window CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996Pages: 1938, PDF Size: 55.84 MB
Page 1868 of 1938

SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS
WARNING: WEAR EYE PROTECTION WHEN SER-
VICING THE AIR CONDITIONING REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM. SERIOUS EYE INJURY CAN RESULT
FROM EYE CONTACT WITH REFRIGERANT. IF EYE
CONTACT IS MADE, SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION
IMMEDIATELY.
DO NOT EXPOSE REFRIGERANT TO OPEN
FLAME. POISONOUS GAS IS CREATED WHEN
REFRIGERANT IS BURNED. AN ELECTRONIC TYPE
LEAK DETECTOR IS RECOMMENDED.
LARGE AMOUNTS OF REFRIGERANT RELEASED
IN A CLOSED WORK AREA WILL DISPLACE THE
OXYGEN AND CAUSE SUFFOCATION.
THE EVAPORATION RATE OF REFRIGERANT AT
AVERAGE TEMPERATURE AND ALTITUDE IS
EXTREMELY HIGH. AS A RESULT, ANYTHING THAT
COMES IN CONTACT WITH THE REFRIGERANT
WILL FREEZE. ALWAYS PROTECT SKIN OR DELI-
CATE OBJECTS FROM DIRECT CONTACT WITH
REFRIGERANT. R-134a SERVICE EQUIPMENT OR
VEHICLE A/C SYSTEM SHOULD NOT BE PRES-
SURE TESTED OR LEAK TESTED WITH COM-
PRESSED AIR.
SOME MIXTURES OF AIR and R-134a HAVE BEEN
SHOWN TO BE COMBUSTIBLE AT ELEVATED
PRESSURES. THESE MIXTURES ARE POTENTIALLY
DANGEROUS AND MAY RESULT IN FIRE OR
EXPLOSION CAUSING INJURY OR PROPERTY
DAMAGE.
ANTIFREEZE IS AN ETHYLENE GLYCOL BASE
COOLANT AND IS HARMFUL IF SWALLOWED OR
INHALED. SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION IMMEDI-
ATELY IF SWALLOWED OR INHALED. DO NOT
STORE IN OPEN OR UNMARKED CONTAINERS.
WASH SKIN AND CLOTHING THOROUGHLY AFTER
COMING IN CONTACT WITH ETHYLENE GLYCOL.
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN AND PETS.
DO NOT OPEN A COOLING SYSTEM WHEN THE
ENGINE IS AT RUNNING TEMPERATURE. PER-
SONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
CAUTION: The engine cooling system is designed
to develop internal pressure of 97 to 123 kPa (14 to
18 psi). Allow the vehicle to cool a minimum of 15
minutes before opening the cooling system. Refer
to Group 7, Cooling System.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
AIR DISTRIBUTION DUCTS
The air distribution ducts for the A/C, Heater,
Defroster, and Second Seating Air Distribution arenot serviceable in vehicle. The procedures for service
of these ducts are covered in Group 8E, Instrument
Panel and Gauges.
The only ducts that are serviceable in the vehicle
are the side window demister ducts and the ducts
that feed the front door outlets for the first rear pas-
senger(s) seating. To service the door ducts refer to
Group 23, Body.
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER
The A/C Pressure Transducer (Fig. 1) monitors the
refrigerant gas pressure on the high side of the sys-
tem. The transducer is located on the liquid line. The
pressure transducer turns off the voltage to the com-
pressor clutch coil when refrigerant gas pressure
drops to levels that could damage the compressor.
The transducer also is used to adjust condenser fan
speeds and will turn off compressor at high refriger-
ant pressures. The pressure transducer is a sealed
factory calibrated unit. It must be replaced if defec-
tive. O-ring replacement is required whenever the
pressure transducer is serviced. Be sure to use the
O-ring specified for the transducer.
A/C SERVICE PORTS
The A/C service port valve cores are located within
the A/C lines. The High Side (Discharge) valve ser-
vice port is located on the liquid line near the right
strut tower. The Low Side (Suction) valve service
port is located on the suction line near the compres-
sor.
The High Side service port is a two piece port and
is serviceable. The Low Side service port is not ser-
viceable, and the suction line would have to be
replaced.
COMPRESSOR
The A/C compressor for the 2.5L Turbo Diesel, is
located on the front side of the engine block. It is
mounted to the engine block by four bolts. The com-
Fig. 1 A/C Pressure Transducer
24 - 2 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONINGNS/GS
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 1870 of 1938

and washer operation, front & rear window defogger,
recirculation door operation, and A/C compressor
operation if equipped. Refer to Group 8E, Instrument
Panel and Systems for service procedures.
The rear blower speed switch is serviced separately
from the control head.
SIDE DOOR HEATER A/C OUTLETS
The driver's and passenger side doors have supple-
mental air outlets and duct work. The air is chan-
neled from the instrument panel to the door duct and
either to the lower floor or upper door outlets (Fig.
3). The air can be adjusted to blow on the first rear
passenger seat(s).
