air condition CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2005 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: CARAVAN, Model: CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 288 of 2339

The BCM utilizes integrated circuitry and informa-
tion carried on the Programmable Communications
Interface (PCI) data bus network along with many
hard wired inputs to monitor many sensor and
switch inputs throughout the vehicle. In response to
those inputs, the internal circuitry and programming
of the BCM allow it to control and integrate many
electronic functions and features of the vehicle
through both hard wired outputs and the transmis-
sion of electronic message outputs to other electronic
modules in the vehicle over the PCI data bus.
OPERATION
The Body Control Module (BCM) supplies vehicle
occupants with visual and audible information and
controls various vehicle functions. To provide and
receive information, the BCM is interfaced to the
vehicle's serial bus communications network, referred
to as the Programmable Communications Interface
(PCI) bus.
This network consists of the;
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Transmission Control Module (TCM)
²Mechanical Instrument Cluster (MIC)
²Occupant Restraint Controller (ORC)
²Compass/Mini-Trip Computer (CMTC)
²Electronic Vehicle Information Center (EVIC)
²Controller Antilock Brake (CAB)
²HVAC Control Module
²Sliding Door Control Modules (driver and pas-
senger side doors)
²Power Liftgate Module (PLG)
²Audio system equipped with RAZ, RBU, RBK,
and RBB radios.
²Sentry Key Remote Entry Module (SKREEM).
²Side Impact Airbag Control Module (SIACM)²Memory Seat Module (MSM)
²Sentry Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM)
The BCM is operational when battery power is
supplied to the module.
The BCM provides the following features:
²Power Door Locks
²Automatic Door Locks
²Battery Protection - The BCM will automatically
turn off all exterior lamps after 3 minutes, and all
interior lamps after 15 minutes after the ignition is
turned off, if they are not turned off by the driver.
²Chime Control
²Compass/Mini-Trip support.
²Interior Lighting (Courtesy/Reading Lamps)
²BCM Diagnostic Reporting
²Electronic Liftgate Release (with Power Door
Locks)
²Exterior Lighting
²Headlamp Time Delay (with/without Automatic
Headlamps)
²Illuminated Entry
²Fade to Off Interior Lamps - This feature dims
the interior lighting (courtesy lamps) gradually if the
BCM does not receive any new inputs that would
cause the interior lamps to remain on.
²Pulse Width Modulated Instrument Panel Dim-
ming
²Door Lock Inhibit - This feature disables the
door lock functions if the key is in the ignition and
either front door is ajar. Pressing the Remote Keyless
Entry (RKE) lock/unlock button under these condi-
tions result in normal lock/unlock activation.
The BCM has the ability to LEARN additional fea-
tures in the vehicle, provided the appropriate switch
input and PCI data bus messages are received. Refer
to the LEARNED FEATURES table.
LEARNED FEATURES
FEATURE LEARNING KEY
REAR WIPER CONTROL ON HVAC CONTROL ON
INSTRUMENT PANELPCI BUS MESSAGE RECEIVED FROM HVAC
CONTROL
AUTOMATIC HEADLAMPS PCI MESSAGE FROM OVERHEAD OR HEADLAMP
SWITCH POSITION (AUTO)
REMOTE KEYLESS ENTRY SKREEM MESSAGE RECEIVED FROM MODULE
FRONT FOG LAMPS HEADLAMP SWITCH POSITION (PARK W/FRONT
FOG LAMPS)
POWER SLIDING DOOR PCI IFR RECEIVED FROM MODULE
THE BCM HAS FOUR SWITCH INPUTS FOR THE POWER SLIDING DOOR FEATURE; LOCATED IN THE
OVERHEAD CONSOLE ARE THE LEFT AND RIGHT SIDE SLIDING DOOR SWITCHES TO ACTIVATE EITHER
OR BOTH SLIDING DOORS UNDER THE PROPER CONDITIONS. ALSO ARE B-PILLAR SWITCHES LOCATED
ON THE LEFT AND RIGHT B-PILLAR POSTS.
