abs CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 152 of 2438
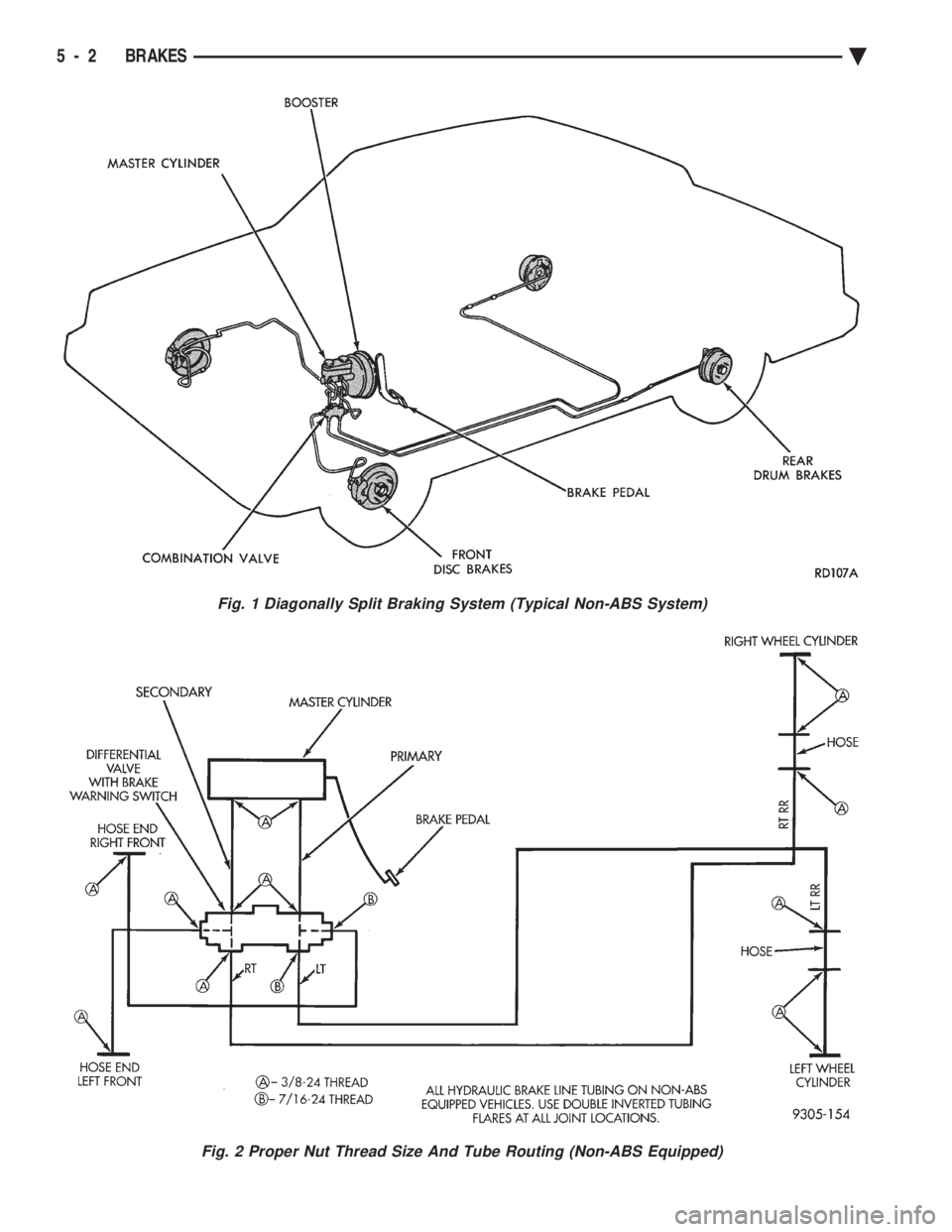
Fig. 1 Diagonally Split Braking System (Typical Non-ABS System)
Fig. 2 Proper Nut Thread Size And Tube Routing (Non-ABS Equipped)
5 - 2 BRAKES Ä
Page 153 of 2438
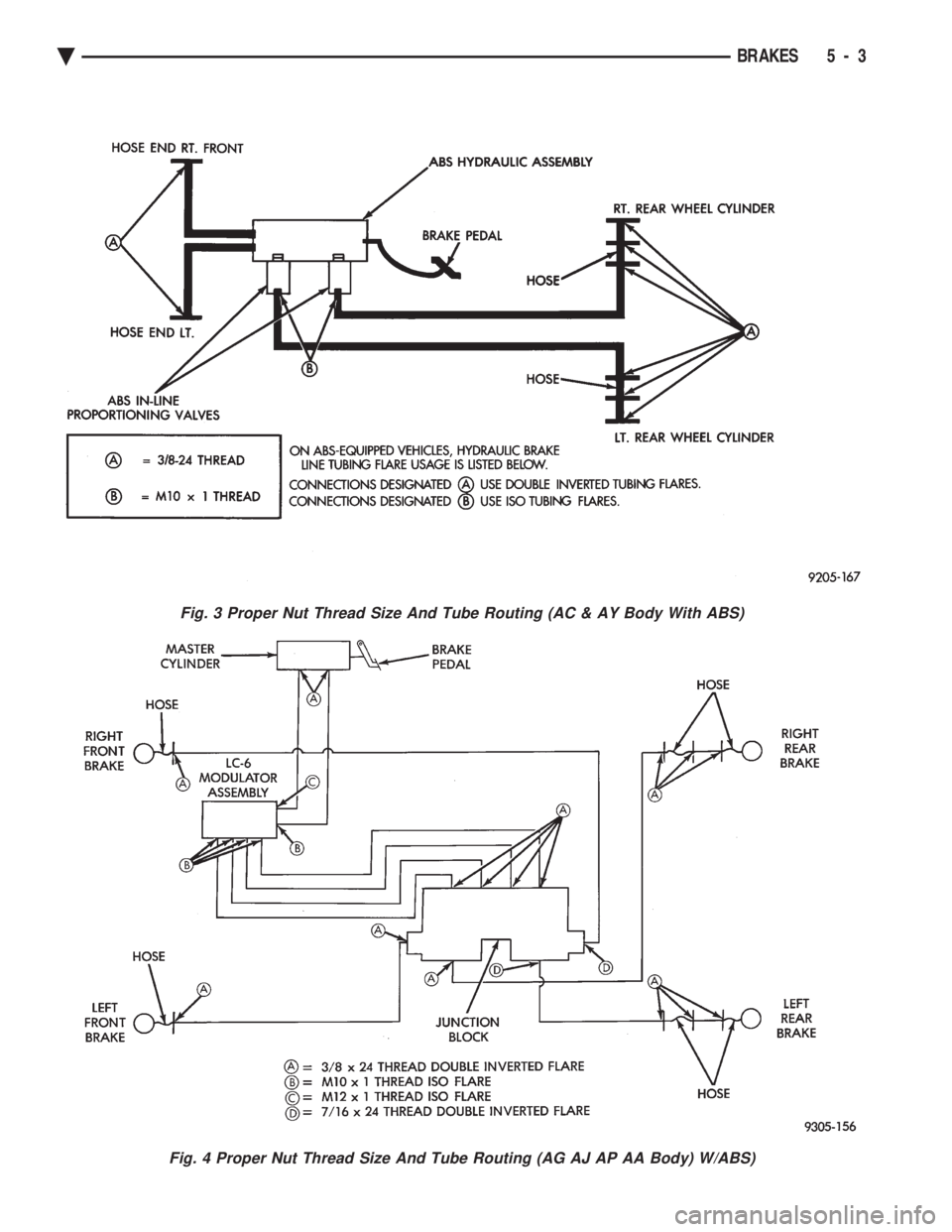
Fig. 3 Proper Nut Thread Size And Tube Routing (AC & AY Body With ABS)
Fig. 4 Proper Nut Thread Size And Tube Routing (AG AJ AP AA Body) W/ABS)
Ä BRAKES 5 - 3
Page 154 of 2438

SERVICE ADJUSTMENTS INDEX
page page
Adjusting Rear Service Brakes ............... 4
Bleeding Brake System ..................... 6
Brake Hose and Tubing ................... 11
Master Cylinder Fluid Level .................. 4 Stop Lamp Switch Adjustment (All Vehicles)
.... 13
Test for Fluid Contamination ................. 7
Testing Application Adjuster Operation ......... 6
Wheel Stud Nut Tightening .................. 7
MASTER CYLINDER FLUID LEVEL
ALL EXCEPT AC/AY BODY WITH ABS
Check master cylinder reservoir brake fluid level a
minimum of twice a year. Master cylinder reservoirs are marked with the
words fill to bottom of rings indicating proper fluid
level (Fig. 1). If necessary, add fluid to bring the level to the bot-
tom of the primary reservoir split ring. Use only Mopar tbrake fluid or an equivalent from
a sealed container. Brake fluid must conform to DOT
3, specifications. DO NOT use brake fluid with a lower boiling
point, as brake failure could result during prolonged