SIDE WINDOW DEMISTER
The side window demisters direct air from the
heater assembly. The outlets are located on the top
forward corners of the front door panels (Fig. 4). The
demisters operate when the control mode selector is
on FLOOR, MIX or DEFROST setting.
SYSTEM AIRFLOW
The system pulls outside (ambient) air through the
cowl opening at the base of the windshield. Then it
goes into the plenum chamber above the heaterÐA/C
unit housing. On air conditioned vehicles, the air
passes through the evaporator. At this point the air
flow can be directed either through or around the
heater core. This is done by adjusting the blend- air
door with the TEMP control on the control head. An
optional zone control HVAC control module is available.
This unit has dual blend-air doors that can be regu-
lated independently of each other. The temperature set-
ting can be different from driver's side to passenger
side. After the air passes the blend-air door(s), the air
flow can then be directed from the Panel, Floor, and
Defrost outlets. Air flow velocity can be adjusted with
the blower speed selector switch on the control head.
Ambient air intake can be shut off by closing the
recirculating air door. This will recirculate the air
that is already inside the vehicle. This is done by
depressing the Recirc. button on the control head. On
air conditioned vehicles, moving the control to Mix or
Defrost depresses the A/C button and will engage the
compressor. This will send refrigerant through the
evaporator, and remove heat and humidity from the
air before it goes through the heater core.
CAUTION: In cold weather, use of the Recirculation
mode may lead to excessive window fogging. The
Recirculation mode is automatically deactivated in
Mix and Defrost modes to improve window clearing
operation.
SYSTEM OIL LEVEL
It is important to have the correct amount of oil in
the A/C system to ensure proper lubrication of the
compressor. Too little oil will result in damage to the
compressor. Too much oil will reduce the cooling
Fig. 2 HVAC Control Module
Fig. 3 Door Outlets
Fig. 4 Demister Inlet
24 - 4 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONINGNS/GS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1873 of 1938

COOLDOWN TEST ENTRY
TO INITIATE TESTS:
²Set Blower motor ON HIGH
²Set Mode position to Panel
²Open all A/C outlets
²Set Temperature to Cold (Both slide pots if
equipped)
²Depress WASH and A/C simultaneously for 5
Seconds
NOTE: Prior to start of test, If the evaporator is
already cold, the system will fail test. To correct,
operate system with A/C OFF and the blower motor
ON high for three minutes prior to starting test.
RESULTS:
²All LED's will turn on for 5 Seconds
²Cooldown Test is running when A/C and
RECIRC. are alternately flashing. If A/C and
RECIRC. are flashing simultaneously, Cooldown has
failed.
CALIBRATION DIAGNOSTICS AND
COOLDOWN ABORT
Test can be aborted by doing one of the following:
²Depressing Rear Window Defogger, RECIRC and
Rear Wiper buttons.²Cycling Ignition OFF and then ON.
²Control will automatically abort after 15 min-
utes from the time Calibration Diagnostics and
Cooldown was entered.
The HVAC control module will return to normal
operation or may indicate unsuccessful Calibration
Diagnostics or Cooldown test by LED's flashing
simultaneously.
EEPROM DATA
Calibration Diagnostics, Cooldown Status and
evaporator temperature Fin Sensor values are stored
in an EEPROM memory internal to the control. The
microcomputer within the HVAC control module uses
this information:
²To determine if Cooldown needs to run
²For proper position of the Heater-A/C unit
assembly doors
ACTUATOR CALIBRATION AND
DIAGNOSTICS.
NOTE: Do not run actuators unless they are prop-
erly mounted on the HVAC control module.
Actuator end point calibration takes approximately
60 seconds. The REAR WIPER and INTERMITTENT
LED's will flash alternately during the test. The con-
trol will cycle the Blend actuator(s) to the Heat stop
first then back to Cold. After the Blend actuator(s)
have been calibrated the Mode actuator will be cycled
to Defrost and then to Panel. Successful calibration
is defined as actuator travel falling within their min-
imum and maximum limits.
BLEND/PASSENGER ACTUATOR BACKGROUND
The Blend/Passenger Actuator can move the tem-
perature door in two directions. When the voltage at
Pin 12 of the control module is high, about 11.5 volts,
and the voltage at Pin 17 is low, about 1.5 volts, the
door will move towards the Heat position. When Pin
17 is High and Pin 12 is Low the door will move
towards the Cold position. When both Pins are high
or both Pins are low, the actuator will not move. The
Blend/Passenger feedback signal is a voltage signal
that is supplied by the actuator to the control. The
signal will be about 4.0 volts in the Heat position
and 1.0 volt in the Cold position. As the position of
the Blend/Passenger actuator changes, so will the
feedback signal. The feedback signal is necessary for
the correct positioning of the temperature door.