POWER LIFTGATE PCI IFR RECEIVED FROM MODULE
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-3
BODY CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 296 of 2339
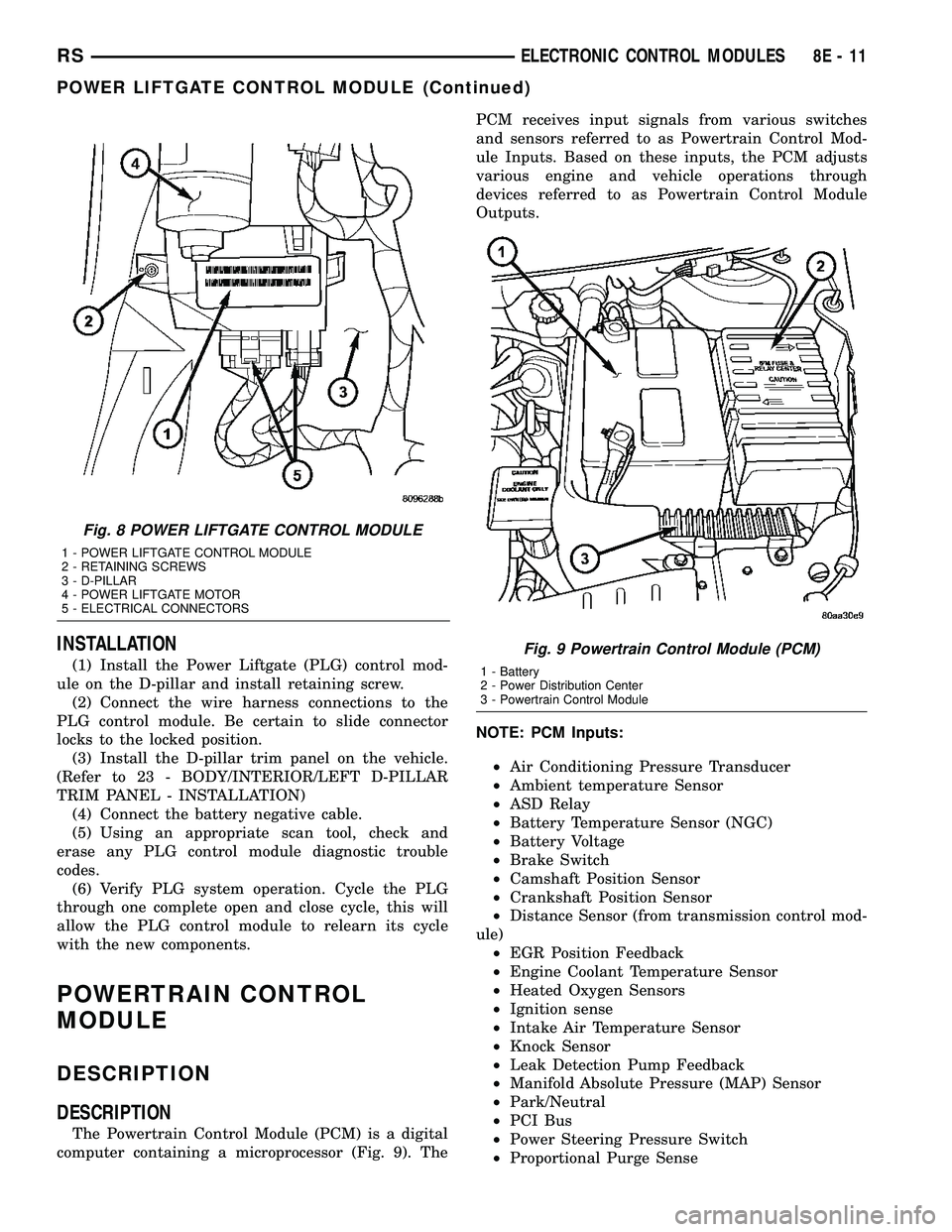
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the Power Liftgate (PLG) control mod-
ule on the D-pillar and install retaining screw.
(2) Connect the wire harness connections to the
PLG control module. Be certain to slide connector
locks to the locked position.
(3) Install the D-pillar trim panel on the vehicle.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/LEFT D-PILLAR
TRIM PANEL - INSTALLATION)
(4) Connect the battery negative cable.
(5) Using an appropriate scan tool, check and
erase any PLG control module diagnostic trouble
codes.
(6) Verify PLG system operation. Cycle the PLG
through one complete open and close cycle, this will
allow the PLG control module to relearn its cycle
with the new components.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL
MODULE
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is a digital
computer containing a microprocessor (Fig. 9). ThePCM receives input signals from various switches
and sensors referred to as Powertrain Control Mod-
ule Inputs. Based on these inputs, the PCM adjusts
various engine and vehicle operations through
devices referred to as Powertrain Control Module
Outputs.