hard braking. Use only brake fluid that was stored in a tightly-
sealed container. DO NOT use petroleum-based fluid because seal
damage in the brake system will result.
AC AND AY BODY WITH ANTI-LOCK BRAKES
The hydraulic assembly is equipped with a plastic
fluid reservoir with a filter/strainer in the filler neck
of the reservoir. The Anti-Lock brake system requires that the hy-
draulic accumulator be de-pressurized whenever
checking the brake fluid level. To check the brake
fluid level, the following procedure should be used: (1) With the ignition switch turned to the off position
and key removed. De-pressurize hydraulic accumula-
tor by applying brake pedal approximately 40 times,
using a pedal force of approximately 220 N (50 lbs.). A
noticeable change in pedal feel will occur when accu-
mulator is de-pressurized. Continue to apply brake
pedal several times after this change in pedal feel
occurs to insure that brake system is fully de-
pressurized. (2) Thoroughly clean both reservoir caps and sur-
rounding area of reservoir, (Fig. 2) before removing
caps. This is to avoid getting dirt into the reservoir and
contaminating the brake fluid. (3) Inspect the brake fluid to see if it is at the proper
level, see instructions on top of reservoir. (FILL TO
TOP OF WHITE SCREEN ON FRONT
FILTER/STRAINER.) (4) Fill reservoir with brake fluid to top of screen
(Fig. 3) on the filter/strainer located in brake fluid
reservoir. Only use brake fluid conforming to DOT 3