DRIVER ACTUATOR BACKGROUND
The Driver Actuator can move the temperature
door in two directions. When the voltage at Pin 15 of
the control module is high, about 11.5 volts, and the
voltage at Pin 13 is low, about 1.5 volts the door will
LED'S PASS/FAILCORRECTIVE
ACTION
NO LED'S
FLASHING-
NORMAL
OPERATIONPASSED
CALIBRATION,
DIAGNOSTICS
AND
COOLDOWNNONE
REAR WIPER
AND
INTERMITTENT
LED'S FLASH
SIMULTANEOUSLYFAILED
CALIBRATION
DIAGNOSTICSRUN
CALIBRATION
TEST
A/C AND RECIRC
LED'S FLASH
SIMULTANEOUSLYFAILED
COOLDOWNRUN
COOLDOWN
TEST
REAR WIPER
AND
INTERMITTENT
LED'S ARE
FLASHING
SIMULTANEOUSLY
A/C AND RECIRC
LED'S ARE
FLASHING
SIMULTANEOUSLYFAILED
CALIBRATION,
DIAGNOSTICS
AND FAILED
COOLDOWN
TESTRUN
CALIBRATION
TEST
NS/GSHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1877 of 1938

²No charge
²Compressor not operating
Verify that the test was done with the evaporator
at room temperature. The test consists of starting
the compressor and measuring the time it takes for
the evaporator temperature to fall 7ÉC (20ÉF). If the
compressor has been running, the evaporator is cold
already and will not be capable of falling 7ÉC (20ÉF).
If the test was run with a cold evaporator, turn A/C
off and turn the blower motor switch to high position
for 3 to 5 minutes till the evaporator is to room tem-
perature. Then repeat the Calibration Diagnostic and
Cooldown test.
If refrigerant system is performing properly and
the system will not pass test. Repeat the Calibration
Diagnostic and Cooldown test to determine if the
evaporator temperature FIN sensor has developed an
open or a short circuit. If the HVAC control module
still passes Calibration test, verify Cooldown test
manually with a pocket thermometer. The outlet air
temperature must drop at least 7ÉC (20ÉF) within
two minutes. If the vehicle passes with the manual
thermometer, take HVAC control to level 4 (evapora-
tor probe temperature readout) and repeat the
Cooldown test. Ensure the evaporator is at room tem-
perature before starting test. Check if evaporator
probe will drop the temperature 7ÉC (20ÉF) in two
minutes. If the Evaporator Probe is found to be
faulty, check that the sensor is positioned in the
evaporator fins properly. If not, correct and repeat
test. If OK, replace the evaporator probe.
Once the repairs are completed, repeat the Calibra-
tion Diagnostic and Cooldown test. Repeating the
test is necessary to clear the fault codes.
A/C PERFORMANCE TEST
The air conditioning system is designed to remove
heat and humidity from the air entering the passen-
ger compartment. The evaporator, located in the
heater A/C unit, is cooled to temperatures near the
freezing point. As warm damp air passes over the
fins in the evaporator, moisture in the air condenses
to water, dehumidifying the air. Condensation on the
evaporator fins reduces the evaporators ability to
absorb heat. During periods of high heat and humid-
ity, an air conditioning system will be less effective.
With the instrument control set to RECIRC, only air
from the passenger compartment passes through the
evaporator. As the passenger compartment air dehu-
midifies, A/C performance levels rise.
PERFORMANCE TEST PROCEDURE
Review Safety Precautions and Warnings in this
group before proceeding with this procedure. Air tem-
perature in test room and on vehicle must be 21É C
(70ÉF) minimum for this test.
NOTE: When connecting the service equipment
coupling to the line fitting, verify that the valve of
the coupling is fully closed. This will reduce the
amount of effort required to make the connection.
(1) Connect a tachometer and manifold gauge set.
(2) Set control to A/C, RECIRC, and PANEL, tem-
perature lever on full cool and blower on high.
(3) Start engine and hold at 1000 rpm with A/C
clutch engaged.
(4) Engine should be warmed up with doors and
windows closed.
(5) Insert a thermometer in the left center A/C
outlet and operate the engine for five minutes. The
A/C clutch may cycle depending on ambient condi-
tions.
(6) With the A/C clutch engaged, compare the dis-
charge air temperature to the A/C Performance Tem-
peratures chart (Fig. 7).
(7) If the discharge air temperature fails to meet
the specifications in the performance temperature
chart. Refer to the Refrigerant Service Procedures for
further diagnosis.
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER
The work area temperature must not be below
10ÉC (50ÉF) to test the compressor clutch circuit.
Before starting to test the transducer ensure that the
wire connector is clean of corrosion and connected
properly.
(1) With gear selector in park or neutral and park
brake set, start engine and allow to idle.
(2) Install scan tool (DRB):
²Go to main menu
²Select stand alone scan tool (DRB)
²Select refer to the proper year diagnostics
²Select climate control
²Select sensor display
²Select A/C high side volts
For A/C system to operate a voltage between .451
(Low Pressure Cutout) to 4.519 (High Pressure Cut-
out is required. Voltages outside this range indicate a
low or high pressure condition andwill notallow
the compressor to cycle.
