light CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 154 of 2438

SERVICE ADJUSTMENTS INDEX
page page
Adjusting Rear Service Brakes ............... 4
Bleeding Brake System ..................... 6
Brake Hose and Tubing ................... 11
Master Cylinder Fluid Level .................. 4 Stop Lamp Switch Adjustment (All Vehicles)
.... 13
Test for Fluid Contamination ................. 7
Testing Application Adjuster Operation ......... 6
Wheel Stud Nut Tightening .................. 7
MASTER CYLINDER FLUID LEVEL
ALL EXCEPT AC/AY BODY WITH ABS
Check master cylinder reservoir brake fluid level a
minimum of twice a year. Master cylinder reservoirs are marked with the
words fill to bottom of rings indicating proper fluid
level (Fig. 1). If necessary, add fluid to bring the level to the bot-
tom of the primary reservoir split ring. Use only Mopar tbrake fluid or an equivalent from
a sealed container. Brake fluid must conform to DOT
3, specifications. DO NOT use brake fluid with a lower boiling
point, as brake failure could result during prolonged
hard braking. Use only brake fluid that was stored in a tightly-
sealed container. DO NOT use petroleum-based fluid because seal
damage in the brake system will result.
AC AND AY BODY WITH ANTI-LOCK BRAKES
The hydraulic assembly is equipped with a plastic
fluid reservoir with a filter/strainer in the filler neck
of the reservoir. The Anti-Lock brake system requires that the hy-
draulic accumulator be de-pressurized whenever
checking the brake fluid level. To check the brake
fluid level, the following procedure should be used: (1) With the ignition switch turned to the off position
and key removed. De-pressurize hydraulic accumula-
tor by applying brake pedal approximately 40 times,
using a pedal force of approximately 220 N (50 lbs.). A
noticeable change in pedal feel will occur when accu-
mulator is de-pressurized. Continue to apply brake
pedal several times after this change in pedal feel
occurs to insure that brake system is fully de-
pressurized. (2) Thoroughly clean both reservoir caps and sur-
rounding area of reservoir, (Fig. 2) before removing
caps. This is to avoid getting dirt into the reservoir and
contaminating the brake fluid. (3) Inspect the brake fluid to see if it is at the proper
level, see instructions on top of reservoir. (FILL TO
TOP OF WHITE SCREEN ON FRONT
FILTER/STRAINER.) (4) Fill reservoir with brake fluid to top of screen
(Fig. 3) on the filter/strainer located in brake fluid
reservoir. Only use brake fluid conforming to DOT 3
specifications such as Mopar tor equivalent.
(5) Replace brake fluid reservoir caps.
ADJUSTING REAR SERVICE BRAKES
Normally, self adjusting drum brakes will not
require manual brake shoe adjustment. Al-
though in the event of a brake reline it is advis-
able to make the initial adjustment manually to
speed up the adjusting time. (1) Raise the vehicle so all wheels are free to turn.
See Hoisting Recommendations in the Lubrication And
Maintenance Section, at the front of this service
manual. (2) Remove rear brake adjusting hole rubber plug
(Fig. 4), from the rear brake shoe support plate. (3) Be sure parking brake lever is fully re-
leased. Then back off parking brake cable adjust-
ment so there is slack in the cable. (4) Insert Brake Adjuster, Special Tool C-3784, (Fig.
5) or equivalent through the adjusting hole in support
plate and against star wheel of adjusting screw. Move
handle of tool upward until a slight drag is felt when
the road wheel is rotated. (5) Insert a thin screwdriver or piece of welding rod
into brake adjusting hole (Fig. 5). Push adjusting lever
out of engagement with star wheel. Care
Fig. 1 Master Cylinder Fluid Level (All Except AC/AY
Body W/ABS)
5 - 4 BRAKES Ä
Page 163 of 2438

(3) Position the tubing in the jaws of the Flaring
Tool so that it is flush with the top surface of the
flaring tool bar assembly. (See Fig. 17). (4) Install the correct size adaptor for the brake
tubing being flared, on the feed screw of the yoke as-
sembly. Center the yoke and adapter over the end of
the tubing. Apply lubricant to the adapter area that
contacts brake tubing. Making sure the adapter pilot
is fully inserted in the end of the brake tubing.
