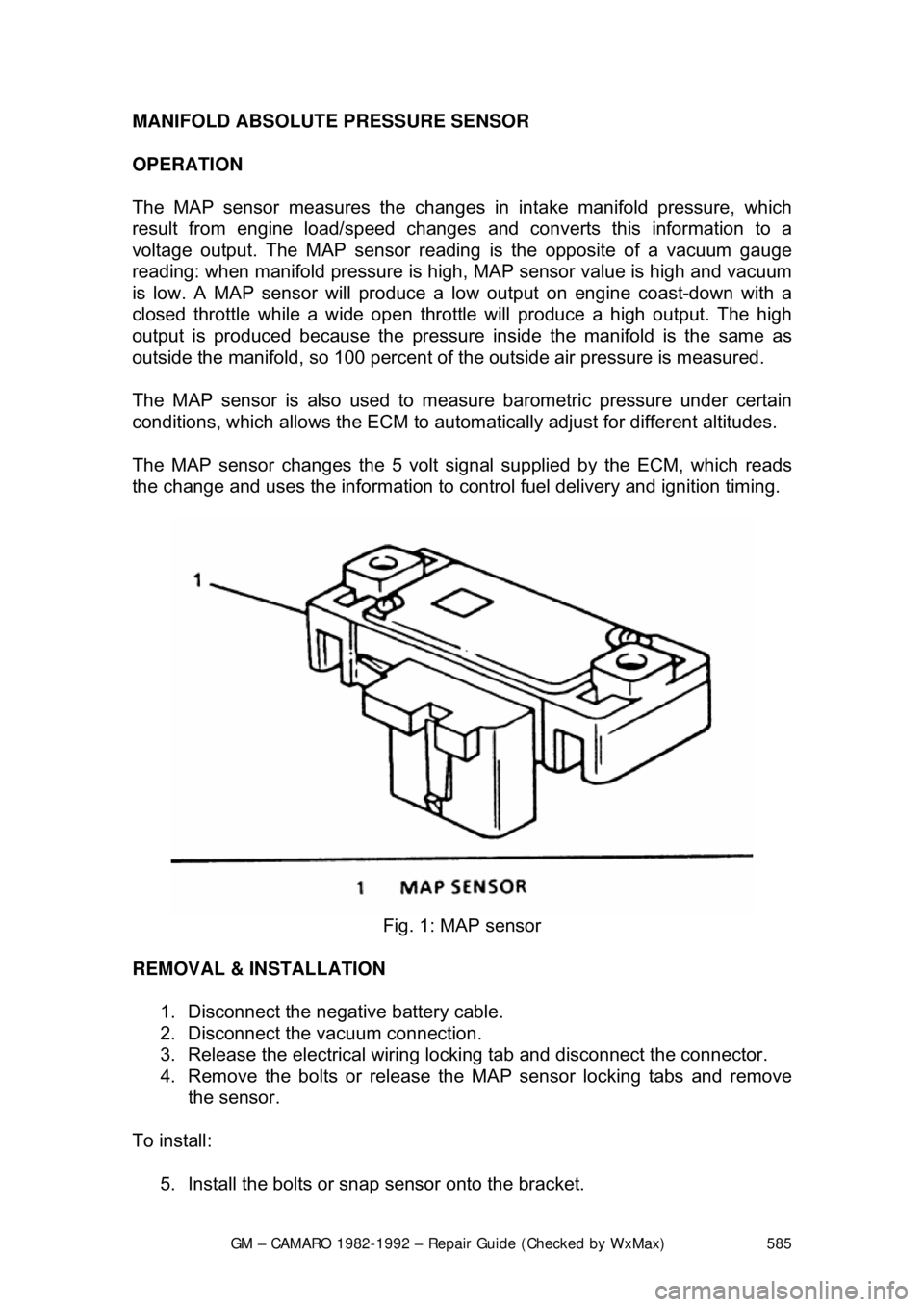
Fig. 1: MAP sensor
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the vacuum connection.
3. Release the electrical wiring lo cking tab and disconnect the connector.
4. Remove the bolts or release the MAP sensor locking tabs and remove
the sensor.
To install: 5. Install the bolts or snap sensor onto the bracket.
Page 586 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 586
6. Connect the MAP sensor
electrical wiring.
