CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM 1993 Service Manual
Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM, Model: CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 1671 of 2438

(3) Before removing valves, remove any burrs
from valve stem lock grooves to prevent damage
to the valve guides. Identify valves to insure instal-
lation in original location.
VALVE INSPECTION
(1) Clean valves thoroughly and discard burned,
warped and cracked valves. (2) Measure valve stems for wear. Refer to specifica-
tions (Fig. 19). Valve stems are chrome plated and should not
be polished. (3) Remove carbon and varnish deposits from inside
of valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner. (4) Measure valve stem guide clearance as follows:(a) Install valve into cylinder head so it is 14mm
(.551 inch) off the valve seat. A small piece of hose
may be used to hold valve in place. (b) Attach dial indicator Tool C-3339 to cylinder
head and set it at right angle of valve stem being
measured (Fig. 17). (c) Move valve to and from the indicator. Refer to
specifications (Fig. 19).
Ream the guides for valves with oversized stems if
dial indicator reading is excessive or if the stems are
scuffed or scored. (5) Service valves with oversize stems and over size
seals are available in 0.15mm (.005 inch), 0.40mm,
(.015 inch) and 0.80mm (.030 inch) oversize. Oversize seals must be used with oversize
valves. Reamers to accommodate the oversize valve stem are
as follows:
(6) Slowly turn reamer by hand and clean guide
thoroughly before installing new valve. Do not at-
tempt to ream the valve guides from standard
directly to 0.80mm (.030 inch) Use step procedure
of 0.15mm (.005 inch), 0.40mm (.015 inch) and
0.80mm (.030 inch) so the valve guides may be
reamed true in relation to the valve seat. After
reaming guides, the seat runout should be mea-
sured and resurfaced if necessary. See Refacing
Valves and Valve Seats.
VALVE GUIDES
Replace cylinder head if guide does not clean
up with 0.80mm (.030 inch) oversize reamer, or if
guide is loose in cylinder head.
Fig. 18 Intake and Exhaust Valves
Fig. 19 Valve Guide Specifications
Fig. 16 Compress Valve Springs with Special Tool C-3422B with adapter 6412
Fig. 17 Measuring Valve Guide Wear
Ä 3.3/3.8L ENGINE 9 - 105
Page 1672 of 2438

REFACING VALVES AND VALVE SEATS
The intake and exhaust valves have a 44-1/2 to 45
degree face angle. The valve seats have a 45 to 45-
1/2 degree face angle. The valve face and valve seat
angles are shown in (Fig. 21).
VALVES
(1) Inspect the remaining margin after the valves
are refaced Refer to specifications (Fig. 20).
VALVE SEATS
CAUTION: Do not un-shroud cylinder head from
around the valve during valve seat refacing (Fig.
22).
(1) When refacing valve seats, it is important that
the correct size valve guide pilot be used for reseat-
ing stones. A true and complete surface must be ob-
tained. (2) Measure the concentricity of valve seat using
dial indicator. Total runout should not exceed
.051mm (.002 inch) total indicator reading.
(3) Inspect the valve seat with Prussian blue to de-
termine where the valve contacts the seat. To do this, coat valve seat
LIGHTLYwith Prussian blue
then set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light
pressure. If the blue is transferred to the center of
valve face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is trans-
ferred to top edge of valve face,lower valve seat with a
15 degree stone. If the blue is transferred to the bottom
edge of valve face raise valve seat with a 65 degrees
stone. Valve seats which are worn or burned can be
reworked, provided that correct angle and seat
width are maintained. Otherwise cylinder head
must be replaced. (4) When seat is properly positioned the width of
intake seats should be 1.75 to 2.25mm (0.69 to .088
inch) The width of the exhaust seats should be 1.50 to
2.00mm (.059 to .078 inch) (Fig. 21) (5) Check the valve spring installed height after
refacing the valve and seat (Fig. 24).