The following chart denotes voltages and the
appropriate condition(s):
NS/GSHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1880 of 1938

(6) If coil current reads zero, the coil is open and
should be replaced. If the ammeter reading is 4
amperes or more, the coil is shorted and should be
replaced. If the coil voltage is not within two volts of
the battery voltage, test clutch coil feed circuit for
excessive voltage drop.
EXPANSION VALVE
NOTE: Special effort must be used to keep all
R-134a system components moisture-free. Moisture
in the oil is very difficult to remove and will cause a
reliability problem with the compressor.
TESTS
NOTE: Expansion valve tests should be performed
after compressor tests.
Review Safety Precautions and Warnings in this
group. The work area and vehicle temperature must
be 21ÉC to 27ÉC (70ÉF to 85ÉF). To test the expansion
valve:
NOTE: Liquid CO2 is required to test the expansion
valve. It is available from most welding supply facil-
ities. CO2 is also available from companies which
service and sell fire extinguishers.
(1) Connect a charging station or manifold gauge
set to the refrigerant system service ports. Verify the
refrigerant charge level.
(2) Close all doors, windows and vents to the pas-
senger compartment.
(3) Set heater A/C control to A/C, full heat,
FLOOR, and high blower.
(4) Start the engine and allow to idle (1000 rpm).
After the engine has reached running temperature,
allow the passenger compartment to heat up. This
will create the need for maximum refrigerant flow
into the evaporator.
(5) I
f the refrigerant charge is sufficient, discharge
(high pressure) gauge should read 965 to 1655 kPa (140
to 240 psi). Suction (low pressure) gauge should read
140 kPa to 207 kPa (20 psi to 30 psig). If system cannot
achieve proper pressure readings, replace the expan-
sion valve. If pressure is correct, proceed with test.
WARNING: PROTECT SKIN AND EYES FROM CON-
TACTING CO2 PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
(6) If suction side low pressure is within specified
range, freeze the expansion valve control head for 30
seconds. Use a super cold substance (liquid CO2).Do
not spray R-134a Refrigerant on the expansion
valve for this test.Suction side low pressure should
drop by 10 psi. If not, replace expansion valve.(7) Allow expansion valve to thaw. The low pres-
sure gauge reading should stabilize at 140 kPa to
240 kPa (20 psi to 30 psig). If not, replace expansion
valve.
(8) When expansion valve test is complete, test
A/C overall performance. Remove all test equipment
before returning vehicle to use.
HEATER PERFORMANCE TEST
PRE-DIAGNOSTIC PREPARATIONS
Review Safety Precautions and Warnings in this
group before performing the following procedures.
Check the coolant level, drive belt tension, vacuum
line connections, radiator air flow and fan operation.
Start engine and allow to warm up to normal tem-
perature.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE RADIATOR CAP
WHEN ENGINE IS HOT, PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
If vehicle has been run recently, wait 15 minutes
before removing cap. Place a rag over the cap and
turn it to the first safety stop. Allow pressure to
escape through the overflow tube. When the system
stabilizes, remove the cap completely.
MAXIMUM HEATER OUTPUT: TEST AND
ACTION
Engine coolant is provided to the heater system by
two 16 mm (5/8 inch inside diameter) heater hoses.
With engine idling at normal running temperature,
set the control to maximum heat, floor, and high
blower setting. Using a test thermometer, check the
air temperature coming from the floor outlets, refer
to Temperature Reference chart.
If the floor outlet air temperature is insufficient,
refer to Group 7, Cooling Systems for specifications.
Both heater hoses should be HOT to the touch (cool-
ant return hose should be slightly cooler than the
supply hose). If coolant return hose is much cooler
than the supply hose, locate and repair engine cool-
ant flow obstruction in heater system.
TEMPERATURE REFERENCE CHART
AMBIENT TEMP.MINIMUM FLOOR
OUTLET TEMP.
CELSIUS FAHRENHEIT CELSIUS FAHRENHEIT
15.5É 60É 62.2É 144É
21.1É 70É 63.8É 147É
26.6É 80É 65.5É 150É
32.2É 90É 67.2É 153É
24 - 14 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONINGNS/GS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1881 of 1938

POSSIBLE LOCATIONS OR CAUSE OF
OBSTRUCTED COOLANT FLOW
(1) Pinched or kinked heater hoses.
(2) Improper heater hose routing.
(3) Plugged heater hoses or supply and return
ports at cooling system connections, refer to Group 7,
Cooling System.
(4) Plugged heater core.
(5) Air locked heater core.
(6) If coolant flow is verified and outlet tempera-
ture is insufficient, a mechanical problem may exist.
POSSIBLE LOCATION OR CAUSE OF
INSUFFICIENT HEAT
(1) Obstructed cowl air intake.
(2) Obstructed heater system outlets.
(3) Blend-air door not functioning properly.