Screw in the feed screw of the yoke assembly until
the adaptor has seated squarely on the surface of the
bar assembly (Fig. 17). This process has created the
(metric) ISO tubing flare.STOP LAMP SWITCH ADJUSTMENT (ALL
VEHICLES)
The stop lamp switch incorporates a self adjusting
feature. If adjustment or replacement is required,
proceed as follows: Install the switch in the retaining
bracket and push the switch forward as far as it will
go. The brake pedal will move forward slightly (Fig.
18). Gently pull back on the brake pedal bringing the
striker back toward the switch until the brake pedal
will go back no further. This will cause the switch to
ratchet backward to the correct position. Very little
movement is required, and no further adjustment is
necessary.
Fig. 17 ISO Tubing Flare ProcessFig. 18 Stop Lamp Switch
BASIC DIAGNOSIS GUIDE
Ä BRAKES 5 - 13
Page 173 of 2438

WHEEL CYLINDERS INDEX
page page
General Information ....................... 23
Installing Wheel Cylinders .................. 24 Service Procedures
....................... 23
GENERAL INFORMATION
The piston boots are of the push-on type and pre-
vent moisture from entering the wheel cylinder. To perform service operations or inspections of the
rear wheel brake cylinders. It will be necessary to re-
move the cylinders from the support plate and disas-
semble on the bench.
CAUTION: Wheel cylinders with cup expanders
must have cup expanders after any service proce-
dures (reconditioning or replacement).
SERVICE PROCEDURES
REMOVING WHEEL CYLINDERS FROM BRAKE SUPPORT PLATES
With brake drums removed, inspect the wheel cyl-
inder boots for evidence of a brake fluid leak. Then
block the brake pedal in the stroke position, and vi-
sually check the boots for cuts, tears, or heat cracks.
If any of these conditions exist, the wheel cylinders
should be completely cleaned, inspected and new
parts installed. (A slight amount of fluid on the boot
may not be a leak, but may be preservative fluid
used at assembly.) (1) In case of a leak, remove brake shoes, (replace
if soaked with grease or brake fluid.) (2) Thoroughly clean area of wheel cylinder, where
hydraulic brake line connects to wheel cylinder. Dis-
connect hydraulic brake tube from wheel cylinder
(Fig. 1). (3) Remove the rear wheel cylinder attaching bolts
(Fig. 1). Then pull wheel cylinder assembly off the
brake support plate (Fig. 2). (4) Clean the surface sealant off the support plate
and wheel cylinder surfaces.
DISASSEMBLING WHEEL CYLINDERS
To disassemble the wheel cylinders, (Fig. 3) pro-
ceed as follows: (1) Pry boots away from cylinders and remove.