specifications such as Mopar tor equivalent.
(5) Replace brake fluid reservoir caps.
ADJUSTING REAR SERVICE BRAKES
Normally, self adjusting drum brakes will not
require manual brake shoe adjustment. Al-
though in the event of a brake reline it is advis-
able to make the initial adjustment manually to
speed up the adjusting time. (1) Raise the vehicle so all wheels are free to turn.
See Hoisting Recommendations in the Lubrication And
Maintenance Section, at the front of this service
manual. (2) Remove rear brake adjusting hole rubber plug
(Fig. 4), from the rear brake shoe support plate. (3) Be sure parking brake lever is fully re-
leased. Then back off parking brake cable adjust-
ment so there is slack in the cable. (4) Insert Brake Adjuster, Special Tool C-3784, (Fig.
5) or equivalent through the adjusting hole in support
plate and against star wheel of adjusting screw. Move
handle of tool upward until a slight drag is felt when
the road wheel is rotated. (5) Insert a thin screwdriver or piece of welding rod
into brake adjusting hole (Fig. 5). Push adjusting lever
out of engagement with star wheel. Care
Fig. 1 Master Cylinder Fluid Level (All Except AC/AY
Body W/ABS)
5 - 4 BRAKES Ä
Page 155 of 2438

should be taken so as not to bend adjusting lever
or distort lever spring. While holding adjusting
lever out of engagement with star wheel, back off star
wheel to ensure a free wheel with no brake shoe drag. (6) Repeat above adjustment at the other rear wheel.