7. Connect the MAP sensor vacuum harness connector.
8. Connect the negative battery cable.
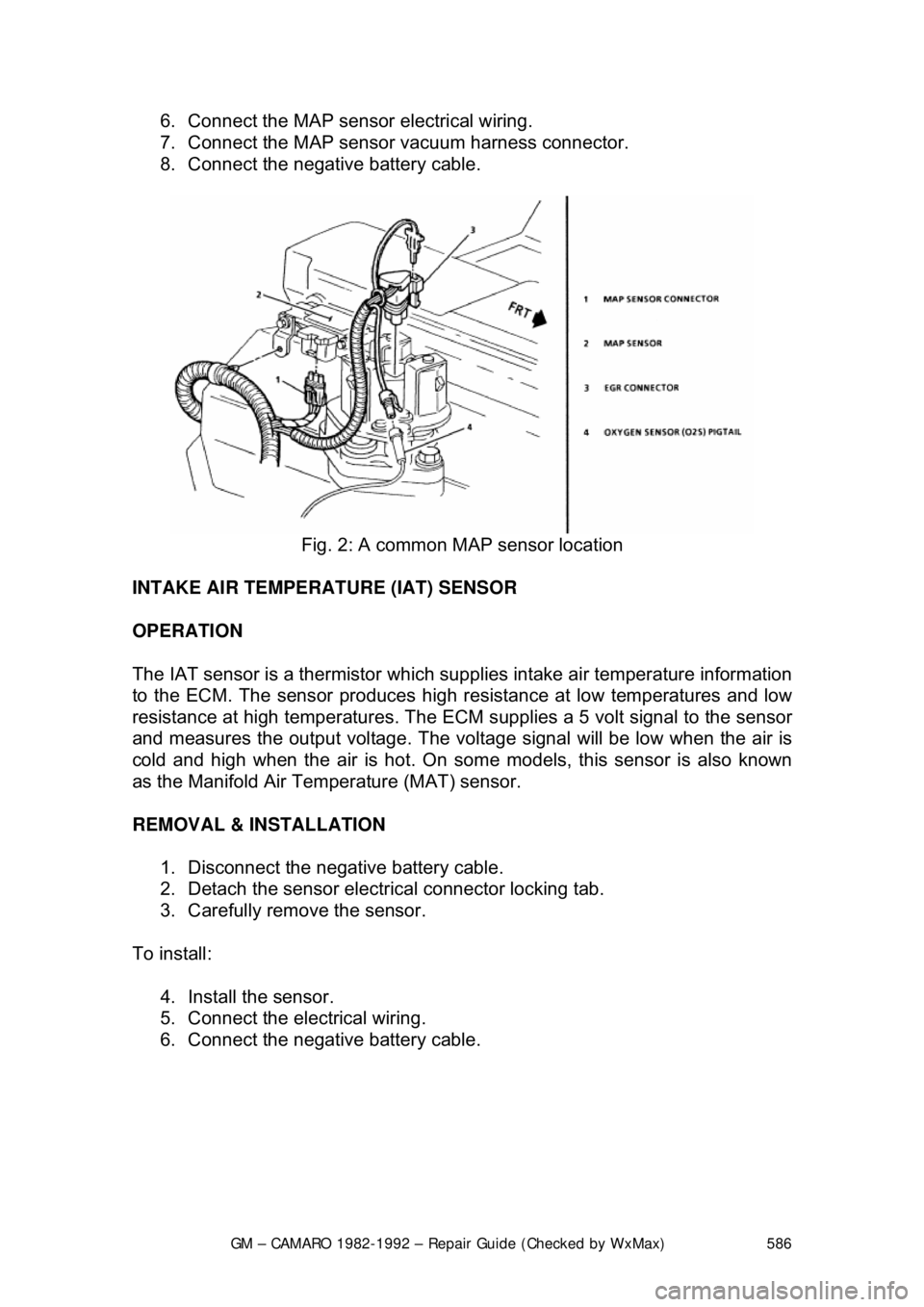
Fig. 2: A common MAP sensor location
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE (IAT) SENSOR
OPERATION
The IAT sensor is a thermistor which su pplies intake air temperature information
to the ECM. The sensor produces high re sistance at low temperatures and low
resistance at high temperatures. The ECM supplies a 5 volt signal to the sensor
and measures the output voltage. The vo ltage signal will be low when the air is
cold and high when the air is hot. On so me models, this sensor is also known
as the Manifold Air Tem perature (MAT) sensor.
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Detach the sensor electr ical connector locking tab.
3. Carefully remove the sensor.
To install: 4. Install the sensor.