TESTING VALVE SPRINGS
Whenever valves have been removed for inspection,
reconditioning or replacement, valve springs should be
tested (Fig. 23). As an example; the compression
Fig. 23 Testing Valve Spring with Tool C-647
Fig. 20 Valve Dimensions
Fig. 21 Valve Seats
Fig. 22 Refacing Valve Seats
9 - 106 3.3/3.8L ENGINE Ä
Page 1673 of 2438

length of the spring to be tested is 33.34mm (1-5/16
inches). Turn table of Tool C-647 until surface is in line
with the 33.34mm (1-5/16 inch) mark on the threaded
stud and the zero mark on the front. Place spring over
stud on the table and lift compressing lever to set tone
device. Pull on torque wrench until ping is heard. Take
reading on torque wrench at this instant. Multiply this
reading by two. This will give the spring load at test
length. Fractional measurements are indicated on the
table for finer adjustments. Refer to specifications to
obtain specified height and allowable tensions. Discard
the springs that do not meet specifications.
VALVE INSTALLATION
(1) Coat valve stems with clean engine oil and insert
them in cylinder head. (2) Check valve tip to spring seat dimension A after
grinding the valve seats or faces. Grind valve tip to give
49.541 to 51.271 mm (1.950 to 2.018 inch.) over spring
seat when installed in the head (Fig. 17). Check valve
tip for scoring, if necessary, the tip chamfer should be
reground to prevent seal damage when the valve is
installed. (3) Install new cup seals on all valve stems and over
valve guides (Fig. 24). Install valve springs and valve
retainers.
(4) Compress valve springs with Valve Spring Com-
pressor Tool C-3422-B, with adapter 6412 install locks
and release tool. If valves and/or seats are re-
ground, measure the installed height of springs
dimension B, make sure measurements is taken
from top of spring seat to the bottom surface of
spring retainer. If height is greater than 1-19/32
inches, (40.6mm), install a 1/32 inch (.794mm)
spacer in head counterbore to bring spring
height back to normal 1-17/32 to 1-19/32 inch (39.1
to 40.6mm) .
REPLACE VALVE STEM SEALS OR VALVE
SPRINGS, CYLINDER HEAD NOT REMOVED
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
before attempting any repairs (2) Disconnect negative battery cable. (3) Remove Air Cleaner Cover and hose assembly.
(4) Remove Intake Manifold; Refer to
Intake/Exhaust Manifold 3.3/3.8L Engine Group 11
Exhaust System and Intake Manifolds of this manual
for removal procedure. (5) Remove cylinder head covers and spark plugs.
(6) Remove connector wire from ignition coils.
(7) Using suitable socket and flex handle at crank-
shaft pulley retaining screw, turn engine so the num-
ber 1 piston is at Top Dead Center on the compression
stroke. (8) Remove rocker arms with rocker shaft and in-
stall a dummy shaft. The rocker arms should not be
disturbed and left on shaft. (9) With air hose attached to spark plug adapter
installed in number 1 spark plug hole, apply 90 to 100
psi air pressure (620.5 to 689 kPa). This is to hold
valves into place while servicing components. (10) Using Tool C-4682 or Equivalent compress
valve spring and remove retainer valve locks and valve
spring. (11) The intake valve stem seals should be pushed
firmly and squarely over the valve guide using the
valve stem as guide. Do Not Forceseal against top of
guide. When installing the valve retainer locks, com-
press the spring only enoughto install the locks.
CAUTION:Do not pinch seal between retainer and top
of valve guide .
(12) Follow the same procedure on the remaining 5
cylinders using the firing sequence 1-2-3-4-5-6. Make
sure piston in cylinder is at TDC on the valve
spring that is being covered. (13) Remove spark plug adapter tool .
(14) Remove dummy shaft and install rocker shaft
assembly and tighten screws to 28 N Im (250 in. lbs.).
Fig. 24 Checking Valve Installed Height
Fig. 25 Installing Valve, Cup Seal, Spring and Re-
tainer
Ä 3.3/3.8L ENGINE 9 - 107
Page 1674 of 2438

(15) Install rocker arm covers tighten screws to 14
N Im (120 in. lbs.) and connector to ignition coils.
(16) Install Intake Manifold; Refer to Intake Mani-
fold Installation 3.3/3.8L Engine, Group 11 Exhaust
System and Intake Manifold.
HYDRAULIC TAPPETS
The valve train includes roller tappet assemblies,
aligning yokes and yoke retainer. Roller tappet alignment is maintained by machined
flats on tappet body being fitted in pairs into six
aligning yokes. The yokes are secured by an alignment
yoke retainer (Fig. 26).