NOTE: PCM Inputs:
²Air Conditioning Pressure Transducer
²Ambient temperature Sensor
²ASD Relay
²Battery Temperature Sensor (NGC)
²Battery Voltage
²Brake Switch
²Camshaft Position Sensor
²Crankshaft Position Sensor
²Distance Sensor (from transmission control mod-
ule)
²EGR Position Feedback
²Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
²Heated Oxygen Sensors
²Ignition sense
²Intake Air Temperature Sensor
²Knock Sensor
²Leak Detection Pump Feedback
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Park/Neutral
²PCI Bus
²Power Steering Pressure Switch
²Proportional Purge Sense
Fig. 8 POWER LIFTGATE CONTROL MODULE
1 - POWER LIFTGATE CONTROL MODULE
2 - RETAINING SCREWS
3 - D-PILLAR
4 - POWER LIFTGATE MOTOR
5 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
Fig. 9 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
1 - Battery
2 - Power Distribution Center
3 - Powertrain Control Module
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-11
POWER LIFTGATE CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 297 of 2339

²SCI Receive
²Speed Control
²Throttle Position Sensor
²Transmission Control Relay (Switched B+)
²Transmission Pressure Switches
²Transmission Temperature Sensor
²Transmission Input Shaft Speed Sensor
²Transmission Output Shaft Speed Sensor
²Transaxle Gear Engagement
²Vehicle Speed
NOTE: PCM Outputs:
²Air Conditioning Clutch Relay
²Automatic Shut Down (ASD) and Fuel Pump
Relays
²Data Link Connector (PCI and SCI Transmit)
²Double Start Override
²EGR Solenoid
²Fuel Injectors
²Generator Field
²High Speed Fan Relay
²Idle Air Control Motor
²Ignition Coils
²Leak Detection Pump
²Low Speed Fan Relay
²MTV Actuator
²Proportional Purge Solenoid
²SRV Valve
²Speed Control Relay
²Speed Control Vent Relay
²Speed Control Vacuum Relay
²8 Volt Output
²5 Volt Output
²Torque Reduction Request
²Transmission Control Relay
²Transmission Solenoids
²Vehicle Speed
Based on inputs it receives, the powertrain control
module (PCM) adjusts fuel injector pulse width, idle
speed, ignition timing, and canister purge operation.
The PCM regulates the cooling fans, air conditioning
and speed control systems. The PCM changes gener-
ator charge rate by adjusting the generator field.
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width (air-fuel
ratio) based on the following inputs.
²Battery Voltage
²Intake Air Temperature Sensor
²Engine Coolant Temperature
²Engine Speed (crankshaft position sensor)
²Exhaust Gas Oxygen Content (heated oxygen
sensors)
²Manifold Absolute Pressure
²Throttle Position
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed through the
idle air control motor based on the following inputs.
²Brake Switch²Engine Coolant Temperature
²Engine Speed (crankshaft position sensor)
²Park/Neutral
²Transaxle Gear Engagement
²Throttle Position
²Vehicle Speed
The PCM adjusts ignition timing based on the fol-
lowing inputs.
²Intake Air Temperature
²Engine Coolant Temperature
²Engine Speed (crankshaft position sensor)
²Knock Sensor
²Manifold Absolute Pressure
²Park/Neutral
²Transaxle Gear Engagement
²Throttle Position
The automatic shut down (ASD) and fuel pump
relays are mounted externally, but turned on and off
by the powertrain control module through the same
circuit.
The camshaft and crankshaft signals are sent to
the powertrain control module. If the PCM does not
receive both signals within approximately one second
of engine cranking, it deactivates the ASD and fuel
pump relays. When these relays are deactivated,
power is shut off to the fuel injectors, ignition coils,
fuel pump and the heating element in each oxygen
sensor.
The PCM contains a voltage converter that
changes battery voltage to a regulated 8.0 volts. The
8.0 volts power the camshaft position sensor, crank-
shaft position sensor and vehicle speed sensor. The
PCM also provides a 5.0 volts supply for the engine
coolant temperature sensor, intake air temperature
sensor, manifold absolute pressure sensor and throt-
tle position sensor.
The PCM engine control strategy prevents reduced
idle speeds until after the engine operates for 320 km
(200 miles). If the PCM is replaced after 320 km (200
miles) of usage, update the mileage in new PCM. Use
the DRBIIItscan tool to change the mileage in the
PCM. Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic
Manual and the DRBIIItscan tool.
TRANSMISSION CONTROL
CLUTCH VOLUME INDEX (CVI)
An important function of the PCM is to monitor
Clutch Volume Index (CVI). CVIs represent the vol-
ume of fluid needed to compress a clutch pack.
The PCM monitors gear ratio changes by monitor-
ing the Input and Output Speed Sensors. The Input,
or Turbine Speed Sensor sends an electrical signal to
the PCM that represents input shaft rpm. The Out-
put Speed Sensor provides the PCM with output
shaft speed information.
8E - 12 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRS
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 300 of 2339

The power grounds are used to control the ground
side relays, solenoids, ignition coil or injectors. The
signal ground is used for any input that uses sensor
return for ground, and the ground side of any inter-
nal processing component.