5. Connect the electrical wiring.
6. Connect the negative battery cable.
Page 587 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 587
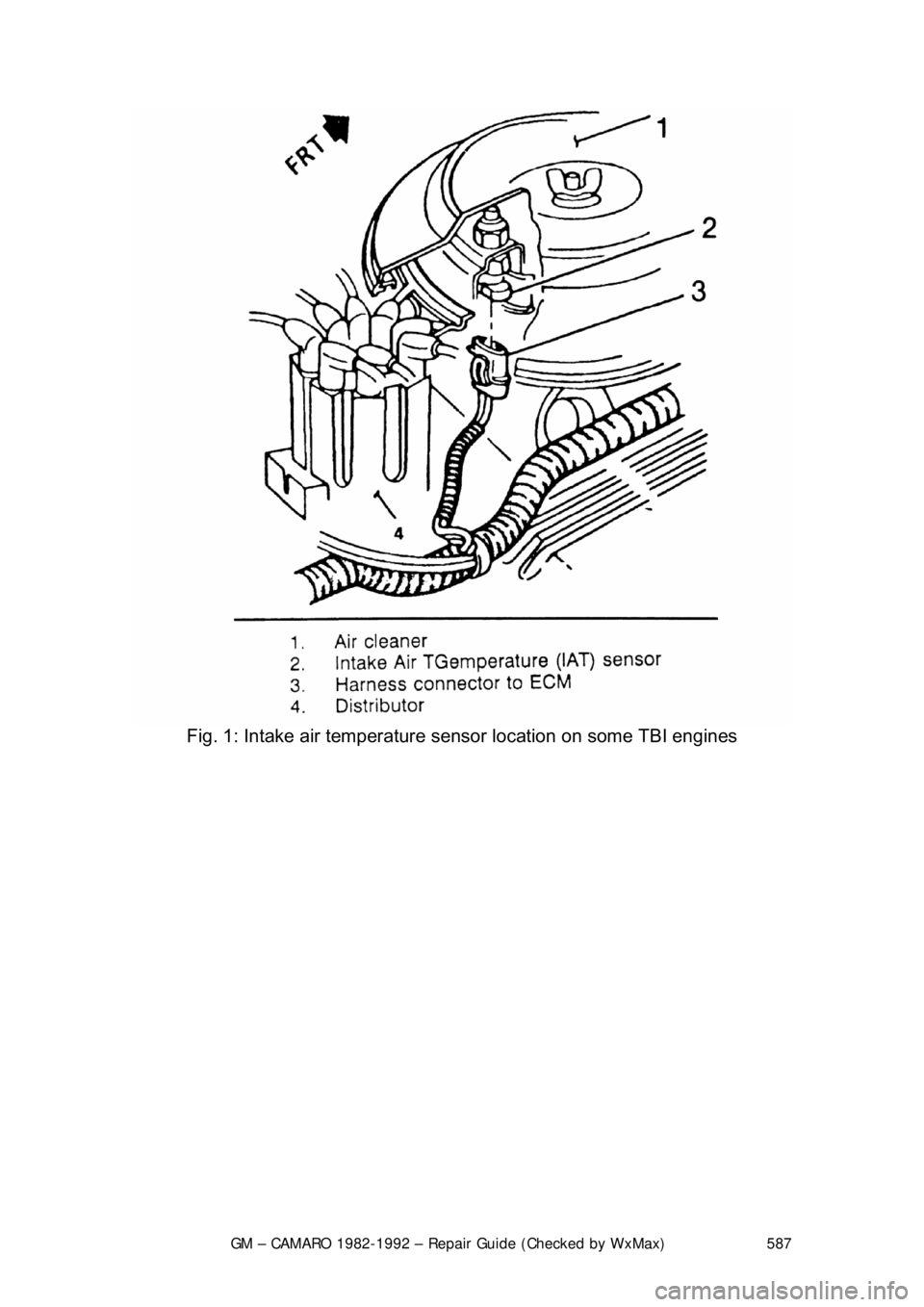
Fig. 1: Intake air te mperature sensor location on some TBI engines
Page 588 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 588
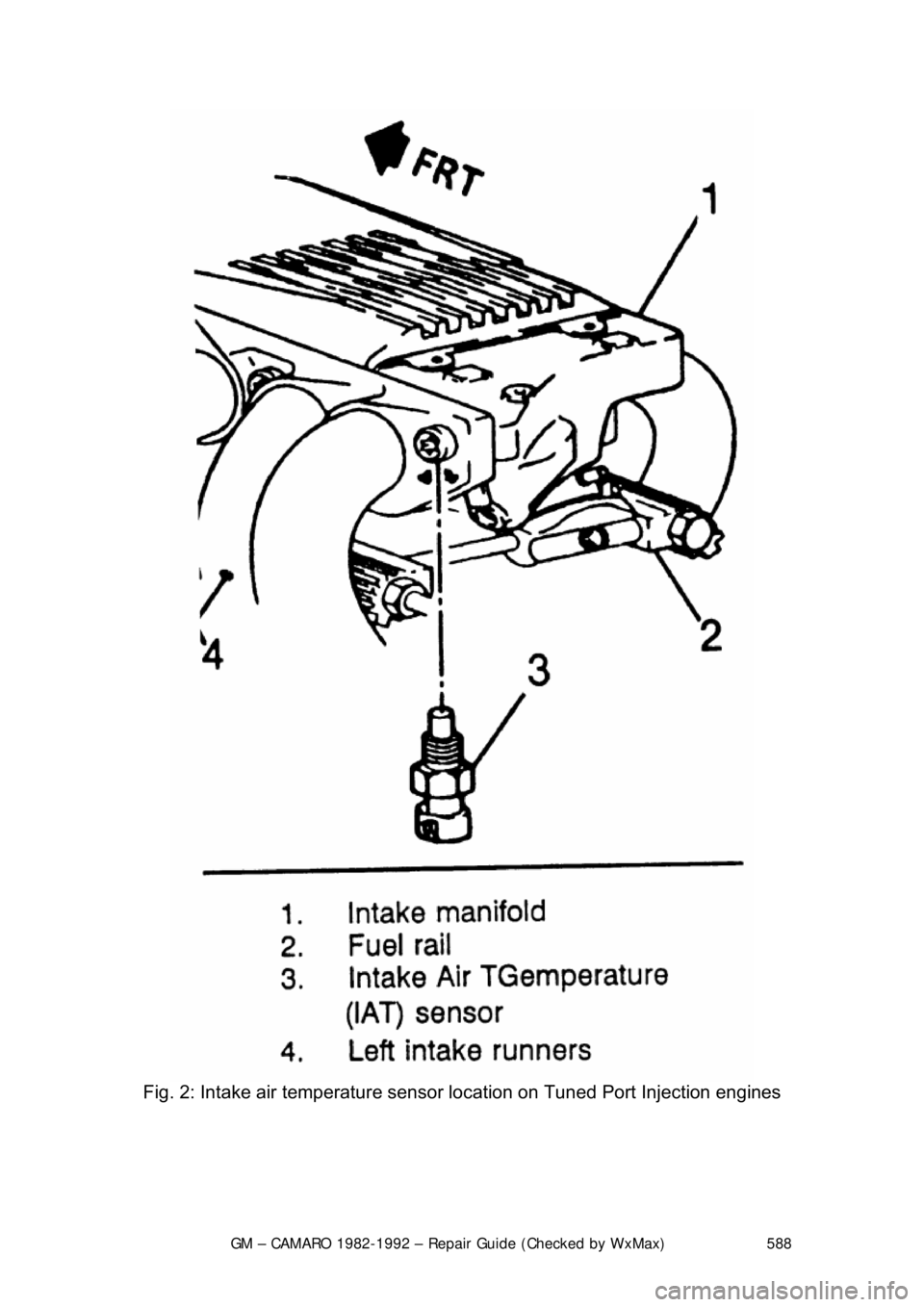
Fig. 2: Intake air temperature sensor location on Tuned Port Injection engines