PRELIMINARY STEP TO CHECKING THE HY- DRAULIC TAPPETS
Before disassembling any part of the engine to cor-
rect tappet noise, read the oil pressure at the gauge.
Install a reliable gauge at pressure sending unit if
vehicle has no oil pressure gauge and check the oil level
in the oil pan. The pressure should be between 30 and
80 psi (206.8 to 551.6 kPa) at 2000 rpm. The oil level in the pan should never be above the
MAX mark on dipstick, or below the MIN mark. Either
of these two conditions could be responsible for noisy
tappets. Oil Level Check: stop engine after reach-
ing normal operating temperature . Allow 5 min-
utes to stabilize oil level, check dipstick.
OIL LEVEL TOO HIGH
If oil level is above the MAX mark on dip stick, it is
possible for the connecting rods to dip into the oil while
engine is running and create foam. Foam in oil pan
would be fed to the hydraulic tappets by the oil pump
causing them to become soft and allow valves to seat
noisily.
OIL LEVEL TOO LOW
Low oil level may allow pump to take in air which
when fed to the tappets, causes them to become soft
and allows valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on intake
side of pump through which air can be drawn will
create the same tappet action. Check the lubri- cation system from the intake strainer to the pump
cover, including the relief valve retainer cap. When
tappet noise is due to aeration, it may be intermittent
or constant, and usually more than one tappet will be
noisy. When oil level and leaks have been corrected,
engine should be operated at fast idle to allow all of the
air inside of the tappets to be bled out.
VALVE TRAIN NOISE DIAGNOSIS
To determine source of valve train noise, operate
engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed and
listen for source of the noise. Worn valve guides or cocked springs are some-
times mistaken for noisy tappets. If such is the
case, noise may be dampened by applying side
thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not appre-
ciably reduced, it can be assumed the noise is in
the tappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod
sockets and push rod ends for wear. Valve tappet noise ranges from light noise to a heavy
click. A light noise is usually caused by excessive
leakdown around the unit plunger which will necessi-
tate replacing the tappet, or by the plunger partially
sticking in the tappet body cylinder. A heavy click is
caused either by a tappet check valve not seating, or by
foreign particles becoming wedged between the
plunger and the tappet body causing the plunger to
stick in the down position. This heavy click will be
accompanied by excessive clearance between the valve
stem and rocker arm as valve closes. In either case,
tappet assembly should be removed for inspection and
cleaning.
TAPPET REMOVAL
(1) Refer to Cylinder Head Removal of this section to
remove intake manifold and cylinder heads for access
to tappets for service. (2) Remove yoke retainer and aligning yokes.
(3) Use Tool C-4129 to remove tappets from their
bores. If all tappets are to be removed, identify tappets
to insure installation in original location. If the tappet or bore in cylinder block is scored,
scuffed, or shows signs of sticking, ream the bore
to next oversize and replace with oversize tap-
pet.
CAUTION: The plunger and tappet bodies are not
interchangeable. The plunger and valve must always
be fitted to the original body. It is advisable to work on
one tappet at a time to avoid mixing of parts. Mixed
parts are not compatible. Do not disassemble a tap-
pet on a dirty work bench.
DISASSEMBLY (FIG. 27)
(1) Pry out plunger retainer spring clip.
Fig. 26 Roller Tappets Aligning Yoke and Retainer
9 - 108 3.3/3.8L ENGINE Ä
Page 1675 of 2438

(2) Clean varnish deposits from inside of tappet
body above plunger cap. (3) Invert tappet body and remove plunger cap,
plunger, flat or ball check valve, check valve spring,
check valve retainer and plunger spring. Check valve
could be flat or ball.
CLEANING AND ASSEMBLY
(1) Clean all tappet parts in a solvent that will re-
move all varnish and carbon. (2) Replace tappets that are unfit for further ser-
vice with new assemblies. (3) If plunger shows signs of scoring or wear, valve
is pitted, or valve seat on end of plunger indicates
any condition that would prevent valve from seating,
install a new tappet assembly. (4) Assemble tappets (Fig. 27).
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate tappets.
(2) Install tappets in their original positions.
(3) With roller tappets, install aligning yokes with
(Fig. 26). (4) Install yoke retainer and torque screws to 12
N Im (105 in. lbs.) (Fig. 26).