(2) Press INon one piston to force out opposite pis-
ton, cup and spring (with cup expanders). Then using
a soft tool such as a dowel rod, press out the cup and
piston that remain in the wheel cylinder. (3) Wash wheel cylinder, pistons, and spring in
clean brake fluid or alcohol; (DO NOT USE ANY
PETROLEUM BASE SOLVENTS) clean thor- oughly and blow dry with compressed air. Inspect
Fig. 1 Brake Tube Disconnected
Fig. 2 Remove or Install Wheel Cylinder
Ä
BRAKES 5 - 23
Page 174 of 2438
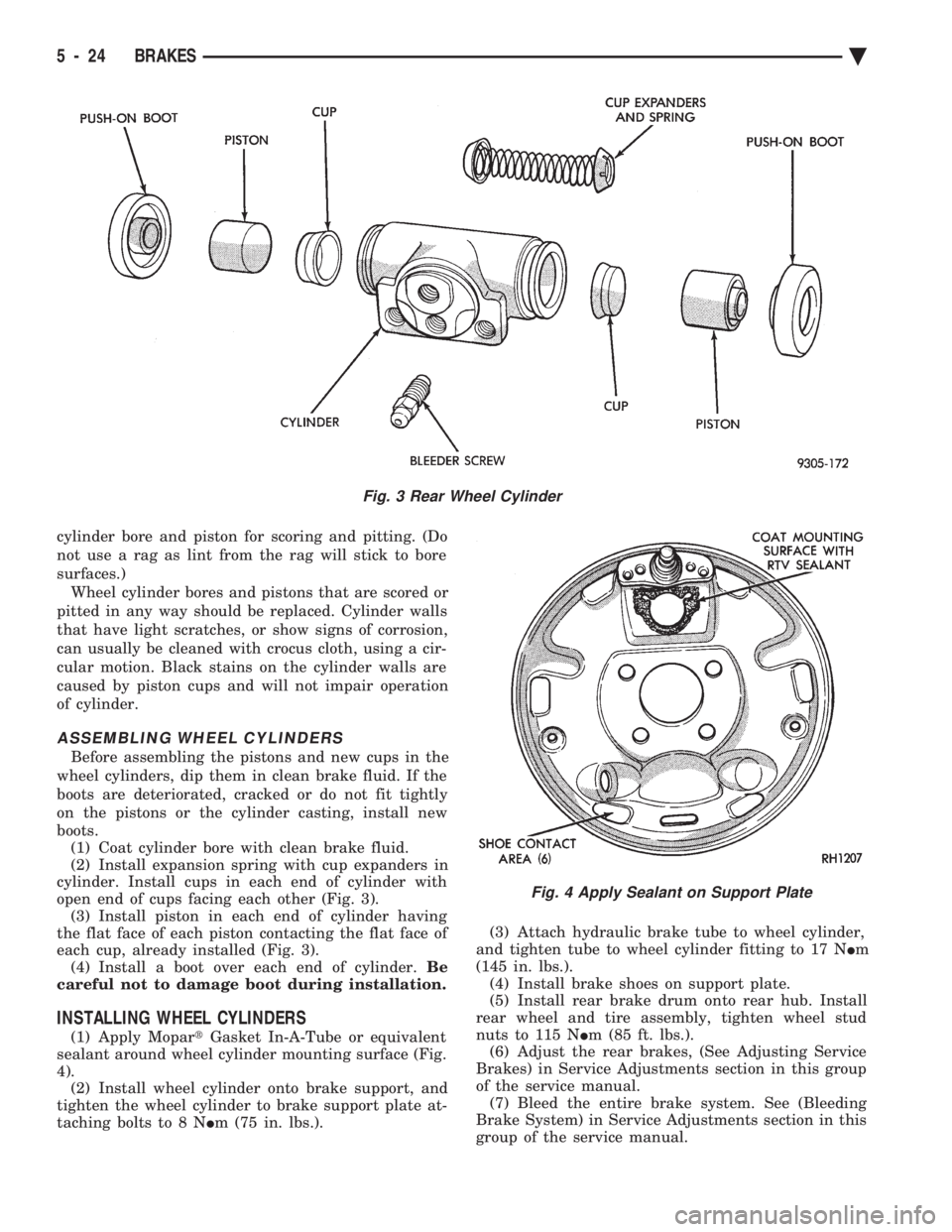
cylinder bore and piston for scoring and pitting. (Do
not use a rag as lint from the rag will stick to bore
surfaces.) Wheel cylinder bores and pistons that are scored or
pitted in any way should be replaced. Cylinder walls
that have light scratches, or show signs of corrosion,
can usually be cleaned with crocus cloth, using a cir-
cular motion. Black stains on the cylinder walls are
caused by piston cups and will not impair operation
of cylinder.
ASSEMBLING WHEEL CYLINDERS
Before assembling the pistons and new cups in the
wheel cylinders, dip them in clean brake fluid. If the
boots are deteriorated, cracked or do not fit tightly
on the pistons or the cylinder casting, install new
boots. (1) Coat cylinder bore with clean brake fluid.