Page 589 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 589
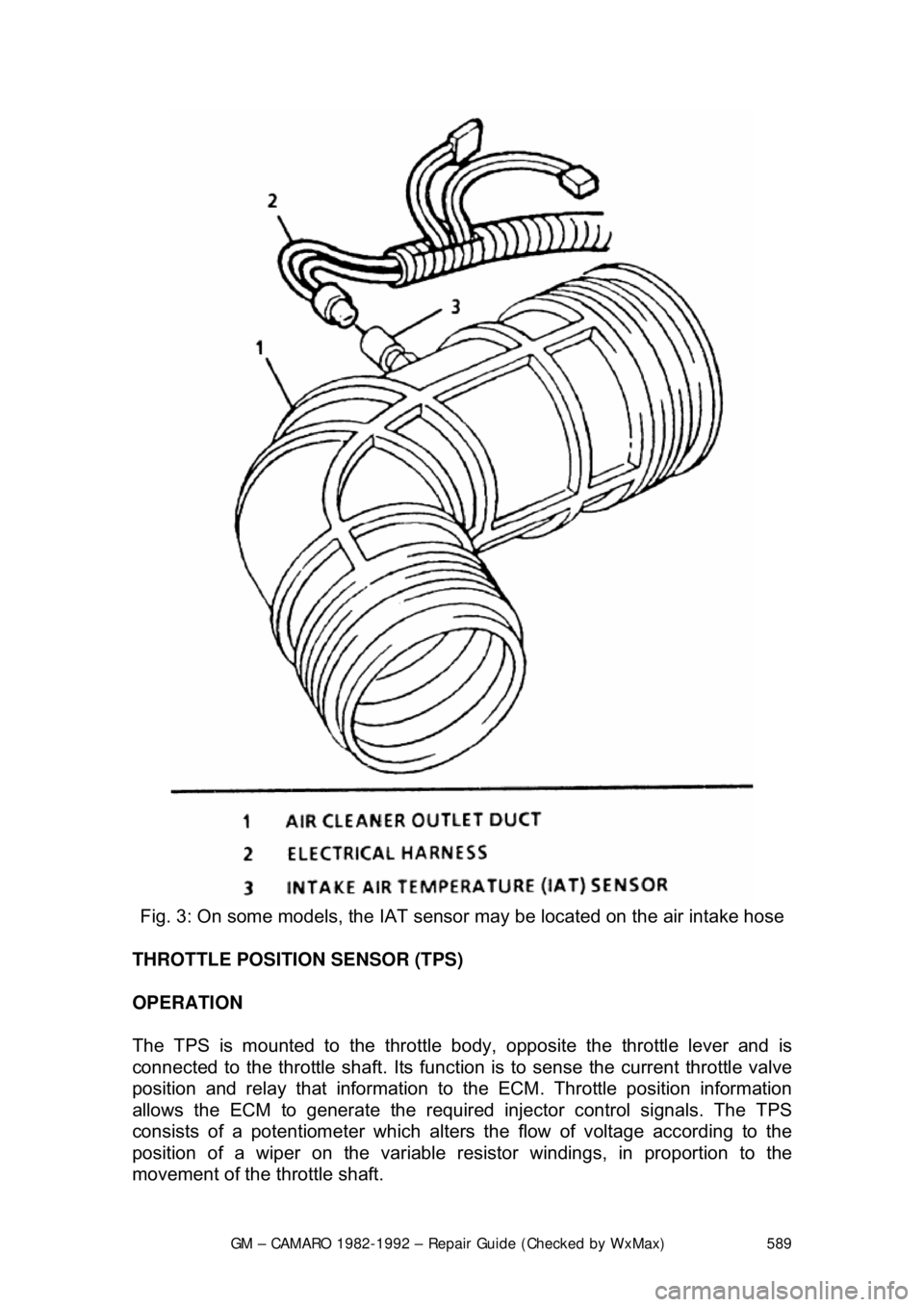
Fig. 3: On some models, the IAT sens or may be located on the air intake hose
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS)
OPERATION
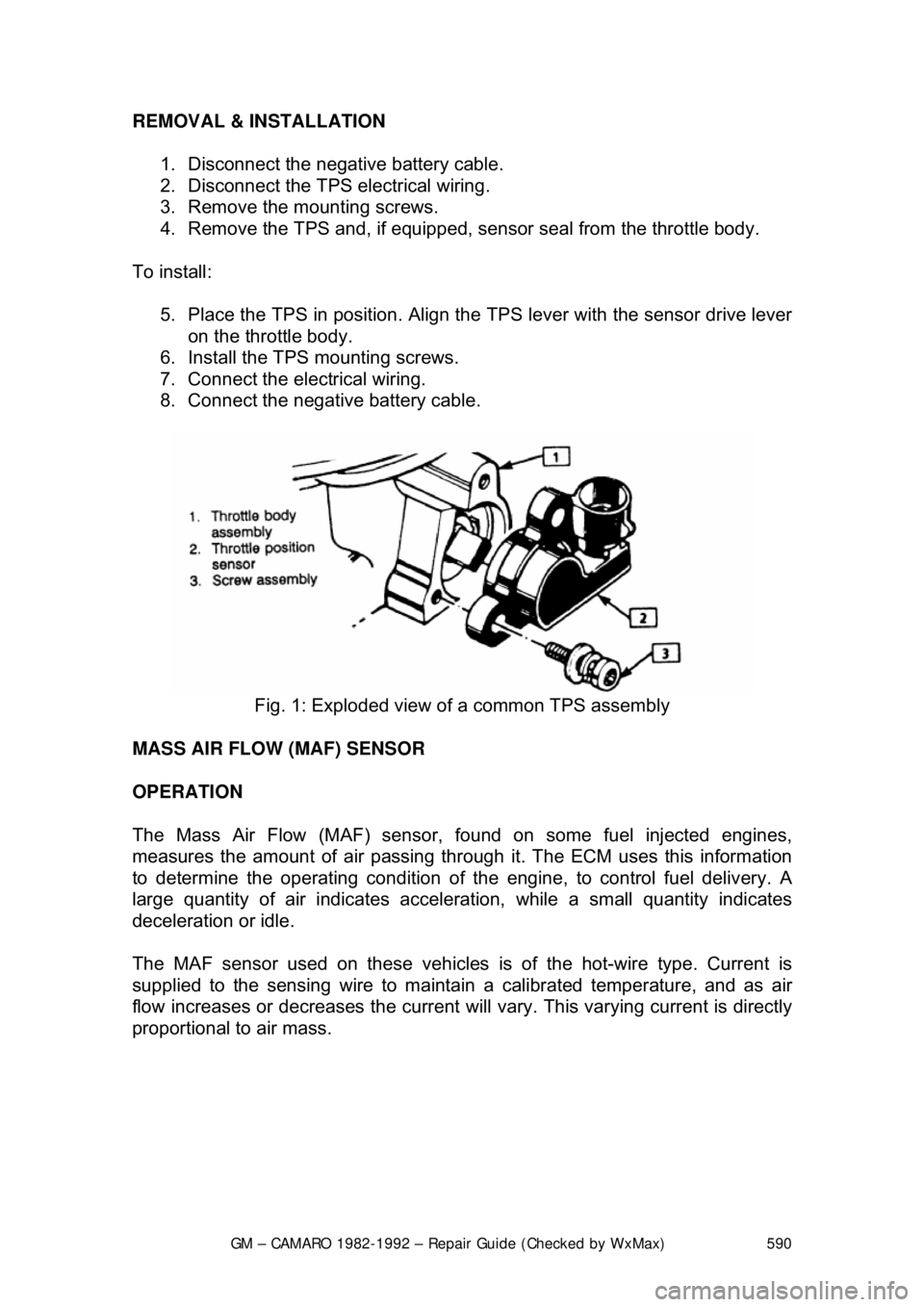
The TPS is mounted to the throttle body, opposite the throttle lever and is
connected to the throttle shaft. Its functi on is to sense the current throttle valve
position and relay that information to the ECM. Throttle position information
allows the ECM to generate the required injector control signals. The TPS
consists of a potentiometer which alters the flow of voltage according to the
position of a wiper on the variable resi stor windings, in proportion to the
movement of the throttle shaft.