(5) Install cylinder heads. Refer to cylinder head
installation of this section for procedure. (6) Start and operate engine. Warm up to normal
operating temperature.
CAUTION: To prevent damage to valve mechanism,
engine must not be run above fast idle until all hy-
draulic tappets have filled with oil and have become
quiet.
VALVE TIMING
(1) Remove front valve cover and all 6 spark plugs.
(2) Rotate engine until the #2 piston is at TDC of
the compression stroke. (3) Install a degree wheel on the crankshaft pulley.
(4) With proper adaptor, install a dial into #2
spark plug hole. Using the indicator find TDC on the
compression stroke. (5) Position the degree wheel to zero.
(6) Remove dial indicator from spark plug hole. (7) Place a 5.08mm (.200 inch) spacer between the
valve stem tip of #2 intake valve and rocker arm
pad. Allow tappet to bleed down to give a solid tap-
pet effect. (8) Install a dial indicator so plunger contacts the
#2 intake valve spring retainer as nearly perpendic-
ular as possible. Zero the indicator. (9) Rotate the engine clockwise until the in take
valve has lifted .254mm (0.010 inch).
CAUTION: Do not turn crankshaft any further clock-
wise as intake valve might bottom and result in se-
rious damage.
(10) Degree wheel should read 3 degrees BTDC to
4 degrees ATDC.
TIMING CHAIN COVER, OIL SEAL AND CHAIN
COVER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery.
(2) Drain cooling system. Refer to Cooling System
Group 7 for procedure. (3) Support engine and remove right engine
mount. (4) Raise vehicle on hoist. Drain engine oil.
(5) Remove oil pan and oil pump pick-up. It may
necessary to remove transmission inspection cover. (6) Remove right wheel and inner splash shield.
(7) Remove drive belt. Refer to Cooling System
Group 7 for procedure. (8) Remove A/C compressor and set aside.
(9) Remove A/C compressor mounting bracket.
(10) Remove crankshaft pulley (Fig. 1).
(11) Remove idler pulley from engine bracket.
(12) Remove engine bracket (Fig. 2).
(13) Remove cam sensor from chain case cover
(Fig. 3).
Fig. 27 Hydraulic Roller Tappet Assembly
Fig. 1 Removing Crankshaft Pulley
Ä 3.3/3.8L ENGINE 9 - 109
Page 1676 of 2438

(14) Remove chain case cover (Fig. 3).
MEASURING TIMING CHAIN FOR STRETCH
(1) Place a scale next to timing chain so that any
movement of chain may be measured. (2) Place a torque wrench and socket on camshaft
sprocket attaching bolt and apply torque in direction of
crankshaft rotation to take up slack; 41 N Im (30 ft. lb.)
with cylinder head installed or 20 N Im (15 ft. lb.) with
cylinder heads removed. With a torque applied to
the camshaft sprocket bolt, crankshaft should
not be permitted to move. It may be necessary to
block crankshaft to prevent rotation. (3) Holding a scale even, with dimension reading as
shown (Fig. 4 ), along edge of chain links. Apply torque
in the reverse direction to 41 N Im (30 ft. lbs.) with
cylinder heads installed, or 20 N Im (15 ft. lbs.) with
cylinder heads removed. Check amount of chain move-
ment (Fig. 4). (4) Install a new timing chain, if its movement
exceeds 3.175mm (1/8 inch) (Fig. 4). (5) If chain is not satisfactory, remove camshaft
sprocket attaching bolt, and remove timing chain with
camshaft sprocket. (6) Using a suitable puller remove the crankshaft
sprocket. Be careful not to damage the crankshaft
surface. (7) Position a new crankshaft sprocket on the shaft,
install sprocket with suitable tool and mallet. Be sure
sprocket is seated into position. (8) Rotate crankshaft so the timing arrow is to the
12 O'clock position. (9) Place timing chain around camshaft sprocket
and place the timing mark to the 6 O'clock position. (10) Align the dark colored links with the dot on the
camshaft sprocket, place timing chain around crank-
shaft sprocket with the dark colored link lined up with
the dot on the sprocket and install camshaft sprocket
into position. (11) Using straight edge to check alignment of tim-
ing marks (Fig. 5). (12) Install camshaft bolt and washer. Tighten to 54
N Im (40 ft. lbs.).