The PCM case is shielded to prevent RFI and EMI.
The PCM case is grounded and must be firmly
attached to a good, clean body ground.
Internally all grounds are connected together, how-
ever there is noise suppression on the sensor ground.
For EMI and RFI protection the housing and cover
are also grounded separately from the ground pins.
OPERATION - 5 VOLT SUPPLY - PCM OUTPUT
The PCM supplies 5 volts to the following sensors:
²A/C pressure transducer
²Ambient Temperature sensor
²Battery temperature
²Camshaft Position Sensor (NGC)
²Crankshaft Position Sensor (NGC)
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Inlet Air Temperature Sensor
²Knock sensor
²Linear EGR solenoid (if equipped)
²Manifold absolute pressure sensor
²Oil Pressure Switch
²Throttle position sensor
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - OBTAINING
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
BULB CHECK
Key on: Bulb illuminated until vehicle starts, as
long as all once per trip (readiness) monitors com-
pleted. If monitors havenotbeen completed, then:
Key on: bulb check for about 5 to 8 seconds, lamp
then flashes if once per trip (readiness) monitors
havenotbeen completed until vehicle is started,
then MIL is extinguished.
OBTAINING DTC'S USING DRB SCAN TOOL
(1) Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
(2) Turn the ignition switch on and access the
ªRead Faultº screen.
(3) Record all the DTC's and ªfreeze frameº infor-
mation shown on the DRB scan tool.
(4) To erase DTC's, use the ªErase Trouble Codeº
data screen on the DRB scan tool.Do not erase any
DTC's until problems have been investigated
and repairs have been performed.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PINION FACTOR
SETTING
NOTE: This procedure must be performed if the
PCM has been replaced with a NEW or replacement
unit. Failure to perform this procedure will result in
an inoperative or improperly calibrated speedome-
ter.
The vehicle speed readings for the speedometer are
taken from the output speed sensor. The PCM must
be calibrated to the different combinations of equip-
ment (final drive and tires) available. Pinion Factor
allows the technician to set the Powertrain Control
Module initial setting so that the speedometer read-
ings will be correct. To properly read and/or reset the
Pinion Factor, it is necessary to use a DRBIIItscan
tool.
(1) Plug the DRBIIItscan tool into the diagnostic
connector located under the instrument panel.
(2) Select the Transmission menu.
(3) Select the Miscellaneous menu.
(4) Select Pinion Factor. Then follow the instruc-
tions on the DRBIIItscan tool screen.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - QUICK LEARN
PROCEDURE
The quick learn procedure requires the use of the
DRBIIItscan tool. This program allows the PCM to
recalibrate itself. This will provide the best possible
transaxle operation.
NOTE: The quick learn procedure should be per-
formed if any of the following procedures are per-
formed:
²Transaxle Assembly Replacement
²Powertrain Control Module Replacement
²Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly Replacement
²Clutch Plate and/or Seal Replacement
²Valve Body Replacement or Recondition
To perform the Quick Learn Procedure, the follow-
ing conditions must be met:
²The brakes must be applied
²The engine speed must be above 500 rpm
²The throttle angle (TPS) must be less than 3
degrees
²The shift lever position must stay until
prompted to shift to overdrive
²The shift lever position must stay in overdrive
after the Shift to Overdrive prompt until the
DRBIIItindicates the procedure is complete
²The calculated oil temperature must be above
60É and below 200É
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-15
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 308 of 2339

BATTERY SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
THE BATTERY SEEMS
WEAK OR DEAD WHEN
ATTEMPTING TO START
THE ENGINE.1. The electrical system
ignition-off draw is excessive.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY
SYSTEM/BATTERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE
- IGNITION-OFF DRAW TEST) for the proper test
procedures. Repair the excessive ignition-off
draw, as required.
2. The charging system is
inoperative.2. Determine if the charging system is performing
to specifications. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
CHARGING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) for
additional charging system diagnosis and testing
procedures. Repair the inoperative charging
system, as required.
3. The battery is discharged. 3. Determine the battery state-of-charge using the
Micro 420 battery tester. Refer to the Standard
Procedures in this section for additional test
procedures. Charge the inoperative battery, as
required.
4. The battery terminal
connections are loose or
corroded.4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY
SYSTEM/CABLES - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
for the proper battery cable diagnosis and testing
procedures. Clean and tighten the battery
terminal connections, as required.
5. The battery has an
incorrect size or rating for
this vehicle.5. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM
- SPECIFICATIONS) for the proper size and
rating. Replace an incorrect battery, as required.
6. The battery is inoperative. 6. Test the battery using the Micro 420 battery
tester. Refer to the Standard Procedures in this
section for additional test procedures. Replace
the inoperative battery, as required.