Install adjusting hole rubber plugs (Fig. 4) in rear
brake supports. (7) Adjust parking brake
afterwheel brake adjust-
ment. See parking brake adjustment, under Parking
Brakes in this group of the service manual. It is important to follow the above sequence to
avoid the possibility of the parking brake system
causing brake drag. This could occur if the park-
ing brakes are adjusted before the service
brakes.
Fig. 4 Brake Adjusting Hole Plug
Fig. 2 Master Cylinder Fluid Level (W/ABS)
Fig. 3 ABS Reservoir Fill Level On Filter/Strainer
Ä BRAKES 5 - 5
Page 158 of 2438

FIG. 10 BRAKE LINE ROUTING NON ABS BRAKES
5 - 8 BRAKES Ä
Page 161 of 2438

BRAKE HOSE AND TUBING
INSPECTION OF BRAKE HOSE AND TUBING
Flexible rubber hose is used at both front brakes and
at the rear axle. Inspection of brake hoses should be
performed whenever the brake system is serviced and
every 7,500 miles or 12 months, whichever comes first
(every engine oil change). Inspect hydraulic brake
hoses for severe surface cracking, scuffing, or worn
spots. Should the fabric casing of the rubber hose be
exposed due to cracks or abrasions in the rubber hose
cover, the hose should be replaced immediately. Even-
tual deterioration of the hose can take place with
possible burst failure. Faulty installation can cause
twisting and wheel, tire or chassis interference. The steel brake tubing should be inspected periodi-
cally for evidence of physical damage or contact with
moving or hot components.
INSTALLATION OF BRAKE HOSE
Always use factory recommended brake hose to en-
sure quality, correct length and superior fatigue life.
Care should be taken to make sure that the tube and
hose mating surfaces are clean and free from nicks and
burrs. Front right and left side hoses are not
interchangeable. Connections should be correct and properly made.
Use new copper seal washers on all connections using
Banjo Bolts and tighten all fittings to their specified
torques. The flexible front hydraulic brake hose should al-
ways be installed on the vehicle by first attaching the
Banjo connector to the caliper assembly. Then bolt the
intermediate hose bracket to the strut assembly allow-
ing the bracket to position the hose to prevent twisting.
Attach the hose to the body bracket and steel brake
tubing. Tighten all fittings to specified torque. The
body bracket and hose end are keyed so that they will
only fit one way. Install rear brake hoses first to the trailing arm
tubes and then to the floor pan tubes. Minimize hose
twisting. Vehicles equipped with rear disc brakes have
brake hoses attached to the caliper on each side. The
brake hose should be first attached by the Banjo bolt to
the caliper and then secured to the hose bracket with
the retaining clip. The attach the steel brake tubing to
the hose fitting.
REPAIR AND INSTALLATION OF BRAKE TUB- ING
Only double wall 4.75mm (3/16 in.) steel tubing
should be used for replacement. Care should be taken
when replacing brake tubing, to be sure the proper
bending and flaring tools and procedures are used, to
avoid kinking. Do not route the tubes against sharp edges, moving components or into hot areas. All
tubes should be properly attached with recommended
retaining clips.
TYPES OF TUBING FLARES
Two different tubing flares (Fig. 13) are used on 93
M.Y. vehicles. On some ABS brake systems the tub-
ing connections made to the hydraulic assembly use
an ISO flare. All other ABS brake system compo-
nent, tubing connections are made using a double in-
verted flare. On non-ABS brake systems all
component tubing connections use only the double in-
verted flare. No ISO flares are used.
CAUTION: ALWAYS USE THE PROPER FLARING
TOOL AND PROCEDURE, FOR THE TYPE OF
BRAKE SYSTEM THAT IS BEING SERVICED TO IN-
SURE THE INTEGRITY OF THE HYDRAULIC SYS-
TEM.
TO REPAIR OR FLARE TUBING
Using Tubing Cutter, Special Tool C-3478-A or
equivalent, cut off damaged seat or tubing (Fig. 14).