(13) Rotate crankshaft 2 revolutions. Timing marks
should line up. If timing marks do not line up remove
cam sprocket and realign. (14) Check camshaft endplay. With new thrust plate
specification is .0127 to .304 mm (.005 to .012 inches.).
Old thrust plate specification is .31 mm (.012 inch.)
maximum. If not within these limits install new thrust
plate. (15) Install timing chain snubber. Tighten retaining
screws to 12 N Im (105 in. lbs.). These bolts are
20mm long for this model year, they should not
be interchanged with previous year engines .
INSTALLATION (1) Be sure mating surfaces of chain case cover and
cylinder block are clean and free from burrs. Crank-
shaft oil seal must be removed to insure correct oil
pump engagement. (2) Use a new cover gasket, O-rings. (Fig. 6).
Fig. 3 Timing Chain Case Cover
Fig. 4 Measuring Timing Chain Wear and Stretch
Fig. 2 Engine Bracket
9 - 110 3.3/3.8L ENGINE Ä
Page 1677 of 2438

(3) Rotate crankshaft so that the oil pump drive
flats are vertical. (4) Position oil pump inner rotor so the mating
flats are in the same position as the crankshaft drive
flats (Fig. 6). (5) Install cover onto crankshaft. Make sure the oil
pump is engaged on the crankshaft correctly or se-
vere damage may result. (6) Install chain case cover screws and torque to 27
N Im (20 ft. lbs.).
(7) Install crankshaft oil seal (Fig. 7).
(8) Install crankshaft pulley (Fig. 8).
(9) Install engine bracket (Fig. 2) torque screws to
54 N Im (40 ft. lbs.).
(10) Install idler pulley on engine bracket. (11) Install cam sensor Refer to Ignition System
Group 8D for installation procedure. (12) Install A/C compressor mounting bracket.
(13) Install A/C compressor.
(14) Install drive belt Refer to Cooling System
Group 7 for installation procedure. (15) Install inner splash shield and wheel.
(16) Install oil pump pick-up and oil pan and
transmission inspection cover if removed. (17) Install engine mount.
(18) Fill crankcase with oil to proper level.
(19) Fill cooling system Refer to Cooling System
Group 7 for procedure. (20) Connect battery.
TIMING CHAIN COVER EXTERNAL OIL SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist. Remove right wheel and
inner splash shield. (2) Remove drive belt. (Refer to Cooling System
Group 7) for procedure. (3) Remove crankshaft pulley (Fig. 1).
Fig. 5 Alignment of Timing Marks
Fig. 6 Timing Chain Case Cover Gaskets and O-Rings
Fig. 7 Install Crankshaft Oil Seal
Fig. 8 Installing Crankshaft Pulley
Ä 3.3/3.8L ENGINE 9 - 111
Page 1678 of 2438

(4) Using Tool C-4991 to remove oil seal (Fig. 9).
Be careful not to damage that crankshaft seal sur-
face of cover.
INSTALLATION (1) Install new seal by using Tool C-4992 (Fig. 7).
(2) Place seal into opening with seal spring to-
wards the inside of engine. Install seal until flush
with cover. (3) Install crankshaft pulley using plate L-4524.
Thrust Bearing/washer and 5.9 inch screw (Fig. 8). (4) Install drive belt (Refer to Cooling System
Group 7) for installation procedure. (5) Install inner splash shield and wheel.
CAMSHAFT
REMOVALÐENGINE REMOVED FROM VEHICLE
Remove intake manifold, cylinder head covers, cyl-
inder heads, timing chain case cover and timing
chain. (1) Remove rocker arm and shaft assemblies.
(2) Remove push rods and tappets; identify so each
part will be replaced in its original location. (3) Remove camshaft thrust plate (Fig. 10).