7. The starting system is
inoperative.7. Determine if the starting system is performing
to specifications. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) for the
proper starting system diagnosis and testing
procedures. Repair the inoperative starting
system, as required.
8. The battery is physically
damaged.8. Inspect the battery for loose terminal posts or a
cracked and leaking case. Replace the damaged
battery, as required.
RSBATTERY SYSTEM8F-3
BATTERY SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 309 of 2339
BATTERY SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
THE BATTERY STATE OF
CHARGE CANNOT BE
MAINTAINED.1. The battery has an
incorrect size or rating for
this vehicle.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM
- SPECIFICATIONS) for the proper specifications.
Replace an incorrect battery, as required.
2. The battery terminal
connections are loose or
corroded.2. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY
SYSTEM/CABLES - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
for the proper cable diagnosis and testing
procedures. Clean and tighten the battery
terminal connections, as required.
3. The electrical system
ignition-off draw is excessive.3. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY
SYSTEM/BATTERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE
- IGNITION-OFF DRAW TEST) for the proper test
procedures. Repair the inoperative electrical
system, as required.
4. The battery is inoperative. 4. Test the battery using the Micro 420 battery
tester. Refer to Standard Procedures for
additional test procedures. Replace the
inoperative battery, as required.
5. The starting system is
inoperative.5. Determine if the starting system is performing
to specifications. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) for the
proper starting system diagnosis and testing
procedures. Repair the inoperative starting
system, as required.
6. The charging system is
inoperative.6. Determine if the charging system is performing
to specifications. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
CHARGING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) for
charging system diagnosis and testing
procedures. Repair the inoperative charging
system, as required.
7. Electrical loads exceed the
output of the charging
system.7. Inspect the vehicle for aftermarket electrical
equipment which might cause excessive electrical
loads.
8. Slow driving or prolonged
idling with high-amperage
draw loads in use.8. Advise the vehicle operator, as required.
THE BATTERY WILL NOT
ACCEPT A CHARGE.1. The battery is inoperative. 1. Test the battery using the Micro 420 battery
tester.. Charge or replace the inoperative battery,
as required.
8F - 4 BATTERY SYSTEMRS
BATTERY SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 327 of 2339

ULES/POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE -
DESCRIPTION) section for more DTC information.
The Charging system ªBatteryº light indicates
problems with the charging system (voltage too high/
low, generator failure, etc.). If an extreme condition is
indicated, the lamp will be illuminated. The signal to
activate the lamp is sent via the PCI bus circuits.
The lamp is located on the instrument panel. Refer
to the Instrument Cluster section for additional infor-
mation.
The PCM uses the ambient air temperature sensor
to control the charge system voltage. This tempera-
ture, along with data from monitored line voltage, is
used by the PCM to vary the battery charging rate.
The system voltage is higher at cold temperatures
and is gradually reduced as the calculated battery
temperature increases.
The ambient temperature sensor is used to control
the battery voltage based upon ambient temperature
(approximation of battery temperature). The PCM
maintains the optimal output of the generator by
monitoring battery voltage and controlling it to a
range of 13.5 - 14.7 volts based on battery tempera-
ture.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
critical input and output circuits of the charging sys-
tem, making sure they are operational. A Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) is assigned to each input and
output circuit monitored by the OBD system. Some
circuits are checked continuously and some are
checked only under certain conditions.
If the OBD system senses that a monitored circuit
is bad, it will put a DTC into electronic memory. The
DTC will stay in electronic memory as long as the
circuit continues to be bad. The PCM is programmed
to clear the memory after 40 good trip if the problem
does not occur again.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A DTC description can be read using the DRBIIIt
scan tool. Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diag-
nostic Procedures manual for information.
A DTC does not identify which component in a cir-
cuit is bad. Thus, a DTC should be treated as a
symptom, not as the cause for the problem. In some
cases, because of the design of the diagnostic test
procedure, a DTC can be the reason for another DTC
to be set. Therefore, it is important that the test pro-
cedures be followed in sequence, to understand what
caused a DTC to be set.ERASING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
The DRBIIItScan Tool must be used to erase a
DTC.
The following procedures may be used to diagnose
the charging system if:
²the check gauges lamp or battery lamp is illumi-
nated with the engine running
²the voltmeter (if equipped) does not register
properly
²an undercharged or overcharged battery condi-
tion occurs.
Remember that an undercharged battery is often
caused by:
²accessories being left on with the engine not
running
²a faulty or improperly adjusted switch that
allows a lamp to stay on. Refer to Ignition-Off Draw
Test (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/
BATTERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
²loose generator belt.