(2) Install expansion spring with cup expanders in
cylinder. Install cups in each end of cylinder with
open end of cups facing each other (Fig. 3). (3) Install piston in each end of cylinder having
the flat face of each piston contacting the flat face of
each cup, already installed (Fig. 3). (4) Install a boot over each end of cylinder. Be
careful not to damage boot during installation.
INSTALLING WHEEL CYLINDERS
(1) Apply Mopar tGasket In-A-Tube or equivalent
sealant around wheel cylinder mounting surface (Fig.
4). (2) Install wheel cylinder onto brake support, and
tighten the wheel cylinder to brake support plate at-
taching bolts to 8 N Im (75 in. lbs.). (3) Attach hydraulic brake tube to wheel cylinder,
and tighten tube to wheel cylinder fitting to 17 N Im
(145 in. lbs.). (4) Install brake shoes on support plate.
(5) Install rear brake drum onto rear hub. Install
rear wheel and tire assembly, tighten wheel stud
nuts to 115 N Im (85 ft. lbs.).
(6) Adjust the rear brakes, (See Adjusting Service
Brakes) in Service Adjustments section in this group
of the service manual. (7) Bleed the entire brake system. See (Bleeding
Brake System) in Service Adjustments section in this
group of the service manual.
Fig. 3 Rear Wheel Cylinder
Fig. 4 Apply Sealant on Support Plate
5 - 24 BRAKES Ä
Page 176 of 2438

HYDRAULIC SYSTEM CONTROL VALVES INDEX
page page
ABS Brake Proportioning Valve Operation ...... 27
General Information ....................... 26
Hydraulic System Service Procedures ......... 27 Non-ABS Proportioning Unit Operation
........ 26
Pressure Differential Warning Light Switch ...... 26
Testing ABS Proportioning Valves ............ 29
GENERAL INFORMATION
Most models not equipped with an Anti-Lock brak-
ing system have a combination hydraulic system con-
trol valve in the brake hydraulic system (Fig. 1). The
valve is attached to the frame rail below the master
cylinder.
The control valve assembly combines a warning
switch with a dual proportioning valve (Fig. 2) Proportioning valves balance front to rear braking
by controlling at a given ratio, the increase in rear
system hydraulic pressure above a preset level. Un-
der light pedal application, the valve allows full hy-
draulic pressure to the rear brakes. There is only one valve assembly in each vehicle,
see Valve Application Chart. During any service pro-
cedures identify valve assemblies by part number as
well as split point (PSI) and slope.
PRESSURE DIFFERENTIAL WARNING LIGHT
SWITCH
The hydraulic brake system, on non-ABS vehicles,
is split diagonally. The left front and right rear
brakes are part of one system. And the right front and left rear are part of another. Both systems are
routed through, but hydraulically separated by a Pres-
sure Differential Switch. The function of the Pressure
Differential Switch is to alert the driver of a malfunc-
tion in the brake system. If hydraulic pressure is lost in one system, the
warning light switch will activate a red light on the
instrument panel, when the brake pedal is depressed.
At this point the brakes require service. However, since
the brake systems are split diagonally the vehicle will
retain 50% of its stopping capability in the event of a
failure in either half. The warning light switch is the latching type. It
will automatically center itself after the repair is
made and the brake pedal is depressed. The instrument panel bulb can be checked each time
the ignition switch is turned to the start position or the
parking brake is set.
NON-ABS PROPORTIONING UNIT OPERATION
The proportioning valve section operates by trans-
mitting full input pressure to the rear brakes up to a
certain point. This is called the split point. Beyond this
point it reduces the amount of pressure increase to the
rear brakes according to a certain ratio. On light pedal applications equal brake pressure will
be transmitted to the front and rear brakes. On heavier
pedal applications the pressure transmitted
Fig. 1 Brake Combination Valve And Warning Switch Location
Fig. 2 Switch and Valve Assembly
5 - 26 BRAKES Ä
Page 177 of 2438

to the rear will be lower than the front brakes. This will
prevent premature rear wheel lock-up and skid. If
hydraulic pressure is lost in one half of the diagonally
split system, the operation of the proportioning valve
in the remaining half is not effected.