TEMPERATURE CONTROL
If temperature cannot be adjusted with the TEMP
lever on the control panel, the following could require
service:
(1) Blend-air door binding.
(2) Faulty blend-air door motor.
(3) Improper engine coolant temperature.
(4) Faulty Instrument Panel Control.
SYSTEM CHARGE LEVEL TEST
The procedure below should be used to check
and/or fill the refrigerant charge in the air condition-
ing system.
NOTE: The amount of R134a refrigerant that the air
conditioning system holds is 0.96 kg (34 oz. or 2.13
lbs.).
NOTE: Low Charge, condition may be described
as:
²Loss of A/C performance
²Fog from A/C outlets
²evaporator may have a HISS sound
There are two different ways the system can be
tested:
²With a scan tool (DRB), thermocouple and the
Charge Determination Graph. Use the scan tool
(DRB) diagnostic topic: Engine±System Monitors, A/C
Pressure.
²Using a manifold gauge set, a thermocouple and
the Charge Determination Graph.
It is recommended to use the gauges or reclaim/re-
cycle equipment.
WARNING: AVOID BREATHING A/C REFRIGERANT
AND LUBRICANT VAPOR OR MIST. EXPOSURE MAY
IRRITATE EYES, NOSE AND THROAT. USE ONLY
APPROVED SERVICE EQUIPMENT MEETING SAEREQUIREMENTS TO DISCHARGE R-134a SYSTEM. IF
ACCIDENTAL SYSTEM DISCHARGE OCCURS, VEN-
TILATE WORK AREA BEFORE RESUMING SERVICE.
R-134a SERVICE EQUIPMENT OR VEHICLE A/C
SYSTEM SHOULD NOT BE PRESSURE TESTED OR
LEAK TESTED WITH COMPRESSED AIR. SOME
MIXTURES OF AIR/R-134a HAVE BEEN SHOWN TO
BE COMBUSTIBLE AT ELEVATED PRESSURES.
THESE MIXTURES ARE POTENTIALLY DANGER-
OUS AND MAY RESULT IN FIRE OR EXPLOSION
CAUSING INJURY OR PROPERTY DAMAGE.
(1) Establish your preferred method of measuring
liquid line pressure. Use a manifold gauge set or a
DRB scan tool.
(2) A
ttach a clamp-on thermocouple (Professional
Service Equipment 66-324-0014 or 80PK-1A) or equiv-
alent to the liquid line. It must be placed as close to
the A/C Pressure Transducer as possible to observe liq-
uid line temperature. Refer to ªThermocouple Probeº in
this section for more information on probe.
(3) The vehicle must be in the following modes:
²Transaxle in Park
²Engine Idling at 700 rpm
²A/C Controls Set to Outside Air
²Panel Mode
²Full Cool
²High Blower motor, (vehicle equipped with rear
A/C turn rear blower motor ON HIGH)
²A/C Button in the ON position
²Vehicle Windows Open.
²Recirc. button turned OFF
(4) Operate system for a couple of minutes to allow
the system to stabilize.
(5) Set system pressure to about 1793 kPa (260
psi) by placing a piece of cardboard over part of the
front side of the condenser. To place cardboard prop-
erly, remove the upper radiator-condenser cover.
Insert cardboard between condenser and radiator
front. This will maintain a constant pressure.
(6) Observe Liquid Line pressure and Liquid line
temperature. Using theCharge Determination
Chartdetermine where the system is currently oper-
ating. If the system is in the undercharged region,
ADD 0.057 Kg. (2 oz.) to the system and recheck
readings. If the system is in the overcharged region,
RECLAIM 0.057 Kg. (2 oz.) from the system and
recheck readings. Continue this process until the sys-
tem readings are in the proper charge area on the
Charge Determination Chart.
(7) The same procedure can be performed using
the scan tool (DRB). To determine liquid line pres-
sure, attach the scan tool, go to System Moni-
tors±A/C Pressure. Observe liquid line pressure from
A/C Pressure Transducer on digital display and digi-
tal thermometer. Refer toCharge Determination
Chartand determine where the system is operating.
NS/GSHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1883 of 1938

The use of R-134a will have a positive environmen-
tal impact due to it's zero ozone depletion and low
global warming impact.
CHARGING REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
CAUTION: Do not overcharge refrigerant system,
as excessive compressor head pressure can cause
noise and system failure.
After the system has been tested for leaks and
evacuated, a refrigerant (R-134a) charge can be
injected into the system.
NOTE: When connecting the service equipment
coupling to the line fitting, verify that the valve of
the coupling is fully closed. This will reduce the
amount of effort required to make the connection.
(1) Connect manifold gauge set.
(2) Measure refrigerant 0.96 kg (34 oz. or 2.13 lb.)
and heat to 52ÉC (125ÉF) with the charging station.
Refer to the instructions provided with the equip-
ment being used.
(3) Open the suction and discharge valves. Open
the charge valve to allow the heated refrigerant to
flow into the system. When the transfer of refriger-
ant has stopped, close the suction and discharge
valve.