INSPECTION
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
critical input and output circuits of the charging sys-
tem, making sure they are operational. A Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) is assigned to each input and
output circuit monitored by the On-Board Diagnostic
(OBD) system. Some charging system circuits are
checked continuously, and some are checked only
under certain conditions.
Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Codes in; Powertrain
Diagnostic manual for more DTC information. This
will include a complete list of DTC's including DTC's
for the charging system.
To perform a complete test of the charging system,
refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Proce-
dures service manual and the DRBIIItscan tool.
Perform the following inspections before attaching
the scan tool.
(1) Inspect the battery condition. Refer to the Bat-
tery section (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY
SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) for proce-
dures.
(2) Inspect condition of battery cable terminals,
battery posts, connections at engine block, starter
solenoid and relay. They should be clean and tight.
Repair as required.
(3) Inspect all fuses in both the fuseblock and
Power Distribution Center (PDC) or IPM (if
equipped) for tightness in receptacles. They should be
properly installed and tight. Repair or replace as
required.
(4) Inspect generator mounting bolts for tightness.
Replace or tighten bolts if required. Refer to the Gen-
erator Removal/Installation section of this group for
8F - 22 CHARGINGRS
CHARGING (Continued)
Page 328 of 2339
torque specifications (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
CHARGING - SPECIFICATIONS).
(5) Inspect generator drive belt condition and ten-
sion. Tighten or replace belt as required. Refer to
Belt Tension Specifications(Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ACCESSORY DRIVE - SPECIFICATIONS).
(6) Inspect decoupler pulley (if equipped). Ensure
decoupler pulley is driving the alternator rotor.(7) Inspect automatic belt tensioner (if equipped).
Refer to the Cooling System for more information.
(8) Inspect generator electrical connections at gen-
erator field, battery output, and ground terminal (if
equipped). Also check generator ground wire connec-
tion at engine (if equipped). They should all be clean
and tight. Repair as required.
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERATOR
Type Engine Minimun Test
Amperage
Denso 2.4 L 80 Amp (HOT)
Denso 3.3/3.8L 100 Amp or 115
Amp (HOT)
Test Specification:
Type Engine Minimun Test
Amperage
1. Engine RPM : 2500 RPM 20 RPM (HOT)
2. Voltage Output : 14.0 V 0.5 V
3. Field Current : 5 amps 0.1 amps
Part number is located on the side of the generator.
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Battery Hold Down Clamp
Bolt20 14.7 180
Generator B+ Nut 12.4 9.2 110
Battery Terminal Nut 4 35
Generator Mounting Bolt
2.4L28.2 20.8 250
Generator Mounting Bolts
3.3/3.8L54.2 40
Starter Solenoid Battery
Nut 3.3/3.8L11.3 8.3 100
Generator Decoupler 109.8 81
SPECIFICATIONS - BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR
ÉC ÉF K-Ohms Min. K-Ohms Max.
(40) (40) 291.4 381.7
(20) (4) 85.8 108.4
20 68 11.4 13.6
25 77 9.1 10.9
120 248 0.37 0.41
130 266 0.28 0.32
RSCHARGING8F-23
CHARGING (Continued)
Page 337 of 2339
the battery, if required. Refer to the Battery section
for more information.
²Ignition Switch- Visually inspect the ignition
switch for indications of physical damage and loose
or corroded wire harness connections.
²Transmission Range Sensor or Park/Neu-
tral Switch- Visually inspect the transmission
range sensor for indications of physical damage and
loose or corroded wire harness connections.
²Starter Relay- Visually inspect the starter
relay for indications of physical damage and loose or
corroded wire harness connections.
²Starter Motor- Visually inspect the starter
motor for indications of physical damage and loose or
corroded wire harness connections.²Starter Solenoid- Visually inspect the starter
solenoid for indications of physical damage and loose
or corroded wire harness connections.
²Wiring- Visually inspect the wire harness for
damage. Repair or replace any faulty wiring, as
required. Check for loose or corroded wire harness
connections at main engine ground and remote jump
post.
²Power Distribution Center (PDC)- Visually
inspect the B+ connections at the PDC for physical
damage and loose or corroded harness connections.
STARTING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
STARTER FAILS
TO ENGAGE.1. BATTERY
DISCHARGED OR
FAULTY.1. REFER TO THE BATTERY SECTION FOR MORE
INFORMATION. CHARGE OR REPLACE BATTERY, IF
REQUIRED.
2. STARTING CIRCUIT
WIRING FAULTY.2. REFER TO FEED CIRCUIT RESISTANCE TEST AND FEED
CIRCUIT TEST IN THIS SECTION.