Ream out any burrs or rough edges showing on in-
side of tubing (Fig. 15). This will make the ends of
tubing square (Fig. 15) and ensure better seating of
flared end tubing. PLACE TUBE NUT ON TUB-
ING BEFORE FLARING THE TUBING.
DOUBLE INVERTED TUBING FLARES.
To make a double inverted tubing flare (Fig. 13 &
16). Open handles of Flaring Tool, Special Tool
C-4047 or equivalent. Then rotate jaws of tool until
the mating jaws of tubing size are centered between
vertical posts on tool. Slowly close handles with tub-
Fig. 13 Identifying Hydraulic Brake Tubing Flares
Ä BRAKES 5 - 11
Page 176 of 2438

HYDRAULIC SYSTEM CONTROL VALVES INDEX
page page
ABS Brake Proportioning Valve Operation ...... 27
General Information ....................... 26
Hydraulic System Service Procedures ......... 27 Non-ABS Proportioning Unit Operation
........ 26
Pressure Differential Warning Light Switch ...... 26
Testing ABS Proportioning Valves ............ 29
GENERAL INFORMATION
Most models not equipped with an Anti-Lock brak-
ing system have a combination hydraulic system con-
trol valve in the brake hydraulic system (Fig. 1). The
valve is attached to the frame rail below the master
cylinder.
The control valve assembly combines a warning
switch with a dual proportioning valve (Fig. 2) Proportioning valves balance front to rear braking
by controlling at a given ratio, the increase in rear
system hydraulic pressure above a preset level. Un-
der light pedal application, the valve allows full hy-
draulic pressure to the rear brakes. There is only one valve assembly in each vehicle,
see Valve Application Chart. During any service pro-
cedures identify valve assemblies by part number as
well as split point (PSI) and slope.
PRESSURE DIFFERENTIAL WARNING LIGHT
SWITCH
The hydraulic brake system, on non-ABS vehicles,
is split diagonally. The left front and right rear
brakes are part of one system. And the right front and left rear are part of another. Both systems are
routed through, but hydraulically separated by a Pres-
sure Differential Switch. The function of the Pressure
Differential Switch is to alert the driver of a malfunc-
tion in the brake system. If hydraulic pressure is lost in one system, the
warning light switch will activate a red light on the
instrument panel, when the brake pedal is depressed.
At this point the brakes require service. However, since
the brake systems are split diagonally the vehicle will
retain 50% of its stopping capability in the event of a
failure in either half. The warning light switch is the latching type. It
will automatically center itself after the repair is
made and the brake pedal is depressed. The instrument panel bulb can be checked each time
the ignition switch is turned to the start position or the
parking brake is set.
NON-ABS PROPORTIONING UNIT OPERATION
The proportioning valve section operates by trans-
mitting full input pressure to the rear brakes up to a
certain point. This is called the split point. Beyond this
point it reduces the amount of pressure increase to the
rear brakes according to a certain ratio. On light pedal applications equal brake pressure will
be transmitted to the front and rear brakes. On heavier
pedal applications the pressure transmitted
Fig. 1 Brake Combination Valve And Warning Switch Location
Fig. 2 Switch and Valve Assembly
5 - 26 BRAKES Ä
Page 177 of 2438

to the rear will be lower than the front brakes. This will
prevent premature rear wheel lock-up and skid. If
hydraulic pressure is lost in one half of the diagonally
split system, the operation of the proportioning valve
in the remaining half is not effected.
ABS BRAKE PROPORTIONING VALVE OPERATION
On vehicles using the ABS braking system, screw in
proportioning valves are used in place of the conven-
tional differential pressure/proportioning valve. Each rear brake circuit has its own screw-in propor-
tioning valve which is attached to the rear brake outlet
ports of the hydraulic assembly. These valves limit
brake pressure to the rear brakes after a certain
pressure is reached. This improves front to rear brake
balance during normal braking.