(4) If all of the charge did not transfer from the
dispensing device, run engine at a high idle (1400
rpm). Set the A/C control to A/C, low blower speed,
and open windows. If the A/C compressor does not
engage, test the compressor clutch control circuit andcorrect any failure. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Dia-
grams.
(5) Open the suction valve to allow the remaining
refrigerant to transfer to the system.
WARNING: TAKE CARE NOT TO OPEN THE DIS-
CHARGE (HIGH-PRESSURE) VALVE AT THIS TIME.
(6) Close all valves and test the A/C system perfor-
mance.
(7) Disconnect the charging station or manifold
gauge set. Install the service port caps.
EVACUATING REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
NOTE: Special effort must be used to prevent mois-
ture from entering the A/C system oil. Moisture in
the oil is very difficult to remove and will cause a
reliability problem with the compressor.
If a compressor designed to use R-134a refrigerant
is left open to the atmosphere for an extended period
of time. It is recommended that the refrigerant oil be
drained and replaced with new oil or a new compres-
sor be used. This will eliminate the possibility of con-
taminating the refrigerant system.
If the refrigerant system has been open to the
atmosphere, it must be evacuated before the system
can be filled. Moisture and air mixed with the refrig-
erant will raise the compressor head pressure above
acceptable operating levels. This will reduce the per-
formance of the air conditioner and damage the com-
pressor. Moisture will boil at near room temperature
when exposed to vacuum. To evacuate the refrigerant
system:
NOTE: When connecting the service equipment
coupling to the line fitting, verify that the valve of
the coupling is fully closed. This will reduce the
amount of effort required to make the connection.
(1) Connect a suitable charging station, refrigerant
recovery machine, or a manifold gauge set with vac-
uum pump to the service ports (Fig. 10).
(2) Open the suction and discharge valves and
start the vacuum pump. The vacuum pump should
run a minimum of 45 minutes prior to charge to
eliminate all moisture in system. When the suction
gauge reads -88 kPa (-26 in. Hg) vacuum or greater
for 45 minutes, close all valves and turn off vacuum
pump. If the system fails to reach specified vacuum,
the refrigerant system likely has a leak that must be
corrected. If the refrigerant system maintains speci-
fied vacuum for at least 30 minutes, start the vac-
uum pump, open the suction and discharge valves.
Then allow the system to evacuate an additional 10
minutes.
Fig. 9 Manifold Gauge Set- Typical
NS/GSHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 17
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1885 of 1938

SYSTEM LEAK CHECKING
WARNING: R-134a SERVICE EQUIPMENT OR VEHI-
CLE A/C SYSTEM SHOULD NOT BE PRESSURE
TESTED OR LEAK TESTED WITH COMPRESSED
AIR. SOME MIXTURES OF AIR/R-134a HAVE BEEN
SHOWN TO BE COMBUSTIBLE AT ELEVATED
PRESSURES. THESE MIXTURES ARE POTENTIALLY
DANGEROUS AND MAY RESULT IN FIRE OR
EXPLOSION CAUSING INJURY OR PROPERTY
DAMAGE.
If the A/C system is not cooling properly, determine
if the refrigerant system is fully charged with
R-134a. This is accomplished by performing a system
Charge Level-Check or Fill. If while performing this
test A/C liquid line pressure is less than 207 kPa (30
psi) proceed to Empty Refrigerant System Leak Test.
If liquid line pressure is greater than 207 kPa (30
psi) proceed to low refrigerant level leak test. If the
refrigerant system is empty or low in refrigerant
charge, a leak at any line fitting or component seal is
likely. A review of the fittings, lines and components
for oily residue is an indication of the leak location.
To detect a leak in the refrigerant system, perform
one of the following procedures as indicated by the
symptoms.
WARNING: AVOID BREATHING A/C REFRIGERANT
AND LUBRICANT VAPOR OR MIST. EXPOSURE MAY
IRRITATE EYES, NOSE AND THROAT. USE ONLY
APPROVED SERVICE EQUIPMENT MEETING SAE
REQUIREMENTS TO DISCHARGE R-134a SYSTEM.
IF ACCIDENTAL SYSTEM DISCHARGE OCCURS,
VENTILATE WORK AREA BEFORE RESUMING SER-
VICE.
EMPTY REFRIGERANT SYSTEM LEAK TEST
(1) Evacuate the refrigerant system to the lowest
degree of vacuum possible (about 28 in Hg.). Deter-
mine if the system holds a vacuum for 15 minutes. If
vacuum is held, a leak is probably not present. If sys-
tem will not maintain vacuum level, proceed with
this procedure.
(2) Prepare a .284 Kg. (10 oz.) refrigerant charge
to be injected into the system.
(3) Connect and dispense .284 Kg. (10 oz.) of
refrigerant into the evacuated refrigerant system.
(4) Proceed to step two of Low Refrigerant Level
Leak Test.