3. STARTER RELAY
FAULTY.3. REFER TO RELAY TEST, IN THIS SECTION. REPLACE
RELAY, IF NECESSARY.
4. IGNITION SWITCH
FAULTY.4. REFER TO IGNITION SWITCH TEST, IN THE STEERING
SECTION OR 8 WIRING DIAGRAMS. REPLACE SWITCH, IF
NECESSARY.
5. PARK/NEUTRAL
POSITION SWITCH
(AUTO TRANS) FAULTY
OR MIS-ADJUSTED.5. REFER PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH TEST, IN THE
TRANSAXLE. SECTION FOR MORE INFORMATION. REPLACE
SWITCH, IF NECESSARY.
6. CLUTCH INTERLOCK
SWITCH (MAN TRANS)
FAULTY.6. REFER TO CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH TEST, IN
THE CLUTCH. SECTION. REPLACE SWITCH, IF NECESSARY.
7. STARTER SOLENOID
FAULTY.7. REFER TO SOLENOID TEST, IN THIS SECTION. REPLACE
STARTER ASSEMBLY, IF NECESSARY.
8. STARTER ASSEMBLY
FAULTY.8. IF ALL OTHER STARTING SYSTEM COMPONENTS AND
CIRCUITS CHECK OK, REPLACE STARTER ASSEMBLY.
9. FAULTY TEETH ON
RING GEAR.9. ROTATE FLYWHEEL 360É, AND INSPECT TEETH AND RING
GEAR REPLACED IF DAMAGED.
10. PCM DOUBLE
START OVERRIDE
OUTPUT FAILURE.10. REFER TO PCM DIAGNOSTIC. CHECK FOR CONTINUITY
BETWEEN PCM AND TERMINAL 85. REPAIR OPEN CIRCUIT
AS REQUIRED. IF OK, PCM MAY BE DEFECTIVE.
STARTER
ENGAGES,
FAILS TO TURN
ENGINE.1. BATTERY
DISCHARGED OR
FAULTY.1. REFER TO THE BATTERY SECTION FOR MORE
INFORMATION. CHARGE OR REPLACE BATTERY AS
NECESSARY.
8F - 32 STARTINGRS
STARTING (Continued)
Page 338 of 2339
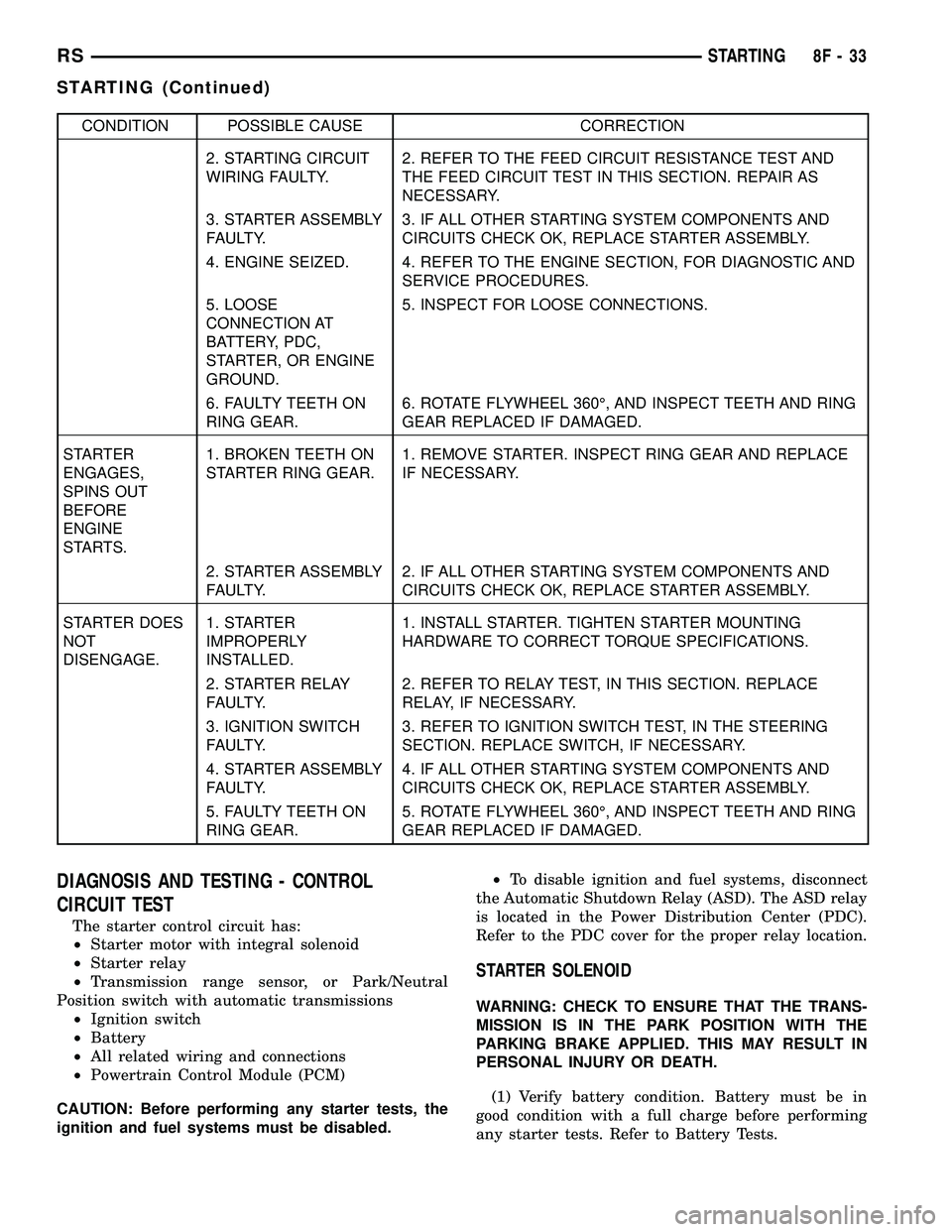
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
2. STARTING CIRCUIT
WIRING FAULTY.2. REFER TO THE FEED CIRCUIT RESISTANCE TEST AND
THE FEED CIRCUIT TEST IN THIS SECTION. REPAIR AS
NECESSARY.
3. STARTER ASSEMBLY
FAULTY.3. IF ALL OTHER STARTING SYSTEM COMPONENTS AND
CIRCUITS CHECK OK, REPLACE STARTER ASSEMBLY.
4. ENGINE SEIZED. 4. REFER TO THE ENGINE SECTION, FOR DIAGNOSTIC AND
SERVICE PROCEDURES.
5. LOOSE
CONNECTION AT
BATTERY, PDC,
STARTER, OR ENGINE
GROUND.5. INSPECT FOR LOOSE CONNECTIONS.
6. FAULTY TEETH ON
RING GEAR.6. ROTATE FLYWHEEL 360É, AND INSPECT TEETH AND RING