ABS BRAKE PROPORTIONING VALVE OPERATION
On vehicles using the ABS braking system, screw in
proportioning valves are used in place of the conven-
tional differential pressure/proportioning valve. Each rear brake circuit has its own screw-in propor-
tioning valve which is attached to the rear brake outlet
ports of the hydraulic assembly. These valves limit
brake pressure to the rear brakes after a certain
pressure is reached. This improves front to rear brake
balance during normal braking.
Screw in proportioning valves can be identified by
the numbers stamped on the body of the valve. The
first digit represents the slope, the second digit repre-
sents the split (cut-in) point, and the arrow represents
the flow direction of the valve. Be sure that the
numbers listed on the replacement valve are the
same as on the valve that is being removed. See
(Fig. 3) for detail of the valve identification.
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURES
BRAKE WARNING SYSTEM
CHECKING BRAKE WARNING SWITCH UNIT
The Red Brake Warning light will come on when
the parking brake is applied with the ignition key
turned ON. The same light will also illuminate
should one of the two service brake hydraulic sys-
tems fail.
CAUTION:Make sure air does not enter the hydrau-
lic system during this test procedure. See bleeding
without a pressure bleeder at the beginning of this
section for master cylinder fluid level checking pro-
cedures.
To test the service brake warning system lamp.
Raise the vehicle on a hoist and open a wheel cylin-
der bleeder while a helper depresses the brake pedal
and observes the warning light. If the light fails to light, inspect for a burned out
bulb, disconnected socket, or a broken or discon-
nected wire at the switch. If the bulb is not burned
out and the wire continuity is uninterrupted. Check
the service brake warning switch operation with a
test lamp between the switch terminal and a known
good ground. Be sure to fill master cylinder and
bleed brake system after correction has been made, if
necessary.
PROPORTIONING VALVES