LOW REFRIGERANT LEVEL LEAK TEST
(1) Determine if there is any (R-134a) refrigerant
in the system. Use the scan tool (DRB) under the
menu Systems Sensors±A/C Pressure test or pressuregauge liquid line temperature partial charge check.
See system charge level check or fill for procedure.
(2) Position the vehicle in a wind free work area.
This will aid in detecting small leaks.
(3) Bring the refrigerant system up to operating
temperature and pressure. This is done by allowing
the engine to run for five minutes with the system
set to the following:
²Transaxle in Park
²Engine Idling at 700 rpm
²A/C Controls Set in 100 percent outside air
²Full Panel Mode
²Blower motor ON HIGH
²A/C in the ON position
²Front Windows Open.
²Rear Air Off (If Equipped)
CAUTION: A leak detector designed for R-12 refrig-
erant will not detect leaks in a R-134a refrigerant
system.
(4) Shut off the vehicle and wait 2 to 7 minutes.
Then use an Electronic Leak Detector that is
designed to detect R-134a type refrigerant and search
for leaks. Fittings, lines, or components that appear
to be oily usually indicates a refrigerant leak. To
inspect the evaporator core for leaks, insert the leak
detector probe into the recirculating air door opening
or a heat duct.
If a thorough leak check has been completed with-
out indication of a leak, proceed to System Charge
Level-Check or Fill.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the wire connector at the pressure
transducer.
(2) Using an open end wrench, remove the trans-
ducer from the liquid line (Fig. 11).
INSTALLATION
(1) Replace transducer O-ring.
(2) For installation, reverse the above procedures.
A/C SERVICE PORTS
WARNING: THE REFRIGERATION SYSTEM MUST
BE COMPLETELY EMPTY BEFORE PROCEEDING
WITH THIS OPERATION.
The High Side service port is serviceable, the Low
Side is not serviceable.
NS/GSHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 19
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1895 of 1938

MODE DOOR ACTUATOR
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the lower left side steering column
cover. Refer to Group 8E, Instrument Panel and Sys-
tems.
(2) Remove ABS control module (Fig. 40).
(3) Remove mode actuator connector (Fig. 41).
(4) Remove mode door actuator (Fig. 42).
INSTALLATION
(1) For installation, reverse the above procedures.
(2) Perform the HVAC control Calibration Diagnos-
tic and Cooldown test.
SIDE WINDOW DEMISTER DUCTS
LEFT SIDE
The LEFT side window demister duct is a two
piece design. The left side has a long duct that
attaches to an intermediate duct and then to the dis-tribution housing. The duct is located on top of the
instrument panel. To service the duct, remove the I/P
cover and remove duct retainers/fasteners. (Fig. 43).
RIGHT SIDE
The demister duct on the right side is a one piece
design. It is one long duct that attaches to the distri-
bution housing. The duct is located on top of the
instrument panel and it is not serviceable (Fig. 44).
SUCTION LINE
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Recover A/C system refrigerant.