(4) Install a long bolt into front of camshaft to fa-
cilitate removal of the camshaft; remove camshaft,
being careful not to damage cam bearing with the
cam lobes.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate camshaft lobes and camshaft bearing
journals and insert the camshaft to within 2 inches
of its final position in cylinder block. Whenever an engine has been rebuilt or a new
camshaft or tappets have been installed, add one
pint of Chrysler Crankcase Conditioner or
equivalent to engine oil to aid in break in. The oil
mixture should be left in engine for a minimum
of 805km (500 miles) and drained at the next
normal oil change. (2) Install camshaft thrust plate with two screws as
shown in (Fig. 10). Tighten to 12 N Im (105 in. lbs.)
torque. (3) Rotate crankshaft so the timing arrow is to the
12 O'clock position. (4) Place timing chain around camshaft sprocket
and place the timing mark to the 6 O'clock position. (5) Align the dark colored links with the dot on the
camshaft sprocket, place timing chain around crank-
shaft sprocket with the dark colored link lined up with
the dot on the sprocket and install camshaft sprocket
into position. (6) Using straight edge to check alignment of timing
marks (Fig. 5). (7) Install the camshaft bolt. Tighten bolt to 54 N Im
(40 ft. lbs.). (8) Rotate crankshaft 2 revolutions. Timing marks
should line up. If timing marks do not line up, remove
cam sprocket and realign.
Fig. 9 Removing Crankshaft Oil Seal
Fig. 10 Camshaft Thrust Plate
Fig. 11 Camshaft and Sprocket Assembly
9 - 112 3.3/3.8L ENGINE Ä
Page 1679 of 2438

(9) Measure camshaft end play. End Play should
measure .0127 to .304 mm (.005 to .012 inches.) .310
mm (.012 inch. Max.). If not within limits install a new
thrust plate. (10) Each tappet reused must be installed in the
same position from which it was removed. When
camshaft is replaced, all of the tappets must be
replaced .
CAMSHAFT BEARINGSÐENGINE REMOVED FROM
VEHICLE
REMOVAL
(1) With engine completely disassembled, drive out
rear cam bearing core hole plug. (2) Install proper size adapters and horseshoe wash-
ers (part of Tool C-3132-A) at back of each bearing shell
to be removed and drive out bearing shells (Fig. 13).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install new camshaft bearings with Tool
C-3132-A by sliding the new camshaft bearing shell
over proper adapter. (2) Position rear bearing in the tool. Install horse-
shoe lock and by reversing removal procedure, care-
fully drive bearing shell into place. (3) Install remaining bearings in the same manner.
Bearings must be carefully aligned to bring oil holes
into full register with oil passages from the main
bearing. Number two bearing must index with the oil
passage to the left cylinder head and Number three
bearing must index with the oil passage to the right
cylinder head. If the camshaft bearing shell oil holes
are not in exact alignment, remove and reinstall them
correctly. Install a new core hole plug at the rear of
camshaft. Be sure this plug does not leak.
ENGINE CORE OIL AND CAM PLUGS
REMOVAL
Using a blunt tool such as a drift and a hammer,
strike the bottom edge of the cup plug. With the cup
plug rotated, grasp firmly with pliers or other suit-
able tool and remove plug (Fig. 14).
CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting as
restricted cooling can result and cause serious en-
gine problems.
INSTALLATION
Thoroughly clean inside of cup plug hole in cylin-
der block or head. Be sure to remove old sealer.
Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole with Loctite Stud
N' Bearing Mount or equivalent. Make certain the
new plug is cleaned of all oil or grease. Using proper
drive plug, drive plug into hole so that the sharp
edge of the plug is at least 0.5mm (.020 inch) inside
the lead-in chamfer. It is not necessary to wait for curing of the sealant.
The cooling system can be refilled and the vehicle
placed in service immediately.