TESTING PROPORTIONING VALVE UNIT
If premature rear wheel skid occurs on hard brake
application, it could be an indication that a malfunc-
tion has occurred with the proportioning valve unit. The proportioning valve is designed with two sep-
arate systems. One half controls the right rear
brake, and the other half controls the left rear brake.
Therefore, a road test to determine which rear brake
slides first is essential.
RIGHT REAR WHEEL SLIDES FIRST To test the proportioning valve when the right rear
wheel slides first, leave the front brakes connected to
the valve, proceed as follows: (1) Install one gauge and (TEE) of set C-4007-A
between the brake line from the master cylinder sec-
ondary port and the brake valve assembly. (2) Install the second gauge of set C-4007-A to the
right rear brake outlet port (Fig. 4). Using an
adapter tube, made from a short piece of brake tube
and (2) 3/8 x 24 tube nuts. Connect the hose to the
valve. Bleed the hose and gauge. (3) Have a helper exert pressure on the brake
pedal (holding pressure) to get a reading on the valve
inlet gauge and check the reading on the outlet
Fig. 3 ABS PROPORTIONING VALVE IDENTIFICA- TION
Ä BRAKES 5 - 27
Page 191 of 2438
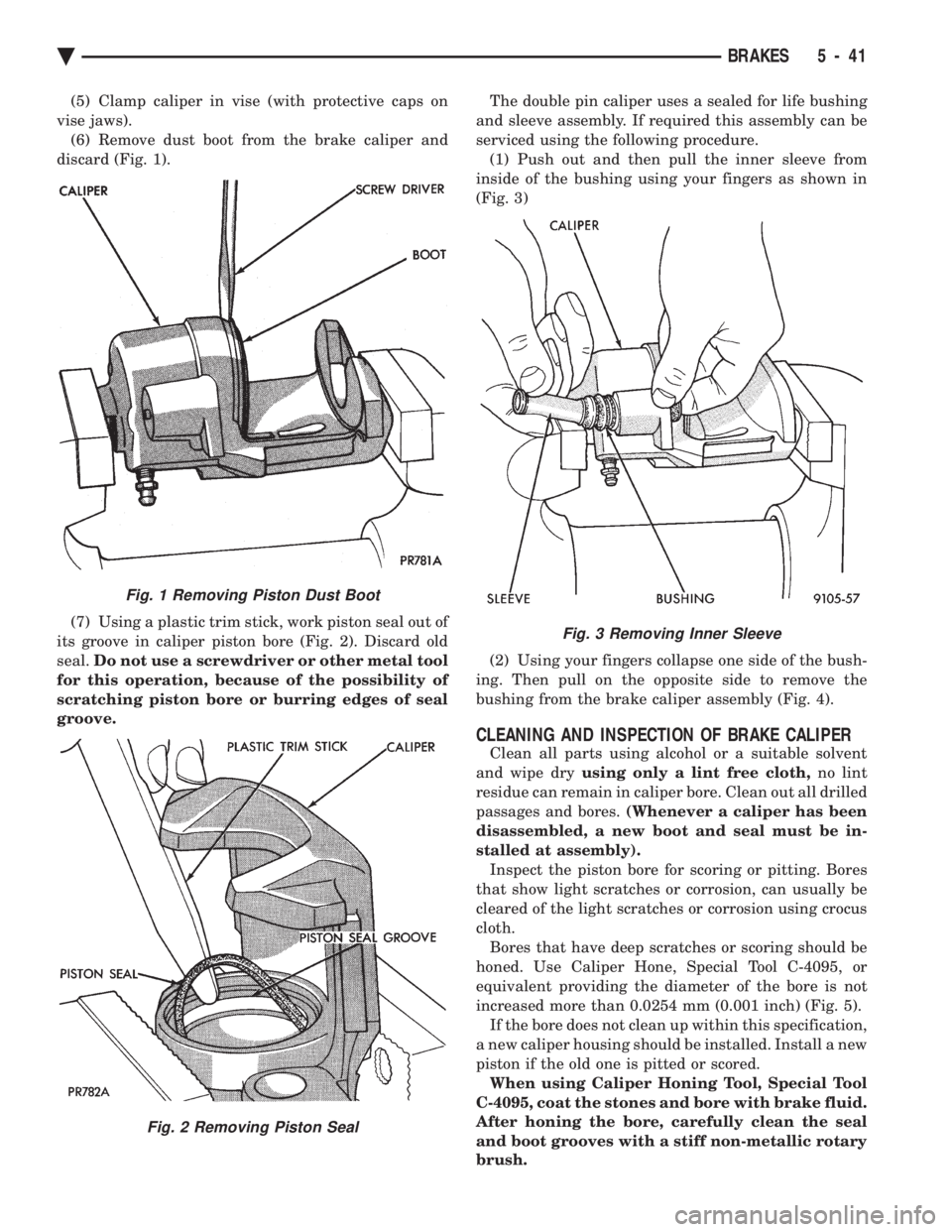
(5) Clamp caliper in vise (with protective caps on
vise jaws). (6) Remove dust boot from the brake caliper and
discard (Fig. 1).
(7) Using a plastic trim stick, work piston seal out of
its groove in caliper piston bore (Fig. 2). Discard old
seal. Do not use a screwdriver or other metal tool
for this operation, because of the possibility of
scratching piston bore or burring edges of seal
groove. The double pin caliper uses a sealed for life bushing
and sleeve assembly. If required this assembly can be
serviced using the following procedure. (1) Push out and then pull the inner sleeve from
inside of the bushing using your fingers as shown in
(Fig. 3)
(2) Using your fingers collapse one side of the bush-
ing. Then pull on the opposite side to remove the
bushing from the brake caliper assembly (Fig. 4).