(3) Remove ground wire at dash panel.
(4) Remove the nut retaining the refrigerant line
sealing plate to the expansion valve (Fig. 27).
(5) Remove the stud from the expansion valve (Fig.
28).
(6) Remove suction line from expansion valve.
Fig. 40 ABS Control Module
Fig. 41 Mode Door Actuator Connector
Fig. 42 Mode Door Actuator
Fig. 43 Left Side Demister Duct
NS/GSHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 29
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1911 of 1938
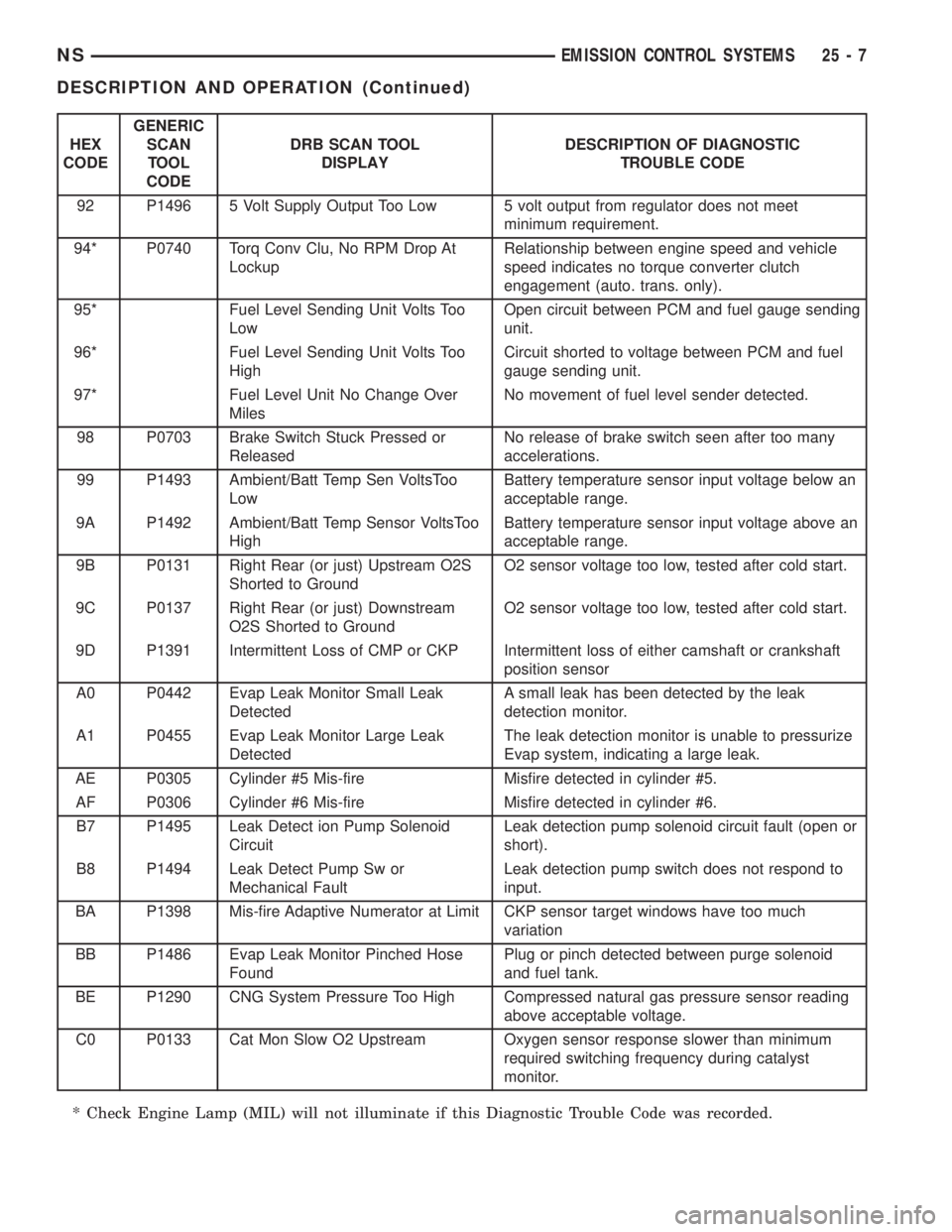
HEX
CODEGENERIC
SCAN
TOOL
CODEDRB SCAN TOOL
DISPLAYDESCRIPTION OF DIAGNOSTIC
TROUBLE CODE
92 P1496 5 Volt Supply Output Too Low 5 volt output from regulator does not meet
minimum requirement.
94* P0740 Torq Conv Clu, No RPM Drop At
LockupRelationship between engine speed and vehicle
speed indicates no torque converter clutch
engagement (auto. trans. only).
95* Fuel Level Sending Unit Volts Too
LowOpen circuit between PCM and fuel gauge sending
unit.
96* Fuel Level Sending Unit Volts Too
HighCircuit shorted to voltage between PCM and fuel
gauge sending unit.
97* Fuel Level Unit No Change Over
MilesNo movement of fuel level sender detected.
98 P0703 Brake Switch Stuck Pressed or
ReleasedNo release of brake switch seen after too many
accelerations.
99 P1493 Ambient/Batt Temp Sen VoltsToo
LowBattery temperature sensor input voltage below an
acceptable range.
9A P1492 Ambient/Batt Temp Sensor VoltsToo
HighBattery temperature sensor input voltage above an
acceptable range.
9B P0131 Right Rear (or just) Upstream O2S
Shorted to GroundO2 sensor voltage too low, tested after cold start.
9C P0137 Right Rear (or just) Downstream
O2S Shorted to GroundO2 sensor voltage too low, tested after cold start.
9D P1391 Intermittent Loss of CMP or CKP Intermittent loss of either camshaft or crankshaft
position sensor
A0 P0442 Evap Leak Monitor Small Leak
DetectedA small leak has been detected by the leak
detection monitor.
A1 P0455 Evap Leak Monitor Large Leak
DetectedThe leak detection monitor is unable to pressurize
Evap system, indicating a large leak.
AE P0305 Cylinder #5 Mis-fire Misfire detected in cylinder #5.
AF P0306 Cylinder #6 Mis-fire Misfire detected in cylinder #6.
B7 P1495 Leak Detect ion Pump Solenoid
CircuitLeak detection pump solenoid circuit fault (open or
short).
B8 P1494 Leak Detect Pump Sw or
Mechanical FaultLeak detection pump switch does not respond to
input.
BA P1398 Mis-fire Adaptive Numerator at Limit CKP sensor target windows have too much
variation
BB P1486 Evap Leak Monitor Pinched Hose
FoundPlug or pinch detected between purge solenoid
and fuel tank.
BE P1290 CNG System Pressure Too High Compressed natural gas pressure sensor reading
above acceptable voltage.
C0 P0133 Cat Mon Slow O2 Upstream Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum
required switching frequency during catalyst
monitor.
* Check Engine Lamp (MIL) will not illuminate if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
NSEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)