Screw in proportioning valves can be identified by
the numbers stamped on the body of the valve. The
first digit represents the slope, the second digit repre-
sents the split (cut-in) point, and the arrow represents
the flow direction of the valve. Be sure that the
numbers listed on the replacement valve are the
same as on the valve that is being removed. See
(Fig. 3) for detail of the valve identification.
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURES
BRAKE WARNING SYSTEM
CHECKING BRAKE WARNING SWITCH UNIT
The Red Brake Warning light will come on when
the parking brake is applied with the ignition key
turned ON. The same light will also illuminate
should one of the two service brake hydraulic sys-
tems fail.
CAUTION:Make sure air does not enter the hydrau-
lic system during this test procedure. See bleeding
without a pressure bleeder at the beginning of this
section for master cylinder fluid level checking pro-
cedures.
To test the service brake warning system lamp.
Raise the vehicle on a hoist and open a wheel cylin-
der bleeder while a helper depresses the brake pedal
and observes the warning light. If the light fails to light, inspect for a burned out
bulb, disconnected socket, or a broken or discon-
nected wire at the switch. If the bulb is not burned
out and the wire continuity is uninterrupted. Check
the service brake warning switch operation with a
test lamp between the switch terminal and a known
good ground. Be sure to fill master cylinder and
bleed brake system after correction has been made, if
necessary.
PROPORTIONING VALVES
TESTING PROPORTIONING VALVE UNIT
If premature rear wheel skid occurs on hard brake
application, it could be an indication that a malfunc-
tion has occurred with the proportioning valve unit. The proportioning valve is designed with two sep-
arate systems. One half controls the right rear
brake, and the other half controls the left rear brake.
Therefore, a road test to determine which rear brake
slides first is essential.
RIGHT REAR WHEEL SLIDES FIRST To test the proportioning valve when the right rear
wheel slides first, leave the front brakes connected to
the valve, proceed as follows: (1) Install one gauge and (TEE) of set C-4007-A