Page 590 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 590
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the TPS electrical wiring.
3. Remove the mounting screws.
4. Remove the TPS and, if equipped, s ensor seal from the throttle body.
To install: 5. Place the TPS in positi on. Align the TPS lever with the sensor drive lever
on the throttle body.
6. Install the TPS mounting screws.
7. Connect the electrical wiring.
8. Connect the negative battery cable.
Fig. 1: Exploded view of a common TPS assembly
MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) SENSOR
OPERATION
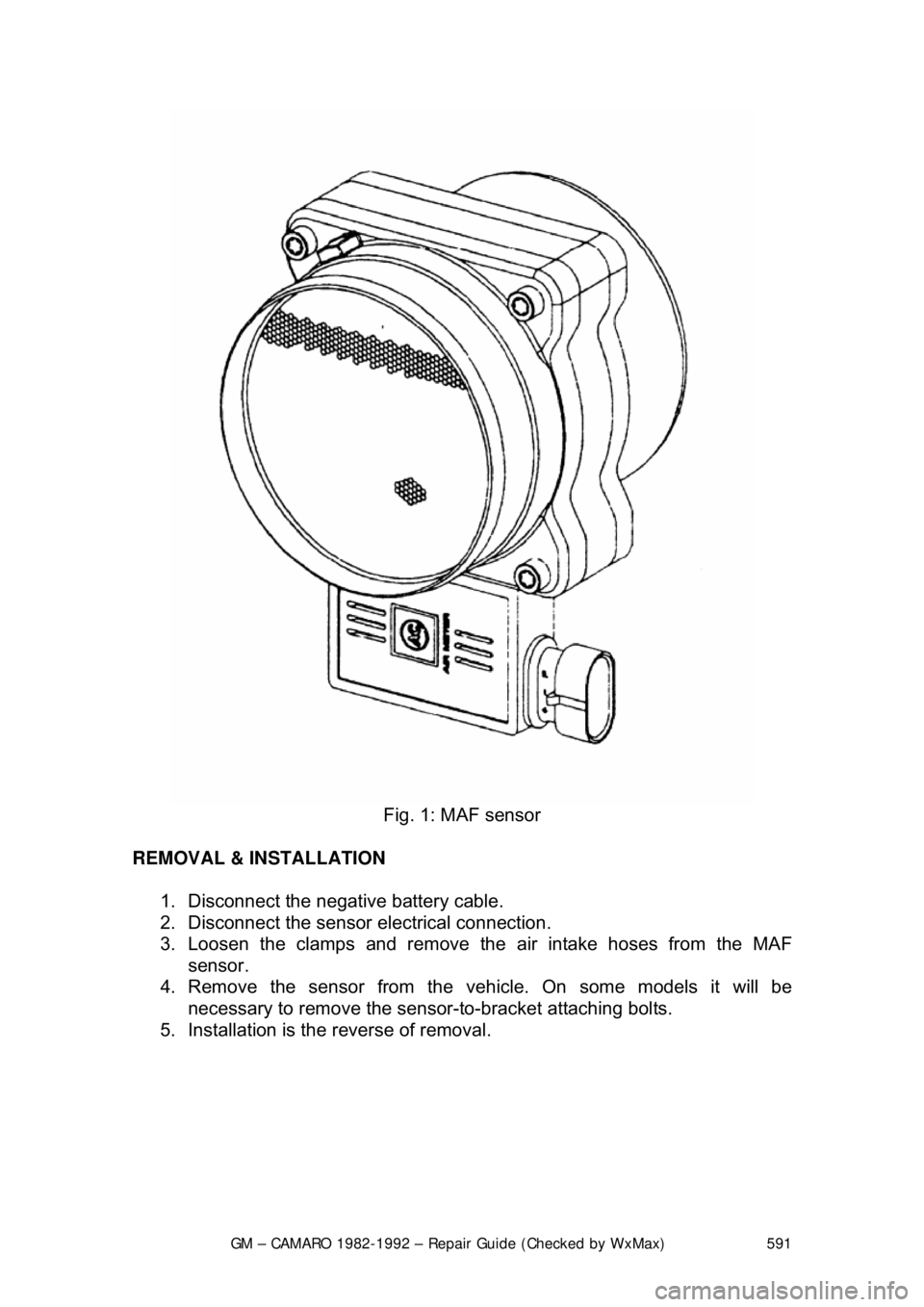
The Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor, found on some fuel injected engines,
measures the amount of air passing through it. The ECM uses this information
to determine the operating cond ition of the engine, to control fuel delivery. A
large quantity of air indicates acceleration, while a small quantity indicates
deceleration or idle.