GEAR REPLACED IF DAMAGED.
STARTER
ENGAGES,
SPINS OUT
BEFORE
ENGINE
STARTS.1. BROKEN TEETH ON
STARTER RING GEAR.1. REMOVE STARTER. INSPECT RING GEAR AND REPLACE
IF NECESSARY.
2. STARTER ASSEMBLY
FAULTY.2. IF ALL OTHER STARTING SYSTEM COMPONENTS AND
CIRCUITS CHECK OK, REPLACE STARTER ASSEMBLY.
STARTER DOES
NOT
DISENGAGE.1. STARTER
IMPROPERLY
INSTALLED.1. INSTALL STARTER. TIGHTEN STARTER MOUNTING
HARDWARE TO CORRECT TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS.
2. STARTER RELAY
FAULTY.2. REFER TO RELAY TEST, IN THIS SECTION. REPLACE
RELAY, IF NECESSARY.
3. IGNITION SWITCH
FAULTY.3. REFER TO IGNITION SWITCH TEST, IN THE STEERING
SECTION. REPLACE SWITCH, IF NECESSARY.
4. STARTER ASSEMBLY
FAULTY.4. IF ALL OTHER STARTING SYSTEM COMPONENTS AND
CIRCUITS CHECK OK, REPLACE STARTER ASSEMBLY.
5. FAULTY TEETH ON
RING GEAR.5. ROTATE FLYWHEEL 360É, AND INSPECT TEETH AND RING
GEAR REPLACED IF DAMAGED.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CONTROL
CIRCUIT TEST
The starter control circuit has:
²Starter motor with integral solenoid
²Starter relay
²Transmission range sensor, or Park/Neutral
Position switch with automatic transmissions
²Ignition switch
²Battery
²All related wiring and connections
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
CAUTION: Before performing any starter tests, the
ignition and fuel systems must be disabled.²To disable ignition and fuel systems, disconnect
the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The ASD relay
is located in the Power Distribution Center (PDC).
Refer to the PDC cover for the proper relay location.
STARTER SOLENOID
WARNING: CHECK TO ENSURE THAT THE TRANS-
MISSION IS IN THE PARK POSITION WITH THE
PARKING BRAKE APPLIED. THIS MAY RESULT IN
PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH.
(1) Verify battery condition. Battery must be in
good condition with a full charge before performing
any starter tests. Refer to Battery Tests.
RSSTARTING8F-33
STARTING (Continued)