between the brake line from the master cylinder sec-
ondary port and the brake valve assembly. (2) Install the second gauge of set C-4007-A to the
right rear brake outlet port (Fig. 4). Using an
adapter tube, made from a short piece of brake tube
and (2) 3/8 x 24 tube nuts. Connect the hose to the
valve. Bleed the hose and gauge. (3) Have a helper exert pressure on the brake
pedal (holding pressure) to get a reading on the valve
inlet gauge and check the reading on the outlet
Fig. 3 ABS PROPORTIONING VALVE IDENTIFICA- TION
Ä BRAKES 5 - 27
Page 179 of 2438
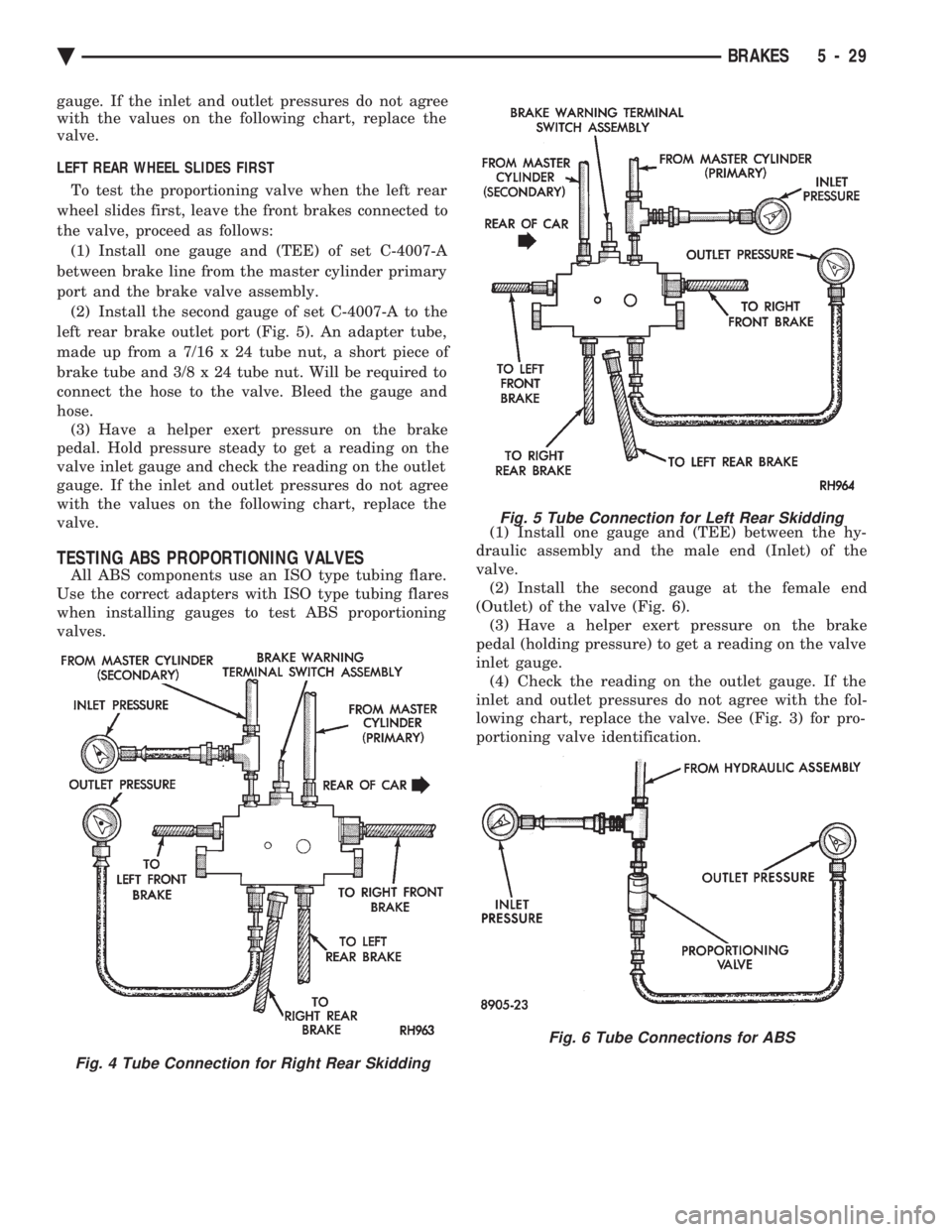
gauge. If the inlet and outlet pressures do not agree
with the values on the following chart, replace the
valve.
LEFT REAR WHEEL SLIDES FIRST To test the proportioning valve when the left rear
wheel slides first, leave the front brakes connected to
the valve, proceed as follows: (1) Install one gauge and (TEE) of set C-4007-A
between brake line from the master cylinder primary
port and the brake valve assembly. (2) Install the second gauge of set C-4007-A to the
left rear brake outlet port (Fig. 5). An adapter tube,
made up from a 7/16 x 24 tube nut, a short piece of
brake tube and 3/8 x 24 tube nut. Will be required to
connect the hose to the valve. Bleed the gauge and
hose. (3) Have a helper exert pressure on the brake
pedal. Hold pressure steady to get a reading on the
valve inlet gauge and check the reading on the outlet
gauge. If the inlet and outlet pressures do not agree
with the values on the following chart, replace the
valve.
TESTING ABS PROPORTIONING VALVES
All ABS components use an ISO type tubing flare.
Use the correct adapters with ISO type tubing flares
when installing gauges to test ABS proportioning
valves. (1) Install one gauge and (TEE) between the hy-
draulic assembly and the male end (Inlet) of the
valve. (2) Install the second gauge at the female end
(Outlet) of the valve (Fig. 6). (3) Have a helper exert pressure on the brake
pedal (holding pressure) to get a reading on the valve
inlet gauge. (4) Check the reading on the outlet gauge. If the
inlet and outlet pressures do not agree with the fol-
lowing chart, replace the valve. See (Fig. 3) for pro-
portioning valve identification.