The MAF sensor used on these vehicles is of the hot-wire type. Current is
supplied to the sensing wire to maintain a calibrated temperature, and as air
flow increases or decreases the current will vary. This varying current is directly
proportional to air mass.
Page 591 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 591
Fig. 1: MAF sensor
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the sensor electrical connection.
3. Loosen the clamps and remove the air intake hoses from the MAF
sensor.
4. Remove the sensor from the v ehicle. On some models it will be
necessary to remove the senso r-to-bracket attaching bolts.
5. Installation is the reverse of removal.
Page 592 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 592
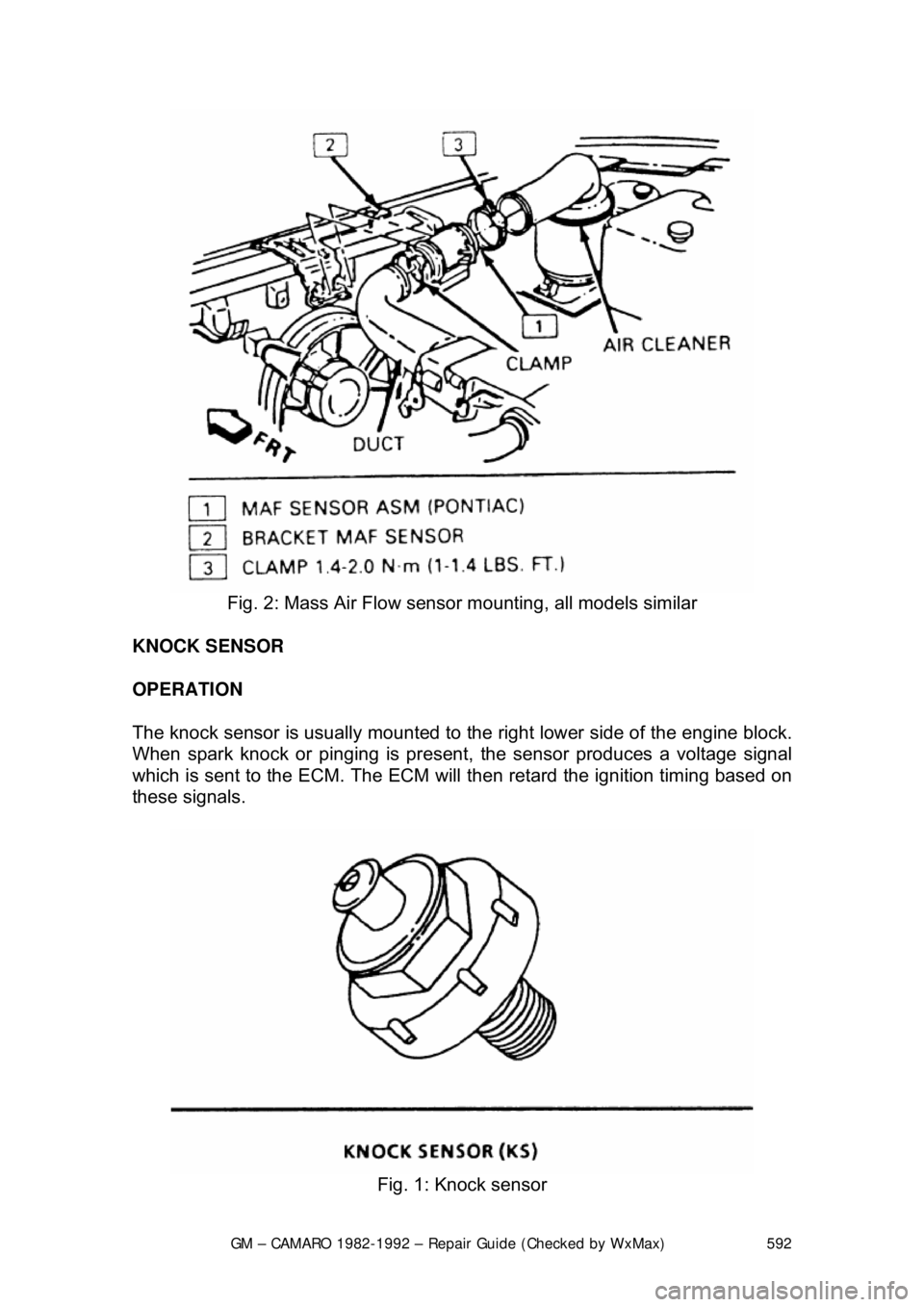
Fig. 2: Mass Air Flow sensor mounting, all models similar
KNOCK SENSOR
OPERATION
The knock sensor is usually mounted to the right lower side of the engine block.