Fig. 13 Removed Installation of Camshaft Bearings with Tool C-3132AÐTypical
Fig. 14 Core Hole Plug Removal
Fig. 12 Alignment of Timing Marks
Ä 3.3/3.8L ENGINE 9 - 113
Page 1680 of 2438
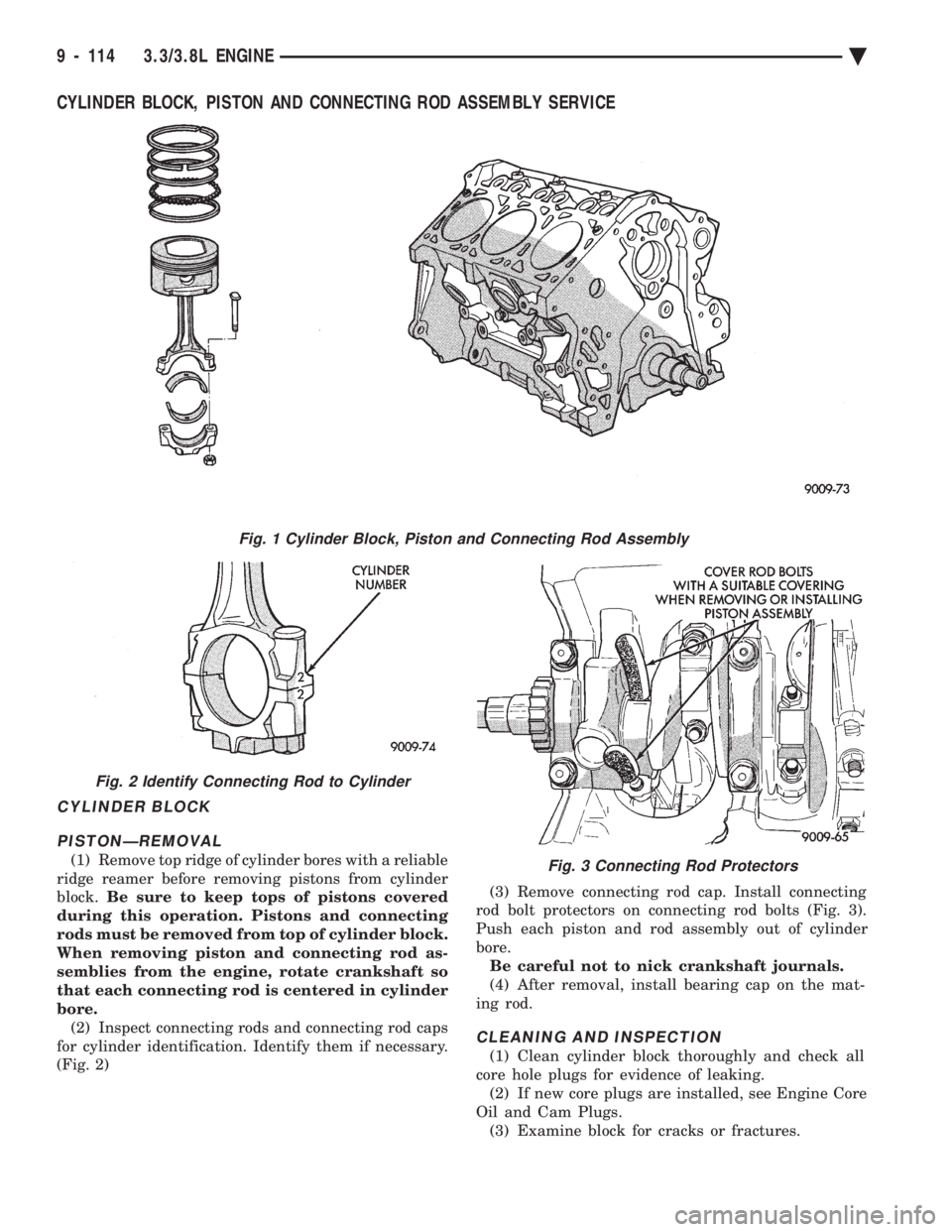
CYLINDER BLOCK, PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD ASSEMBLY SERVICE
CYLINDER BLOCK PISTONÐREMOVAL
(1) Remove top ridge of cylinder bores with a reliable
ridge reamer before removing pistons from cylinder
block. Be sure to keep tops of pistons covered
during this operation. Pistons and connecting
rods must be removed from top of cylinder block.
When removing piston and connecting rod as-
semblies from the engine, rotate crankshaft so
that each connecting rod is centered in cylinder
bore. (2) Inspect connecting rods and connecting rod caps
for cylinder identification. Identify them if necessary.
(Fig. 2) (3) Remove connecting rod cap. Install connecting
rod bolt protectors on connecting rod bolts (Fig. 3).
Push each piston and rod assembly out of cylinder
bore. Be careful not to nick crankshaft journals.
(4) After removal, install bearing cap on the mat-
ing rod.
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
(1) Clean cylinder block thoroughly and check all
core hole plugs for evidence of leaking. (2) If new core plugs are installed, see Engine Core
Oil and Cam Plugs. (3) Examine block for cracks or fractures.
Fig. 1 Cylinder Block, Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly
Fig. 2 Identify Connecting Rod to Cylinder
Fig. 3 Connecting Rod Protectors
9 - 114 3.3/3.8L ENGINE Ä