Fig. 4 Tube Connection for Right Rear Skidding
Fig. 5 Tube Connection for Left Rear Skidding
Fig. 6 Tube Connections for ABS
Ä BRAKES 5 - 29
Page 180 of 2438
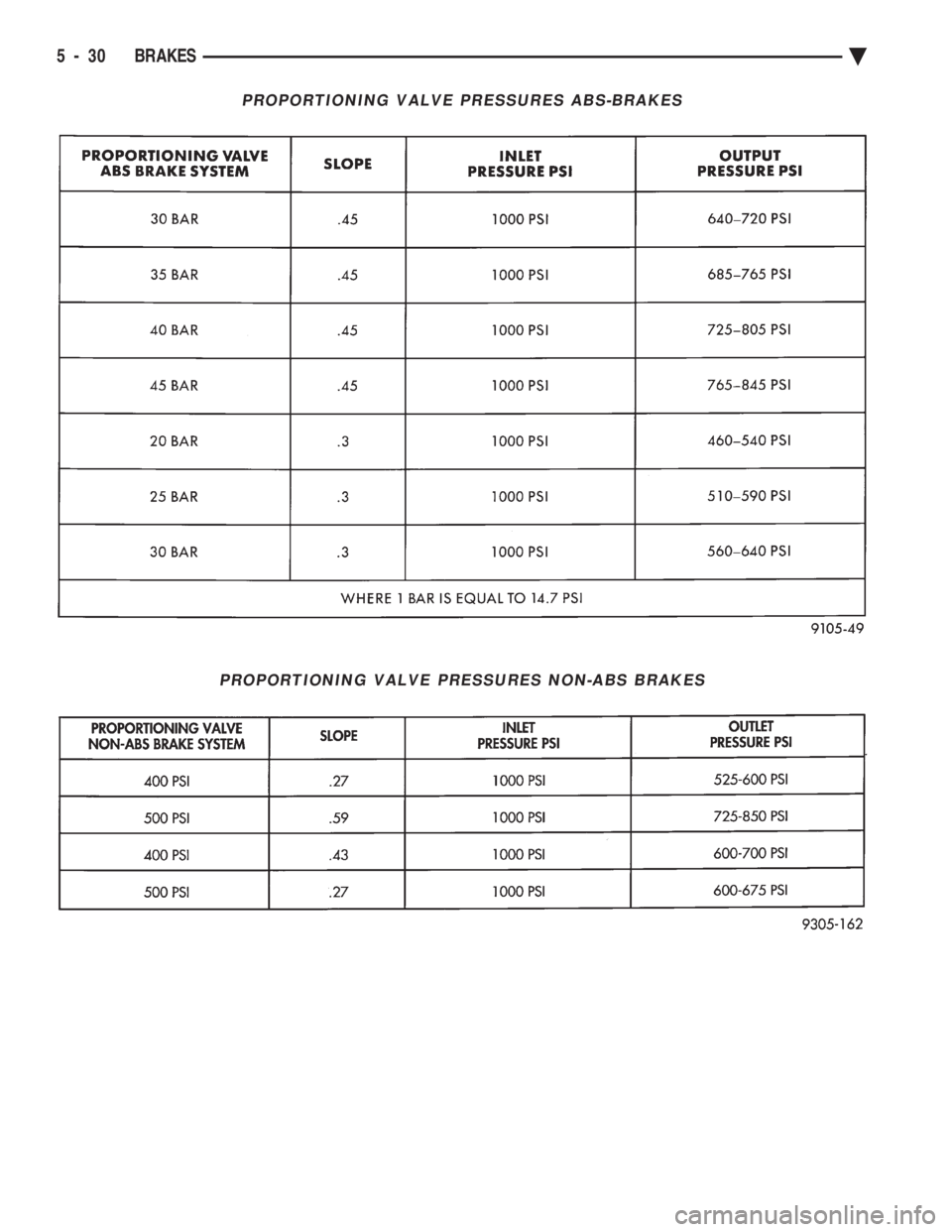
PROPORTIONING VALVE PRESSURES ABS-BRAKES
PROPORTIONING VALVE PRESSURES NON-ABS BRAKES
5 - 30 BRAKES Ä