CLEANING AND INSPECTION OF BRAKE CALIPER
Clean all parts using alcohol or a suitable solvent
and wipe dry using only a lint free cloth, no lint
residue can remain in caliper bore. Clean out all drilled
passages and bores. (Whenever a caliper has been
disassembled, a new boot and seal must be in-
stalled at assembly). Inspect the piston bore for scoring or pitting. Bores
that show light scratches or corrosion, can usually be
cleared of the light scratches or corrosion using crocus
cloth. Bores that have deep scratches or scoring should be
honed. Use Caliper Hone, Special Tool C-4095, or
equivalent providing the diameter of the bore is not
increased more than 0.0254 mm (0.001 inch) (Fig. 5). If the bore does not clean up within this specification,
a new caliper housing should be installed. Install a new
piston if the old one is pitted or scored. When using Caliper Honing Tool, Special Tool
C-4095, coat the stones and bore with brake fluid.
After honing the bore, carefully clean the seal
and boot grooves with a stiff non-metallic rotary
brush.
Fig. 1 Removing Piston Dust Boot
Fig. 2 Removing Piston Seal
Fig. 3 Removing Inner Sleeve
Ä BRAKES 5 - 41
Page 199 of 2438

tool for this operation, because of the possibility
of scratching piston bore or burring edges of seal
groove. The double pin caliper uses a sealed for life bushing
and sleeve assembly. If required this assembly can be
serviced using the following procedure. (1) Using your fingers push on one end the inner
sleeve until it pops out of the bushing. Then grasp the
inner sleeve with your fingers and pull the inner sleeve
out from the inside of the bushing (Fig. 3). (2) Using your fingers collapse one side of the bush-
ing. Then pull on the opposite side to remove the
bushing from the caliper assembly (Fig. 4).
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
Clean all parts using alcohol or a suitable solvent
and wipe dry. Clean out all drilled passages and bores
on the caliper assembly body. (Whenever a caliper
has been disassembled, a new boot and seal must
be installed at assembly). Inspect the caliper assembly piston bore for scoring
or pitting. Bores that show light scratches or corrosion,
can usually have the scratches or corrosion removed
using crocus cloth. Bores that have deep scratches or scoring should be
honed. Use Caliper Hone, Special Tool C-4095, or
equivalent providing the diameter of the bore is not
increased more than 0.0254 mm (0.001 inch) (Fig. 5). If the bore does not clean up within this specification,
a new caliper housing should be installed. Install a new
piston if the old one is pitted or scored. When using Caliper Honing Tool, Special Tool
C-4095, coat the stones and bore with brake fluid.
After honing the bore, carefully clean the seal
and boot grooves with a stiff non-metallic rotary
brush. Use extreme care in cleaning the caliper after
honing. Remove all dirt and grit by flushing the
caliper with brake fluid; wipe dry with a clean,
lint free cloth and then clean a second time.
ASSEMBLING REAR DISC BRAKE CALIPER
Clamp caliper in vise (with protective caps on vise
jaws).
Fig. 2 Removing Piston Seal
Fig. 3 Removing Inner Sleeve From Bushing
Fig. 4 Removing Bushings From Caliper
Ä BRAKES 5 - 49
Page 204 of 2438

knuckle. Position stem so it contacts hub face near
outer diameter. Care must be taken to position stem
outside the stud circle but inside the chamfer on the
hub rim. Clean hub surface before checking. (See
Fig. 3)
Runout should not exceed 0.08 mm (0.003 inch). If
runout exceeds this specification, hub must be re-
placed. See Suspension Group 2. If hub runout does
not exceed this specification, install disc on hub with
chalk marks two wheel studs apart (Fig. 4). Tighten
nuts in the proper sequence and torque to specifica-
tions. Finally, check runout of disc to see if runout is
now within specifications. If runout is not within specifications. Install a new
braking disc or reface disc, being careful to remove
as little as possible from each side of disc. Remove
equal amounts from each side of disc. Do not reduce
thickness below minimum thickness cast into the un-
machined surface of the rotor. Thickness variation measurements of disc should
be made in conjunction with runout. Measure thick-
ness of disc at 12 equal points with a micrometer at
a radius approximately 25.4 mm (1 inch) from edge
of disc (Fig. 5). If thickness measurements vary by
more than 0.013 mm (0.0005 inch) disc should be re-
moved and resurfaced (Figs. 6 and 7), or a new disc
installed. If cracks or burned spots are evident in the
disc, disc must be replaced. Light scoring and/or wear is acceptable. If heavy
scoring or warping is evident, the disc must be refin-
ished or replaced (See Refinishing/Refacing Braking
Disc). If cracks are evident in the disc, replace the
disc.