When spark knock or pinging is present, the sensor produces a voltage signal
which is sent to the ECM. The ECM will then retard the ignition timing based on
these signals.
Fig. 1: Knock sensor
Page 593 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 593
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Drain the engine coolant.
3. Raise and properly support the vehicle.
4. Disconnect the knock sensor wiring harness.
5. Remove the knock sensor from the engine block.
CAUTION - The knock sensor is mounted in the engine block cooling passage.
Engine coolant in the block will dr ain when the sensor is removed.
6. Installation is the reverse of remova l. Tighten the sensor to 14 ft. lbs (19
Nm).
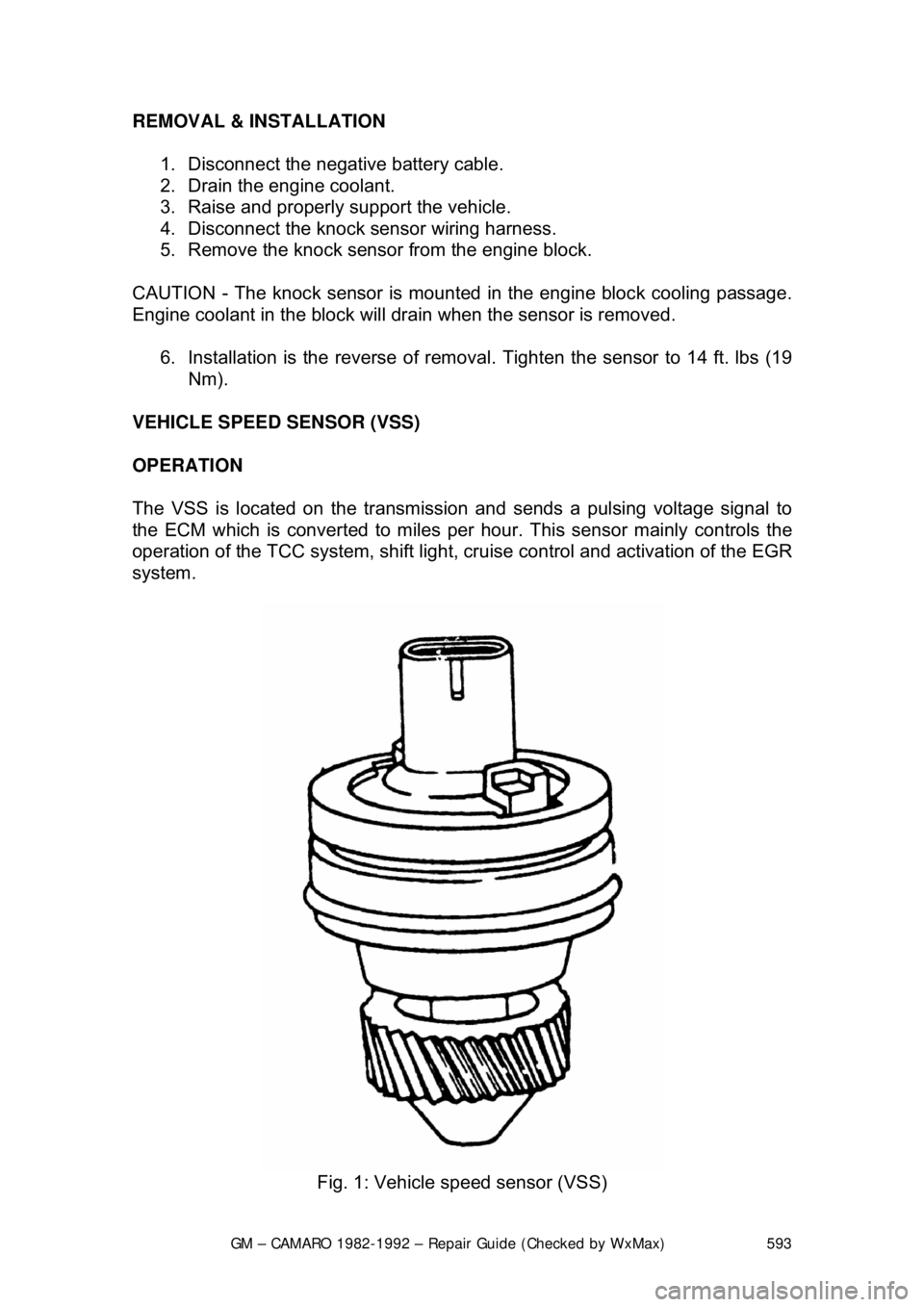
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR (VSS)
OPERATION
The VSS is located on the transmission and sends a pulsing voltage signal to
the ECM which is converted to miles per hour. This sensor mainly controls the
operation of the TCC system, shift light, cr uise control and activation of the EGR
system.
Fig. 1: Vehicle speed sensor (VSS)