BRAKING DISC REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist or jackstands. Remove
wheel and tire assembly. (2) Remove caliper assembly, as described under
Brake Shoe Removal in this Group, (but do not dis-
connect brake line). Suspend caliper from wire hook
or loop to avoid strain on flexible hose. (3) Remove braking disc from the hub.
INSTALLING BRAKING DISC
(1) Slide braking disc on hub. Clean both sides of
braking disc with alcohol or suitable solvent. (2) Install caliper assembly, as described in Brake
Shoe Installation paragraph.
Fig. 2 Marking Braking Disc and Wheel Stud
Fig. 3 Checking Hub for Runout
Fig. 4 Index Braking Disc and Wheel Stud
5 - 54 BRAKES Ä
Page 207 of 2438

PARKING BRAKES INDEX
page page
Adjust Parking Brake (AG & AJ Body) ........ 61
General Information ....................... 57
Installing Parking Brake Front Cable (AA, AC, AP AY Body) ............................. 62
Installing Parking Brake Shoes .............. 64
Parking Brake Hand Lever Assembly Removal and Installation ............................ 63
Rear Parking Brake Cable Installation ......... 62 Rear Parking Brake Cable Removal (AA, AC, AP,
AY Body) ............................. 61
Removal and Installation Parking Brake Shoes . . 63
Removing Parking Brake Front Cable (AA, AC, AP, AY Body) ............................. 62
Self Adjusting Procedures (AG & AJ Body) ..... 61
Service Procedures ....................... 57
GENERAL INFORMATION
The parking brake mechanism on vehicles with
rear disc brake applications. Consists of a small duo-
servo brake which is mounted to the adapter. The
hat (center) section (Fig. 1) of the rear rotor serves as
the braking surface (drum) for the parking brakes.
On AA, AC, AP, AY body vehicles with rear disc
brake applications, the parking brake cable system is
similar in design to the drum brake parking brake
system. The parking brake system on the AG and AJ body
vehicles i s a 2 cable design. One individual park
brake cable operates each rear park brake mecha-
nism, and brake application is balanced by an equal-
izer at the park brake lever. On rear drum brake applications, the rear wheel
service brakes also act as parking brakes. The rear
drum brake shoes are mechanically operated by an
internal lever and strut connected to a flexible steel
cable. The wheel brake cables are joined to an inter-
mediate cable which attaches to the front cable lead-
ing to the foot lever (Figs. 2, 3 and 4).
SERVICE PROCEDURES
ADJUSTING PARKING BRAKE
AP, AA, AC & AY (WITH FOOT LEVER)
The service brakes must be properly adjusted be-
fore adjusting the parking brake. Release the parking brake lever then back-off
parking brake cable adjustment so there is slack in
the cable (Figs. 2 and 3). Before loosening cable adjusting nut, clean threads
with a wire brush, and lubricate with Mopar Multi-
Purpose grease on equivalent. The rear brakes adjust every time you depress the
brake pedal. Adjust the parking brake after service brake ad-
justment by tightening the adjusting nut until a
slight drag is felt while rotating the wheels. Loosen the cable adjusting nut until both rear
wheels can be rotated freely, then back-off the cable
adjusting nut two full turns. Apply and release the parking brake several times
to see that the rear wheels rotate freely without
dragging.
AG AND AJ BODY (WITH HAND LEVER) The parking brake hand lever assembly contains a
self adjuster for the cable system. Routine parking
brake adjustment is no longer required (Fig. 5).
Fig. 1 Drum In Hat Braking Disc
Ä BRAKES 5 - 57